Abstract
This article presents studies on the precipitation of Pt, Pd, Rh, and Ru nanoparticles (NPs) from model and real multicomponent solutions using sodium borohydride, ascorbic acid, sodium formate, and formic acid as reducing agents and polyvinylpyrrolidone as a stabilizing agent. As was expected, apart from PGMs, non-precious metals were coprecipitated. The influence of the addition of non-precious metal ions into the feed solution on the precipitation yield and catalytic properties of the obtained precipitates was studied. A strong reducing agent, NaBH4 precipitates Pt, Pd, Rh, Fe and Cu NPs in most cases with an efficiency greater than 80% from three- and four-component model solutions. The morphology of the PGMs nanoparticles was analyzed via SEM-EDS and TEM. The size of a single nanoparticle of each precipitated metal was not larger than 5 nm. The catalytic properties of the obtained nanomaterials were confirmed via the reaction of the reduction of 4-nitrophenol (NPh) to 4-aminophenol (NAf). Nanocatalysts containing Pt/Pd/Fe NPs obtained from a real solution (produced as a result of the leaching of spent automotive catalysts) showed high catalytic activity (86% NPh conversion after 30 min of reaction at pH 11 with 3 mg of the nanocatalyst).
1. Introduction
Nanoparticles (NPs) are a group of materials with at least one dimension not exceeding 100 nm. Depending on size, the material can have completely different properties, e.g., nanomaterials have a larger specific surface area than micromaterials do and therefore have better catalytic properties than micromaterials do [1]. Additionally, the hardness and mechanical strength of pure metal nanoparticles (~10 nm) were found to be up to sevenfold higher than those of metal particles larger than 1 μm [2].
Nanoparticles can be pure metals, metal oxides, metals, silicon compounds, ceramic compounds, organic and biological particles, semiconductors, or polymers [3]. Recently, there have also been many studies on bimetal NPs containing two different metals, e.g., Pt–Cu NPs [4,5,6], Pt–Fe NPs [7,8], Pd–Pt NPs [9,10], and Ag–Fe NPs [11], on metal NPs deposited on supports, e.g., Pt@TiO2, Pd@TiO2 [12], Pt–Pd@carbon [13], and Pt–Zn@carbon [14], or on nanoliquids, e.g., nanoparticles of CuO, Al2O3, TiO2, or Fe2O3 dispersed in water or ethylene glycol [3,15,16]. Moreover, atomically monodispersed heterogeneous Pt was proven to be an ideal heterogeneous catalytic material [17]. Nanoliquids are produced by dispersing solid NPs (e.g., metals and metal oxides) in liquids such as water, ethylene glycol, or oils. The large total surface area of the NP results in good thermal transfer properties and the increased stability of the suspension [3].
PGMs (platinum-group metals) are the most expensive metals due to their high demand and scarce natural resources [18,19]. Platinum, palladium, and rhodium form an active layer in automotive converters. The role of the Pt–Pd–Rh layer is to neutralize volatile organic compounds CxHy, CO and NOx to harmless CO2, N2 and H2O [20]. As the automotive industry is the largest secondary resource of PGMs, it is a crucial issue to recover these valuable metals from spent automotive converters (SAC), and reuse them in new products. Among various pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical methods, leaching has often been used to separate PGMs from SAC [21,22,23,24,25,26]. Afterwards, several subsequent steps must be implemented to separate and purify these metals, and form new products, which are cementation [23], ion exchange/adsorption [27,28], and liquid–liquid extraction [25,29]. For example, our team has developed a multistep process for the separation of Pt(IV), Pd(II), Rh(III) and Ru(III) from multicomponent solutions [30,31]. Pt(IV) and Pd(II) can be extracted with Cyphos IL 101 or 104 from acidic solutions obtained after PGM leaching from SAC, and then selectively stripped from the loaded organic phases with 0.1 M thiourea in 0.5 M HCl (for Pd(II)) or 3 M nitric(V) acid (for Pt(IV)). Since the solutions after subsequent steps of the process contain PGMs recovered from SAC in rather small quantities, looking for a way to manage them, we have decided to investigate the leaching and stripping solutions for the precipitation of PGM nanoparticles [10,12].
The aim of this research is to obtain catalytically active PGM NPs (nanocatalysts) from model and real multicomponent solutions. In our previous studies [10], catalytically active PGM NPs were precipitated from one- or two-component model solutions containing PGMs. The scientific novelty of this research is the formation of PGM NPs from real acidic solutions, obtained as a result of the hydrometallurgical processing of spent automotive catalysts, carried out by our team [30]. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that acidic leachates have been applied for the formation of PGM NPs. The effect of the addition of non-precious metals (Fe ions, Cu(II), Zn(II) or Mg(II)) into the model feed solutions on the precipitation yield was studied. Afterwards, multicomponent nanocatalysts were formed from the real solutions after metal leaching from SAC. Finally, the catalytic properties of the obtained PGM NPs with the addition of non-precious metals were also investigated.
2. Results
2.1. One- and Two-Component Model Solutions
In this work, the influence of the addition of non-precious metals to the feed solution was studied on the efficiency of precipitation of PGMs. Fe ions, Cu(II), Zn(II) and Mg(II) were chosen because they are present in real leach solutions (Table A1 in Appendix A).
Initially, the precipitation yield (P) of Fe, Cu, Zn and Mg from one-component model solutions is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Precipitation yield of Fe, Cu, Zn and Mg from one-component model solutions using four reducers: AA (ascorbic acid), NaBH4, SF (sodium formate), and FA (formic acid) (the ratio of non-precious metal:PVP:reducer was 1:1:1).
The precipitation yield of Fe from the one-component solution is 100% using NaBH4 or SF as a reducer. Cu can also be precipitated with high efficiency (~80%) using NaBH4 or SF. The most efficient reducers for Zn are SF and FA (~90%). AA only precipitates Zn, but the precipitation yield of Zn does not exceed 50%. Regardless of the reducer used, the precipitation efficiency of Mg is poor (<12%). The effect of the type of reducer and the concentration of PVP on the precipitation yield of PGMs from the one-component model solutions (containing Pt, Pd, Rh or Ru) or a mixture of two PGMs (Pt–Pd, Pt–Rh, Pt–Ru, Pd–Rh, Pd–Ru and Rh–Ru) was presented in our previous study [10].
The precipitation yield of PGM with the addition of Fe ions, Cu(II), Zn(II) or Mg(II) from two-component model solutions is presented in Table 2. The molar ratio of PGMs to non-precious metals was 1:1.

Table 2.
Precipitation yield of Pt, Pd, Ru, Rh, Fe, Cu, Zn and Mg from two-component model solutions (PGM–non precious metal: Fe, Cu, Zn or Mg ions) using four reducers: AA, NaBH4, SF and FA (the ratio of PGM:PVP:reducer was 1:1:1).
On the one hand, the use of a strong reducing agent, NaBH4, in the precipitation reaction caused Pt, Pd, Rh, Fe and Cu to precipitate in most cases with an efficiency greater than 90%. On the other hand, AA turned out to be a weak reducing agent with which to precipitate Pd and Rh with high efficiency, which was confirmed in previous studies [10]. When comparing the results of SF and FA, it can be seen that they are similar and that the difference between them is not greater than 10 percentage points in most cases. Slight differences are visible in the PGM–Cu systems; FA turned out to be a weaker reducer than SF was. Due to the position in the table of the redox potentials of Mg(II) and Zn(II) of −2.36 and −0.76 V, their reduction to the zero oxidation state can be difficult. The low metal potential would explain the problem of the efficient precipitation of Mg(II) and Zn(II) (Table 2). In addition, the presence of these metals directly affects the efficiency of reducing PGMs from two-component solutions by lowering the efficiency of reducing all metals [32,33]. The redox potential of PGMs is as follows: Pd2+/Pd (0.95 V vs. standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)), Rh3+/Rh (0.76 V vs. SHE), Ru3+/Ru (0.6 V vs. SHE) and Pt4+/Pt (2.28 V vs. SHE). For base metals, it was as follows: Cu2+/Cu (0.34 V vs. SHE), Fe3+/Fe2+ (0.77 V vs. SHE) and Fe2+/Fe (−0.44 V vs. SHE) [33,34]. As expected from the reduction potential of PGMs and base metals, only PGMs precipitated from the feed solution, while Mg(II) or Zn(II) remained in solution. According to the potentials, the order of precipitation of PGM ions should be as follows: Pt(IV) > Pd(II) > Rh(III).That for base metals should be Fe(III) > Cu(II) > Fe(II), Zn(II) and Mg(II), which was confirmed by the results obtained in our work.
