Chemo-/Regio-Selective Synthesis of Novel Functionalized Spiro[pyrrolidine-2,3′-oxindoles] under Microwave Irradiation and Their Anticancer Activity
Abstract
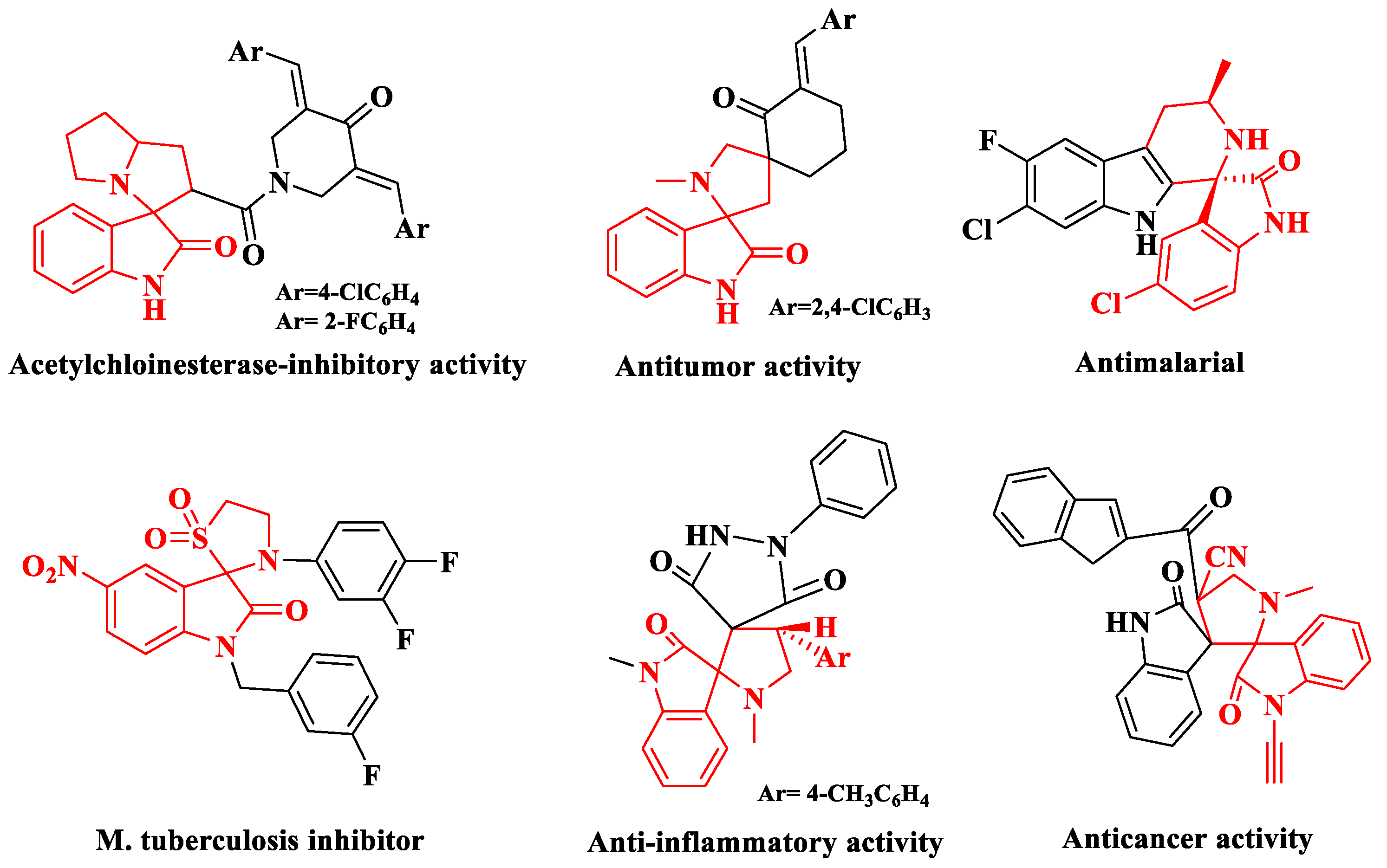
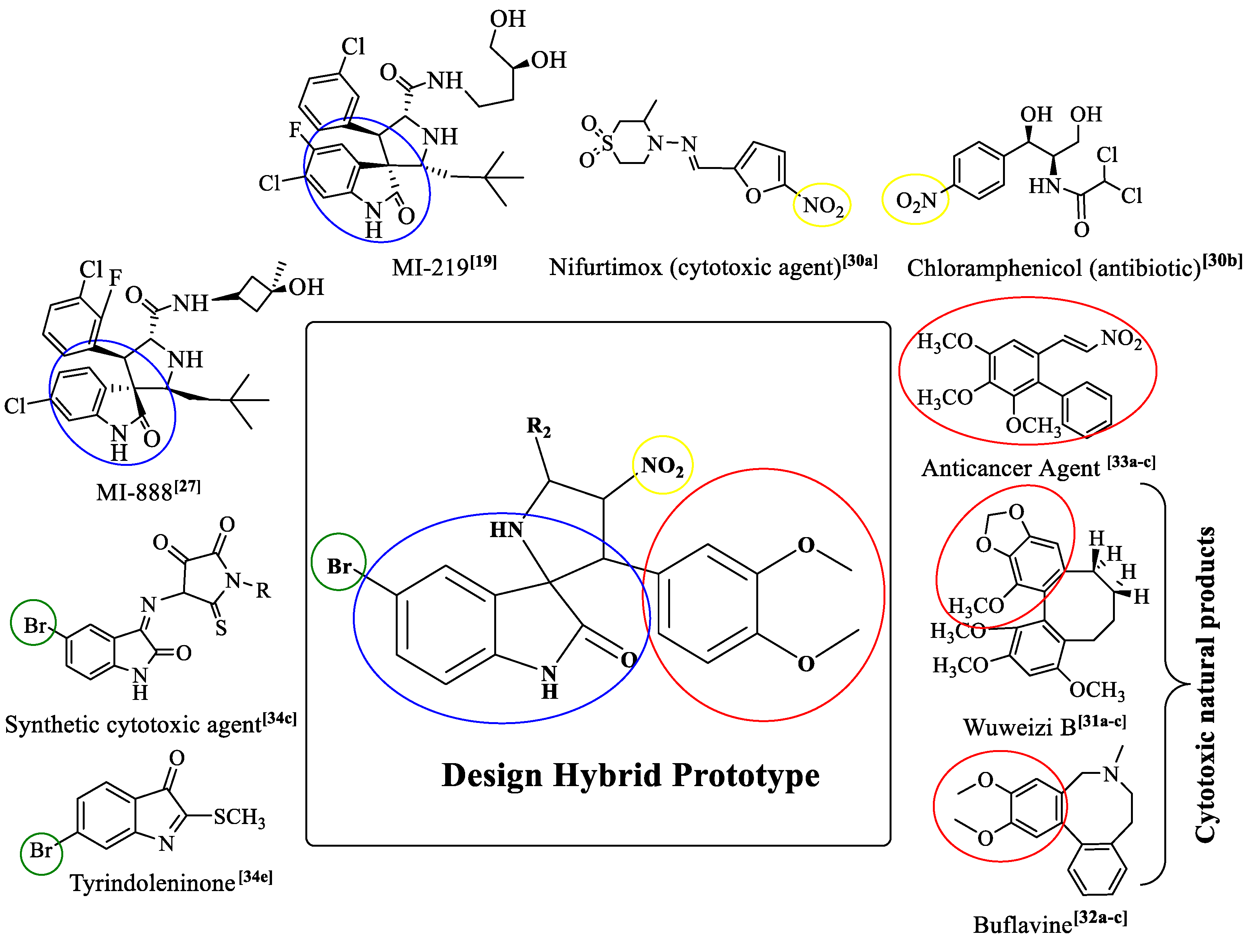
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
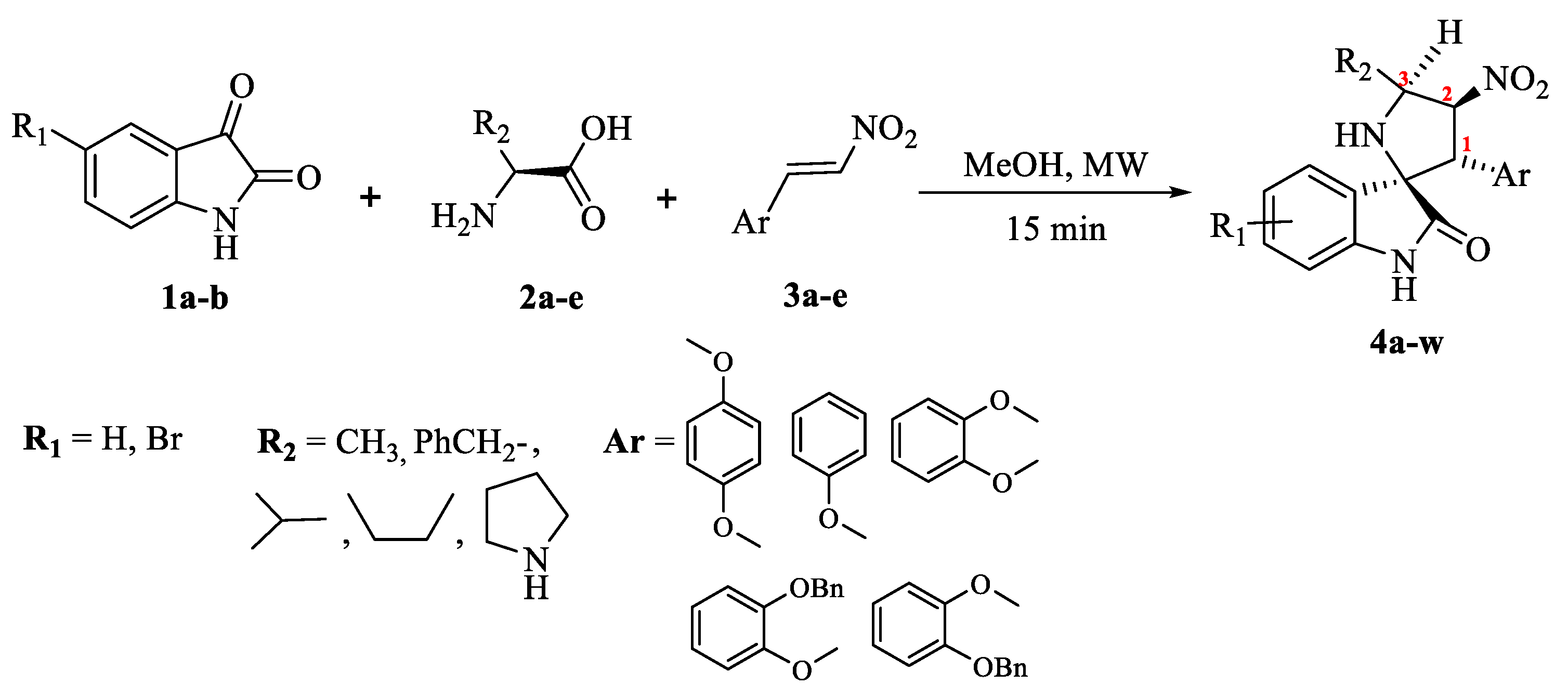
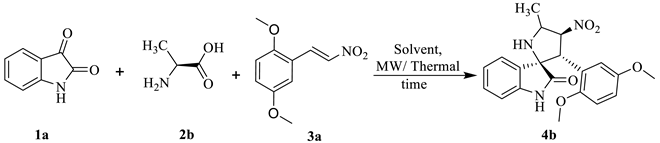
2.1.1. Synthesis
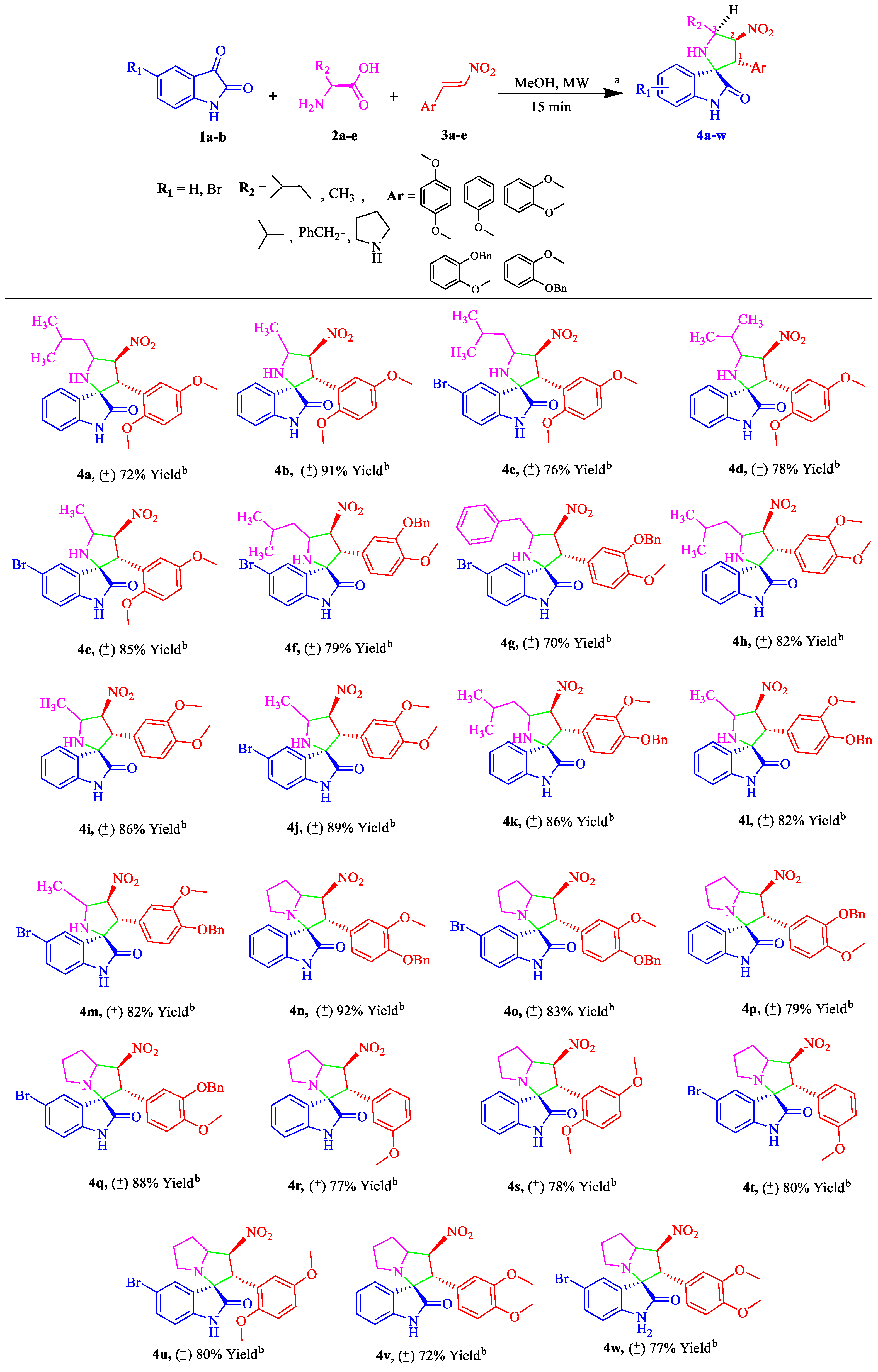
2.1.2. Substrate Scope from the Reaction of Isatin 1a–b with Differently Substituted Amino Acids 2a–e and Nitrostyrenes 3a–e to Furnish Spiro[pyrrolidine-2,3′-oxindoles] 4a–w Derivatives
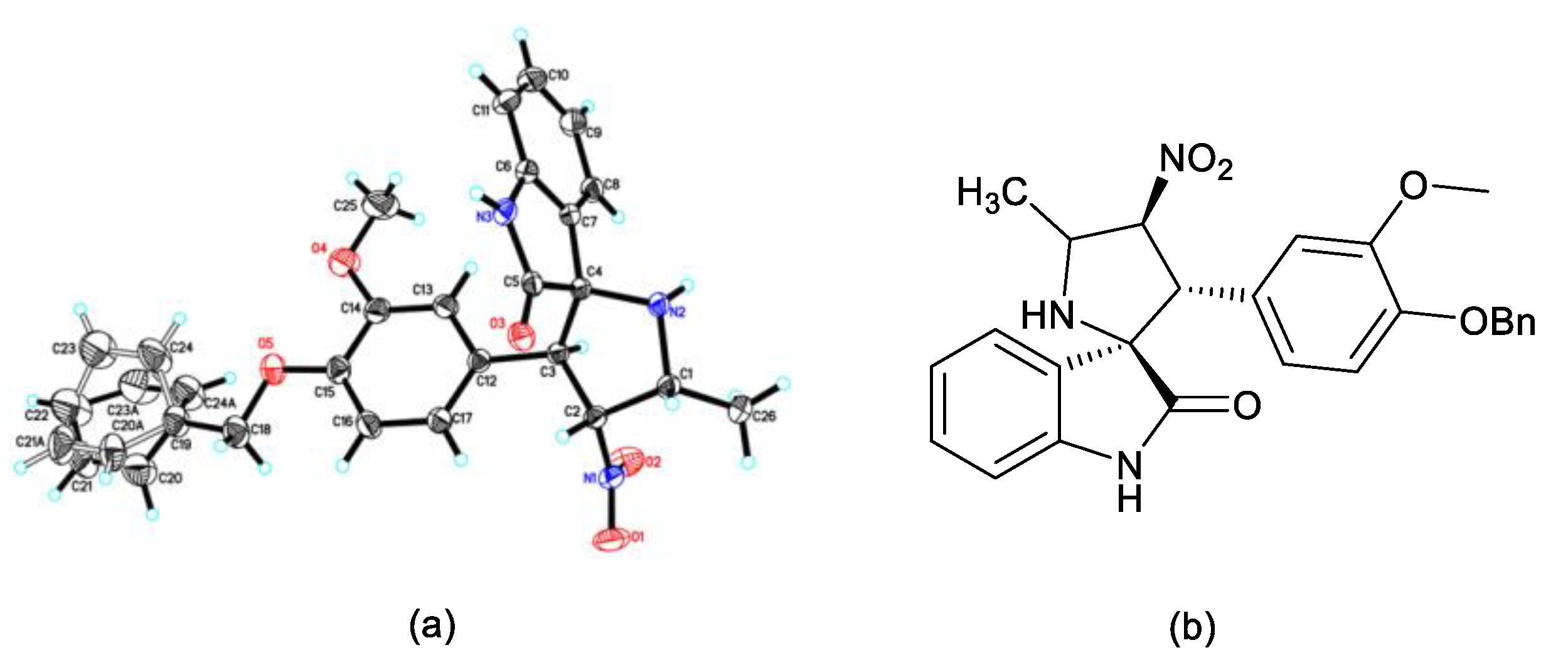
2.1.3. Single Crystal X-ray Diffraction Studies
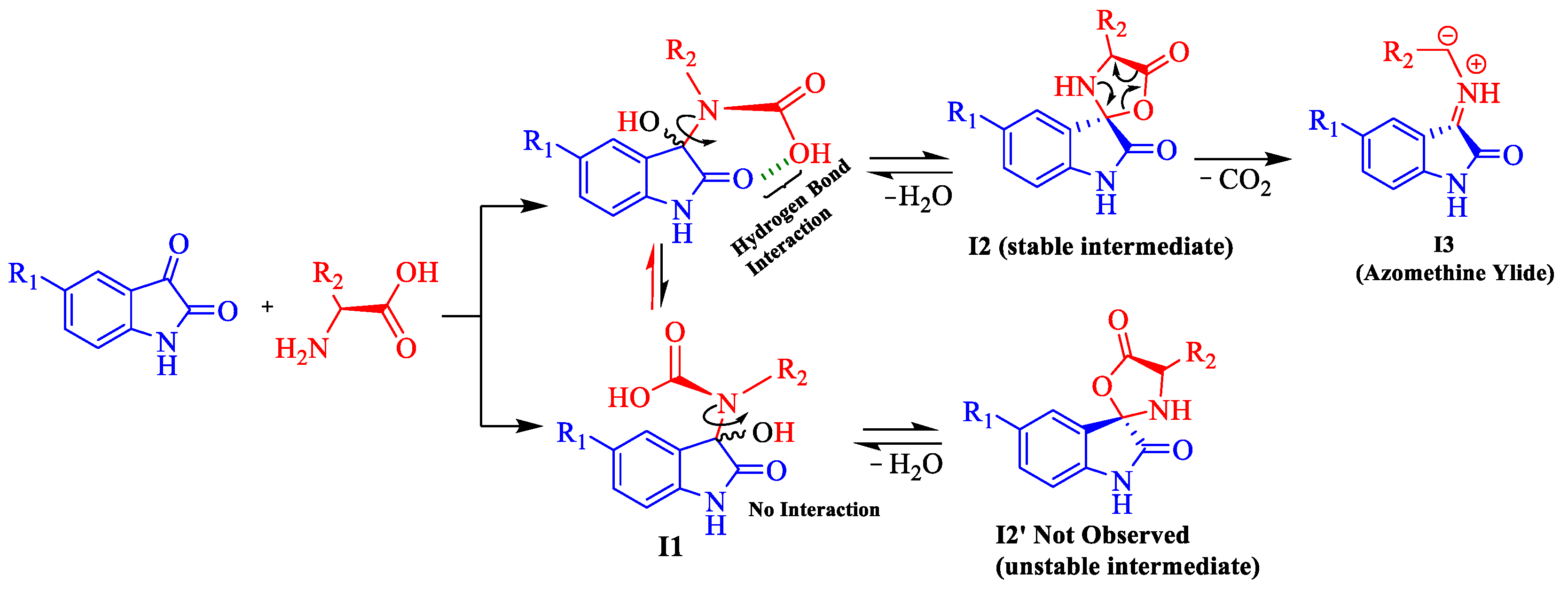
2.1.4. Plausible Mechanism
2.2. In Vitro Anticancer Activity against Lung/Liver Cancer and Normal Cell Lines
2.2.1. Structure–Activity Relationship [Anticancer Activity against Lung Cancer (A549) Cell Line]
2.2.2. Structure–Activity Relationship [Anticancer Activity against Liver Cancer (HepG2) Cell Line]
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of (E)-2-Aryl-1-nitroethenes (3a–e)
3.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Spiro[pyrrolidine-2,3′-oxindoles] (4a–w)
3.4. Characterization Data of Spiro[pyrrolidine-2,3′-oxindoles] (4a–w)
3.5. Cell Culture, Reagents and Cells
3.6. Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Singh, M.S.; Chowdhury, S. Recent developments in solvent-free multicomponent reactions: A perfect synergy for eco-compatible organic synthesis. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 4547–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shi, D. Efficient one-pot synthesis of novel spirooxindole derivatives via three-component reaction in aqueous medium. J. Comb. Chem. 2010, 12, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremner, W.S.; Organ, M.G. Multicomponent Reactions to Form Heterocycles by Microwave-Assisted Continuous Flow Organic Synthesis. J. Comb. Chem. 2007, 9, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagley, M.C.; Lubinu, M.C. Microwave-assisted oxidative aromatization of Hantzsch 1, 4-dihydropyridines using manganese dioxide. Top. Heterocycl. Chem. 2006, 1, 31–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Török, B. Microwave-assisted multicomponent domino cyclization–aromatization: An efficient approach for the synthesis of substituted quinolines. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Shi, F.; Tu, S.-J. Microwave-assisted multicomponent reactions in the heterocyclic chemistry. Curr. Org. Chem. 2010, 14, 357–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Gadgeel, S. (Eds.) Lung Cancer and Personalized Medicine; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Rumgay, H.; Arnold, M.; Ferlay, J.; Lesi, O.; Cabaseg, C.J.; Vignat, J.; Laversanne, M.; McGlaynn, K.A.; Soerjomataram, I. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1598–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.; Naishadham, D.; Jemal, A. Guidelines on genetic evaluation and management of Lynch syndrome: A consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2013, 63, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruna, Y.; Saranraja, K.; Balachandranb, C.; Perumala, P.T. Novel spirooxindole–pyrrolidine compounds: Synthesis, anticancer and molecular docking studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 74, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Yu, D.-Q.; Liu, H.