Color Reversion of Refined Vegetable Oils: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
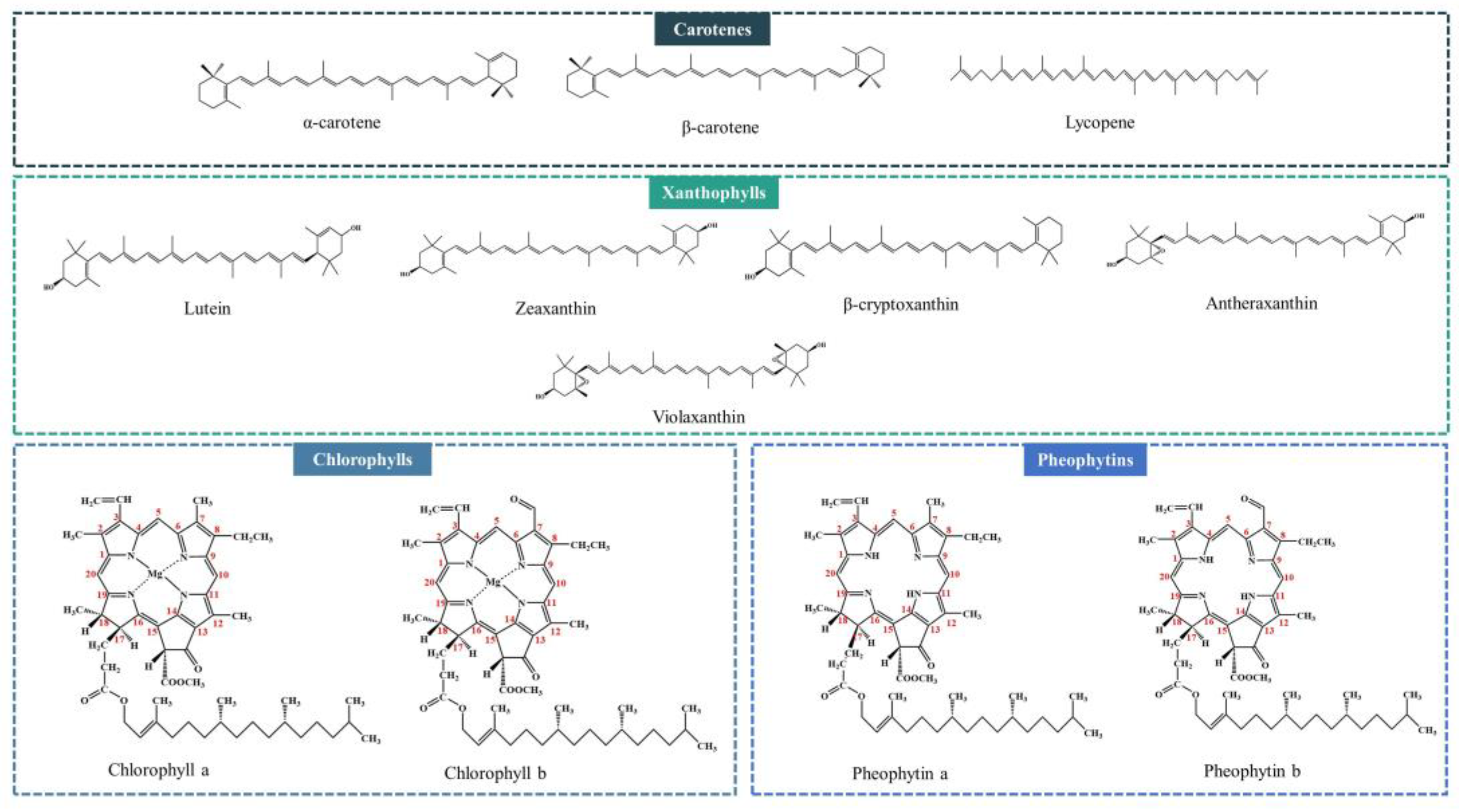
2. The Color of Vegetable Oils
2.1. Natural Pigments
2.2. Processing Pigments
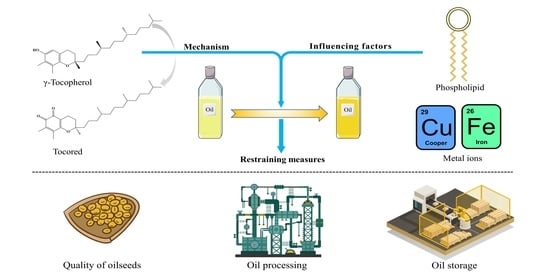
3. The Mechanism of Color Reversion
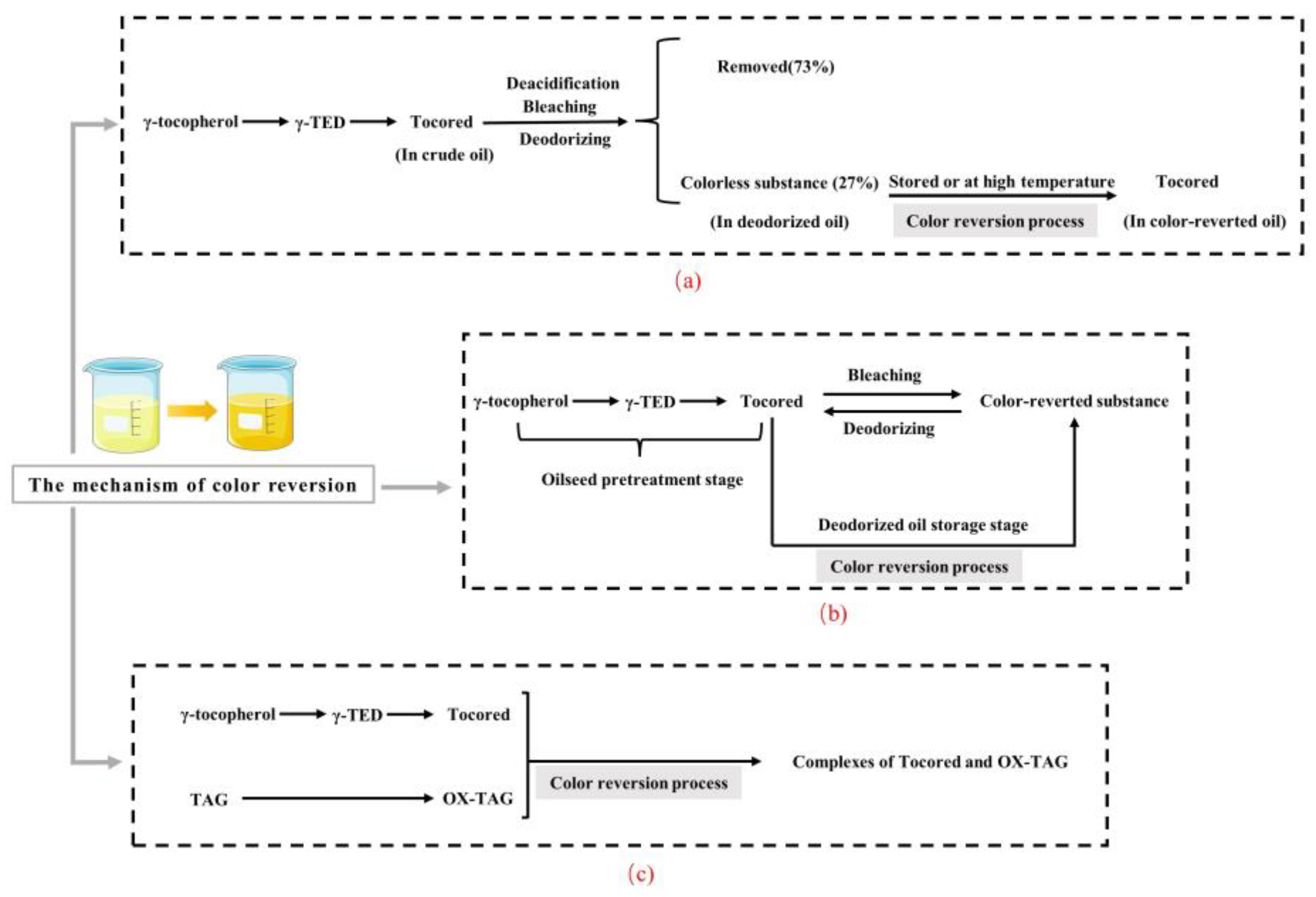
3.1. The Mechanism
3.2. The Relationship between Color Reversion and Oil Oxidation
4. Minor Components Affecting Color Reversion
4.1. Phospholipids
4.2. Metal Ions
5. Restraining Measures for Color Reversion
5.1. The Quality Control of Oilseeds
5.2. Pretreatment Process
5.3. Oil Extraction Process
5.4. Refining Process
5.4.1. Degumming
5.4.2. Deacidification
5.4.3. Bleaching
5.4.4. Deodorization
5.4.5. Dewaxing
5.4.6. Moderate Refining
5.5. Storage of Refined Vegetable Oils
5.5.1. External Environment for Oil Storage
5.5.2. The Use of Antioxidants
6. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Wu, G.-C.; Zheng, L.-Y.; Huang, J.-H.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Q.-Z.; Wang, X.-G. Model Prediction of Color Reversion of Soybean Oil and Its Quantitative Relationship with Oxidation Under Accelerated Conditions. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 111, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzio, C.R.; Díaz, R.J.; Dini, N.G. In-Line Measurement of Sunflower Oil Color in the Lovibond Scale Using a Low-Cost Robust Device. J. Food Eng. 2014, 120, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Saleh, A.S.M.; Chen, J.; Shen, Q. Chemical Alterations Taken Place During Deep-Fat Frying Based on Certain Reaction Products: A Review. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 2012, 165, 662–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyano, M.J.; Heredia, F.J.; Meléndez-Martínez, A.J. The Color of Olive Oils: The Pigments and Their Likely Health Benefits and Visual and Instrumental Methods of Analysis. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. 2010, 9, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.-Y.; Guo, H.-Y.; Xie, L.-L.; Korma, S.A.; Jin, J.; Jin, Q.-Z.; Cacciotti, I. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies of Tocored Thermal Degradation in Lipid Systems with Various Degrees of Unsaturation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 160, 113230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Q.; Xu, X.-B.; Jiang, Y.-R.; Wang, X.-G. Effect of Tocopherols and Phytosterol on Color Reversion of MCT. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2013, 19, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, A.F.; McIntyre, J.D. Observations on the Influence of Free Fatty Acids on Color Changes in Corn Oil. Cotton Oil Press. 1922, 5, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechary, J.M.; Kupperman, R.P.; Thurber, F.H.; O’Connor, R.T. The Pigments of Crude Cottonseed Oils. I. The Inhibition of Color Reversion in Crude Cottonseed Oils. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1954, 31, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, C.E.; Mann, G.E.; Fisher, G.S. Gamma-Tocopherol as a Precursor of a Red Quinoid Substance Developed in Cottonseed Oil During Oxidation. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1944, 21, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Tomita, S.; Komoda, M. On the Color Reversion in Edible Soybean Oil. I. J. Jpn. Oil Chem. Soc. 1960, 9, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, S.; Komoda, M.; Enomoto, S.; Ōnuki, N. Characteristics for the Illinois Soybean of 1963 Crop Color Reversion of the Refined and Deodorized Soybean Oil. II. J. Jpn. Oil Chem. Soc. 1964, 13, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komoda, M.; Ōnuki, N.; Harada, I. Studies on Cause of Color Reversion of Edible Soybean Oil and Its Prevention: Part I. Relation Between the Moisture of Soybeans and the Quantity of Tocopherol in Them. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1966, 30, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komoda, M.; Ōnuki, N.; Harada, I. Studies on Cause of Color Reversion of Edible Soybean Oil and Its Prevention: Part II. Tocored as a Precursor of Color Reversion of Soybean Oil. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1967, 31, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.-T.; Lin, W.-M.; Chu, Y.-H.; Chen, S.-L.Y.; Kong, K.-S.; Chen, C.-W. The Mechanism of Color Reversion in Soybean Salad Oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1989, 66, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.-H.; Lin, W.-M. Effect of Soybean Pretreatment on the Color Quality of Soybean Oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1990, 67, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Q. Study on Mechanism of Color Reversion in Vegetable Oils and Fats during Storage. Ph.D. Thesis, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mariod, A.; Matthäus, B.; Eichner, K.; Hussein, I.H. Effects of Deodorization on the Quality and Stability of Three Unconventional Sudanese Oils. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2006, 108, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamwonglumlert, L.; Devahastin, S.; Chiewchan, N. Natural Colorants: Pigment Stability and Extraction Yield Enhancement via Utilization of Appropriate Pretreatment and Extraction Methods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3243–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamwonglumlert, L.; Devahastin, S.; Chiewchan, N.; Raghavan, V. Plant Carotenoids Evolution during Cultivation, Postharvest Storage, and Food Processing: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1561–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meléndez-Martínez, A.J.; Mandić, A.I.; Bantis, F.; Böhm, V.; Borge, G.I.A.; Brnčić, M.; Bysted, A.; Cano, M.P.; Dias, M.G.; Elgersma, A.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on Carotenoids in Foods and Feeds: Status Quo, Applications, Patents, and Research Needs. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandul-Rojas, B.; Minguez-Mosquera, M.I. Chlorophyll and Carotenoid Composition in Virgin Olive Oils from Various Spanish Olive Varieties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1996, 72, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, A.; Cerretani, L.; Cichelli, A. Chlorophylls in Olive and in Olive Oil: Chemistry and Occurrences. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, E.; Min, D.B. Mechanisms and Factors for Edible Oil Oxidation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2006, 5, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Minor Components in Food Oils: A Critical Review of Their Roles on Lipid Oxidation Chemistry in Bulk Oils and Emulsions. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 901–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.-C.; Moreira, R.; Sun, X. Total Frying-Use Time Effects on Soybean-Oil Deterioration and on Tortilla Chip Quality. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1996, 31, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekha, B.; Lokesh, B.R.; Gopala Krishna, A.G. Chemistry of Color Fixation in Crude, Physically Refined and Chemically Refined Rice Bran Oils Upon Heating. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H. Composition and Quality Characteristics of Sesame Seed (Sesamum Indicum) Oil Roasted at Different Temperatures in an Electric Oven. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1994, 65, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, R.; Olmo, C.; Navarro, J.L.; Hidalgo, F.J. Contribution of Phospholipid Pyrrolization to the Color Reversion Produced during Deodorization of Poorly Degummed Vegetable Oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 4166–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, S.R.; Terao, J.; Matsushita, S. Effect of Browning Reaction Products of Phospholipids on Autoxidation of Methyl Linoleate. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1986, 63, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starowicz, M.; Zieliński, H. How Maillard Reaction Influences Sensorial Properties (Color, Flavor and Texture) of Food Products? Food Rev. Int. 2019, 35, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.; Yokoyama, Y.; Kasahara, Y.; Hamaguchi, N.; Tsuji, T.; Tebayashi, S.-I.; Kim, C.-S.; Koh, H.-S. Heat Deterioration of Phospholipids. V. A New Rearrangement Reaction of Sugars and Phosphatidylethanolamine. J. Oleo Sci. 2007, 56, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthäus, B. Oil Technology. In Advances in Botanical Research; Gupta, S.K., Delseny, M., Kader, J.-C., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; Volume 45, pp. 483–527. [Google Scholar]
- Sono, R.; Ban, N.; Sakamoto, S.; Hamaguchi, N.; Tebayashi, S.-I.; Kim, C.-S.; Koh, H.-S.; Horiike, M. Heat Deterioration of Phospholipids I: Decomposition of Soybean Lecithin and Formation of New Products by Heating. J. Oleo Sci. 2001, 50, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.-H.; Lin, J.-Y. Factors Affecting the Content of Tocopherol in Soybean Oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1993, 70, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.-Y.; Jin, J.; Shi, L.-K.; Huang, J.-H.; Chang, M.; Wang, X.-G.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Q.-Z. Gamma Tocopherol, Its Dimmers, and Quinones: Past and Future Trends. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3916–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namiki, M. Nutraceutical Functions of Sesame: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 651–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, R.; Kinoshita, T.; Iwamoto, S. Iron-Catalyzed Reaction of γ-Tocopherol with Methyl Linoleate Hydroperoxides in Solutions. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2018, 95, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreps, F.; Burčová, Z.; Schmidt, Š. Degradation of Fatty Acids and Tocopherols to Form Tocopheryl Quinone as Risk Factor during Microwave Heating, Pan-Frying and Deep-Fat Frying. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1600309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, R. Vitamin E: Mechanism of Its Antioxidant Activity. Food Sci. Technol. Int. Tokyo 1997, 3, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komoda, M.; Harada, I. A Dimeric Oxidation Product of γ-Tocopherol in Soybean Oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1969, 46, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komoda, M.; Harada, I. Interaction of Tocored with Unsaturated Fatty Esters. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1970, 47, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.-Y.; Karrar, E.; Xie, L.-L.; Jin, J.; Huang, J.-H.; Wang, X.-G.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Q.-Z. High-Purity Tocored Improves the Stability of Stripped Corn Oil Under Accelerated Conditions. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2020, 122, 1900307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.-Y.; Jin, J.; Karrar, E.; Xie, L.-L.; Huang, J.-H.; Chang, M.; Wang, X.-G.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Q.-Z. Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of Tocored through Chemical Assays, Evaluation in Stripped Corn Oil, and CAA Assay. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2020, 122, 1900354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.-Y.; Jin, J.; Karrar, E.; Huang, J.-H.; Chang, M.; Wang, X.-G.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Q.-Z. Insights Into Effects of Temperature and Ultraviolet Light on Degradation of Tocored with HPLC and UPC2-QTOF-MS. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 126, 109302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, N.M.; Al-Okaby, M.F. Study to Solve the Problem of Color Reversion in Refined Soybean Oil. Food Nutr. Sci. 2022, 13, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyasit, W.; Elias, R.J.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Role of Physical Structures in Bulk Oils on Lipid Oxidation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.-C.; Tang, J.-P.; Yan, Z.-H.; Sun, Y.-P.; Zhan, Y.-M.; Hu, J.-H. Effect of Refining Process on the Color Reversion of Soybean Oil. China Oils Fats 2021, 46, 7–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-F.; Jin, Q.-Z.; Wu, S.-M.; Wang, X.-G. Contribution of Phospholipids to the Formation of Fishy Off-Odor and Oxidative Stability of Soybean Oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, S.C.; Nyam, K.L. Refining of Edible Oils. In Lipids and Edible Oil: Properties, Processing, and Applications; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; pp. 213–241. [Google Scholar]
- Garrido, M.D.; Frías, I.; Díaz, C.; Hardisson, A. Concentrations of Metals in Vegetable Edible Oils. Food Chem. 1994, 50, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-N.; Sun, H.; Hu, L.-Z.; Yu, D.-Y. Decolorization of Soybean Oil by Attapulgite Adsorbent and Its Color Reversion. Food Sci. 2013, 34, 1–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-H.; Li, Z.-P.; Shi, M.; Wang, J.-G.; Yu, D.-Y. Effect of Moderate Processing on Color and Lustre of Soybean Oil. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2012, 33, 65–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flider, F.J.; Orthoefer, F.T. Metals in Soybean Oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1981, 58, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, I.; Saratani, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Studies on the Color Reversion of Refined and Deodorized Soybean Oil. Part III Influences of Iron and Antioxidants on Color Reversion. Nippon Nogei Kagaku Kaishi 1960, 34, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Guo, A.-Q.; Wang, H. Mechanisms of Oxidative Browning of Wine. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, I.; Saratani, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Studies on the Color Reversion of Refined and Deodorized Soybean Oil. Part VI The Influence of Tocopherol, Carotenoid and Sterol Isolated from Soybean Oil on the Color Reversion of Refined Soybean Oil. Nippon Nogei Kagaku Kaishi. 1960, 34, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Lü, R.; Xu, H.-C.; Zuo, H. Preventive Measurements for Color Reverse and Acid Reverse of Refined Soybean Oil. China Oils Fats 2019, 44, 30–32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-H.; Gao, Y.-Z.; Chen, F.-X.; Hu, M.; Yang, B.-T. Study on Color Reversion of Corn Oil. Cereals Oils 2010, 9, 10–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, H.B.W. Bleaching of Important Fats and Oils. In Bleaching and Purifying Fats and Oils: Theory and Practice, 2nd ed.; List, G., Ed.; AOCS Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 2010; pp. 97–151. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.-L.; Gu, K.-R.; Sun, D.-X. Effect of Mature Degree of Domestic Soybean on Bleaching and Color Reversion of Soybean Oil. China Oils Fats 2004, 29, 24–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.-Y.; Zhu, M.-M.; Zhang, F.; Jin, J.; Jin, Q.-Z.; Guo, H.-Y. Activity and Characterization of Tocopherol Oxidase in Corn Germs and Its Relationship with Oil Color Reversion. Molecules. 2023, 23, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-S.; Liu, B.-Z.; Zheng, Y.-T.; Yang, F.; Du, X.-L.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Li, Y.-S.; Tang, Y.-E. Effect of Tocopherols on Color Reversion during Soybean Oil Storage. Cereal Food Ind. 2016, 23, 8–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zheng, C.-J.; Liu, G.Q. Effect Factors Analysis of Soybean Oil Color. China Oils Fats 2005, 30, 20–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, G.R.; Mounts, T.L.; Lanser, A.C. Factors Promoting the Formation of Nonhydratable Soybean Phosphatides. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1992, 69, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.P.J.; Prasad, S.R.; Banerjee, R.; Agarwal, D.K.; Kulkarni, K.S.; Ramesh, K.V. Green Solvents and Technologies for Oil Extraction from Oilseeds. Chem. Cent. J. 2017, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Q.; Lü, R.; Xu, H.-C.; Zhang, X.-P.; Zuo, H.; Fan, Z.-B. Color and Acid Reversion Control of First Grade Refined Soybean Oil. China Oils Fats 2021, 46, 129–132. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazani, S.M.; Marangoni, A.G. Minor Components in Canola Oil and Effects of Refining on These Constituents: A Review. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2013, 90, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, A.J. About Water Degumming and the Hydration of Non-hydratable Phosphatides. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1600496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengar, G.; Kaushal, P.; Sharma, H.K.; Kaur, M. Degumming of Rice Bran Oil. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2014, 30, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.P. Analysis of Soybean Salad Oil Color Reversion and Prevention. China Oils Fats 2001, 26, 25–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Gao, Y.-Q. Reasons Analysis and Treatment of Oil Color Reversion. China Oils Fats 2003, 28, 26–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-Y. Color Reversion of Refined Soybean Oil. China Oils Fats 2008, 33, 17–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisali, C.; Charanyaa, S.; Belur, P.D.; Regupathi, I. Refining of Edible Oils: A Critical Appraisal of Current and Potential Technologies. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharby, S. Refining Vegetable Oils: Chemical and Physical Refining. Sci. World J. 2022, 2022, 6627013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Q.; Zhang, J.-X. Reasons and Treatment of Soybean Salad Oil Color Reversion. China Oils Fats 2000, 25, 79–81. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maza, A.; Ormsbee, R.A.; Strecker, L.R. Effects of Deodorization and Steam-Refining Parameters on Finished Oil Quality. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1992, 69, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimal, T.N.B.; Vali, S.R.; Rao, B.V.S.K.; Chakrabarti, P.P.; Vijayalakshmi, P.; Kale, V.; Rani, K.N.P.; Rajamma, O.; Bhaskar, P.S.; Rao, T.C. Origin of Problems Encountered in Rice Bran Oil Processing. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2002, 104, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zschau, W. Bleaching of Edible Fats and Oils. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2001, 103, 505–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, A.D. Some Basic Factors in the Bleaching of Fatty Oils. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1964, 41, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, M.R.; Siew, W.L.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Hussein, R.; Kuntom, A.; Razak, R.A.A.; Nesaretnam, K. Effects of Degumming and Bleaching on 3-MCPD Esters Formation during Physical Refining. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K. Practical Guide to Vegetable Oil Processing; AOCS Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 2017; pp. 217–247. [Google Scholar]
- An, H.; Ma, Y.-X.; Wang, X.-D.; Zheng, Y.-Z. Effects of Deodorization on the Formation of Processing Contaminants and Chemical Quality of Sunflower Oil. J. Oleo Sci. 2022, 71, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decap, P.; Braipson-Danthine, S.; Vanbrabant, B.; Greyt, W.D.; Deroanne, C. Comparison of Steam and Nitrogen in the Physical Deacidification of Soybean Oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2004, 81, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-L. Discuss on the Factors of Affecting Rapeseed Salad Colour Reversion. China Oils Fats 2002, 27, 40–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjula, S.; Subramanian, R. Membrane Technology in Degumming, Dewaxing, Deacidifying, and Decolorizing Edible Oils. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 569–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.-P.; Wei, W.; Guo, Z. Moderate Edible Oil Refining: State-of-the-Art in China. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2020, 97, 1277–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.-Y.; Wang, X.-G.; He, D.-P. Origin, Progress and Development Trend of the Theory of Accurate and Moderate Processing of Edible Oil. China Oils Fats 2019, 44, 1–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Harada, I.; Saratani, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Studies on the Color Reversion of Refined and Deodorized Soybean Oil. Part I Effects of Temperature, Air and Light on the Color Reversion of Refined Soybean Oil, and Method of Measuring Color Reversion. Nippon Nogei Kagaku Kaishi 1960, 34, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.-S. Reason and Prevention of Color Reversion of Corn Oil in Summer. Korean J. Food Preserv. 2004, 11, 485–490. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhao, H.-M.; Hui, J.; Wang, X.-Y.; Wang, M.-Y.; Cao, B.-H.; Liu, R.-L.; Shen, Y.-L.; Li, X.-L. Effect of Ascorbyl Palmitate on the Storage Stability of Maize Oil. China Oils Fats 2021, 46, 108–111. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, S.; Abdullah; Zhang, H.; Weiss, J. A Comprehensive Review on Polarity, Partitioning, and Interactions of Phenolic Antioxidants at Oil-Water Interface of Food Emulsions. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4250–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqsood, S.; Benjakul, S.; Abushelaibi, A.; Alam, A. Phenolic Compounds and Plant Phenolic Extracts as Natural Antioxidants in Prevention of Lipid Oxidation in Seafood: A Detailed Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 1125–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana da Silva, M.; Santos, M.R.C.; Alves Silva, I.R.; Macedo Viana, E.B.; Dos Anjos, D.A.; Santos, I.A.; Barbosa de Lima, N.G.; Wobeto, C.; Jorge, N.; Lannes, S.C.D.S. Synthetic and Natural Antioxidants Used in the Oxidative Stability of Edible Oils: An Overview. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38, 349–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-Q.; Liu, A.-M.; Hu, S.-Y.; Ares, I.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.-R.; Wang, X.; Martínez, M.; Anadón, A.; Martínez, M.-A. Synthetic Phenolic Antioxidants: Metabolism, Hazards and Mechanism of Action. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, M.S. Natural Antioxidants: Sources, Compounds, Mechanisms of Action, and Potential Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.-Y.; Li, S.-L.; Li, X.-L.; Wang, X.-Y.; Wang, F.-Y. Research on Key Factors and Control Measures of Color Reversion in Plant Oils. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2022, 37, 143–149. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Yadav, D.N.; Ahmad, T.; Narsaiah, K. Recent Trends in the Use of Natural Antioxidants for Meat and Meat Products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 796–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
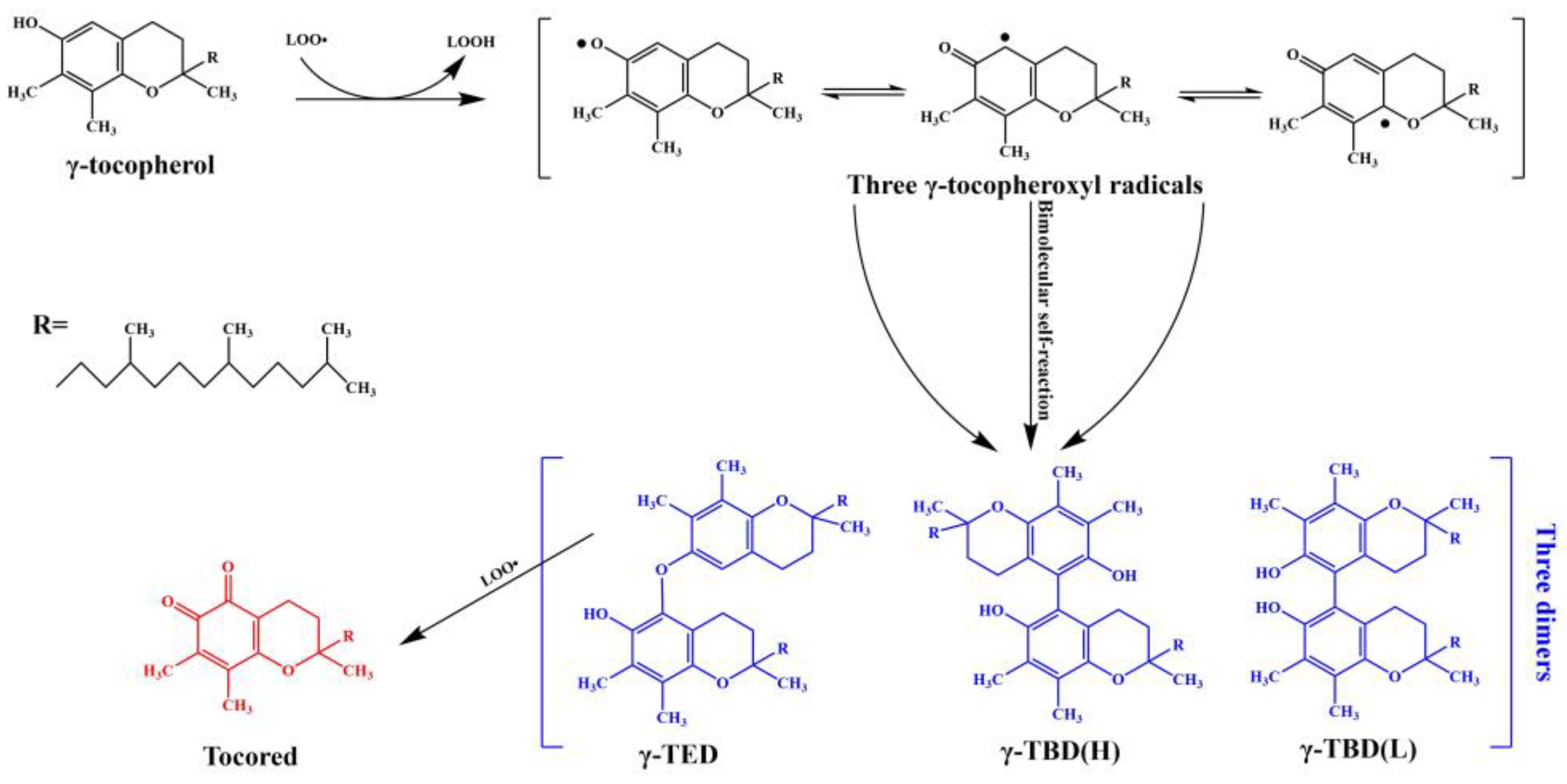

