Phytofabrication of Selenium Nanoparticles with Moringa oleifera (MO-SeNPs) and Exploring Its Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
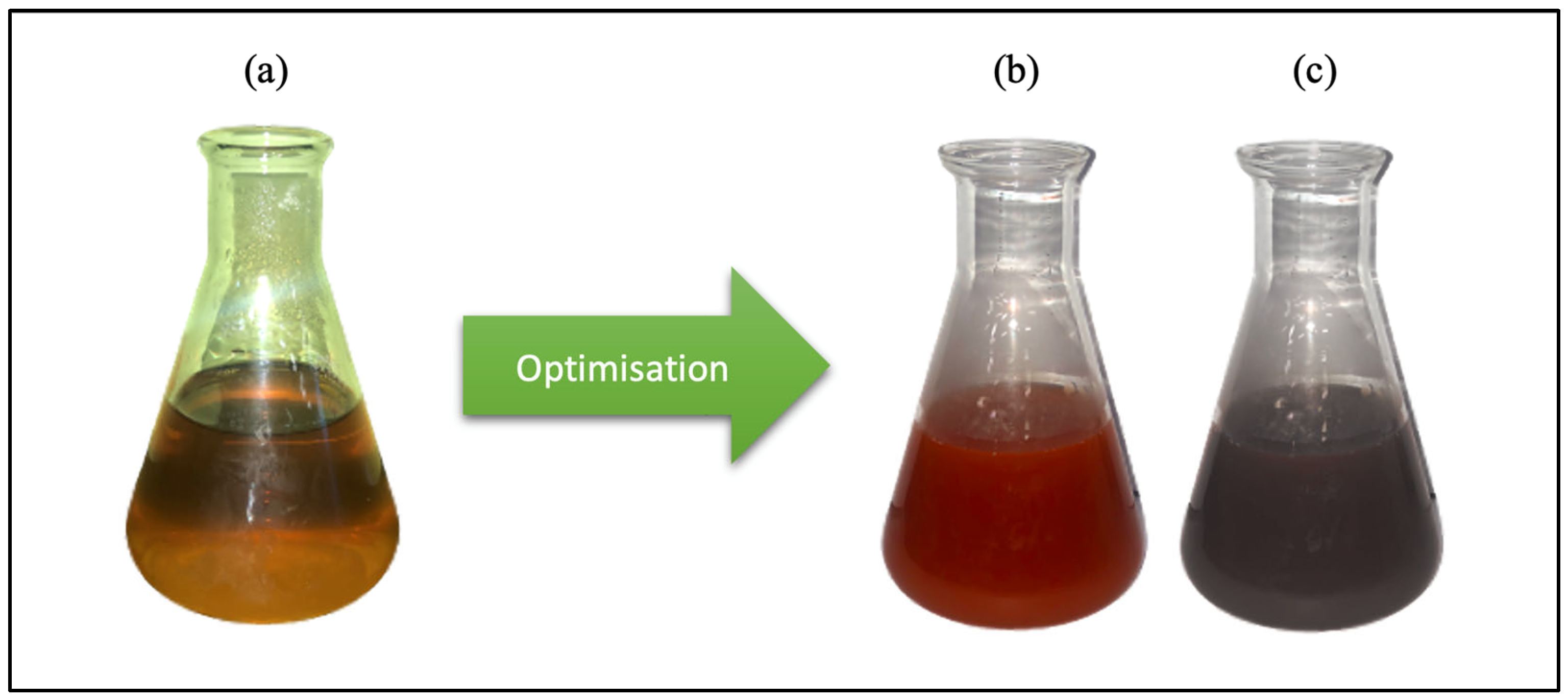
2.1. Biogenic Synthesis and Optimization of MO-SeNPs
2.2. Effects of pH Level on MO-SeNPs Synthesis
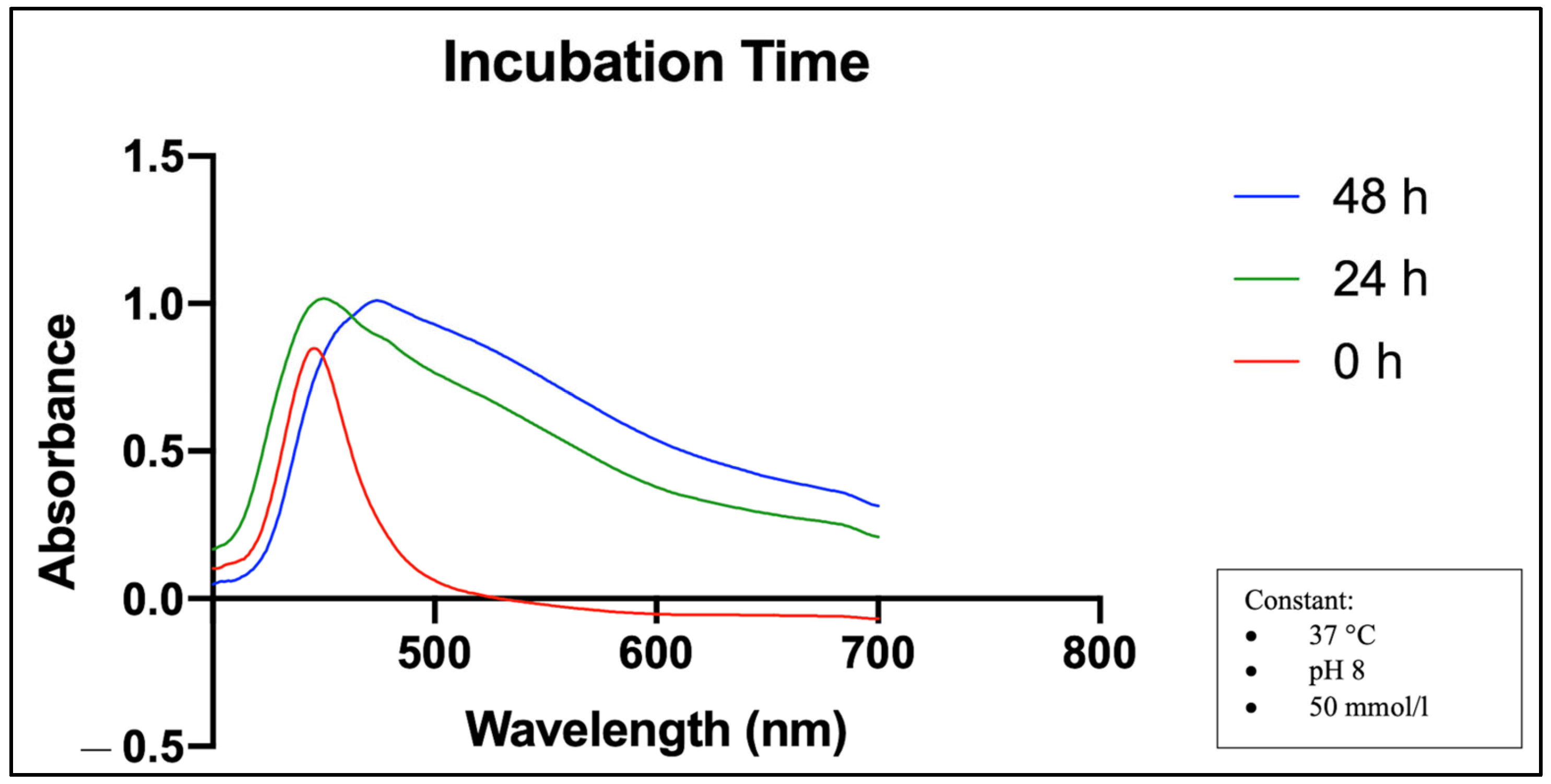
2.3. Effects of Incubation Time on MO-SeNPs Synthesis
2.4. Effects of Temperature on MO-SeNPs Synthesis
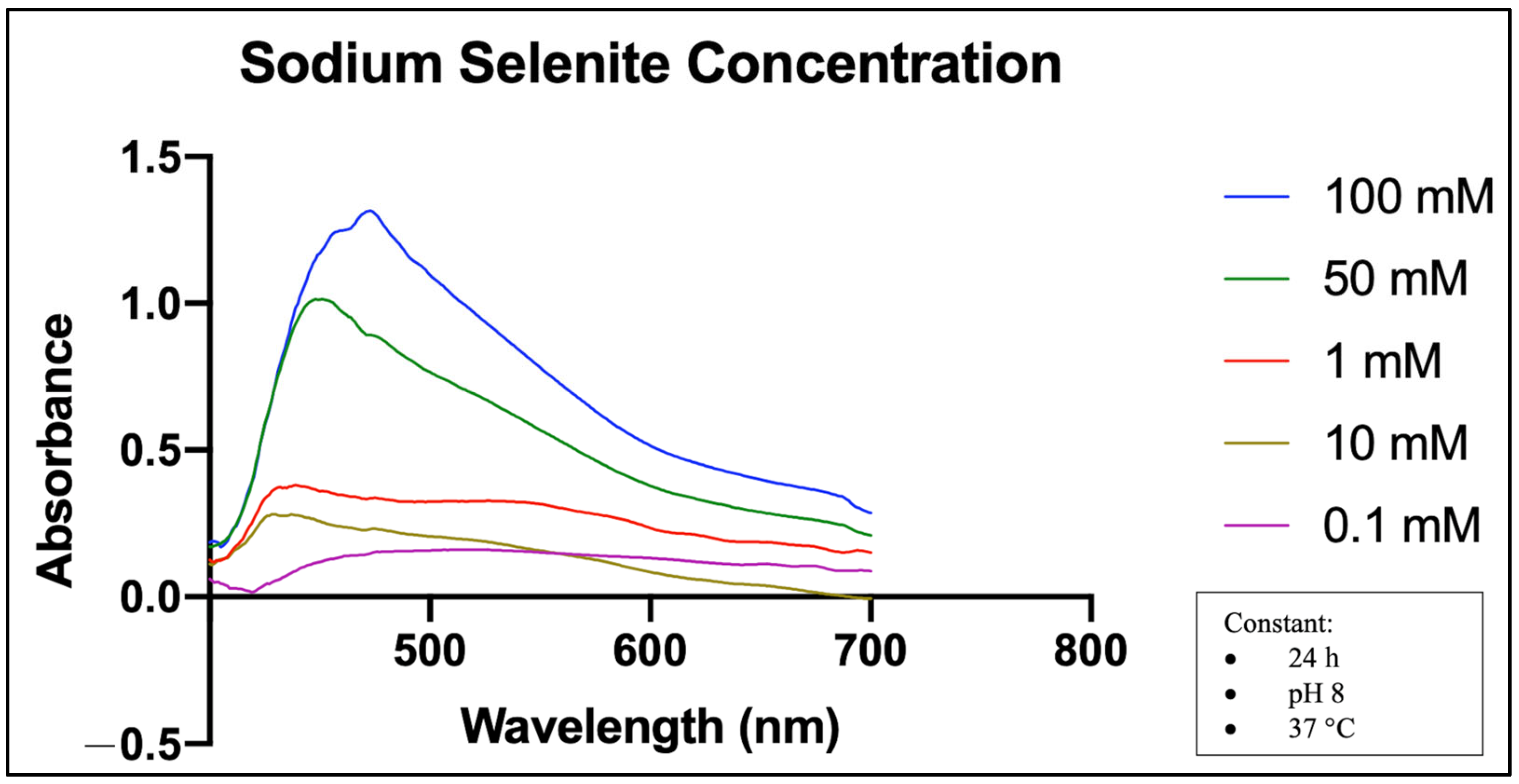
2.5. Effects of Precursor Concentration on MO-SeNPs Synthesis
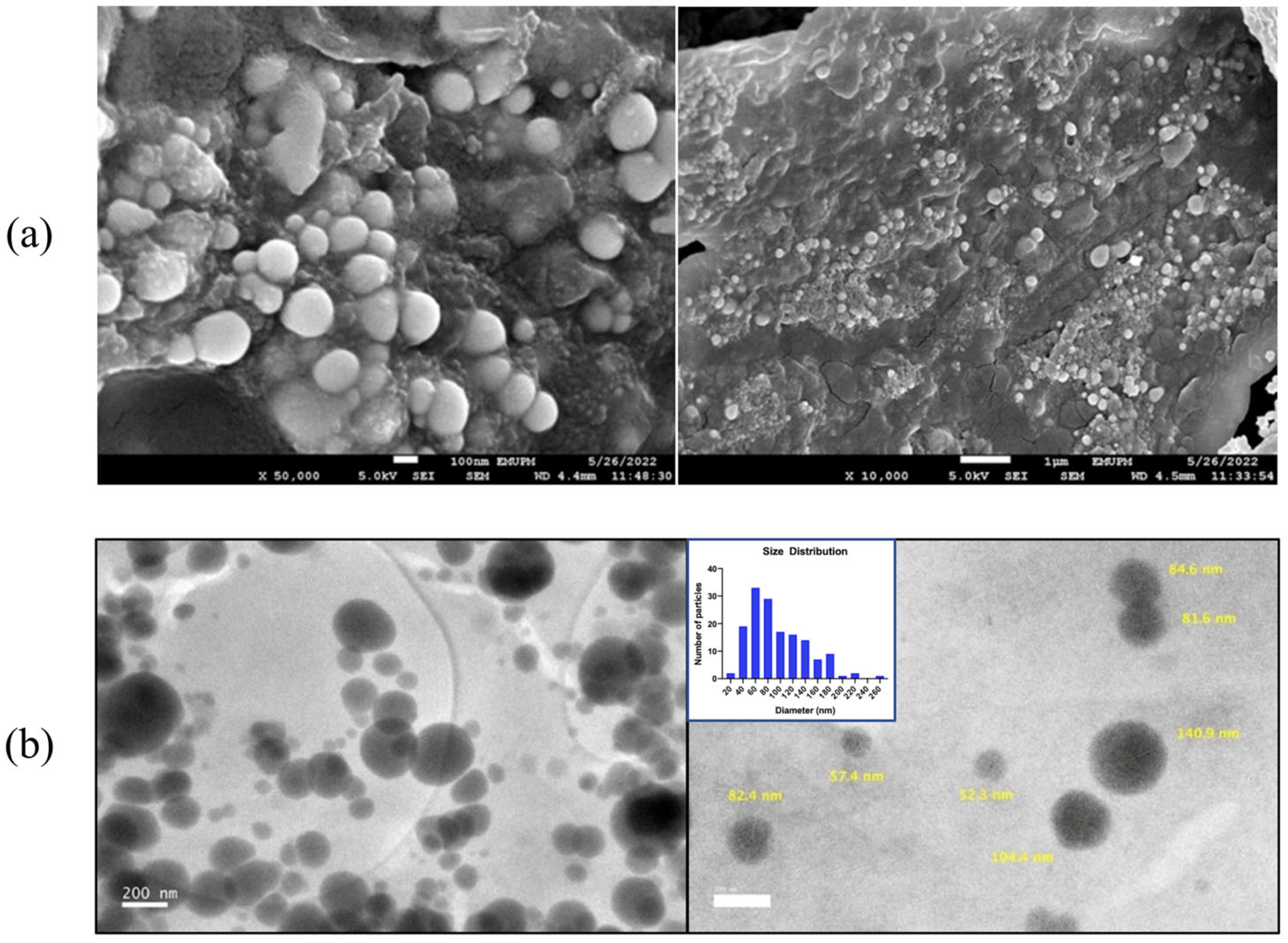
2.6. Characterizations of MO-SeNPs
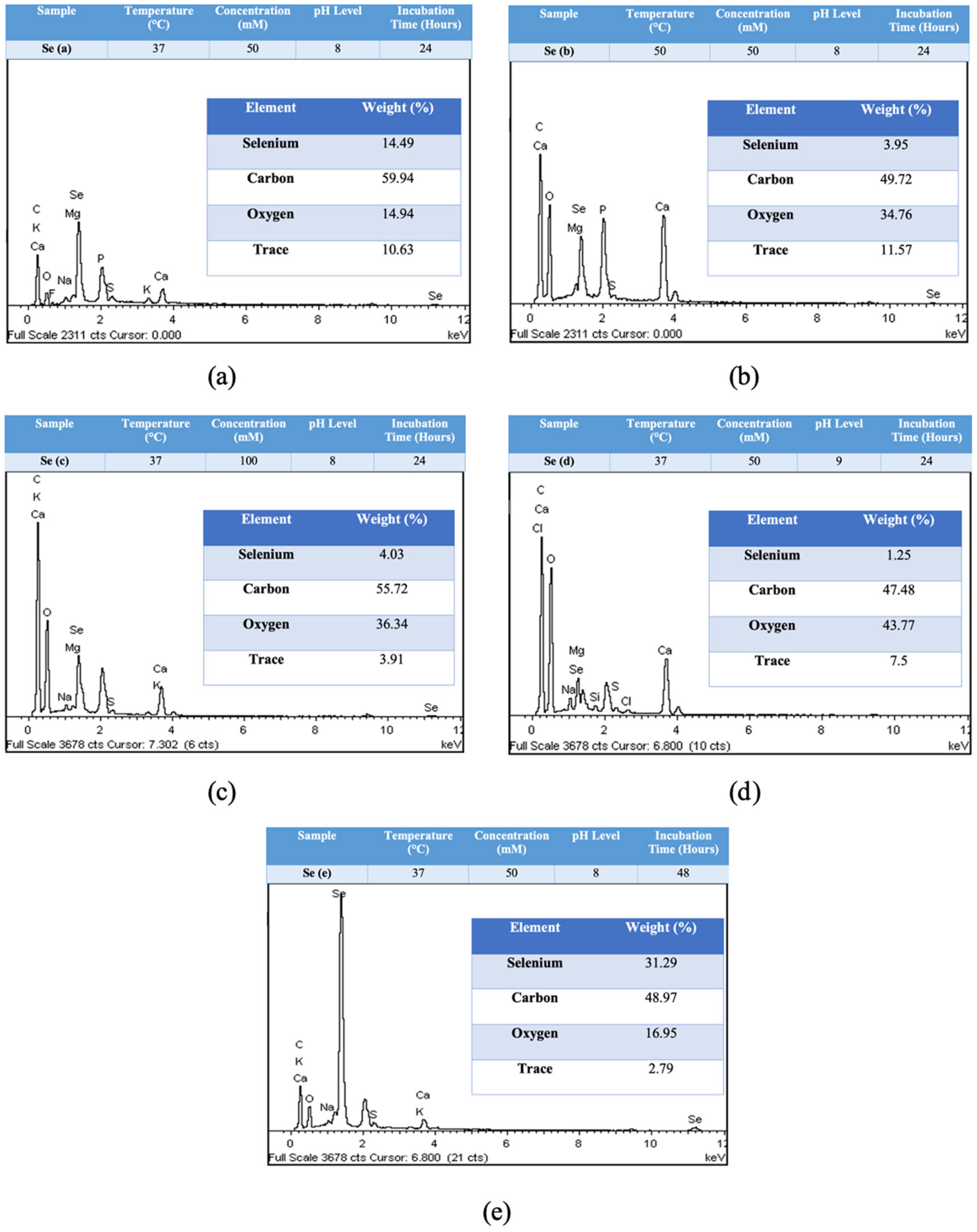
2.6.1. EDX Spectra Analysis
2.6.2. FTIR Analysis
2.6.3. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM) & High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM) Analysis
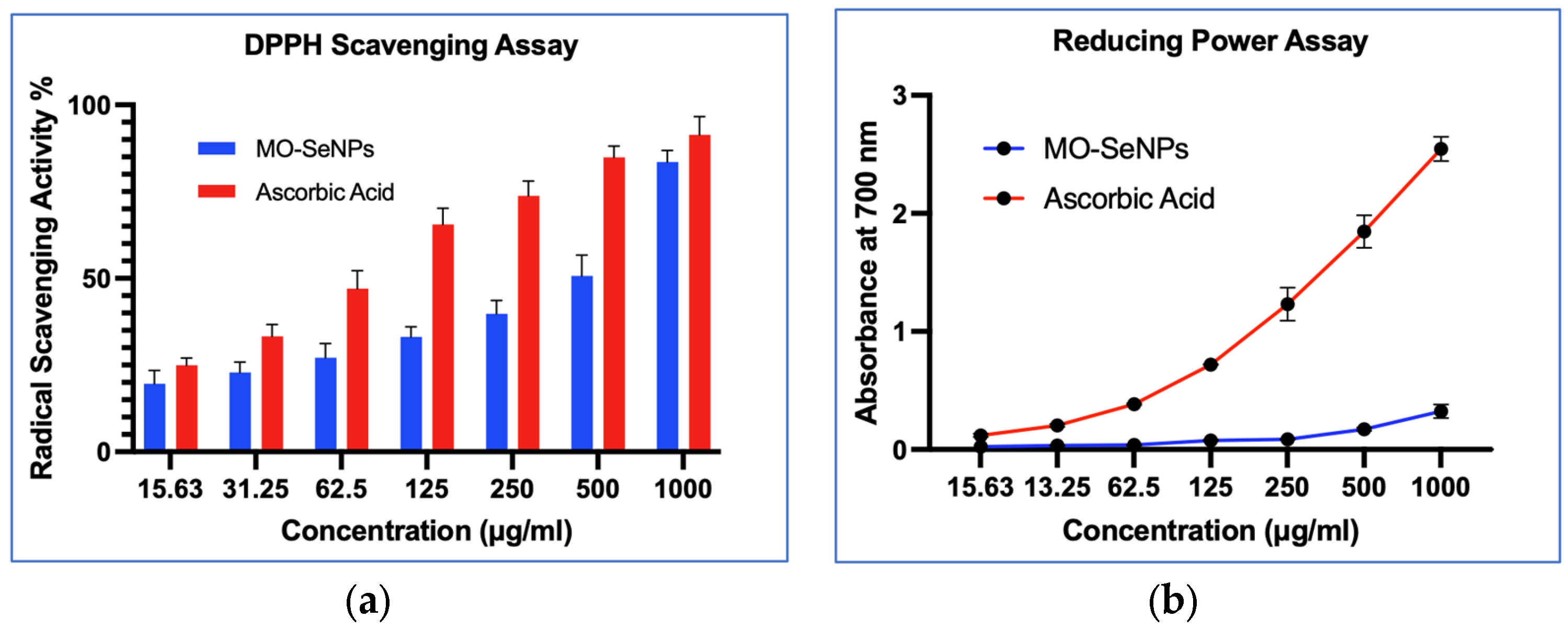
2.7. In-Vitro Antioxidant Assays
2.7.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.7.2. Reducing Power Assay
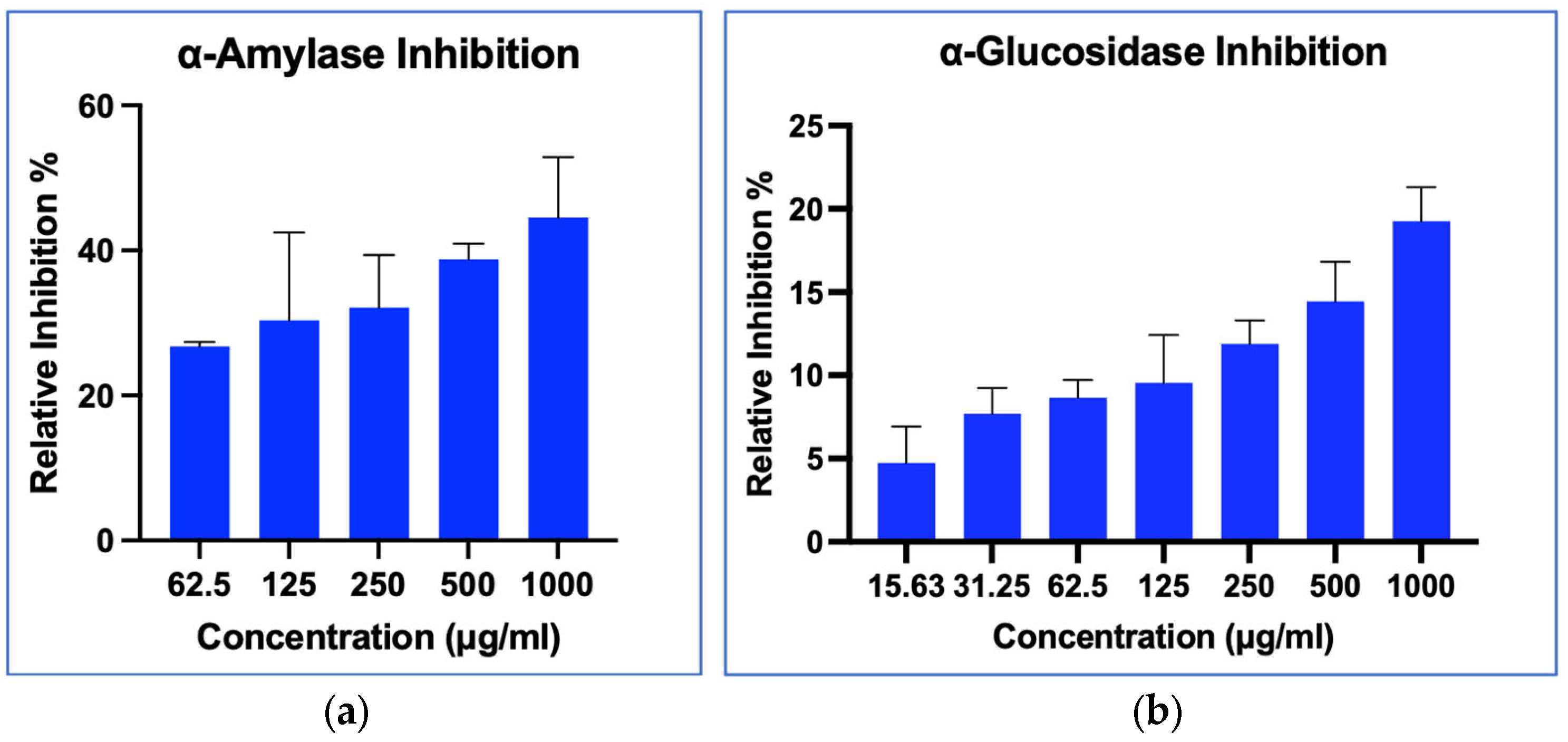
2.8. In-Vitro Antidiabetic Assays
2.8.1. α-Amylase Inhibition Activity
2.8.2. α-Glucosidase Inhibition Activity
3. Discussion
3.1. Biogenic Synthesis and Optimisation of MO-SeNPs
3.2. Characterization of MO-SeNPs
3.3. In-Vitro Antioxidant Assays
3.4. In-Vitro Antidiabetic Assays
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Material
4.2. Moringa oleifera
4.3. Aqueous Extract Preparation
4.4. Green Synthesis of MO-SeNPs
4.5. Optimization of MO-SeNPs Synthesis
4.5.1. pH Level
4.5.2. Temperature
4.5.3. Incubation Time
4.5.4. Precursor (Sodium Selenite) Concentration
4.6. Characterization of MO-SeNPs
4.6.1. Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX)
4.6.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
4.6.3. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FESEM)
4.6.4. High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM)
4.7. In-Vitro Antioxidant Assays
4.7.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
4.7.2. Reducing Power Assay
4.8. In-Vitro Antidiabetic Assays
4.8.1. α-Amylase Inhibition Assay
4.8.2. α-Glucosidase Inhibition Assay
4.9. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Yao, M.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, D.; Wan, G.; Xu, X. Selenium Nanoparticles Based on Morinda Officinalis Polysaccharides: Characterization, Anti-Cancer Activities, and Immune-Enhancing Activities Evaluation In Vitro. Molecules 2023, 28, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eswayah, A.S.; Smith, T.J.; Gardiner, P.H.E. Microbial Transformations of Selenium Species of Relevance to Bioremediation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4848–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, K.; Foltz, C.M. Selenium as an Integral Part of Factor 3 Against Dietary Necrotic Liver