Cascading One-Pot Synthesis of Biodegradable Uronic Acid-Based Surfactants from Oligoalginates, Semi-Refined Alginates, and Crude Brown Seaweeds
Abstract
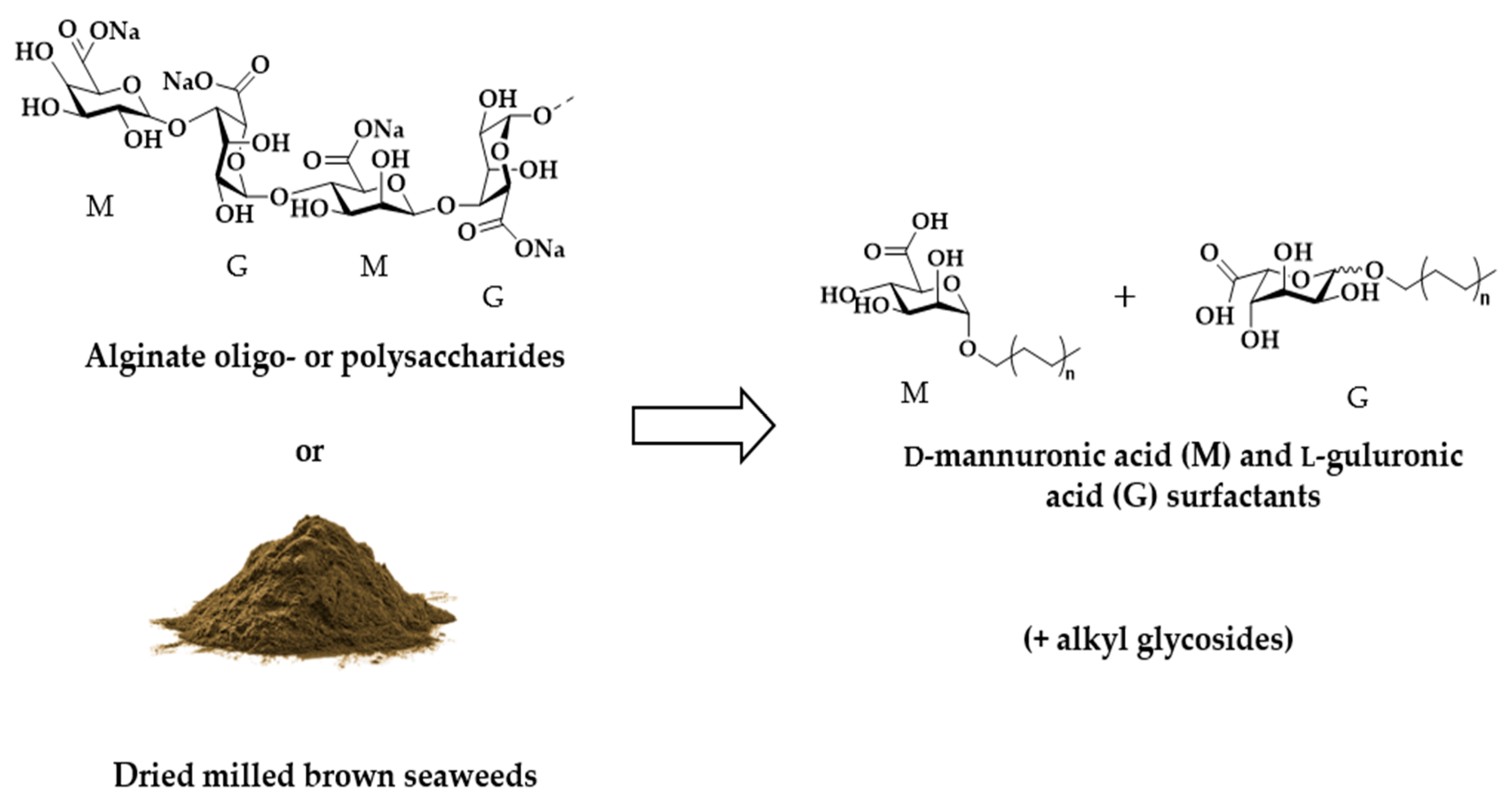
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Preparation of Starting Materials
2.2. Synthesis from Oligoalginates
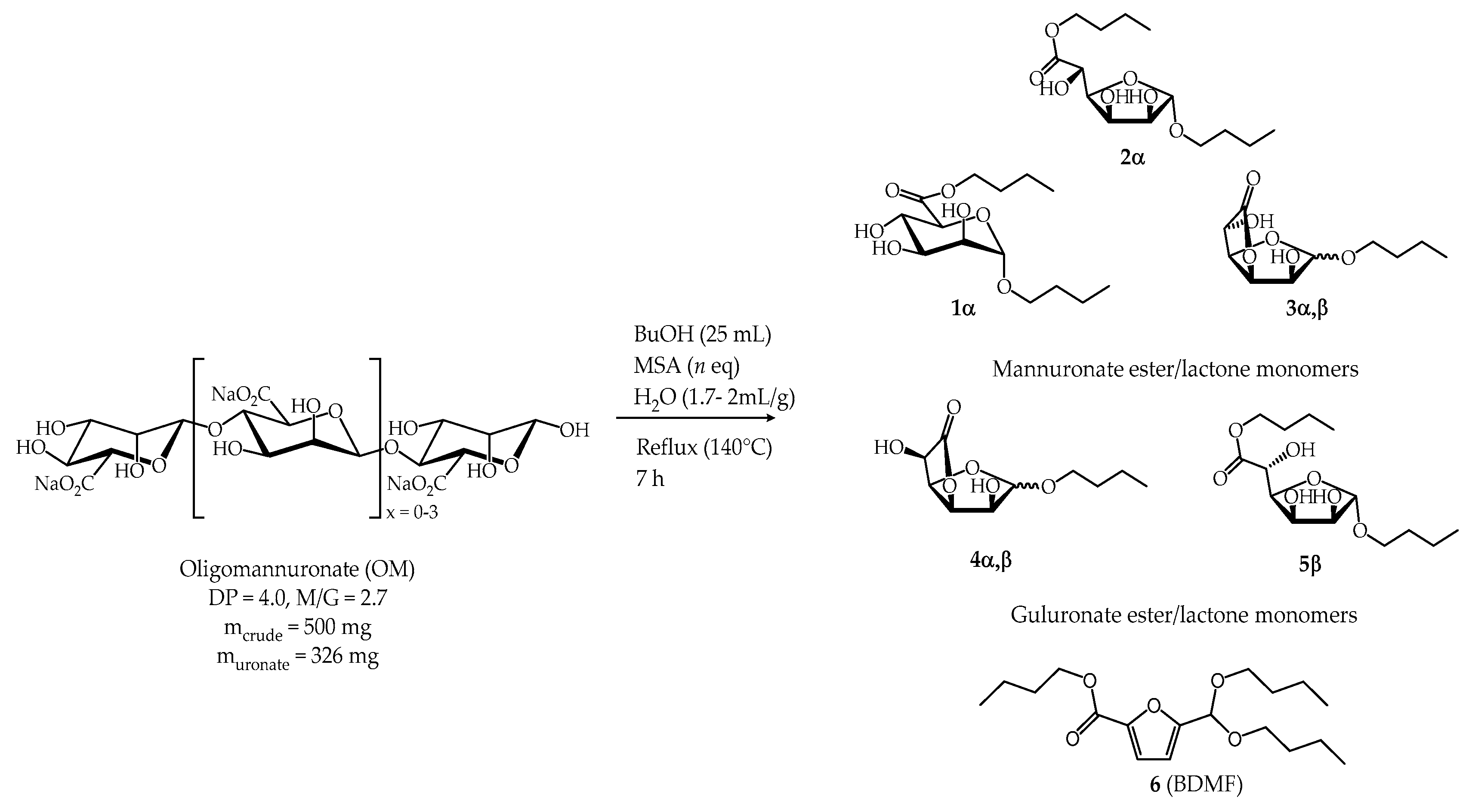
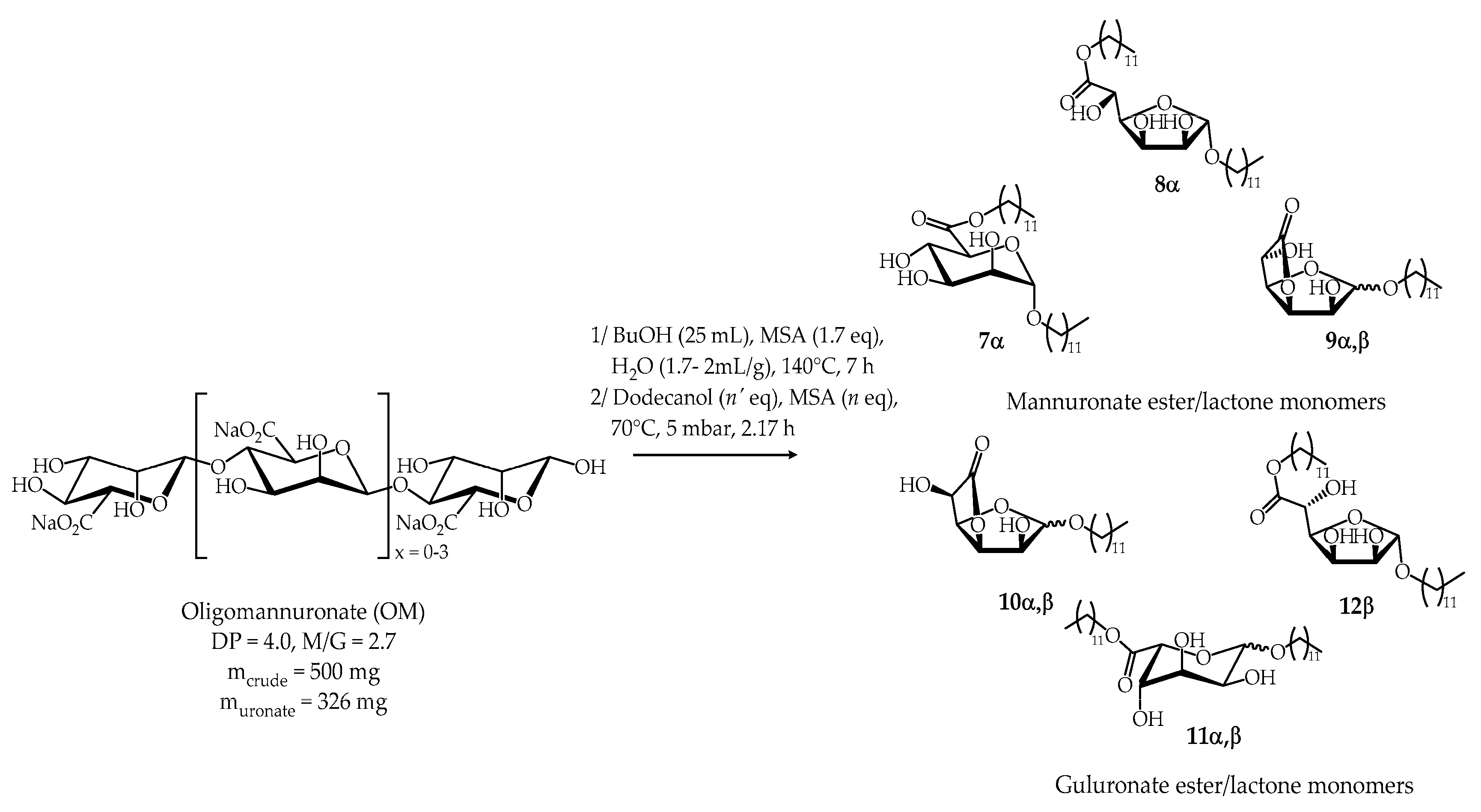
2.2.1. Synthesis from Oligomannuronate (OM)
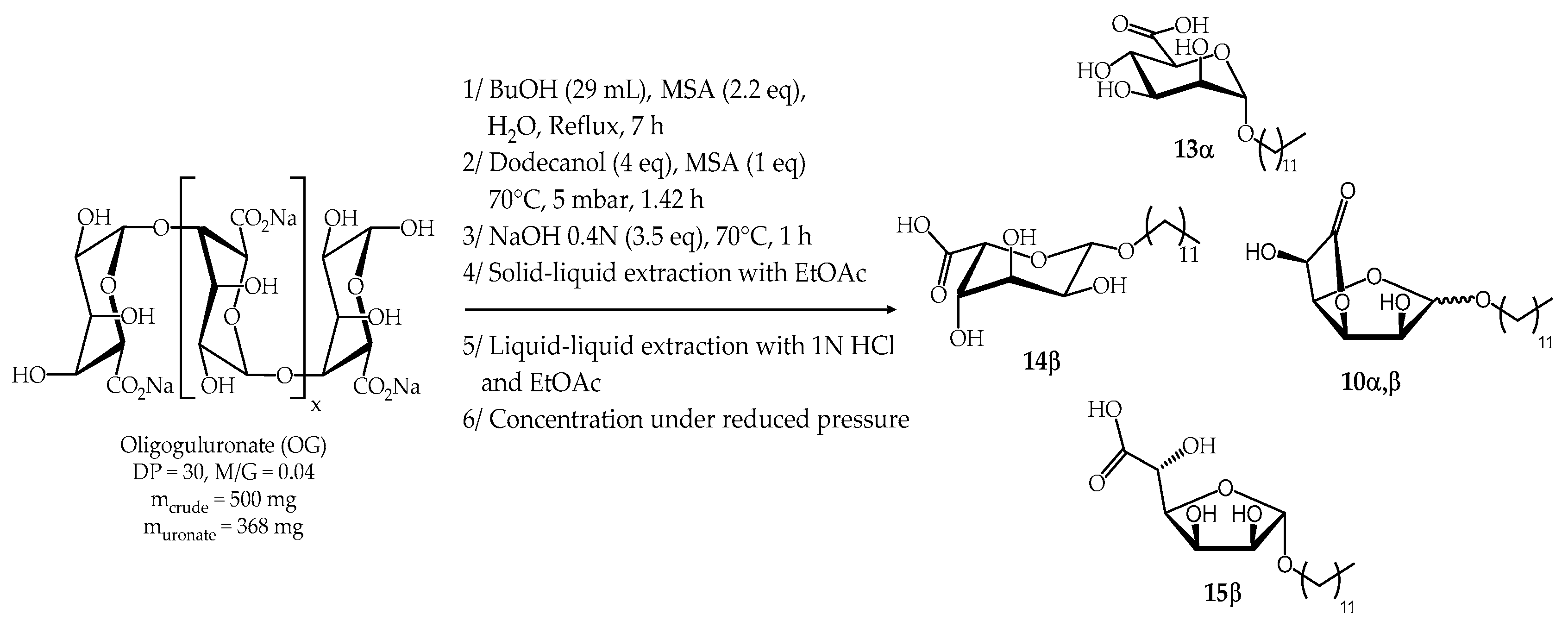
2.2.2. Synthesis from Oligoguluronate (OG)
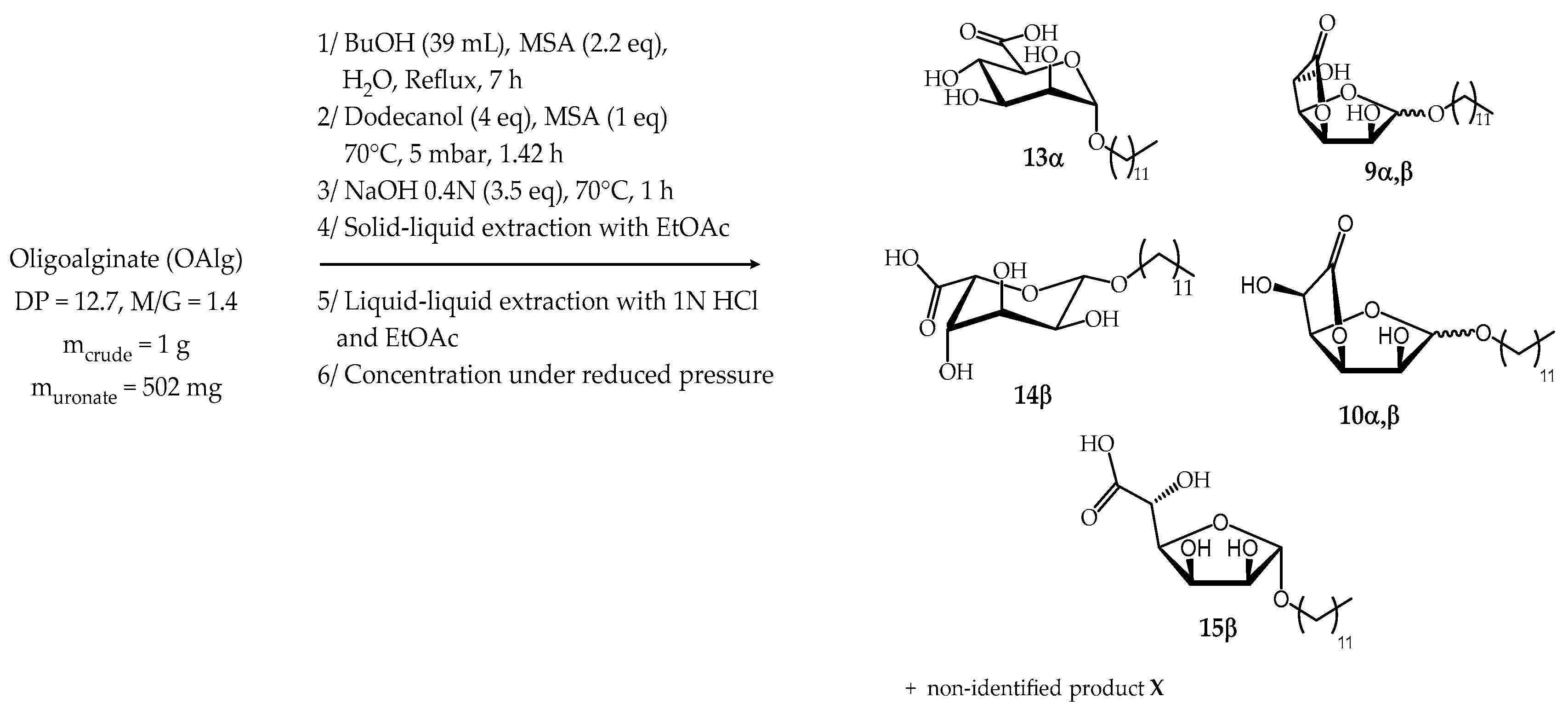
2.2.3. Synthesis from Oligoalginate (OAlg)
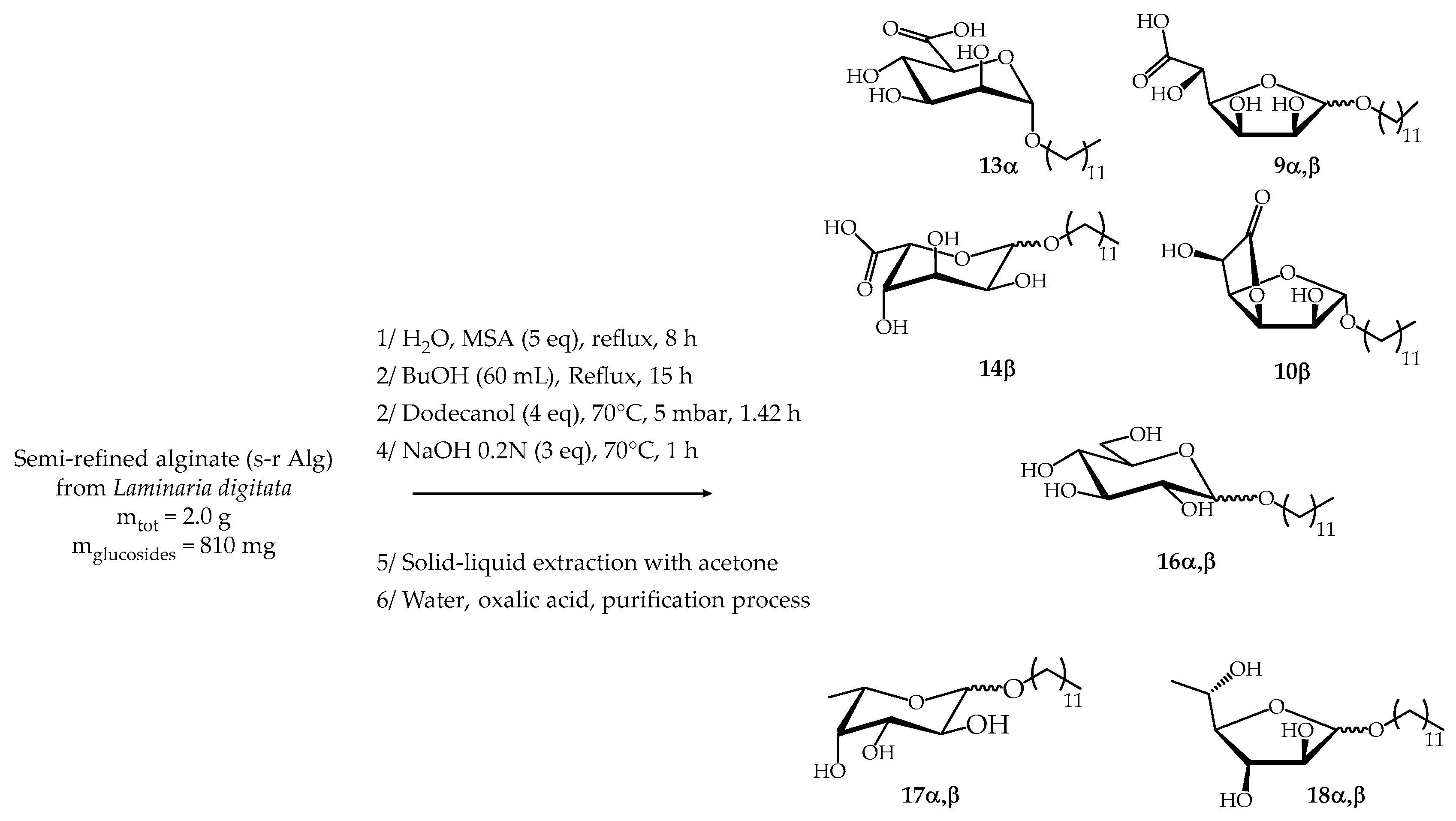
2.3. Synthesis from Semi-Refined Alginate (s-r Alg)
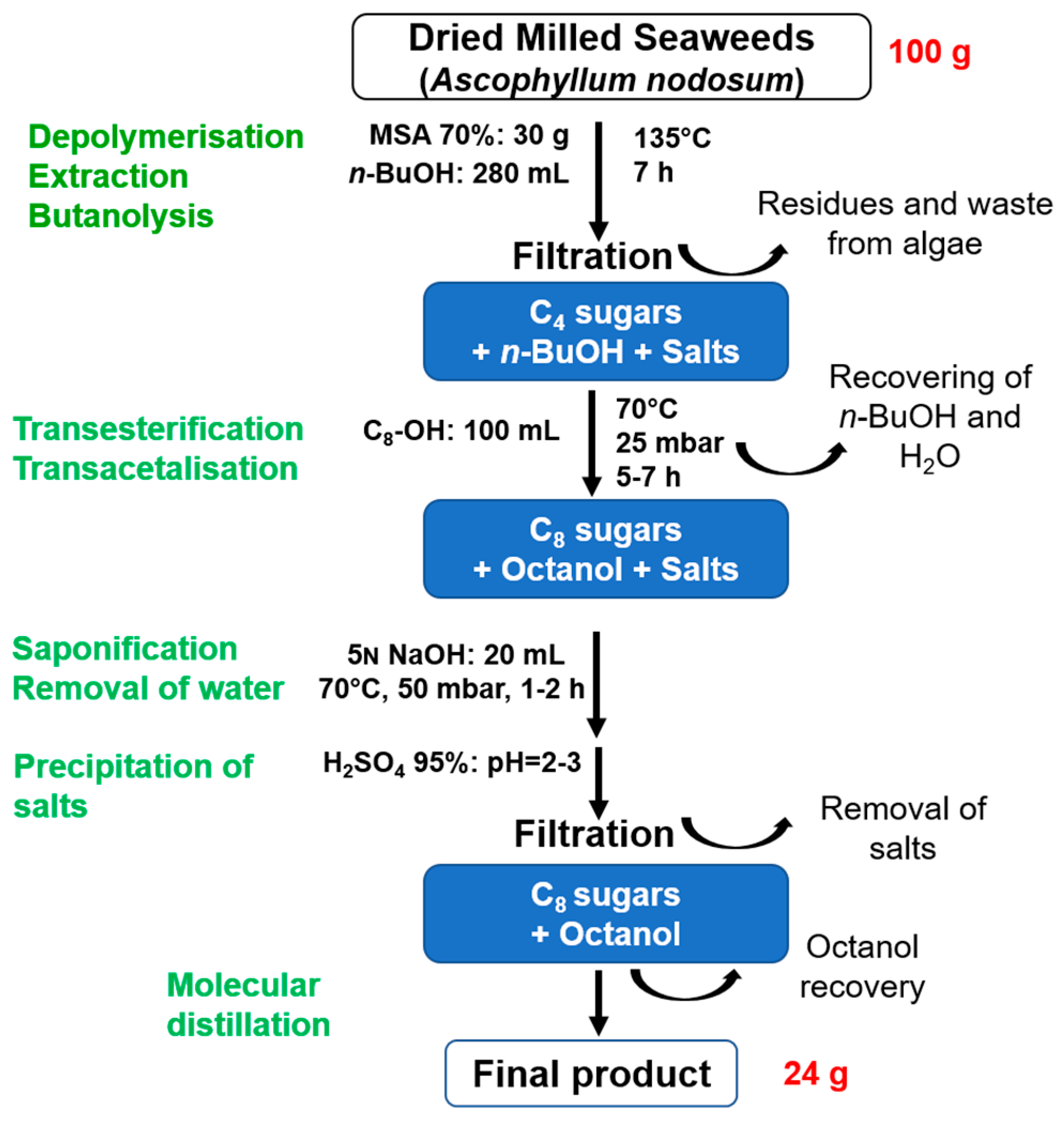
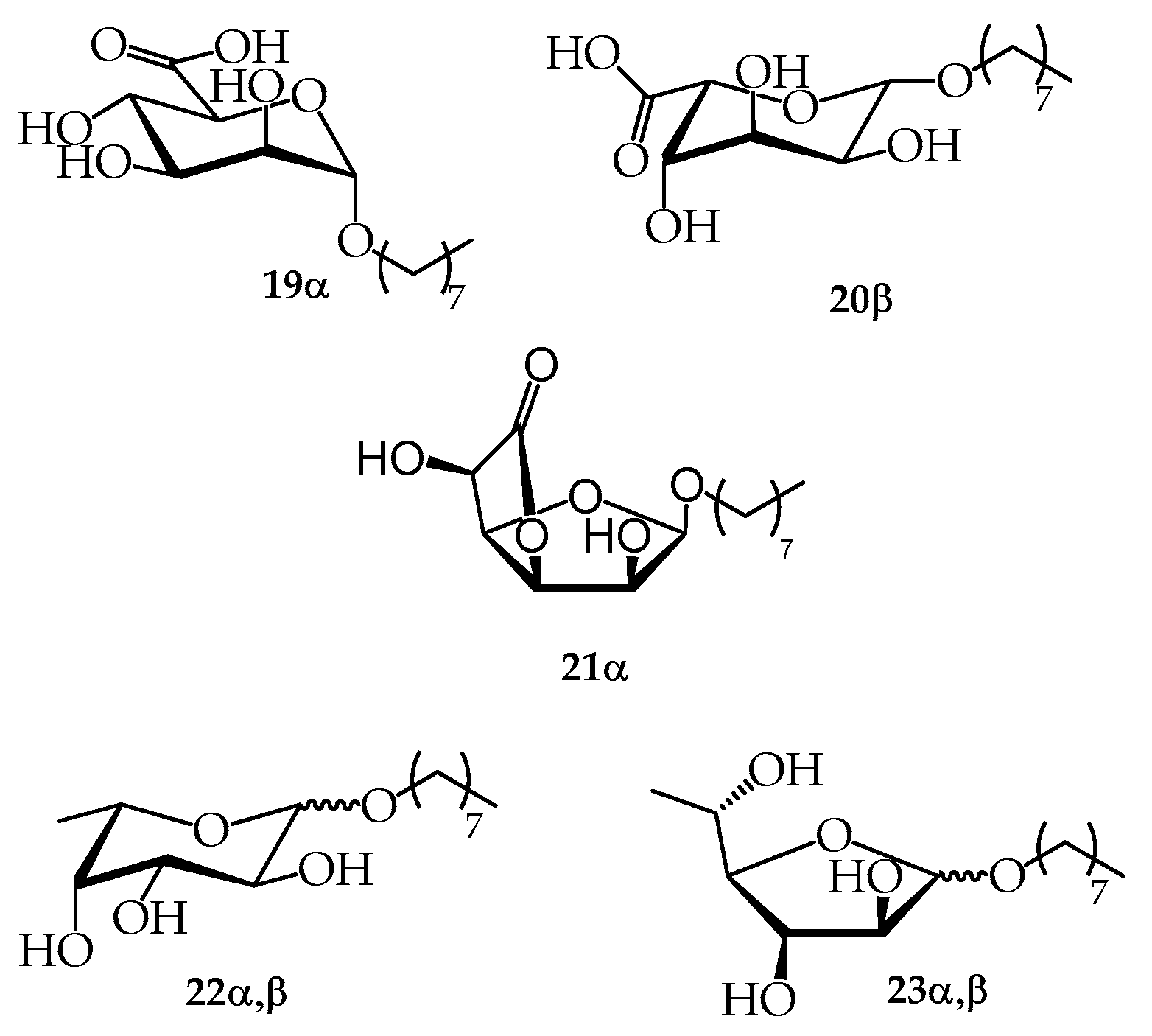
2.4. Synthesis from Crude Brown Seaweeds
2.5. Physico-Chemical Properties of Anionic and Non-Ionic Surfactant Compositions Derived from Oligoalginates, Semi-Refined Alginates, and Crude Brown Seaweed
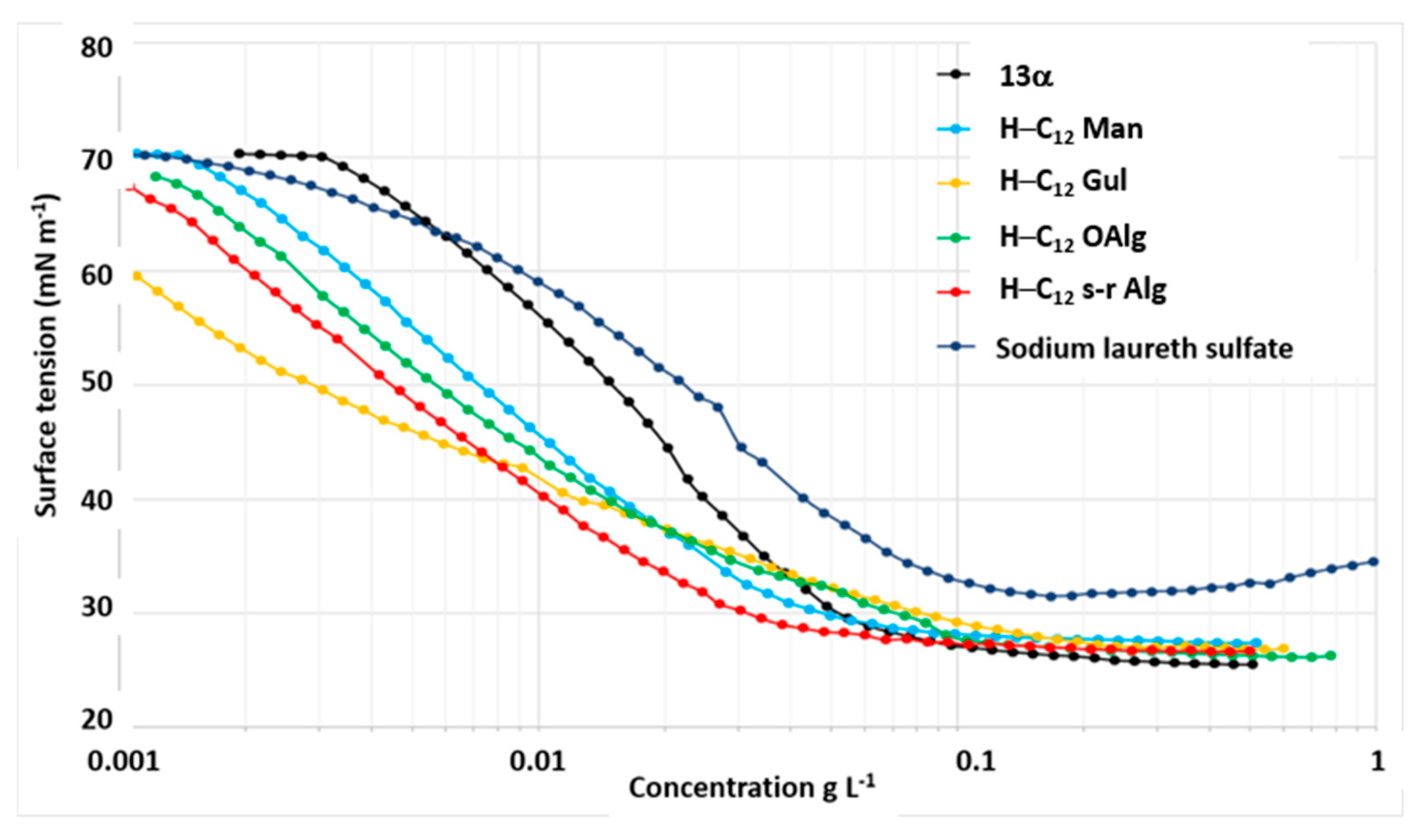
2.5.1. Measurements of Air-Water Interfacial Behavior
H-C12 Derivatives from OM, OG, OAlg, and s-r Alg
H–C8 Surfactant Composition from Crude Seaweed
2.5.2. Ecotoxicity Studies
2.5.3. Biodegradability Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.2. Physico-Chemistry
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Hayes, D.G.; Smith, G.A. Biobased Surfactants (Second Edition): Synthesis, Properties, and Applications; Hayes, D.G., Solaiman, K.Y., Ashby, R.D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; AOCS Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 2019; pp. 3–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ribinsky, W.; Hill, K. Alkyl polyglycosides—Properties and applications of a new class of surfactants. Ang. Chem. Int. Edit. 1998, 37, 1328–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, K.; von Rybinsky, W.; Stoll, G. (Eds.) Alkyl