Research on Diffusible Signal Factor-Mediated Quorum Sensing in Xanthomonas: A Mini-Review
Abstract
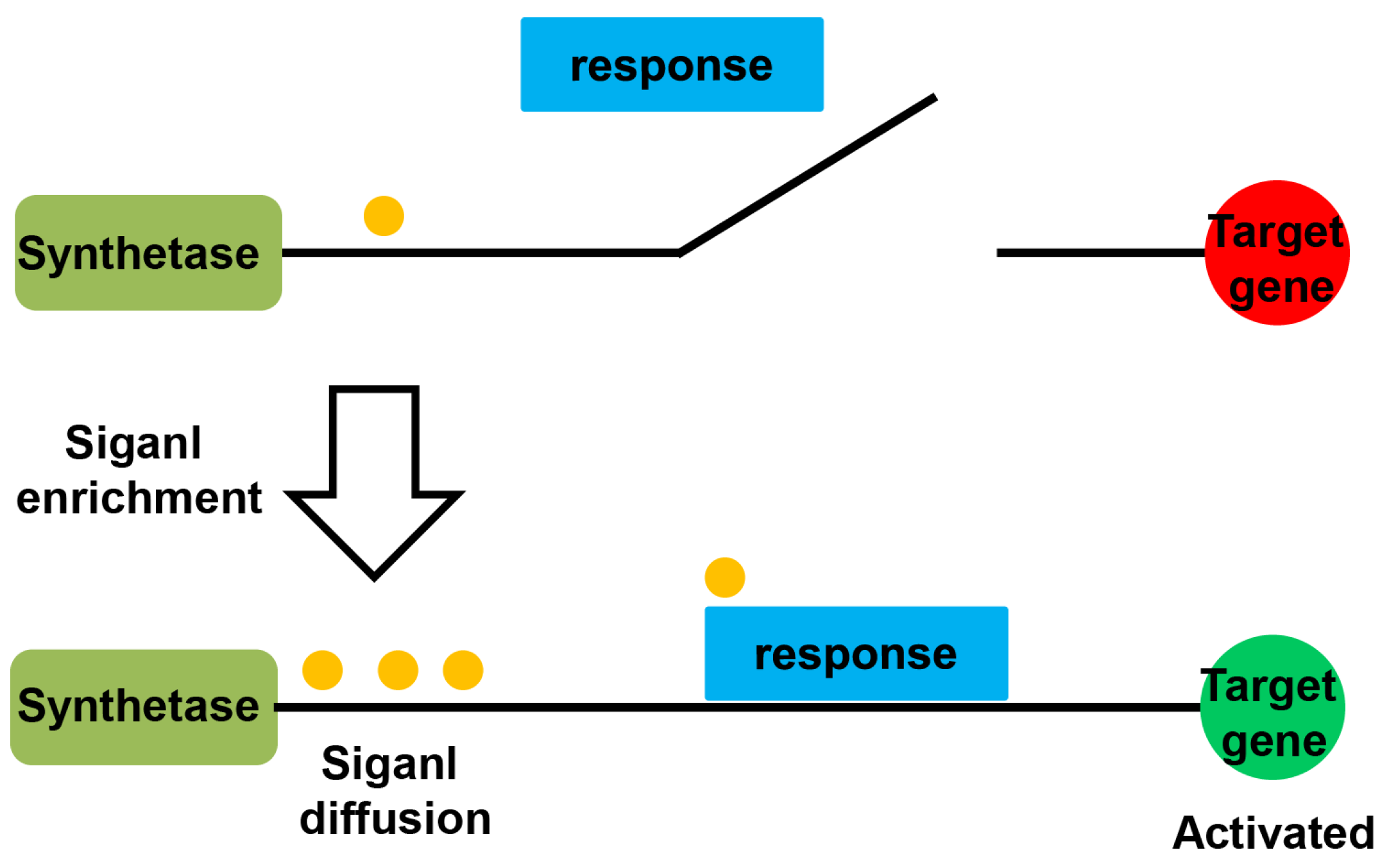
1. Introduction
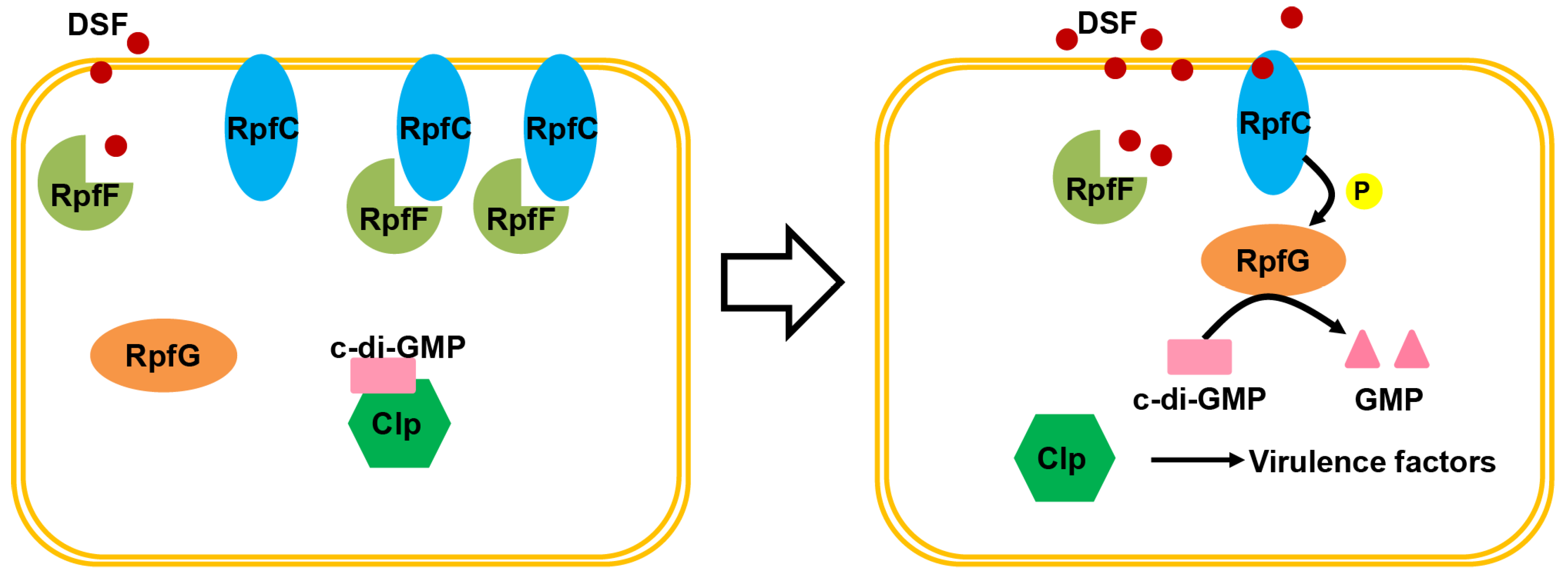
2. Rpf/DSF Quorum Sensing
2.1. The rpf Gene Cluster
2.2. DSF-Family Signals
2.3. The QS Pathway in Xanthomonas
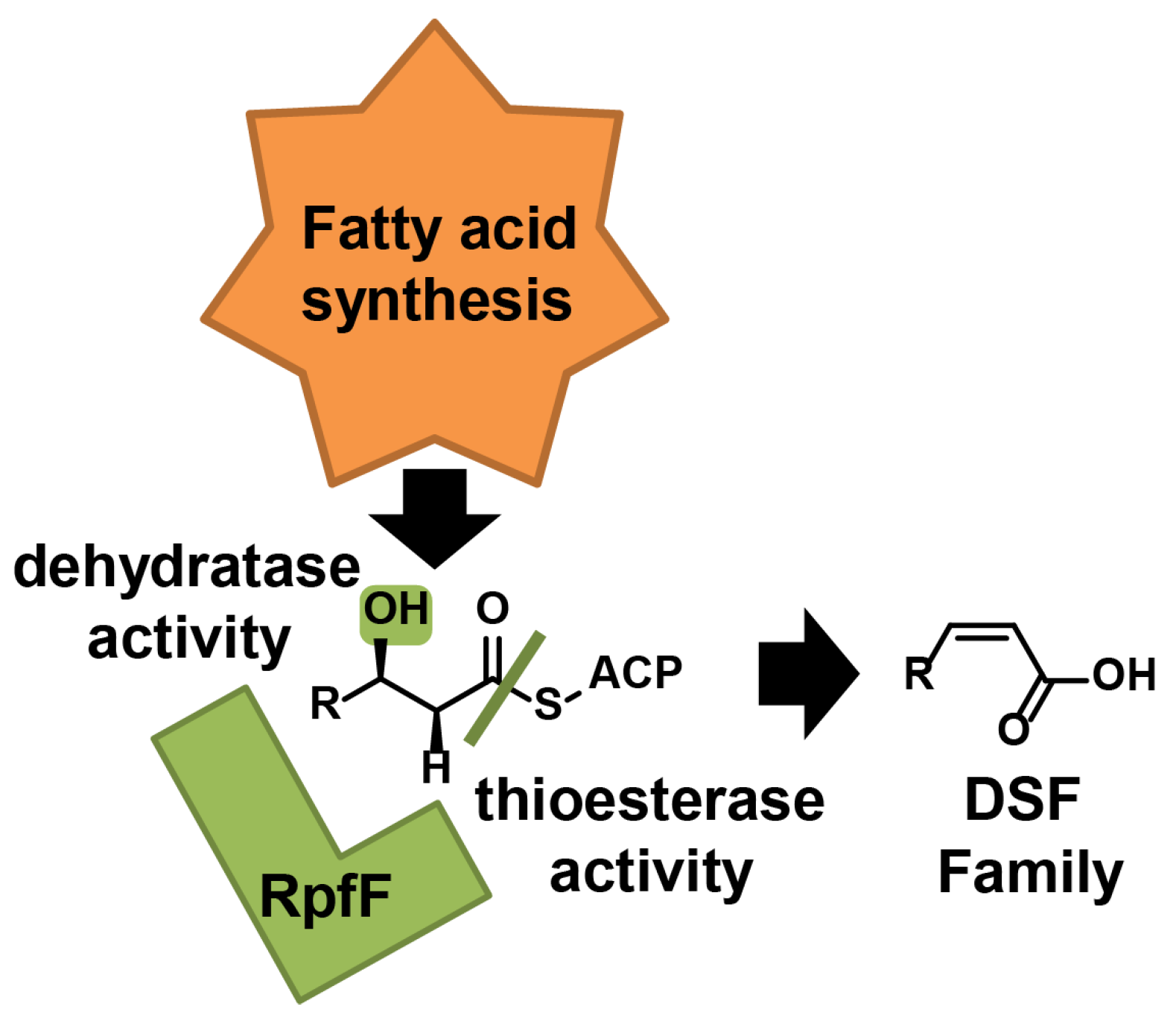
3. DSF Biosynthase
3.1. DSF Synthesis
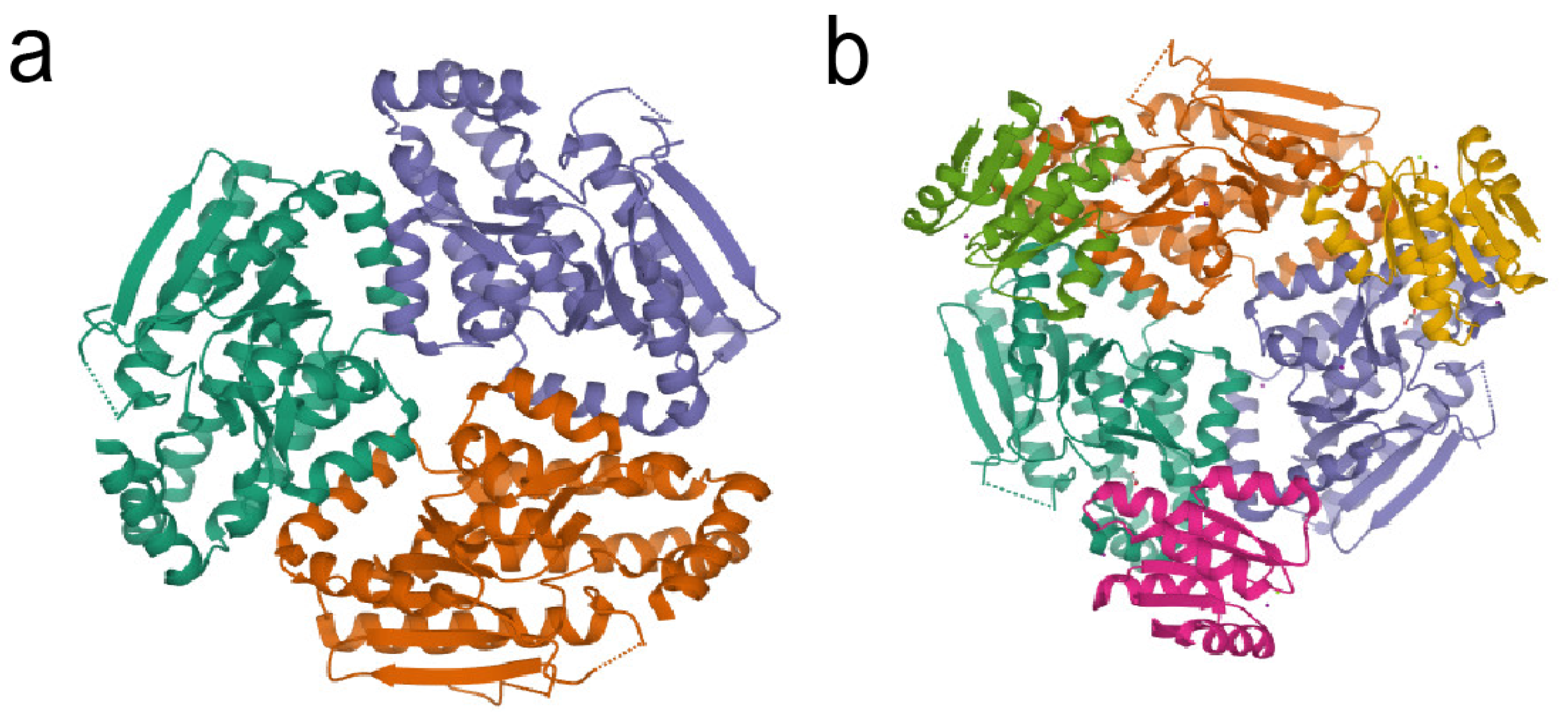
3.2. RpfF Protein
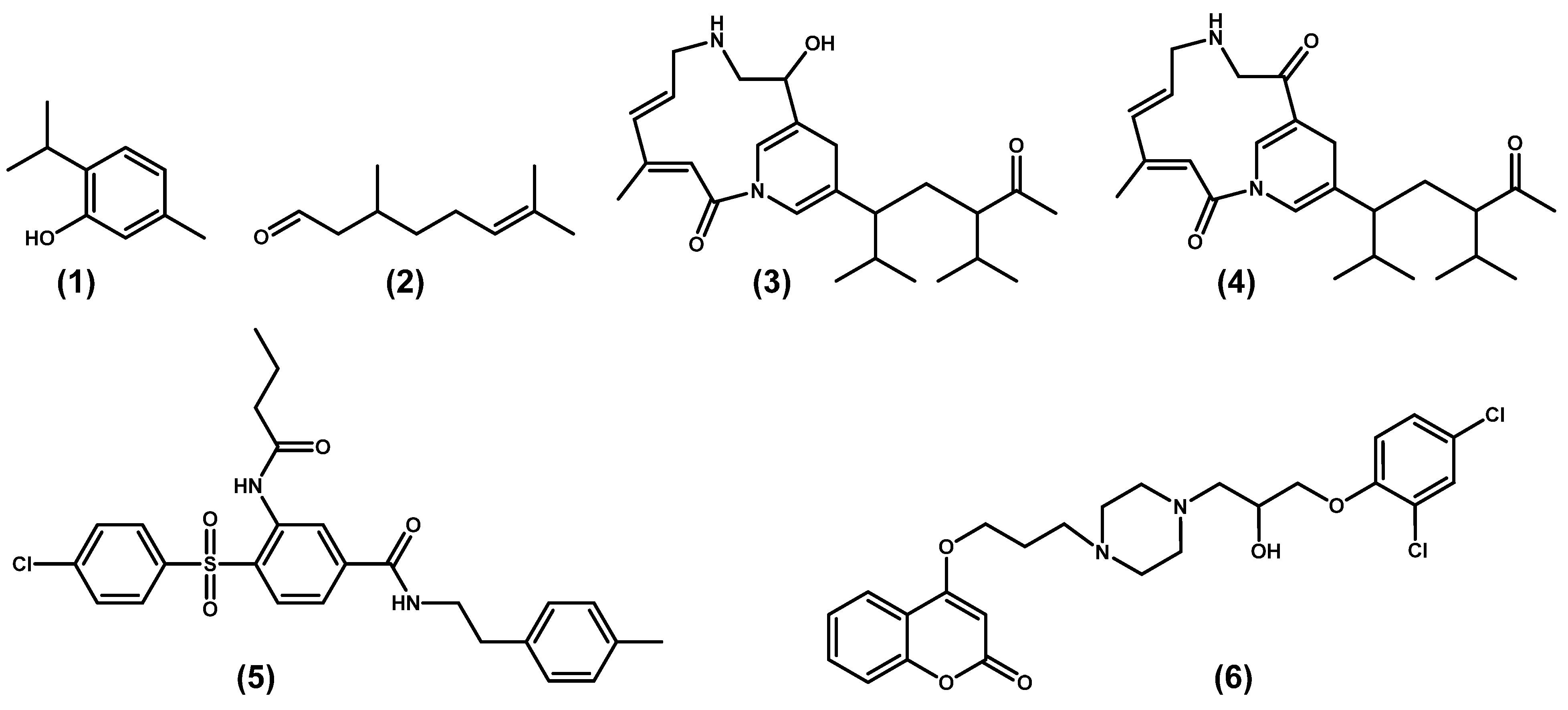
3.3. RpfF Inhibitors
| Inhibitor | Origin | Mechanistic Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thymol | Major component of Thyme oil | Formation of potential hydrogen bonds with some residues Glu161 and Gly169 in the putative RpfF binding pocket; downregulation of rpfF gene; reduction of DSF and BDSF. | Singh et al. [59] |
| Citronellal | Major component of Kaffir lime oil | Down regulation in transcript levels of rpfF; formed probable hydrogen bonds with important catalytic residues (GLY169, TRP258). | Singh et al. [60] |
| Chumacin-1 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain CGK-KS-1 | Inhibition of the production of DSF; suppressed the xanthan gum secretion and also inhibited the biofilms formed; interaction with the residues of RpfF pocket. | Kanugala et al. [61] |
| Chumacin-2 | |||
| Rifampicin analogues | Virtual screening form ZIN Database | Docked into the active site of the RpfF protein. | Srilatha et al. [62] |
| Coumarin derivative | Synthesis based on derivation of natural product | Disturbed biofilm formation; suppressed bacterial virulence factors and production of DSF; reduced expression of rpfF gene. | Feng et al. [64] |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SDH | succinate dehydrogenase |
| PK | pyruvate kinase |
| Xcc | Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris |
| Xoo | Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae |
| QS | quorum sensing |
| AIs | auto-inducers |
| AHL | n-acyl homoserine lactones |
| DSF | diffusible signal factor |
| Rpf | regulation of pathogenicity factor |
| FCL | fatty acyl-CoA ligase |
| HR | hypersensitive response |
| hrp | hypersensitive response pathogenicity |
| ACP | acyl carrier protein |
| KLO | kaffir lime oil |
References
