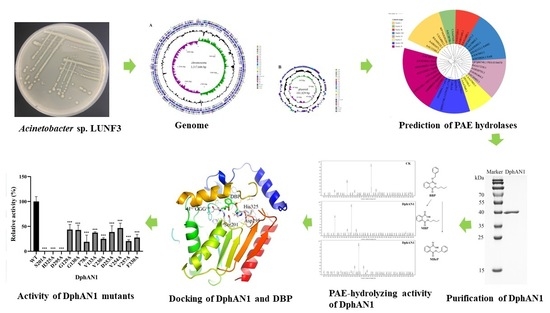
A Novel and Efficient Phthalate Hydrolase from Acinetobacter sp. LUNF3: Molecular Cloning, Characterization and Catalytic Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
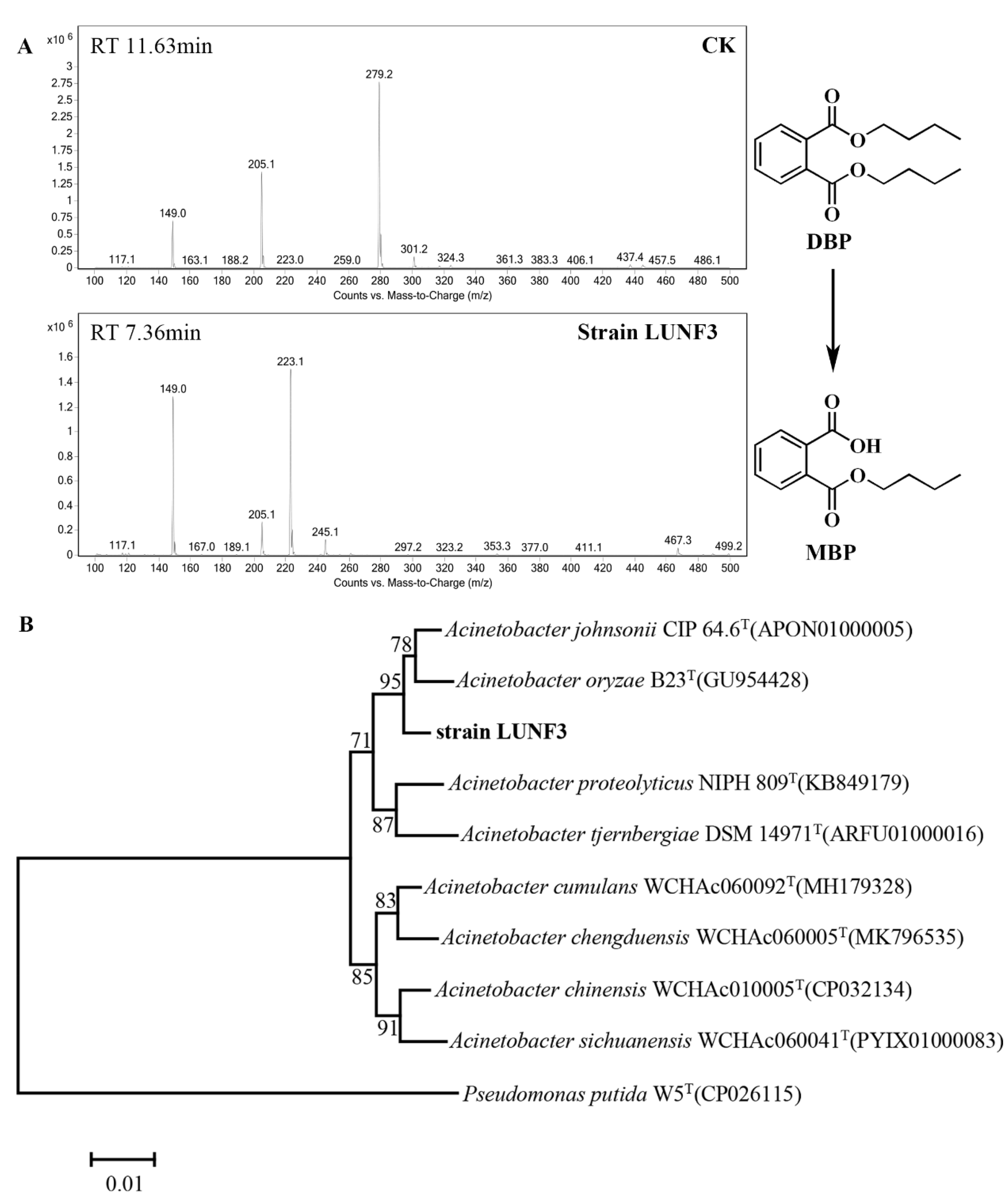
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Acinetobacter sp. LUNF3
2.2. Characterization of PAE Degradation by Strain LUNF3
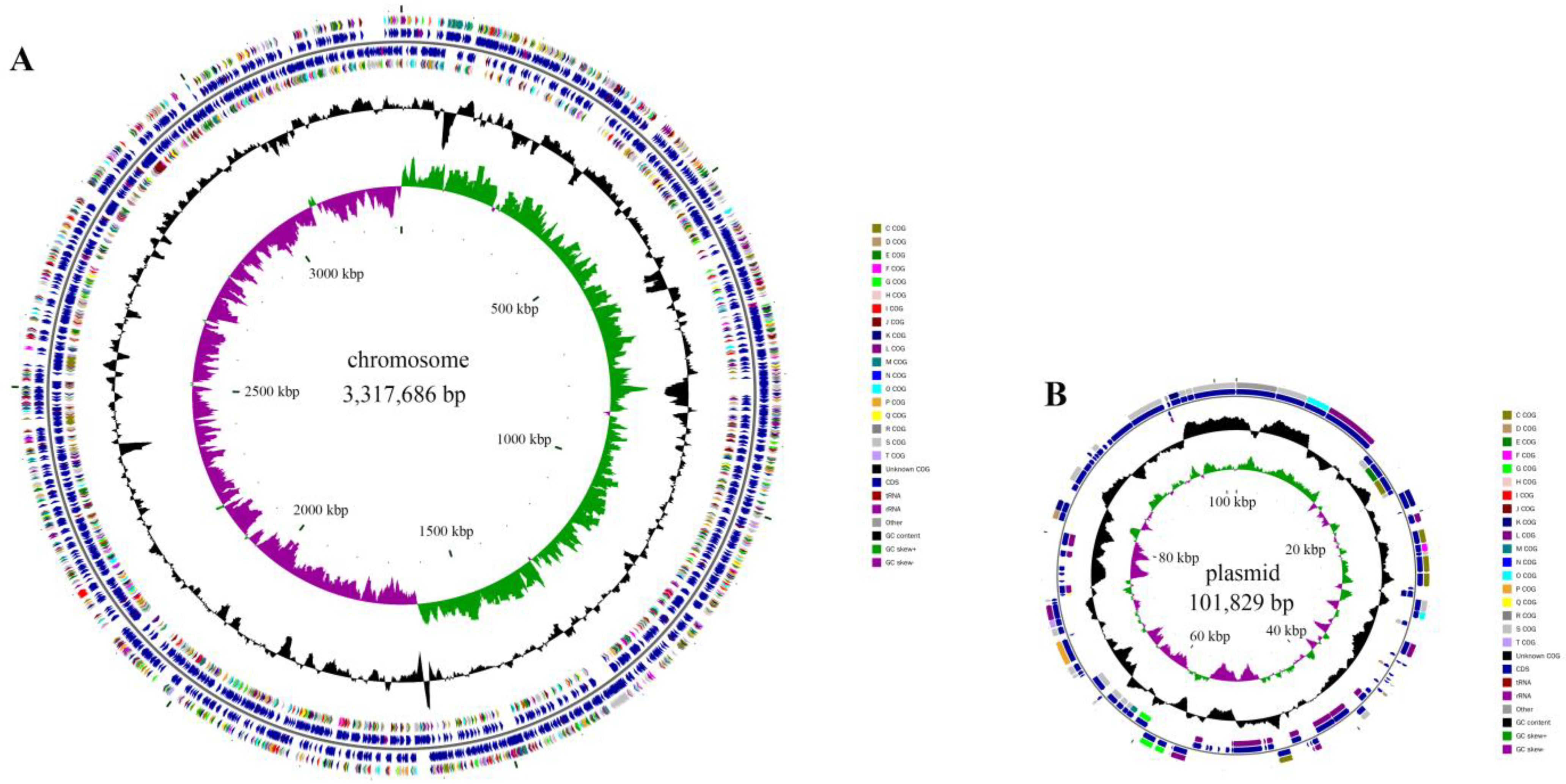
2.3. Cloning of PAE Hydrolase Gene through Complete Genome Sequencing
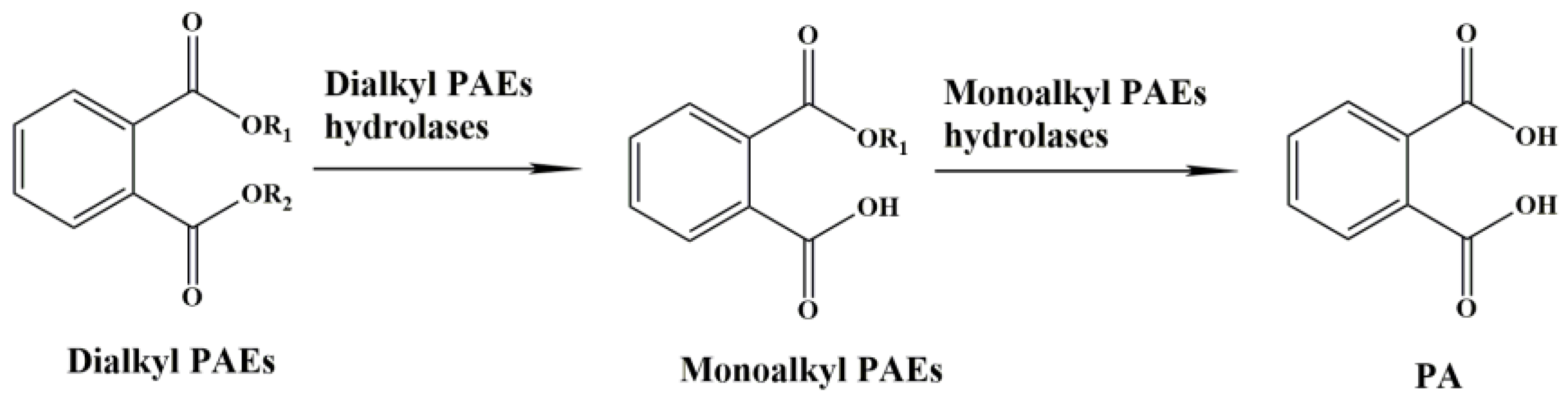
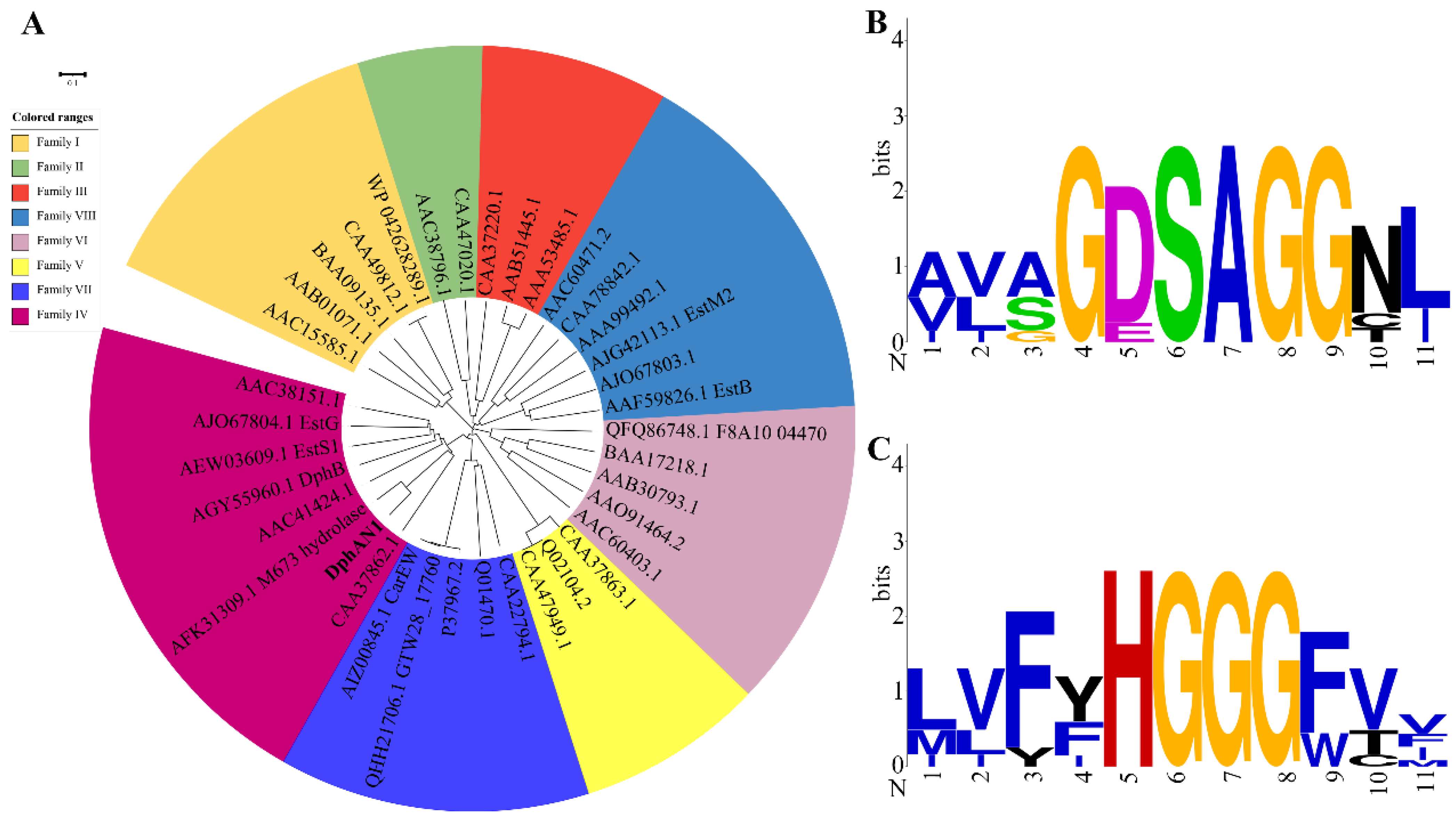
2.4. Functional Identification and Characterization of DphAN1
2.5. Structural Analysis of DphAN1
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Media
3.2. Enrichment, Isolation and Identification of PAE-Degrading Bacteria
3.3. Degradation of PAEs by Strain LUNF3
3.4. Complete Genome Sequencing and Annotation
3.5. Sequence Analysis and Expression of PAE Hydrolase DphAN1
3.6. Biochemical Characterization of DphAN1
3.7. Homology Modeling and Molecular Docking
3.8. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of DphAN1
3.9. Analytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Hu, R.; Zhao, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, K.; Shu, L.; Yan, Q.; Wu, B.; Mo, C.; He, Z.; et al. Bacteria-driven phthalic acid ester biodegradation: Current status and emerging opportunities. Environ. Int. 2021, 154, 106560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peijnenburg, W.J.; Struijs, J. Occurrence of phthalate esters in the environment of The Netherlands. Ecotox Environ. Safe 2006, 63, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clausen, P.A.; Liu, Z.; Kofoed-Sørensen, V.; Little, J.; Wolkoff, P. Influence of temperature on the emission of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) from PVC flooring in the emission cell FLEC. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambe, K.; Sakakibara, Y.; Sakabe, A.; Makino, H.; Ochibe, T.; Tohkin, M. Comparison of the developmental/reproductive toxicity and hepatotoxicity of phthalate esters in rats using an open toxicity data source. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 44, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, J.A.; Beverly, B.E.J.; Keshava, N.; Mudipalli, A.; Arzuaga, X.; Cai, C.; Hotchkiss, A.K.; Makris, S.L.; Yost, E.E. Hazards of diethyl phthalate (DEP) exposure: A systematic review of animal toxicology studies. Environ. Int. 2020, 145, 105848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, E.G.; Braun, J.M.; Nachman, R.M.; Cooper, G.S. Phthalate exposure and neurodevelopment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of human epidemiological evidence. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, S.; Vavilin, V.; Svensson, B. Phthalate hydrolysis under landfill conditions. Water Sci. Technol. A J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2006, 53, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, T.K.; Chu, W.; Graham, N. The degradation of endocrine disruptor Di-n-butyl Phthalate by UV irradiation: A photolysis and product study. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, R.; Verma, S.; Kushwaha, M.; Singh, D.; Akhter, Y.; Chatterjee, S. Biodegradation of dinbutyl phthalate by psychrotolerant Sphingobium yanoikuyae strain P4 and protein structural analysis of carboxylesterase involved in the pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhan, W.; Ren, Q.; Cheng, S.; Wang, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. Biodegradation of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate by a newly isolated Gordonia sp. and its application in the remediation of contaminated soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.-M.; Hu, R.-W.; Chen, X.-B.; Lü, H.; Li, Y.-W.; Li, H.; Mo, C.-H.; Cai, Q.-Y.; Wong, M.-H. Biodegradation pathway of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate by a novel Rhodococcus pyridinivorans XB and its bioaugmentation for remediation of DEHP contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Li, J.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J.; Zhong, W. Combined genomic and transcriptomic analysis of Dibutyl phthalate metabolic pathway in Arthrobacter sp. ZJUTW. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 3712–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, N.-X.; Yu, J.; Mo, C.-H.; Zhao, H.-M.; Li, Y.-W.; Wu, B.-X.; Cai, Q.-Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, D.-M.; Wong, M.-H. Biodegradation of di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) by a novel endophytic Bacillus megaterium strain YJB3. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Li, H.; Gu, J.; Shi, H.; Han, S.; Jiao, Y.; Zhong, G.; Zhang, Q.; Akindolie, M.S.; Lin, Y.; et al. Metabolism of diethyl phthalate (DEP) and identification of degradation intermediates by Pseudomonas sp. DNE-S1. Ecotox Environ. Safe 2019, 173, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liang, R.; Dai, Q.; Jin, D.; Wang, Y.; Chao, W. Complete degradation of di-n-octyl phthalate by biochemical cooperation between Gordonia sp. strain JDC-2 and Arthrobacter sp. strain JDC-32 isolated from activated sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Jin, D.; Tai, X.; Yu, H.; Duan, G.; Yan, X.; Pan, J.; Song, J.; Deng, Y. Bioremediation of dibutyl phthalate in a simulated agricultural ecosystem by Gordonia sp. strain QH-11 and the microbial ecological effects in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Ding, L.; Zou, D.; Qiu, J.; Shao, Y.; Sun, S.; Li, L.; Xin, Z. Characterization of a novel carboxylesterase with catalytic activity toward di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate from a soil metagenomic library. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Wang, J.; Jia, Y. Excellent Degradation Performance of a Versatile Phthalic Acid Esters-Degrading Bacterium and Catalytic Mechanism of Monoalkyl Phthalate Hydrolase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whangsuk, W.; Sungkeeree, P.; Nakasiri, M.; Thiengmag, S.; Mongkolsuk, S.; Loprasert, S. Two endocrine disrupting dibutyl phthalate degrading esterases and their compensatory gene expression in Sphingobium sp. SM42. Int. Biodeter Biodegr 2015, 99, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Huang, H.; Wu, M.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Sun, X.; Sun, B. An efficient phthalate ester-degrading Bacillus subtilis: Degradation kinetics, metabolic pathway, and catalytic mechanism of the key enzyme. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, J.; Dutta, A.; Chowdhury, P.P.; Chakraborty, J.; Dutta, T.K. Characterization of a novel family VIII esterase EstM2 from soil metagenome capable of hydrolyzing estrogenic phthalates. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurane, R.; Suzuki, T.; Fukuoka, S. Purification and Some Properties of a Phthalate Ester-Hydrolyzing Enzyme From Nocardia erythropolis. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 1984, 20, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, J.H.; Prasad, D.T.; Karegoudar, T.B. Initial degradation of dimethylphthalate by esterases from Bacillus species. Fems Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 196, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Hu, R.-W.; Zhao, H.-M.; Huang, H.-B.; Xiang, L.; Liu, B.-L.; Feng, N.-X.; Li, H.; Li, Y.-W.; Cai, Q.-Y.; et al. Mechanistic insight into esterase-catalyzed hydrolysis of phthalate esters (PAEs) based on integrated multi-spectroscopic analyses and docking simulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Yang, H.; Yan, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zou, D.; Ding, L.; Shao, Y.; Li, L.; Khan, U.; Sun, S.; et al. Characterization of XtjR8: A novel esterase with phthalate-hydrolyzing activity from a metagenomic library of lotus pond sludge. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1510–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Minhazul, K.A.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Meng, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Sun, X.; Sun, B. Biodegradation of phthalate esters by Paracoccus kondratievae BJQ0001 isolated from Jiuqu (Baijiu fermentation starter) and identification of the ester bond hydrolysis enzyme. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Du, H.; Zhou, M.-S.; Ji, Y.; Xie, Y.-Q.; Huang, H.-B.; Zhang, S.-H.; Li, F.; Xiang, L.; Cai, Q.-Y.; et al. Substrate-enzyme interactions and catalytic mechanism in a novel family VI esterase with dibutyl phthalate-hydrolyzing activity. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 108054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sun, J.; Yang, L.; Feng, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Wang, Y. Molecular insights into the catalytic mechanism of plasticizer degradation by a monoalkyl phthalate hydrolase. Commun. Chem. 2023, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liao, X.; Yu, F.; Wei, Z.; Yang, L. Cloning of a dibutyl phthalate hydrolase gene from Acinetobacter sp. strain M673 and functional analysis of its expression product in Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2013, 97, 2483–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, B. Biodegradation of Phthalate Esters by a Newly Isolated Acinetobacter sp. Strain LMB-5 and Characteristics of Its Esterase. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lu, Q.; de Toledo, R.A.; Shim, H. Degradation of di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) by an indigenous isolate Acinetobacter sp. SN13. Int. Biodeter Biodegr 2017, 117, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J. Biodegradation and metabolic pathway of sulfamethoxazole by a novel strain Acinetobacter sp. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2018, 102, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Wang, P.; Kang, Y.; He, H.; Luo, H.; Kim, S.; Niu, L.; Jiang, H.; Ma, K. Degradation of Perfluorooctane Sulfonamide by Acinetobacter Sp. M and Its Extracellular Enzymes. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 2780–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kong, D.; Liu, X.; Xie, H.; Lou, X.; Zeng, C. Combined microbial degradation of crude oil under alkaline conditions by Acinetobacter baumannii and Talaromyces sp. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 129666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.-Q.; Xu, L.; Tang, Y.-Q.; Chen, F.-M.; Wu, X.-L. Simultaneous degradation of phenol and n-hexadecane by Acinetobacter strains. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 123, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Wang, L.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, P.; Chen, Z.; Feng, C.