Polyglucosides, Technology, Properties and Applications. In Surfactants from Renewable Resources; Weinheim, 1996; Kjellin, M., Johansson, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schick, M.J.; Hubbard, A.J. Sugar-Based Surfactants: Fundamental and Applications; Ruiz, C.C., Ed.; Surfactant Science Series; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; Volume 143. [Google Scholar]
- Lechuga, M.; Avila-Sierra, A.; Lobato-Guarnido, I.; García-López, A.I.; Ríos, F.; Fernández-Serrano, M. Mitigating the skin irritation potential of mixtures of anionic and non-ionic surfactants by incorporating low-toxicity silica nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 383, 122021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jérôme, F.; Marinkovic, S.; Estrine, B. Transglycosylation: A key reaction to access alkylpolyglycosides from lignocellulosic biomass. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 1395–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.; Shen, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Fan, Y.; Fu, F.; Chen, G. Synthesis and properties of sugar-based surfactants alkoxyethyl β-d-glucopyranoside. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 564, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, S.; Yousaf, S.; Khan, I. A review on the synthesis of bio-based surfactants using green chemistry principles. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 30, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdellahi, B.; Bois, R.; Golonu, S.; Pourceau, G.; Lesur, D.; Chagnault, V.; Drelich, A.; Pezron, I.; Nesterenko, A.; Wadouachi, A. Synthesis and interfacial properties of new 6-sulfate sugar-based anionic surfactants. Tetrahedron Lett. 2021, 74, 153113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Renault, L.; Guégan, J.-P.; Benvegnu, T. Direct conversion of agarose into alkyl mono- and disaccharide surfactants based on 3,6-anhydro l- and d-galactose units. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Drelich, A.; Omri, M.; Pezron, I.; Wadouachi, A.; Pourceau, G. Catalytic synthesis of a new series of alkyl uronates and evaluation of their physicochemical properties. Molecules 2016, 21, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sari-Chmayssem, N.; Pessel, F.; Guégan, J.-P.; Taha, S.; Mawlawi, H.; Benvegnu, T. Direct and one-pot conversion of polyguluronates and alginates into alkyl-l-guluronamide-based surfactant compositions. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 6573–6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.-H.; Gu, J.-Y.; Pu, W.-F.; Dong, Z.-M.; Liu, R. Study on the synthesis and properties of an eco-friendly sugar-based anionic-nonionic surfactant. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 70165–70173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.S.; Mali, S.N.; Sangale, N.R.; Pratap, A.P. Synthesis of (2-hydroxyl-3-butoxyl)propyl-succinyl-chitosan—An amino sugar anionic surfactant under microwave irradiation and its application. Thai J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 45, 461–469. [Google Scholar]
- Abka-khajouei, R.; Tounsi, L.; Shahabi, N.; Patel, A.K.; Abdelkafi, S.; Michaud, P. Structures, properties and applications of alginates. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 364. [Google Scholar]
- Roussel, M.; Benvegnu, T.; Lognoné, V.; Le Deit, H.; Soutrel, I.; Laurent, I.; Plusquellec, D. Synthesis and physico-chemical properties of novel biocompatible alkyl d-mannopyranosiduronate surfactants derived from alginate. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 14, 3085–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brault, D.; Heyraud, A.; Lognoné, V.; Roussel, M. Methods for Obtaining Oligomannuronates and Guluronates, Products Obtained and Use Thereof. Patent WO03099870 (A2), 4 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, R. The Culture of Marine Algae throughout the World, Ifremer, 1992, 613. Available online: https://archimer.ifremer.fr/doc/00000/4402/ (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- Renault, L.; Marchal, R.; Le Guennic, B.; Roussel, X.; Divet, P.