Microbial Diversity and Enzyme Activity as Indicators of Permethrin-Exposed Soil Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Reaction of Bacteria and Fungi to Permethrin
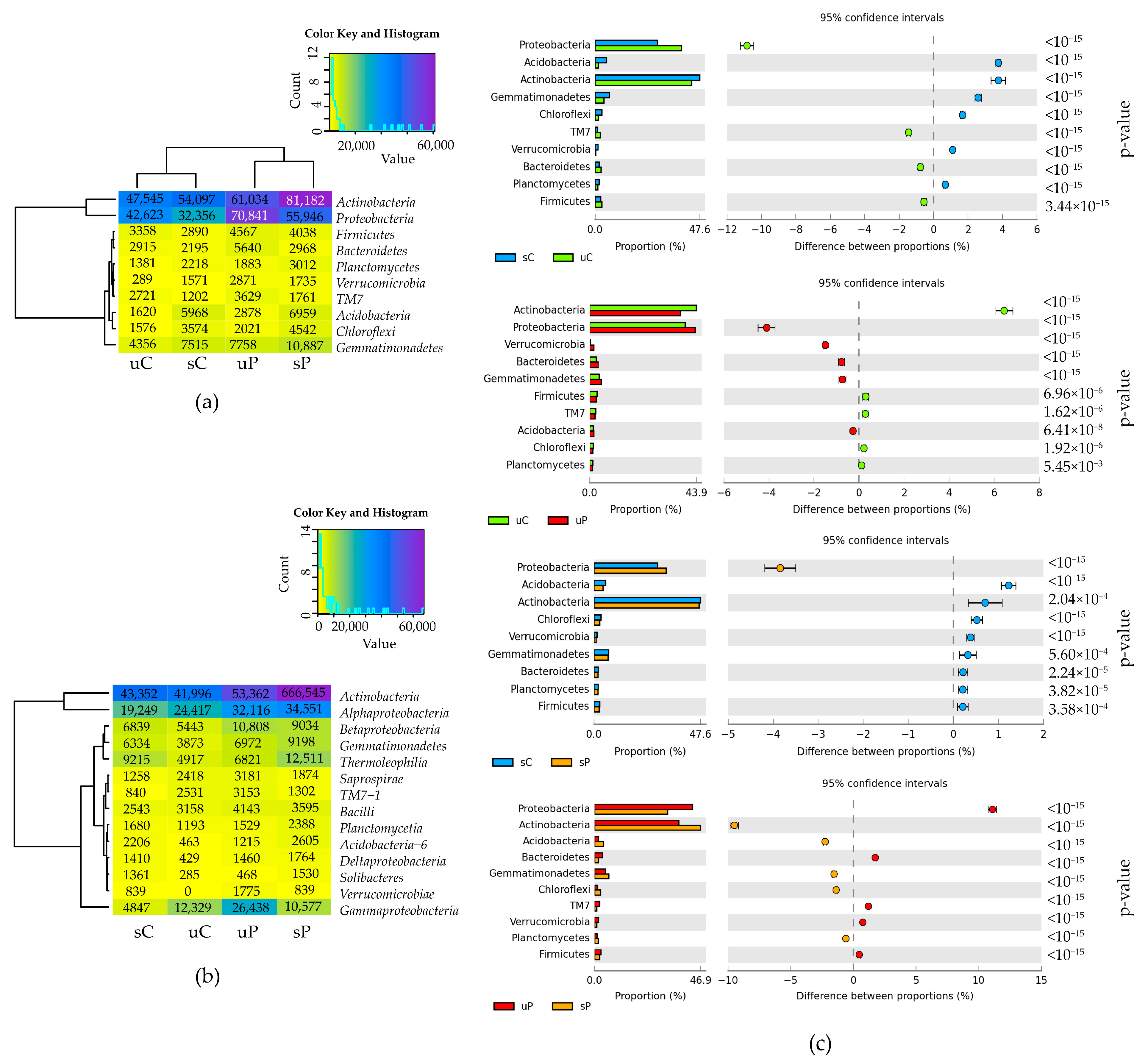
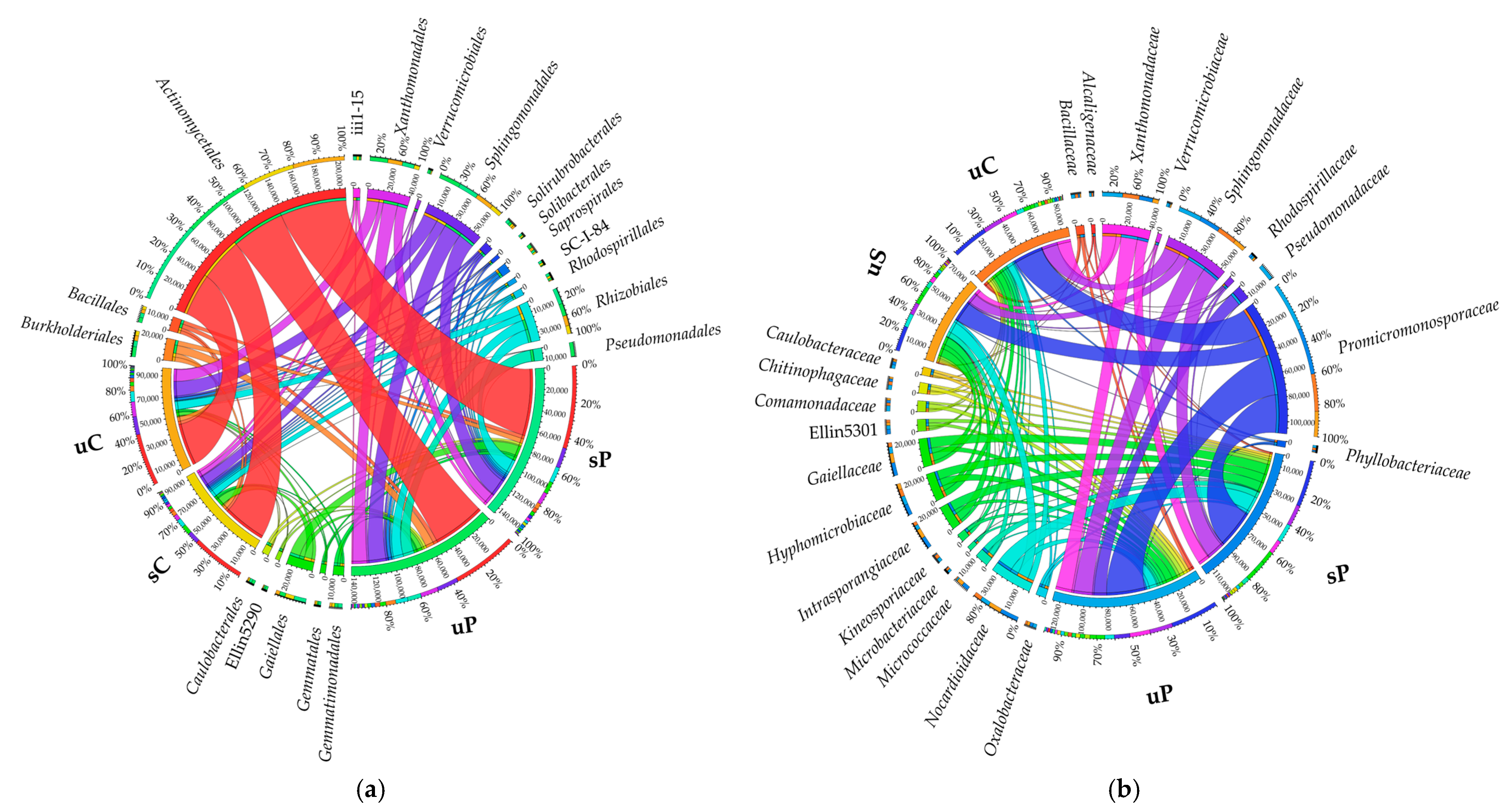
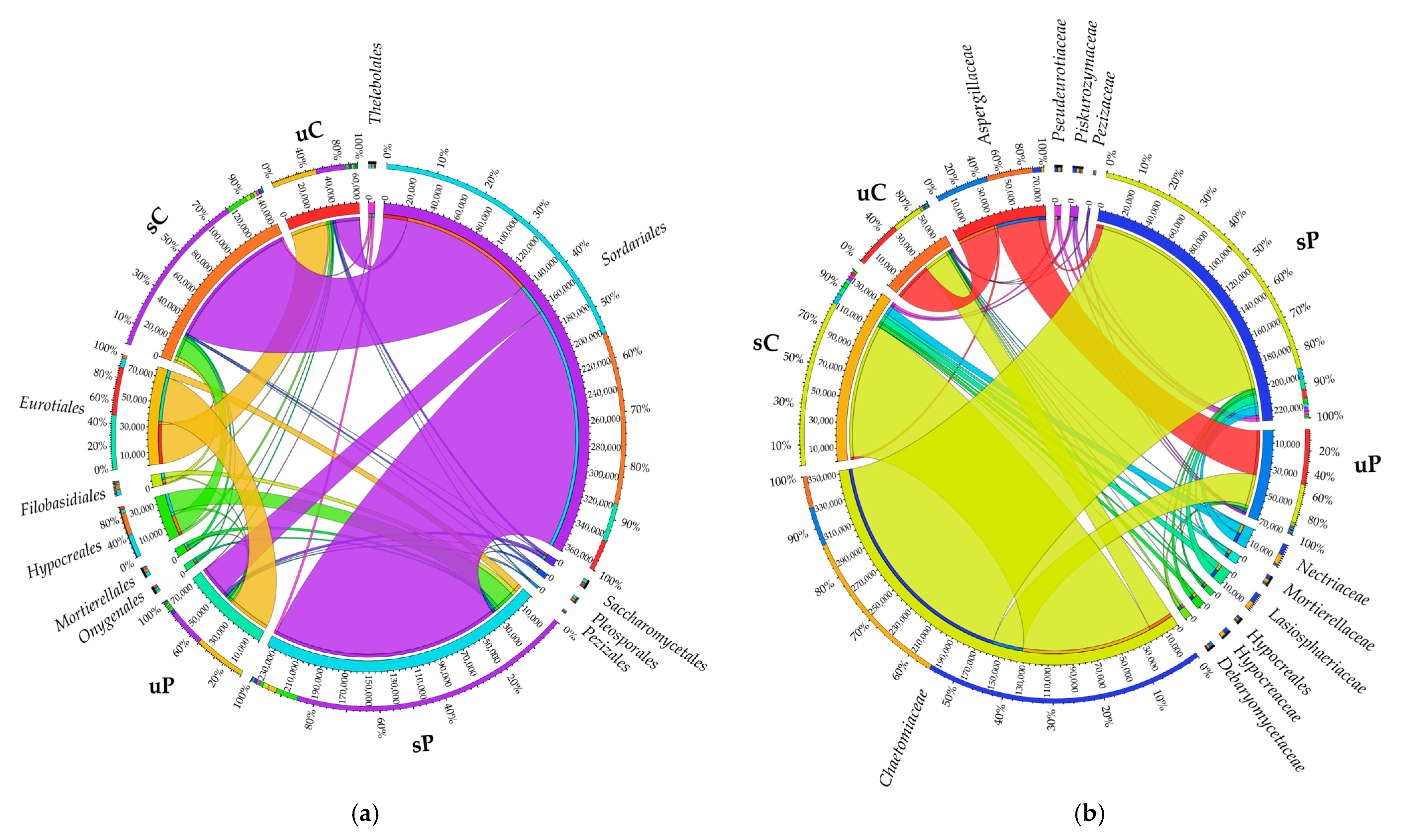
2.1.1. Non-Cultured Bacteria
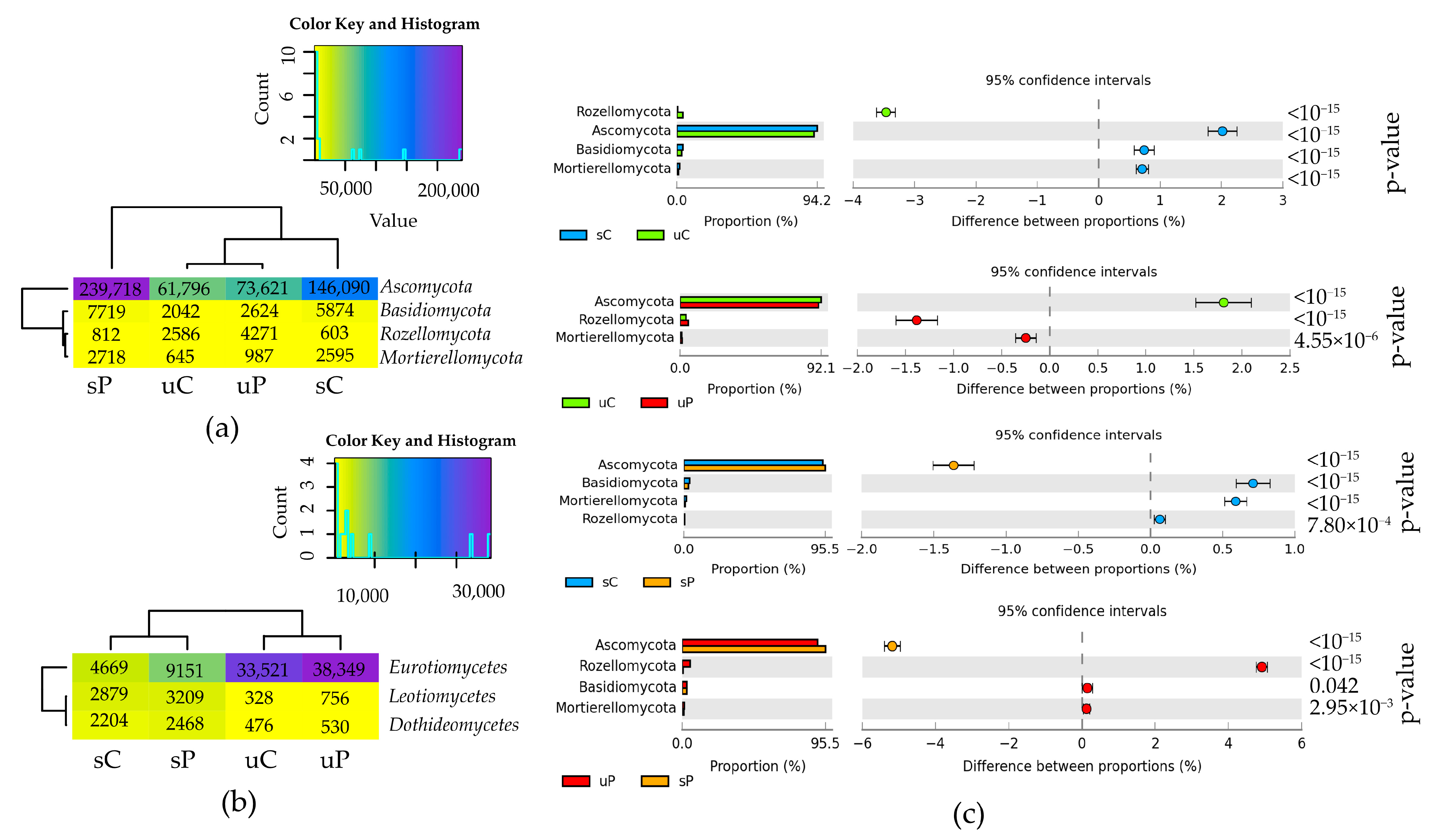
2.1.2. Non-Cultured Fungi
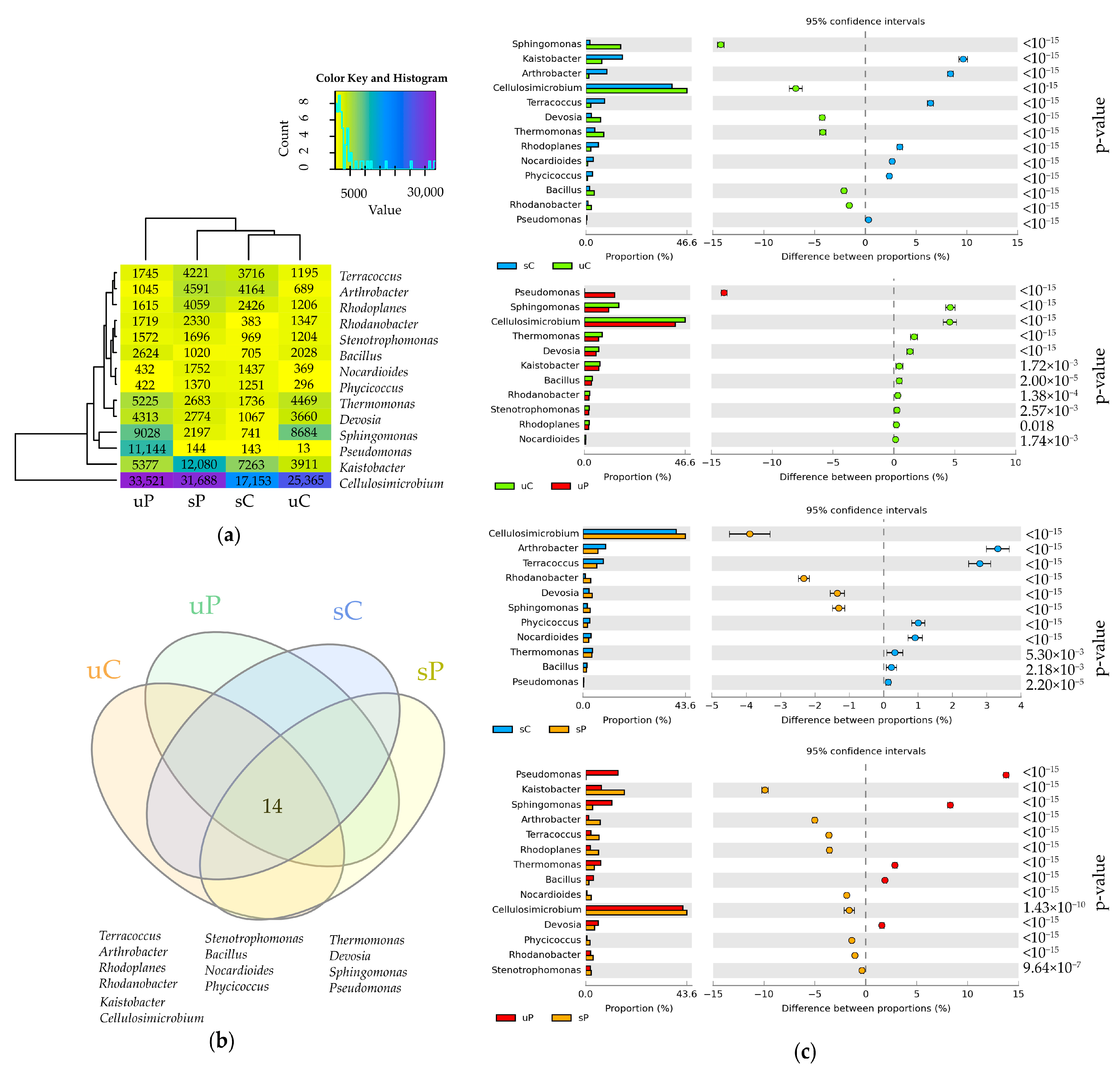
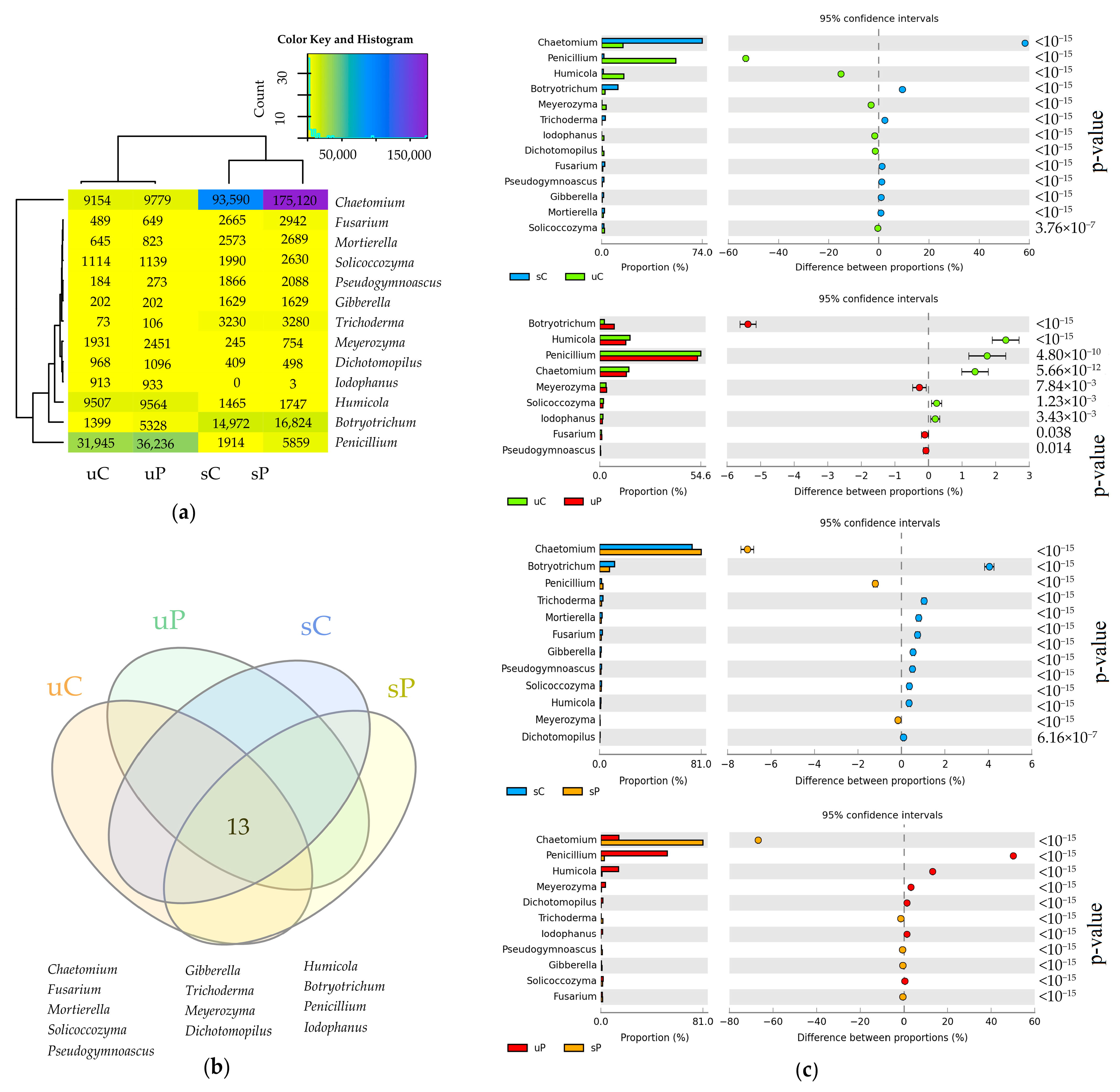
2.2. Cultured Microorganisms
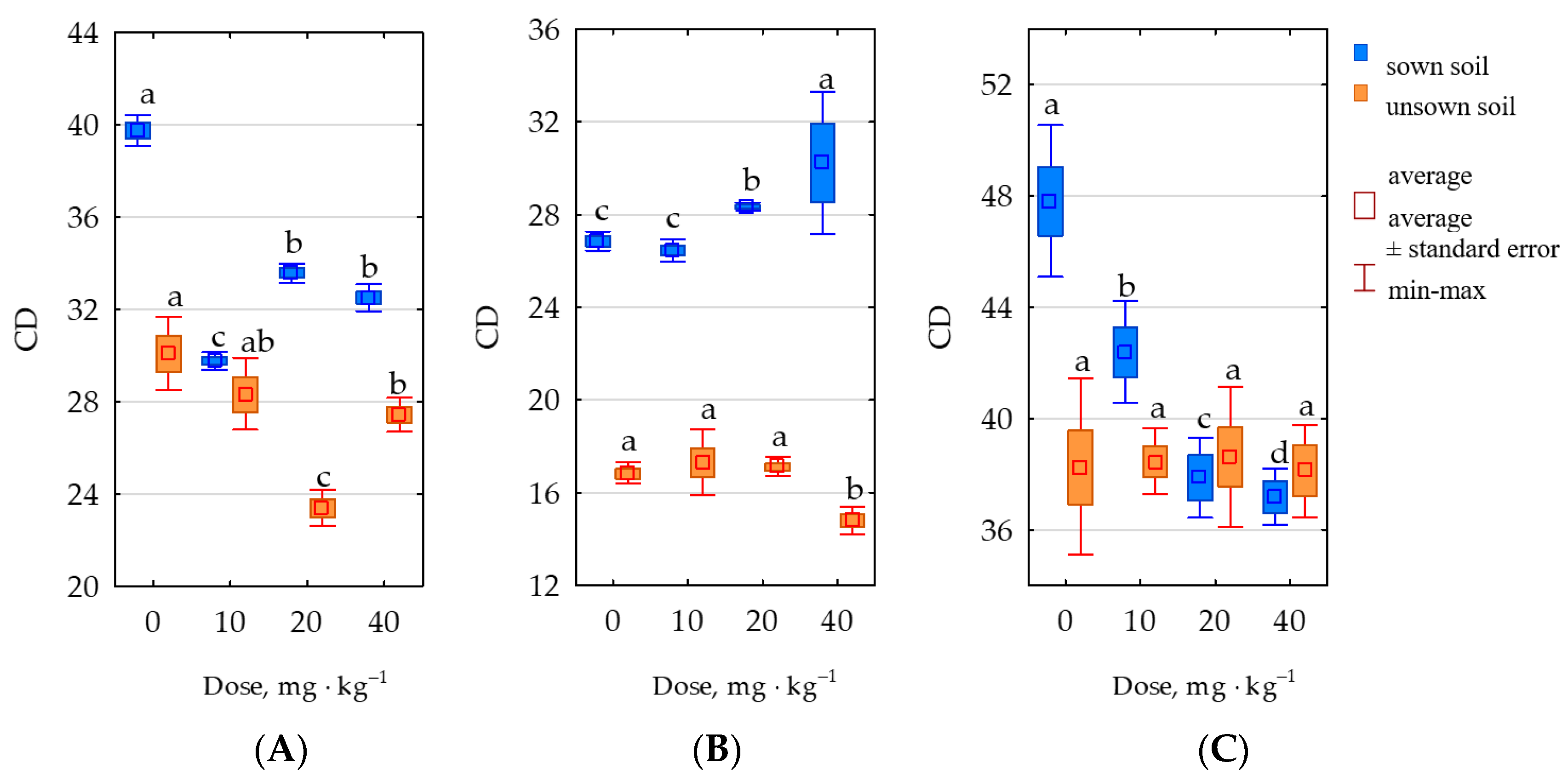
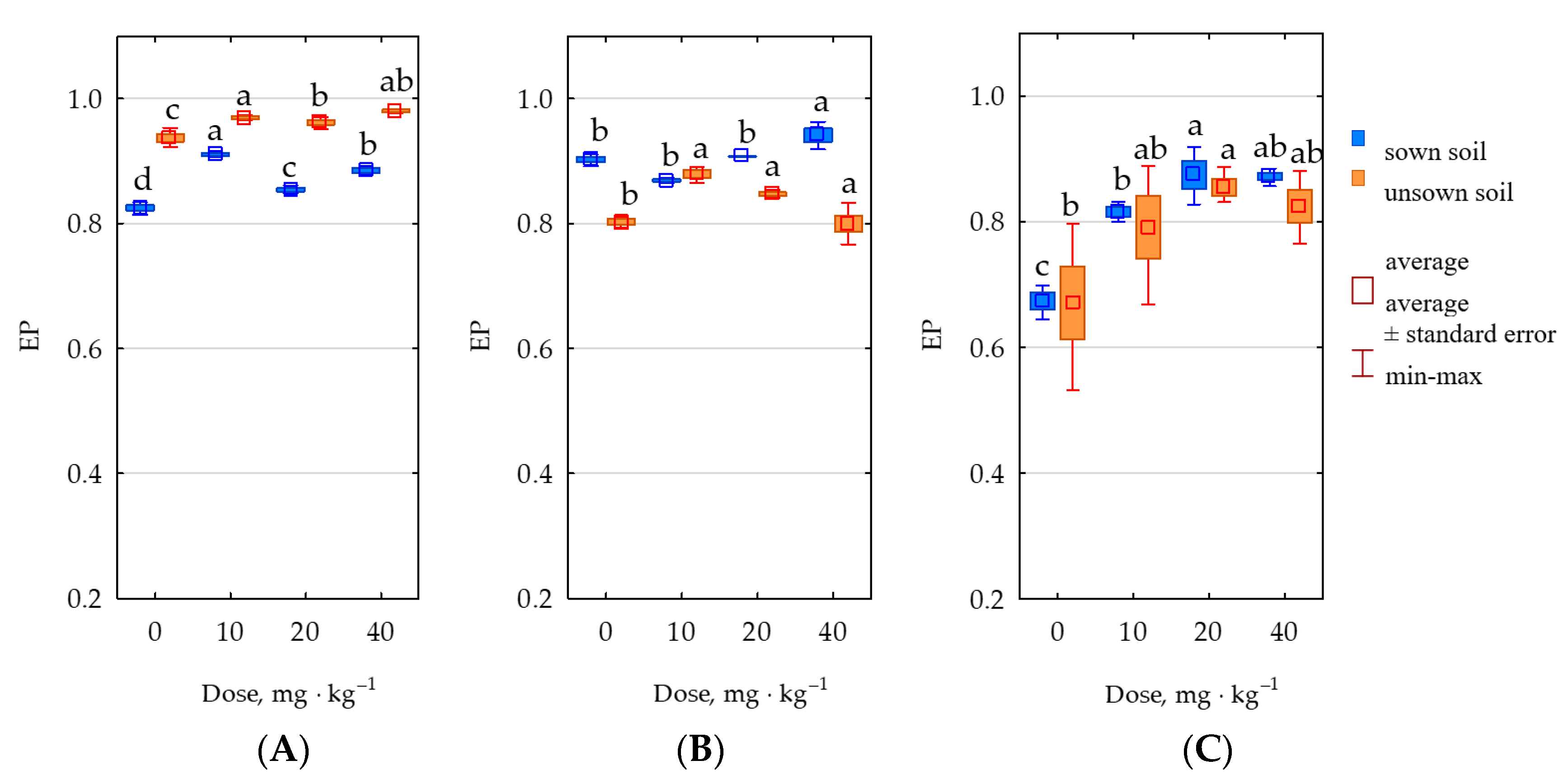
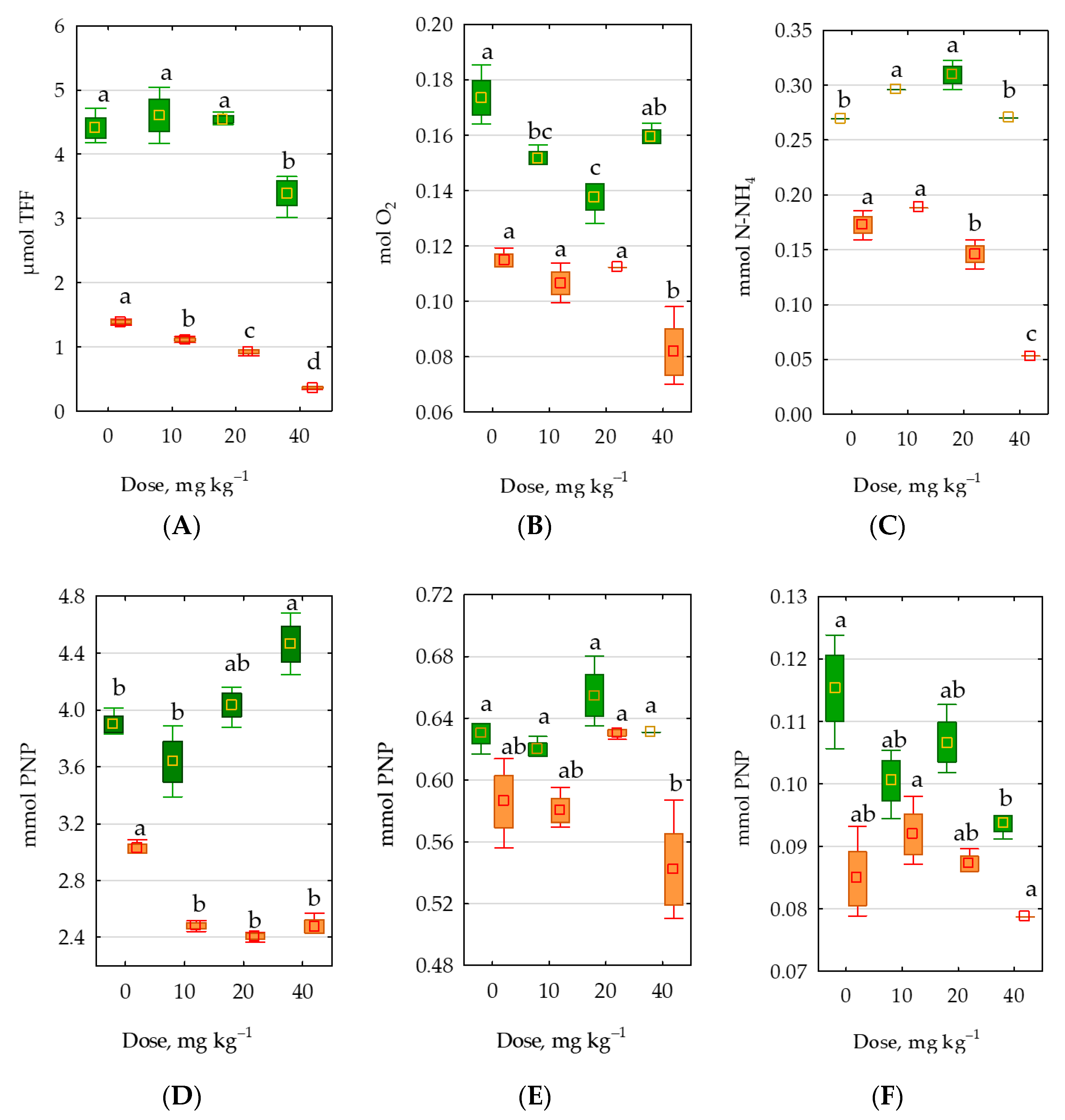
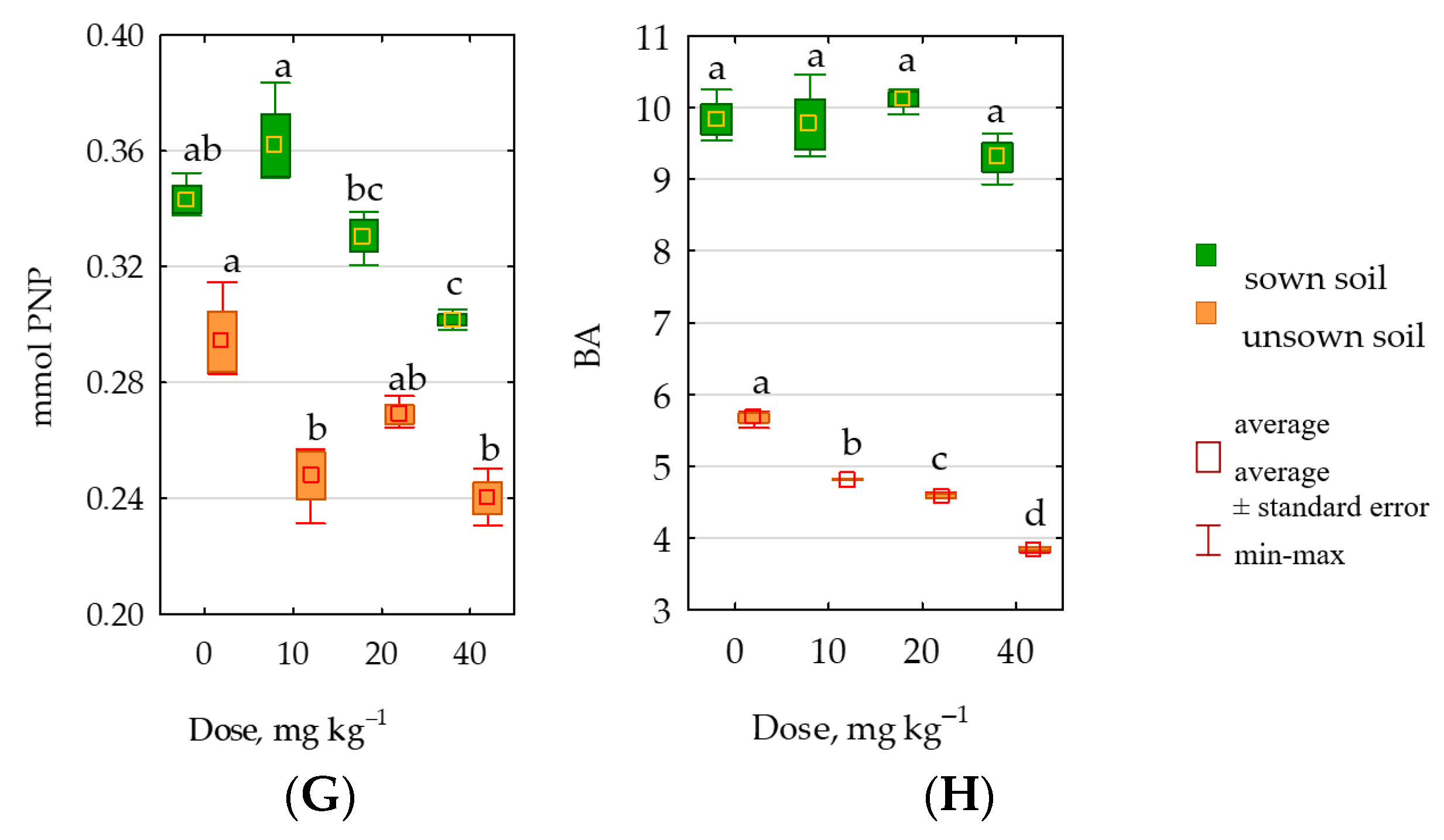
2.3. Response of Soil Enzymes to Permethrin
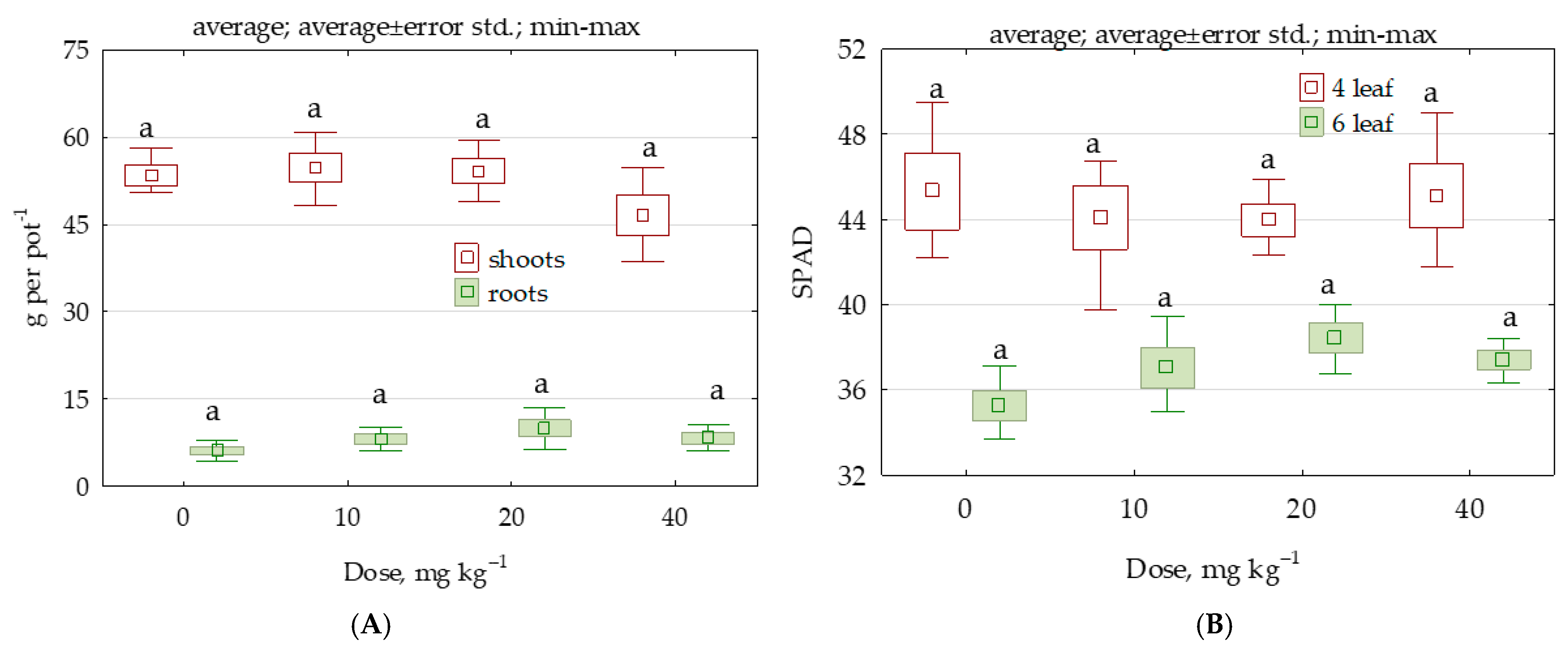
2.4. Response of Zea mays to Permethrin
3. Discussion
3.1. Response of Non-Cultured Bacteria and Fungi to Permethrin
3.2. Response of Cultured Microorganisms
3.3. Response of Soil Enzymes and Zea mays to Permethrin
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Soil Characterization
4.2. Permethrin Characterization
4.3. Design of the Experiment
4.4. Methods of Soil Microbiological Analysis
4.4.1. Breeding Microorganisms
4.4.2. Isolation of DNA and Identification of Bacteria and Fungi Using NGS Method
4.5. Biochemical Analysis of Soil
4.6. Data Analysis and Statistical Processing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
References
- International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS). International Decade of Soils (IDS) 2015–2024. Bulletin 2022, 141. Available online: https://www.iuss.org/ (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- USDA NRCS (United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service). NRCS: Washington, DC, USA. 2023. Available online: http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/ (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Babalola, O.O. Beneficial Bacteria of Agricultural Importance. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneviratne, G.; Zavahir, J.S. Role of Microbial Communities for Sustainability; Microorganisms for Sustainability; Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 29, p. 4. ISBN 9789811599118. [Google Scholar]
- Johns, C. Living Soils: The Role of Microorganisms in Soil Health. Future Directions International, Independent Strategic Analysis of Australia’s Global Interests 2017. Available online: https://apo.org.au/sites/default/files/resource-files/2017-06/apo-nid96931.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Torsvik, V.; Øvreås, L. Microbial Diversity and Function in Soil: From Genes to Ecosystems. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, D.; Lone, R.; Nazim, N.; Alaklabi, A.; Khan, S.; Koul, K.K. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacterial Diversity in Potato Grown Soil in the Gwalior Region of India. Biotechnol. Rep. 2022, 33, e00713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compant, S.; Samad, A.; Faist, H.; Sessitsch, A. A Review on the Plant Microbiome: Ecology, Functions, and Emerging Trends in Microbial Application. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 19, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Hu, K.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, A.; Yao, K.; Liu, S. Current Insights into the Microbial Degradation for Pyrethroids: Strain Safety, Biochemical Pathway, and Genetic Engineering. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Liu, W.; Lu, T.; Hu, B.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Lin, Z.; Qian, H. Rhizosphere Microbiome Assembly and Its Impact on Plant Growth. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 5024–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agler, M.T.; Ruhe, J.; Kroll, S.; Morhenn, C.; Kim, S.-T.; Weigel, D.; Kemen, E.M. Microbial Hub Taxa Link Host and Abiotic Factors to Plant Microbiome Variation. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Pesticide Consumption by Type|Statista. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1263206/global-pesticide-use-by-type/ (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- da Silva Sá, G.C.; Bezerra, P.V.V.; da Silva, M.F.A.; da Silva, L.B.; Barra, P.B.; de Fátima Freire de Melo Ximenes, M.; Uchôa, A.F. Arbovirus Vectors Insects: Are Botanical Insecticides an Alternative for Its Management? J. Pest Sci. 2023, 96, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toxics Release Inventory (TRI) Program|US EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/toxics-release-inventory-tri-program (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Smith, C.D.; Hladik, M.L.; Kuivila, K.M.; Waite, I.R. Field Assessment of Naled and Its Primary Degradation Product (Dichlorvos) in Aquatic Ecosystems Following Aerial Ultra-low Volume Application for Mosquito Control. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2023, 84, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA ERS—Home. Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/ (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- He, Y.; Guo, C.; Lv, J.; Deng, Y.; Xu, J. Occurrence, Sources, and Ecological Risks of Three Classes of Insecticides in Sediments of the Liaohe River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 62726–62735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascale, A.; Laborde, A. Impact of Pesticide Exposure in Childhood. Rev. Environ. Health 2020, 35, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nélieu, S.; Lamy, I.; Karolak, S.; Delarue, G.; Crouzet, O.; Barraud, C.; Bimbot, M.; Allaoui, F.; Hanot, C.; Delorme, A.; et al. Impact of Peri-Urban Landscape on the Organic and Mineral Contamination of Pond Waters and Related Risk Assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 59256–59267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derby, A.P.; Huff Hartz, K.E.; Fuller, N.W.; Landrum, P.F.; Reeve, J.D.; Poynton, H.C.; Connon, R.E.; Lydy, M.J. Effects of Temperature and Salinity on Bioconcentration and Toxicokinetics of Permethrin in Pyrethroid-Resistant Hyalella Azteca. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, A.F.S. Pesticides Environmental Destination: A Study Based on Coffee Productive Areas; Clube de Autores: Joinville, Brazil, 2018; ISBN 978-85-923212-4-6. [Google Scholar]