A strong inorganic reducing agent, NaBH4 allows particle production in the metallic form (M) at an alkaline pH (>9) according to the following reaction [35]:
The reaction of PGM precipitation with a weak organic reducing agent, i.e., ascorbic acid (AA), proceeds as follows [36]:
As a result of the application of another organic reducer, i.e., formic acid, the reaction of which can be presented as follows [37]:
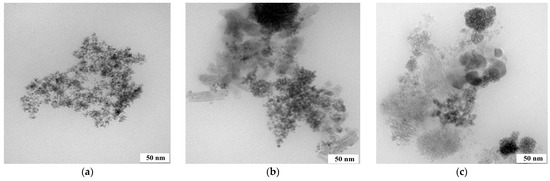
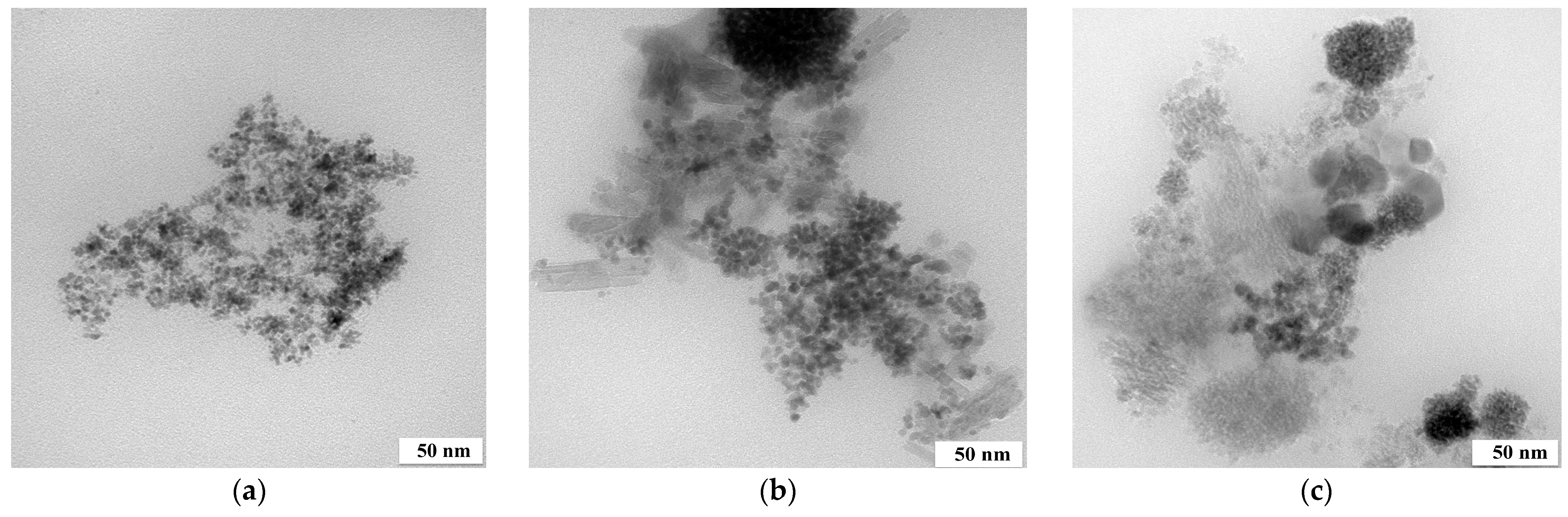
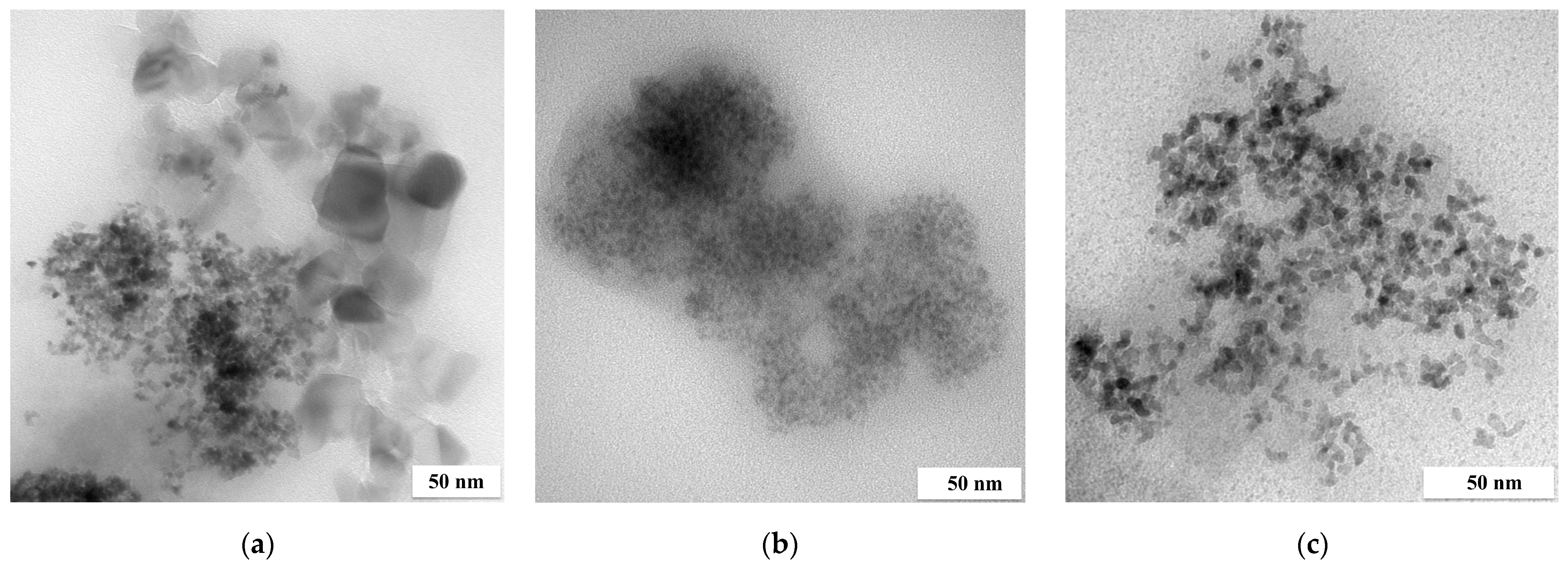
Figure 1.
TEM images of (a) Pt/Fe NPs, (b) Pd/Fe NPs and (c) Rh/Fe NPs from the model solution (the molar ratio of PGM:PVP:NaBH4 was 1:1:1).
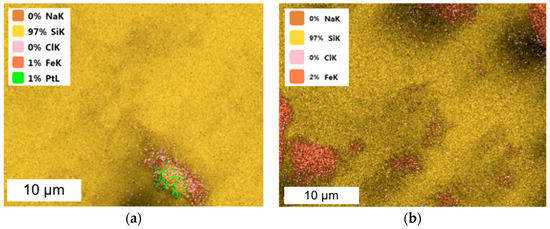
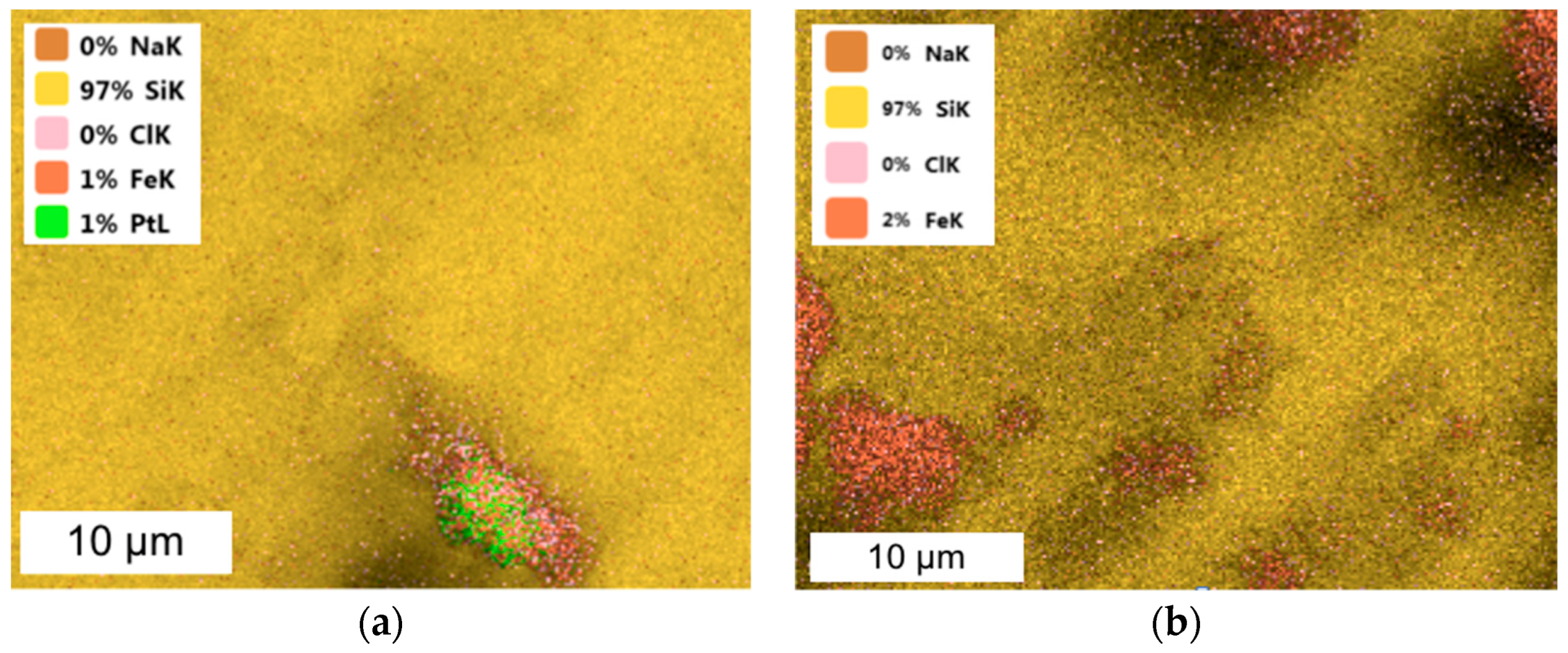
Figure 2.
SEM coupled with EDS images of (a) Pt/Fe NPs and (b) Fe NPs (from model solution; the molar ratio of PGM:PVP:NaBH4 was 1:1:1).