Degeneration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 3292–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selinus, O.; Alloway, B.; Centeno, J.A.; Finkelman, R.B.; Fuge, R.; Lindh, U.; Smedley, P. Essentials of Medical Geology; Selinus, O., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; ISBN 978-94-007-4374-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Kuang, S.; Wang, D.; Shi, Y. Biological Selenite Reduction, Characterization and Bioactivities of Selenium Nanoparticles Biosynthesised by Pediococcus Acidilactici DSM20284. Molecules 2023, 28, 3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchi, R.; Rutigliano, G.; Saponaro, F. Novel Thyroid Hormones. Endocrine 2019, 66, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, S.; Frenis, K.; Oelze, M.; Kalinovic, S.; Kuntic, M.; Jimenez, M.T.B.; Vujacic-Mirski, K.; Helmstädter, J.; Kröller-Schön, S.; Münzel, T.; et al. Vascular Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: Major Triggers for Cardiovascular Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7092151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, M.; Bano, I.; Zare, H. A Comprehensive Review on Selenium and Its Effects on Human Health and Distribution in Middle Eastern Countries. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudshinge, S.R.; Deore, A.B.; Patil, S.; Bhalgat, C.M. Nanoparticles: Emerging Carriers for Drug Delivery. Saudi Pharm. J. 2011, 19, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, A.; Tekula, S.; Saifi, M.A.; Venkatesh, P.; Godugu, C. Therapeutic Applications of Selenium Nanoparticles. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, G.; Rai, P.; Pandey, A. Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles: A Greener Approach for a Cleaner Future; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; ISBN 9780081025796. [Google Scholar]
- Idris Maizuwo, A. Phytochemical Constituents, Biological Activities, Therapeutic Potentials and Nutritional Values of Moringa oleifera (Zogale): A Review. J. Drug Des. Med. Chem. 2017, 3, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegbeleye, O.O. How Functional Is Moringa oleifera? A Review of Its Nutritive, Medicinal, and Socioeconomic Potential. Food Nutr. Bull. 2018, 39, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titus, D.; James Jebaseelan Samuel, E.; Roopan, S.M. Nanoparticle Characterization Techniques; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780081025796. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, S.; Hui, Y.; Chuang, W. Biosynthesis and Antioxidation of Nano-Selenium Using Lemon Juice as a Reducing Agent. Green Process. Synth. 2021, 10, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Saad, A.M.; Taha, T.F.; Najjar, A.A.; Zabermawi, N.M.; Nader, M.M.; AbuQamar, S.F.; El-Tarabily, K.A.; Salama, A. Selenium Nanoparticles from Lactobacillus Paracasei HM1 Capable of Antagonizing Animal Pathogenic Fungi as a New Source from Human Breast Milk. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 6782–6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunti, L.; Dass, R.S.; Kalagatur, N.K. Phytofabrication of Selenium Nanoparticles from Emblica officinalis Fruit Extract and Exploring Its Biopotential Applications: Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and Biocompatibility. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Luo, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Kong, F.; Bi, Y. Synthesis, Characterization, in Vitro Antioxidant and Hypoglycemic Activities of Selenium Nanoparticles Decorated with Polysaccharides of Gracilaria lemaneiformis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagesan, V.; Venugopal, S. Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticle Using Leaves Extract of Withania somnifera and Its Biological Applications and Photocatalytic Activities. Bionanoscience 2019, 9, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Mutalib, M.; Rahmat, A.; Ali, F.; Othman, F.; Ramasamy, R. Nutritional Compositions and Antiproliferative Activities of Different Solvent Fractions from Ethanol Extract of Cyphomandra Betacea (Tamarillo) Fruit. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 24, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouche, T.M.; Haddouchi, F.; Ksouri, R.; Atik-Bekkara, F. Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity of Hydromethanolic Extracts of Some Medicinal Species from South Algeria. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2014, 77, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Ding, H.; Hu, X.; Pan, J.; Liao, Y.; Gong, D.; Zhang, G. Exploring Inhibitory Mechanism of Gallocatechin Gallate on A-Amylase and a-Glucosidase Relevant to Postprandial Hyperglycemia. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 48, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zeid, E.H.; Abdel Fattah, D.M.; Arisha, A.H.; Ismail, T.A.; Alsadek, D.M.; Metwally, M.M.M.; El-Sayed, A.A.; Khalil, A.T. Protective Prospects of Eco-Friendly Synthesized Selenium Nanoparticles Using Moringa oleifera or Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract against Melamine Induced Nephrotoxicity in Male Rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 221, 112424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, M.; Yadav, P.; Dalal, S.; Kataria, S.K. A Review on Ameliorative Green Nanotechnological Approaches in Diabetes Management. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadoun, S.; Arif, R.; Jangid, N.K.; Meena, R.K. Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles Using Plant Extracts: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Suriya, A. Microbial Nanotechnology: Green Synthesis and Applications; Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2021; ISBN 9789811619229. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Atarod, M.; Sajjadi, M.; Sajadi, S.M.; Issaabadi, Z. Plant-Mediated Green Synthesis of Nanostructures: Mechanisms, Characterization, and Applications. In Interface Science and Technology; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 28, pp. 199–322. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.F.; Ahmad, J.; Zhang, H.; Khan, I.; Muhammad, S. Evaluation of Phytochemical and Medicinal Properties of Moringa (Moringa oleifera) as a Potential Functional Food. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 129, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cittrarasu, V.; Kaliannan, D.; Dharman, K.; Maluventhen, V.; Easwaran, M.; Liu, W.C.; Balasubramanian, B.; Arumugam, M. Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles Mediated from Ceropegia bulbosa Roxb Extract and Its Cytotoxicity, Antimicrobial, Mosquitocidal and Photocatalytic Activities. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unegbu, V.; Nkwoemeka, N.; Okey-Ndeche, F.; Obum-Nnadi, C. Phytochemical and Antibacterial Properties of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extracts on Escherichia Coli and Staphylococcus Aureus. Niger. J. Microbiol. 2020, 34, 5145–5152. [Google Scholar]
- Bisht, N.; Phalswal, P.; Khanna, P.K. Selenium Nanoparticles: A Review on Synthesis and Biomedical Applications. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Yang, X.Q.; Su, D.X.; He, S.; Tan, J.C.; Zeng, Q.Z.; Yuan, Y. Development, Structure Characterization and Stability of Food Grade Selenium Nanoparticles Stabilized by Tilapia Polypeptides. J. Food Eng. 2020, 275, 109878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreishi, S.M.; Behpour, M.; Khoobi, A.; Moghadam, Z. Determination of Trace Amounts of Sulfamethizole Using a Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Modified Electrode: Application of Experimental Design in Voltammetric Studies. Anal. Lett. 2012, 46, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreishi, S.M.; Khoobi, A.; Behpour, M.; Masoum, S. Application of Multivariate Curve Resolution Alternating Least Squares to Biomedical Analysis Using Electrochemical Techniques at a Nanostructure-Based Modified Sensor. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 130, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, G.B.; Iqbal, M.S.; Ghaith, M.M.S.; Haseeb, A.; Ahmed, B.; Qadir, M.I. Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles (SeNPs) from Citrus Fruit Have Anti-Bacterial Activities. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, S.N.; Goswami, L.; Sen, S.; Sachan, D.; Sarma, H.; Montes, M.