- Unuofin, J.O. Garbage in Garbage out: The Contribution of Our Industrial Advancement to Wastewater Degeneration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 22319–22335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iľko, I.; Peterková, V.; Heregová, M.; Strelková, L.; Preinerová, K.; Derka, T.; Boršová, K.; Čabanová, V. The Study on Biocidal Resistance of Mosquitoes of Genus Culex and Aedes to Commonly Used Biocides Cypermethrin and Deltamethrin in Central Europe. Biologia 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Khan, M.S. Ecotoxicological Implications of Residual Pesticides to Beneficial Soil Bacteria: A Review. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 188, 105272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kämmer, N.; Erdinger, L.; Braunbeck, T. The Onset of Active Gill Respiration in Post-Embryonic Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Larvae Triggers an Increased Sensitivity to Neurotoxic Compounds. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 249, 106240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Kansız, S.; Doğan, M.; Topel, Ö.; Akkoyunlu, G.; Kandur, M.Y.; Turna Demir, F. Hazard Assessment of the Effects of Acute and Chronic Exposure to Permethrin, Copper Hydroxide, Acephate, and Validamycin Nanopesticides on the Physiology of Drosophila: Novel Insights into the Cellular Internalization and Biological Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Walia, A.; Putatunda, C.; Solanki, P. Chapter 17—Impact of Pesticides on Microbial Diversity. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Singh, J., Pandey, A., Singh, S., Garg, V.K., Ramamurthy, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 427–458. ISBN 978-0-323-91900-5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.-Y.; Smartt, C.T.; Shin, D. Permethrin Resistance in Aedes Aegypti Affects Aspects of Vectorial Capacity. Insects 2021, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaoui, I.; Mateo-Sagasta, J. A Review on Occurrence of Emerging Pollutants in Waters of the MENA Region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 68090–68110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.R.; Biklé, A.; Archuleta, R.; Brown, P.; Jordan, J. Soil Health and Nutrient Density: Preliminary Comparison of Regenerative and Conventional Farming. Peer J. 2022, 10, e12848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günal, A.Ç.; Tunca, S.K.; Arslan, P.; Gül, G.; Dinçel, A.S. How Does Sublethal Permethrin Effect Non-Target Aquatic Organisms? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 52405–52417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowska, J.; Tomkiel, M.; Borowik, A.; Baćmaga, M.; Kucharski, J. Effect of Bentonite and Barley Straw on the Restoration of the Biological Quality of Agriculture Soil Contaminated with the Herbicide Successor T 550 SE. Agriculture 2021, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cycoń, M.