Hesperidin Methyl Chalcone Reduces the Arthritis Caused by TiO2 in Mice: Targeting Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Cytokine Production, and Nociceptor Sensory Neuron Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
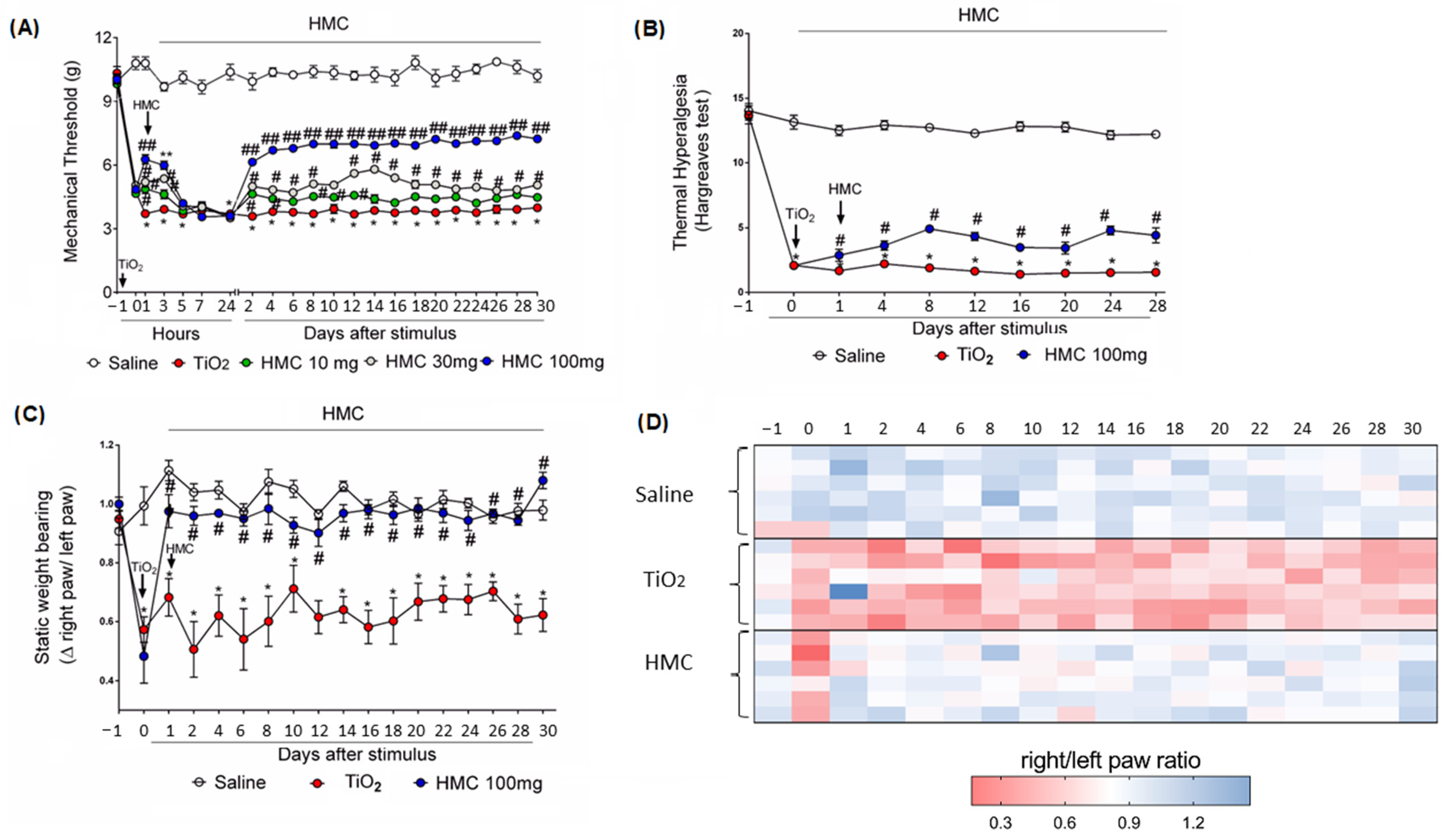
2.1. Hesperidin Methyl Chalcone (HMC) Reduces Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia and Weight Distribution Imbalance in the Titanium Dioxide (TiO2)-Induced Arthritis Model
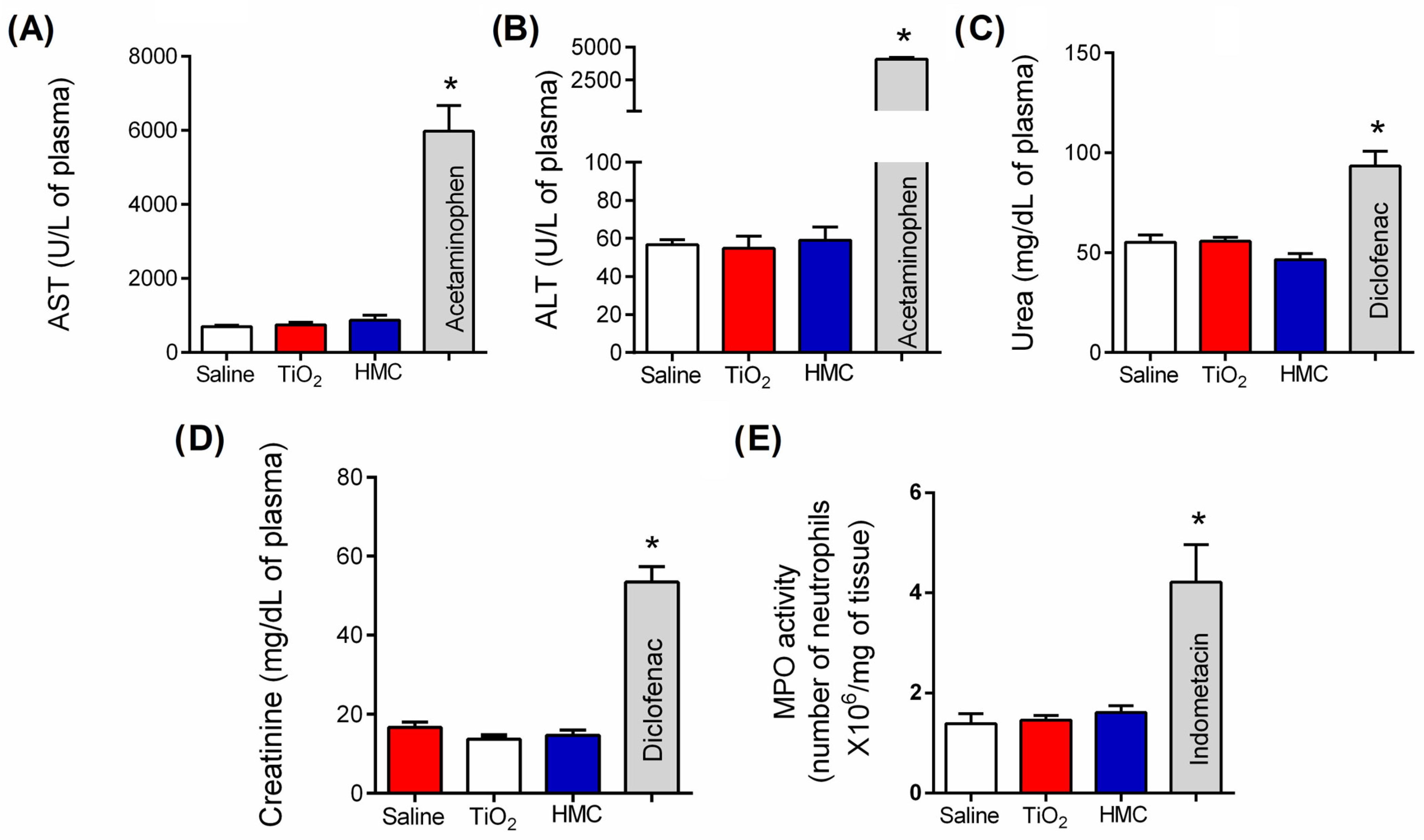
2.2. HMC Does Not Induce Kidney, Liver, or Stomach Damage
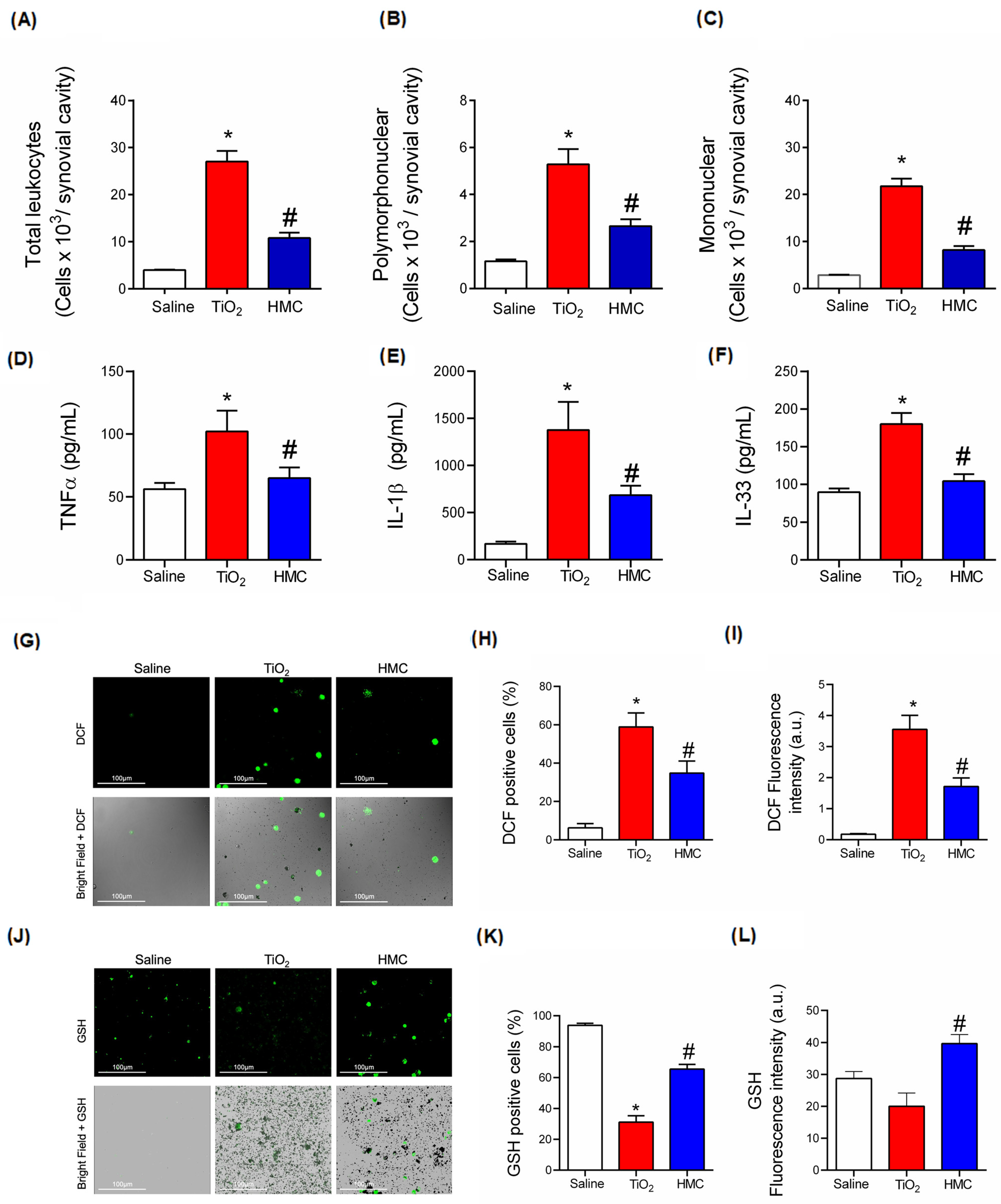
2.3. HMC Reduces Articular Edema and Recruitment of Leukocytes in TiO2 Arthritis
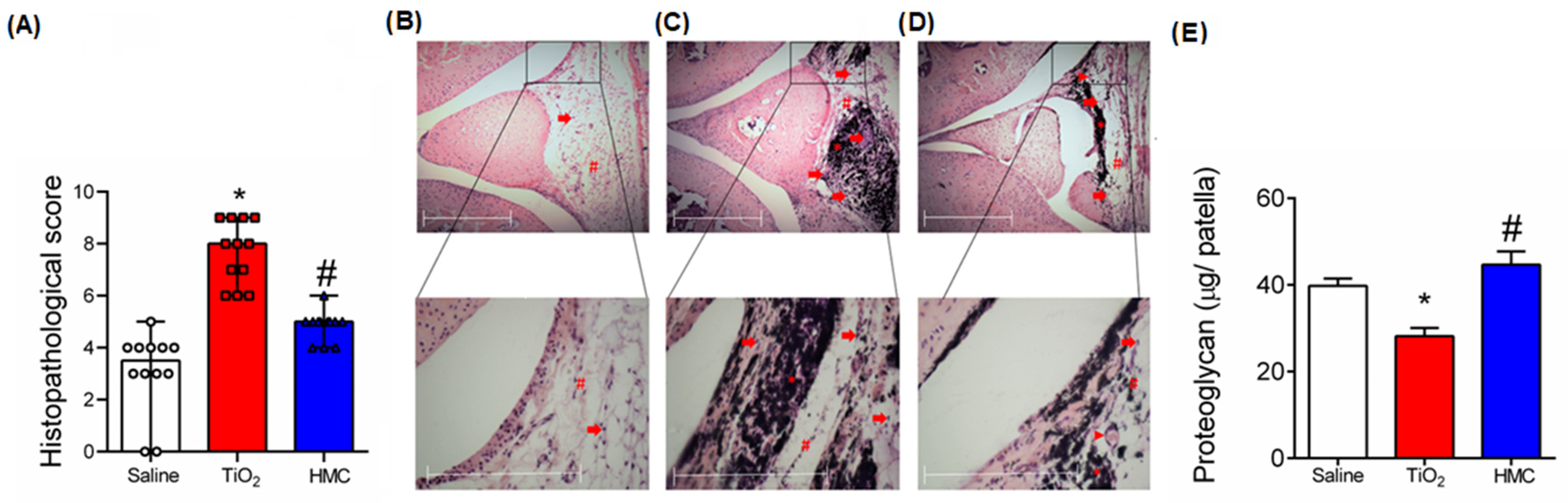
2.4. HMC Reduces the Histopathological Changes and Cartilage Degradation Caused by TiO2-Induced Arthritis
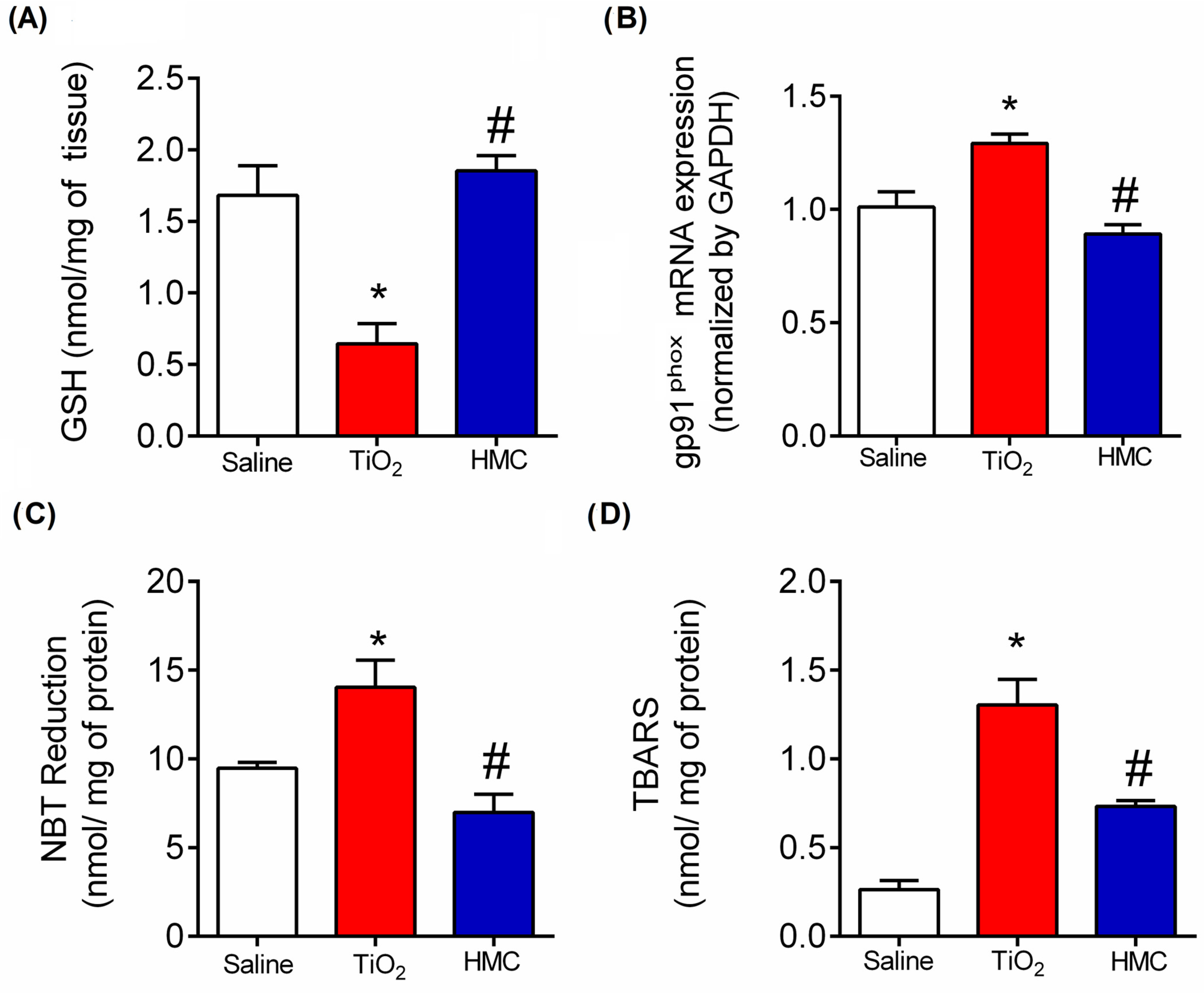
2.5. HMC Reduces Oxidative Stress in TiO2-Induced Arthritis
2.6. HMC Reduces Acute Inflammation in TiO2-Induced Arthritis with Respect to Leukocyte Recruitment, Cytokine Production, and Oxidative Stress
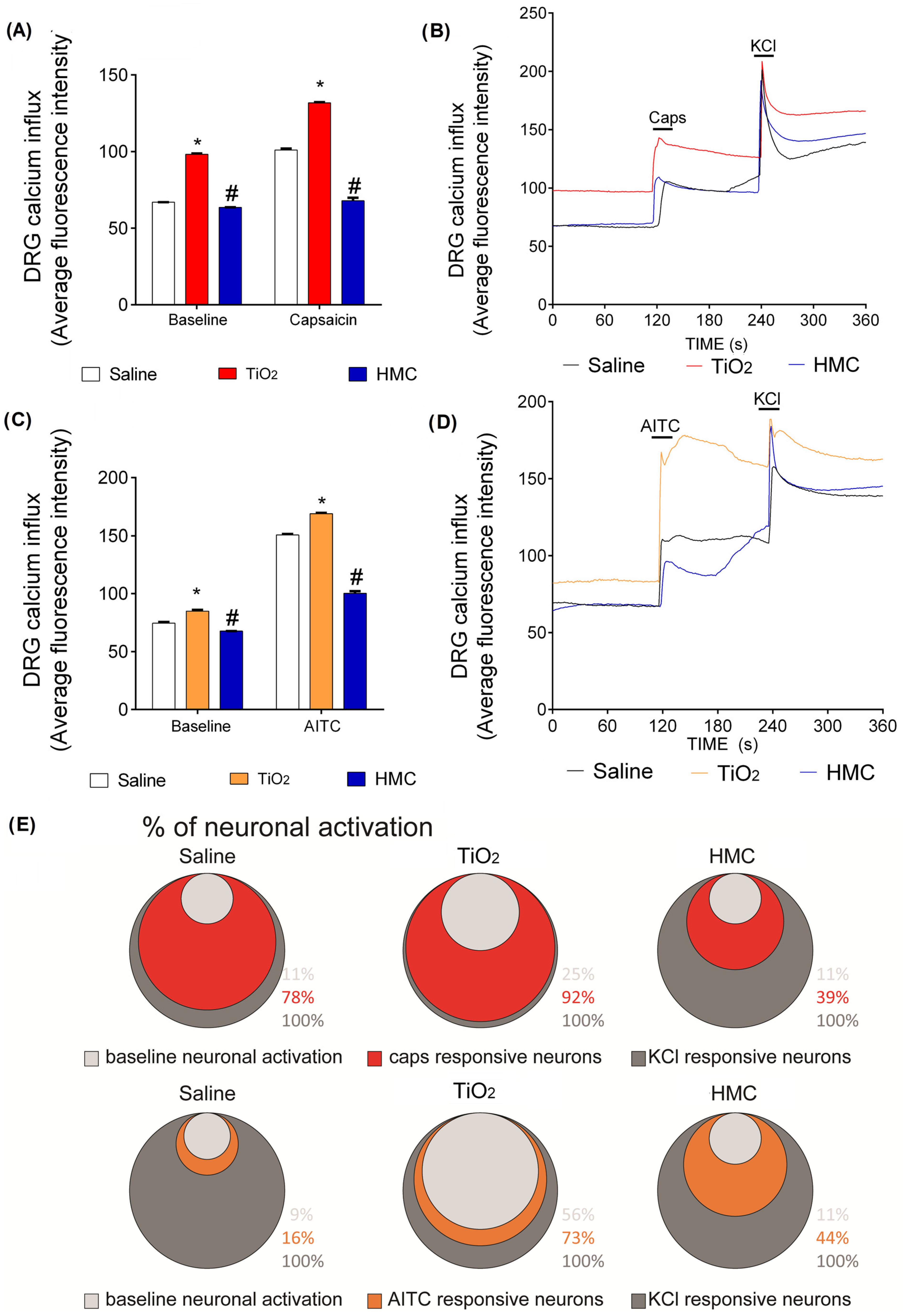
2.7. HMC Reduces Nociceptor Sensory Neuron Activation Caused by TiO2-Induced Arthritis
3. Discussion
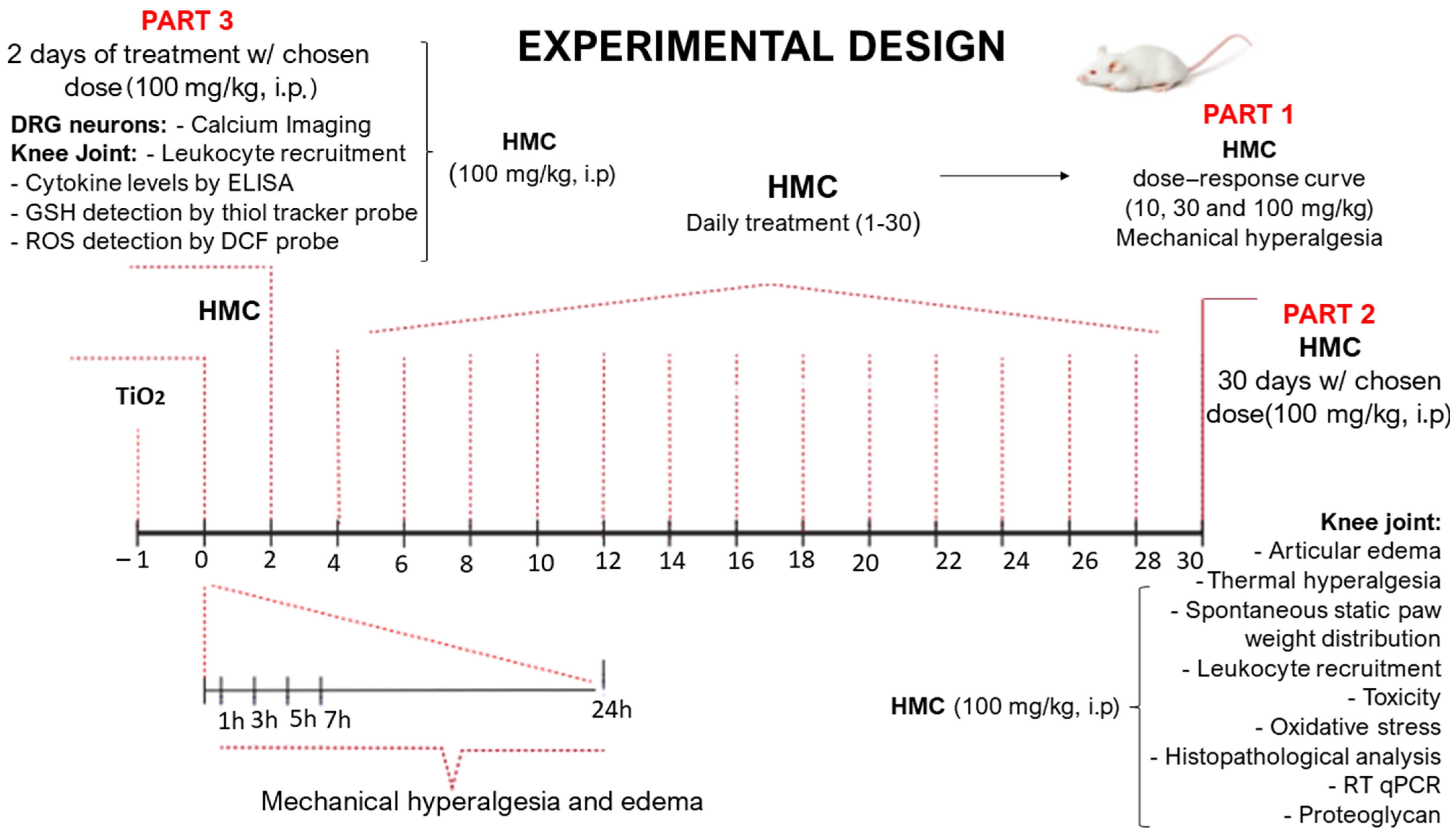
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Animals
4.3. Test Compounds
4.4. Evaluation of Articular Mechanical Hyperalgesia
4.5. Thermal Hyperalgesia
4.6. Static Weight Bearing
4.7. Stomach Toxicity Assay (Myeloperoxidase)
4.8. Liver and Kidney Toxicity Assays
4.9. Articular Edema Measurements
4.10. Leukocyte Migration Evaluation
4.11. Histological Processing
4.12. Proteoglycan Assay
4.13. RT-qPCR
4.14. Measurement of Reduced Glutathione (GSH) Level
4.15. Nitrobluetetrazolium Reduction
4.16. Lipid Peroxidation
4.17. Intracellular GSH Detection in Recruited Leukocytes Using a Thiol-Tracker Fluorescent Probe
4.18. Intracellular Total ROS Detection by DCF Probe in Recruited Leukocytes
4.19. TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-33 Cytokine Levels Determined by ELISA Assay
4.20. Calcium Imaging
4.21. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Cobelli, N.; Scharf, B.; Crisi, G.M.; Hardin, J.; Santambrogio, L. Mediators of the inflammatory response to joint replacement devices. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Goodman, S.B. Current state and future of joint replacements in the hip and knee. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2008, 5, 383–393. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, M.D.C.; Oliveira, J.C.P.; Zidan, F.F.; Franciozi, C.E.D.S.; Luzo, M.V.M.; Abdalla, R.J. Total knee and hip arthroplasty: The reality of assistance in Brazilian public health care. Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2018, 53, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soever, L.J.; MacKay, C.; Saryeddine, T.; Davis, A.M.; Flannery, J.F.; Jaglal, S.B.; Levy, C.; Mahomed, N. Educational needs of patients undergoing total joint arthroplasty. Physiother. Can. 2010, 62, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, K.W.; Freeman, W.J.; Elixhauser, A. Overview of operating room procedures during inpatient stays in US hospitals. Stat. Brief 2018, 2014, 233. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz, S.; Ong, K.; Lau, E.; Mowat, F.; Halpern, M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. Jbjs 2007, 89, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J. Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg. Relat. Res. 2016, 28, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, R.B.; Chesworth, B.; Davis, A.; Mahomed, N.; Charron, K. Comparing patient outcomes after THA and TKA: Is there a difference? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, W.H. Wear and periprosthetic osteolysis: The problem. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2001, 393, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purdue, P.E.; Koulouvaris, P.; Nestor, B.J.; Sculco, T.P. The central role of wear debris in periprosthetic osteolysis. HSS J. 2006, 2, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, S.D.; Seyler, T.M.; Bennett, D.; Delanois, R.E.; Saleh, K.J.; Thongtrangan, I.; Kuskowski, M.; Cheng, E.Y.; Sharkey, P.F.; Parvizi, J.; et al. Total hip arthroplasties: What are the reasons for revision? Int. Orthop. 2008, 32, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostu, D.; Lucaciu, O.; Berce, C.; Lucaciu, D.; Cosma, D. Current methods of preventing aseptic loosening and improving osseointegration of titanium implants in cementless total hip arthroplasty: A review. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 2104–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, A.G.; Schmalzreid, T.P. The clinical significance of metal ion release from cobalt-chromium metal-on-metal hip joint arthroplasty. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2006, 220, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, T.A.; Parvizi, J.; Della Valle, C.J.; Steinbeck, M.J. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species induce protein and DNA modifications driving arthrofibrosis following total knee arthroplasty. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2009, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghi, S.M.; Mizokami, S.S.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Fattori, V.; Crespigio, J.; Clemente-Napimoga, J.T.; Napimoga, M.H.; Pitol, D.L.; Issa, J.P.; Fukada, S.Y.; et al. The flavonoid quercetin inhibits titanium dioxide (TiO2)-induced chronic arthritis in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 53, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchope, M.F.; Artero, N.A.; Fattori, V.; Mizokami, S.S.; Pitol, D.L.; Issa, J.P.; Fukada, S.Y.; Cunha, T.M.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Cunha, F.Q.; et al. Naringenin mitigates titanium dioxide (TiO2)-induced chronic arthritis in mice: Role of oxidative stress, cytokines, and NFκB. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 997–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooley, P.H.; Nasser, S.; Fitzgerald, R.H. The immune response to implant materials in humans. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1996, 326, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, S.B. Wear particles, periprosthetic osteolysis and the immune system. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 5044–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, D.M.; Girard, D. Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles induce neutrophil influx and local production of several pro-inflammatory mediators in vivo. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurr, J.R.; Wang, A.S.; Chen, C.H.; Jan, K.Y. Ultrafine titanium dioxide particles in the absence of photoactivation can induce oxidative damage to human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicology 2005, 213, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Xue, C.; Zhou, S.; Lan, F.; Bi, L.; Xu, H.; Yang, X.; Zeng, F.D. Toxicity and penetration of TiO2 nanoparticles in hairless mice and porcine skin after subchronic dermal exposure. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 191, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.K.; Sharma, V.; Pandey, A.K.; Singh, S.; Sultana, S.; Dhawan, A. ROS-mediated genotoxicity induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in human epidermal cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2011, 25, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambalavanan, N.; Stanishevsky, A.; Bulger, A.; Halloran, B.; Steele, C.; Vohra, Y.; Matalon, S. Titanium oxide nanoparticle instillation induces inflammation and inhibits lung development in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2013, 304, L152–L161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, T.C.; Tajuba, J.; Sama, P.; Saleh, N.; Swartz, C.; Parker, J.; Hester, S.; Lowry, G.V.; Veronesi, B. Nanosize titanium dioxide stimulates reactive oxygen species in brain microglia and damages neurons in vitro. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1631–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawien, A.; Bouskela, E.; Allaert, F.A.; Nicolaides, A.N. The place of Ruscus extract, hesperidin methyl chalcone, and vitamin C in the management of chronic venous disease. Int. Angiol. A J. Int. Union Angiol. 2017, 36, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monjotin, N.; Guillaume, T. Lymphotonic activity of Ruscus extract, hesperidin methyl chalcone and vitamin C in human lymphatic smooth muscle cells. Microvasc. Res. 2022, 139, 104274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Hohmann, M.S.; Borghi, S.M.; Zarpelon, A.C.; Guazelli, C.F.; Manchope, M.F.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Protective effects of the flavonoid hesperidin methyl chalcone in inflammation and pain in mice: Role of TRPV1, oxidative stress, cytokines and NF-κB. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 228, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasquel-Oliveira, F.S.; Manchope, M.F.; Staurengo-Ferrari, L.; Ferraz, C.R.; Saraiva-Santos, T.; Zaninelli, T.H.; Fattori, V.; Artero, N.A.; Badaro-Garcia, S.; de Freitas, A.; et al. Hesperidin methyl chalcone interacts with NFκB Ser276 and inhibits zymosan-induced joint pain and inflammation, and RAW 264.7 macrophage activation. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.M.