Ultrafast Transient Absorption Spectra and Kinetics of Rod and Cone Visual Pigments
Abstract
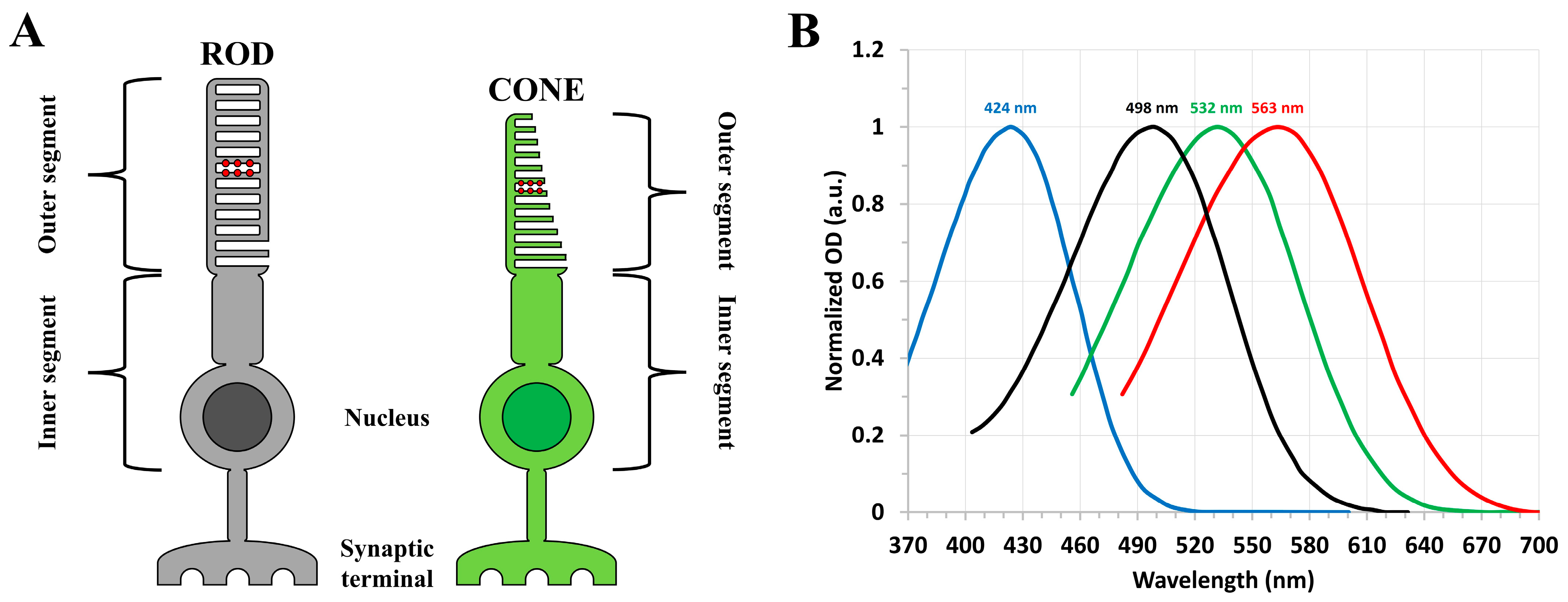
1. Introduction
2. Results
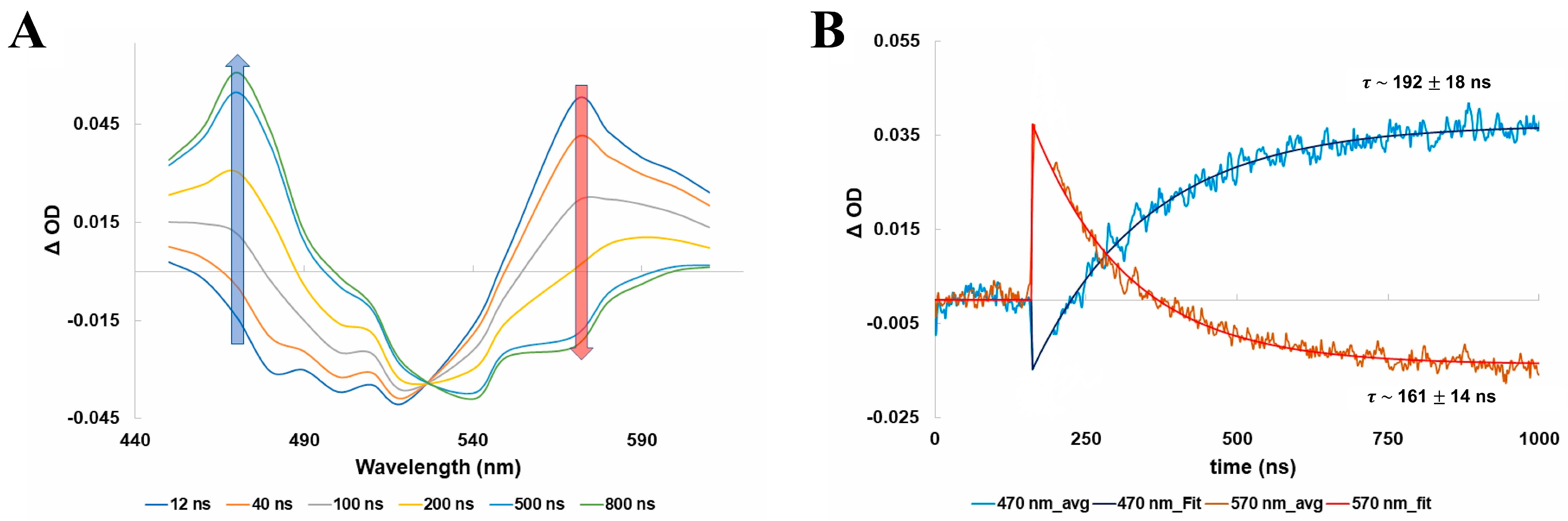
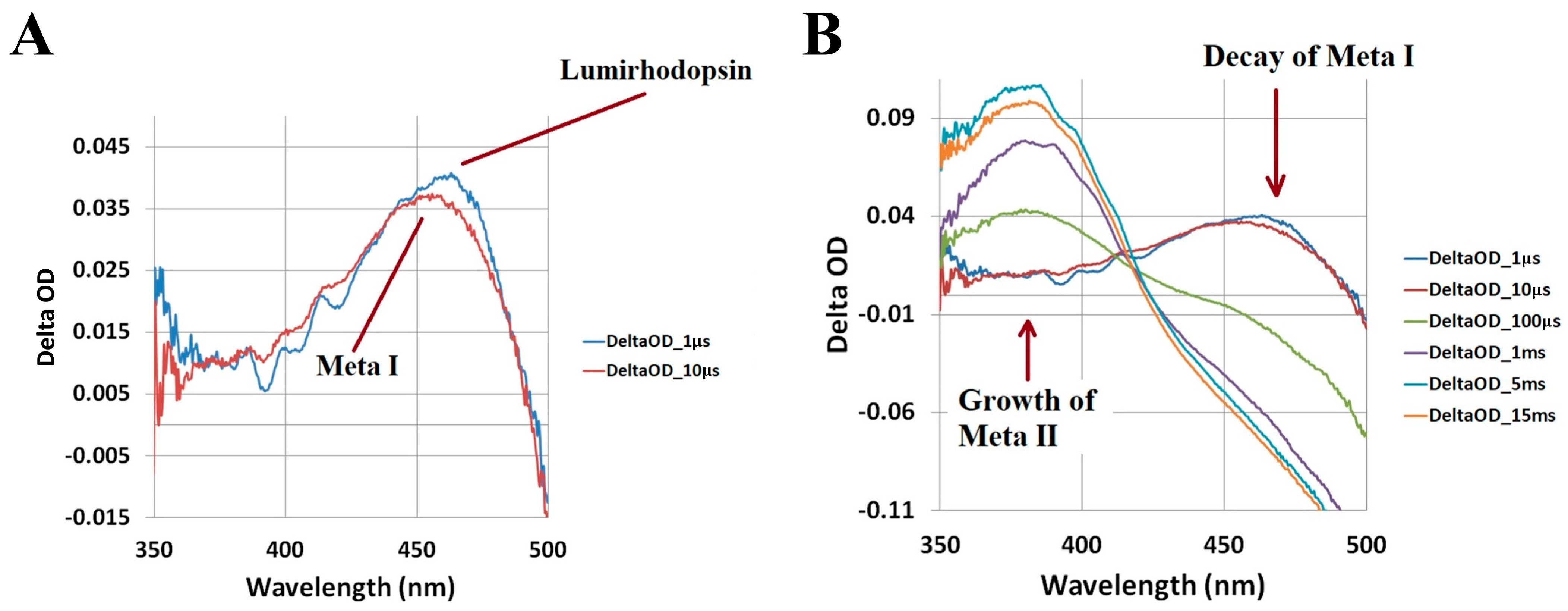
2.1. Bovine Rhodopsin
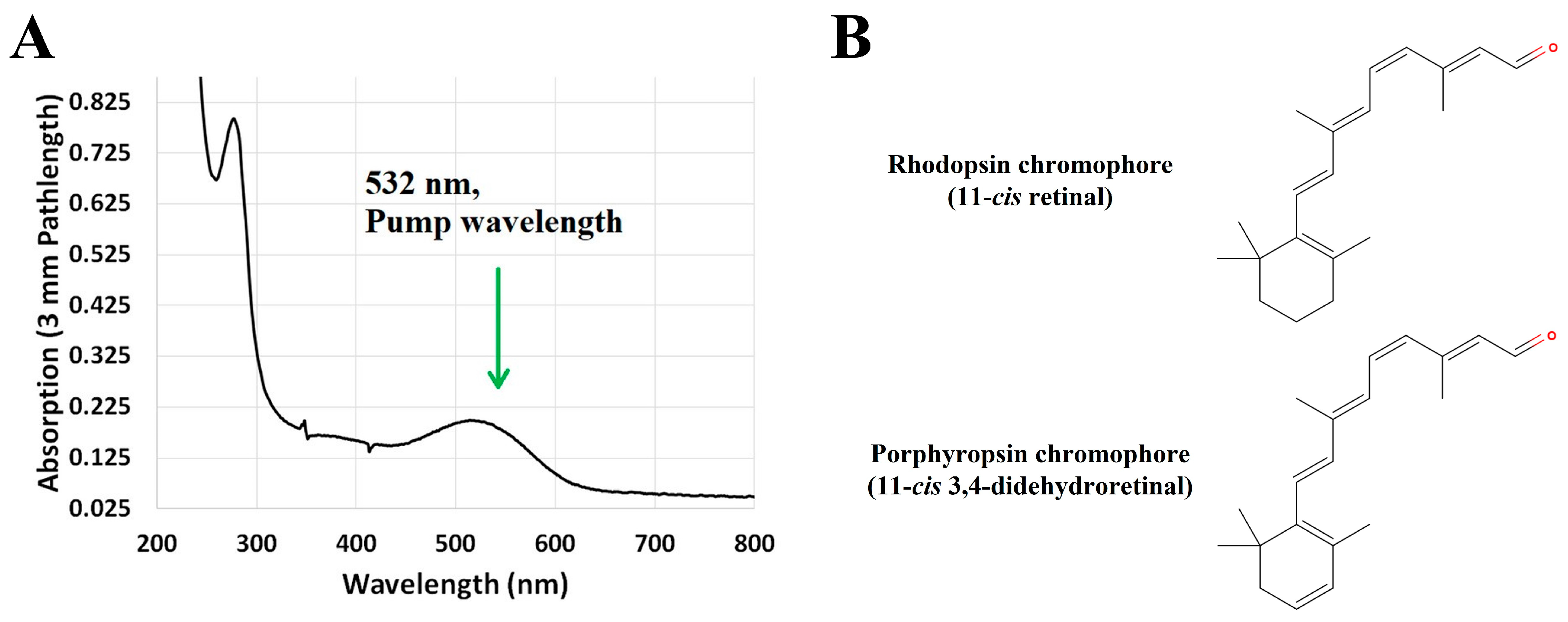
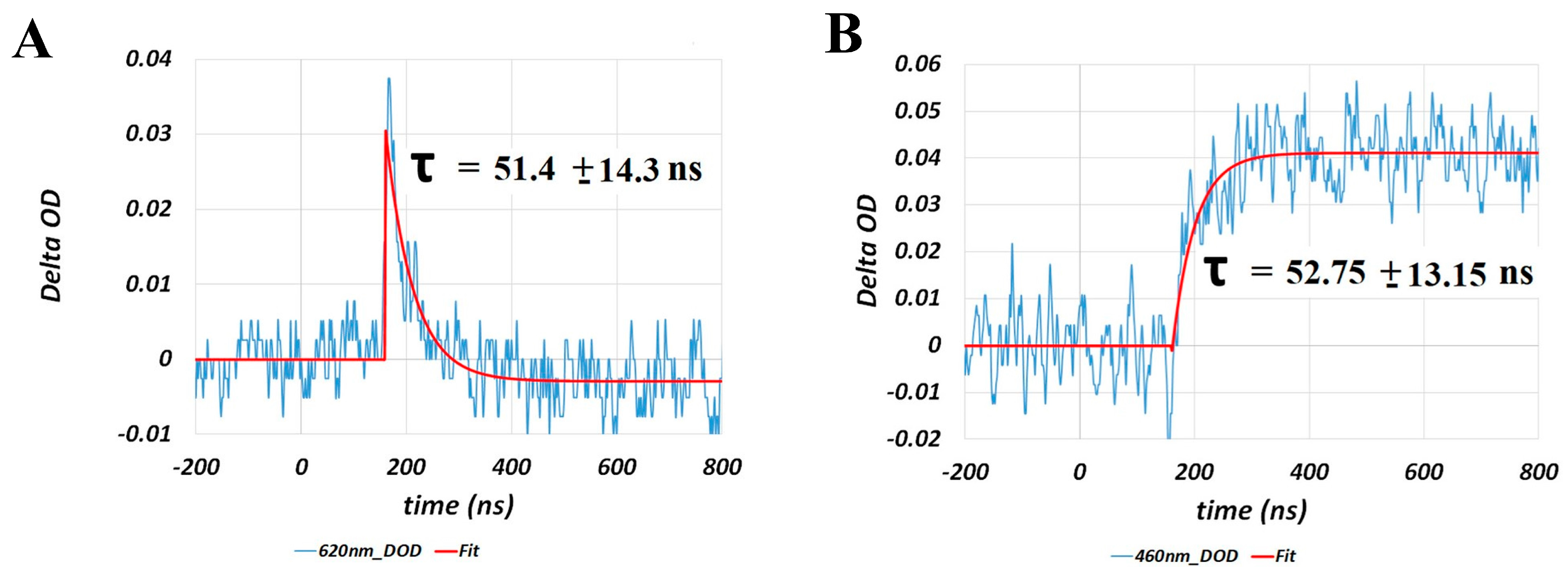
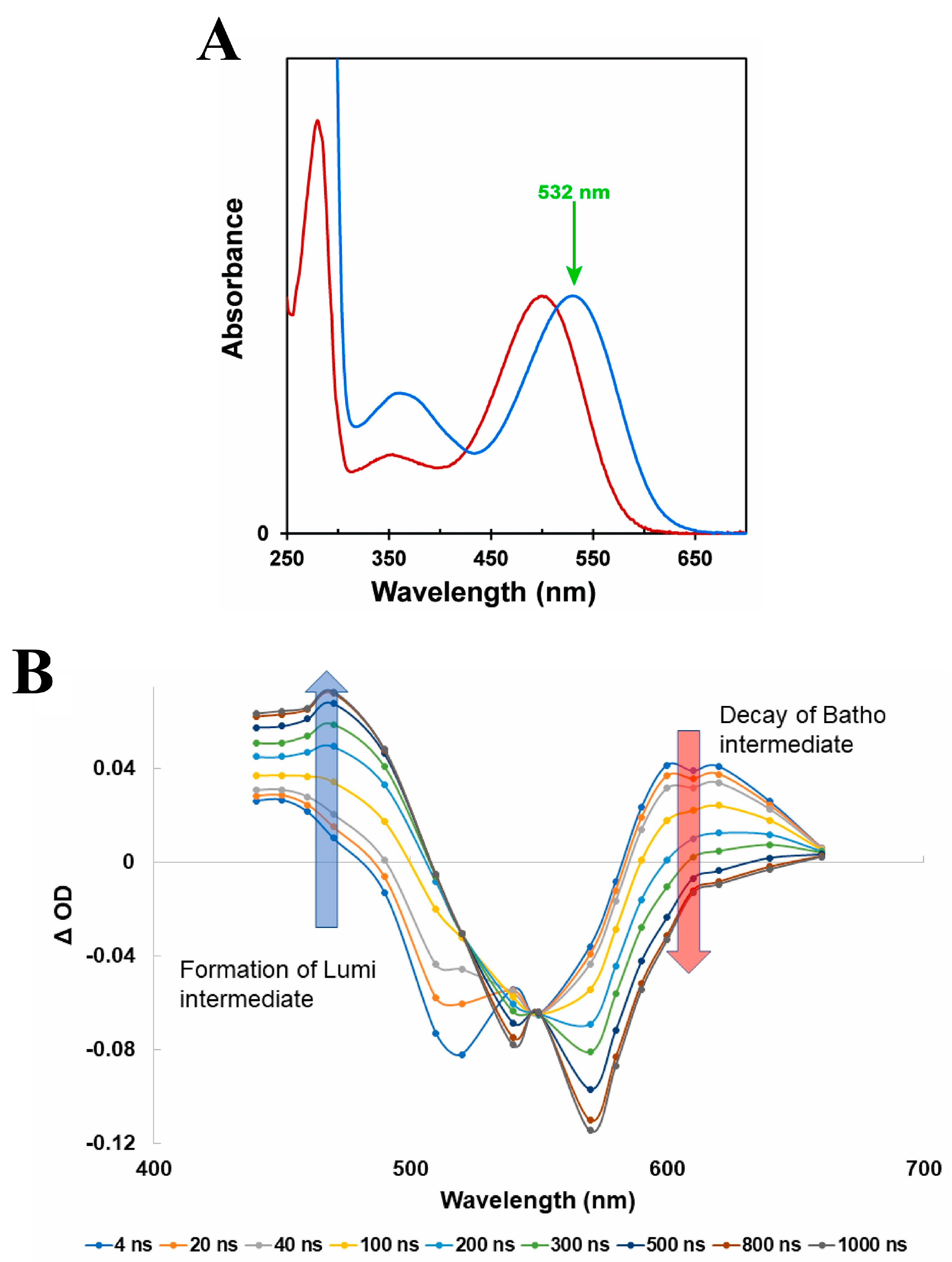
2.2. Porphyropsin (Carp Fish Rhodopsin)
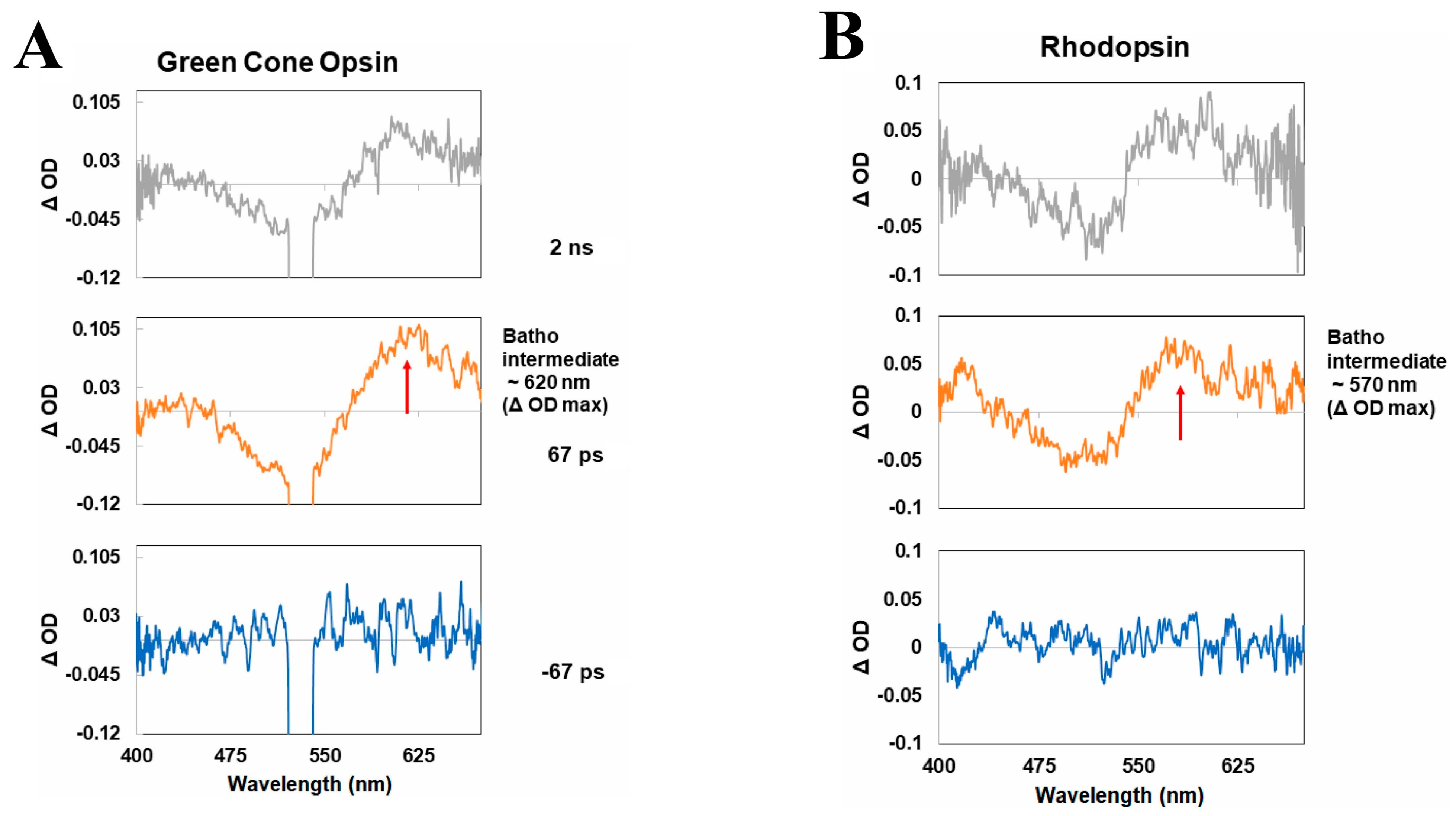
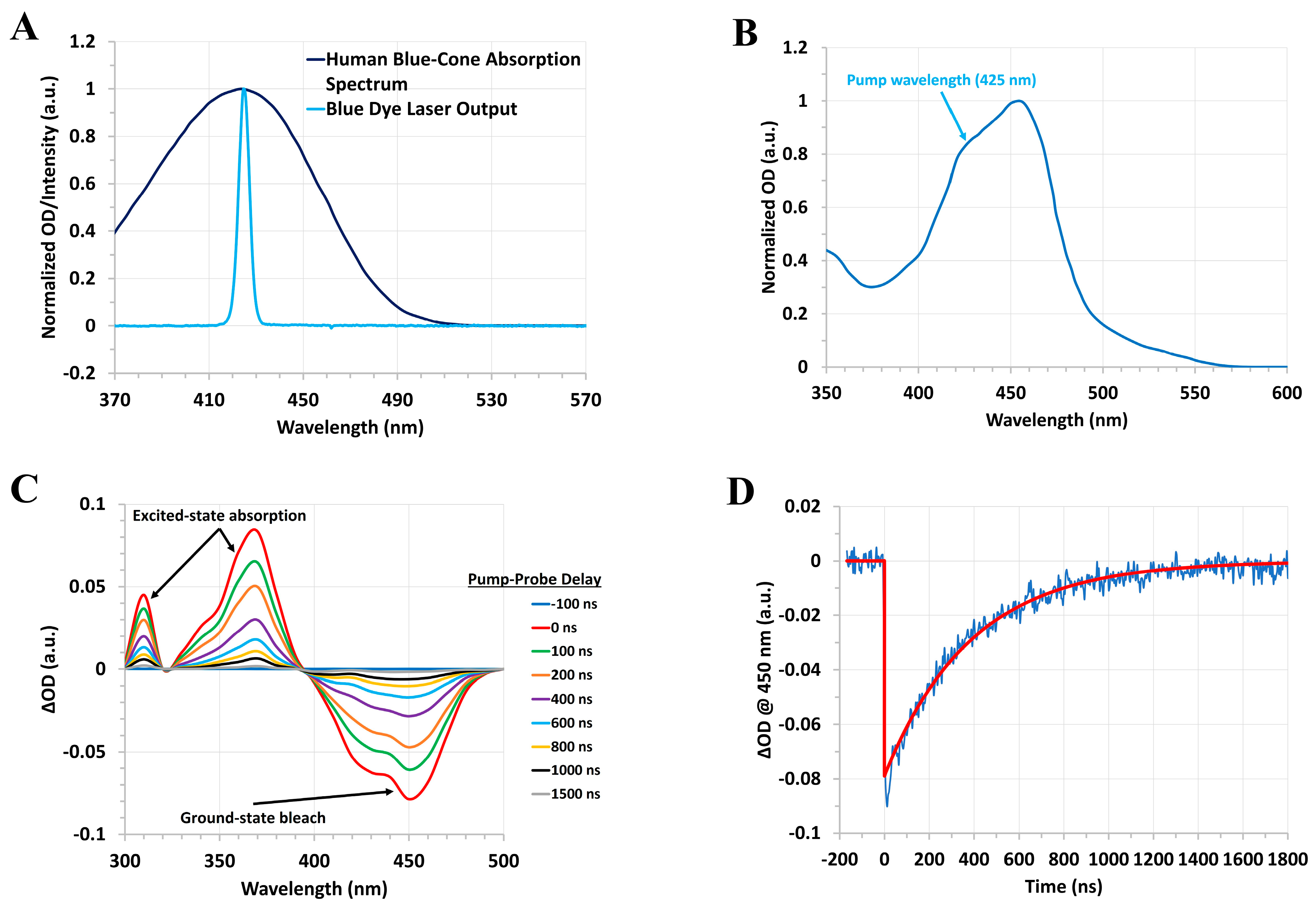
2.3. Human Green-Cone Opsin
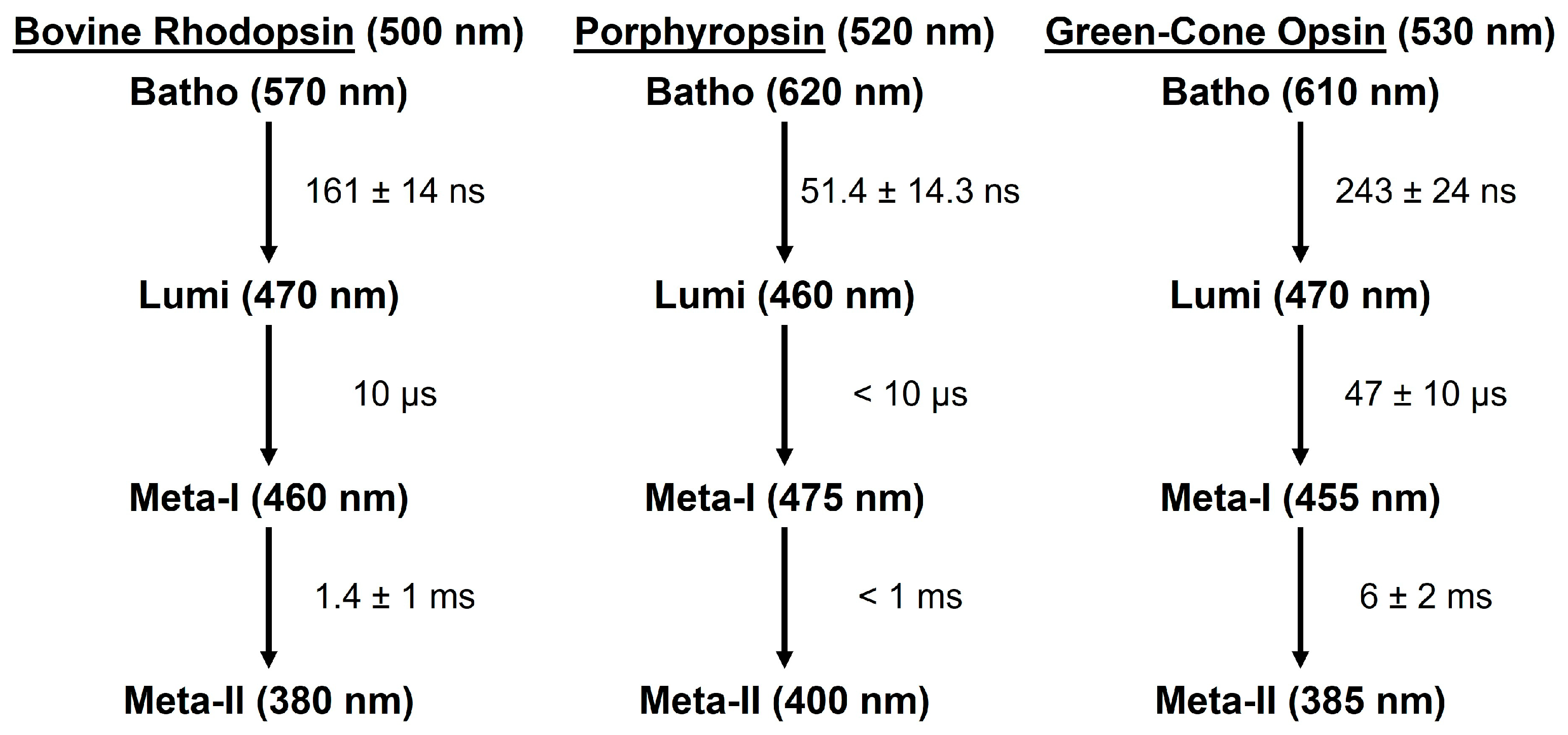
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
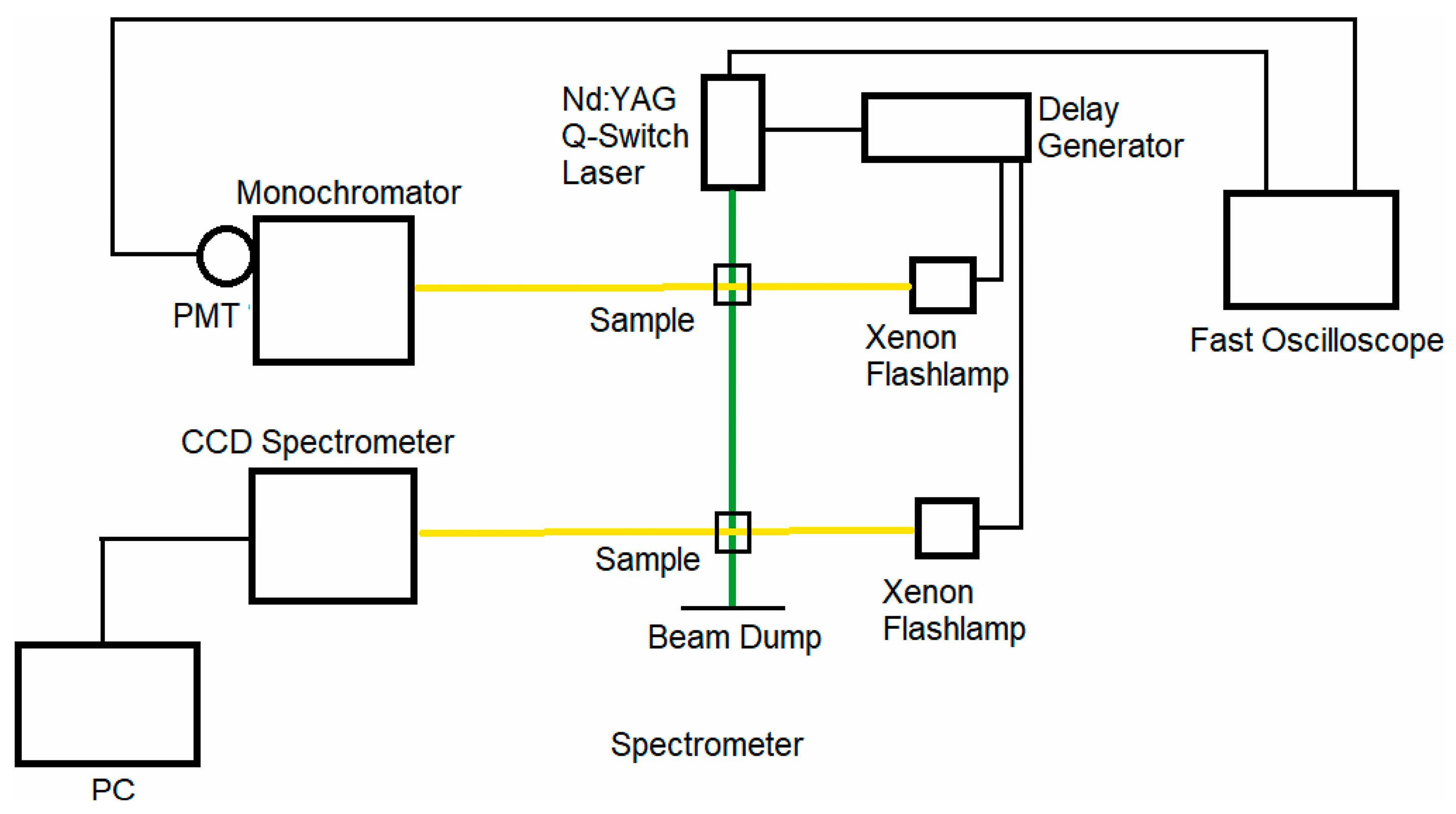
4.1. Nanosecond Transient Absorption System
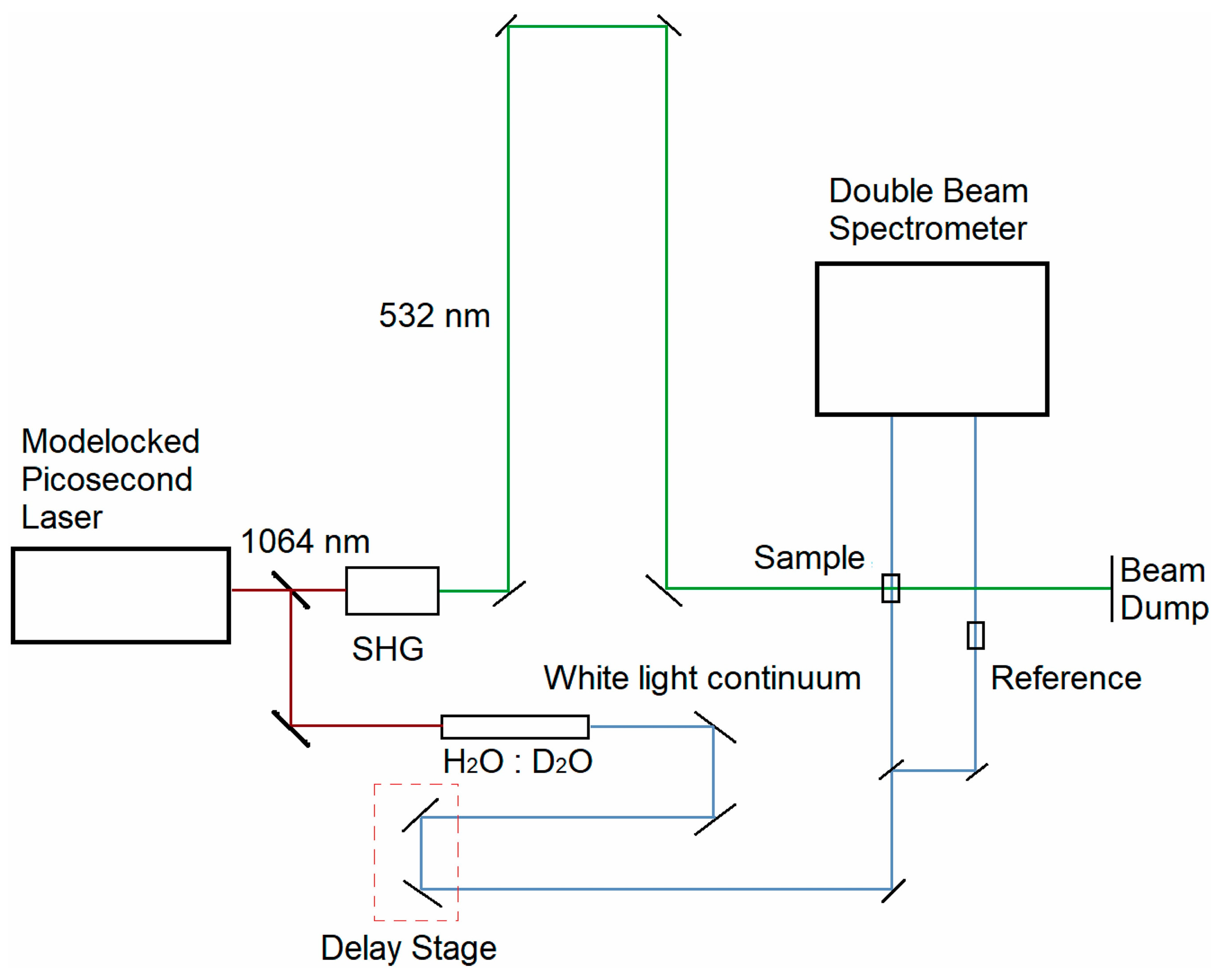
4.2. Picosecond Transient Absorption System
4.3. Rod and Cone Visual Pigments
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Hofmann, K.P.; Lamb, T.D. Rhodopsin, light-sensor of vision. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2023, 93, 101116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L. Principles of Neurobiology; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shichida, Y.; Matsuyama, T. Evolution of opsins and phototransduction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2881–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafi, D.; Engel, A.H.; Palczewski, K. Structure of cone photoreceptors. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2009, 28, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieke, F.; Baylor, D.A. Single-photon detection by rod cells of the retina. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1998, 70, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylor, D.A.; Lamb, T.D.; Yau, K.-W. Responses of retinal rods to single photons. J. Physiol. 1979, 288, 613–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kefalov, V.J. Rod and cone visual pigments and phototransduction through pharmacological, genetic, and physiological approaches. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamoto, Y.; Shichida, Y. Cone visual pigments. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1837, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, S.; Tachibanaki, S. Explaining the functional differences of rods versus cones. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Membr. Transp. Signal. 2012, 1, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowmaker, J.K. Evolution of vertebrate visual pigments. Vis. Res. 2008, 48, 2022–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, K.W.; Hardie, R.C. Phototransduction motifs and variations. Cell 2009, 139, 246–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, S.; Tachibanaki, S. Molecular bases of rod and cone differences. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2022, 90, 101040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, T.D. Photoreceptor physiology and evolution: Cellular and molecular basis of rod and cone phototransduction. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 4585–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowmaker, J.K.; Dartnall, H. Visual pigments of rods and cones in a human retina. J. Physiol. 1980, 298, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, O.P.; Lodowski, D.T.; Elstner, M.; Hegemann, P.; Brown, L.S.; Kandori, H. Microbial and animal rhodopsins: Structures, functions, and molecular mechanisms. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 126–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palczewski, K. G protein–coupled receptor rhodopsin. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006, 75, 743–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terakita, A. The opsins. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathans, J.; Thomas, D.; Hogness, D.S. Molecular genetics of human color vision: The genes encoding blue, green, and red pigments. Science 1986, 232, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, T.; Osorio, D. The Retinal Basis of Vertebrate Color Vision. Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci. 2019, 5, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbo, J.C. Vitamin A(1)/A(2) chromophore exchange: Its role in spectral tuning and visual plasticity. Dev. Biol. 2021, 475, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, J.F.D.; Roberts, N.S.; Johnston, R.J., Jr. The evolutionary history and spectral tuning of vertebrate visual opsins. Dev. Biol. 2023, 493, 40–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandori, H.; Shichida, Y.; Yoshizawa, T. Photoisomerization in rhodopsin. Biochemistry 2001, 66, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Birge, R.R. Nature of the primary photochemical events in rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 1990, 1016, 293–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamoto, Y.; Seki, I.; Yamashita, T.; Shichida, Y. Efficiencies of activation of transducin by cone and rod visual pigments. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 3010–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.-G.; Xue, T.; Yau, K.-W. How vision begins: An odyssey. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9855–9862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.S.; Kefalov, V.J. The cone-specific visual cycle. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2011, 30, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, H.; Kojima, D.; Oura, T.; Tachibanaki, S.; Terakita, A.; Shichida, Y. Single amino acid residue as a functional determinant of rod and cone visual pigments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2322–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wald, G. The porphyropsin visual system. J. Gen. Physiol. 