- Li, X.Y.; Yang, X.Q.; Zheng, X.D.; Bai, M.; Hu, D.Y. Review on structures of pesticide targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonijevic, B.; Stojiljkovic, M.P. Unequal efficacy of pyridinium oximes in acute organophosphate poisoning. Clin. Med. Res. 2007, 5, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xu, H.L.; Wei, X.L.; Ye, Z.Q.; Wei, L.P.; Gong, W.M.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhu, Z. Identification of a glyphosate-resistant mutant of rice 5-enolpyruvylshikimate 3-phosphate synthase using a directed evolution strategy. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Shao, W.B.; Zhu, J.J.; Long, Z.Q.; Liu, L.W.; Wang, P.Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, S. Novel 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole-2-carbohydrazides as prospective agricultural antifungal agents potentially targeting succinate dehydrogenase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13892–13903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.Q.; Yang, L.L.; Zhang, J.R.; Liu, S.T.; Xie, J.; Wang, P.Y.; Zhu, J.J.; Shao, W.B.; Liu, L.W.; Yang, S. Fabrication of versatile pyrazole hydrazide derivatives bearing a 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole core as multipurpose agricultural chemicals against plant fungal, oomycete, and bacterial diseases. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8380–8393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, R.; Qi, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.Y.; Tang, L.F.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.Y.; Fan, Z.J. Discovery of Novel Triazolothiadiazines as Fungicidal Leads Targeting Pyruvate Kinase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeschke, P. Progress of modern agricultural chemistry and future prospects. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 433–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Lee, P.W.; Cao, S. China: Forward to the green pesticides via a basic research program. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2613–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, R.P.; Vorhölter, F.J.; Potnis, N.; Jones, J.B.; Van Sluys, M.A.; Bogdanove, A.J.; Dow, J.M. Pathogenomics of Xanthomonas: Understanding bacterium-plant interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansfield, J.; Genin, S.; Magori, S.; Citovsky, V.; Sriariyanum, M.; Ronald, P.; Dow, M.; Verdier, V.; Beer, S.V.; Machado, M.A.; et al. Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaianni, M.; Paris, D.; Woo, S.L.; Fulgione, A.; Rigano, M.M.; Parrilli, E.; Tutino, M.L.; Marra, R.; Manganiello, G.; Casillo, A.; et al. Plant dynamic metabolic response to bacteriophage treatment after Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris infection. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, X.; Wang, P.Y.; Gan, J.H.; Song, B.A.; Yang, S.; Yang, C.G. Dysregulation of ClpP by Small-Molecule Activators Used Against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Infections. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7545–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.Q.; Potnis, N.; Dow, M.; Vorhölter, F.J.; He, Y.Q.; Becker, A.; Teper, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, N.; Bleris, L.; et al. Mechanistic insights into host adaptation, virulence and epidemiology of the phytopathogen Xanthomonas. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büttner, D.; Bonas, U. Regulation and secretion of Xanthomonas virulence factors. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nealson, K.H.; Platt, T.; Hastings, J.W. Cellular control of the synthesis and activity of the bacterial luminescent system. J. Bacteriol. 1970, 104, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassler, B.L.; Wright, M.; Silverman, M.R. Multiple signaling systems controlling expression of luminescence in Vibrio harveyi-sequence and function of genes encoding a second sensory pathway. Mol. Microbiol. 1994, 13, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P. Quorum sensing, communication and cross-kingdom signalling in the bacterial world. Microbiology 2007, 153, 3923–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturi, V.; Fuqua, C. Chemical signaling between plants and plant-pathogenic bacteria. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defoirdt, T.; Boon, N.; Bossier, P. Can bacteria evolve resistance to quorum sensing disruption? PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard, A.; Burlingame, A.L.; Kenyon, G.L.; Nealson, K.H.; Oppenheimer, N.J. Structural identification of autoinducer of Photobacterium fischeri luciferase. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 2444–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.W.; Zhang, L.H. Quorum sensing and virulence regulation in Xanthomonas campestris. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 842–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.H.; Cámara, M.; He, Y.W. The DSF family of quorum sensing signals: Diversity, biosynthesis, and turnover. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetzner, S. Quorum quenching enzymes. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 201, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaSarre, B.; Federle, M.J. Exploiting quorum sensing to confuse bacterial pathogens. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 73–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, H.; Alvare-Morales, A.; Barber, C.E.; Daniels, M.J.; Dow, J.M. A two-component system involving an HD-GYP domain protein links cell-cell signalling to pathogenicity gene expression in Xanthomonas campestris. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 986–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, J.M.; Daniels, M.J. Xylella genomics and bacterial pathogenicity to plants. Yeast 2000, 17, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, T.J.G.; Bertrand, N.; Tang, J.L.; Feng, J.X.; Pan, M.Q.; Barber, C.E.; Dow, J.M.; Daniels, M.J. The rpfA gene of Xanthomonas campestris pathovar campestris, which is involved in the regulation of pathogenicity factor production, encodes an aconitase. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 28, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, X.Y.; Sun, S.; Yang, L.C.; Jiang, B.L.; He, Y.W. Identification and characterization of naturally occurring DSF-family quorum sensing signal turnover system in the phytopathogen X. anthomonas. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 4646–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Verma, R.K.; Chatterjee, S. The diffusible signal factor synthase, RpfF, in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae is required for the maintenance of membrane integrity and virulence. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 23, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, H.; Yu, Y.; Dong, H.; Wang, H.; Cronan, J.E. Xanthomonas campestris RpfB is a fatty Acyl-CoA ligase required to counteract the thioesterase activity of the RpfF diffusible signal factor (DSF) synthase. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 93, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.S.; Lee, S.E.; Han, J.W.; Yang, S.U.; Lee, B.M.; Noh, T.H.; Cha, J.S. Virulence reduction and differing regulation of virulence genes in rpf mutants of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Plant Pathol. J. 2008, 24, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.W.; Wang, C.; Zhou, L.; Song, H.; Dow, J.M.; Zhang, L.H. Dual signaling functions of the hybrid sensor kinase RpfC of Xanthomonas campestris involve either phosphorelay or receiver domain-protein interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 33414–33421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.L.; Jiang, G.F.; Liu, W.; Yang, L.C.; Yang, L.Y.; Wang, L.; Hao, X.Y.; Tang, J.L. RpfC regulates the expression of the key regulator hrpX of the hrp/T3SS system in Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Yoon, J.M.; Lee, S.W.; Noh, Y.H.; Cha, J.S. Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae RpfE regulates virulence and carbon source utilization without change of the dsf production. Plant Pathol. J. 2013, 29, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, J.M.; Feng, J.X.; Barber, C.E.; Tang, J.L.; Daniels, M.J. Novel genes involved in the regulation of pathogenicity factor production within the rpf gene cluster of Xanthomonas campestris. Microbiology 2000, 146, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O–Connell, A.; An, S.Q.; McCarthy, Y.; Schulte, F.; Niehaus, K.; He, Y.Q.; Tang, J.L.; Ryan, R.P.; Dow, J.M. Proteomics analysis of the regulatory role of Rpf/DSF cell-to-cell signaling system in the virulence of Xanthomonas campestris. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2013, 26, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, C.E.; Tang, J.L.; Feng, J.X.; Pan, M.Q.; Wilson, T.G.; Slater, H.; Dow, J.M.; Williams, P.; Daniels, M.J. A novel regulatory system required for pathogenicity of Xanthomonas campestris is mediated by a small diffusible signal molecule. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 24, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; He, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wu, J.E.; Dong, Y.H.; He, C.Z.; Weng, W.L.; Xu, J.L.; Tay, L.; Fang, X.R.; et al. A bacterial cell-cell communication signal with cross-kingdom structural analogues. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 51, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.W.; Wu, J.E.; Cha, J.S.; Zhang, L.H. Rice bacterial blight pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae produces multiple DSF-family signals in regulation of virulence factor production. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.P.; McCarthy, Y.; Watt, S.A.; Niehaus, K.; Dow, J.M. Intraspecies signaling involving the diffusible signal factor BDSF (cis-2-dodecenoic acid) influences virulence in Burkholderia cenocepacia. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 5013–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.P.; Dow, J.M. Communication with a growing family: Diffusible signal factor (DSF) signaling in bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2011, 19, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, M.; Baccari, C.; Da Silva, A.M.; Garcia, A.; Yokota, K.; Lindow, S.E. Diffusible signal factor (DSF) synthase RpfF of Xylella fastidiosa is a multifunction protein also required for response to DSF. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 5273–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huedo, P.; Yero, D.; Martínez-Servat, S.; Estibariz, I.; Planell, R.; Martínez, P.; Ruyra, A.; Roher, N.; Roca, I.; Vila, J.; et al. Two different rpf clusters distributed among a population of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia clinical strains display differential diffusible signal factor production and virulence regulation. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 2431–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flavier, A.B.; Clough, S.J.; Schell, M.A.; Denny, T.P. Identification of 3-hydroxypalmitic acid methyl ester as a novel autoregulator controlling virulence in Ralstonia solanacearum. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 26, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Li, T.; Cheng, X.J.; Peng, C.T.; Li, C.C.; He, L.H.; Ju, S.M.; Wang, N.Y.; Ye, T.H.; Lian, M.; et al. Structural and functional studies on Pseudomonas aeruginosa DspI: Implications for its role in DSF biosynthesis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, A.; Nizampatnam, N.R.; Kondreddy, A.; Pradhan, B.B.; Chatterjee, S. Xanthomonas campestris cell-cell signalling molecule DSF (diffusible signal factor) elicits innate immunity in plants and is suppressed by the exopolysaccharide xanthan. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 6697–6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.M.; Liu, X.L.; Nath, S.; Sun, H.; Tran, T.M.; Yang, L.; Mayor, S.; Miao, Y.S. Formin nanoclustering-mediated actin assembly during plant flagellin and DSF signaling. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.Y.; Wu, J.; Yin, W.F.; Li, P.; Zhou, J.N.; Chen, S.H.; He, H.; Cai, J.; Zhang, L.H. Diffusible signal factor family signals provide a fitness advantage to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in interspecies competition. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1534–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.Q.; Wu, Y.; Cai, Z.; Qian, W. BDSF is a degradation-prone quorum-sensing signal detected by the histidine kinase RpfC of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2022, 88, e00031-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Ji, G.H.; He, Y.W. The RpfB-dependent quorum sensing signal turnover system is required for adaptation and virulence in rice bacterial blight pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2016, 29, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, M.; Zhang, W.B.