-Y.; Benvegnu, T. Direct conversion of alginate oligo- and polysaccharides into biodegradable and non-ecotoxic anionic furanic surfactants- An experimental and mechanistic study. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2021, 5, 2100108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyère, C.; Galle, F.; Pessel, F.; Roussel, X. Method for obtaining surfactant compositions from raw plant materials. Patent WO2022/013500 A1, 20 January 2022. [Google Scholar]
- OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals. Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, Growth Inhibition Test; OECD/OCDE 201; OECD: Paris, France, 2011; Available online: https://www.oecd.org/chemicalsafety/testing/1946914.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals. Daphnia sp., Acute Immobilisation Test; OECD/OCDE 202; OECD: Paris, France, 2004; Available online: https://www.oecd.org/chemicalsafety/risk-assessment/1948249.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals. Fish, Acute Toxicity Test; OECD/OCDE 203; OECD: Paris, France, 1992; Available online: https://www.oecd.org/chemicalsafety/risk-assessment/1948241.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- Spitsbergen, J.M.; Kent, M.L. The state of the art of the zebrafish model for toxicology and toxicologic pathology research-advantages and current limitations. Toxicol. Pathol. 2003, 31, 62–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals. Readily Biodegradability; OECD/OCDE 301; OECD: Paris, France, 1992; Available online: https://www.oecd.org/chemicalsafety/risk-assessment/1948209.