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Pyrethroid-Degrading Microorganisms and Their Potential for the Bioremediation of Contaminated Soils: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Fernández, V.; García, M.A.; Marina, M.L. Characteristics and enantiomeric analysis of chiral pyrethroids. J. Chrom. A 2010, 1217, 968–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Elliott, A.; Hoffa, A.L.; Herring, N.; Houser, P.M. Characterization of a pyrethroid-degrading Pseudomonas fulva strain p31 and biochemical degradation pathway of d-phenothrin. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, H.; Wang, H.; Liao, L.; Feng, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. Kinetics and novel degradation pathway of permethrin in Acinetobacter baumannii ZH-14. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cycoń, M.; Zmijowska, A.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Enhancement of deltamethrin degradation by soil bioaugmentation with two different strains of Serratia marcescens. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Leoz, B.; Garbisu, C.; Antigüedad, I.; Alonso, M.L.; Alonso, R.M.; Ruiz-Romera, E. Deltamethrin degradation and soil microbial activity in a riparian wetland soil. Soil Sci. 2009, 174, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Permethrin, Resmethrin, d-Phenothrin (Sumithrin®): Synthetic Pyrethroids For Mosquito Control; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/mosquitocontrol/permethrin-resmethrin-d-phenothrin-sumithrinr-synthetic-pyrethroids-mosquito (accessed on 14 January 2023).
- Wei, X.; Peng, H.; Li, Y.; Meng, B.; Wang, S.; Bi, S.; Zhao, X. Pyrethroids exposure alters the community and function of the internal microbiota in Aedes albopictus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 252, 114579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Khan, M.S.; Syed, A.; Marraiki, N.; Elgorban, A.M. Mesorhizobium ciceri as biological tool for improving physiological, biochemical and antioxidant state of Cicer aritienum (L.) under fungicide stress. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil Health and Carbon Management. Food Energy Secur. 2016, 5, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowska, J.; Borowik, A.; Kucharski, J. The Role of Grass Compost and Zea Mays in Alleviating Toxic Effects of Tetracycline on the Soil Bacteria Community. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, J.W.; Zeiss, M.R. Soil Health and Sustainability: Managing the Biotic Component of Soil Quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2000, 15, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgiazzi, A.; Panagos, P.; Fernández-Ugalde, O.; Wojda, P.; Labouyrie, M.; Ballabio, C.; Franco, A.; Pistocchi, A.; Montanarella, L.; Jones, A. LUCAS Soil Biodiversity and LUCAS Soil Pesticides, New Tools for Research and Policy Development. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Bossio, D.A.