-M. Spirooxindoles: Promising scaffolds for anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 673–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, A.; Islam, M.S.; Ghawas, H.M.; Al-Majid, A.M.; El-Senduny, F.F.; Badria, F.A.; Elshaiere, Y.A.M.M.; Ghabbourfg, H.A. Facile one-pot synthesis of spirooxindole-pyrrolidine derivatives and their antimicrobial and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 14335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arun, Y.; Bhaskar, G.; Balachandran, C.; Ignacimuthu, S.; Perumal, P.T. Facile one-pot synthesis of novel dispirooxindole-pyrrolidine derivatives and their antimicrobial and anticancer activity against A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cancer cell line. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 1839–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girgis, A.S. Regioselective synthesis of dispiro[1H-indene-2,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,3″-[3H]indole]-1,2″(1″H)-diones of potential anti-tumor properties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 4, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, S.M.; Perumal, S.; Menendez, J.C.; Yogeeswari, P.; Sriram, D. Antimycobacterial activity of spirooxindolo-pyrrolidine, pyrrolizine and pyrrolothiazole hybrids obtained by a three-component regio- and stereoselective 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition. Med. Chem. Comm. 2011, 2, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, G.; Arun, Y.; Balachandran, C.; Saikumar, C.; Perumal, P.T. Synthesis of novel spirooxindole derivatives by one pot multicomponent reaction and their antimicrobial activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 51, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, A.; Thirumurugan, P.; Perumal, P.T.; Vembu, P.; Ponnuswamy, M.N.; Ramesh, P. One-pot multicomponent synthesis and anti-microbial evaluation of 2′-(indol-3-yl)-2-oxospiro (indoline-3, 4′-pyran) derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, K.; Sivakumar, P.M.; Doble, M.; Perumal, P.T. Synthesis, antibacterial activity evaluation and QSAR studies of novel dispiropyrrolidines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajanarendar, E.; Ramakrishna, S.; Reddy, K.G.; Nagaraju, D.; Reddy, Y.N. A facile synthesis, anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of isoxazolyl-2,3-dihydrospiro[benzo[f]isoindole-1,3′-indoline]-2′,4,9-triones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3954–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, E.M.; Abdel-Monem, M.I. Regioselective synthesis and anti-inflammatory activity of novel dispiro[pyrazolidine-4,3′-pyrrolidine-2′,3″-indoline]-2″,3,5-triones. ARKIVOC 2011, 10, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.S.; Rajesh, S.M.; Perumal, S.; Banerjee, D.; Yogeeswari, P.; Sriram, D. Novel three-component domino reactions of ketones, isatin and amino acids: Synthesis and discovery of antimycobacterial activity of highly functionalised novel dispiropyrrolidines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf Ali, M.; Ismail, R.; Choon, T.S.; Kumar, R.S.; Osman, H.; Arumugam, N.; Almansour, A.I.; Elumalai, K.; Singh, A. AChE inhibitor: A regio- and stereo-selective 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition for the synthesis of novel substituted 5,6-dimethoxy spiro[5.3′]-oxindole-spiro-[6.3″]-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1″-one-7-(substitutedaryl)-tetrahydro-1H-pyrrolo[1,2c][1,3]thiazole. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kia, Y.; Osman, H.; Kumar, R.S.; Murugaiyah, V.; Basiri, A.; Perumal, S.; Wahab, H.A.; Bing, C.S. Synthesis and discovery of novel piperidone-grafted mono- and bis-spirooxindole-hexahydropyrrolizines as potent cholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 7, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Qin, D.; Shangary, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Ding, K.; McEachern, D.; Qiu, S.; Nikolovska-Coleska, Z.; Miller, R.; et al. Potent and Orally Active Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the MDM2−p53 Interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastwood, P.; Gonzalez, J.; Gomez, E.; Caturla, F.; Balague, C.; Orellana, A.; Dominguez, M. Indolin-2-one p38α inhibitors II: Lead optimisation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremov, I.V.; Vajdos, F.F.; Borzilleri, K.A.; Capetta, S.; Chen, H.; Dorff, P.H.; Dutra, J.K.; Goldstein, S.W.; Mansour, M.; McColl, A.; et al. Discovery and Optimization of a Novel Spiropyrrolidine Inhibitor of β-Secretase (BACE1) through Fragment-Based Drug Design. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 9069–9088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, R.F.; Ismail, N.S.M.; Stawinski, J.; Girgis, A.S. Design, synthesis and QSAR studies of dispiroindole derivatives as new antiproliferative agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 68, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vintonyak, V.V.; Warburg, K.; Kruse, H.; Grimme, S.; Hübel, K.; Rauh, D.; Waldmann, H. Identification of Thiazolidinones Spiro-Fused to Indolin-2-ones as Potent and Selective Inhibitors of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 5902–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, B.K.S.; Zou, B.; Rottmann, M.; Lakshminarayana, S.B.; Ang, S.H.; Leong, S.Y.; Tan, J.; Wong, J.; Keller-Maerki, S.; Fischli, C.; et al. Spirotetrahydro β-Carbolines (Spiroindolones): A New Class of Potent and Orally Efficacious Compounds for the Treatment of Malaria. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5155–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jossang, A.; Jossang, P.; Hadi, H.A.; Sevenet, T.; Bodo, B. Horsfiline, an oxindole alkaloid from Horsfieldia superba. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.; Wilkinson, J. A total synthesis of horsfiline via aryl radical cyclisation. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1992, 5, 1767–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascop, S.I.; Sapi, J.; Laronze, J.Y.; Levy, J. On the synthesis of the oxindole alkaloid: (±)-horsfiline. Heterocycles 1994, 38, 725. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini, C.; Strassler, C.; Weber, M.; Borschberg, H.J. Synthesis of the oxindole alkaloid (−)-horsfiline. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1994, 5, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisano, G.; Annunziata, R.; Papeo, G.; Sisti, M. Oxindole alkaloids. A novel non-biomimetic entry to (−)-Horsfiline. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1996, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, G.; Bishnoi, A.K.; Saxena, R.; Saini, K.S.; Konwar, R.; Kumar, S.; Dwivedi, A. Design and synthesis of new bioisosteres of spirooxindoles (MI-63/219) as anti-breast cancer agents. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanga, T.-H.; Murakami, Y.; Matsumotoa, K.; Takayamab, H.; Kitajimab, M.; Aimib, N.; Watanabea, H. Rhynchophylline and isorhynchophylline inhibit NMDA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 455, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, Y.; Taga, N.; Oishi, T. The Synthesis of 3-Spirooxindole Derivatives. VIII. Total Syntheses of (±)-Formosanine, (±)-Isoformosanine, (±)-Mitraphylline and (±)-Isomitraphylline. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1976, 24, 736–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- James, M.N.G.; William, G.J.B. The molecular and crystal structure of an oxindole alkaloid (6-Hydroxy-2’-(2-methylpropyl)-3,3’-spirotetrahydropyrrolidino-oxindole). Can. J. Chem. 1972, 50, 2407–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.H.; Lim, P.B.; Chuah, C.H. Oxindole alkaloids from Alstonia macrophylla. Phytochemistry 1996, 41, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.B.; Kakeya, H.; Osada, H. Novel mammalian cell cycle inhibitors, spirotryprostatins A and B, produced by Aspergillus fumigatus, which inhibit mammalian cell cycle at G2/M phase. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 12651–12666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.B.; Kakeya, H.; Osada, H. Spirotryprostatin B, Novel Mammalian Cell Cycle Inhibitor Produced by Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hu, Y. Small molecule agents targeting the p53-MDM2 pathway for cancer therapy. Med. Res. Rev. 2012, 32, 1159–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, S.; Sun, W.; Liu, L.; Lu, J.; McEachern, D.; Shargary, S.; Bernard, D.; Li, X.; Zhao, T. A Potent Small-Molecule Inhibitor of the MDM2–p53 Interaction (MI-888) Achieved Complete and Durable Tumor Regression in Mice. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 5553–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, M.; Akhter, Z.; Ahmad, I.; Ahmed, S.; Ismail, H.; Mirza, B.; Mckee, V.; Bolte, M. Synthesis, biological and electrochemical evaluation of novel nitroaromatics as potential anticancerous drugs. Bioelectrochemistry 2015, 104, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zereini, W.; Schuhmann, I.; Laatsch, H.; Helmke, E.; Anke, H. New aromatic nitro compounds from Salegentibacter sp. T436, an Arctic sea ice bacterium: Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and biological activities. J. Antibiot. 2007, 60, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, J.D.; Maher, V.M.; McCormick, J.J. Cytotoxic and mutagenic effects of 1-nitropyrene and 1-nitrosopyrene in diploid human fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis 1986, 7, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollo, S.; Nunez-Vergara, L.J.; Bonta, M.; Chauviere, G.; Perie, J.; Squella, J.A. Cyclic voltammetric studies on nitro radical anion formation from megazol and some related nitroimidazole derivatives. J. Elec. Chem. 2001, 511, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan-Kilbeya, G.; Djumpaha, J.; Papadopouloub, M.V.; Bloomer, W.; Huc, L.; Wilkinsona, S.R.; Ashwortha, R. Evaluating the developmental toxicity of trypanocidal nitroaromatic compounds on zebrafish. Acta Trop. 2013, 128, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, K.-S.; Parales, R.E. Nitroaromatic compounds, from synthesis to biodegradation. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 250–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocheleau, S.; Kuperman, R.G.; Simini, M.; Hawari, J.; Checkai, R.T.; Thiboutot, S.; Ampleman, G.; Sunahara, G.I. Toxicity of 2, 4-dinitrotoluene to terrestrial plants in natural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3193–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Padda, R.S.; Wang, C.; Hughes, J.B.; Kutty, R.; Bennett, G.N. Mutagenicity of nitroaromatic degradation compounds. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 2293–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purohit, V.; Basu, A.K. Mutagenicity of nitroaromatic compounds. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2000, 13, 673–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.-L.; Hu, J.