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- Milliasseau, D.; Jeftić, J.; Pessel, F.; Plusquellec, D.; Benvegnu, T. Transformation of pectins into non-ionic or anionic surfactants using a one-pot and cascade mode process. Molecules 2021, 26, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Description | Method | Result | Units | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oligomannuronate (OM) | Solids | Constant weight at 103 °C | 95.6 | %dry/crude |
| Mineral matter | 12 h, 550 °C | 31.9 | %dry/crude | |
| Ratio (M/G) | By calculation, 1H NMR | 2.7 | ||
| DP | By calculation | 4.0 | ||
| Oligoguluronate (OG) | Solids | Constant weight at 103 °C | 100.0 | %dry/crude |
| Mineral matter | 12 h, 550 °C | 26.3 | %dry/crude | |
| Ratio (M/G) | By calculation, 1H NMR | 0.04 | ||
| DP | By calculation | 30.0 | ||
| Oligoalginate (OAlg) | Solids | Constant weight at 103 °C | 90.1 | %dry/crude |
| Mineral matter | 12 h, 550 °C | 44.3 | %dry/crude | |
| Ratio (M/G) | By calculation, 1H NMR | 1.4 | ||
| DP | By calculation | 12.7 | ||
| Semi-refined alginates (s-r Alg) | Solids | Constant weight at 103 °C | 94.9 | %dry/crude |
| Mineral matter | 12 h, 550 °C | 47.0 | %dry/crude | |
| Mannuronic and guluronic content | Methanolysis | 29.2 | %dry/crude | |
| Glucose content | Methanolysis | 10.9 | %dry/crude | |
| Xylose content | Methanolysis | <0.5 | %dry/crude | |
| Fucose content | Methanolysis | 2.1 | %dry/crude | |
| Ratio (M/G) | By calculation, 1H NMR | 2.6 |
| Compounds | δ H1 (ppm) (Multiplicity) | J1,2 (Hz) | Form | Composition (mol%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1α (Man) | 4.91 (d) | 1.7 | α-Pyranose | 52 |
| 2α (Man) | 4.97 (s) | - | α-Furanose | 7 |
| 3α (Man) | 5.05 (d) | 2.0 | α-Lactone | 11 |
| 3β (Man) | 5.03 (d) | 4.6 | β-Lactone | 13 |
| 4α (Gul) | 4.95 (d) | 4.4 | α-Lactone | 5 |
| 4β (Gul) | 5.06 (s) | - | β-Lactone | 5 |
| 5β (Gul) | 4.91 (s) | - | β-Furanose | 3 |