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Metabolic process of di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) by Enterobacter sp. DNB-S2, isolated from Mollisol region in China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gan, D.; Gong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Guan, R.; Zeng, L.; Qu, J.; Dong, M. Analysis of the performance of the efficient di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-degrading bacterium Rhodococcus pyridinovorans DNHP-S2 and associated catabolic pathways. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Huang, H.; Guo, X.; Li, X.; Zou, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Huang, M. Biodegradation of phthalate esters by Pantoea dispersa BJQ0007 isolated from Baijiu. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 105, 104201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, N.-X.; Feng, Y.-X.; Liang, Q.-F.; Chen, X.; Xiang, L.; Zhao, H.-M.; Liu, B.-L.; Cao, G.; Li, Y.-W.; Li, H.; et al. Complete biodegradation of di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) by a novel Pseudomonas sp. YJB6. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 761, 143208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Martin, F.L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Q.; Wang, X.; Shen, H. Phthalate side-chain structures and hydrolysis metabolism associated with steroidogenic effects in MLTC-1 Leydig cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 308, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Yadav, M.P.; Li, X. Biodegradability and biodegradation pathway of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate by Burkholderia pyrrocinia B1213. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, S. Biodegradability of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate by a newly isolated bacterium Achromobacter sp. RX. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Feng, L.; Dong, Y.; Chen, J.; Lan, J.; Hou, H. High-efficiency degradation of phthalic acid esters (PAEs) by Pseudarthrobacter defluvii E5: Performance, degradative pathway, and key genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Peng, Y.; Tong, L.; Feng, L.; Ma, K. New pathways for the biodegradation of diethyl phthalate by Sphingobium yanoikuyae SHJ. Process Biochem. 2018, 71, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, T.; Chang, S.; Zhang, W.; Wu, X.; Wu, M.; Wang, Y.; Long, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Acinetobacter sp. TTH0-4, a cold-active crude oil degrading strain isolated from Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 226, 54–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Yan, H.; Hu, J.; Liu, X. Complete genome sequence of the cyprodinil-degrading bacterium Acinetobacter johnsonii LXL_C1. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.J.; Bosch, R.; Gibson, M.I.; Christie-Oleza, J.A. Plasticizer Degradation by Marine Bacterial Isolates: A Proteogenomic and Metabolomic Characterization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2244–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wu, S.; Li, L.; Shao, Y.; Xin, Z. Identification and characterization of a novel phthalate-degrading hydrolase from a soil metagenomic library. Ecotox Environ. Safe 2020, 190, 110148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Fan, X.; Qiu, Y.-J.; Li, C.-Y.; Xing, S.; Zheng, Y.-T.; Xu, J.-H. Newly Identified Thermostable Esterase from Sulfobacillus acidophilus: Properties and Performance in Phthalate Ester Degradation. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2014, 80, 6870–6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Liao, X.; Xiao, L.; Miao, A.; Wu, J.; Yang, L. Identification and Characterization of a Cold-Active Phthalate Esters Hydrolase by Screening a Metagenomic Library Derived from Biofilms of a Wastewater Treatment Plant. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vingiani, G.M.; Leone, S.; De Luca, D.; Borra, M.; Dobson, A.D.; Ianora, A.; De Luca, P.; Lauritano, C. First identification and characterization of detoxifying plastic-degrading DBP hydrolases in the marine diatom Cylindrotheca closterium. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Xiang, M.; Wang, L.; Yan, Q.; Yang, S.; Jiang, Z. Biochemical characterization of a novel lipase from Malbranchea cinnamomea suitable for production of lipolyzed milkfat flavor and biodegradation of phthalate esters. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.-Q.; Chang, T.-T.; Ren, D.-P.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, B.-C. Rational design to improve activity of the Est3563 esterase from Acinetobacter sp. LMB-5. Enzym. Microb. Tech. 2019, 131, 109331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Long, J.; Feng, C.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, D.; Liu, Y.; Xue, J.; Li, Z. Fe3+ enhanced degradation of oxytetracycline in water by pseudomonas. Water Res. 2019, 160, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.R.; Maester, T.C.; Mercaldi, G.F.; de Macedo Lemos, E.G.; Hyvönen, M.; Balan, A. From a metagenomic source to a high-resolution structure of a novel alkaline esterase. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2017, 101, 4935–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, I.W.; Leaver-Fay, A.; Chen, V.B.; Block, J.N.; Kapral, G.J.; Wang, X.; Murray, L.W.; Arendall, W.B.; Snoeyink, J.; Richardson, J.S.; et al. MolProbity: All-atom contacts and structure validation for proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W375–W383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.; Cho, I.J.; Seo, H.; Son, H.F.; Sagong, H.-Y.; Shin, T.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.