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, H.H.; Ma, J.C. The FabA-FabB Pathway is not Essential for Unsaturated Fatty Acid Synthesis, but Modulates DSF Synthesis in Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Mol. Plant Microbe. Interact. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.H.; Hu, Z.; Dong, H.J.; Ma, J.C.; Wang, H.H. Xanthomonas campestris FabH is required for branched-chain fatty acid and DSF-family quorum sensing signal biosynthesis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; He, Y.W.; Lim, S.C.; Qamra, R.; Walsh, M.A.; Zhang, L.H.; Song, H. Structural basis of the sensor-synthase interaction in autoinduction of the quorum sensing signal DSF biosynthesis. Structure 2010, 18, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Yu, Y.; Chen, X.; Diab, A.A.; Ruan, L.; He, J.; Wang, H.H.; He, Y.W. The multiple DSF-family QS signals are synthesized from carbohydrate and branched-chain amino acids via the FAS elongation cycle. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lv, M.F.; Yin, W.F.; Dong, T.Y.; Chang, C.Q.; Miao, Y.S.; Jia, Y.T.; Deng, Y. Xanthomonas campestris promotes diffusible signal factor biosynthesis and pathogenicity by utilizing glucose and sucrose from host plants. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2019, 32, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Chen, B.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, L.; Chan, K.G.; Zhang, H.Y.; He, Y.W. The Plant Defense Signal Salicylic Acid Activates the RpfB-Dependent Quorum Sensing Signal Turnover via Altering the Culture and Cytoplasmic pH in the Phytopathogen Xanthomonas campestris. Mbio 2022, 13, e03644-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.S.; Kumar, Y.N.; Raghavendra, A.; Sowjenya, G.; Kumar, S.; Ramyasree, G.; Reddy, G.R. In silico model of DSF synthase RpfF protein from Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae: A novel target for bacterial blight of rice disease. Bioinformation 2012, 8, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.Y.; Liao, S.J.; Chin, K.H.; Shih, H.L.; Shen, G.H.; Wang, A.J.; Chou, S.H. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction characterization of RpfF, a key DSF synthase from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Acta Crystallogr. F-Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2009, 65, 1021–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Gupta, R.; Tandon, S.; Pandey, R. Thyme Oil Reduces Biofilm Formation and Impairs Virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Gupta, R.; Tandon, S.; Pandey, R. Anti-biofilm and anti-virulence potential