Ultrastable and Responsive Foams Based on 10-Hydroxystearic Acid Soap for Spore Decontamination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
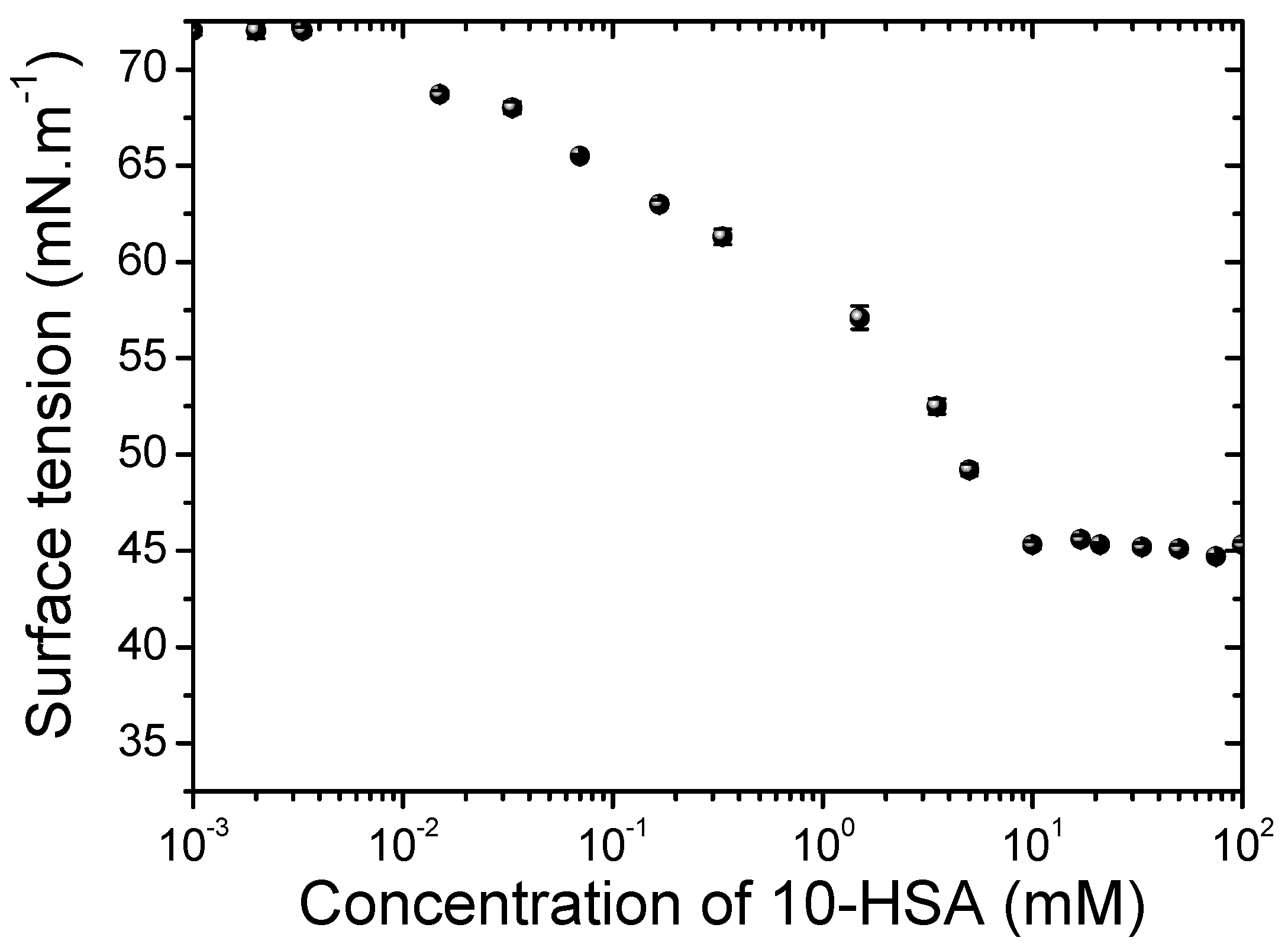
2.1. Critical Aggregation Concentration of 10-HSA Dispersion
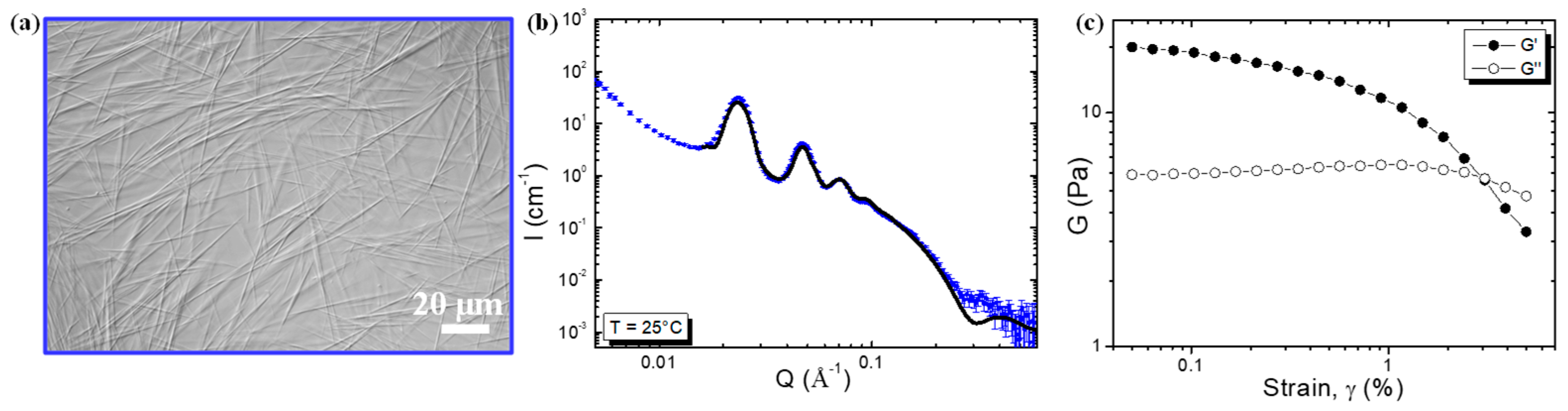