-P.; Tan, W.; Sheng, L.; Chen, H.; Li, Y. Simultaneous quantification of four active schisandra lignans from a traditional Chinese medicine Schisandra chinensis (Wuweizi) in rat plasma using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 865, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, H.; Bauer, R.; Melchart, D.; Xiao, P.-G.; Staudinger, A. Chromatographic Fingerprint Analysis of Herbal Medicines; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2011; pp. 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, H.-H.; Toma, D.; Ren, S.; Huang, L.; Yaramus, M.; Baum, A.; Venkataramanan, R.; et al. Traditional Chinese Medicines Wu Wei Zi (Schisandra chinensis Baill) and Gan Cao (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch) Activate Pregnane X Receptor and Increase Warfarin Clearance in Rats. J. Pharmacol. Experimaental Ther. 2006, 316, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appukkuttan, P.; Dehaen, W.; Eycken, E.V. Microwave-Assisted Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Synthesis of N-Shifted and Ring-Expanded Buflavine Analogues. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 6452–6460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K.; Watanabe, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Kihara, M. Studies on the α-Adrenolytic Activities of Apogalanthamine Analogs. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1977, 25, 1851–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z. Amaryllidaceae and Sceletium alkaloids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 886–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Yada, D.; Shaik, T.B.; Vasantha, G.; Reddy, P.S.; Kalivendi, S.V.; Sreedhar, B. Synthesis and antitumor evaluation of nitrovinyl biphenyls: Anticancer agents based on allocolchicines. Chem. Med. Chem. 2011, 6, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, R.; Rastogi, N.; Namboothiri, I.N.N.; Mobinc, S.M.; Panda, D. Synthesis and evaluation of α-hydroxymethylated conjugated nitroalkenes for their anticancer activity: Inhibition of cell proliferation by targeting microtubules. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 8073–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.A.; Jain, N.; Yada, D.; Kishore, C.; Reddy, V.J.; Reddy, P.S.; Addlagatta, A.; Kalivendi, S.V.; Sreedhar, B. Design and synthesis of resveratrol-based nitrovinylstilbenes as antimitotic agents. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 6751–6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Adhami, H.J.A.; Al-Majidi, S.M.H. Synthesis, identification and evaluation of antibacterial activity of some new substituted N-benzyl-5-bromo isatin. Iraqi J. Sci. 2015, 56, 2732–2744. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, T.B.; Rudd, D.; Smith, J.; Kotiw, M.; Mouatt, P.; Seymour, L.M.; Liu, L.; Benkendorff, K. Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Structure-Activity Relationships of Brominated Indoles from a Marine Mollusc. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhrigua, B.; Pathaka, D.; Siddiquib, N.; Alamb, M.S.; Ahsan, W. Search for biological active isatins: A short review. IJPSDR 2010, 2, 229–235. [Google Scholar]