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Steffen, V.S.; Caviglione, C.V.; Pala, D.; Baracat, M.M.; Georgetti, S.R.; Verri, W.A.; Casagrande, R. Topical formulation containing hesperidin methyl chalcone inhibits skin oxidative stress and inflammation induced by ultraviolet B irradiation. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2016, 15, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.M.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Steffen, V.S.; Caviglione, C.V.; Vignoli, J.A.; Baracat, M.M.; Georgetti, S.R.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Casagrande, R. Hesperidin methyl chalcone inhibits oxidative stress and inflammation in a mouse model of ultraviolet B irradiation-induced skin damage. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 148, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guazelli, C.F.; Fattori, V.; Ferraz, C.R.; Borghi, S.M.; Casagrande, R.; Baracat, M.M.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of hesperidin methyl chalcone in experimental ulcerative colitis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2021, 333, 109315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Miyazawa, K.W.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Borghi, S.M.; Staurengo-Ferrari, L.; Fattori, V.; Amaral, F.A.; Teixeira, M.M.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Cunha, T.M.; Cunha, F.Q.; et al. Hesperidin methylchalcone suppresses experimental gout arthritis in mice by inhibiting NF-κB activation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6269–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaninelli, T.H.; Fattori, V.; Saraiva-Santos, T.; Badaro-Garcia, S.; Staurengo-Ferrari, L.; Andrade, K.C.; Artero, N.A.; Ferraz, C.R.; Bertozzi, M.M.; Rasquel-Oliveira, F.; et al. RvD1 disrupts nociceptor neuron and macrophage activation and neuroimmune communication, reducing pain and inflammation in gouty arthritis in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 4500–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattori, V.; Borghi, S.M.; Guazelli, C.F.; Giroldo, A.C.; Crespigio, J.; Bussmann, A.J.; Coelho-Silva, L.; Ludwig, N.G.; Mazzuco, T.L.; Casagrande, R.; et al. Vinpocetine reduces diclofenac-induced acute kidney injury through inhibition of oxidative stress, apoptosis, cytokine production, and NF-κB activation in mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 120, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohmann, M.S.; Cardoso, R.D.; Fattori, V.; Arakawa, N.S.; Tomaz, J.C.; Lopes, N.P.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Hypericum perforatum reduces paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity and lethality in mice by modulating inflammation and oxidative stress. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valério, D.A.; Cunha, T.M.; Arakawa, N.S.; Lemos, H.P.; Da Costa, F.B.; Parada, C.A.; Ferreira, S.H.; Cunha, F.Q.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of the sesquiterpene lactone budlein A in mice: Inhibition of cytokine production-dependent mechanism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 562, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenco-Gonzalez, Y.; Fattori, V.; Domiciano, T.P.; Rossaneis, A.C.; Borghi, S.M.; Zaninelli, T.H.; Bernardy, C.C.