of 3, 7-dimethyloct-6-enal derived from Citrus hystrix against bacterial blight of rice caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 115, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanugala, S.; Kumar, C.G.; Rachamalla, H.K.R.; Palakeeti, B.; Ramakrishna, K.V.S.; Nimmu, N.V.; Chandrasekhar, C.; Patel, H.K.; Ganapathi, T. Chumacin-1 and Chumacin-2 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain CGK-KS-1 as novel quorum sensing signaling inhibitors for biocontrol of bacterial blight of rice. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 228, 126301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srilatha, M.; Patyal, N.; Saddala, M.S. Functional analysis and screening small molecules to RpfF protein in Xanthomonas oryzae involved in rice bacterial blight disease. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Yang, X.; Ray, S.; Fraceto, L.F.; Singh, H.B. Antibacterial and biofilm inhibition activity of biofabricated silver nanoparticles against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae causing blight disease of rice instigates disease suppression. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.M.; Qi, P.Y.; Xiao, W.L.; Zhang, T.H.; Zhou, X.; Liu, L.W.; Yang, S. Fabrication of Isopropanolamine-Decorated Coumarin Derivatives as Novel Quorum Sensing Inhibitors to Suppress Plant Bacterial Disease. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 6037–6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.-M.; Long, Z.-Q.; Xiang, H.-M.; Ran, J.-N.; Zhou, X.; Yang, S. Research on Diffusible Signal Factor-Mediated Quorum Sensing in Xanthomonas: A Mini-Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 876. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020876
Feng Y-M, Long Z-Q, Xiang H-M, Ran J-N, Zhou X, Yang S. Research on Diffusible Signal Factor-Mediated Quorum Sensing in Xanthomonas: A Mini-Review. Molecules. 2023; 28(2):876. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020876
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yu-Mei, Zhou-Qing Long, Hong-Mei Xiang, Jun-Ning Ran, Xiang Zhou, and Song Yang. 2023. "Research on Diffusible Signal Factor-Mediated Quorum Sensing in Xanthomonas: A Mini-Review" Molecules 28, no. 2: 876. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020876
APA StyleFeng, Y.-M., Long, Z.-Q., Xiang, H.-M., Ran, J.-N., Zhou, X., & Yang, S. (2023). Research on Diffusible Signal Factor-Mediated Quorum Sensing in Xanthomonas: A Mini-Review. Molecules, 28(2), 876. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020876