- Vine, K.L.; Locke, J.M.; Ranson, M.; Pyneb, S.G.; Bremner, J.B. In vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of some substituted isatin derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karali, N.; Terzioglu, N.; Gürsoy, A. Synthesis and Primary Cytotoxicity Evaluation of New 5-Bromo-3-substituted-hydrazono-1H-2-indolinones. Arch. Pharm. Pharm. Med. Chem. 2002, 8, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yang, J.; Gao, S.; He, H.; Li, S.; Di, Y.; Chang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Hao, X. Spiro [pyrrolidine-2, 3′-oxindole] derivatives synthesized by novel regionselective 1, 3-dipolar cycloadditions. Mol. Divers. 2012, 16, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Miao, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Hao, X.-J. Investigation of regioselectivity in the synthesis of spiro [pyrrolidine-2,3′-oxindoles] by use of the Huisgen reaction. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2013, 39, 2445–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvis, C.E.P.; Kouznetsov, V.V. Regio- and stereoselective synthesis of spirooxindole 1′-nitro pyrrolizidines with five concurrent stereocenters under aqueous medium and their bioprospection using the zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo model. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 7372–7386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehn, S.; Bergman, J.; Stensland, B. The Three-Component Reaction between Isatin, α-Amino Acids, and 2π-components. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 2004, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogaku, V.; Krishna, V.S.; Balachandran, C.; Rangan, K.; Sriram, D.; Aoki, S.; Basavoju, S. The design and green synthesis of novel benzotriazoloquinolinyl spirooxindolopyrrolizidines: Antimycobacterial and antiproliferative studies. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 17511. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Zhai, H.; Zhao, Y. An Efficient Synthesis of Oxygen-Bridged Spirooxindoles via Microwave-Promoted Multicomponent Reaction. Molecules 2023, 28, 3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, L.; Yan, Y.; Li, S.; Lu, H.; Liu, J.; Dong, J. 2π-component-Controlled Regioselective 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition: A Switchable Divergent Access to Functionalized N-Fused Pyrrolidinyl Spirooxindoles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gugkaeva, Z.T.; Panova, M.V.; Smol′yakov, A.F.; Medvedev, M.G.; Tsaloev, A.T.; Godovikov, I.A.; Maleev, V.I.; Larionov, V.A. Asymmetric Metal-Templated Route to Amino Acids with 3-Spiropyrrolidine Oxindole Core via a 1,3-Dipolar Addition of Azomethine Ylides to a Chiral Dehydroalanine Ni(II) Complex. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2022, 364, 2395–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-K.; Li, Y.-L.; Chen, R.-X.; Sun, A.-L.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-C.; Wang, M.-Y.; Sheng, S. Substrate-Controlled Regioselectivity Switch in a Three-Component 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition Reaction to Access 3,3′-Pyrrolidinyl-Spirooxindoles Derivatives. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2022, 364, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.; Sana, S.; Sridhar, B.; Shankaraiah, N. Microwave-Assisted One-Pot [3+2] Cycloaddition of Azomethine Ylides and 3-Alkenyl Oxindoles: A Facile Approach to Pyrrolidine-Fused Bis-Spirooxindoles. Chemistryselect 2019, 4, 1727–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marji, S.M.; Bayan, M.F.; Jaradat, A. Facile Fabrication of Methyl Gallate Encapsulated Folate ZIF-L Nanoframeworks as a pH Responsive Drug Delivery System for Anti-Biofilm and Anticancer Therapy. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, R.; Chidambaram, K.; Chandrasekaran, B.; Bayan, M.F.; Maity, T.K.; Alkahtani, A.M.; Chandramoorthy, H.C. Synthesis, pharmacological evaluation, and molecular modeling studies of novel isatin hybrids as potential anticancer agents. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2023, 27, 101598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Gao, D.; Sinko, P.J. Selective Cytotoxicity and Combined Effects of Camptothecin or Paclitaxel with Sodium-R-Alpha Lipoate on A549 Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Nutr. Cancer 2013, 66, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebmann, J.E.; Cook, J.A.; Lipschultz, C.; Teague, D.; Fisher, J.; Mitchell, J.B. Cytotoxic studies of paclitaxel (Taxol®) in human tumour cell lines. Br. J. Cancer 1993, 68, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagandeep, S.; Novikoff, P.M.; Ott, M.; Gupta, S. Paclitaxel shows cytotoxic activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Lett. 1999, 136, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourhis, L.J.; Dolomanov, O.V.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.; Puschmann, H. The anatomy of a comprehensive constrained, restrained refinement program for the modern computing environment–Olex2 dissected. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Adv. 2015, 71, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Worrall, D.E. Nitrostyrene. Org. Synth. 1929, 9, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, M.K.; Coghi, P.; Agrawal, P.; Shyamlal, B.R.K.; Yang, L.J.; Yadav, L.; Peng, Y.; Sharma, R.; Yadav, D.K.; Sahal, D.; et al. Design, Synthesis, Structure-Activity Relationship and Docking Studies of Novel Functionalized Arylvinyl-1,2,4-Trioxanes as Potent Antiplasmodial as well as Anticancer Agents. ChemMedChem 2020, 13, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, M.K.; Coghi, P.; Agrawal, P.; Yadav, D.K.; Yang, L.; Congling, Q.; Sahal, D.; Wong, V.K.W.; Chaudhary, S. Novel halogenated Arylvinyl-1,2,4 trioxanes as potent antiplasmodial as well as anticancer agents: Synthesis, Bioevaluation, structure-activity relationship and in-silico studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 224, 113685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.P.L.; Tiwari, M.K.; Nasim, A.A.; Zhang, R.L.; Qu, Y.; Sharma, R.; Law, B.Y.K.; Yadav, D.K.; Chaudhary, S.; Coghi, P.; et al. Biological Evaluation in Resistant Cancer Cells and Study of Mechanism of Action of Arylvinyl-1,2,4-Trioxanes. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 3, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Tiwari, M.K.; Nasim, A.A.; Yadav, D.K.; Coghi, P.; Wong, V.K.W.; Chaudhary, S. Artemisinin-Inspired Novel Functionalized Aryloxy-Arylvinyl-1,2,4-trioxanes as Potent Anticancer Agents: Design, Synthesis, Bioevaluation, SAR and in silico Studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1288, 135707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

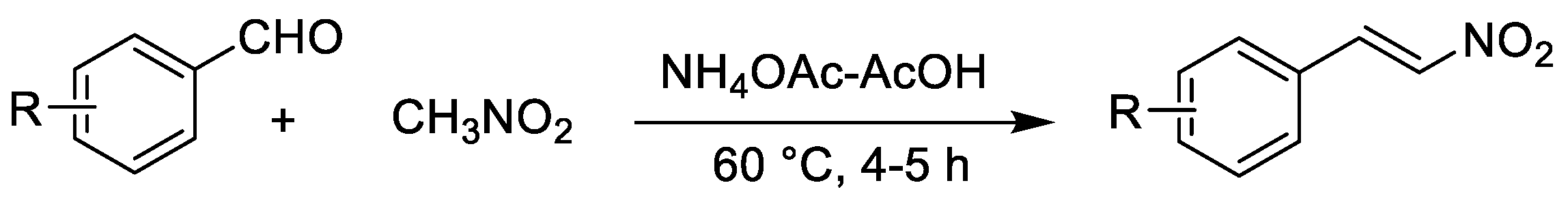
 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S.No. | Solvent | Temp. (°C) | Method A b | Method B c | ||
| Time (min) | Yield (%) d | Time (min) | Yield (%) d | |||
| 1. | H2O | rt | 240 | NR | 30 | Trace |
| 2. | H2O | 90 | 180 | trace | 20 | NR |
| 3. e | H2O | 100/120 | 120 | trace | 10 | NR |
| 4. | MeOH:H2O | 60 | 240 | 55 | 15 | 66 |
| 5 | MeOH:H2O | 90 | 180 | 57 | 10 | 62 |
| 6. f | MeOH:H2O | 100/120 | 120 | 44 | 05 | 48 |
| 7. | MeOH | 60 | 240 | 65 | 15 | 91 |
| 8. | MeOH | 60 | 180 | 56 | 10 | 82 |
| 9. | MeOH | 60 | 120 | 50 | 05 | 61 |
| 10. | EtOH:H2O | 60 | 240 | 63 | 15 | 59 |
| 11. | EtOH:H2O | 90 | 180 | 54 | 10 | 49 |
| 12. g | EtOH:H2O | 100/120 | 120 | 40 | 05 | 36 |
| 13. | MeOH | 90 | 240 | 66 | 15 | 90 |
| 14. h | MeOH | 100/120 | 240 | 64 | 15 | 89 |
| Entry | Trioxane | A549 Cells IC50 [µM] a | BEAS-2B Cells IC50 [µM] a | S.I. b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 4a | >100 | >100 | — |
| 2. | 4b | >100 | >100 | — |