| Compound | Abbreviation | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | IUPAC Name | PubChem CID | UVmax in Methanol (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| γ-Tocopherol | – | C28H48O2 | 416.7 | (2R)-2,7,8-trimethyl-2-[(4R,8R)-4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl]-3,4-dihydrochromen-6-ol | 92729 | 211, 257, 298 |
| 5-(γ-Tocopheroxy)-γ-tocopherol | γ-TED | C56H94O4 | 831.3 | 2,7,8-trimethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-5-[[2,7,8-trimethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-3,4-dihydrochromen-6-yl]oxy]-3,4-dihydrochromen-6-ol | 11735491 | 203, 293 |
| 5-(γ-Tocopheryl)-γ-tocopherol (H) | γ-TBD(H) | C56H94O4 | 831.3 | cis-5-[6-hydroxy-2,7,8-trimethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-3,4-dihydrochromen-5-yl]-2,7,8-trimethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-3,4-dihydrochromen-6-ol | 13517848 | 203, 302 |
| 5-(γ-Tocopheryl)-γ-tocopherol (L) | γ-TBD(L) | C56H94O4 | 831.3 | trans-5-[6-hydroxy-2,7,8-trimethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-3,4-dihydrochromen-5-yl]-2,7,8-trimethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-3,4-dihydrochromen-6-ol | – | 205, 293 |
| γ-Tocopherol-5,6-quinone | Tocored | C28H46O3 | 430.7 | (2R)-2,7,8-trimethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-3,4-dihydrochromene-5,6-dione | 101701364 | 208, 284, 471 |
| Physicochemical Properties | Deodorized Oil | Color-Reverted Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Color (red value) | 1.3 | 4.2 |
| Color (yellow value) | 8 | 18 |
| Peroxide value (meq kg−1) | 0.42 | 0.6 |
| p-Anisidine value | 2.98 | 3.28 |
| Total oxidative value | 0.789 | 1.259 |
| Unsaponifiable matter (%) | 0.45 | 0.40 |
| Saponification value (mg KOH g−1) | 194.62 | 194.28 |
| Total polyphenols (mg kg−1) | 1.85 | 1.64 |
| Pretreatment | Condition | Phosphorus Content (mg kg−1) | γ-Tocopherol (mg kg−1) | Oil Color (Lovibond Red/Yellow Value) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude Oil | Degummed Oil | Reduction (%) | Deodorized Oil | Color-Reverted Oil | ΔR | |||
| Control | Without any treatment | 494 | 426 | 13.80 | 92 | 3.6/42 | 12/70 | 8.4 |
| Steam | 100 °C, 1 min | 708 | 40 | 94.4 | 733 | 0.5/3.0 | 1.4/10 | 0.9 |
| Steam | 100 °C, 1.5 min | 717 | 18 | 97.5 | 651 | 0.5/2.6 | 1.3/9.4 | 0.8 |
| Steam | 100 °C, 2.0 min | 563 | 34 | 94.0 | 686 | 0.5/3.1 | 1.4/10 | 0.9 |
| Toast | 110 °C, 30 min | 535 | 187 | 65.0 | 227 | 2.2/13 | 4.2/35 | 2 |
| Toast | 130 °C, 30 min | 564 | 193 | 65.8 | 377 | 1.4/6.7 | 2.5/20 | 1.1 |
| Toast | 150 °C, 30 min | 587 | 208 | 64.5 | 452 | 1.2/7.6 | 2.1/14 | 0.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Sun, S. Color Reversion of Refined Vegetable Oils: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 5177. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135177
Chen X, Sun S. Color Reversion of Refined Vegetable Oils: A Review. Molecules. 2023; 28(13):5177. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135177
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiaozhong, and Shangde Sun. 2023. "Color Reversion of Refined Vegetable Oils: A Review" Molecules 28, no. 13: 5177. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135177
APA StyleChen, X., & Sun, S. (2023). Color Reversion of Refined Vegetable Oils: A Review. Molecules, 28(13), 5177. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135177