-J. Structural insight into molecular mechanism of poly(ethylene terephthalate) degradation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, H.P.; Allen, M.D.; Donohoe, B.S.; Rorrer, N.A.; Kearns, F.L.; Silveira, R.L.; Pollard, B.C.; Dominick, G.; Duman, R.; El Omari, K.; et al. Characterization and engineering of a plastic-degrading aromatic polyesterase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E4350–E4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.-W.; Ma, J.; Zheng, Y.; Ko, T.-P.; Xu, L.; Cheng, Y.-S.; Chen, C.-C.; Guo, R.-T. Structural insight into catalytic mechanism of PET hydrolase. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.-Y.; Yao, Q.-Q.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Hao, J.; Zhou, B.-C.; Chen, X.-L.; Shi, M.; et al. A Novel Subfamily Esterase with a Homoserine Transacetylase-like Fold but No Transferase Activity. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2017, 83, e117–e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komiya, D.; Hori, A.; Ishida, T.; Igarashi, K.; Samejima, M.; Koseki, T.; Fushinobu, S. Crystal Structure and Substrate Specificity Modification of Acetyl Xylan Esterase from Aspergillus luchuensis. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2017, 83, e1217–e1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Yang, T.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, B.; Yan, Y. Complete genome sequence of Gordonia sp. YC-JH1, a bacterium efficiently degrading a wide range of phthalic acid esters. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 279, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaujiya, D.K.; Sivashanmugam, S.; Pakshirajan, K. Biodegradation and toxicity removal of phthalate mixture by Gordonia sp. in a continuous stirred tank bioreactor system. Environ. Technol. Inno 2022, 26, 102324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.-S.; Peluso, P.; Sedlazeck, F.J.; Nattestad, M.; Concepcion, G.T.; Clum, A.; Dunn, C.; O’Malley, R.; Figueroa-Balderas, R.; Morales-Cruz, A.; et al. Phased diploid genome assembly with single-molecule real-time sequencing. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive κ-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 215087–215116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, T.M.; Eddy, S.R. tRNAscan-SE: A program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besemer, J.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M. GeneMarkS: A self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. Nar. 2001, 29, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagesen, K.; Hallin, P.; Rødland, E.A.; Staerfeldt, H.-H.; Rognes, T.; Ussery, D.W. RNAmmer: Consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Hydrolase | Function | Accession No. | Substrate | Hydrolase Family | Origin | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAE ydrolases | Dialkyl PAE hydrolase | / | DBP, DEHP, DEP, DOP, DMIP, DMTP, DETP | Gene not identified | Nocardia erythropolis | [22] |