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Cunha, T.M.; Cunha, F.Q.; et al. Repurposing of the nootropic drug vinpocetine as an analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent: Evidence in a mouse model of superoxide anion-triggered inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 6481812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, P.; Diehm, C.; Robertson, C. Meta-analysis of clinical trials of Cyclo 3 Fort in the treatment of chronic venous insufficiency. Int. Angiol. 2003, 22, 250. [Google Scholar]
- Kakkos, S.K.; Bouskela, E.; Jawien, A.; Nicolaides, A.N. New data on chronic venous disease: A new place for Cyclo 3® Fort. Int. Angiol. A J. Int. Union Angiol. 2017, 37, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihari, I.; Guex, J.J.; Jawien, A.; Szolnoky, G. Clinical Perspectives and Management of Edema in Chronic Venous Disease—What about Ruscus? Medicines 2022, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghi, S.M.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Hesperidin Methyl Chalcone: An Emerging Compound for the Treatment of Inflammation and Pain. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 203, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero, A.T.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Cunha, T.M.; Silva, T.A.; Schivo, I.R.; Dal-Secco, D.; Canetti, C.; Rocha, F.A.; Parada, C.A.; Cunha, F.Q.; et al. Involvement of LTB4 in zymosan-induced joint nociception in mice: Participation of neutrophils and PGE2. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verri, W.A., Jr.; Vicentini, F.T.; Baracat, M.M.; Georgetti, S.R.; Cardoso, R.D.; Cunha, T.M.; Ferreira, S.H.; Cunha, F.Q.; Fonseca, M.J.; Casagrande, R. Flavonoids as anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs: Mechanisms of action and perspectives in the development of pharmaceutical forms. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2012, 36, 297–330. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraz, C.R.; Carvalho, T.T.; Manchope, M.F.; Artero, N.A.; Rasquel-Oliveira, F.S.; Fattori, V.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Therapeutic potential of flavonoids in pain and inflammation: Mechanisms of action, pre-clinical and clinical data, and pharmaceutical development. Molecules 2020, 25, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, R.; Georgetti, S.R.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Dorta, D.J.; dos Santos, A.C.; Fonseca, M.J. Protective effect of topical formulations containing quercetin against UVB-induced oxidative stress in hairless mice. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2006, 84, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Porreca, F.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Galen, K.; Lightfoot, R.; Masini, E.; Muscoli, C.; Mollace, V.; Ndengele, M.; Ischiropoulos, H.; et al. A newly identified role for superoxide in inflammatory pain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 309, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattori, V.; Amaral, F.A.