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Rillig, M.C. The Concept and Future Prospects of Soil Health. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atwood, L.W.; Racette, K.A.; Diggelmann, M.; Masala, C.A.; Maund, S.; Oliver, R.; Screpanti, C.; Wironen, M.; Wood, S.A. Soil Health: New Opportunities to Innovate in Crop Protection Research and Development. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 821742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, T.; McCullum-Gomez, C.; Harmon, A.; Roberts, S. Organic Agriculture Supports Biodiversity and Sustainable Food Production. J. Hunger Environ. Nutr. 2011, 6, 398–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, P.; Mathieu, J.; Spain, A.; Brown, G.; Fragoso, C.; Lapied, E.; De Aquino, A.; Barois, I.; Barrios, E.; Barros, M.E.; et al. Soil Macroinvertebrate Communities: A World-Wide Assessment. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2022, 31, 1261–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, U.R.; Das, J.; Bano, S. Biological Indicators of Soil Health and Biomonitoring. In Advances in Bioremediation and Phytoremediation for Sustainable Soil Management: Principles, Monitoring and Remediation; Malik, J.A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 327–347. ISBN 978-3-030-89984-4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Ren, C.; Sun, H.; Min, L. Sorption, Desorption and Degradation of Neonicotinoids in Four Agricultural Soils and Their Effects on Soil Microorganisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streletskii, R.; Astaykina, A.; Krasnov, G.; Gorbatov, V. Changes in Bacterial and Fungal Community of Soil under Treatment of Pesticides. Agronomy 2022, 12, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letourneau, D.K.; Bothwell, S.G. Comparison of Organic and Conventional Farms: Challenging Ecologists to Make Biodiversity Functional. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mírian Rabelo de Faria; Lilian Simara Abreu Soares Costa; Josiane Barros Chiaramonte; Wagner Bettiol; Rodrigo Mendes The Rhizosphere Microbiome: Functions, Dynamics, and Role in Plant Protection. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2021, 46, 13–25. [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, N.; Guo, X.; Qiao, C. Cloning of Mpd Gene from a Chlorpyrifos-Degrading Bacterium and Use of This Strain in Bioremediation of Contaminated Soil. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 265, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myresiotis, C.K.; Vryzas, Z.; Papadopoulou-Mourkidou, E. Biodegradation of Soil-Applied Pesticides by Selected Strains of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) and Their Effects on Bacterial Growth. Biodegradation 2012, 23, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Peng, X.; Li, W.; Yan, Y. Mineralization of Chlorpyrifos by Co-Culture of Serratia and Trichosporon spp. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 1469–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Sultan, S.; Kertesz, M. Determination of Cypermethrin Degradation Potential of Soil Bacteria Along with Plant Growth-Promoting Characteristics. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 70, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neher, D.A.; Barbercheck, M.E. Soil Microarthropods and Soil Health: Intersection of Decomposition and Pest Suppression in Agroecosystems. Insects 2019, 10, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, J.; Ahnström, J.; Weibull, A.-C. The Effects of Organic Agriculture on Biodiversity and Abundance: A Meta-Analysis. J. Appl. Ecol. 2005, 42, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imade, E.E.; Babalola, O.O. Biotechnological Utilization: The Role of Zea Mays Rhizospheric Bacteria in Ecosystem Sustainability. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 4487–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Sharma, A.; Chen, S. Enhanced Cypermethrin Degradation Kinetics and Metabolic Pathway in Bacillus Thuringiensis Strain SG4. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokade, P.; Gaur, V.K.; Tripathi, V.; Bobate, S.; Manickam, N.; Bajaj, A. Bacterial Remediation of Pesticide Polluted Soils: Exploring the Feasibility of Site Restoration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Al-Tawaha, A.R.; Pandey, D.K.; Nongdam, P.; Shekhawat, M.S.; Dey, A.; Choudhary, K.; Sahay, S. Halophilic, Acidophilic, Alkaliphilic, Metallophilic, and Radioresistant Fungi: Habitats and Their Living Strategies. In Extremophilic Fungi: Ecology, Physiology and Applications; Sahay, S., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 171–193. ISBN 9789811649073. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell, J.A.; Witt, W.W.; Vencill, W.K. Sulfentrazone Absorption by Plant Roots Increases as Soil or Solution PH Decreases. Weed Sci. 2003, 51, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowik, A.; Wyszkowska, J.; Kucharski, M.; Kucharski, J. The Role of Dactylis Glomerata and Diesel Oil in the Formation of Microbiome and Soil Enzyme Activity. Sensors 2020, 20, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Hernández, M.L.; Sánchez-Salinas, E.; Dantán-González, E.; Castrejón-Godínez, M.L.; Ortiz-Hernández, M.L.; Sánchez-Salinas, E.; Dantán-González, E.; Castrejón-Godínez, M.L. Pesticide Biodegradation: Mechanisms, Genetics and Strategies to Enhance the Process; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-953-51-1154-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, Y.; Benmati, M.; Guendouzi, S.; Benmati, H.; Yuan, Y.; Song, J.; Xia, C.; Berkani, M. Latest Eco-Friendly Approaches for Pesticides Decontamination Using Microorganisms and Consortia Microalgae: A Comprehensive Insights, Challenges, and Perspectives. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.; García, C.; Hernández, T.; Gómez, I. Response of Soil Microbial Activity and Biodiversity in Soils Polluted with Different Concentrations of Cypermethrin Insecticide. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Sarkar, B.; Mandal, S.; Vithanage, M.; Patra, A.K.; Manna, M.C. Chapter 7—Impact of Agrochemicals on Soil Health. In Agrochemicals Detection, Treatment and Remediation; Prasad, M.N.V., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 161–187. ISBN 978-0-08-103017-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sogorb, M.A.; Vilanova, E. Enzymes Involved in the Detoxification of Organophosphorus, Carbamate and Pyrethroid Insecticides through Hydrolysis. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 128, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, D.H.; Fraser, N.J.; Mabbitt, P.D.; Carr, P.D.; Oakeshott, J.G.; Jackson, C.J. Structure of an Insecticide Sequestering Carboxylesterase from the Disease Vector Culex Quinquefasciatus: What Makes an Enzyme a Good Insecticide Sponge? Biochemistry 2017, 56, 5512–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Bhatt, K.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Chen, S. Esterase Is a Powerful Tool for the Biodegradation of Pyrethroid Insecticides. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, W.; Guang, C.; Mu, W. Microbial Elimination of Pyrethroids: Specific Strains and Involved Enzymes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 6915–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. New Insights into the Microbial Degradation and Catalytic Mechanism of Synthetic Pyrethroids. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, D.L.; Hobbie, S.E. The Effects of Substrate Composition, Quantity, and Diversity on Microbial Activity. Plant Soil 2010, 335, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shen, X.; Zhang, X.-C.; Liu, W.; Yang, F. Microbial Degradation of Alpha-Cypermethrin in Soil by Compound-Specific Stable Isotope Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 295, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kráľová, K.; Jampílek, J. Phytoremediation of Environmental Matrices Contaminated with Photosystem II-Inhibiting Herbicides. In Pesticides Bioremediation; Siddiqui, S., Meghvansi, M.K., Chaudhary, K.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 31–80. ISBN 978-3-030-97000-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wyszkowska, J.; Borowik, A.; Zaborowska, M.; Kucharski, J. Evaluation of the Usefulness of Sorbents in the Remediation of Soil Exposed to the Pressure of Cadmium and Cobalt. Materials 2022, 15, 5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarella, M.; Knutie, S.A.; Voss, M.A.; Cunninghame, F.; Florence-Bennett, B.J.; Robson, G.; Keyzers, R.A.; Taylor, L.M.; Lester, P.J.; Heimpel, G.E.; et al. Sub-Lethal Effects of Permethrin Exposure on a Passerine: Implications for Managing Ectoparasites in Wild Bird Nests. Conserv. Physiol. 2020, 8, coaa076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunt, J.S.; Rovira, A.D. Microbiological Studies of Some Subantarctic Soils. J. Soil Sci. 1955, 6, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowska, J.; Borowik, A.; Zaborowska, M.; Kucharski, J. Sensitivity of Zea Mays and Soil Microorganisms to the Toxic Effect of Chromium (VI). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowik, A.; Wyszkowska, J.; Wyszkowski, M. Resistance of Aerobic Microorganisms and Soil Enzyme Response to Soil Contamination with Ekodiesel Ultra Fuel. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24346–24363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarathchandra, S.U.; Burch, G.; Cox, N.R. Growth Patterns of Bacterial Communities in the Rhizoplane and Rhizosphere of White Clover (Trifolium Repens L.) and Perennial Ryegrass (Lolium Perenne L.) in Long-Term Pasture. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1997, 6, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leij, F.A.A.M.; Whipps, J.M.; Lynch, J.M. The Use of Colony Development for the Characterization of Bacterial Communities in Soil and on Roots. Microb. Ecol. 1994, 27, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibco Software Inc. Statistica, Version 13. Data Analysis Software System. Tibco Software Inc.: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.statsoft.pl/statistica-i-tibco-software/ (accessed on 18 October 2021).
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical Analysis of Taxonomic and Functional Profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2019; Available online: http://www.Rstudio.com/ (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Warnes, G.R.; Bolker, B.; Bonebakker, L.; Gentleman, R.; Huber, W.; Liaw, A.; Lumley, T.; Maechler, M.; Magnusson, A.; Moeller, S.; et al. Gplots: Various R Programming Tools for Plotting Data 2022 R Package Version 2.17.0. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-Project.Org/Package=gplots (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, İ.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An Information Aesthetic for Comparative Genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heberle, H.; Meirelles, G.V.; da Silva, F.R.; Telles, G.P.; Minghim, R. InteractiVenn: A Web-Based Tool for the Analysis of Sets through Venn Diagrams. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borowik, A.; Wyszkowska, J.; Zaborowska, M.; Kucharski, J. Microbial Diversity and Enzyme Activity as Indicators of Permethrin-Exposed Soil Health. Molecules 2023, 28, 4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124756
Borowik A, Wyszkowska J, Zaborowska M, Kucharski J. Microbial Diversity and Enzyme Activity as Indicators of Permethrin-Exposed Soil Health. Molecules. 2023; 28(12):4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124756
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorowik, Agata, Jadwiga Wyszkowska, Magdalena Zaborowska, and Jan Kucharski. 2023. "Microbial Diversity and Enzyme Activity as Indicators of Permethrin-Exposed Soil Health" Molecules 28, no. 12: 4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124756
APA StyleBorowik, A., Wyszkowska, J., Zaborowska, M., & Kucharski, J. (2023). Microbial Diversity and Enzyme Activity as Indicators of Permethrin-Exposed Soil Health. Molecules, 28(12), 4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124756