The size of the obtained nanoparticles did not exceed 5 nm. Extensive agglomerate clusters are visible in all images, but Pd and Rh/Fe NPs form larger and more rounded clusters than Pt/Fe NPs do. Similar results for PGM NPs were obtained from one- and two-component solutions and described in our previous article [10]. In the current study, the presence of Fe did not affect the appearance of the obtained PGM NPs. Both PGM and Fe NPs themselves formed agglomerates, which was also confirmed via the TEM images (Figure 1). SEM-EDS was performed for materials containing PGM/Fe or only Fe after reduction with NaBH4 (Figure 2).
The SEM-EDS performed confirmed that the metals were reduced to the metallic species and did not form chloride compounds (Figure 2). SEM-EDS images of Pt/Fe nanocatalysts precipitated with AA, FA and SF reducers are shown in Figure A1 in Appendix A. SEM-EDS images for other nanocatalysts are presented in Figure A2 in Appendix A. The absence of Na+ and Cl− ions from the EDS images of Pt/Fe NPs and Fe NPs indicates that the synthesized nanocatalyst was well-purified through washing. However, the presence of chlorides was detected in Rh and Ru NPs. The comparison of the results shown in Table 2 indicates that the Ru precipitation from the two-component solution contained Fe ion efficiency by that the NaBH4 reducer was below 40% and Ru did not precipitate in the form of metallic NPs or ruthenium oxide. The EDS spectra confirmed the presence of chloride ions in both PGM materials (Figure A2 in Appendix A).
2.2. Multicomponent Model Solutions
As in real leachates obtained from various spent materials, PGMs exist in mixtures. The precipitation of Pt, Pd, Ru, and Rh was also carried out from model three- (Pt-Pd-Rh) and four-component (Pt-Pd-Ru-Rh) solutions and the results are presented in Table 3. The molar ratio of Pt:Pd:Rh and Pt:Pd:Ru:Rh was 1:1:1 and 1:1:1:1, respectively.

Table 3.
Precipitation yield of Pt, Pd, Ru and Rh from three- and four-component model solutions using various reducers: AA, NaBH4, SF and FA (the ratio of PGM:PVP:reducer was 1:1:1).
The precipitation of a three-component catalyst with NaBH4 or FA was the most effective (above 73%) compared to that with AA and SF. Three-component NPs precipitated with AA contained a small amount of Pd, similar to the case of a two-component nanocatalyst. The order of PGM precipitation from the three-component solution can be written as follows: Pt > Pd > Rh for NaBH4, Pd > Rh > Pt for FA and Pt > Rh > Pd for AA. However, this dependence changes when the fourth component is introduced to the solution, in which case the order is as follows: Ru > Pt > Pd > Rh for AA, Pd > Rh > Ru–Pt for NaBH4 and Ru > Pd > Pt > Rh for FA and SF. Figure 3 shows the TEM images of the catalysts obtained.
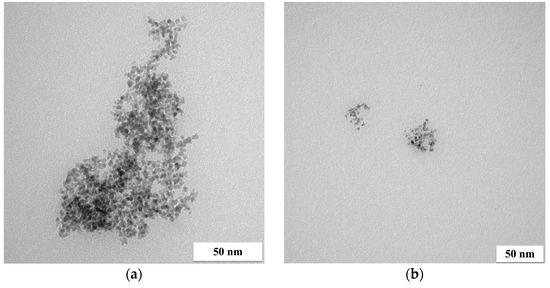
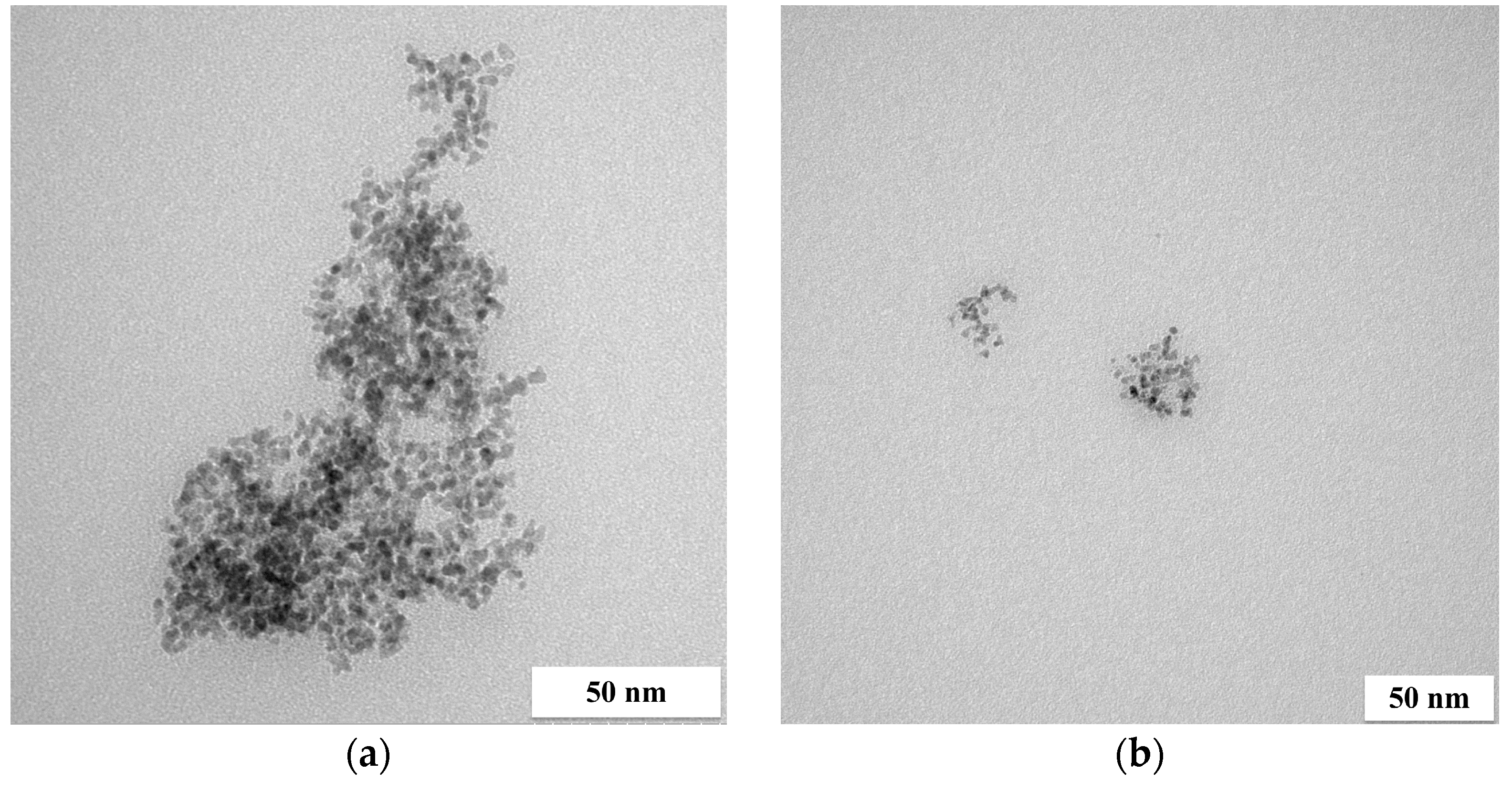
Figure 3.
TEM images of four-component NPs from model solution ((a) big agglomerate and (b) small agglomerate; the molar ratio of PGM:PVP:NaBH4 was 1:1:1).
Some highly developed agglomerates of the four-component NPs were formed, while small groups of metal NPs are visible in other images as well. The size of a single particle did not exceed 5 nm (similarly to the particles obtained from two-component solutions). The materials obtained were characterized using the SEM-EDS technique (Figure 4).