| 3. | 4c | 34.99 (±1.77) | 33.49 (±3.15) | 0.96 |
| 4. | 4d | >100 | >100 | — |
| 5. | 4e | 85.63 (±5.97) | >100 | 1.17 |
| 6. | 4f | 41.12 (±7.77) | >100 | 2.43 |
| 7. | 4g | >100 | >100 | — |
| 8. | 4h | >100 | >100 | — |
| 9. | 4i | >100 | >100 | — |
| 10. | 4j | >100 | >100 | — |
| 11. | 4k | >100 | >100 | — |
| 12. | 4l | >100 | >100 | — |
| 13. | 4m | 45.94 (±3.43) | 63.5 (±4.22) | 1.38 |
| 14. | 4n | >100 | >100 | — |
| 15. | 4o | >100 | >100 | — |
| 16. | 4p | >100 | >100 | — |
| 17. | 4q | 47.92 (±1.61) | >100 | 2.09 |
| 18. | 4r | >100 | >100 | — |
| 19. | 4s | >100 | >100 | — |
| 20. | 4t | 45.22 (±2.40) | 67.7 (±2.18) | 1.50 |
| 21. | 4u | >100 | >100 | — |
| 22. | 4v | >100 | >100 | — |
| 23. | 4w | >100 | >100 | — |
| 24. | ART | 100 | 100 | — |
| 25. | AS | 9.85 | 7.53 | 0.76 |
| 26. | CQ | 100 | 3.07 | 0.03 |
| 27. | Paclitaxel c | 0.003 | 0.1 | 33.3 |
| Entry | Trioxane | HepG2 Cells IC50 [µM] a | LO2 Cells IC50 [µM] a | S.I. b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 4a | >100 | >100 | — |
| 2. | 4b | >100 | >100 | — |
| 3. | 4c | 60.28 (±4.15) | 37.6 (±3.32) | 0.62 |
| 4. | 4d | >100 | >100 | — |
| 5. | 4e | >100 | 81.26 (±0.97) | 0.81 |
| 6. | 4f | 81.95 (±4.05) | >100 | — |
| 7. | 4g | >100 | >100 | — |
| 8. | 4h | >100 | >100 | — |
| 9. | 4i | >100 | >100 | — |
| 10. | 4j | >100 | >100 | — |
| 11. | 4k | 67.76 (±8.27) | 33.32 (±4.02) | 0.49 |
| 12. | 4l | >100 | >100 | — |
| 13. | 4m | 41.56 (±8.24) | 36.65 (±2.20) | 0.88 |
| 14. | 4n | >100 | >100 | — |
| 15. | 4o | >100 | >100 | — |
| 16. | 4p | >100 | >100 | — |
| 17. | 4q | 86.53 (±17.30) | 46.8 (±9.17) | 0.54 |
| 18. | 4r | >100 | >100 | — |
| 19. | 4s | >100 | >100 | — |
| 20. | 4t | 46.05 (±2.23) | 45.49 (±2.50) | 0.99 |
| 21. | 4u | >100 | >100 | — |
| 22. | 4v | >100 | >100 | — |
| 23. | 4w | >100 | >100 | — |
| 24. | ART | >100 | >100 | --- |
| 25. | AS | 4.09 ± 0.4 | 8.25 | 2.01 |
| 26. | CQ | 49.02 ± 0.4 | 15 | 0.30 |
| 27. | Paclitaxel c | 0.19 ± 0.4 | <0.1 | 0.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, R.; Yadav, L.; Nasim, A.A.; Yadav, R.K.; Chen, R.H.; Kumari, N.; Ruiqi, F.; Sharon, A.; Sahu, N.K.; Ippagunta, S.K.; et al. Chemo-/Regio-Selective Synthesis of Novel Functionalized Spiro[pyrrolidine-2,3′-oxindoles] under Microwave Irradiation and Their Anticancer Activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 6503. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186503
Sharma R, Yadav L, Nasim AA, Yadav RK, Chen RH, Kumari N, Ruiqi F, Sharon A, Sahu NK, Ippagunta SK, et al. Chemo-/Regio-Selective Synthesis of Novel Functionalized Spiro[pyrrolidine-2,3′-oxindoles] under Microwave Irradiation and Their Anticancer Activity. Molecules. 2023; 28(18):6503. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186503
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Richa, Lalit Yadav, Ali Adnan Nasim, Ravi Kant Yadav, Rui Hong Chen, Neha Kumari, Fan Ruiqi, Ashoke Sharon, Nawal Kishore Sahu, Sirish Kumar Ippagunta, and et al. 2023. "Chemo-/Regio-Selective Synthesis of Novel Functionalized Spiro[pyrrolidine-2,3′-oxindoles] under Microwave Irradiation and Their Anticancer Activity" Molecules 28, no. 18: 6503. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186503
APA StyleSharma, R., Yadav, L., Nasim, A. A., Yadav, R. K., Chen, R. H., Kumari, N., Ruiqi, F., Sharon, A., Sahu, N. K., Ippagunta, S. K., Coghi, P., Wong, V. K. W., & Chaudhary, S. (2023). Chemo-/Regio-Selective Synthesis of Novel Functionalized Spiro[pyrrolidine-2,3′-oxindoles] under Microwave Irradiation and Their Anticancer Activity. Molecules, 28(18), 6503. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186503