| MSA (n eq) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compounds | 1.7 | 2.2 | 2.6 | 4.7 |
| 1α | 183 mg (yld = 33%) | 132 mg (yld = 24%) | 150 mg (yld = 27%) | 69 mg (yld = 12%) |
| 2α, 3α,β, 4α,β, 5β | 126 mg | 118 mg | 117 mg | 31 mg |
| 6 | 57 mg | 166 mg | 148 mg | 380 mg |
| Entries | DodOH (n’ eq) | MSA (n eq) | 7α | 8α, 9α,β, 10α,β, 11α,β, 12β |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 a | 16 | 2 | 229 mg (yld = 24%) | 153 mg |
| 2 | 4 | 1 | 240 mg (yld = 25%) | 168 mg |
| 3 | 4 | 0.5 | 200 mg (yld = 21%) | 184 mg |
| Compounds | δ H1 (ppm) (Multiplicity) | J1,2 (Hz) | Form | Composition (mol%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7α (Man) | 4.92 (d) | 1.7 | α-Pyranose | 48 |
| 8α (Man) | 4.97 (s) | - | α-Furanose | 9 |
| 9α (Man) | 5.05 (d) | 2.0 | α-Lactone | 5 |
| 9β (Man) | 5.03 (d) | 4.5 | β-Lactone | 22 |
| 10α (Gul) | 4.95 (d) | 4.5 | α-Lactone | 3 |
| 10β (Gul) | 5.07 (s) | - | β-Lactone | 3 |
| 11β (Gul) * | n.d. | n.d. | β-Pyranose | 5 |
| 12β (Gul) | 4.91 (s) | - | β-Furanose | 6 |
| Compounds | δ H1 (ppm) (Multiplicity) | J1,2 (Hz) | Form | Composition (mol%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13α (Man) | 4.80 (d) | 2.1 | α-Pyranose | 47 |
| 9α (Man) | 5.00 (d) | 1.6 | α-Lactone | 4 |
| 9β (Man) | 4.96 (d) | 3.8- | β-Lactone | 12 |
| 14β (Gul) | 4.62 (d) | 8.3 | β-Pyranose | 4 |
| 10α (Gul) | 4.92 (d) | 4.4 | α-Lactone | 9 |
| 10β (Gul) | 4.98 (s) | - | β-Lactone | 9 |
| 15β (Gul) * | n.d. | n.d. | β-Furanose | 4 |
| Compounds | δ H1 (ppm) (Multiplicity) | J1,2 (Hz) | Form | Composition (mol%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13α (Man) | 4.80 (d) | 2.1 | α-Pyranose | 15 |
| 14β (Gul) | 4.62 (d) | 8.4 | β-Pyranose | 13 |
| 10α (Gul) | 4.92 (d) | 4.5 | α-Lactone | 26 |
| 10β (Gul) | 4.98 (s) | - | β-Lactone | 26 |
| 15β (Gul) * | n.d. | n.d. | β-Furanose | 21 |
| Compounds | δ H1 (ppm) (Multiplicity) | J1,2 (Hz) | Form | Composition (mol%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13α (Man) | 4.80 (d) | 2.1 | α-Pyranose | 23 |