1939, 22, 775–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, G.; Brown, P.K. The molar extinction of rhodopsin. J. Gen. Physiol. 1953, 37, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, G.; Brown, P.K.; Smith, P.H. Iodopsin. J. Gen. Physiol. 1955, 38, 623–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, G.; Brown, P.K. Human rhodopsin. Science 1958, 127, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.K. A system for microspectrophotometry employing a commercial recording spectrophotometer. JOSA 1961, 51, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.K.; Wald, G. Visual pigments in single rods and cones of the human retina. Science 1964, 144, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wald, G. Molecular basis of visual excitation. Science 1968, 162, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, R.G.; Hubbard, R.; Brown, P.K.; Wald, G. Tautomeric forms of metarhodopsin. J. Gen. Physiol. 1963, 47, 215–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshizawa, T.; Wald, G. Pre-lumirhodopsin and the bleaching of visual pigments. Nature 1963, 197, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, T.; Wald, G. Photochemistry of iodopsin. Nature 1967, 214, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, G.-N. Flash photolysis and spectroscopy. A new method for the study of free radical reactions. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1950, 200, 284–300. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, G. Flash photolysis and some of its applications. Science 1968, 160, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentzepis, P. Direct measurements of radiationless transitions in liquids. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1968, 2, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentzepis, P. Ultrafast processes. Science 1970, 169, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, G.; Applebury, M.; Lamola, A.; Rentzepis, P. Formation and decay of prelumirhodopsin at room temperatures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 2802–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensasson, R.; Land, E.J.; Truscott, T. Nanosecond flash photolysis of rhodopsin. Nature 1975, 258, 768–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensasson, R.; Land, E.J.; Truscott, T. Laser flash photolysis of rhodopsin at room temperature. Photochem. Photobiol. 1977, 26, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundstrom, V.; Rentzepis, P.; Peters, K.; Applebury, M. Kinetics of rhodopsin at room temperature measured by picosecond spectroscopy. Nature 1977, 267, 645–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, J.; Lewis, J.; Powers, M.; Kliger, D. Nanosecond laser photolysis of rhodopsin and isorhodopsin. Photochem. Photobiol. 1983, 37, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitienko, O.A.; Mozgovaya, M.N.; Shelaev, I.V.; Gostev, F.E.; Feldman, T.B.; Nadtochenko, V.A.; Sarkisov, O.M.; Ostrovsky, M.A. Femtosecond formation dynamics of primary photoproducts of visual pigment rhodopsin. Biochemistry 2010, 75, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovsky, M.A.; Nadtochenko, V.A. Femtochemistry of Rhodopsins. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 15, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukura, P.; McCamant, D.W.; Yoon, S.; Wandschneider, D.B.; Mathies, R.A. Structural observation of the primary isomerization in vision with femtosecond-stimulated Raman. Science 2005, 310, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, T.B.; Smitienko, O.A.; Shelaev, I.V.; Gostev, F.E.; Nekrasova, O.V.; Dolgikh, D.A.; Nadtochenko, V.A.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Ostrovsky, M.A. Femtosecond spectroscopic study of photochromic reactions of bacteriorhodopsin and visual rhodopsin. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2016, 164, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.; Applebury, M.; Rentzepis, P. Primary photochemical event in vision: Proton translocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 3119–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applebury, M.L.; Peters, K.S.; Rentzepis, P.M. Primary intermediates in the photochemical cycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys. J. 1978, 23, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorgeirsson, T.E.; Lewis, J.W.; Wallace-Williams, S.E.; Kliger, D.S. Effects of temperature on rhodopsin photointermediates from lumirhodopsin to metarhodopsin II. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 13861–13872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibanaki, S.; Imai, H.; Mizukami, T.; Okada, T.; Imamoto, Y.; Matsuda, T.; Fukada, Y.; Terakita, A.; Shichida, Y. Presence of two rhodopsin intermediates responsible for transducin activation. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 14173–14180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, Y.G.; Szundi, I.; Lewis, J.W.; Kliger, D.S. Microsecond time-resolved circular dichroism of rhodopsin photointermediates. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 12283–12289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandberg, M.N.; Greco, J.A.; Wagner, N.L.; Amora, T.L.; Ramos, L.A.; Chen, M.-H.; Knox, B.E.; Birge, R.R. Low-temperature trapping of photointermediates of the rhodopsin E181Q mutant. SOJ Biochem. 2014, 1, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Gruhl, T.; Weinert, T.; Rodrigues, M.J.; Milne, C.J.; Ortolani, G.; Nass, K.; Nango, E.; Sen, S.; Johnson, P.J.M.; Cirelli, C.; et al. Ultrafast structural changes direct the first molecular events of vision. Nature 2023, 615, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Yamashita, T.; Imamoto, Y.; Shichida, Y. Comparative studies on the late bleaching processes of four kinds of cone visual pigments and rod visual pigment. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 4300–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandori, H.; Mizukami, T.; Okada, T.; Imamoto, Y.; Fukada, Y.; Shichida, Y.; Yoshizawa, T. Bathoiodopsin, a primary intermediate of iodopsin at physiological temperature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8908–8912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shichida, Y.; Okada, T.; Kandori, H.; Fukada, Y.; Yoshizawa, T. Nanosecond laser photolysis of iodopsin, a chicken red-sensitive cone visual pigment. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 10832–10838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, T.; Imamoto, Y. Structure and photobleaching process of chicken iodopsin. Biophys. Chem. 1995, 56, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhankhar, D.; Nagpal, A.; Tachibanaki, S.; Li, R.; Cesario, T.C.; Rentzepis, P.M. Comparison of Bovine and Carp Fish Visual Pigment Photo-Intermediates at Room Temperature. Photochem. Photobiol. 2022, 98, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhankhar, D.; Salom, D.; Palczewski, K.; Rentzepis, P.M. Ultrafast spectra and kinetics of human green-cone visual pigment at room temperature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2214276120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, T.S.; Salom, D.; Sun, W.; Palczewski, K. Increasing the Stability of Recombinant Human Green Cone Pigment. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.W.; Kliger, D.S. Photointermediates of visual pigments. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1992, 24, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, E.C.; Kazmi, M.A.; Ganim, Z.; Hou, J.