The Therapeutic Value of Solanum Steroidal (Glyco)Alkaloids: A 10-Year Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
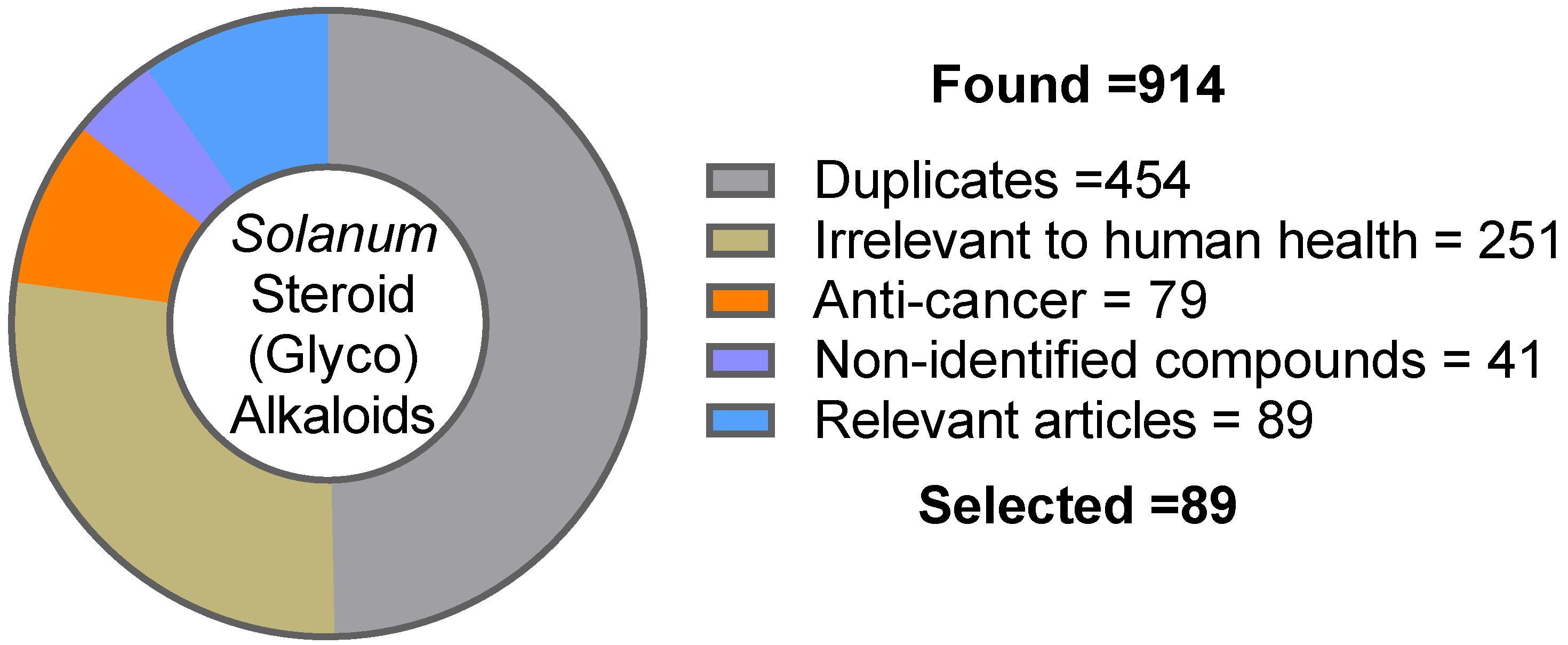
2. Methodology
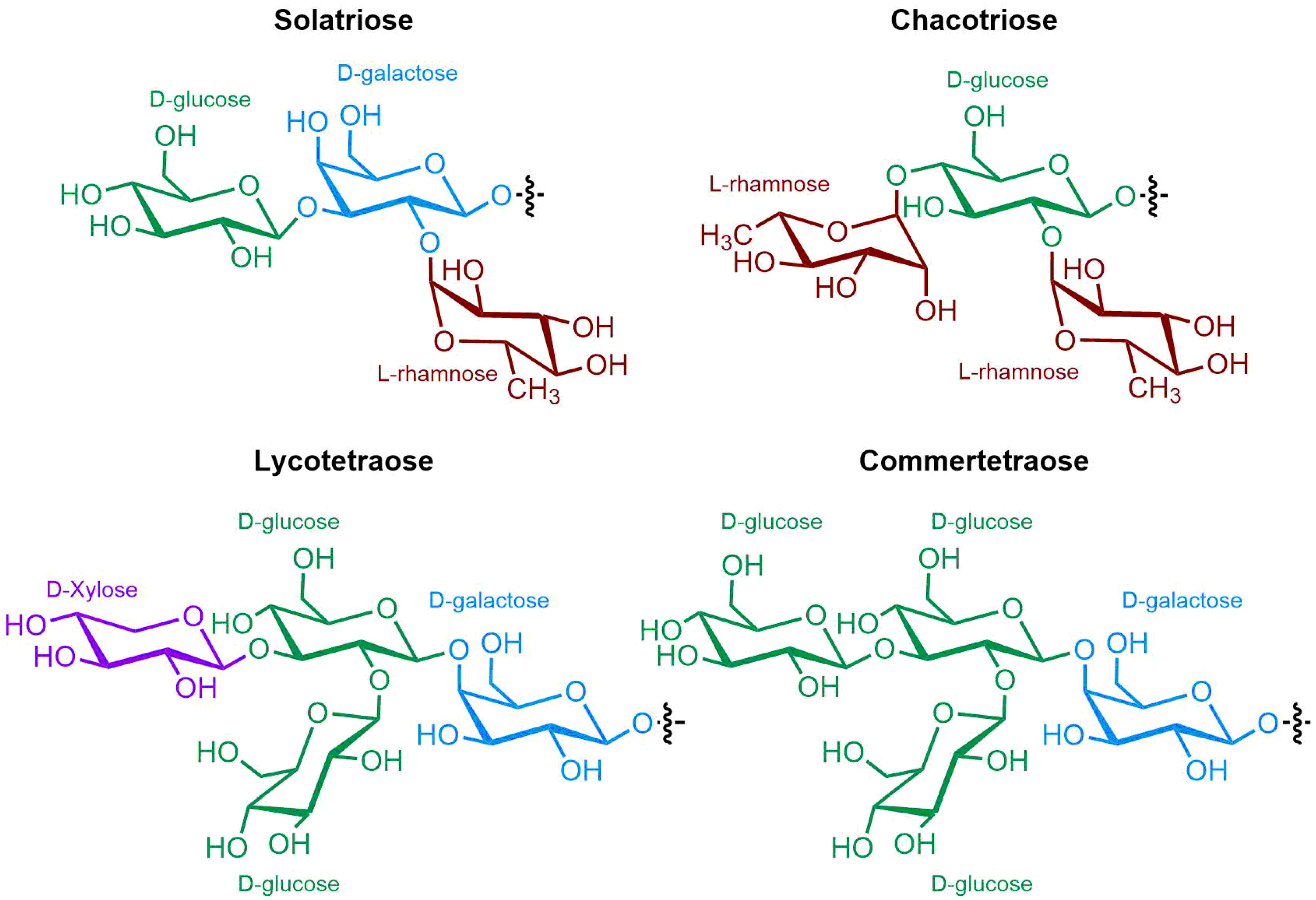
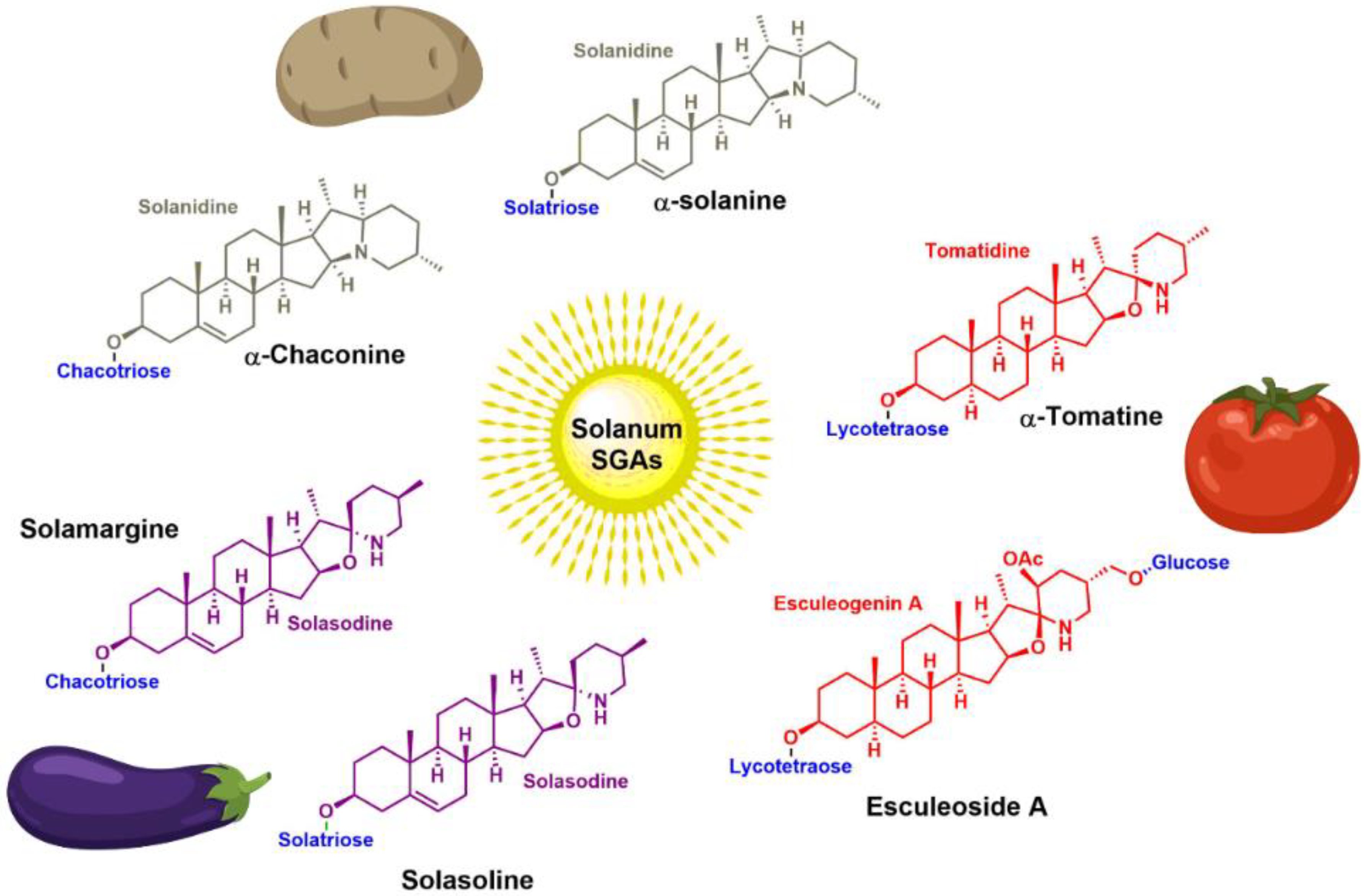
3. Steroidal (Glyco)Alkaloids: Classification
4. Occurrence of Solanum SGAs
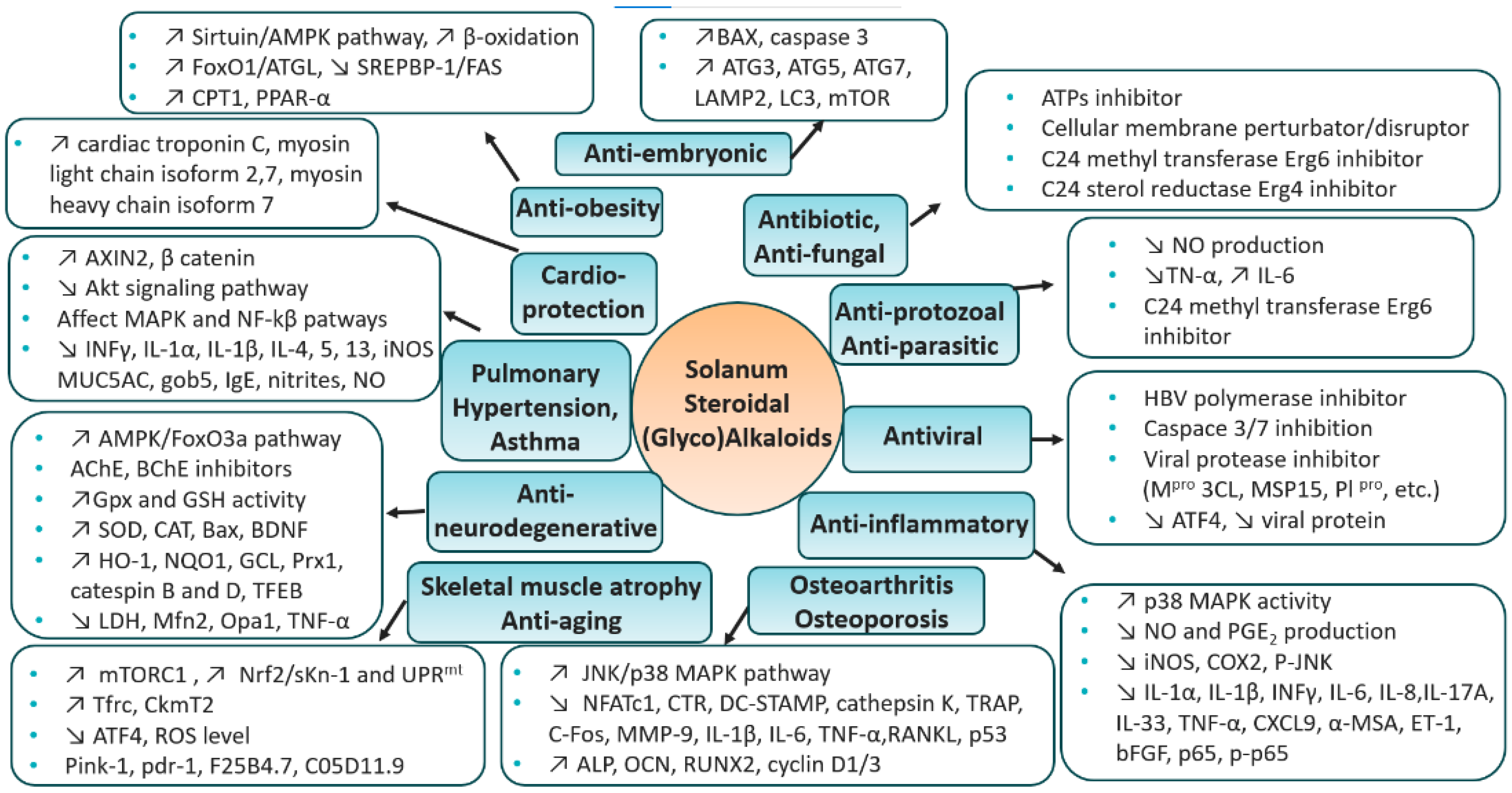
5. Therapeutic Context—Solanum S(G)As
5.1. Antibiotic
5.2. Antifungal
5.3. Anti-Protozoal/Anti-Parasitic
5.4. Antiviral
5.5. Anti-Inflammatory
5.6. Osteoarthritis
5.7. Osteoporosis
5.8. Skeletal Muscle Atrophy
5.9. Anti-Aging
5.10. Anti-Neurodegenerative
5.11. Pulmonary Hypertension
5.12. Asthma
5.13. Antitussive
5.14. Cardioprotection
5.15. Anti-Obesity
5.16. Anti-Embryonic
5.17. Cancer Treatment
5.18. Summary
6. Toxicity & Therapeutic Challenges
6.1. Gastrointestinal Distress
6.2. Neurological Symptoms
6.3. Cardiac Effects
6.4. Respiratory Effects
6.5. Renal Effects
6.6. Teratogenic Effects
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
References
- Jain, R.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, S.; Sarethy, I.P.; Gabrani, R. Solanum Nigrum: Current Perspectives on Therapeutic Properties. Altern. Med. Rev. 2011, 16, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M.; Levin, C.E. Dehydrotomatine Content in Tomatoes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4571–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Potato Glycoalkaloids and Metabolites: Roles in the Plant and in the Diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8655–8681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarz, H.; Roloff, N.; Niehaus, K. Mass Spectrometry Imaging of the Spatial and Temporal Localization of Alkaloids in Nightshades. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13470–13477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingey, W.M. Glycoalkaloids as Pest Resistance Factors. Am. Potato J. 1984, 61, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, P.; Muller, M.C.; Ekengren, S.; McKee, L.S.; Bulone, V. The Impact of Steroidal Glycoalkaloids on the Physiology of Phytophthora Infestans, the Causative Agent of Potato Late Blight. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2017, 30, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Tomato Glycoalkaloids: Role in the Plant and in the Diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5751–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogelman, E.; Oren-Shamir, M.; Hirschberg, J.; Mandolino, G.; Parisi, B.; Ovadia, R.; Tanami, Z.; Faigenboim, A.; Ginzberg, I. Nutritional Value of Potato (Solanum tuberosum) in Hot Climates: Anthocyanins, Carotenoids, and Steroidal Glycoalkaloids. Planta 2019, 249, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowanski, S.; Winkiel, M.; Szymczak-Cendlak, M.; Marciniak, P.; Manczak, D.; Walkowiak-Nowicka, K.; Spochacz, M.; Bufo, S.A.; Scrano, L.; Adamski, Z. Solanaceae Glycoalkaloids: Alpha-Solanine and Alpha-Chaconine Modify the Cardioinhibitory Activity of Verapamil. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panelon Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM); Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.; Nebbia, C.S.; et al. Risk Assessment of Glycoalkaloids in Feed and Food, in Particular in Potatoes and Potato-derived Products. EFS2 2020, 18, e06222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D. Potato Glycoalkaloids: Some Unanswered Questions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1996, 7, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.; Lee, K.-R.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, I.-S.; Kozukue, N. Anticarcinogenic Effects of Glycoalkaloids from Potatoes against Human Cervical, Liver, Lymphoma, and Stomach Cancer Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6162–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sinani, S.S.S.; Eltayeb, E.A. The Steroidal Glycoalkaloids Solamargine and Solasonine in Solanum Plants. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 112, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbhatu, D.B.; Abraha, H.B. Preliminary Antimicrobial Profile of Solanum incanum L.: A Common Medicinal Plant. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2020, 2020, 3647065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, O.M.; McCarthy, C.M.; Brunton, N.P.; Hossain, M.B.; Rai, D.K.; Collins, S.G.; Jones, P.W.; Maguire, A.R.; O’Brien, N.M. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Potato Glycoalkaloids in Stimulated Jurkat and Raw 264.7 Mouse Macrophages. Life Sci. 2013, 92, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Most, R.G.; Himbeck, R.; Aarons, S.; Carter, S.J.; Larma, I.; Robinson, C.; Currie, A.; Lake, R.A. Antitumor Efficacy of the Novel Chemotherapeutic Agent Coramsine Is Potentiated by Cotreatment With CpG-Containing Oligodeoxynucleotides. J. Immunother. 2006, 29, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, S.E.; Brunton, N.P.; Jones, P.W.; O’ Brien, N.M.; Collins, S.G.; Maguire, A.R. Bioactivities of Glycoalkaloids and Their Aglycones from Solanum Species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3454–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.-K.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.-Y.; Kennelly, E.J. Solanum Steroidal Glycoalkaloids: Structural Diversity, Biological Activities, and Biosynthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 1423–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munafo, J.P., Jr.; Gianfagna, T.J. Chemistry and Biological Activity of Steroidal Glycosides from the Lilium Genus. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 454–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.-L.; Hu, B.-Y.; Qi, Z.-H.; Wang, X.-N.; Xie, T.-Z.; Wang, Z.-J.; Ma, D.-Y.; Zeng, Q.; Luo, X.-D. Chemistry and Bioactivities of Natural Steroidal Alkaloids. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2022, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eich, E. Solanaceae and Convolvulaceae: Secondary Metabolites; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria-Silva, C.; de Sousa, M.; Carvalheiro, M.C.; Simões, P.; Simões, S. Alpha-Tomatine and the Two Sides of the Same Coin: An Anti-Nutritional Glycoalkaloid with Potential in Human Health. Food Chem. 2022, 391, 133261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailly, C. The Steroidal Alkaloids α-Tomatine and Tomatidine: Panorama of Their Mode of Action and Pharmacological Properties. Steroids 2021, 176, 108933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, G.; Gattuso, M.; Grondin, G.; Marsault, É.; Bouarab, K.; Malouin, F. Tomatidine Inhibits Replication of Staphylococcus aureus Small-Colony Variants in Cystic Fibrosis Airway Epithelial Cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestergaard, M.; Roshanak, S.; Ingmer, H. Targeting the ATP Synthase in Staphylococcus aureus Small Colony Variants, Streptococcus Pyogenes and Pathogenic Fungi. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, G.; Lafrance, M.; Boulanger, S.; Seguin, D.L.; Guay, I.; Gattuso, M.; Marsault, E.; Bouarab, K.; Malouin, F. Tomatidine Acts in Synergy with Aminoglycoside Antibiotics against Multiresistant Staphylococcus aureus and Prevents Virulence Gene Expression. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, R.; Fazeli, H.; Bahri Najafi, R.; Jelokhanian, A. Evaluation of the Synergistic Effect of Tomatidine with Several Antibiotics against Standard and Clinical Isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 16, 290–296. [Google Scholar]