| DMP hydrolases | Dialkyl PAE hydrolase | / | DMP | Gene not identified | Bacillus sp. | [23] |
| GTW28_09400 | Dialkyl PAE hydrolase | QHH20153.1 | DBP, DIBP, DEHP | II | Bacillus subtilis BJQ0005 | [20] |
| GTW28_13725 | Dialkyl PAE hydrolase | QHH20954.1 | DEHP | V | Bacillus subtilis BJQ0005 | [20] |
| HylD1 | Dialkyl PAE hydrolase | QFQ86055.1 | DMP, DEP | IV | Paracoccus kondratievae BJQ0001 | [26] |
| HylD2 | Dialkyl PAE hydrolase | QFQ86748.1 | DEHP | VI | Paracoccus kondratievae BJQ0001 | [26] |
| Hyd | Dialkyl PAE hydrolase | AYW76486 | DMP, DEP, DBP, DOP, DEHP, BBP, DINP | New family | Rhodococcus sp. 2G | [24] |
| GTW28_17760 | Dialkyl/monoalkyl PAE hydrolase | QHH21706.1 | DMP, DEP, DBP, DIBP, DEHP, MBP, MEHP | VII | Bacillus subtilis BJQ0005 | [20] |
| EstM2 | Dialkyl/monoalkyl PAE hydrolase | AJG42113.1 | DMP, DEP, BBP, DBP, DPP, MBzP, MMP, MEP, MBP, MPP | VIII | soil metagenomic library | [21] |
| EstG | Dialkyl/monoalkyl PAE hydrolase | AJO67804.1 | DBP | VIII | Sphingobium sp. SM42 | [19] |
| MphG1 | Monoalkyl PAE hydrolase | AUH70054.1 | MEP, MBP, MHP, MEHP | V | Gordonia sp. YC-JH1 | [18] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, S.; Guo, J.; Han, S.; Du, H.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Han, H.; Hou, X.; Wang, W. A Novel and Efficient Phthalate Hydrolase from Acinetobacter sp. LUNF3: Molecular Cloning, Characterization and Catalytic Mechanism. Molecules 2023, 28, 6738. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186738
Fan S, Guo J, Han S, Du H, Wang Z, Fu Y, Han H, Hou X, Wang W. A Novel and Efficient Phthalate Hydrolase from Acinetobacter sp. LUNF3: Molecular Cloning, Characterization and Catalytic Mechanism. Molecules. 2023; 28(18):6738. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186738
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Shuanghu, Jingjing Guo, Shaoyan Han, Haina Du, Zimeng Wang, Yajuan Fu, Hui Han, Xiaoqiang Hou, and Weixuan Wang. 2023. "A Novel and Efficient Phthalate Hydrolase from Acinetobacter sp. LUNF3: Molecular Cloning, Characterization and Catalytic Mechanism" Molecules 28, no. 18: 6738. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186738
APA StyleFan, S., Guo, J., Han, S., Du, H., Wang, Z., Fu, Y., Han, H., Hou, X., & Wang, W. (2023). A Novel and Efficient Phthalate Hydrolase from Acinetobacter sp. LUNF3: Molecular Cloning, Characterization and Catalytic Mechanism. Molecules, 28(18), 6738. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186738