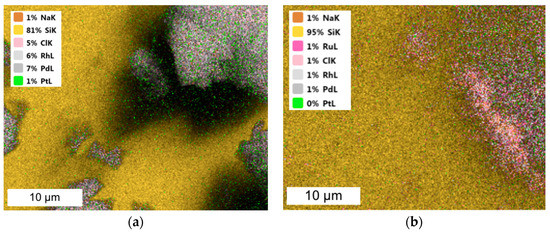
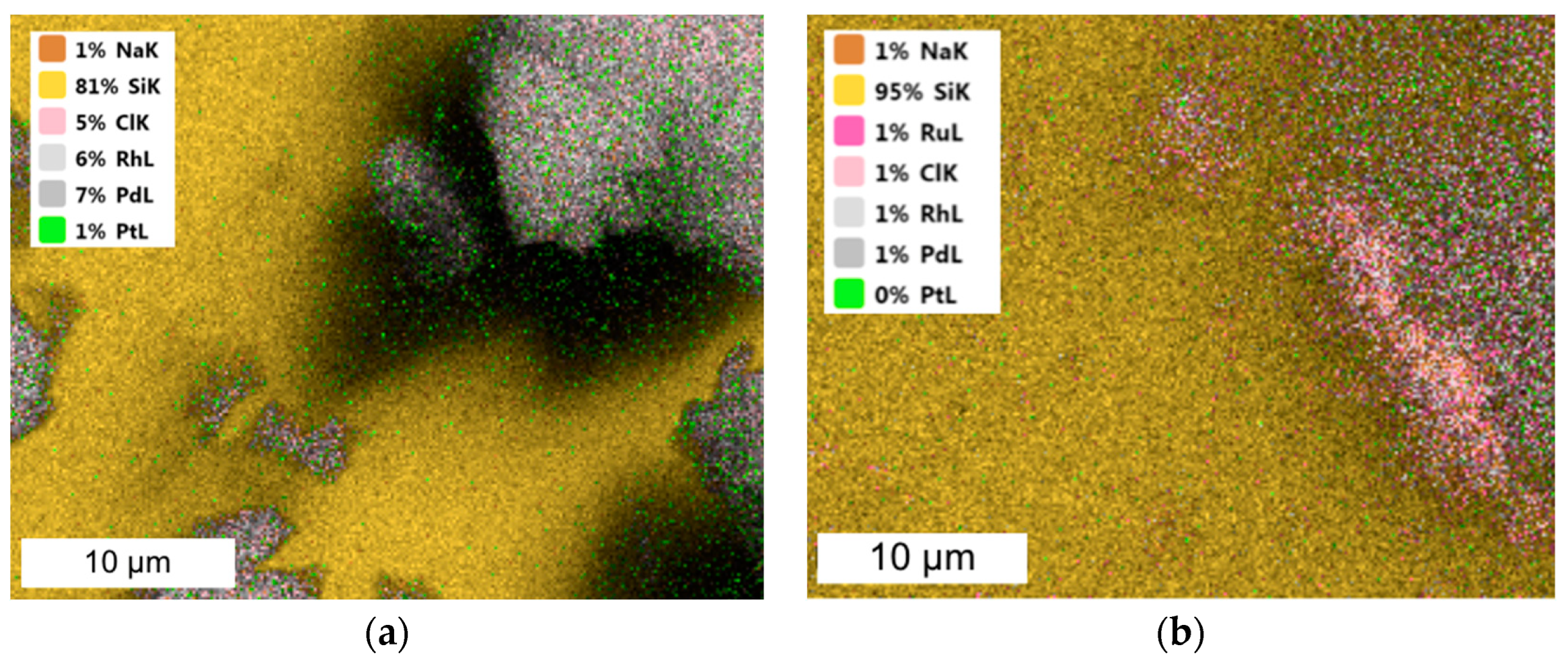
Figure 4.
SEM-EDS images of (a) three- and (b) four-component catalysts precipitated from model solution (the molar ratio of PGM:PVP:NaBH4 was 1:1:1).
In the case of three- or four-component catalysts, Pd and Rh or Ru agglomerated with one another, while Pt also formed separate clusters, which are visible as the smaller agglomerates present in the TEM images.
2.3. Multicomponent Real Solutions
Due to the fact that NaBH4 appeared to be the most efficient reducing agent, it was used to precipitate PGMs and other metal ions from multicomponent real solutions. The precipitation of PGMs was carried out from real multicomponent solutions and the results are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Precipitation yield of PGMs and Fe ions from real solutions using NaBH4 (ratio of PGM:PVP:NaBH4 was 1:1:2 or 1:1:10 for R2 solution).
The concentrations of metal ions in the R1–R3 feed solutions are shown in Table A1 in Appendix A. A 3 M HNO3 solution was used as the stripping phase for R1 and R3 and 0.1 M thiourea in 0.5 M HCl were used for R2. The efficiency of the precipitation of PGMs and base metals from the real solutions was almost quantitative. Only the efficiency of Fe precipitation from solution R2 was below 70%. Due to problems during the precipitation of Pd(II) from the R2 solution, a fivefold excess of the reducing agent was applied. This may have been due to the presence of thiourea in the feed solution, the particles of which strongly coordinate PGMs, and, thus, the presence of thiourea affects the reducing capacity of PGMs via NaBH4 [38]. TEM images characterizing the formed nanocatalysts are shown in Figure 5.
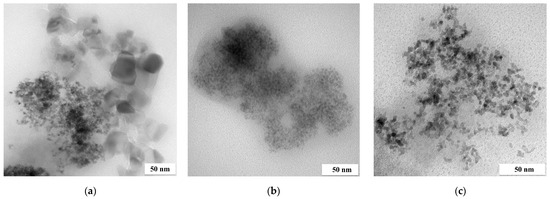
Figure 5.
TEM images of (a) Pt/Fe NPs from solution R1, (b) Pt/Pd/Fe NPs from solution R2 and (c) Pt/Pd/Fe NPs from solution R3 (the molar ratio of PGM:PVP:NaBH4 was 1:1:2 or 1:1:10).
Additionally, in the case of precipitation from real multicomponent solutions, the size of a single nanoparticle is not larger than 5 nm. The materials obtained from the R1 and R3 solutions look similar, while a kind of shell (visible in all the images obtained is formed) around the Pd NP catalyst was synthesized from the R2 solution. Additionally, it is impossible to see the full outline of the NPs because they look blurred.
2.4. Catalytic Reactions
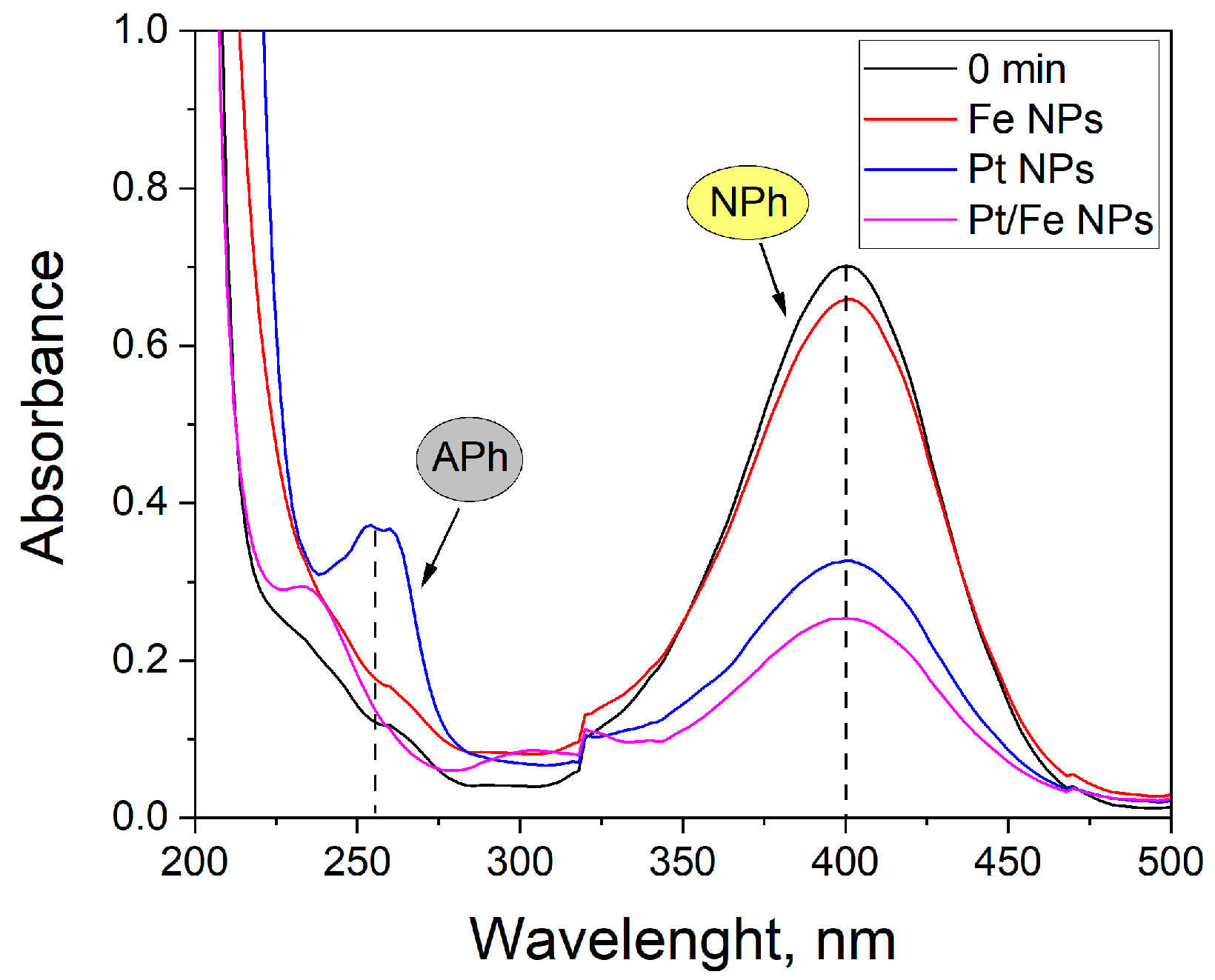
The catalytic activity of the obtained materials was tested via the catalytic reduction of nitrophenol (NPh) to aminophenol (APh) (Table A2 in Appendix A). Due to the change in the reaction mechanism of the NPh reduction with the increasing pH [12], the reactions were carried out at two different pHs, 11 and 14. The highest catalytic activity was observed for Pd/Fe, Rh/Fe and Cu NPs at pH 11. An increase in the reaction pH caused the decrease in catalytic activity of Cu NPs and probably converted copper into its hydroxide, as evidenced by the green color of the solution. Therefore, further research should be mainly focused on Fe addition to newly synthesized PGM NPs. It was observed that the increase in pH to 14, resulted in an improvement in the NPh conversion catalyzed by Pt/Fe NPs and Zn. Figure 6 shows the UV-Vis spectra of the NPh reduction reaction using Pt NPs, Fe NPs and Pt/Fe NPs as a catalyst.