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Pakshirajan, K.; Narayan, M. Selenite Bioreduction and Biosynthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles by Bacillus paramycoides SP3 Isolated from Coal Mine Overburden Leachate. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, G.; Kumari, R.M.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, A.; Chandra, R.; Nimesh, S. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Prosopis Juliflora Bark Extract: Reaction Optimization, Antimicrobial and Catalytic Activities. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thamer, N.A.; Muftin, N.Q.; Al-Rubae, S.H.N. Optimization Properties and Characterization of Green Synthesis of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Extract of Cordia Myxa L. Leaves. Asian J. Chem. 2018, 30, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani-e-Zahra; Iqbal, M.S.; Abbas, K.; Qadir, M.I. Synthesis, Characterization and Evaluation of Biological Properties of Selenium Nanoparticles from Solanum Lycopersicum. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, M.; Hoseinpour, V.; Shakeri, A.; Ghaemi, N. Optimisation of Green Synthesis of MnO Nanoparticles via Utilising Response Surface Methodology. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 12, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, R.; Sharma, K. Biogenic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Terminalia Chebula Retz. Leaf Extract and Evaluation of Biological Activities. J. Nepal Chem. Soc. 2022, 43, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, V.; Muniraj, S. Neem Flower Extract Assisted Green Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles—Optimisation, Characterisation and Anti-Bacterial Study. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 36, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezealisiji, K.M.; Siwe-Noundou, X.; Maduelosi, B.; Nwachukwu, N.; Krause, R.W.M. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Solanum Torvum (L) Leaf Extract and Evaluation of the Toxicological Profile of the ZnO Nanoparticles–Hydrogel Composite in Wistar Albino Rats. Int. Nano Lett. 2019, 9, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kora, A.J.; Rastogi, L. Biomimetic Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa ATCC 27853: An Approach for Conversion of Selenite. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirupagaran, A.R.; Saritha, S.B. Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles from Leaf and Stem Extract of Leucas Lavandulifolia Sm. and Their Application. J. Nanosci. Technol. 2016, 2, 224–226. [Google Scholar]