-M.; Pan, D.; Chang, B.S.; Sakmar, T.P.; Mathies, R.A. Retinal counterion switch in the photoactivation of the G protein-coupled receptor rhodopsin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9262–9267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, H.; Terakita, A.; Tachibanaki, S.; Imamoto, Y.; Yoshizawa, T.; Shichida, Y. Photochemical and biochemical properties of chicken blue-sensitive cone visual pigment. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 12773–12779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, P.; Brettel, K. [Ru(bpy)(3)](2+) as a reference in transient absorption spectroscopy: Differential absorption coefficients for formation of the long-lived (3)MLCT excited state. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2012, 11, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krishnamoorthi, A.; Khosh Abady, K.; Dhankhar, D.; Rentzepis, P.M. Ultrafast Transient Absorption Spectra and Kinetics of Rod and Cone Visual Pigments. Molecules 2023, 28, 5829. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155829
Krishnamoorthi A, Khosh Abady K, Dhankhar D, Rentzepis PM. Ultrafast Transient Absorption Spectra and Kinetics of Rod and Cone Visual Pigments. Molecules. 2023; 28(15):5829. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155829
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrishnamoorthi, Arjun, Keyvan Khosh Abady, Dinesh Dhankhar, and Peter M. Rentzepis. 2023. "Ultrafast Transient Absorption Spectra and Kinetics of Rod and Cone Visual Pigments" Molecules 28, no. 15: 5829. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155829
APA StyleKrishnamoorthi, A., Khosh Abady, K., Dhankhar, D., & Rentzepis, P. M. (2023). Ultrafast Transient Absorption Spectra and Kinetics of Rod and Cone Visual Pigments. Molecules, 28(15), 5829. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155829