| 9α (Man) * | n.d. | n.d. | α-Lactone | 4 |
| 9β (Man) | 4.95 (d) | 4.1- | β-Lactone | 9 |
| 14β (Gul) | 4.61 (d) | 8.2 | β-Pyranose | 9 |
| 10α (Gul) | 4.91 (d) | 4.5 | α-Lactone | 20 |
| 10β (Gul) | 4.97 (s) | - | β-Lactone | 20 |
| 15β (Gul) ** | n.d. | n.d. | β-Furanose | 9 |
| Compounds | δ H1 (ppm) (Multiplicity) | J1,2 (Hz) | Form | Composition (mol%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13α (Man) | 4.85 (d) | 2.0 | α-Pyranose | 23 |
| 9α (Man) * | n.d. | n.d. | α-Lactone | 5 |
| 9β (Man) | 4.95 (d) | 4.7- | β-Lactone | 13 |
| 14β (Gul) ** | n.d. | n.d. | β-Pyranose | 11 |
| 10β (Gul) | 5.03 (s) | - | β-Lactone | 20 |
| 17α (Fuc) | 4.83 (d) | 3.8 | α-Pyranose | 5 |
| 17β (Fuc) | 4.27 (d) | 7.7 | β-Pyranose | 8 |
| 18α (Fuc) | 4.75 (d) | 3.6 | α-Furanose | (+18β) 15 |
| 18β (Fuc) | 4.75 (d) | n.d. | β-Furanose | (+18α) 15 |
| Compounds | δ H1 (ppm) (Multiplicity) | J1,2 (Hz) | Form | Composition (mol%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19α (Man) | 4.82 (d) | 2.0 | α-Pyranose | 30 |
| 20β (Gul) | 4.64 (d) | 8.1 | β-Pyranose | 6 |
| 21α (Gul) | 4.93 (d) | 4.6 | α-Lactone | 5 |
| 22α (Fuc) | 4.78 (d) | 3.8 | α-Pyranose | 13 |
| 22β (Fuc) | 4.26 (d) | 7.8 | β-Pyranose | 9 |
| 23α (Fuc) | 4.72 (d) | 3.7 | α-Furanose | 9 |
| 23β (Fuc) | 4.75 (d) | 2.2 | β-Furanose | 28 |
| Category Acute 1 (very toxic) | |
| CL50 96 h (for the fish) | ≤1 mg L−1 and/or |
| CE50 48 h (for the shellfish) | ≤1 mg L−1 and/or |
| CEr50 72 h (for the seaweed) | ≤1 mg L−1 |
| Category Acute 2 (toxic) | |
| CL50 96 h (for the fish) | >1 but ≤10 mg L−1 and/or |
| CE50 48 h (for the shellfish) | >1 but ≤10 mg L−1 and/or |
| CEr50 72 h (for the seaweed) | >1 but ≤10 mg L−1 |
| Category Acute 3 (poorly toxic) | |
| CL50 96 h (for the fish) | >10 but ≤100 mg L−1 and/or |
| CE50 48 h (for the shellfish) | >10 but ≤100 mg L−1 and/or |