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Neutrophils and arthritis: Role in disease and pharmacological perspectives. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 112, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verri, W.A., Jr.; Cunha, T.M.; Ferreira, S.H.; Wei, X.; Leung, B.P.; Fraser, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Liew, F.Y.; Cunha, F.Q. IL-15 mediates antigen-induced neutrophil migration by triggering IL-18 production. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 3373–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verri, W.A.; Souto, F.O.; Vieira, S.M.; Almeida, S.C.; Fukada, S.Y.; Xu, D.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Cunha, T.M.; Guerrero, A.T.; Mattos-Guimaraes, R.B.; et al. IL-33 induces neutrophil migration in rheumatoid arthritis and is a target of anti-TNF therapy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1697–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamacita-Borin, F.Y.; Zarpelon, A.C.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Fattori, V.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Cunha, F.Q.; Cunha, T.M.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Superoxide anion-induced pain and inflammation depends on TNFα/TNFR1 signaling in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 605, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattori, V.; Staurengo-Ferrari, L.; Zaninelli, T.H.; Casagrande, R.; Oliveira, R.D.; Louzada-Junior, P.; Cunha, T.M.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Teixeira, M.M.; Cunha, F.Q.; et al. IL-33 enhances macrophage release of IL-1β and promotes pain and inflammation in gouty arthritis. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 69, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarpelon, A.C.; Cunha, T.M.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Pinto, L.G.; Ferreira, S.H.; McInnes, I.B.; Xu, D.; Liew, F.Y.; Cunha, F.Q.; Verri, W.A., Jr. IL-33/ST 2 signalling contributes to carrageenin-induced innate inflammation and inflammatory pain: Role of cytokines, endothelin-1 and prostaglandin E 2. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verri, W.A., Jr.; Guerrero, A.T.; Fukada, S.Y.; Valerio, D.A.; Cunha, T.M.; Xu, D.; Ferreira, S.H.; Liew, F.Y.; Cunha, F.Q. IL-33 mediates antigen-induced cutaneous and articular hypernociception in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2723–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarpelon, A.C.; Rodrigues, F.C.; Lopes, A.H.; Souza, G.R.; Carvalho, T.T.; Pinto, L.G.; Xu, D.; Ferreira, S.H.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; McInnes, I.B.; et al. Spinal cord oligodendrocyte-derived alarmin IL-33 mediates neuropathic pain. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussmann, A.J.; Zaninelli, T.H.; Saraiva-Santos, T.; Fattori, V.; Guazelli, C.F.; Bertozzi, M.M.; Andrade, K.C.; Ferraz, C.R.; Camilios-Neto, D.; Casella, A.M.; et al. The Flavonoid Hesperidin Methyl Chalcone Targets Cytokines and Oxidative Stress to Reduce Diclofenac-Induced Acute Renal Injury: Contribution of the Nrf2 Redox-Sensitive Pathway. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Pyo, J.; Kim, G.Y.; Yu, R.; Ju, S.; Kim, W.; Kim, B.S. Capsaicin induces apoptosis by generating reactive oxygen species and disrupting mitochondrial transmembrane potential in human colon cancer cell lines. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2009, 14, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cavanaugh, D.J.; Nemenov, M.I.; Basbaum, A.I. The modality-specific contribution of peptidergic and non-peptidergic nociceptors is manifest at the level of dorsal horn nociresponsive neurons. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 1097–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterina, M.J.; Leffler, A.; Malmberg, A.B.; Martin, W.J.; Trafton, J.; Petersen-Zeitz, K.R.; Koltzenburg, M.; Basbaum, A.I.; Julius, D. Impaired nociception and pain sensation in mice lacking the capsaicin receptor. Science 2000, 288, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanaugh, D.J.; Lee, H.; Lo, L.; Shields, S.D.; Zylka, M.J.; Basbaum, A.I.; Anderson, D.J. Distinct subsets of unmyelinated primary sensory fibers mediate behavioral responses to noxious thermal and mechanical stimuli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9075–9080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattori, V.; Zaninelli, T.H.; Ferraz, C.R.; Brasil-Silva, L.; Borghi, S.M.; Cunha, J.M.; Chichorro, J.G.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Maresin 2 is an analgesic specialized pro-resolution lipid mediator in mice by inhibiting neutrophil and monocyte recruitment, nociceptor neuron TRPV1 and TRPA1 activation, and CGRP release. Neuropharmacology 2022, 216, 109189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meseguer, V.; Alpizar, Y.A.; Luis, E.; Tajada, S.; Denlinger, B.; Fajardo, O.; Manenschijn, J.A.; Fernández-Pena, C.; Talavera, A.; Kichko, T.; et al. TRPA1 channels mediate acute neurogenic inflammation and pain produced by bacterial endotoxins. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanal, J.L.; Cousse, H.; Sicart, M.T.; Bonnaud, B.; Marignan, R. Absorption and elimination of (14C) hesperidin methylchalcone in the rat. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 1981, 6, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, L. Hesperidin methyl chalcone alleviates spinal tuberculosis in New Zealand white rabbits by suppressing immune responses. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2020, 43, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubayev, V.I.; Myers, R.R. Axonal transport of TNF-α in painful neuropathy: Distribution of ligand tracer and TNF receptors. J. Neuroimmunol. 2001, 114, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfers, M.; Geis, C.; Brors, D.; Yaksh, T.L.; Sommer, C. Anterograde transport of tumor necrosis factor-α in the intact and injured rat sciatic nerve. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funez, M.I.; Ferrari, L.F.; Duarte, D.B.; Sachs, D.; Cunha, F.Q.; Lorenzetti, B.B.; Parada, C.A.; Ferreira, S.H. Teleantagonism: A pharmacodynamic property of the primary nociceptive neuron. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19038–19043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattori, V.; Rasquel-Oliveira, F.S.; Artero, N.A.; Ferraz, C.R.; Borghi, S.M.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Diosmin treats lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory pain and peritonitis by blocking NF-κB activation in mice. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staurengo-Ferrari, L.; Ruiz-Miyazawa, K.W.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Domiciano, T.P.; Fattori, V.; Mizokami, S.S.; Pelayo, J.S.; Bordignon, J.; Figueiredo, F.; Casagrande, R.; et al. The nitroxyl donor Angeli’s salt ameliorates Staphylococcus aureus-induced septic arthritis in mice. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattori, V.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Staurengo-Ferrari, L.; Borghi, S.M.; Rossaneis, A.C.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. The specialised pro-resolving lipid mediator maresin 1 reduces inflammatory pain with a long-lasting analgesic effect. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 1728–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Artero, N.A.; Manchope, M.F.; Carvalho, T.T.; Saraiva-Santos, T.; Bertozzi, M.M.; Carneiro, J.A.; Franciosi, A.; Dionisio, A.M.; Zaninelli, T.H.; Fattori, V.; et al. Hesperidin Methyl Chalcone Reduces the Arthritis Caused by TiO2 in Mice: Targeting Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Cytokine Production, and Nociceptor Sensory Neuron Activation. Molecules 2023, 28, 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020872
Artero NA, Manchope MF, Carvalho TT, Saraiva-Santos T, Bertozzi MM, Carneiro JA, Franciosi A, Dionisio AM, Zaninelli TH, Fattori V, et al. Hesperidin Methyl Chalcone Reduces the Arthritis Caused by TiO2 in Mice: Targeting Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Cytokine Production, and Nociceptor Sensory Neuron Activation. Molecules. 2023; 28(2):872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020872
Chicago/Turabian StyleArtero, Nayara A., Marília F. Manchope, Thacyana T. Carvalho, Telma Saraiva-Santos, Mariana M. Bertozzi, Jessica A. Carneiro, Anelise Franciosi, Amanda M. Dionisio, Tiago H. Zaninelli, Victor Fattori, and et al. 2023. "Hesperidin Methyl Chalcone Reduces the Arthritis Caused by TiO2 in Mice: Targeting Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Cytokine Production, and Nociceptor Sensory Neuron Activation" Molecules 28, no. 2: 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020872
APA StyleArtero, N. A., Manchope, M. F., Carvalho, T. T., Saraiva-Santos, T., Bertozzi, M. M., Carneiro, J. A., Franciosi, A., Dionisio, A. M., Zaninelli, T. H., Fattori, V., Ferraz, C. R., Piva, M., Mizokami, S. S., Camilios-Neto, D., Casagrande, R., & Verri, W. A. (2023). Hesperidin Methyl Chalcone Reduces the Arthritis Caused by TiO2 in Mice: Targeting Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Cytokine Production, and Nociceptor Sensory Neuron Activation. Molecules, 28(2), 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020872