- Chagnon, F.; Guay, I.; Bonin, M.-A.; Mitchell, G.; Bouarab, K.; Malouin, F.; Marsault, É. Unraveling the Structure–Activity Relationship of Tomatidine, a Steroid Alkaloid with Unique Antibiotic Properties against Persistent Forms of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 80, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, S.; Mitchell, G.; Bouarab, K.; Marsault, É.; Cantin, A.; Frost, E.H.; Déziel, E.; Malouin, F. Bactericidal Effect of Tomatidine-Tobramycin Combination against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Is Enhanced by Interspecific Small-Molecule Interactions. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 7458–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay, I.; Boulanger, S.; Isabelle, C.; Brouillette, E.; Chagnon, F.; Bouarab, K.; Marsault, E.; Malouin, F. Tomatidine and Analog FC04–100 Possess Bactericidal Activities against Listeria, Bacillus and Staphylococcus Spp. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamontagne Boulet, M.; Isabelle, C.; Guay, I.; Brouillette, E.; Langlois, J.-P.; Jacques, P.-É.; Rodrigue, S.; Brzezinski, R.; Beauregard, P.B.; Bouarab, K.; et al. Tomatidine Is a Lead Antibiotic Molecule That Targets Staphylococcus aureus ATP Synthase Subunit C. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02197-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, J.-P.; Millette, G.; Guay, I.; Dubé-Duquette, A.; Chamberland, S.; Jacques, P.-É.; Rodrigue, S.; Bouarab, K.; Marsault, É.; Malouin, F. Bactericidal Activity of the Bacterial ATP Synthase Inhibitor Tomatidine and the Combination of Tomatidine and Aminoglycoside Against Persistent and Virulent Forms of Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doghri, I.; Cherifi, T.; Goetz, C.; Malouin, F.; Jacques, M.; Fravalo, P. Counteracting Bacterial Motility: A Promising Strategy to Narrow Listeria Monocytogenes Biofilm in Food Processing Industry. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 673484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorsaz, S.; Snaka, T.; Favre-Godal, Q.; Maudens, P.; Boulens, N.; Furrer, P.; Ebrahimi, S.N.; Hamburger, M.; Allemann, E.; Gindro, K.; et al. Identification and Mode of Action of a Plant Natural Product Targeting Human Fungal Pathogens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00829-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diosa-Toro, M.; Troost, B.; van de Pol, D.; Heberle, A.M.; Urcuqui-Inchima, S.; Thedieck, K.; Smit, J.M. Tomatidine, a Novel Antiviral Compound towards Dengue Virus. Antivir. Res. 2019, 161, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, S.M.; Dyle, M.C.; Bullard, S.A.; Dierdorff, J.M.; Murry, D.J.; Fox, D.K.; Bongers, K.S.; Lira, V.A.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Talley, J.J.; et al. Identification and Small Molecule Inhibition of an Activating Transcription Factor 4 (ATF4)-Dependent Pathway to Age-Related Skeletal Muscle Weakness and Atrophy. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 25497–25511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, J.E.; Wang, C.; Chan, K.W.K.; Vasudevan, S.G.; Jans, D.A. Novel Dengue Virus Inhibitor 4-HPR Activates ATF4 Independent of Protein Kinase R–like Endoplasmic Reticulum Kinase and Elevates Levels of EIF2α Phosphorylation in Virus Infected Cells. Antivir. Res. 2016, 130, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troost, B.; Mulder, L.M.; Diosa-Toro, M.; van de Pol, D.; Rodenhuis-Zybert, I.A.; Smit, J.M. Tomatidine, a Natural Steroidal Alkaloid Shows Antiviral Activity towards Chikungunya Virus in Vitro. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troost-Kind, B.; van Hemert, M.J.; van de Pol, D.; van der Ende-Metselaar, H.; Merits, A.; Borggrewe, M.; Rodenhuis-Zybert, I.A.; Smit, J.M. Tomatidine Reduces Chikungunya Virus Progeny Release by Controlling Viral Protein Expression. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Bai, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Jiang, P. Tomatidine Inhibits Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication by Targeting 3CL Protease. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrieq, R.; Ahmad, I.; Snoussi, M.; Noumi, E.; Iriti, M.; Algahtani, F.D.; Patel, H.; Saeed, M.; Tasleem, M.; Sulaiman, S.; et al. Tomatidine and Patchouli Alcohol as Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Enzymes (3CLpro, PLpro and NSP15) by Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergoten, G.; Bailly, C. In Silico Analysis of Echinocandins Binding to the Main Proteases of Coronaviruses PEDV (3CLpro) and SARS-CoV-2 (Mpro). In Silico Pharmacol. 2021, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, J.M.; Rodrigues, J.C.F.; De Souza, W.; Atella, G.C.; Barrabin, H. Tomatidine Promotes the Inhibition of 24-Alkylated Sterol Biosynthesis and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Leishmania amazonensis Promastigotes. Parasitology 2012, 139, 1253–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wu, Q.; You, X.; Zhou, H.; Xu, S.; He, W.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; Xia, J.; Zhu, H.; et al. Tomatidine Alleviates Osteoporosis by Downregulation of P53. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e923996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyle, M.C.; Ebert, S.M.; Cook, D.P.; Kunkel, S.D.; Fox, D.K.; Bongers, K.S.; Bullard, S.A.; Dierdorff, J.M.; Adams, C.M. Systems-Based Discovery of Tomatidine as a Natural Small Molecule Inhibitor of Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 14913–14924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, F.; Liu, X.; Mao, Y.; Diao, L.; Wen, C.; Liu, M. Tomatidine Suppresses the Destructive Behaviors of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes and Ameliorates Type II Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 670707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, X.; Yu, T.; Huang, X.; Xi, Y.; Ni, B.; Zhang, R.; You, H. Tomatidine Suppresses Inflammation in Primary Articular Chondrocytes and Attenuates Cartilage Degradation in Osteoarthritic Rats. Aging 2020, 12, 12799–12811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Sun, X.; Yang, Y.; Ying, Z.; Meng, J.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, G.; Li, S.; Wu, F.; Zhao, X.; et al. Tomatidine Suppresses Osteoclastogenesis and Mitigates Estrogen Deficiency-induced Bone Mass Loss by Modulating TRAF6-mediated Signaling. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 2574–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Hasler, M.; de Oliveira, G.M.; da Gama, A.N.; de Fiuza, L.F.A.; Fesser, A.F.; Cal, M.; Rocchetti, R.; Peres, R.B.; Guan, X.L.; Kaiser, M.; et al. Combination With Tomatidine Improves the Potency of Posaconazole Against Trypanosoma cruzi. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 617917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, J.M.; Rodrigues, J.C.; Moreira, O.C.; Atella, G.; Souza, W.; Barrabin, H. Mechanisms of Growth Inhibition of Phytomonas Serpens by the Alkaloids Tomatine and Tomatidine. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2015, 110, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.M.; Ebert, S.M.; Dyle, M.C. Use of MRNA Expression Signatures to Discover Small Molecule Inhibitors of Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, E.F.; Waltz, T.B.; Kassahun, H.; Lu, Q.; Kerr, J.S.; Morevati, M.; Fivenson, E.M.; Wollman, B.N.; Marosi, K.; Wilson, M.A.; et al. Tomatidine Enhances Lifespan and Healthspan in C. elegans through Mitophagy Induction via the SKN-1/Nrf2 Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Hameed, R.; Mishra, A.; Bhatta, R.S.; Nazir, A. Genetic Modulators Associated with Regulatory Surveillance of Mitochondrial Quality Control, Play a Key Role in Regulating Stress Pathways and Longevity in C. elegans. Life Sci. 2022, 290, 120226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradeepkiran, J.A.; Hindle, A.; Kshirsagar, S.; Reddy, P.H. Are Mitophagy Enhancers Therapeutic Targets for Alzheimer’s Disease? Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.L.; He, H.B.; Zou, K.; Bai, C.H.; Xue, Y.H.; Wang, J.Z.; Chen, J.F. Protective Effect of Tomatine against Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Neurotoxicity in Neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) Cells. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshirsagar, S.; Sawant, N.; Morton, H.; Reddy, A.P.; Reddy, P.H. Protective Effects of Mitophagy Enhancers against Amyloid Beta-Induced Mitochondrial and Synaptic Toxicities in Alzheimer Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2022, 31, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lyu, X.; Li, Y.; Ahsan, A.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, X. Tomatidine Provides Mitophagy-independent Neuroprotection after Ischemic Injury. FEBS Open Bio 2021, 11, 2647–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, A.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, S.; Liu, M.; Cao, M.; Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, X.; Xin, M.; Hu, W.; et al. Tomatidine Protects against Ischemic Neuronal Injury by Improving Lysosomal Function. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 882, 173280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Dai, Y.; Tan, J.; Chen, Y.; Qin, G.; Mao, W.; Zou, J.; Chang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J. α-Solanine Reverses Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling and Vascular Angiogenesis in Experimental Pulmonary Artery Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 2419–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-C.; Wu, S.-J.; Chen, Y.-L.; Lin, C.-F.; Liou, C.-J. Tomatidine Improves Pulmonary Inflammation in Mice with Acute Lung Injury. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 4544294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Nainwal, L.M.; Gupta, G.; Singh, S.K.; Chellappan, D.K.; Oliver, B.G.; Dua, K. Orally Administered Solasodine, a Steroidal Glycoalkaloid, Suppresses Ovalbumin-Induced Exaggerated Th2-Immune Response in Rat Model of Bronchial Asthma. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 366, 110138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusu, H.; Yoshida, H.; Kudo, M.; Okuyama, M.; Harada, N.; Tsuji-Naito, K.; Akagawa, M. Tomatidine Reduces Palmitate-Induced Lipid Accumulation by Activating AMPK via Vitamin D Receptor-Mediated Signaling in Human HepG2 Hepatocytes. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, 1801377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-J.; Huang, W.-C.; Yu, M.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Shen, S.-C.; Yeh, K.-W.; Liou, C.-J. Tomatidine Ameliorates Obesity-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 91, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Oqani, R.K.; Lee, J.E.; Kang, J.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, E.S.; Jeong, Y.D.; Baek, J.J.; Jin, D.I. α-Solanine Impairs Oocyte Maturation and Quality by Inducing Autophagy and Apoptosis and Changing Histone Modifications in a Pig Model. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 75, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taveira, M.; Sousa, C.; Valentão, P.; Ferreres, F.; Teixeira, J.P.; Andrade, P.B. Neuroprotective Effect of Steroidal Alkaloids on Glutamate-Induced Toxicity by Preserving Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and Reducing Oxidative Stress. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 140, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Kanetake, S.; Wu, Y.-H.; Tam, C.; Cheng, L.W.; Land, K.M.; Friedman, M. Antiprotozoal Effects of the Tomato Tetrasaccharide Glycoalkaloid Tomatine and the Aglycone Tomatidine on Mucosal Trichomonads. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8806–8810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, M.K.; Al-Dosari, M.S.; Rehman, M.T.; Al-Rehaily, A.J.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Alajmi, M.F. The Anti-Hepatitis B Virus and Anti-Hepatotoxic Efficacies of Solanopubamine, a Rare Alkaloid from Solanum schimperianum. Saudi Pharm. J. 2022, 30, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rehaily, A.J.; Ahmad, M.S.; Mustafa, J.; Al-Oqail, M.M.; Hassan, W.H.; Khan, S.I.; Khan, I.A. Solanopubamine, a Rare Steroidal Alkaloid from Solanum Schimperianum: Synthesis of Some New Alkyl and Acyl Derivatives, Their Anticancer and Antimicrobial Evaluation. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2013, 17, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.G.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, H.H.; Lee, H.J.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, N.J.; An, H.J.; Nam, J.H.; Jang, D.S.; Lee, K.T. Alpha-Chaconine Isolated from a Solanum tuberosum L. Cv Jayoung Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide-Induced pro-Inflammatory Mediators via AP-1 Inactivation in RAW 264.7 Macrophages and Protects Mice from Endotoxin Shock. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 235, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandakumar, S.; Kannan, D.; Wilson, E.; Narayanan, K.B.; Suresh, G.; Kanakavalli, K.; Manoharan, M.T. Potential Phytopharmaceutical Constituents of Solanum trilobatum L. as Significant Inhibitors Against COVID-19: Robust-Binding Mode of Inhibition by Molecular Docking, PASS-Aid Bioactivity and ADMET Investigations. Chemrxiv 2020. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.S.; Lee, K.G.; Lee, H.H.; Lee, H.J.; An, H.J.; Nam, J.H.; Jang, D.S.; Lee, K.T. Alpha-Solanine Isolated From Solanum tuberosum L. Cv Jayoung Abrogates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses Via NF-KappaB Inactivation in RAW 264.7 Macrophages and Endotoxin-Induced Shock Model in Mice. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 117, 2327–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piana, M.; Camponogara, C.; Boligon, A.A.; Oliveira, S.M. Solanum paranense Extracts and Solanine Present Anti-Inflammatory Activity in an Acute Skin Inflammation Model in Mice. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 4295680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.-K.; Shih, Y.-W.; Chang Chien, T.-T.; Fang, L.-H.; Huang, H.-C.; Chen, P.-S. ALPHA.-Solanine Inhibits Human Melanoma Cell Migration and Invasion by Reducing Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/9 Activities. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Narisawa, M.; Jin, E.; Li, X. α-Solanine as Potential Therapeutic Target in Pulmonary Artery Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 2377–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.-Y.; Huang, W.-C.; Liou, C.-J.; Chen, L.-C.; Shen, J.-J.; Kuo, M.-L. Tomatidine Attenuates Airway Hyperresponsiveness and Inflammation by Suppressing Th2 Cytokines in a Mouse Model of Asthma. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 5261803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, C.; Yuan, A.; Gu, T.; Zhang, F.; Fan, X.; Wu, X.; Xiong, X.; Yang, Q. α-Solanine Causes Cellular Dysfunction of Human Trophoblast Cells via Apoptosis and Autophagy. Toxins 2021, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Yang, Y.K.; Wang, J.N.; Ren, J.G. Steroidal Alkaloids from Solanum Nigrum and Their Cytotoxic Activities. Phytochemistry 2022, 202, 113317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Di, S.N.; Xu, Q.; Ren, Q.C.; Chen, S.Z.; Huang, N.; Jia, D.; Shen, X.F. Steroidal Alkaloid Solanine A from Solanum Nigrum Linn. Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory Activity in Lipopolysaccharide/Interferon Gamma-Activated Murine Macrophages and Animal Models of Inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chang, W.; Zhang, M.; Ying, Z.; Lou, H. Natural Product Solasodine-3-O-β-D-Glucopyranoside Inhibits the Virulence Factors of Candida albicans. FEMS Yeast Res. 2015, 15, fov060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chang, W.; Li, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Y.; Lou, H. Solasodine-3-O-β-d-Glucopyranoside Is Hydrolyzed by a Membrane Glucosidase into Active Molecule Solasodine against Candida albicans. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanillas, B.; Chassagne, F.; Vásquez-Ocmín, P.; Tahrioui, A.; Chevalier, S.; Vansteelandt, M.; Triastuti, A.; Amasifuen Guerra, C.A.; Fabre, N.; Haddad, M. Pharmacological Validation of Solanum mammosum L. as an Anti-Infective Agent: Role of Solamargine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 280, 114473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, C.; Sheu, H.M.; Lin, C.S.; Xiang, L. Solamargine Alleviated UVB-Induced Inflammation and Melanogenesis in Human Keratinocytes and Melanocytes via the P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway, a Promising Agent for Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2022, 9, 812653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu Miranda, M.; Tiossi, R.F.J.; da Silva, M.R.; Rodrigues, K.C.; Kuehn, C.C.; Rodrigues Oliveira, L.G.; Albuquerque, S.; McChesney, J.D.; Lezama-Davila, C.M.; Isaac-Marquez, A.P.; et al. In Vitro Leishmanicidal and Cytotoxic Activities of the Glycoalkaloids from Solanum lycocarpum (Solanaceae) Fruits. Chem. Biodivers. 2013, 10, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lezama-Davila, C.M.; McChesney, J.D.; Bastos, J.K.; Miranda, M.A.; Tiossi, R.F.; da Costa Jde, C.; Bentley, M.V.; Gaitan-Puch, S.E.; Isaac-Marquez, A.P. A New Antileishmanial Preparation of Combined Solamargine and Solasonine Heals Cutaneous Leishmaniasis through Different Immunochemical Pathways. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2732–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, R.D.; Planeta, C.; Almeida, A.; Bastos, J.; Salgueiro, L.; Cavaleiro, C.; do Céu Sousa, M.; Martins, G. Effects of the Extract and Glycoalkaloids of Solanum Lycocarpum St. Hill on Giardia lamblia Trophozoites. Phcog. Mag. 2015, 11, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Moreira, R.R.D.; Martins, G.Z.; Magalhaes, N.O.; Almeida, A.E.; Pietro, R.C.L.R.; Silva, F.A.J.; Cicarelli, R.M.B. In Vitro Trypanocidal Activity of Solamargine and Extracts from Solanum palinacanthum and Solanum lycocarpum of Brazilian Cerrado. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2013, 85, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsherbiny, M.A.; El Badawy, S.A.; Elbedewy, H.; Ezzat, S.M.; Elsakhawy, F.S.; Abdel-Kawy, M.A. Comparative Molluscicidal and Schistosomicidal Potentiality of Two Solanum Species and Its Isolated Glycoalkaloids. Pharmacogn. Res. 2018, 10, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Su, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, Q. Khasianine Ameliorates Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation and Represses TNF-Alpha/NF-KappaB Axis Mediated Transactivation of IL-17A and IL-33 in Keratinocytes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 292, 115124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Yoon, J.W.; Kim, D.; Choi, S.; Kim, H.K.; Youm, J.B.; Han, J.; Heo, S.C.; Hyun, S.-A.; Seo, J.-W.; et al. Tomatidine-Stimulated Maturation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes for Modeling Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, L. Solasonine Relieves Sevoflurane-Induced Neurotoxicity via Activating the AMP-Activated Protein Kinase/FoxO3a Pathway. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2022, 41, 096032712110699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaunda, J.S.; Qin, X.J.; Zhu, H.T.; Wang, D.; Yang, C.R.; Zhang, Y.J. Previously Undescribed Pyridyl-Steroidal Glycoalkaloids and 23S,26R-Hydroxylated Spirostanoid Saponin from the Fruits of Solanum Violaceum Ortega and Their Bioactivities. Phytochemistry 2021, 184, 112656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yi, X.; He, X. Steroidal Alkaloid Glycosides and Phenolics from the Immature Fruits of Solanum Nigrum. Fitoterapia 2019, 137, 104268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.Y.; Yin, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D.Y.; Kuang, H.X. New Steroidal Saponins from the Roots of Solanum melongena L. Fitoterapia 2018, 128, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshirsagar, S.; Sawant, N.; Morton, H.; Reddy, A.P.; Reddy, P.H. Mitophagy Enhancers against Phosphorylated Tau-Induced Mitochondrial and Synaptic Toxicities in Alzheimer Disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 174, 105973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiełczewska, U.; Jorda, R.; Gonzalez, G.; Morzycki, J.W.; Ajani, H.; Svrčková, K.; Štěpánková, Š.; Wojtkielewicz, A. The Synthesis and Cholinesterase Inhibitory Activities of Solasodine Analogues with Seven-Membered F Ring. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 205, 105776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njeh, F.; Feki, H.; Koubaa, I.; Hamed, N.; Damak, M.; Ayadi, A.; Hammami, H.; Mezghani-Jarraya, R. Molluscicidal Activity of Solanum elaeagnifolium Seeds against Galba truncatula Intermediate Host of Fasciola hepatica: Identification of β-Solamarine. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, S.; Miyasaka, K.; Shimoda, H. Lycoperoside H, a Steroidal Alkaloid Saponin in Tomato Seeds, Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis-like Symptoms in IL-33 Transgenic Mice. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Li, M.; Chen, L.; Peng, X.; Que, Z.J.; An, H.M.; Shen, K.P.; Hu, B. AlphaSolanine Inhibits Growth and Metastatic Potential of Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaboga Arslan, A.K.; Yerer, M.B. Alpha-Chaconine and Alpha-Solanine Inhibit RL95-2 Endometrium Cancer Cell Proliferation by Reducing Expression of Akt (Ser473) and ERalpha (Ser167). Nutrients 2018, 10, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Chen, J.; Lu, F.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, X.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, L. Anti-Cancer Effect of Alpha-Solanine by Down-Regulating S100P Expression in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 2018, 13, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Zhong, W.; Deng, Z.; Lai, C.; Chu, J.; Jiao, G.