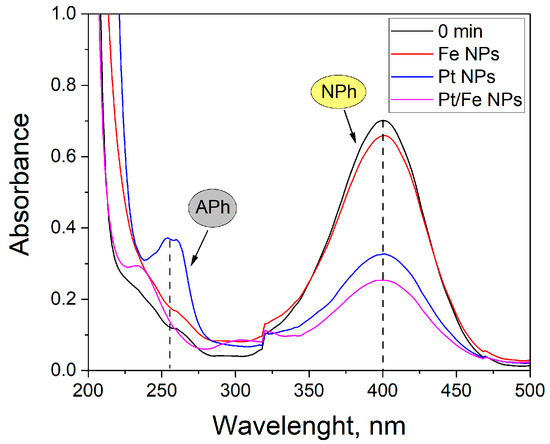
Figure 6.
UV-Vis spectra of NPh solutions at pH 11 after 30 min of reduction reaction catalyzed by 1 mg of Fe NPs, Pt NPs and Pt/Fe NPs.
The nanoparticles used for the reduction reaction have catalytic properties. After 30 min of the reaction, the conversion of NPh with the use of one-component catalysts was 5% for Fe NPs, and 52% for Pt NPs. The application of a two-component Pt–Fe catalyst improved substrate conversion by 12 percentage points.
The NPh conversion values with various amounts of PGMs/Fe NPs (1, 2 and 3 mg) are shown in Table A3 in Appendix A. The pH and the amount of the catalyst (Pd and Rh/Fe NPs) had no effect on the increasing conversion of NPh.
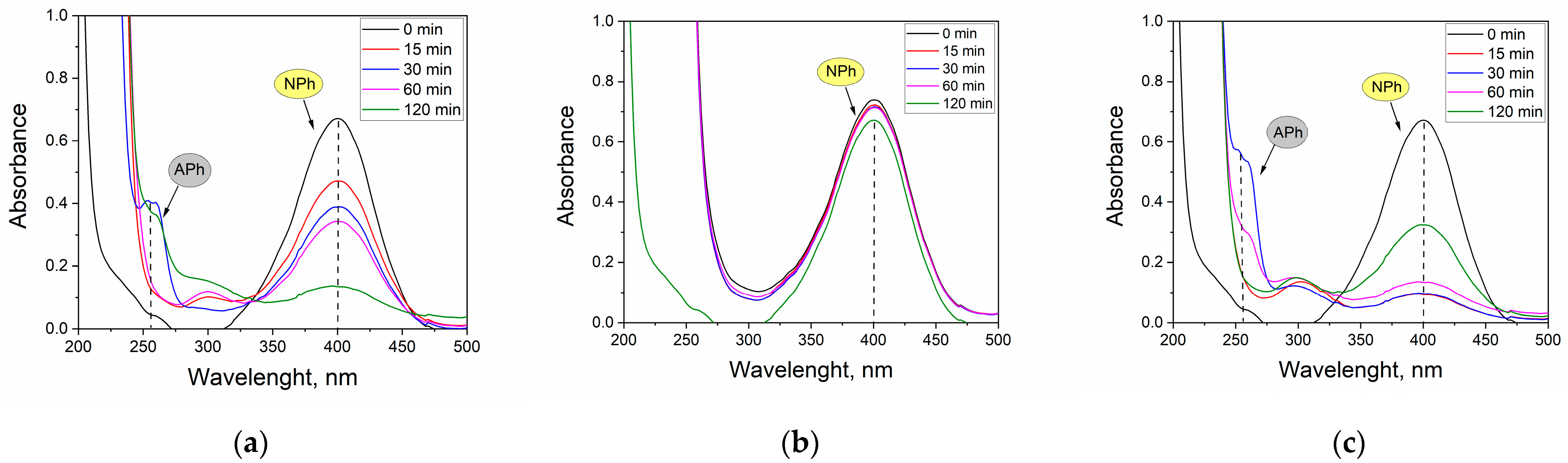
Finally, nanocatalysts precipitated from real solutions (R1–R3) were used to reduce NPh to APh (Figure 7).
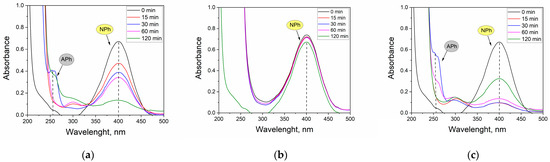
Figure 7.
UV-Vis spectra of NPh solutions at pH 11 after 120 min of reduction reaction catalyzed by 3 mg of a catalyst from real solution: (a) R1, (b) R2 and (c) R3.
The maximum at λ = 400 nm corresponds to the dissociated form of NPh found under alkaline conditions (pH 11) and that at λ = 313 nm corresponds to the undissociated form of NPh. Already after 15 min of the reaction, a decrease in absorbance for NPh for R1 and R3 could be seen. In both cases, there was also a slight maximum at λ = 300 nm, which is characteristic of APh in its undissociated form. After 30 min of the reaction, a maximum appeared at λ = 260 nm, corresponding to the dissociated form of APh. The conversion of NPh after 30 min was 42.2 and 85.7%, and after 120 min it was 80 and 51.7%, for Pt/Fe NP and Pt/Pd/Fe NP catalysts, respectively (precipitated from R1 or R3 solution). The Pt/Pd/Fe NP catalyst formed from the R2 solution showed no catalytic activity. This may have been due to the presence of thiourea, which may have blocked the active sites of the catalyst. This would explain the casing visible behind the TEM images of R2 (Figure 5b).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Solutions
Two-component model solutions (PGM–non-precious metal) were prepared by dissolving in 0.1 M HCl the required amounts of PtCl4 (96%), PdCl2 (99.9%), RhCl3 (99.9%), RuCl3 (99.9%), FeCl3 (97%), ZnCl2 (98%), MgCl2 (97%) and CuCl2 (97%) (Sigma Aldrich, Schnelldorf, Germany). Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP, Mw ≈ 55,000, Sigma Aldrich, Schnelldorf, Germany) was used as the stabilizing agent. Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) (>98.0%, Sigma Aldrich, Schnelldorf, Germany), ascorbic acid (C6H8O6) (AA, p.a., Chempur, Piekary Śląskie, Poland), sodium formate (HCOONa) (SF, p.a., Sigma Aldrich, Schnelldorf, Germany), and formic acid (HCOOH) (FA, p.a., Sigma Aldrich, Schnelldorf, Germany) were used as the reducers in the study.
The real solutions used in the research as feed solutions were from the hydrometallurgical treatment of spent automotive converters. As the material, two different spent automotive catalysts containing Pt–Rh and Pt–Pd–Rh were used, which were leached in the first stage with oxalic acid in order to purify the material from base metals, and then in the second stage with a mixture of concentrated acids with an oxidant HCl/H2SO4/H2O2. The separation and purification procedure was presented in the previous article [30]. The real solutions applied for NP formation (Section 2.3) originated from the stripping step and were used to separate Pd(II) from Pt(IV) and non-precious metals, with 3 M HNO3 for R1 and R3 and 0.1 M thiourea in 0.5 M HCl for R2. The concentrations of metal ions in the feed solutions used for precipitation are shown in Table A1.
3.2. Synthesis of Nanoparticles
In our previous study [10], the effect of PVP concentration, the type of reducer, and the addition of other PGMs to the feed solution on the precipitation yield of PGMs was studied. The stabilizing agent PVP was added to the PGM precursor solution and mixed for 10 min. Next, the reducer was added drop by drop, and the solution was still mixed. The pH of the solution was then adjusted to pH 7–8 with 1 M Na2CO3 (p.a., Chempur, Poland, for model solutions) or 30% NaOH (p.a., Chempur, Poland, for real solutions). The molar ratio of the PGM precursor to the stabilizing agent and the reducer for the model solutions (PGM:PVP:reducer) was 1:1:1 and that for the real solutions R1 and R3 was 1:2:1. Due to the lack of color change in the solution and the low precipitation yield (P) for R2, the concentration of the reducing agent was 10 times higher. The precipitation yield (P) was calculated as in the previous studies [10].
3.3. Catalytic Reaction
The precipitated NPs were used as catalysts in the reduction reaction of 4-nitrophenol (NPh) to 4-aminophenol (APh) in the presence of NaBH4.
