pH-Responsive Cobalt(II)-Coordinated Assembly Containing Quercetin for Antimicrobial Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Quercetin–Cobalt(II) Complex
2.2. Poly(acrylic acid)–Cobalt(II) Complex
2.3. Quercetin–Cobalt(II)–Polymer Assembly
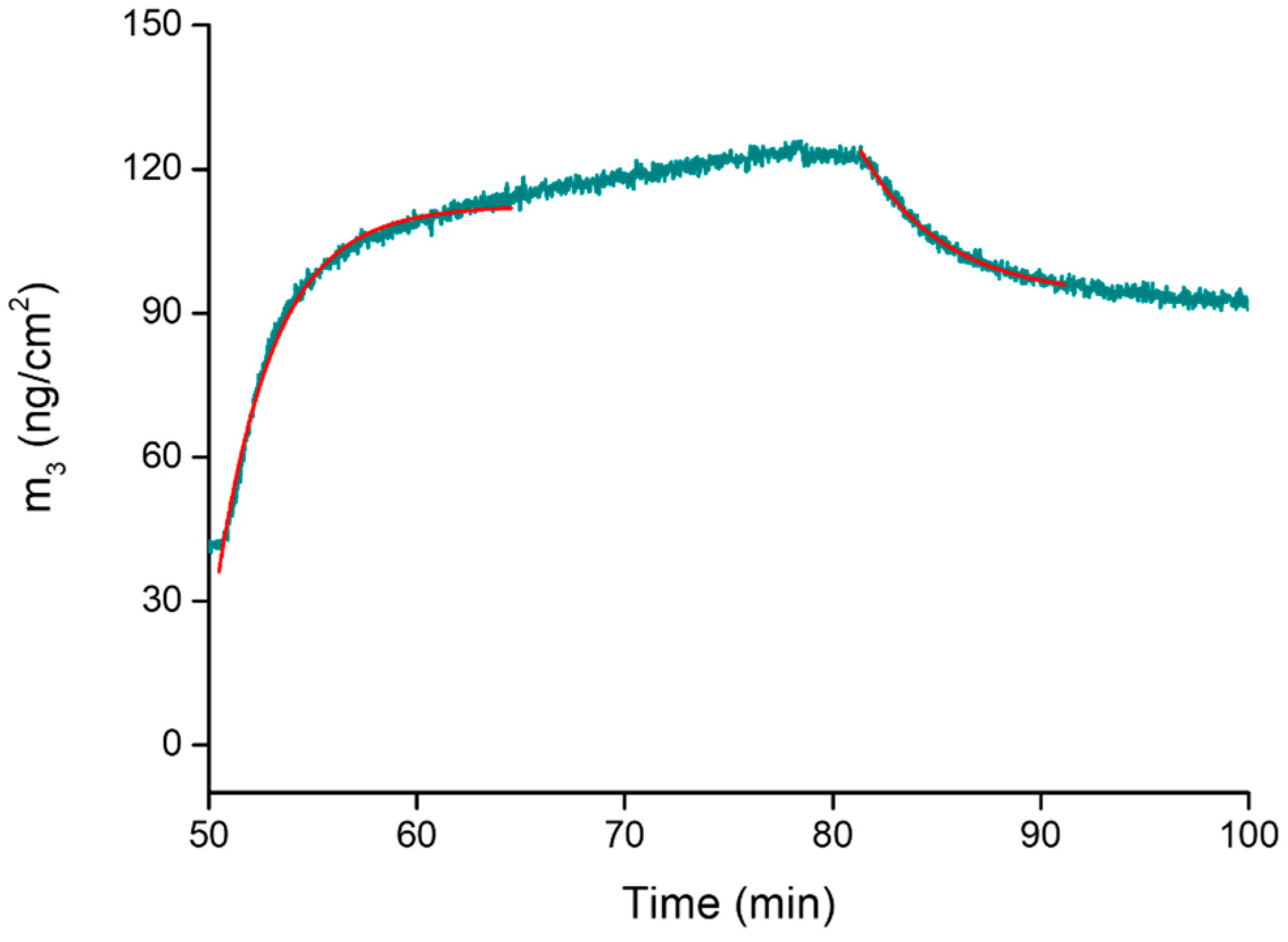
2.4. Assembly Formation at the Interface and Drug Release at Controlled pH
L + M(PAA)2 ⇄ LM(PAA)2
koff
- -
- θ(t) is the time-dependent surface coverage,
- -
- θeq is the concentration-dependent equilibrium surface coverage,
- -
- kon and koff are the kinetic rate constants for the binding and unbinding process,
- -
- C is the concentration of the adsorptive ligand;
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. UV-Vis Titrations
3.3. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC) Measurements
3.4. Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Monitoring (QCM-D) Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Levy, S.B.; Marshall, B. Antibacterial resistance worldwide: Causes, challenges and responses. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S122–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekshun, M.N.; Levy, S.B. Molecular mechanisms of antibacterial multidrug resistance. Cell 2007, 128, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.C.; Huang, T.H.; Yang, S.C.; Chen, C.C.; Fang, J.Y. Nano-based drug delivery or targeting to eradicate bacteria for infection mitigation: A review of recent advances. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak, M.M.; Erxleben, A.; Ochocki, J. Properties and applications of flavonoid metal complexes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 45853–45877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushnie, T.T.; Lamb, A.J. Recent advances in understanding the antibacterial properties of flavonoids. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 38, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penalva, R.; González-Navarro, C.J.; Gamazo, C.; Esparza, I.; Irache, J.M. Zein Nanoparticles for oral delivery of quercetin: Pharmacokinetic studies and preventive anti-inflammatory effects in a mouse model of endotoxemia. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatahet, T.; Morille, M.; Hommoss, A.; Devoisselle, J.M.; Müller, R.H.; Begu, S. Liposomes, lipid nanocapsules and smart crystals: A comparative study for an effective quercetin delivery to the skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 542, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kost, B.; Svyntkivska, M.; Brzeziński, M.; Makowski, T.; Piorkowska, E.; Rajkowska, K.; Biela, T. PLA/β-CD-based fibres loaded with quercetin as potential antibacterial dressing materials. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 190, 110949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.L.A.; Bhattacharya, D. Antimicrobial activity of quercetin: An approach to its mechanistic principle. Molecules 2022, 27, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, H.; Chen, J.C.; Cao, Y.; Fu, W.; Zhou, P.; Pang, J. Apigenin, a novel candidate involving herb-drug interaction (HDI), interacts with organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1). Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 69, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; He, M.; Zang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, T.; Pan, S.; Xiaoyun, X. A structure-activity relationship study of flavonoids as inhibitors of E. coli by membrane interaction effect. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 2751–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daglia, M. Polyphenols as antimicrobial agents. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osonga, F.J.; Akgul, A.; Miller, R.M.; Eshun, G.B.; Yazgan, I.; Akgul, A.; Sadik, O.A. Antimicrobial activity of a new class of phosphorylated and modified flavonoids. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 12865–12871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Xing, S.; Wang, M.; Peng, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, X. Anticomplement and antimicrobial activities of flavonoids from Entada phaseoloides. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.U.; Khurram, M.; Khattak, B.; Khan, J. Antibiotic additive and synergistic action of rutin, morin and quercetin against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Tripathi, A. Quercetin inhibits carbapenemase and efflux pump activities among carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Apmis 2020, 128, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Kaleem, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Shafiq, H. Therapeutic potential of flavonoids and their mechanism of action against microbial and viral infections—A review. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, T.; Long, M.; Li, P. Quercetin: Its main pharmacological activity and potential application in clinical medicine. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8825387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yao, J.; Zhou, B.; Yang, J.; Chaudry, M.T.; Wang, M.; Xiao, F.; Li, Y.; Yin, W. Bacteriostatic effect of quercetin as an antibiotic alternative in vivo and its antibacterial mechanism in vitro. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushnie, T.P.T.; Lamb, A.J. Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 26, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Sun, F.; Feng, W.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, X.; Xiong, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Quercetin is an effective inhibitor of quorum sensing, biofilm formation and virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.M.; Andrades, N.E.; Paulino, N.; Sawaya, A.C.; Eberlin, M.N.; Marcucci, M.C.; Bydlowski, S.P. Synthesis and characterization of a metal complex containing naringin and Cu, and its antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiinflammatory and tumor cell cytotoxicity. Molecules 2007, 12, 1352–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panhwar, Q.K.; Memon, S. Synthesis and evaluation of antioxidant and antibacterial properties of morin complexes. J. Coord. Chem. 2011, 64, 2117–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Machin, L.; Monzote, L.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Ezzat, S.M.; Salem, M.A.; Merghany, R.M.; El Mahdy, N.M.; Kılıç, C.S.; Sytar, O.; et al. Therapeutic potential of quercetin: New insights and perspectives for human health. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 11849–11872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazo, H.; Colino, C.I.; Lanao, J.M. Current applications of nanoparticles in infectious diseases. J. Control Release 2016, 224, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canaparo, R.; Foglietta, F.; Giuntini, F.; Della Pepa, C.; Dosio, F.; Serpe, L. Recent developments in antibacterial therapy: Focus on stimuli-responsive drug-delivery systems and therapeutic nanoparticles. Molecules 2019, 24, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, R.; Luan, S.; Huang, Y.; Khan, A. Bacterial adaptability of enzyme and pH dual-responsive surface for infection resistance. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 7710–7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Lai, H.; Zhang, X. Smart bacteria-responsive drug delivery systems in medical implants. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, P.; Xu, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, D.; Wu, J. A pH and hyaluronidase dual-responsive multilayer-based drug delivery system for resisting bacterial infection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 527, 146806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Dastgheyb, S.S.; Hickok, N.J.; Eckmann, D.M.; Composto, R.J. Targeted release of tobramycin from a pH-responsive grafted bilayer challenged with S. aureus. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofridam, F.; Tarhini, M.; Lebaz, N.; Gagnière, É.; Mangin, D.; Elaissari, A. pH-sensitive polymers: Classification and some fine potential applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 1455–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Hu, X. UV–Vis spectroscopy combined with chemometric study on the interactions of three dietary flavonoids with copper ions. Food Chem. 2018, 263, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonowicz, M.; Regulska, E. Spectroscopic study of molecular structure, antioxidant activity and biological effects of metal hydroxyflavonol complexes. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. 2017, 173, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Du, S.; Kokot, S. Interaction between quercetin–copper (II) complex and DNA with the use of the Neutral Red dye fluorophor probe. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 584, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrente, G.A.; Malacaria, L.; Beneduci, A.; Furia, E.; Marino, T.; Mazzone, G. Experimental and theoretical study on the coordination properties of quercetin towards aluminum (III), iron (III) and copper (II) in aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 325, 115171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherrak, S.A.; Mokhtari-Soulimane, N.; Berroukeche, F.; Bensenane, B.; Cherbonnel, A.; Merzouk, H.; Elhabiri, M. In vitro antioxidant versus metal ion chelating properties of flavonoids: A structure-activity investigation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glade, M.J.; Meguid, M.M. A glance at antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of dietary cobalt. Nutrition 2018, 46, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.L.; Simmers, C.; Knight, D.A. Cobalt complexes as antiviral and antibacterial agents. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 1711–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santonoceta, G.D.G.; Sgarlata, C. Metal-coordinated assemblies containing quercetin: A solution equilibria study for the development of pH-responsive drug delivery systems. In Proceedings of the Acta of the International Symposia on Thermodynamics of Metal Complexes, ISMEC 2022, València, Spain, 5–8 June 2022; ISMEC Group Series. Volume 11, p. OC22, ISSN: 2239–2459. [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari, S.B.; Memon, S.; Tahir, M.M.; Bhanger, M.I. Synthesis, characterization and investigation of antioxidant activity of cobalt–quercetin complex. J. Mol. Struct. 2008, 892, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowska, M.; Lewandowska, H.; Pruszyński, M.; Świderski, G.; Gołębiewska, E.; Gryko, K.; Lewandowski, W. Co(II) complex of quercetin–spectral, anti/pro-oxidant and cytotoxic activity in HaCaT cell lines. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castilho, T.S.; Matias, T.B.; Nicolini, K.P.; Nicolini, J. Sudy of interaction between metal ions and quercetin. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2018, 7, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, S.V.; Steenken, S.; Tosic, M.; Marjanovic, B.; Simic, M.G. Flavonoids as antioxidants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 4846–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malešev, D.; Kuntić, V. Investigation of metal-flavonoid chelates and the determination of flavonoids via metal-flavonoid complexing reactions. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2007, 72, 921–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, B.L.; Seguel, G.V. Poly (acrylic acid-co-maleic acid)–metal complexes with copper(II), cobalt(II), and nickel(II): Synthesis, characterization and structure of its metal chelates. Polyhedron 1999, 18, 2511–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabukina, E.B.; Fatullaev, E.I.; Filippov, A.P.; Abzaeva, K.A. Behavior of metal complexes of polyacrylic acid in solutions. Int. J. Polym. Anal. 2019, 24, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomida, T.; Hamaguchi, K.; Tunashima, S.; Katoh, M.; Masuda, S. Binding properties of a water-soluble chelating polymer with divalent metal ions measured by ultrafiltration. Poly (acrylic acid). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 3557–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litmanovich, O.E.; Ostaeva, G.Y.; Tatarinov, V.S.; Bogdanov, A.G.; Papisov, I.M. Effect of complexation of poly (acrylic acid) with Cu2+ ions on the size of copper nanoparticles prepared via reduction in aqueous solutions. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2010, 52, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmaker, S.; Saha, T.K.; Sakurai, H. Investigation of a CuII–poly (γ-glutamic acid) complex in aqueous solution and its insulin-mimetic activity. Macromol. Biosci. 2007, 7, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, R.; Grasso, G.I.; Milana, P.; Cusmano, S.; Santonoceta, G.D.G.; Sgarlata, C. Adsorption of calixarene-based supramphiphiles at the solid–liquid interface monitored by QCM-D. Supramol. Chem. 2021, 33, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykut, D.Y.; Yolaçan, Ö.; Deligöz, H. pH stimuli drug loading/release platforms from LbL single/blend films: QCM-D and in-vitro studies. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 602, 125113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deligoez, H.; Tieke, B. QCM-D study of layer-by-layer assembly of polyelectrolyte blend films and their drug loading-release behavior. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 441, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, J.; Atefyekta, S.; Andersson, M. Controlling drug delivery kinetics from mesoporous titania thin films by pore size and surface energy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notley, S.M.; Eriksson, M.; Wågberg, L. Visco-elastic and adhesive properties of adsorbed polyelectrolyte multilayers determined in situ with QCM-D and AFM measurements. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2005, 292, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easley, A.D.; Ma, T.; Eneh, C.I.; Yun, J.; Thakur, R.M.; Lutkenhaus, J.L. A practical guide to quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring of thin polymer films. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 60, 1090–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devnarain, N.; Osman, O.; Fasiku, V.O.; Makhathini, S.; Salih, M.; Ibrahim, U.H.; Govender, T. Intrinsic stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for smart drug delivery of antibacterial agents—An in-depth review of the last two decades. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 13, e1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebara, Y.; Okahata, Y. A kinetic study of concanavalin. A binding to glycolipid monolayers by using a quartz-crystal microbalance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 11209–11212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okahata, Y.; Kawase, M.; Niikura, K.; Ohtake, F.; Furusawa, H.; Ebara, Y. Kinetic measurements of DNA hybridization on an oligonucleotide-immobilized 27-MHz quartz crystal microbalance. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, S.; Kelkenberg, M.; Nöll, T.; Steinhoff, B.; Schönherr, H.; Merzendorfer, H.; Nöll, G. Rapid determination of binding parameters of chitin binding domains using chitin-coated quartz crystal microbalance sensor chips. Analyst 2018, 143, 5255–5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaschka, H. EDTA Titrations; Pergamon Press: London, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Gans, P.; Sabatini, A.; Vacca, A. Investigation of equilibria in solution. Determination of equilibrium constants with the HYPERQUAD suite of programs. Talanta 1996, 43, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgarlata, C.; Zito, V.; Arena, G. Conditions for calibration of an isothermal titration calorimeter using chemical reactions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, G.; Gans, P.; Sgarlata, C. HypCal, a general-purpose computer program for the determination of standard reaction enthalpy and binding constant values by means of calorimetry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 6413–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgarlata, C.; Bonaccorso, C.; Gulino, F.G.; Zito, V.; Arena, G.; Sciotto, D. Inclusion of aromatic and aliphatic anions into a cationic water soluble calix [4]arene at different pH values. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 1610–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorso, C.; Ciadamidaro, A.; Sgarlata, C.; Sciotto, D.; Arena, G. Guest-induced capsule formation based on concerted interactions in water at neutral pH. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 7139–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reviakine, I.; Johannsmann, D.; Richter, R.P. Hearing what you cannot see and visualizing what you hear: Interpreting quartz crystal microbalance data from solvated interfaces. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8838–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanazi, N.; Almutairi, M.; Alodhayb, A. A review of quartz crystal microbalance for chemical and biological sensing applications. Sens. Imaging 2023, 24, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

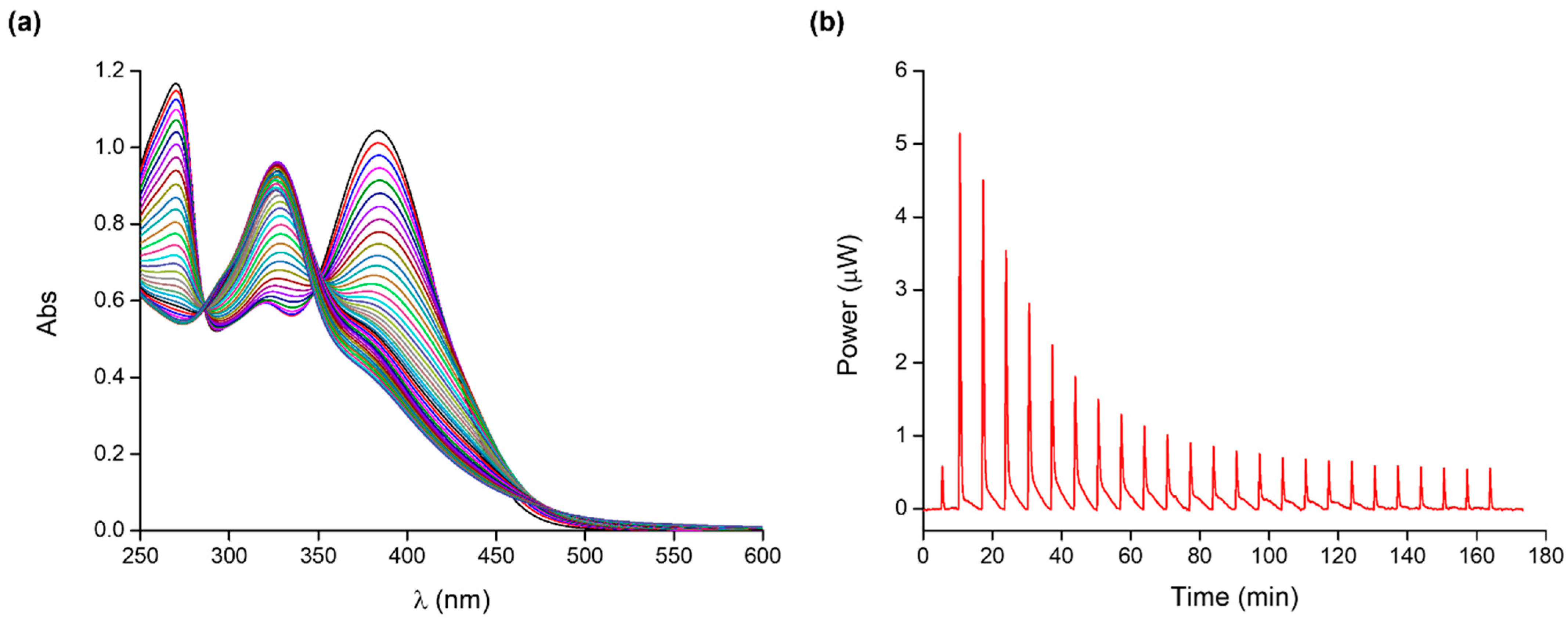
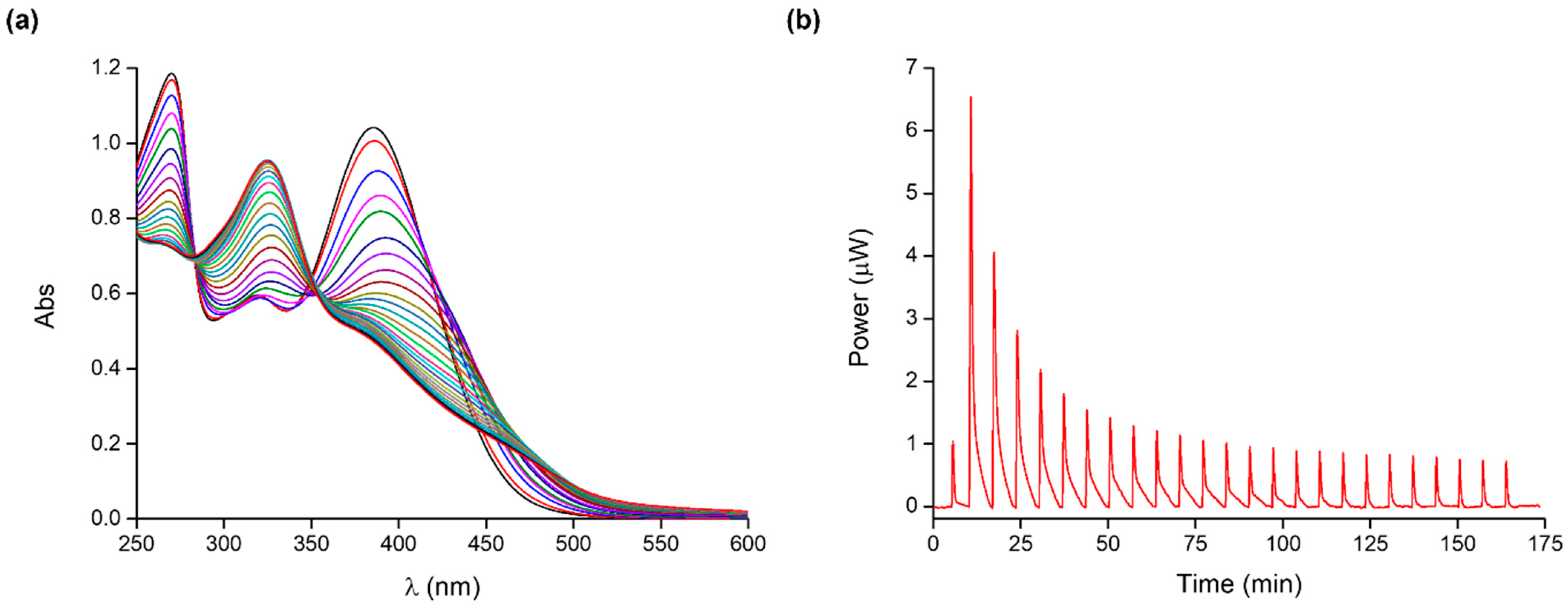
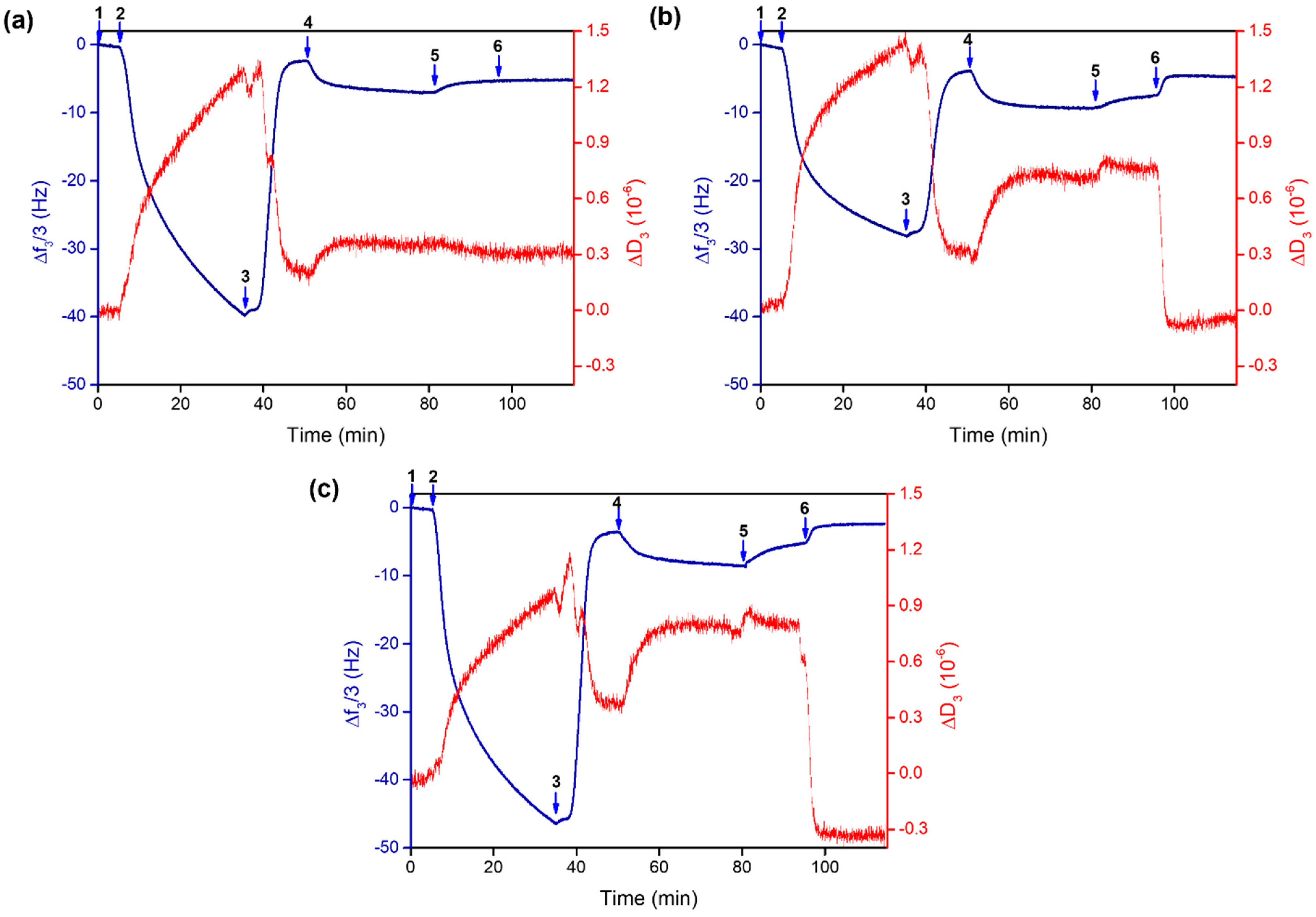
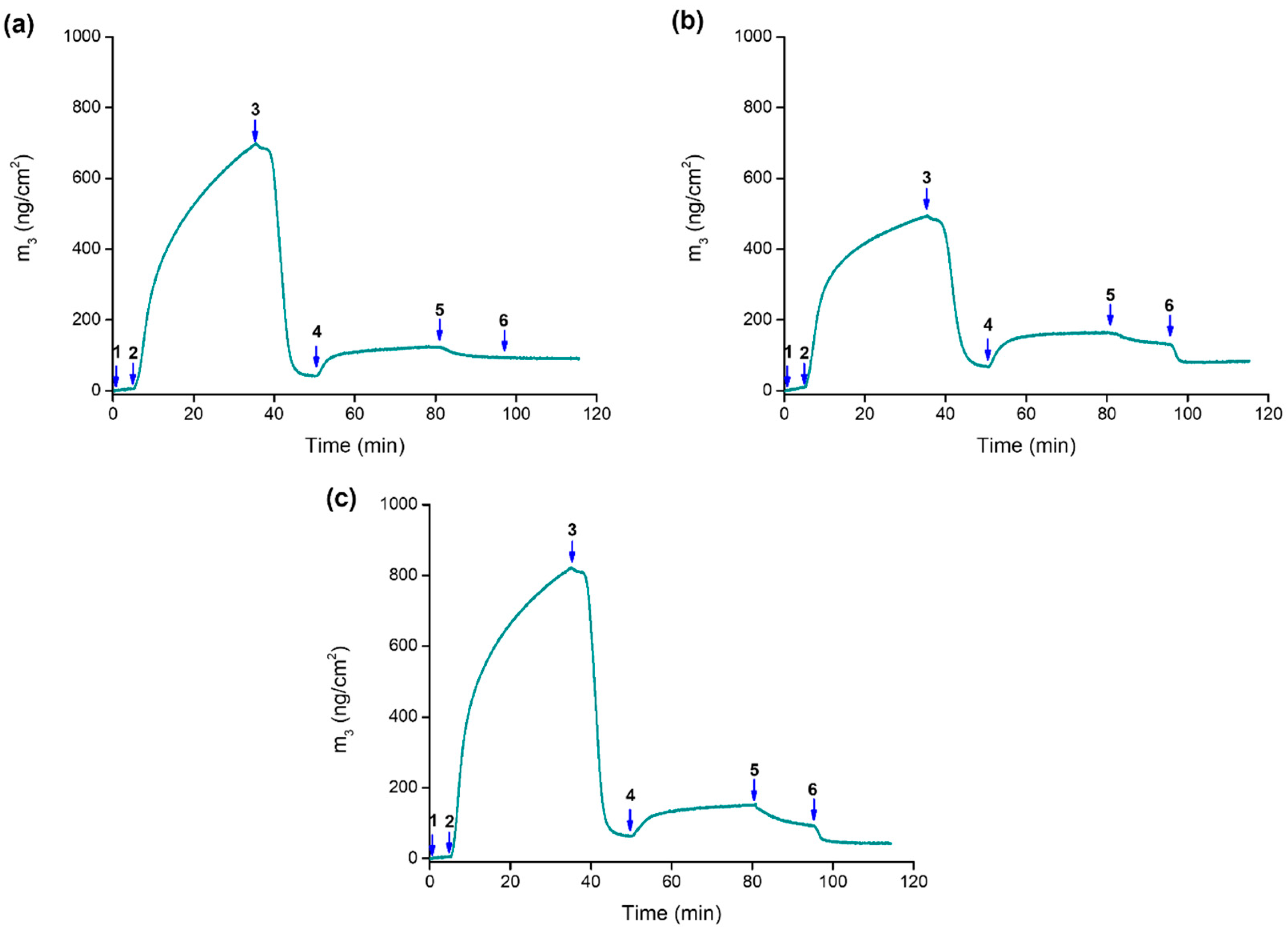
| Species | Log K UV-Vis | Log K ITC | ΔH0 (kJ mol−1) | ΔS0 (J K−1 mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ML | 5.66 (2) | 5.7 (1) | −11.45 (2) | 71 (3) |
| ML2 | 4.52 (8) | 3.3 (2) | −24.33 (4) | −19 (3) |
| Species | Log K | ΔH0 (kJ mol−1) | ΔS0 (J K−1 mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M(PAA) | 4.3 (2) | 7.39 (6) | 108 (5) |
| M(PAA)2 | 3.8 (3) | −1.23 (8) | 68 (2) |
| Species b | Log K UV-Vis | Log K ITC | ΔH0 (kJ mol−1) | ΔS0 (J K−1 mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LM(PAA)2 | 3.75 (1) | 4.5 (2) | −14.17 (6) | 38 (5) |
| Que Loaded | % Que Released | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 7.4 | pH 5.4 | pH 4.5 | ||
| Adsorbed mass (ng cm−2) | 50 ± 12 | 6% | 62% | 64% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santonoceta, G.D.G.; Sgarlata, C. pH-Responsive Cobalt(II)-Coordinated Assembly Containing Quercetin for Antimicrobial Applications. Molecules 2023, 28, 5581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145581
Santonoceta GDG, Sgarlata C. pH-Responsive Cobalt(II)-Coordinated Assembly Containing Quercetin for Antimicrobial Applications. Molecules. 2023; 28(14):5581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145581
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantonoceta, Giuseppina D. G., and Carmelo Sgarlata. 2023. "pH-Responsive Cobalt(II)-Coordinated Assembly Containing Quercetin for Antimicrobial Applications" Molecules 28, no. 14: 5581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145581
APA StyleSantonoceta, G. D. G., & Sgarlata, C. (2023). pH-Responsive Cobalt(II)-Coordinated Assembly Containing Quercetin for Antimicrobial Applications. Molecules, 28(14), 5581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145581