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q. Inhibition of Prostate Cancer Growth by Solanine Requires the Suppression of Cell Cycle Proteins and the Activation of ROS/P38 Signaling Pathway. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3214–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.H.; Liao, A.C.; Hung, J.H.; Lee, W.J.; Hu, K.C.; Lin, P.T.; Liao, R.F.; Chen, P.S. Alpha-Solanine Inhibits Invasion of Human Prostate Cancer Cell by Suppressing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and MMPs Expression. Molecules 2014, 19, 11896–11914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashoji, S.; Matsuda, T. Synergistic Cytotoxicity Induced by Alpha-Solanine and Alpha-Chaconine. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, T.; Gu, L.; Yang, L.; Wei, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, J.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Du, F.; Chen, Y.; et al. Alpha-Solanine Anti-Tumor Effects in Non-Small Cell Lung CancerThrough Regulating the Energy Metabolism Pathway. PRA 2022, 17, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouhar, S.A.; Abo-elfadl, M.T.; Gamal-Eldeen, A.M.; El-Daly, S.M. Involvement of MiRNAs in Response to Oxidative Stress Induced by the Steroidal Glycoalkaloid A-solanine in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2022, 37, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Yuan, W.; Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Wen, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, Q.; Xiong, X.; Yuan, A. α-Solanine Inhibits Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration, and Induces Apoptosis in Human Choriocarcinoma JEG-3 Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Toxins 2021, 13, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Ying, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y. Solanine Inhibits Immune Escape Mediated by Hepatoma Treg Cells via the TGFβ/Smad Signaling Pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 9749631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, L.; Gao, Q.; Niu, B.; Wang, H. Solanine Inhibits Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis of the Human Leukemia Cells by Targeting the MiR-16/Bcl-2 Axis. J. BUON 2020, 25, 1614–1618. [Google Scholar]
- El-Daly, S.M.; Gouhar, S.A.; Gamal-Eldeen, A.M.; Abdel Hamid, F.F.; Ashour, M.N.; Hassan, N.S. Synergistic Effect of α-Solanine and Cisplatin Induces Apoptosis and Enhances Cell Cycle Arrest in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. ACAMC 2020, 19, 2197–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Park, M.Y.; Song, G.; Lim, W. Alpha-Solanine Inhibits Cell Proliferation via Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Inhibin Synthesis in Mouse Testis In Vitro and In Vivo. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hao, T.; Sun, J.; Wei, P.; Zhang, H. Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 Modulates α-Solanine-Induced Radiosensitivity by Negatively Regulating MiR-18a in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Du, X.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Zang, W.; Liu, K.; Zhao, G. α-Solanine Enhances the Chemosensitivity of Esophageal Cancer Cells by Inducing MicroRNA-138 Expression. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Guo, W.; Sun, Q.; Chen, X.; Zang, W.; Dong, Z.; Zhao, G. α-Solanine Modulates the Radiosensitivity of Esophageal Cancer Cells by Inducing MicroRNA 138 Expression. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 996–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsenikia, M.; Farhangi, B.; Alizadeh, A.M.; Khodayari, H.; Khodayari, S.; Khori, V.; Arjmand Abbassi, Y.; Vesovic, M.; Soleymani, A.; Najafi, F. Therapeutic Effects of Dendrosomal Solanine on a Metastatic Breast Tumor. Life Sci. 2016, 148, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, R.; Zhang, G.; Cheng, R.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, H.; Lu, X.; Li, H.; Chen, S.; Li, J.; et al. Anticancer Function of α-Solanine in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells by Inducing MicroRNA-138 Expression. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 6437–6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Lv, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, S.; Kong, H.; Wang, M.; Xie, J.; Zhang, C.; et al. Solanine Induces Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 805926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsenikia, M.; Alizadeh, A.M.; Khodayari, S.; Khodayari, H.; Kouhpayeh, S.A.; Karimi, A.; Zamani, M.; Azizian, S.; Mohagheghi, M.A. The Protective and Therapeutic Effects of Alpha-Solanine on Mice Breast Cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 718, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Tan, H.; Lang, L.; Bai, J.; Ji, Y. The Effect of Alpha-Solanine on the Activity, Gene Expression, and Kinetics of Arylamine N-Acetyltransferase in HepG2 Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 2427–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Huang, C.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, L.; Dai, J.; Sun, H.; Chen, B.; Zhou, M. α-Solanine Inhibits Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression by down-Regulating the ERK1/2-HIF-1α and STAT3 Signaling Pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 771, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanain, M.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Pandey, P.; Ashraf, R.; Singh, N.; Sharma, S.; Vishwakarma, A.L.; Datta, D.; Mitra, K.; Sarkar, J. α-Solanine Induces ROS-Mediated Autophagy through Activation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Inhibition of Akt/MTOR Pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Bai, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, H.; Dong, X.; Chen, B. Solamargine Induces Autophagy-Mediated Apoptosis and Enhances Bortezomib Activity in Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2022, 49, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Shimode, M.; Tsutsumi, S.; Yasuda, S.; Okawa, M.; Kinjo, J.; Miyashita, H.; Ikeda, T.; Yoshimitsu, H.; Nohara, T. A New Steroidal Glycoside from the Fruits of Solanum Myriacanthum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Du, H.; Dong, B.; Ao, S.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lv, G.; et al. Solamargine Inhibits Gastric Cancer Progression by Regulating the Expression of LncNEAT1_2 via the MAPK Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, T.; Mokoka, T.; Fouche, G.; Steenkamp, P.; Steenkamp, V.; Cordier, W. Solamargine, a Bioactive Steroidal Alkaloid Isolated from Solanum Aculeastrum Induces Non-Selective Cytotoxicity and P-Glycoprotein Inhibition. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhu, L.; Guo, Z.; Shen, W.; Wang, D. Solamargine Inhibits the Migration and Invasion of HepG2 Cells by Blocking Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Zhu, H.; Yang, H.; Huang, W.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, D.; Shao, G. Solamargine Triggers Hepatoma Cell Death through Apoptosis. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sani, I.K.; Marashi, S.H.; Kalalinia, F. Solamargine Inhibits Migration and Invasion of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through Down-Regulation of Matrix Metalloproteinases 2 and 9 Expression and Activity. Toxicol. In Vitro 2015, 29, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, F.; Li, L.