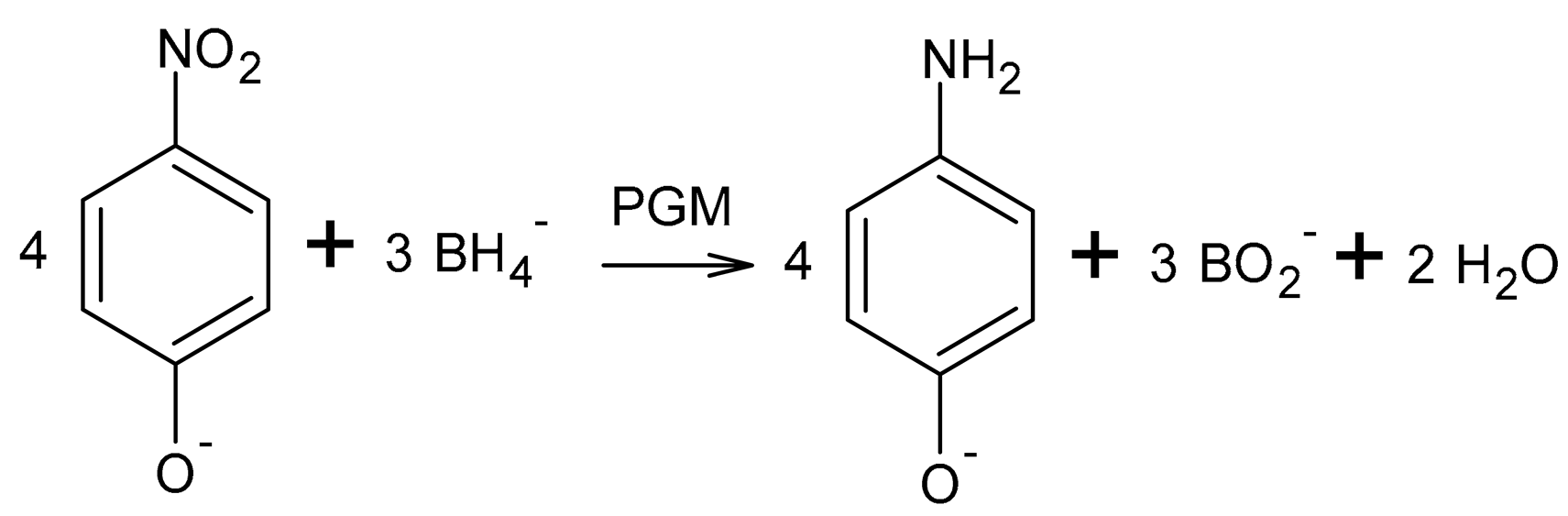

NaOH was added to the solution to raise the pH to 11 or 14 and keep NPh in an anionic form. Additionally, due to the differences in the mechanism, the reactions were carried out at two different pHs. At a pH above 13, the reaction was dominated by slow hydride reduction. In contrast, at pH 10, the reaction was dominated by rapid hydrogen reduction and exhibited typical surface reaction behavior. Therefore, the use of two different pH values (11 and 14) was performed to investigate the effect of the course of the reaction [39]. The maximum of the NPh in the UV-Vis spectrum in the basic solution is at λ = 400 nm, and that for APh is at λ = 260 nm. The equation for calculating the NPh conversion degree (αNPh) was presented in the previous study [10].
3.4. Apparatus
The concentrations of metal ions in the solutions before and after precipitation were measured using atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS ContrAA 300, Analytik Jena, Jena, Germany) at the following wavelengths: 266.0, 244.8, 343.5, 349.9, 248.3, 285.2, 213.9 and 324.7 nm for Pt(IV), Pd(II), Rh(III), Ru(III), Fe ions, Mg(II), Zn(II) and Cu(II), respectively.
SEM-EDS (SEM FEI Quanta 250 FEG, ThermoFisher, Hillsboro, OR, USA) and the Hitachi HT7700 transmission electron microscope (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) working in high-contrast and high-resolution mode were applied to analyze the structure and morphology of the obtained nanoparticles. The solutions after the reduction of NPh to APh were analyzed via UV-Vis (spectrophotometer, Specord 40, Analytik Jena, Jena, Germany) to confirm the conversion of NPh.
4. Conclusions
The research conducted confirms that it is possible to obtain catalytically active nanomaterials from processing spent automotive converters. The most effective reducing agent is NaBH4 with a precipitation efficiency greater than 80% for Pt, Pd and Rh NPs from three- and four-component solutions. Due to the high efficiency of PGM precipitation, NaBH4 was selected to reduce metal ions from real solutions, and the efficiency of precipitation was almost quantitative. The size of single NPs did not exceed 5 nm in all cases. The presence of Fe in the Pt/Fe NP catalyst improved the NPh conversion (52% conversion of NPh with Pt/Fe NPs) compared to the 64% NPh conversion with Pt NPs. The catalyst containing Pt, Pd and Fe NPs obtained from the real solution had a satisfactory catalytic activity, which was confirmed by the NPh conversion of 86% after 30 min at pH 11 with the use of 3 mg of the catalyst. Thus, this shows that there is no need to purify real leach solutions from ions of non-precious metals before the precipitation of PGM NPs. However, other species (e.g., organics) present in the solution can negatively influence the activity of the NPs formed, for example the blocking of the surface of the precipitated material via the thiourea present in the stripping solution R2.
To the best of our knowledge, there are no literature data on PGM NP precipitation from real acidic leachates. Such a waste-to-product procedure is an important approach from the point of view of sustainability and protection of the environment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.W., M.R.-P. and M.R.-R.; methodology, Z.W., M.N. and M.R.-P.; investigation, M.N., Z.W. and M.R.-P.; resources, Z.W., M.N., M.R.-P. and M.R.-R.; data curation, M.R.-P. and Z.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.W., M.R.-P. and M.R.-R.; writing—review and editing, M.N., M.R.-P. and M.R.-R.; visualization, M.N., M.R.-P. and Z.W.; supervision, M.R.-R.; project administration, M.R.-P. and M.R.-R.; funding acquisition, M.R.-P. and M.R.-R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science Centre—NCN (Poland) under the program MINIATURA 4, grant no. 2020/04/X/ST5/00498, and co-financed by the Ministry of Education and Science, Poland (grants no. 0912/SBAD/2210 and 0512/SBAD/2320).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Available from the corresponding authors.
Appendix A
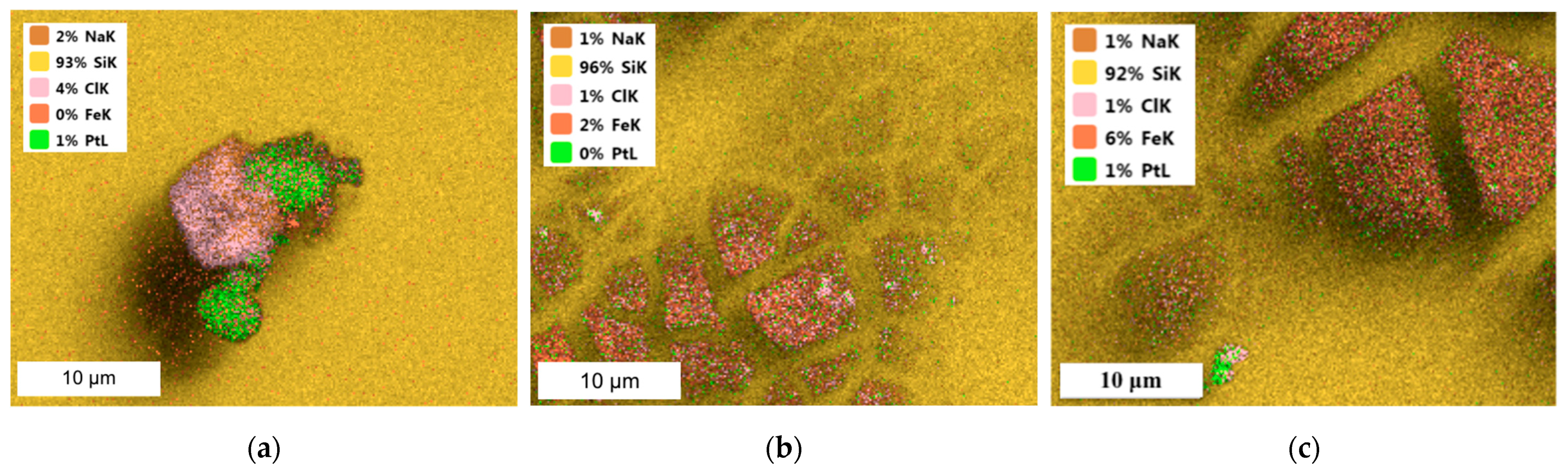
SEM-EDS images of Pt/Fe NPs after reduction with AA, FA or SF from the model solution are presented in Figure A1.
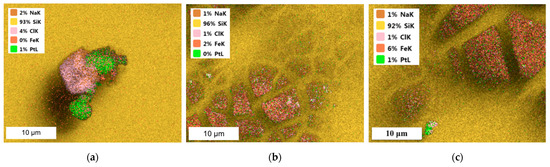
Figure A1.
SEM coupled with EDS images of Pt/Fe NPs after reduction by (a) AA, (b) FA and (c) SF from the model solution (the molar ratio of PGM:PVP:reducer was 1:1:1).
Figure A1.
SEM coupled with EDS images of Pt/Fe NPs after reduction by (a) AA, (b) FA and (c) SF from the model solution (the molar ratio of PGM:PVP:reducer was 1:1:1).
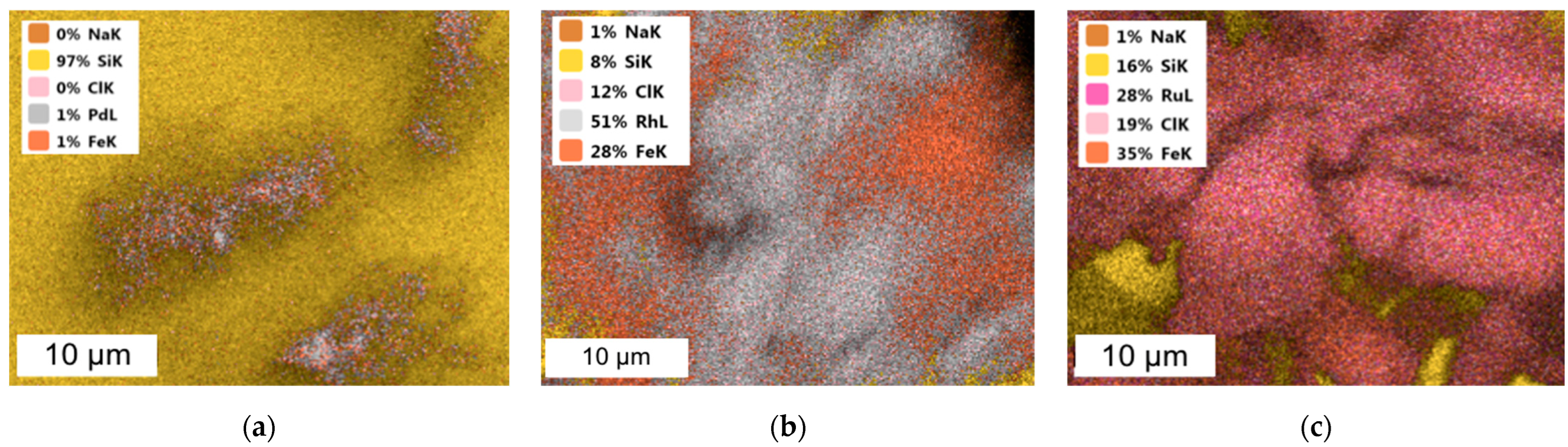
SEM-EDS images of Pd/Fe NPs, Rh/Fe NPs and Ru/Fe NPs after precipitation with NaBH4 from model solution are presented in Figure A2.
