Design and Synthesis of (Z)-2-(Benzylamino)-5-benzylidenethiazol-4(5H)-one Derivatives as Tyrosinase Inhibitors and Their Anti-Melanogenic and Antioxidant Effects
Abstract
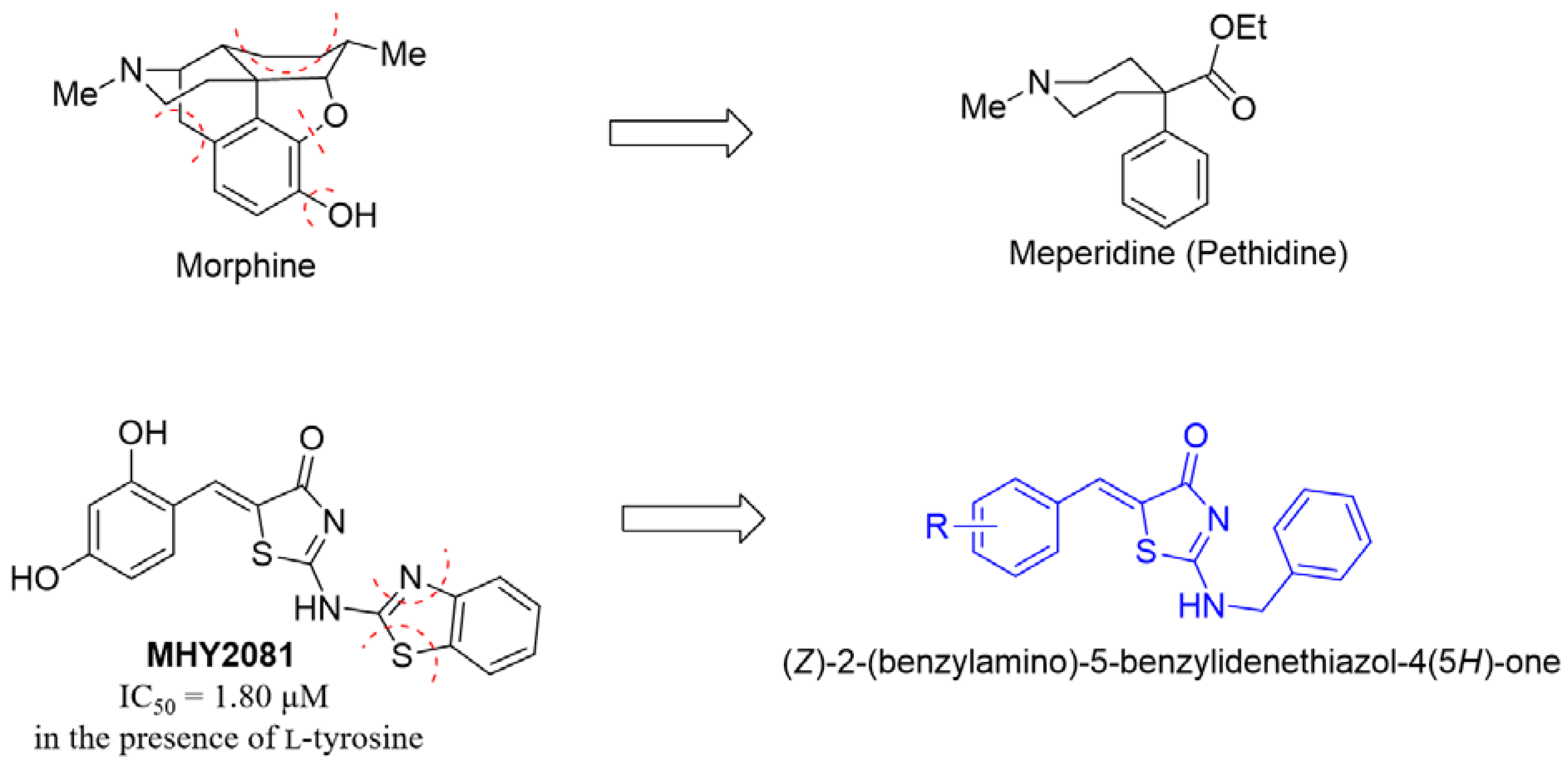
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Mushroom Tyrosinase Inhibition of BABT Derivatives
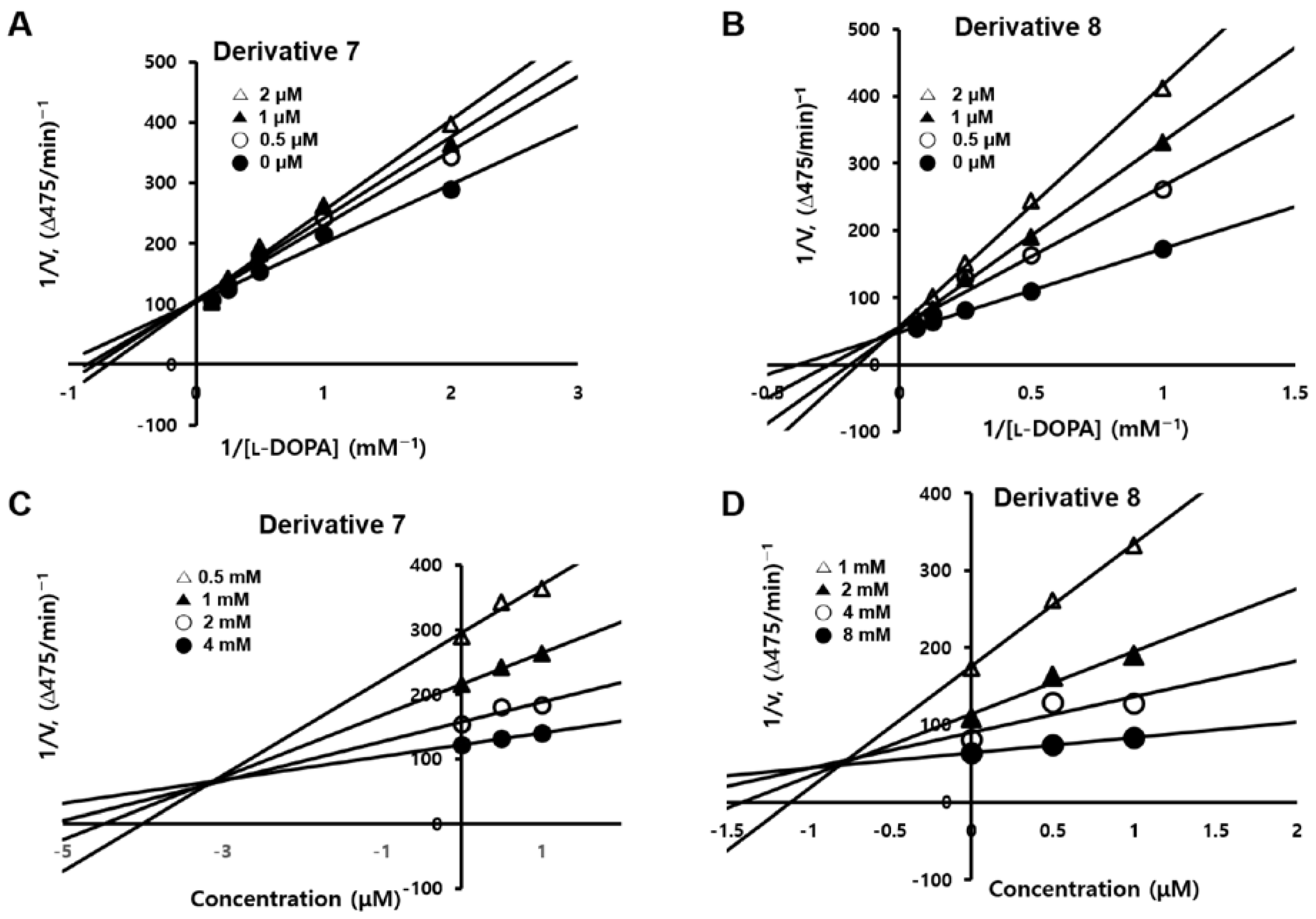
2.3. Inhibitory Mechanisms of Derivatives 7 and 8 against Mushroom Tyrosinase
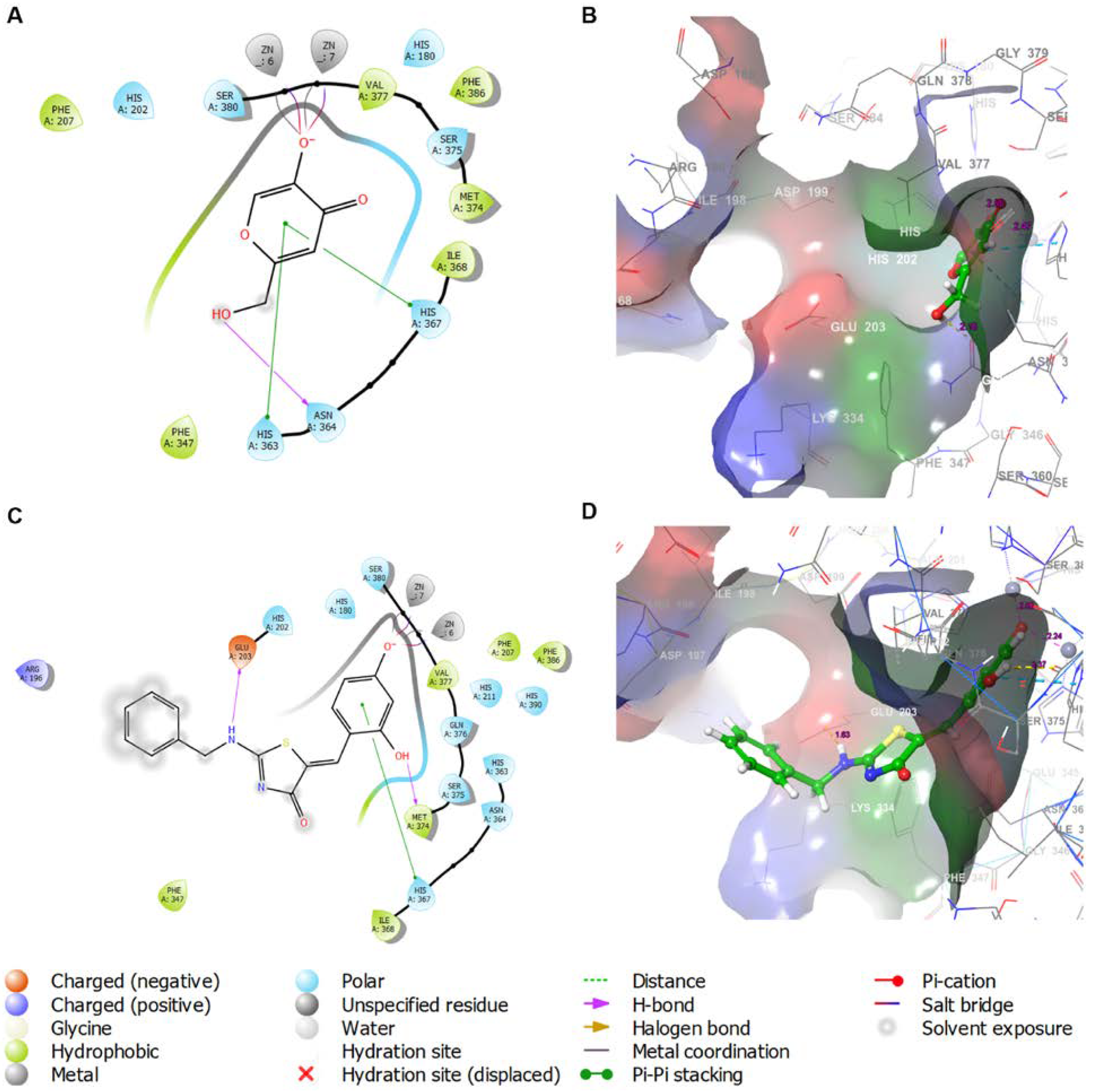
2.4. In Silico Docking Simulations of BABT Derivatives 7 and 8 with Various Tyrosinases
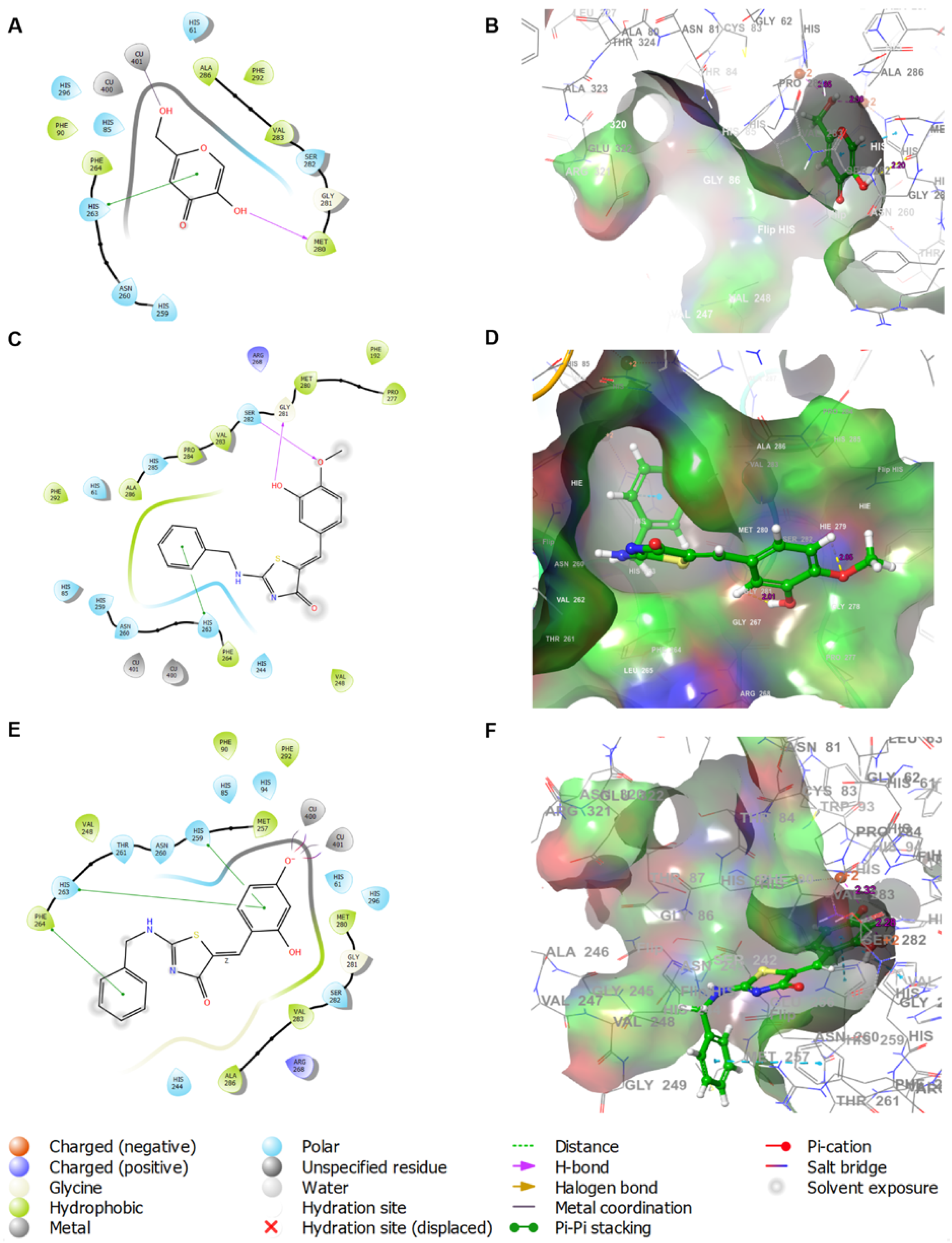
2.4.1. In Silico Docking Simulations of BABT Derivatives 7 and 8 with Mushroom Tyrosinase
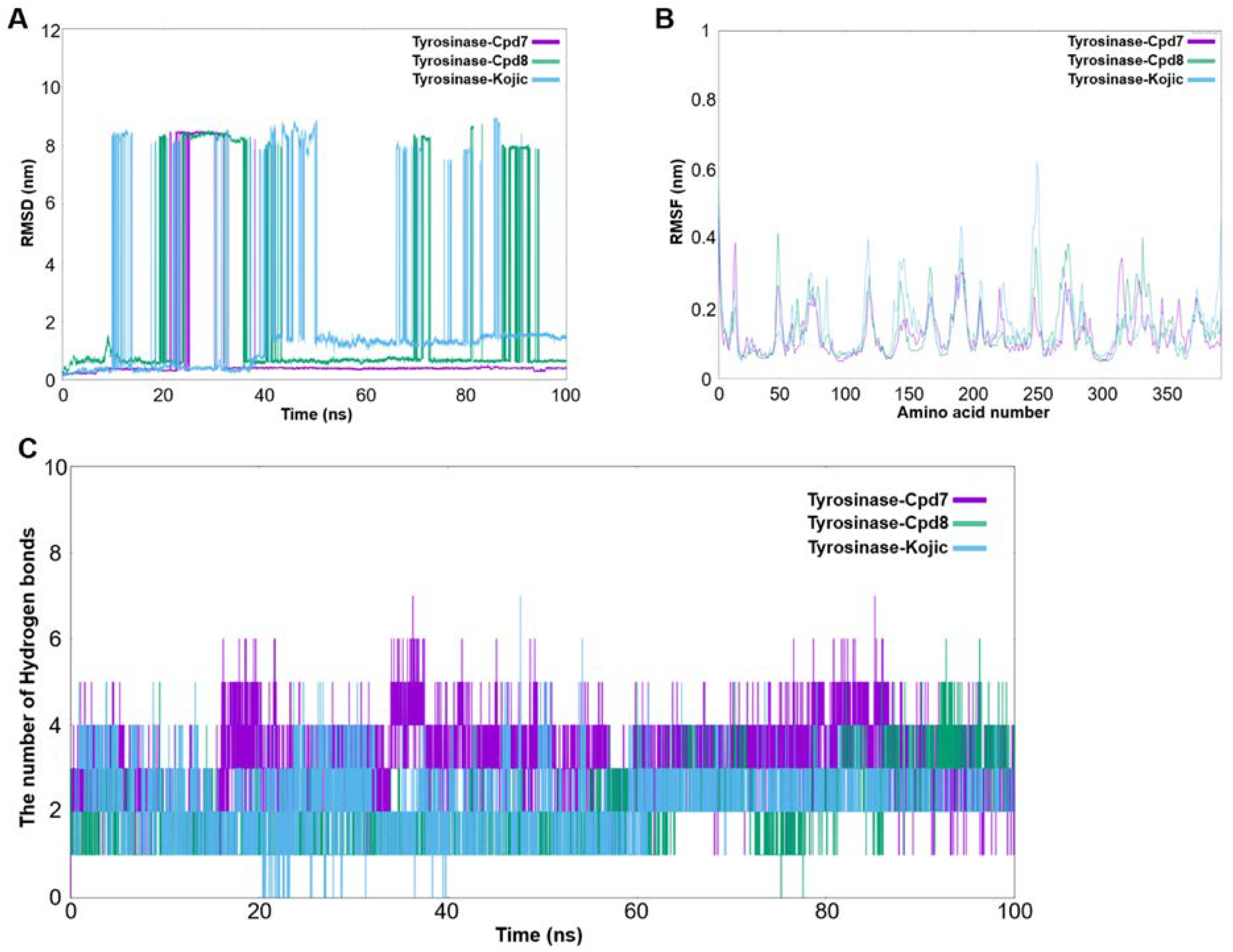
2.4.2. Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Simulation
2.4.3. In Silico Docking Simulations of BABT Derivatives 7 and 8 with Human Tyrosinase
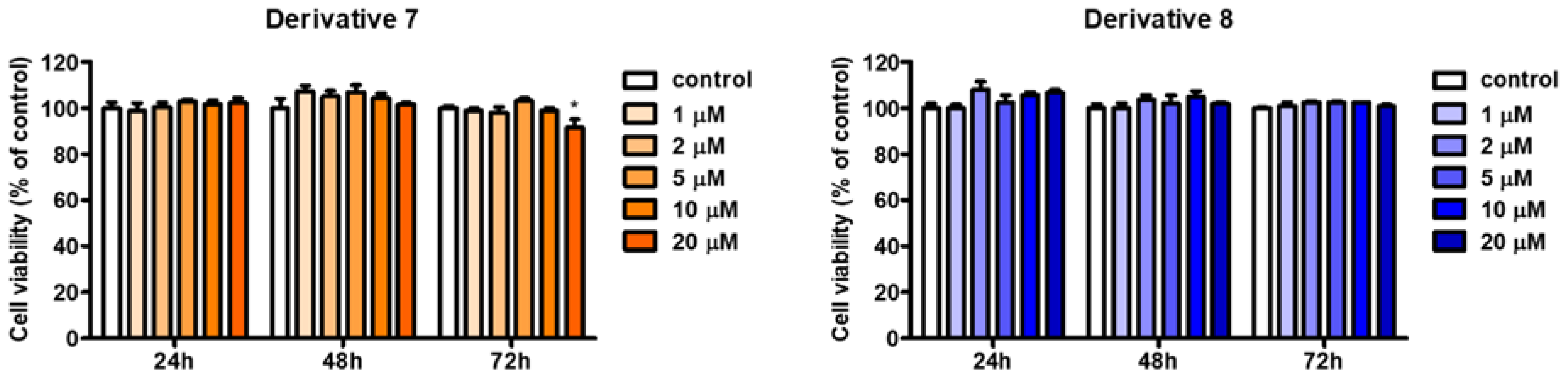
2.5. Cell Viabilities of BABT Derivatives 7 and 8 in B16F10 Cells
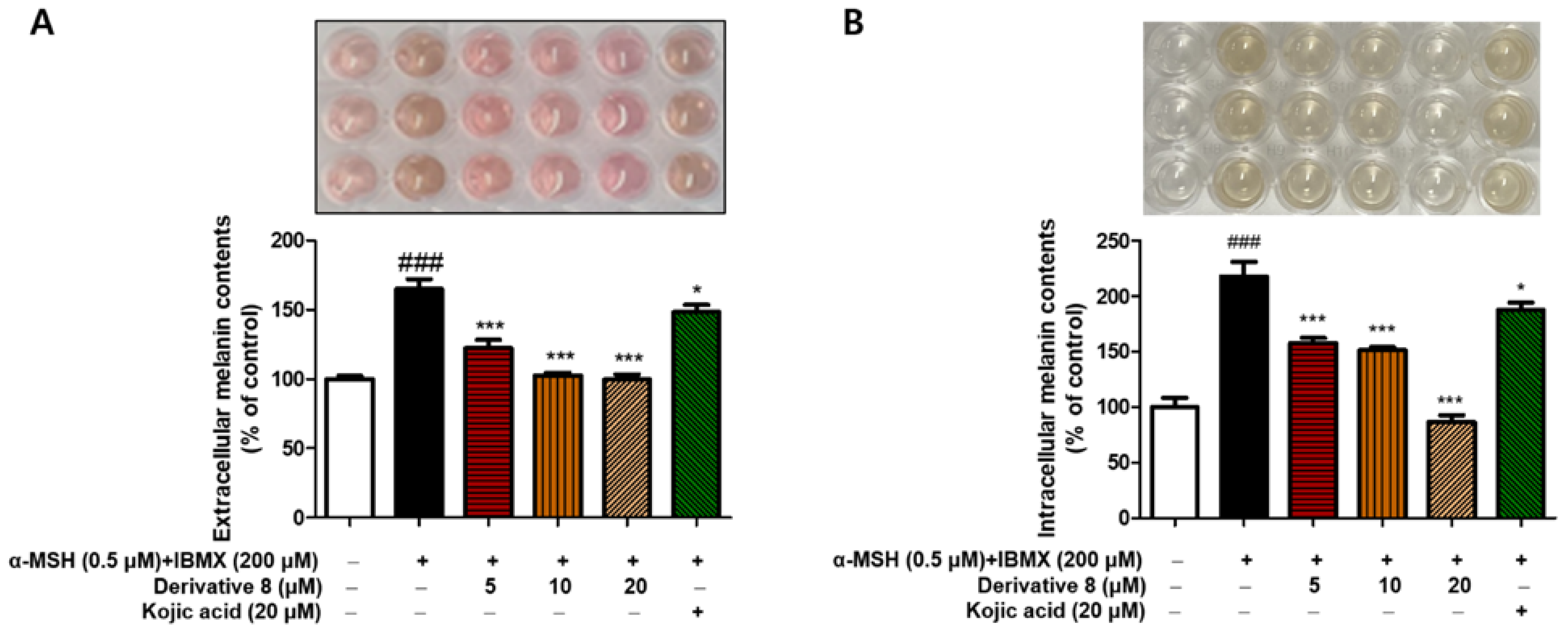
2.6. Effects of BABT Derivative 8 on Extracellular and Intracellular Melanin Production in B16F10 Cells
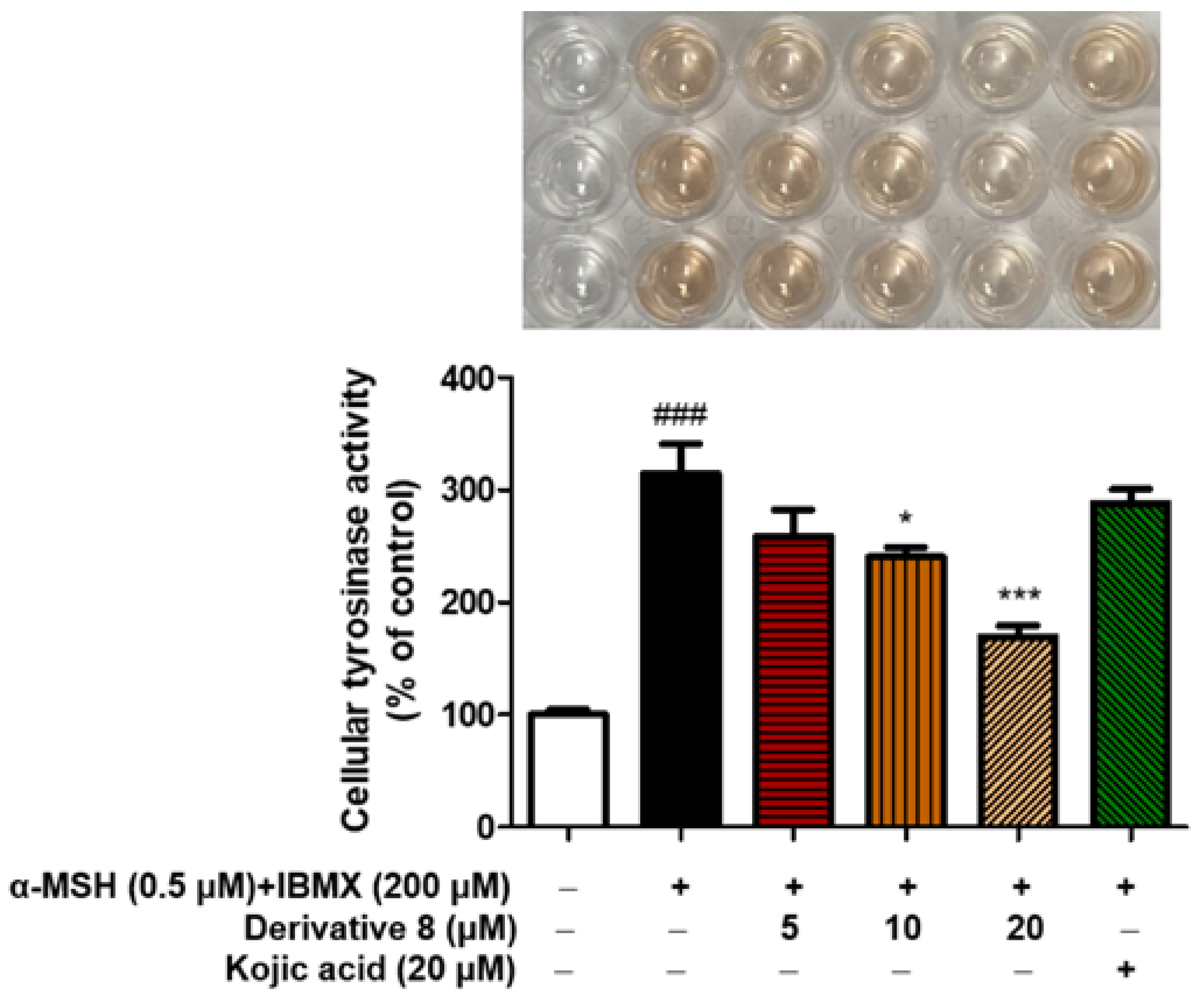
2.7. Effect of BABT Derivative 8 on Tyrosinase Activity in B16F10 Cells
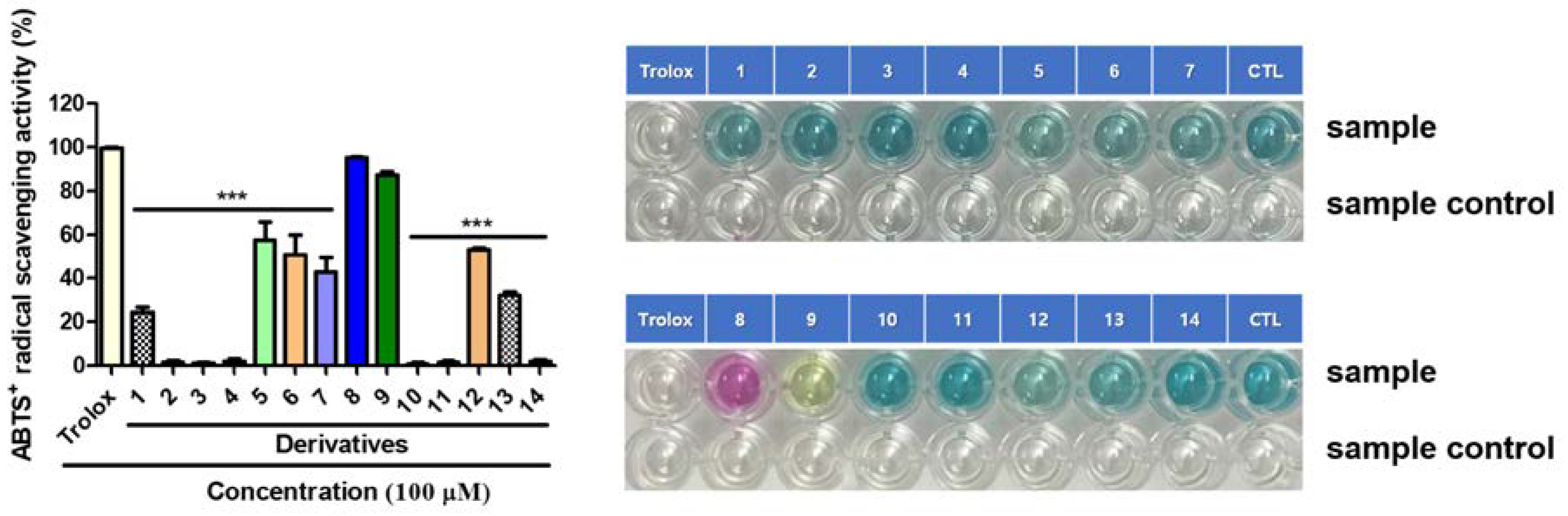
2.8. Radical Scavenging Effects of BABT Derivatives 1–14 on 2,2-Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2′-Azino-Bis(3-Ethylbenzothiazoline-6-Sulfonic Acid) (ABTS)
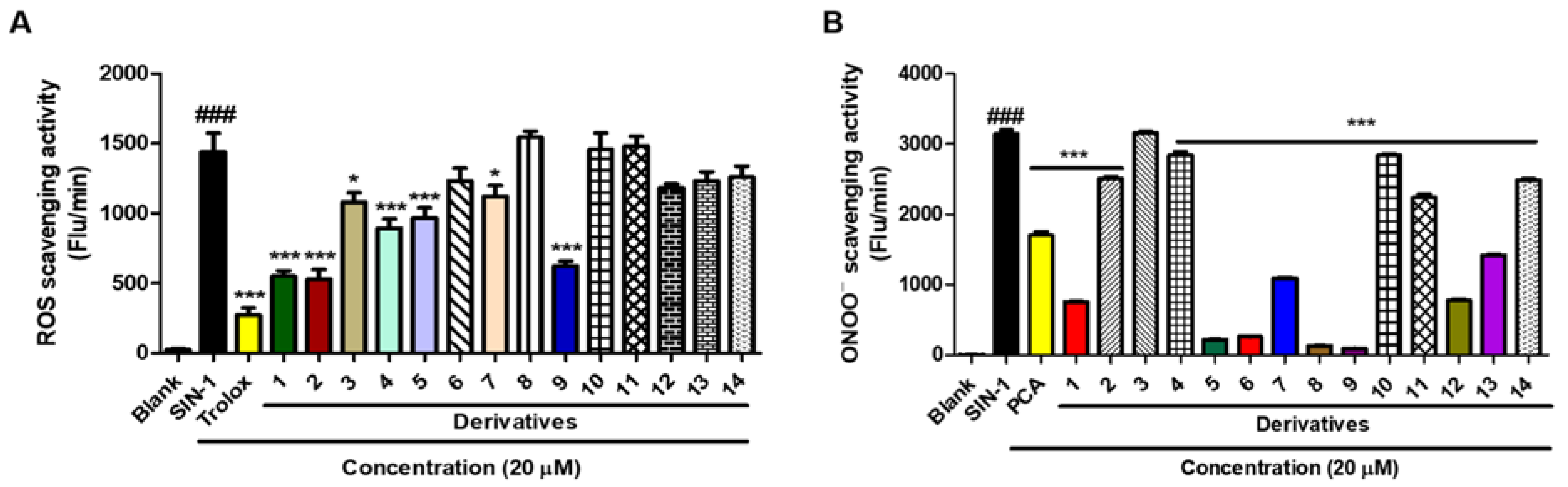
2.9. Scavenging Activities of BABT Derivatives against Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Peroxynitrite
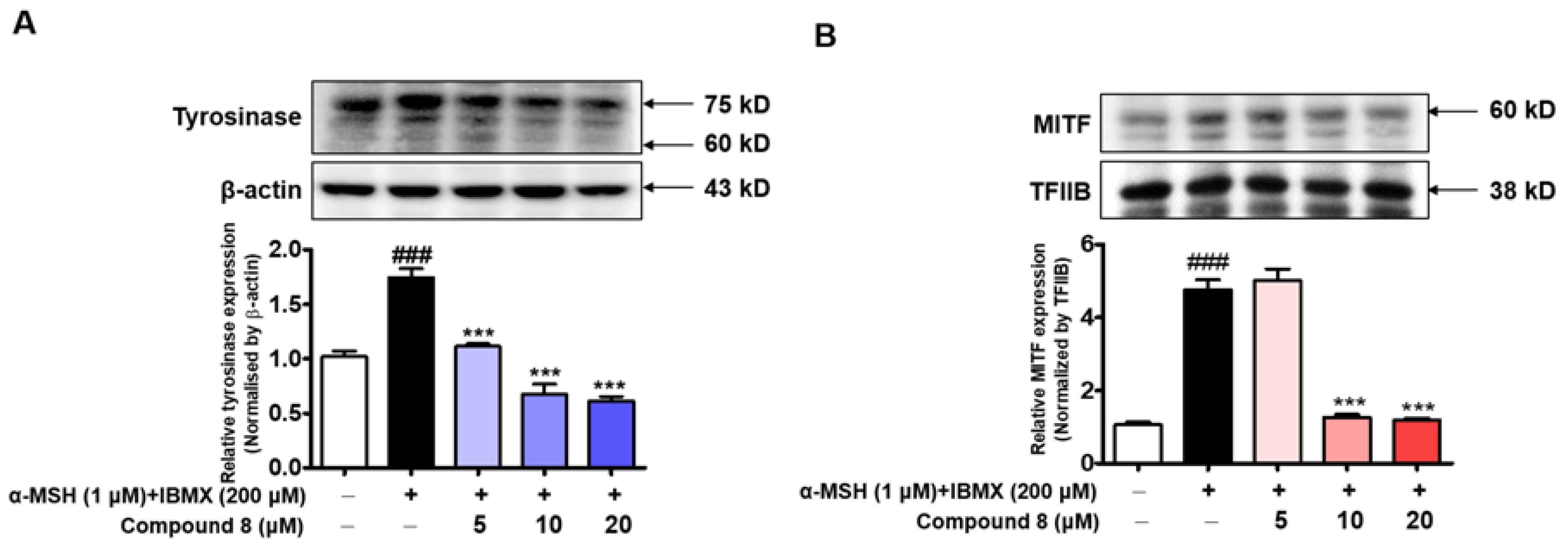
2.10. Effects of BABT Derivative 8 on the Expression Levels of Tyrosinase and Microphthalmia-associated Transcription Factor (MITF) Proteins
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. In Vitro Assays and In Silico and Kinetic Studies
3.2.1. Mushroom Tyrosinase Inhibition Assay
3.2.2. Kinetic Studies of the Efficacies of Derivatives 7 and 8 in Mushroom Tyrosinase Inhibition