| CEr50 72 h (for the seaweed) | >10 but ≤100 mg L−1 |
| Above 100 mg L−1, the substance is considered as non-toxic | |
| Test | Effect | Toxicological Descriptor * | SLES | H–C12 s-r Alg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microalgae | Rate of growth | CEr50—72 h | 7.0 mg L−1 Toxic | 45.8 mg L−1 Poorly toxic |
| Daphnia | Immobilization | CE50—24 h | 11.6 mg L−1 Poorly toxic | >100 mg L−1 Non-toxic |
| Fish | Mortality | CL50—96 h | 11.2 mg L−1 Poorly toxic | 67.0 mg L−1 Poorly toxic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pessel, F.; Noirbent, G.; Boyère, C.; Arnaud, S.P.; Wong, T.; Durand, L.; Benvegnu, T. Cascading One-Pot Synthesis of Biodegradable Uronic Acid-Based Surfactants from Oligoalginates, Semi-Refined Alginates, and Crude Brown Seaweeds. Molecules 2023, 28, 5201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135201
Pessel F, Noirbent G, Boyère C, Arnaud SP, Wong T, Durand L, Benvegnu T. Cascading One-Pot Synthesis of Biodegradable Uronic Acid-Based Surfactants from Oligoalginates, Semi-Refined Alginates, and Crude Brown Seaweeds. Molecules. 2023; 28(13):5201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135201
Chicago/Turabian StylePessel, Freddy, Guillaume Noirbent, Cédric Boyère, Sacha Pérocheau Arnaud, Tiphaine Wong, Laura Durand, and Thierry Benvegnu. 2023. "Cascading One-Pot Synthesis of Biodegradable Uronic Acid-Based Surfactants from Oligoalginates, Semi-Refined Alginates, and Crude Brown Seaweeds" Molecules 28, no. 13: 5201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135201
APA StylePessel, F., Noirbent, G., Boyère, C., Arnaud, S. P., Wong, T., Durand, L., & Benvegnu, T. (2023). Cascading One-Pot Synthesis of Biodegradable Uronic Acid-Based Surfactants from Oligoalginates, Semi-Refined Alginates, and Crude Brown Seaweeds. Molecules, 28(13), 5201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135201