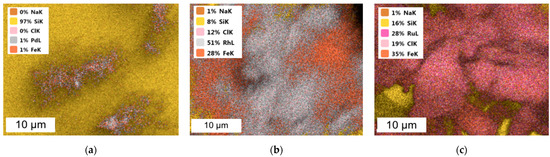
Figure A2.
SEM coupled with EDS images of (a) Pd/Fe NPs, (b) Rh/Fe NPs and (c) Ru/Fe NPs from the model solution (the molar ratio of PGM:PVP:NaBH4 was 1:1:1).
Figure A2.
SEM coupled with EDS images of (a) Pd/Fe NPs, (b) Rh/Fe NPs and (c) Ru/Fe NPs from the model solution (the molar ratio of PGM:PVP:NaBH4 was 1:1:1).
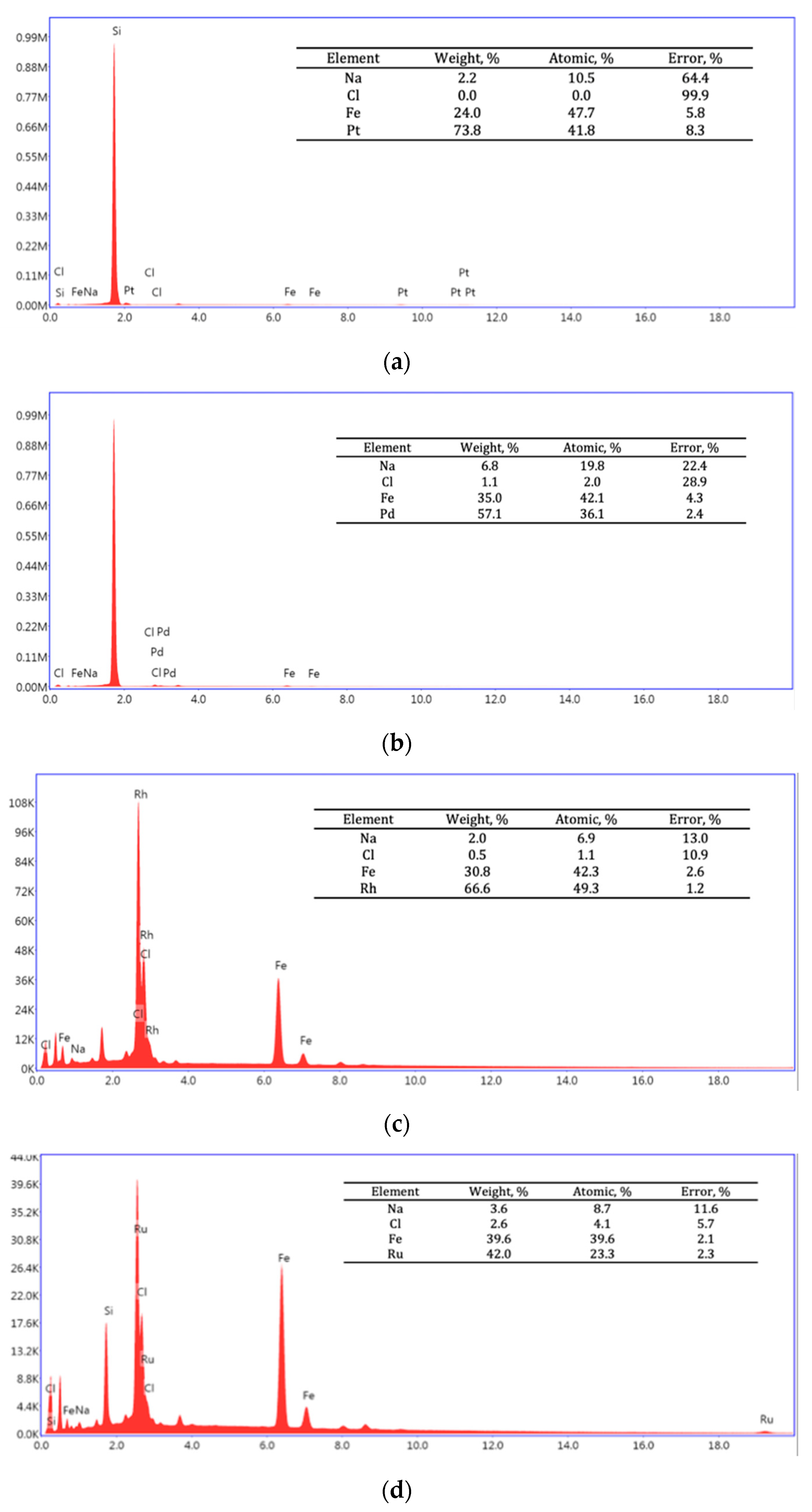
SEM-EDS spectra of Pt/Fe NPs, Pd/Fe NPs, Rh/Fe NPs and Ru/Fe NPs after precipitation with NaBH4 from the model solution are presented in Figure A3.
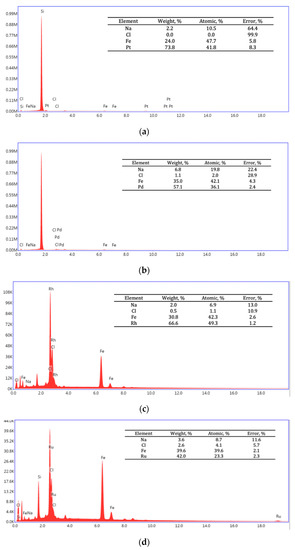
Figure A3.
SEM-EDS spectra of (a) Pt/Fe NPs, (b) Pd/Fe NPs, (c) Rh/Fe NPs and (d) Ru/Fe NPs from the model solution (the molar ratio of PGM:PVP:NaBH4 was 1:1:1).
Figure A3.
SEM-EDS spectra of (a) Pt/Fe NPs, (b) Pd/Fe NPs, (c) Rh/Fe NPs and (d) Ru/Fe NPs from the model solution (the molar ratio of PGM:PVP:NaBH4 was 1:1:1).
Concentrations of metal ions in the feed solutions are shown in Table A1.

Table A1.
Metal ion concentrations in the real solutions used as feeds for the precipitation of metal nanoparticles.
Table A1.
Metal ion concentrations in the real solutions used as feeds for the precipitation of metal nanoparticles.
| Chemical Element | Concentration of Metal Ions, mg/dm3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | R3 | |
| Pt(IV) | 247.0 | 19.0 | 89.4 |
| Pd(II) | - | 80.0 | 67.6 |
| Rh(III) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Fe ions | 30.1 | 61.0 | 80.0 |
| Mg(II) | 0.64 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| Zn(II) | 6.9 | 0.2 | 4.3 |
| Cu(II) | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
The conversion of NPh at pH 11 and 14 depending on the type of the non-precious metals (Fe, Cu, and Zn) is presented in Table A2.

Table A2.
Conversion of NPh at pH 11 and 14 depending on the type of the non-precious metals (Fe, Cu, and Zn). Catalyst mass: 1 mg.
Table A2.
Conversion of NPh at pH 11 and 14 depending on the type of the non-precious metals (Fe, Cu, and Zn). Catalyst mass: 1 mg.
| Reducer | Conversions of NPh, % at pH 11/14 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Cu | Mg | Zn | |
| AA | - | 56.6/8.4 | - | 0.0/0.8 |
| NaBH4 | 5/7.7 | 93.9/9.2 | - | 0.5/3.0 |
| SF | 3.3/1.6 | 46.8/0.0 | - | 0.0/15.6 |
| FA | 12.3/12.0 | 87.5/0.0 | - | 0.0/3.0 |
The conversion of NPh at pH 11 and 14 depending on the type of PGM NPs and the addition of a non-precious metal, Fe, Cu, or Zn, is presented in Table A3.

Table A3.
Conversion of NPh at pH 11 and 14 depending on the type of PGM NPs and the addition of a non-precious metal: Fe. Catalyst mass: 1 mg.
Table A3.
Conversion of NPh at pH 11 and 14 depending on the type of PGM NPs and the addition of a non-precious metal: Fe. Catalyst mass: 1 mg.
| Amount of Catalyst, mg | Conversions of NPh, % at pH 11/14 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt/Fe | Pd/Fe | Ru/Fe | Rh/Fe | |
| 1 | 63.8/95.5 | 100/100 | - | 100/96.6 |
| 2 | 100/95.5 | 100/96.4 | - | 100/95.0 |
| 3 | 100/95.8 | 100/96.2 | - | 100/96.4 |
The conversion of NPh at pH 11 and 14 depending on the type of three- or four-component NPs is presented in Table A4.

Table A4.
Conversion of NPh at pH 11 and 14 depending on the type of three- or four-component NPs.
Table A4.