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Hann, S. Targeting Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Contributes to the Solamargine-Inhibited Growth and -Induced Apoptosis of Human Lung Cancer Cells. Tumour. Biol. 2014, 35, 8169–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tang, X.; Ma, C.; Shi, Y.; Wu, W.; Hann, S.S. The Regulation and Interaction of Colon Cancer-associated Transcript-1 and MiR7-5p Contribute to the Inhibition of SP1 Expression by Solamargine in Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, Q.; Zheng, F.; Wu, J.; Yang, L.; Hann, S.S. Activation of AMPKα Mediates Additive Effects of Solamargine and Metformin on Suppressing MUC1 Expression in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhu, F.; Yang, Y.; Li, M. Purification, Antitumor Activity in Vitro of Steroidal Glycoalkaloids from Black Nightshade (Solanum nigrum L.). Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Zheng, F.; Wu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Li, L.; Hann, S.S. Combination of Solamargine and Metformin Strengthens IGFBP1 Gene Expression Through Inactivation of Stat3 and Reciprocal Interaction Between FOXO3a and SP1. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 2310–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-H.; Zhang, L.-L.; Wu, G.-S.; Chen, X.; Li, T.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.-T.; Lu, J.-J. Solasodine Induces Apoptosis, Affects Autophagy, and Attenuates Metastasis in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Planta Med. 2016, 83, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Li, W.; Wang, T.; Rong, Y.; He, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Liu, C. α-Tomatine, a Novel Early-Stage Autophagy Inhibitor, Inhibits Autophagy to Enhance Apoptosis via Beclin-1 in Skov3 Cells. Fitoterapia 2021, 152, 104911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Chen, N.; Chen, Y.; He, B.; Zhou, Z. Solasonine Induces Apoptosis of the SGC-7901 Human Gastric Cancer Cell Line in Vitro via the Mitochondria-mediated Pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 3387–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Hu, C.; Han, M.; Liu, C.; Sun, X.; Yu, K.; Gu, H.; Zhang, J. Solasonine Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Progression With Involvement of Ferroptosis Induction. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 834729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Hao, L.; Shi, Z.D.; Fang, K.; Yu, H.; Zang, G.H.; Fan, T.; Han, C.H. Solasonine Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation of Bladder Cancer Cells by Suppressing NRP1 Expression. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 7261486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, M.Q.; Tran, T.H.V.; Pham, Q.L.; Gairin, J.E. In Silico Analysis of the Binding Properties of Solasonine to Mortalin and P53, and in Vitro Pharmacological Studies of Its Apoptotic and Cytotoxic Effects on Human HepG2 and Hep3b Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 33, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, W.; Tan, W. Solasonine, A Natural Glycoalkaloid Compound, Inhibits Gli-Mediated Transcriptional Activity. Molecules 2016, 21, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malojirao, V.H.; Vigneshwaran, V.; Thirusangu, P.; Mahmood, R.; Prabhakar, B.T. The Tumor Antagonistic Steroidal Alkaloid Solanidine Prompts the Intrinsic Suicidal Signal Mediated DFF-40 Nuclear Import and Nucleosomal Disruption. Life Sci. 2018, 199, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wang, J.N.; Sun, J.; Wu, T.; Cao, X.Q.; Liu, L.Y.; Yang, Y.K. Steroidal Glycoalkaloids from Solanum Lyratum Inhibit the Pro-Angiogenic Activity of A549-Derived Exosomes. Fitoterapia 2020, 141, 104481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.L.; Lv, J.; Wang, W.F.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.J.; Xu, T.H. New Steroidal Alkaloid and Furostanol Glycosides Isolated from Solanum Lyratum with Cytotoxicity. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qi, X. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effect of Lycoperoside H against the 1,2-Dimethyl Hydrazine (DMH) Induced Colorectal Cancer in Rats. J. Oleo Sci. 2022, 71, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, S.J.; Rico, C.W.; Um, I.C.; Kang, M.Y. Hypoglycemic and Antioxidative Effects of Hydroxyethyl Methylcellulose in Mice Fed with High Fat Diet. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1716–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, P.; Kundu, A.; Chakraborty, H.J.; Kar, B.; Choi, W.S.; Lee, B.M.; Bhakta, T.; Atanasov, A.G.; Kim, H.S. Therapeutic Value of Steroidal Alkaloids in Cancer: Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1731–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng-Zhen, Z.; Li-Juan, G.; Shi-Fang, X.U.; Wen-Kang, H.; Xiao-Yu, L.I.; Yi-Ping, Y.E. Advances in studies on steroidal alkaloids and their pharmacological activities in genus Veratrum. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2020, 45, 5129–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heretsch, P.; Giannis, A. The Veratrum and Solanum Alkaloids. Alkaloids Chem. Biol. 2015, 74, 201–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, M.; Takara, Y.; Egami, M.; Uranaka, K.; Yoshimitsu, H.; Matsushita, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Nohara, T. Steroidal Alkaloid Glycosides, Esculeosides C and D, from the Ripe Fruit of Cherry Tomato. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimitsu, H.; Nishida, M.; Nohara, T. Steroidal Glycosides from the Fruits of Solanum abutiloides. Phytochemistry 2003, 64, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heftmann, E. Biogenesis of Steroids in Solanaceae. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 1843–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, R.; Watanabe, B.; Nakayasu, M.; Lee, H.J.; Kato, J.; Umemoto, N.; Muranaka, T.; Saito, K.; Sugimoto, Y.; Mizutani, M. The Biosynthetic Pathway of Potato Solanidanes Diverged from That of Spirosolanes Due to Evolution of a Dioxygenase. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, P.D.; Jozwiak, A.; Panda, S.; Aharoni, A. ‘Hijacking’ Core Metabolism: A New Panache for the Evolution of Steroidal Glycoalkaloids Structural Diversity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2020, 55, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, P.D.; Sonawane, P.D.; Pollier, J.; Vanden Bossche, R.; Dewangan, V.; Weithorn, E.; Tal, L.; Meir, S.; Rogachev, I.; Malitsky, S.; et al. GAME9 Regulates the Biosynthesis of Steroidal Alkaloids and Upstream Isoprenoids in the Plant Mevalonate Pathway. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nohara, T.; Ono, M.; Ikeda, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; El-Aasr, M. The Tomato Saponin, Esculeoside A. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1734–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghisalberti, E.L. Steroidal Glycoalkaloids: Isolation, Structure, Analysis, and Biosynthesis. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2006, 1, 1934578X0600101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanasiou, F.; Mitchell, S.H.; Watson, S.; Harvey, B.M. Effect of Environmental Stress during Tuber Development on Accumulation of Glycoalkaloids in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, G. Light-Induced Glycoalkaloid Accumulation of Potato Tubers (Solanum tuberosum L.). J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, K.S.; Masud, T.; Qayyum, A.; Ahmad, A.; Mehmood, A.; Bibi, Y.; Sher, A. Photo-Induced Changes in Quality Attributes of Potato Tubers during Storage. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2017, 89, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Analysis of Biologically Active Compounds in Potatoes (Solanum tuberosum), Tomatoes (Lycopersicon esculentum), and Jimson Weed (Datura stramonium) Seeds. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1054, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, P.D.; Sonawane, P.D.; Heinig, U.; Bocobza, S.E.; Burdman, S.; Aharoni, A. The Bitter Side of the Nightshades: Genomics Drives Discovery in Solanaceae Steroidal Alkaloid Metabolism. Phytochemistry 2015, 113, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, T.; Vincken, J.-P.; Zuilhof, H.; Legger, A.; Takada, N.; Gruppen, H. C22 Isomerization in α-Tomatine-to-Esculeoside A Conversion during Tomato Ripening Is Driven by C27 Hydroxylation of Triterpenoidal Skeleton. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 3786–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Takaki, A.; Uehara, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Okawa, M.; Yamauchi, K.; Ono, M.; Yoshimitsu, H.; Nohara, T. Tomato Steroidal Alkaloid Glycosides, Esculeosides A and B, from Ripe Fruits. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 4915–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelario, F.; De Maria, S.; Rivelli, A.R.; Russo, D.; Milella, L.; Bufo, S.A.; Scrano, L. A Complete Survey of Glycoalkaloids Using LC-FTICR-MS and IRMPD in a Commercial Variety and a Local Landrace of Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) and Their Anticholinesterase and Antioxidant Activities. Toxins 2019, 11, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M.; McDonald, G.M.; Filadelfi-Keszi, M. Potato Glycoalkaloids: Chemistry, Analysis, Safety, and Plant Physiology. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1997, 16, 55–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, G.; Hong, C.; Zheng, X.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y. Potential of Steroidal Alkaloids in Cancer: Perspective Insight Into Structure–Activity Relationships. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 733369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M. Chemistry and Anticarcinogenic Mechanisms of Glycoalkaloids Produced by Eggplants, Potatoes, and Tomatoes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3323–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.-W.; Chen, M.-W.; Cheng, K.-J.; Yu, P.-Z.; Wei, X.; Shi, Z. Therapeutic Potential of Steroidal Alkaloids in Cancer and Other Diseases: Therapeutic Potential of Steroidal Alkaloids. Med. Res. Rev. 2016, 36, 119–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, A.; Ijaz, S.; Mohammad, I.S.; Muhammad, K.S.; Akhtar, N.; Khan, H.M.S. Aglycone Solanidine and Solasodine Derivatives: A Natural Approach towards Cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrock, R.W.; VanEtten, H.D. Fungal Sensitivity to and Enzymatic Degradation of the Phytoanticipin α-Tomatine. Phytopathology 1998, 88, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osbourn, A. Fungal Pathogens of Oat Roots and Tomato Leaves Employ Closely Related Enzymes to Detoxify Different Host Plant Saponins. MPMI 1995, 8, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Lamothe, R.; Mitchell, G.; Gattuso, M.; Diarra, M.; Malouin, F.; Bouarab, K. Plant Antimicrobial Agents and Their Effects on Plant and Human Pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3400–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarek, P.; Osbourn, A. Plant-Microbe Interactions: Chemical Diversity in Plant Defense. Science 2009, 324, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareja-Jaime, Y.; Roncero, M.I.G.; Ruiz-Roldán, M.C. Tomatinase from Fusarium oxysporum f. Sp. Lycopersici Is Required for Full Virulence on Tomato Plants. MPMI 2008, 21, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, F.R.S.; Araújo-Filho, H.G.; Monteiro, B.S.; Shanmugam, S.; de Araújo, A.A.S.; da Almeida, J.R.G.S.; Thangaraj, P.; Júnior, L.J.Q.; de Quintans, J.S.S. Anti-Inflammatory and Modulatory Effects of Steroidal Saponins and Sapogenins on Cytokines: A Review of Pre-Clinical Research. Phytomedicine 2022, 96, 153842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.Y.; Shen, X.F.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z.W.; Li, F.; Chen, B.; Zhang, G.L.; Wang, M.K. Bioactive Steroidal Alkaloids from the Fruits of Solanum Nigrum. Phytochemistry 2018, 147, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltz, T.B.; Fivenson, E.M.; Morevati, M.; Li, C.; Becker, K.G.; Bohr, V.A.; Fang, E.F. Sarcopenia, Aging and Prospective Interventional Strategies. CMC 2019, 25, 5588–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.-E.; Shin, S.-K.; Cho, H.-W.; Im, S.-S.; Bae, J.-H.; Woo, S.M.; Kwon, T.-K.; Song, D.-K. Tomatidine Inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Induced Apoptosis in C2C12 Myoblasts via Ameliorating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 444, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.E.; Borioni, J.L.; Cavallaro, V.; Puiatti, M.; Pierini, A.B.; Murray, A.P.; Penenory, A.B. Solanocapsine Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of Acetylcholinesterase: Synthesis, Molecular Docking and Biological Studies. Steroids 2015, 104, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Qin, X.-J.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.-W.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Wang, B.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.-P.; Luo, X.-D. Spiralosides A–C, Three New C27-Steroidal Glycoalkaloids from the Fruits of Solanum Spirale. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2016, 6, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Tian, G.J.; Yu, F.X.; Wen, Z.D. A Narrative Review of the Antitumor Studies of Solanine. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1578–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.H.; Gul, S.; Zahra, H.S.; Maryam, A.; Shakir, H.A.; Khan, M.; Irfan, M. Alpha Solanine: A Novel Natural Bioactive Molecule with Anticancer Effects in Multiple Human Malignancies. Nutr. Cancer 2021, 73, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaunda, J.S.; Zhang, Y.J. The Genus Solanum: An Ethnopharmacological, Phytochemical and Biological Properties Review. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2019, 9, 77–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalalinia, F.; Karimi-Sani, I. Anticancer Properties of Solamargine: A Systematic Review. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M.; Rasooly, R. Review of the Inhibition of Biological Activities of Food-Related Selected Toxins by Natural Compounds. Toxins 2013, 5, 743–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, G.; Romero, M.A.; Tahir, F.; Farooqi, A.A. Emerging Themes of Regulation of Oncogenic Proteins by Solanum Nigrum and Its Bioactive Molecules in Different Cancers. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 9640–9644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sucha, L.; Tomsik, P. The Steroidal Glycoalkaloids from Solanaceae: Toxic Effect, Antitumour Activity and Mechanism of Action. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.T.; Choong, C.Y.; Tai, C.J. Solanine Attenuated Hepatocarcinoma Migration and Invasion Induced by Acetylcholine. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 1534735420909895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.R.; DasGupta, B.R. Molecular Differences between Type A Botulinum Neurotoxin and Its Toxoid. Toxicon 1989, 27, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, E.L.; Jones, E.B. Cholinergic Toxicity. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.-J.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Wang, X.-S.; Xu, S.-W.; Li, M.; Li, S. Effects of Avermectin on Microsomal Cytochrome P450 Enzymes in the Liver and Kidneys of Pigeons. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 38, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, D.J.S. John’s Wort and S-Adenosyl Methionine as “Natural” Alternatives to Conventional Antidepressants in the Era of the Suicidality Boxed Warning: What Is the Evidence for Clinically Relevant Benefit? Altern. Med. Rev. 2011, 16, 17–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, M.; Tayyab, M.; Naz, F.; Jamil, A.; Ashraf, M.; Gilani, A.H. Activity-Guided Isolation of a Novel Protein from Croton tiglium with Antifungal and Antibacterial Activities: A Novel Antimicrobial Protein From Croton tiglium. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 1646–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Tian, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Ren, A. Maternal Periconceptional Consumption of Sprouted Potato and Risks of Neural Tube Defects and Orofacial Clefts. Nutr. J. 2018, 17, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuschieri, A.; Calleja-Agius, J. Wnt/PCP Signalling Cascade Disruption by JNK Inhibition as a Potential Mechanism Underlying the Teratogenic Effects of Potato Glycoalkaloids. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 9235–9238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Compound | Structure | Applications Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Tomatidine |  | Antibiotic or antibiotic adjuvant (S. aureus [24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32], L monocytogenes [30,33], B. subtilis [30], P. aeruginosa [27,29], E. faecalis [27]) Antifungal (C. krusei [34], C. tropicalis [34], C. parapsilosis [34]) Antiviral (DENV-2 [35,36,37], CHIKV [38,39], PEDV [40], SARS-CoV-2 [41,42]) Anti-leishmanial (L. amazonensis [43]) Osteoporosis [44,45] Osteoarthritis [46,47,48] Anti-protozoal (T. cruzei Tulahuen C2C4 strain [49], P. serpens [50]) Skeletal muscle atrophy [36,51,52] Anti-aging [53,54] Anti-neurodegenerative [55,56,57,58,59] Asthma [60,61] Cardio-protection [62] Obesity [63,64] |
| α-Tomatine |  | Anti-neurodegenerative [65] Anti-protozoal (T. fetus feline, T. fetus bovine, T. vaginalis human) [66] |
| Solano-pubamine |  | Antiviral (HBV [67]) Antifungal (C. albicans, C. tenuis) [68] |
| α-Chaconine | 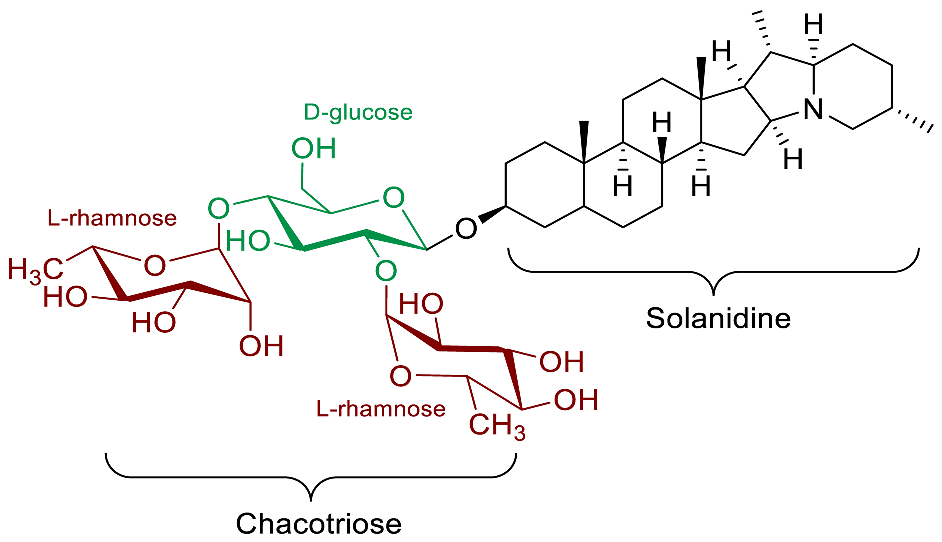 | Cardio-protection [9] Anti-inflammatory [69] Anti-protozoal (T. fetus feline, T. fetus bovine, T. vaginalis human) [66] |
| α-Solanine | 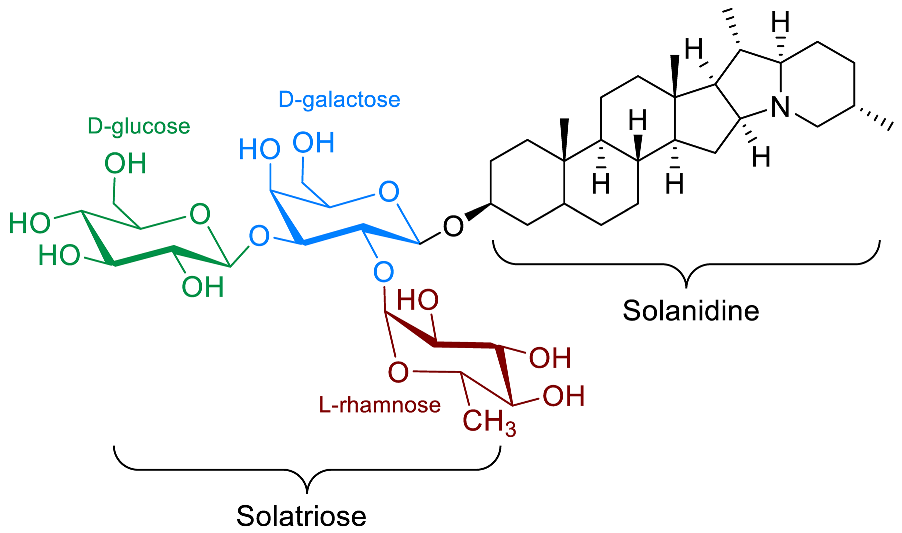 | Antiviral (SARS-CoV-2 [70]) Cardio-protection [9] Anti-inflammatory [71,72] Pulmonary hypertension [73,74,75] Anti-embryonic [76,77] Anti-protozoal (T. fetus feline, T. fetus bovine, T. vaginalis human) [66] |
| Solanine A |  | Anti-inflammatory [78] |
| Solasodine-3-O-β-D-glucopyran-oside | 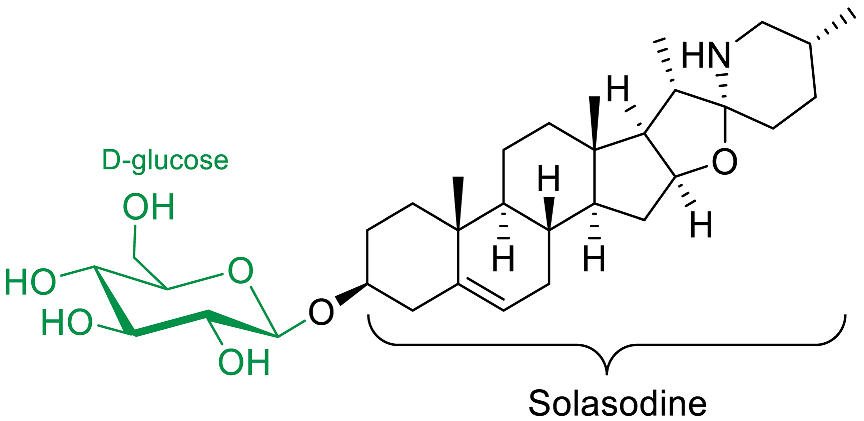 | Antifungal (C. albicans [79,80]) |
| Solamargine | 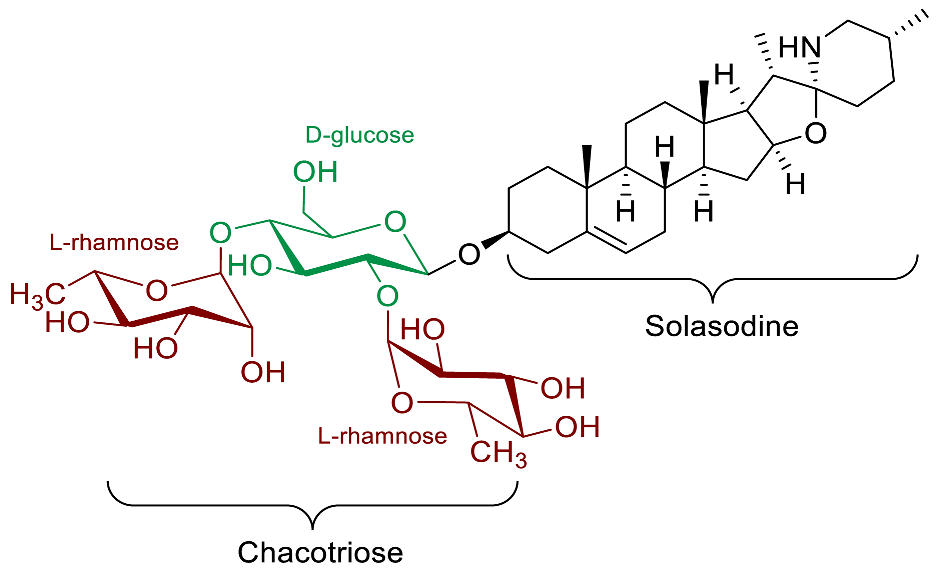 | Antibacterial effects (P. aeruginosa [81]) Anti-inflammatory [82] Anti-leishmanial (L. amazonensis [83], L. mexicana [84]) Antifungal (T. lentagrophytes [81]) Anti-protozoal (G. lamblia [85], T. cruzei Y stain [86]) Molluscicidal (B. alexandrina [87]) Schistosomicidal (S. mansoni [87]) |
| Khasianine |  | Anti-inflammatory [88] |
| Spiralosides A-C | 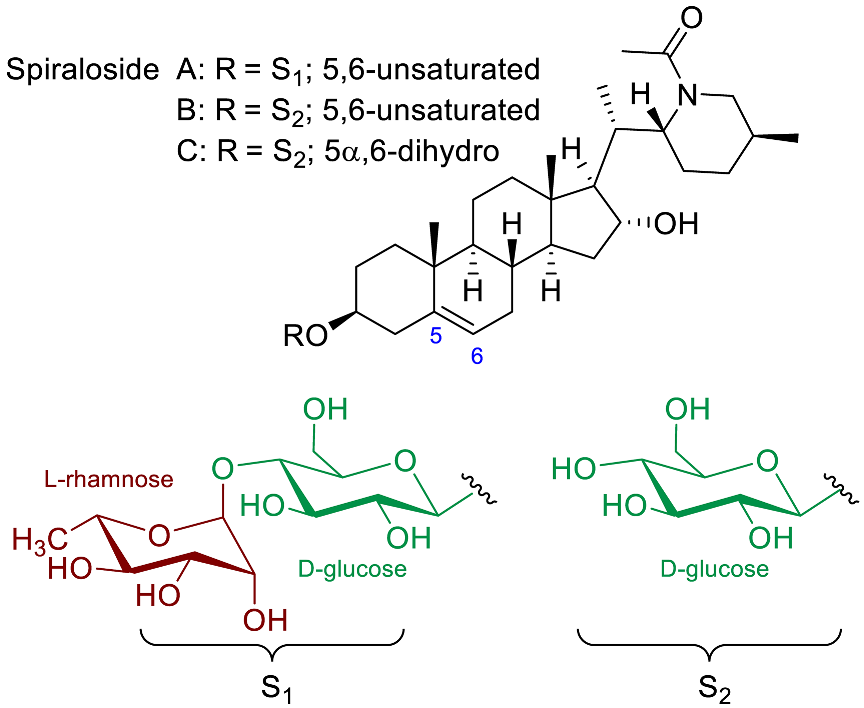 | Antitussive [89] |
| Solasodine + 22a(N)-Homosolasodine | 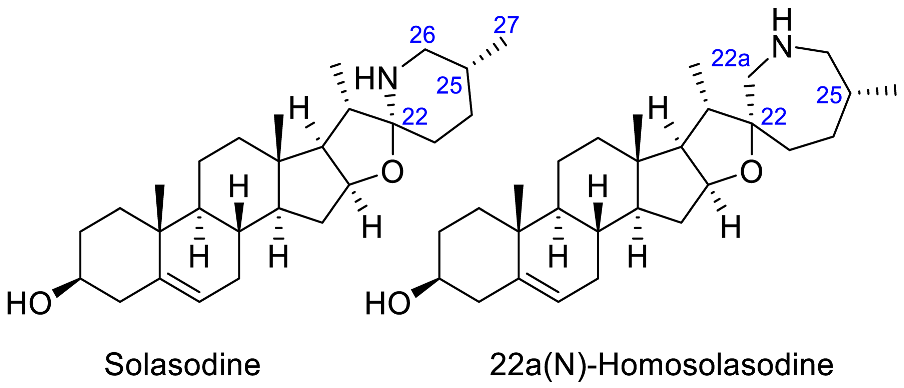 | Antineurodegenerative (Alzheimer’s [90]) |
| Solanindin B | 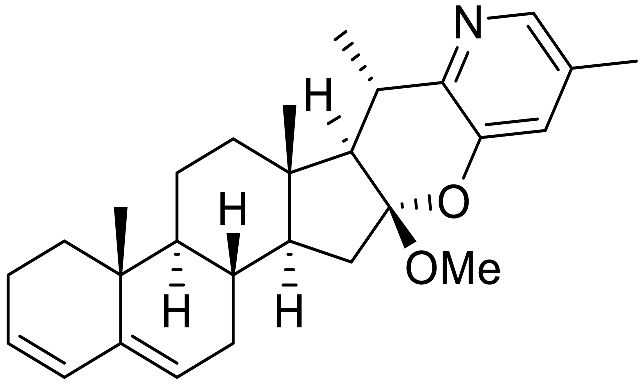 | Antibiotic (S. aureus [91]) |
| (25R)-22αN-4-nor-spirosol-5(6)-en-3β-ol-6-al glycosides | 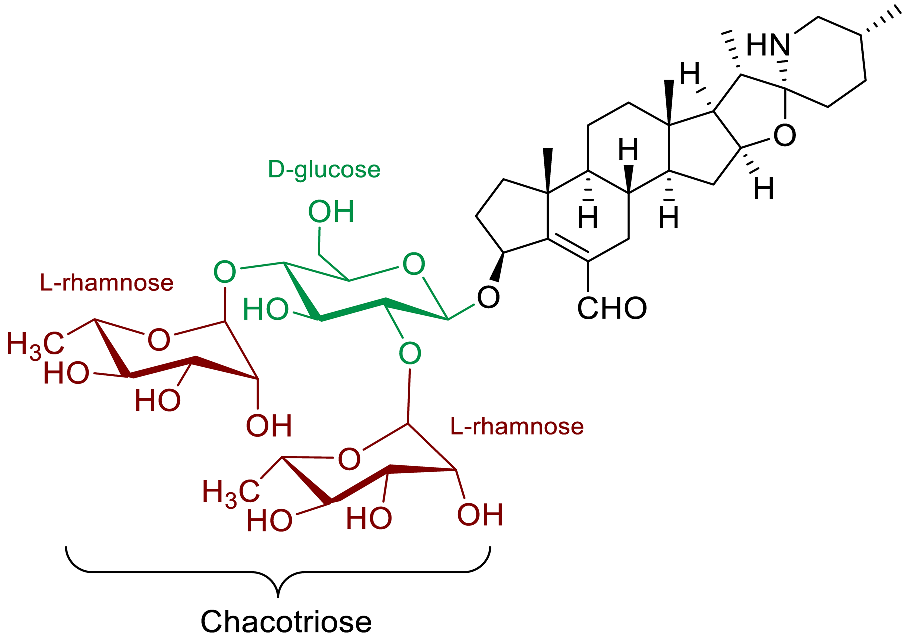 | Anti-inflammatory [92] |
| Abutiloside U |  | Anti-inflammatory [93] |
| Solasonine |  | Antiviral (SARS-CoV-2 [70]) Anti-leishmanial (L. amazonensis [83], L. mexicana [84]) Anti-protozoal (G. lamblia [85]) Molluscicidal (B. alexandrina [87]) Schistosomicidal (S. mansoni [87]) Anti-neurodegenerative [94] |
| Solanocapsine and derivatives | 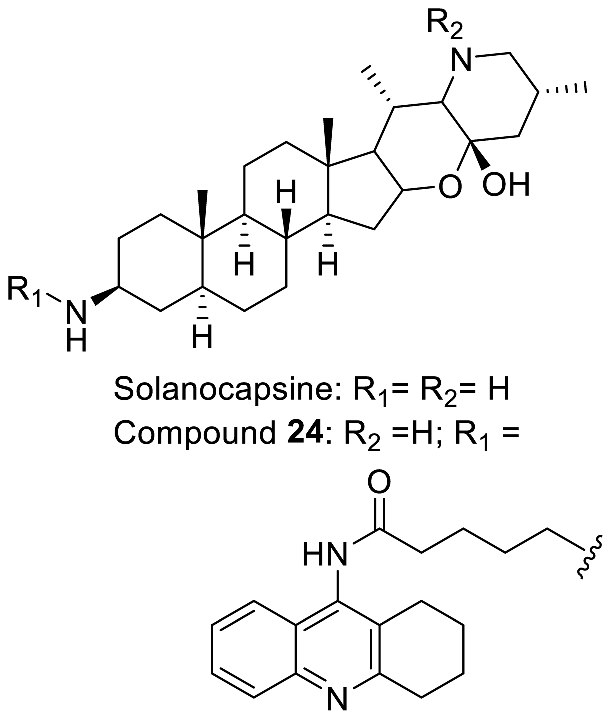 | Anti-neurodegenerative [95] |
| β-Solamarine | 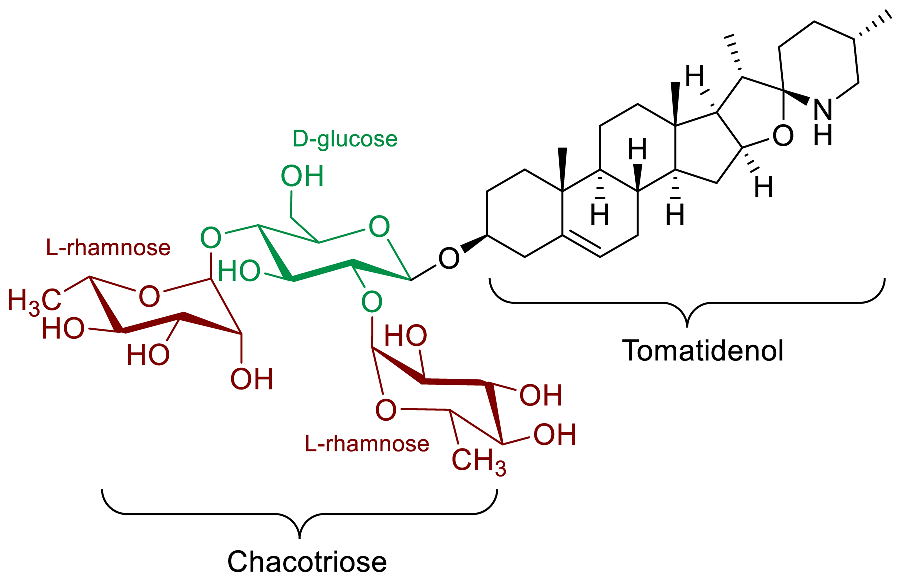 | Molluscicidal(G. truncatula Müll. [96]) |
| Lycoperoside H | 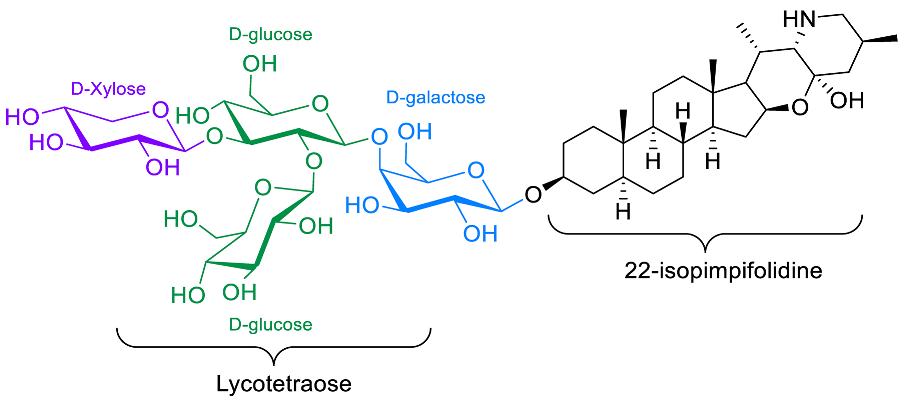 | Anti-inflammatory [97] |
| Solanidine | 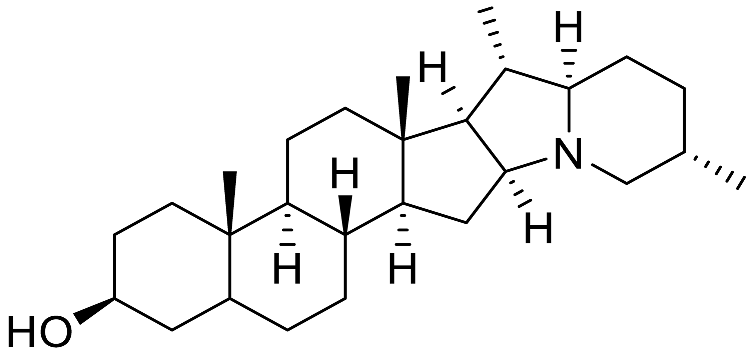 | Antiviral (SARS-CoV-2 [70]) |
| Compound | Cancer Type | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| α-Solanine | Non small-cell lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, choriocarcinoma, leukemia, esophageal, pancreatic, breast, adenocarcinoma, colorectal, endometrium, prostate, glioma, testicular, lung carcinoma, epithelial carcinoma | [98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121] |
| Solamargine | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma, prostate, multiple myeloma, lung cancer, leukemia, hepatoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, non-selective cytotoxicity, gastric | [122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133] |
| Solasodine | Ovarian | [134] |
| α-Tomatine | Ovarian | [135] |
| Solasonine | Gastric, pancreatic, bladder, leukemia, hepatocellular carcinoma | [123,132,136,137,138,139,140] |
| Khasianine | Leukemia | [123] |
| α-Chaconine | Endometrium, glioma | [100,104] |
| Solanidine | EAC solid tumor, CAM xenograft | [141] |
| Solanindin | Leukemia, lung, breast, colon | [91] |
| Solalyraine A-E | Lung carcinoma | [142] |
| (25R)-22αN-4-nor-spirosol-5(6)-en-3β-ol-6-al glycosides | Leukemia, histiocytic lymphoma, hepatocellular carcinoma | [92] |
| 16, 23-epoxy-22, 26-epimino-cholest22(N), 23, 25(26)-trien-3β-ol | Gastric, hepatic | [143] |
| Solanigroside P | Gastric | [132] |
| Lycoperoside H | Colorectal | [144] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delbrouck, J.A.; Desgagné, M.; Comeau, C.; Bouarab, K.; Malouin, F.; Boudreault, P.-L. The Therapeutic Value of Solanum Steroidal (Glyco)Alkaloids: A 10-Year Comprehensive Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 4957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134957
Delbrouck JA, Desgagné M, Comeau C, Bouarab K, Malouin F, Boudreault P-L. The Therapeutic Value of Solanum Steroidal (Glyco)Alkaloids: A 10-Year Comprehensive Review. Molecules. 2023; 28(13):4957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134957
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelbrouck, Julien A., Michael Desgagné, Christian Comeau, Kamal Bouarab, François Malouin, and Pierre-Luc Boudreault. 2023. "The Therapeutic Value of Solanum Steroidal (Glyco)Alkaloids: A 10-Year Comprehensive Review" Molecules 28, no. 13: 4957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134957
APA StyleDelbrouck, J. A., Desgagné, M., Comeau, C., Bouarab, K., Malouin, F., & Boudreault, P.-L. (2023). The Therapeutic Value of Solanum Steroidal (Glyco)Alkaloids: A 10-Year Comprehensive Review. Molecules, 28(13), 4957. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134957