- Elshafei, A.M.; Othman, A.M.; Elsayed, M.A.; Al-Balakocy, N.G.; Hassan, M.M. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Aspergillus Oryzae NRRL447 Exogenous Proteins: Optimization via Central Composite Design, Characterization and Biological Applications. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, E.; Kahrizi, D.; Arkan, E. Comparison of Different Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized by the Green (Using Juglans Regia L. Leaf Extract) and Chemical Methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 286, 110831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.H.; Ramli, N.F.; Tan, T.C.; Muhamad, N.; Haron, M.N. Effect of Extraction Solvents and Drying Conditions on Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Properties of Watermelon Rind Powder. Sains Malays. 2018, 47, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satgurunathan, T.; Bhavan, P.S.; Komathi, S. Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles from Sodium Selenite Using Garlic Extract and Its Enrichment on Artemia Nauplii to Feed the Freshwater Prawn Macrobrachium Rosenbergii Post-Larvae. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2017, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Oktiani, R.; Ragadhita, R. How to Read and Interpret Ftir Spectroscope of Organic Material. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardsadegh, B.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Aloe Vera Leaf Extract Mediated Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles and Assessment of Their In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity against Spoilage Fungi and Pathogenic Bacteria Strains. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, R.S.; Adibian, F.; Sabouri, Z.; Davoodi, J.; Kazemi, M.; Amel Jamehdar, S.; Meshkat, Z.; Soleimanpour, S.; Daroudi, M. Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticle by Abelmoschus Esculentus Extract and Assessment of Its Antibacterial Activity. Mater. Technol. 2022, 37, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.; Liang, T.; Sun, L.; Meng, L.; Yang, C.; Wang, L.; Liang, T.; Li, Q. Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles with Extract of Hawthorn Fruit Induced Hepg2 Cells Apoptosis. Pharm. Biol. 2018, 56, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhlou, K.; Allahyari, S.; Sabouri, S.; Najian, Y.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Walnut Leaf Extract-Based Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles via Microwave Irradiation and Their Characteristics Assessment. Open. Agric. 2020, 5, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcin, İ. Antioxidants and Antioxidant Methods: An Updated Overview. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 651–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Shehata, A.M.; Saad, A.M.; Aldhumri, S.A.; Ouda, S.M.; Mesalam, N.M. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Spirulina platensis Extracts and Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles against Selected Pathogenic Bacteria and Fungi. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 29, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, A.; Patil, S. Tinospora cordifolia Stem Extract-Mediated Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles and Its Biological Applications. Pharmacogn. Res. 2022, 14, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, M.; Yan, J.K. Construction, Stability, and Enhanced Antioxidant Activity of Pectin-Decorated Selenium Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Yang, Y.; Yue, C.; Wang, Y.; Fu, P.; Bi, Y. Preparation, Characteristics, and Antioxidant Activity of the Selenium Nanoparticles Stabilized by Polysaccharides Isolated from Grateloupia filicina. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2020, 16, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, Q.V.; Nam, P.C.; Thong, N.M.; Trung, N.T.; Phan, C.T.D.; Mechler, A. Antioxidant Motifs in Flavonoids: O–H versus C–H Bond Dissociation. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 8935–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentkowska, A.; Pyrzyńska, K. The Influence of Synthesis Conditions on the Antioxidant Activity of Selenium Nanoparticles. Molecules 2022, 27, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonocore, V.; Petrucci, T.; Silano, V. Wheat Protein Inhibitors of α-Amylase. Phytochemistry 1977, 16, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, T.; Mohan, S.; Manimaran, P. A Crucial Role of Selenium Nanoparticles for Future Perspectives. Results Chem. 2022, 4, 100367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros-Yupanqui, M.; Lante, A.; Mihaylova, D.; Krastanov, A.I.; Rizzi, C. The α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase Inhibition Capacity of Grape Pomace: A Review. Food Bioproc. Tech. 2023, 16, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasathkumar, M.; Sakthivel, C.; Becky, R.; Dhrisya, C.; Prabha, I.; Sadhasivam, S. Phytofabrication of Cost-Effective Selenium Nanoparticles from Edible and Non-Edible Plant Materials of Senna Auriculata: Characterization, Antioxidant, Antidiabetic, Antimicrobial, Biocompatibility, and Wound Healing. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 366, 120337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.H.; Hong, J.; McGuffie, M.; Yeom, B.; Vanepps, J.S.; Kotov, N.A. Shape-Dependent Biomimetic Inhibition of Enzyme by Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Activity. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9097–9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Beltrán, J.M.; Mansour, A.T.; Alsaqufi, A.S.; Ali, H.M.; Esteban, M.Á. Effects of Aqueous and Ethanolic Leaf Extracts from Drumstick Tree (Moringa oleifera) on Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata L.) Leucocytes, and Their Cytotoxic, Antitumor, Bactericidal and Antioxidant Activities. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 106, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, H.U.; Raja, N.I.; Abasi, F.; Mehmood, A.; Qureshi, R.; Manzoor, Z.; Shahbaz, M.; Proćków, J. Comparative Study of Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Potential of Olea Ferruginea Fruit Extract and Its Mediated Selenium Nanoparticles. Molecules 2022, 27, 5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashem, A.H.; Khalil, A.M.A.; Reyad, A.M.; Salem, S.S. Biomedical Applications of Mycosynthesized Selenium Nanoparticles Using Penicillium Expansum ATTC 36200. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 3998–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulmalek, S.A.; Balbaa, M. Synergistic Effect of Nano-Selenium and Metformin on Type 2 Diabetic Rat Model: Diabetic Complications Alleviation through Insulin Sensitivity, Oxidative Mediators and Inflammatory Markers. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Heo, J.W.; Kim, J.S.; Jeong, U.Y.; Bae, U.J.; Jang, H.N.; Shim, C.K.; Joung, Y.; Lee, S.H. Functionality of Allium Hookeri Leaves and Roots Grown in a Hydroponic Plant Factory Using Artificial Lights. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 51, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahamad Tarmizi, A.A.; Nik Ramli, N.N.; Adam, S.H.; Abdul Mutalib, M.; Mokhtar, M.H.; Tang, S.G.H. Phytofabrication of Selenium Nanoparticles with Moringa oleifera (MO-SeNPs) and Exploring Its Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Potential. Molecules 2023, 28, 5322. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145322
Ahamad Tarmizi AA, Nik Ramli NN, Adam SH, Abdul Mutalib M, Mokhtar MH, Tang SGH. Phytofabrication of Selenium Nanoparticles with Moringa oleifera (MO-SeNPs) and Exploring Its Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Potential. Molecules. 2023; 28(14):5322. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145322
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhamad Tarmizi, Anas Ahzaruddin, Nik Nasihah Nik Ramli, Siti Hajar Adam, Maisarah Abdul Mutalib, Mohd Helmy Mokhtar, and Shirley Gee Hoon Tang. 2023. "Phytofabrication of Selenium Nanoparticles with Moringa oleifera (MO-SeNPs) and Exploring Its Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Potential" Molecules 28, no. 14: 5322. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145322
APA StyleAhamad Tarmizi, A. A., Nik Ramli, N. N., Adam, S. H., Abdul Mutalib, M., Mokhtar, M. H., & Tang, S. G. H. (2023). Phytofabrication of Selenium Nanoparticles with Moringa oleifera (MO-SeNPs) and Exploring Its Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Potential. Molecules, 28(14), 5322. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145322