Conversion of NPh at pH 11 and 14 depending on the type of three- or four-component NPs.
| Reducer | Conversion of NPh, % at pH 11/14 |
|---|---|
| Pt/Pd/Rh | |
| AA | 88.7/88.2 |
| NaBH4 | 92.8/94.2 |
| FA | 80.1/79.7 |
| Pt/Pd/Rh/Ru | |
| AA | 92.0/91.9 |
| NaBH4 | 78.8/97.4 |
| SF | 88.1/69.1 |
| FA | 85.5/97.0 |
The conversion of NPh at pH 11 and 14 using a catalyst, precipitated from real solutions after 30 min, is presented in Table A5.

Table A5.
Conversion of NPh at pH 11 and 14 using catalyst from real solutions after 30 min.
Table A5.
Conversion of NPh at pH 11 and 14 using catalyst from real solutions after 30 min.
| Amount of Catalyst, mg | Conversions of NPh, % at pH 11/14 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | R3 | |
| 1 | 39.3/- | 0.0/0.0 | 13.3/96.7 |
| 3 | 42.2/- | 0.0/0.0 | 86.0/97.6 |
References
- Żelechowska, K. Nanotechnologia w Chemii i Medycynie; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Gdańskiej: Gdańsk, Poland, 2014; ISBN 9788373485457. [Google Scholar]
- Murty, B.S.; Shankar, P.; Raj, B.; Rath, B.B.; Murday, J. Textbook of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; ISBN 9783642280306. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, Applications and Toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husin, M.H.M.; Nordin, M.R.; Mohamad, I.S.; Yong, L.K. Pt–Cu Bimetallic Nanoparticles Synthesized by Polyol Method under Different Reduction Conditions. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. 2022, 6, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Viñes, F.; Görling, A. Explaining Cu@Pt Bimetallic Nanoparticles Activity Based on NO Adsorption. Chem. A Eur. J. 2020, 26, 11478–11491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.E.; Fakhri, D.; Seland, F.; Sunde, S.; Burheim, O.S.; Pollet, B.G. Sonochemical Synthesis of Cu@Pt Bimetallic Nanoparticles. Molecules 2022, 27, 5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.R.; Félix, R.M.; Reynoso, E.A.; Gochi-Ponce, Y.; Gómez, Y.V.; Moyado, S.F.; Alonso-Núñez, G. Synthesis of Pt and Pt-Fe Nanoparticles Supported on MWCNTs Used as Electrocatalysts in the Methanol Oxidation Reaction. J. Energy Chem. 2014, 23, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Wang, Q.; Xu, G.L.; Qin, X.; Hwang, I.; Sun, C.J.; Liu, M.; Hua, W.; Wu, H.-w.; Zhu, S.; et al. Atomically Dispersed Pt and Fe Sites and Pt–Fe Nanoparticles for Durable Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigarre, J.; Lecas, T.; Brault, P.; Caillard, A.; Bigarre, J.; Lecas, T.; Brault, P.; Pdpt, A.C.; Bigarre, J.; Lecas, T.; et al. PdPt Nanocatalyst Synthesis via Liquid Medium Sputtering. In Proceedings of the 24th International Symposium on Plasma Chemistry, Naples, Italy, 9–14 June 2019. Id: Hal-02394305. [Google Scholar]
- Rzelewska-Piekut, M.; Wiecka, Z.; Regel-Rosocka, M. Studies on the Formation of Catalytically Active PGM Nanoparticles from Model Solutions as a Basis for the Recycling of Spent Catalysts. Molecules 2022, 27, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Cruz, A.L.; Garza-Cervantes, J.A.; Vasto-Anzaldo, X.G.; García-Rivas, G.; León-Buitimea, A.; Morones-Ramírez, J.R. Synthesis and Design of Ag–Fe Bimetallic Nanoparticles as Antimicrobial Synergistic Combination Therapies against Clinically Relevant Pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiecka, Z.; Cota, I.; Tylkowski, B.; Regel-Rosocka, M. Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Automotive Converters and Their Conversion into Efficient Recyclable Nanocatalysts. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kancharla, S.; Sasaki, K. Selective extraction of precious metals from simulated automotive catalyst waste and their conversion to carbon supported PdPt nanoparticle catalyst. Colloids Surf. A 2023, 665, 131179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zheng, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Han, L.; Lin, R.; Xin, H.L.; Wang, D. Structurally Ordered Pt-Zn/C Series Nanoparticles as Efficient Anode Catalysts for Formic Acid Electrooxidation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 22129–22135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zou, C.; Wang, C.; Liang, H.; Chen, W.; Li, W. Effect of TiO2 Nanoparticles and SDBS on Corrosion Behavior of 3003 Aluminum Alloy in Aqueous Ethylene Glycol Containing Chloride Ions at High Temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 873, 159820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmat Esfe, M.; Alirezaie, A.; Toghraie, D. Thermal Conductivity of Ethylene Glycol Based Nanofluids Containing Hybrid Nanoparticles of SWCNT and Fe3O4 and Its Price-Performance Analysis for Energy Management. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Wang, B.; Gong, W.; He, Z.; Xu, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Fu, Q.; et al. Dual-Atom Pt Heterogeneous Catalyst with Excellent Catalytic Performances for the Selective Hydrogenation and Epoxidation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, P.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Design Strategy and Recent Progress of Fluorescent Probe for Noble Metal Ions (Ag, Au, Pd, and Pt). Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 432, 213712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Delgado, E.; Estirado, S.; Espino, J.; Viñuelas-Zahínos, E.; Luna-Giles, F.; Rodríguez Moratinos, A.B.; Pariente, J.A. Influence of Ligand Lipophilicity in Pt(II) Complexes on Their Antiproliferative and Apoptotic Activities in Tumour Cell Lines. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2022, 227, 111688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, B.C.F.J. Platinum Anti-Cancer. Plotinurn Metals Rev. 1989, 33, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Firmansyah, M.L.; Kubota, F.; Goto, M. Selective Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Automotive Catalysts by Leaching and Solvent Extraction. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2019, 52, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, M.L.; Slobozeanu, A.E.; Larosa, C.; Paneva, D.; Yakoumis, I.; Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z. Platinum Group Metals: Green Recovery from Spent Auto-Catalysts and Reuse in New Catalysts—A Review. Crystals 2023, 13, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birloaga, I.; Vegliò, F. An Innovative Hybrid Hydrometallurgical Approach for Precious Metals Recovery from Secondary Resources. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 307, 114567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.; Ting, Y.P. Recycling Pathways for Platinum Group Metals from Spent Automotive Catalyst: A Review on Conventional Approaches and Bio-Processes. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 170, 105588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, A.; Nogueira, C.A.; Paiva, A.P. Recovery of Platinum from a Spent Automotive Catalyst through Chloride Leaching and Solvent Extraction. Recycling 2021, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liu, C.; Cao, H.; Ning, P.; Jin, W.; Yang, Z. Understanding the Features of PGMs in Spent Ternary Automobile Catalysts for Development of Cleaner Recovery Technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 118031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, M. Selective Recovery of Pt, Pd, and Rh from Spent Catalysts by Functionalized Magnetite Nanoparticles. J. Min. Environ. 2022, 13, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajiv Gandhi, M.; Yamada, M.; Kondo, Y.; Shibayama, A.; Hamada, F. P-Sulfonatothiacalix [6]Arene-Impregnated Resins for the Sorption of Platinum Group Metals and Effective Separation of Palladium from Automotive Catalyst Residue. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 30, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Riaño, S.; Aktan, E.; Deferm, C.; Fransaer, J.; Binnemans, K. Solvometallurgical Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Automotive Catalysts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiecka, Z.; Rzelewska-Piekut, M.; Regel-Rosocka, M. Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Automotive Converters by Leaching with Organic and Inorganic Acids and Extraction with Quaternary Phosphonium Salts. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 280, 119933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzelewska-Piekut, M.; Regel-Rosocka, M. Separation of Pt(IV), Pd(II), Ru(III) and Rh(III) from Model Chloride Solutions by Liquid-Liquid Extraction with Phosphonium Ionic Liquids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, K.; Bárczy, P.; Somosvári, B.M. Impact of Corrosive Liquid on Trivalent Chromium over Aluminium Alloys. J. Surf. Eng. Mater. Adv. Technol. 2017, 7, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Understanding of the Major Reactions in Solution Synthesis of Functional Nanomaterials. Sci. China Mater. 2016, 59, 938–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, L.; Amato, A.; Beolchini, F. Recovery of Indium from Liquid Crystal Displays. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 116, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.M.; Zhou, D.B.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ichino, R.; Okido, M. Preparation of Cu Nanoparticles with NaBH4 by Aqueous Reduction Method. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, F.; Riaño, S.; Binnemans, K. Dissolution of Noble Metals in Highly Concentrated Acidic Salt Solutions. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 8230–8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyribey, B.; Çorbacioǧlu, B.; Altin, Z. Synthesis of Platinum Particles from H2PtCl6 with Hydrazine as Reducing Agent. Gazi Univ. J. Sci. 2009, 22, 351–357. [Google Scholar]
- Awadalla, F.T.; Molnar, R.E.; Ritcey, G.M. Recovery of Platinum Group Metals (PGM) from Acidic Solutions by Reduction Precipitation with Sodium Borohydride. Patent CA2016492A1, 10 November 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Grzeschik, R.; Schäfer, D.; Holtum, T.; Küpper, S.; Hoffmann, A.; Schlücker, S. On the Overlooked Critical Role of the PH Value on the Kinetics of the 4-Nitrophenol NaBH 4-Reduction Catalyzed by Noble-Metal Nanoparticles (Pt, Pd, and Au). J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 2939–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).