3.2.3. In Silico Study of Chemical Interactions between Kojic Acid and Derivatives 7 and 8 and Mushroom Tyrosinase
3.2.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3.2.5. In Silico Study of Chemical Interactions between Kojic Acid and Derivative 8 and the Human Tyrosinase Homology Model
3.2.6. Cell Culture
3.2.7. Cell Viability Assays
3.2.8. Measurement of Melanin Levels
3.2.9. Anti-Tyrosinase Activity Assay
3.2.10. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
3.2.11. ABTS Radical Scavenging Assay
3.2.12. SIN-1-Induced ROS Scavenging Assays
3.2.13. Peroxynitrite Scavenging Assays
3.2.14. Western Blotting Analysis of Tyrosinase and MITF Proteins
3.2.15. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flurkey, A.; Cooksey, J.; Reddy, A.; Spoonmore, K.; Rescigno, A.; Inlow, J.; Flurkey, W.H. Enzyme, Protein, Carbohydrate, and Phenolic Contaminants in Commercial Tyrosinase Preparations: Potential Problems Affecting Tyrosinase Activity and Inhibition Studies. J. Agri. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4760–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galasiti Kankanamalage, A.C.; Weerawarna, P.M.; Kim, Y.; Chang, K.-O.; Groutas, W.C. Anti-norovirus therapeutics: A patent review (2010-2015). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.Y.; Fisher, D.E. Melanocyte biology and skin pigmentation. Nature 2007, 445, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamura, Y.; Coelho, S.G.; Wolber, R.; Miller, S.A.; Wakamatsu, K.; Zmudzka, B.Z.; Ito, S.; Smuda, C.; Passeron, T.; Choi, W. Regulation of human skin pigmentation and responses to ultraviolet radiation. Pigment Cell Res. 2007, 20, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Son, S.; Yun, H.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Chun, P.; Moon, H.R. Tyrosinase inhibitors: A patent review (2011–2015). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, Y.J.; Woo, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Park, M.H.; Lee, H.W.; Chun, P.; Chung, H.Y.; et al. Benzylidene-linked thiohydantoin derivatives as inhibitors of tyrosinase and melanogenesis: Importance of the β-phenyl-α,β-unsaturated carbonyl functionality. MedChemComm 2014, 5, 1410–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, P.A. Melanogenesis and melanoma. Pigment. Cell Res. 2003, 16, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, X.; Nie, H.; Kifat, J.; Li, J.; Huo, Z.; Bi, J.; Yan, X. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of TYR gene family in Ruditapes philippinarum under the challenge of Vibrio anguillarum. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 37, 100788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulier, B.; Pérès, B.; Haudecoeur, R. Advances in the Design of Genuine Human Tyrosinase Inhibitors for Targeting Melanogenesis and Related Pigmentations. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 13428–13443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearing, V.J.; Tsukamoto, K. Enzymatic control of pigmentation in mammals. FASEB J. 1991, 5, 2902–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.W.; Park, Y.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, M.H.; Ha, Y.M.; Uehara, Y.; Yoon, J.H.; Chun, P.; Moon, H.R.; Chung, H.Y. Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo anti-melanogenic activity of a newly synthesized strong tyrosinase inhibitor (E)-3-(2,4 dihydroxybenzylidene)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione (3-DBP). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Kang, D.; Lee, S.; Ikram, M.; Park, C.; Park, Y.; Yoon, S.; Chun, P.; Moon, H.R. Synthesis of cinnamic amide derivatives and their anti-melanogenic effect in α-MSH-stimulated B16F10 melanoma cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.J.; Choi, D.C.; Noh, S.G.; Choi, H.; Choi, I.; Ryu, I.Y.; Chung, H.Y.; Moon, H.R. New Benzimidazothiazolone Derivatives as Tyrosinase Inhibitors with Potential Anti-Melanogenesis and Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging Activities. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, I.Y.; Choi, I.; Jung, H.J.; Ullah, S.; Choi, H.; Al-Amin, M.; Chun, P.; Moon, H.R. In vitro anti-melanogenic effects of chimeric compounds, 2-(substituted benzylidene)-1,3-indanedione derivatives with a β-phenyl-α, β -unsaturated dicarbonyl scaffold. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 109, 104688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Young Ryu, I.; Choi, I.; Ullah, S.; Jin Jung, H.; Park, Y.; Hwang, Y.; Jeong, Y.; Hong, S.; Chun, P.; et al. Identification of (Z)-2-benzylidene-dihydroimidazothiazolone derivatives as tyrosinase inhibitors: Anti-melanogenic effects and in silico studies. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Lee, J.; Jung, H.J.; Ullah, S.; Jeong, Y.; Hong, S.; Kang, M.K.; Park, Y.J.; Hwang, Y.; Kang, D.; et al. Design and Synthesis of (Z)-5-(Substituted benzylidene)-3-cyclohexyl-2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one Analogues as Anti-Tyrosinase and Antioxidant Compounds: In Vitro and In Silico Insights. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.; Hong, S.; Jung, H.J.; Ullah, S.; Hwang, Y.; Choi, H.; Ko, J.; Lee, J.; Chun, P.; Chung, H.Y.; et al. Identification of a Novel Class of Anti-Melanogenic Compounds, (Z)-5-(Substituted benzylidene)-3-phenyl-2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one Derivatives, and Their Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging Activities. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.H.; Lee, B.; Son, S.; Yun, H.Y.; Moon, K.M.; Jeong, H.O.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, E.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, D.H.; et al. (Z)-2-(Benzo[d]thiazol-2-ylamino)-5-(substituted benzylidene)thiazol-4(5H)-one Derivatives as Novel Tyrosinase Inhibitors. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranga, R.; Sharma, V.; Kumar, V. New thiazolidinyl analogs containing pyridine ring: Synthesis, biological evaluation and QSAR studies. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 1538–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vögeli, U.; von Philipsborn, W.; Nagarajan, K.; Nair, M.D. Structures of Addition Products of Acetylenedicarboxylic Acid Esters with Various Dinucleophiles. An application of C, H-spin-coupling constants. Helv. Chim. Acta 1978, 61, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ma, L.; Zheng, H.; Chen, L.; Li, R.; He, C.; Yang, S.; Ye, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. Discovery of (Z)-5-(4-Methoxybenzylidene)thiazolidine-2,4-dione, a Readily Available and Orally Active Glitazone for the Treatment of Concanavalin A-Induced Acute Liver Injury of BALB/c Mice. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashantha Kumar, B.R.; Baig, N.R.; Sudhir, S.; Kar, K.; Kiranmai, M.; Pankaj, M.; Joghee, N.M. Discovery of novel glitazones incorporated with phenylalanine and tyrosine: Synthesis, antidiabetic activity and structure–activity relationships. Bioorg. Chem. 2012, 45, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.; Park, Y.; Ryu, I.Y.; Jung, H.J.; Ullah, S.; Choi, H.; Park, C.; Kang, D.; Lee, S.; Chun, P.; et al. In silico and in vitro insights into tyrosinase inhibitors with a 2-thioxooxazoline-4-one template. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahomoodally, M.F.; Picot-Allain, M.C.N.; Zengin, G.; Llorent-Martínez, E.J.; Abdullah, H.H.; Ak, G.; Senkardes, I.; Chiavaroli, A.; Menghini, L.; Recinella, L.; et al. Phytochemical Analysis, Network Pharmacology and in Silico Investigations on Anacamptis pyramidalis Tuber Extracts. Molecules 2020, 25, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashooriha, M.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Moradi, S.E.; Rafiei, A.; Kardan, M.; Emami, S. 1, 2, 3-Triazole-based kojic acid analogs as potent tyrosinase inhibitors: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 82, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Mo, J.; Xiong, B.; Liao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xing, S.; He, S.; Lyu, W.; Zhang, N.; et al. Discovery of Resorcinol-Based Polycyclic Structures as Tyrosinase Inhibitors for Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi-Matsunaga, Y.; Ishii, T.; Hamaguchi, T.; Osada, H.; Sato, M. Synthesis and Characterization of a Novel Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Inhibitor, 2-(Cyclobutylamino)- N- (2-Furylmethyl)-2-Thioxoacetamide. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2005, 2, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigalapalli, D.K.; Pooladanda, V.; Kadagathur, M.; Guggilapu, S.D.; Uppu, J.L.; Godugu, C.; Bathini, N.B.; Tangellamudi, N.D. Novel chromenyl-based 2-iminothiazolidin-4-one derivatives as tubulin polymerization inhibitors: Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modelling studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1225, 128847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Ashraf, Z.; Abbas, Q.; Raza, H.; Seo, S.-Y. Exploration of Novel Human Tyrosinase Inhibitors by Molecular Modeling, Docking and Simulation Studies. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2018, 10, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Mahesar, P.A.; Channar, P.A.; Abbas, Q.; Larik, F.A.; Hassan, M.; Raza, H.; Seo, S.-Y. Synthesis, molecular docking studies of coumarinyl-pyrazolinyl substituted thiazoles as non-competitive inhibitors of mushroom tyrosinase. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 74, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larik, F.A.; Saeed, A.; Channar, P.A.; Muqadar, U.; Abbas, Q.; Hassan, M.; Seo, S.-Y.; Bolte, M. Design, synthesis, kinetic mechanism and molecular docking studies of novel 1-pentanoyl-3-arylthioureas as inhibitors of mushroom tyrosinase and free radical scavengers. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 141, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra Precision Glide: Docking and Scoring Incorporating a Model of Hydrophobic Enclosure for Protein−Ligand Complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboraia, A.S.; Abdel-Rahman, H.M.; Mahfouz, N.M.; El-Gendy, M.A. Novel 5-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-substituted-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thione derivatives: Promising anticancer agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ullah, S.; Park, C.; Won Lee, H.; Kang, D.; Yang, J.; Akter, J.; Park, Y.; Chun, P.; Moon, H.R. Inhibitory effects of N-(acryloyl)benzamide derivatives on tyrosinase and melanogenesis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3929–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Park, C.; Ikram, M.; Kang, D.; Lee, S.; Yang, J.; Park, Y.; Yoon, S.; Chun, P.; Moon, H.R. Tyrosinase inhibition and anti-melanin generation effect of cinnamamide analogues. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBel, C.P.; Bondy, S.C. Sensitive and rapid quantitation of oxygen reactive species formation in rat synaptosomes. Neurochem. Int. 1990, 17, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.F.; LeBel, C.P.; Bondy, S.C. Reactive oxygen species formation as a biomarker of methylmercury and trimethyltin neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 1992, 13, 637–648. [Google Scholar]
- Kooy, N.W.; Royall, J.A.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Beckman, J.S. Peroxynitrite-mediated oxidation of dihydrorhodamine 123. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1994, 16, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compd | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | IC50 (µM) a | |
| l-Tyrosine | l-Dopa | |||||
| 1 | H | H | OH | H | 27.5 ± 2.93 | 65.1 ± 8.29 |
| 2 | H | H | OMe | H | 125.5 ± 10.04 | 239.4 ± 2.38 |
| 3 | F | H | F | H | >300 | >300 |
| 4 | H | F | F | H | 288.7 ± 14.72 | >300 |
| 5 | H | OMe | OH | H | 148.3 ± 1.12 | >300 |
| 6 | H | OEt | OH | H | 198.9 ± 8.57 | 248.1 ± 11.54 |
| 7 | H | OH | OMe | H | 10.0 ± 0.90 | 10.3 ± 0.24 |
| 8 | OH | H | OH | H | 0.27 ± 0.03 | 1.04 ± 0.05 |
| 9 | H | OH | OH | H | >300 | >300 |
| 10 | OMe | H | OMe | H | 293.3 ± 13.12 | 213.6 ± 6.29 |
| 11 | H | OMe | OMe | H | >300 | >300 |
| 12 | H | OMe | OH | OMe | 166.0 ± 8.04 | >300 |
| 13 | H | t-Bu | OH | t-Bu | 136.7 ± 10.69 | >300 |
| 14 | H | OMe | OMe | OMe | 192.4 ± 9.04 | 231.1 ± 7.43 |
| b KA | 28.6 ± 3.56 | 20.1 ± 0.46 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Park, Y.J.; Jung, H.J.; Ullah, S.; Yoon, D.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Kang, M.K.; Kang, D.; Park, Y.; et al. Design and Synthesis of (Z)-2-(Benzylamino)-5-benzylidenethiazol-4(5H)-one Derivatives as Tyrosinase Inhibitors and Their Anti-Melanogenic and Antioxidant Effects. Molecules 2023, 28, 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020848
Lee J, Park YJ, Jung HJ, Ullah S, Yoon D, Jeong Y, Kim GY, Kang MK, Kang D, Park Y, et al. Design and Synthesis of (Z)-2-(Benzylamino)-5-benzylidenethiazol-4(5H)-one Derivatives as Tyrosinase Inhibitors and Their Anti-Melanogenic and Antioxidant Effects. Molecules. 2023; 28(2):848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020848
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jieun, Yu Jung Park, Hee Jin Jung, Sultan Ullah, Dahye Yoon, Yeongmu Jeong, Ga Young Kim, Min Kyung Kang, Dongwan Kang, Yujin Park, and et al. 2023. "Design and Synthesis of (Z)-2-(Benzylamino)-5-benzylidenethiazol-4(5H)-one Derivatives as Tyrosinase Inhibitors and Their Anti-Melanogenic and Antioxidant Effects" Molecules 28, no. 2: 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020848
APA StyleLee, J., Park, Y. J., Jung, H. J., Ullah, S., Yoon, D., Jeong, Y., Kim, G. Y., Kang, M. K., Kang, D., Park, Y., Chun, P., Chung, H. Y., & Moon, H. R. (2023). Design and Synthesis of (Z)-2-(Benzylamino)-5-benzylidenethiazol-4(5H)-one Derivatives as Tyrosinase Inhibitors and Their Anti-Melanogenic and Antioxidant Effects. Molecules, 28(2), 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020848