2.2. Self-Assembled Structure and Rheological Properties at 25 °C
2.3. Evolution of the Self-Assembled Structure and Rheological Properties with Increasing Temperature
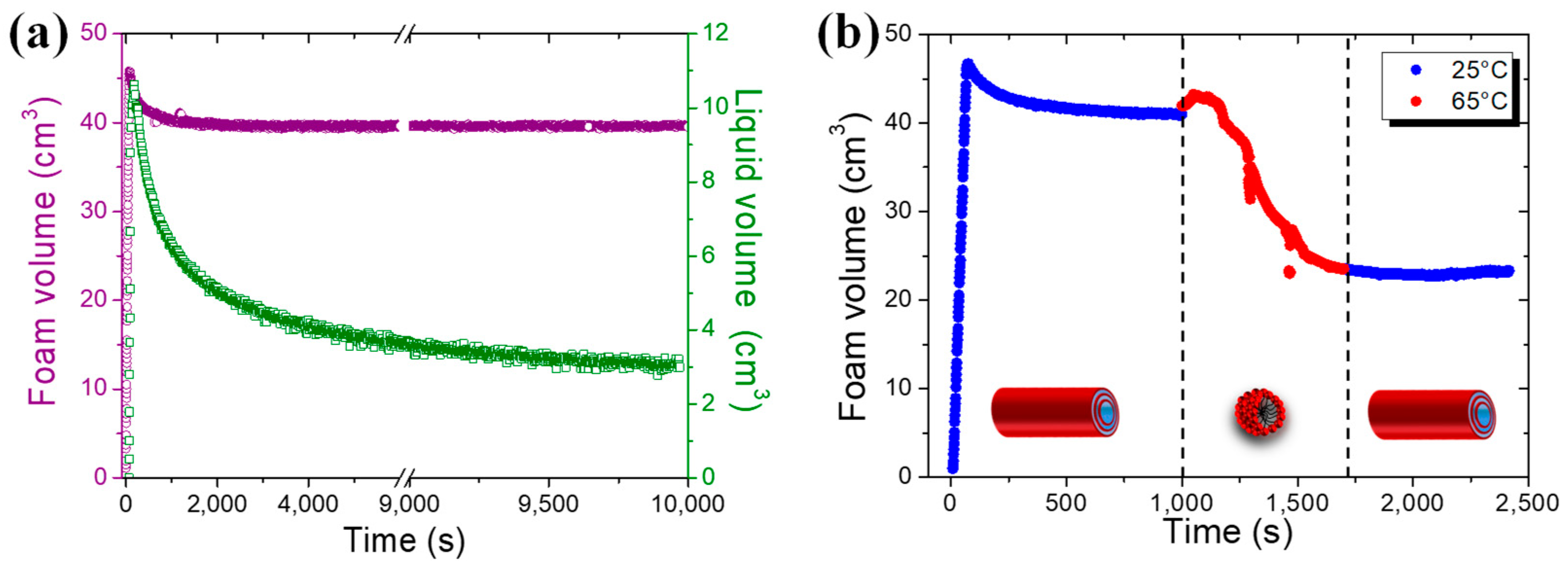
2.4. Foaming Properties with Time and Temperature
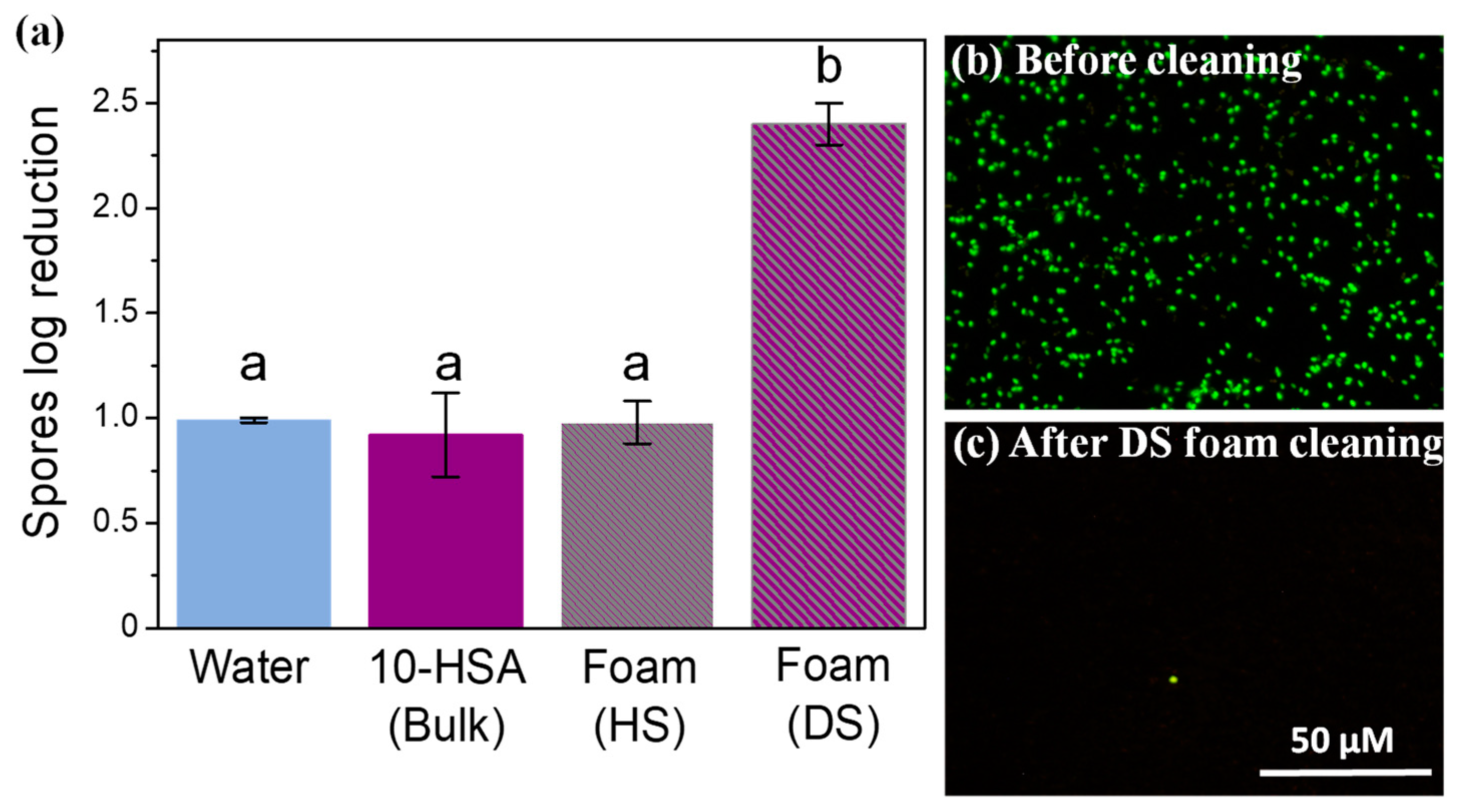
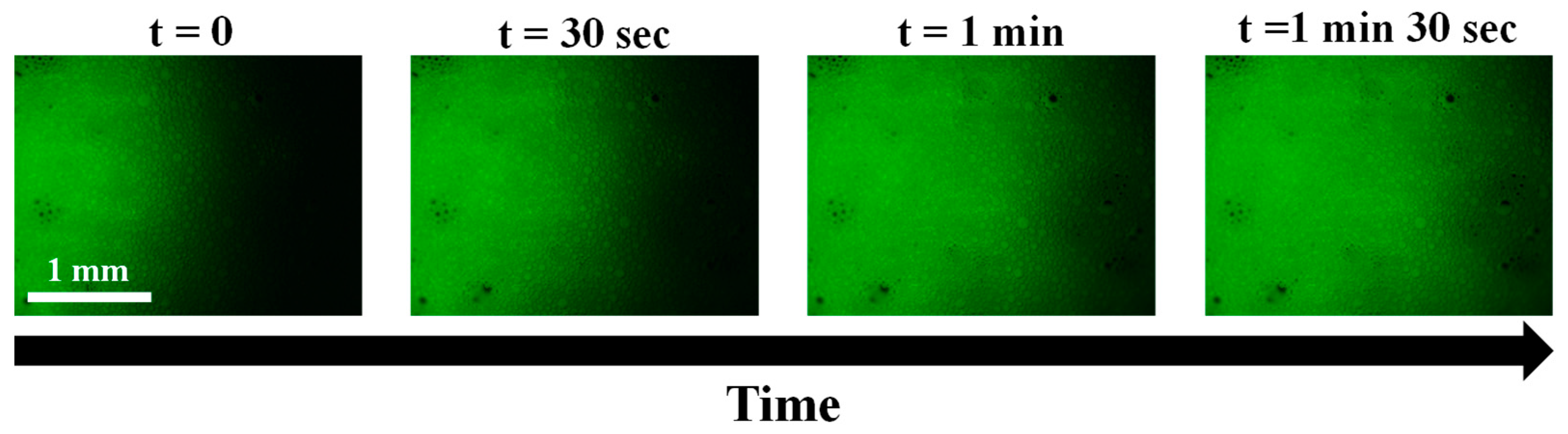
2.5. Cleaning of Spore Contamination on Surfaces by Foam Imbibition
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.1.1. Preparation of 10-Hydroxystearic Acid Dispersion
3.1.2. Preparation of Solid Model Surfaces
3.1.3. Preparation of Hydrophilic Spore Suspension
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Determination of Critical Aggregation Concentration via Surface Tension Measurements
3.2.2. Microscopic Observation of the 10-HSA Dispersion
3.2.3. Rheological Measurements
3.2.4. Small-Angle Neutron Scattering (SANS) and Wide-Angle X-ray Scattering (WAXS)
3.2.5. Foam Characterization with Temperature and Time
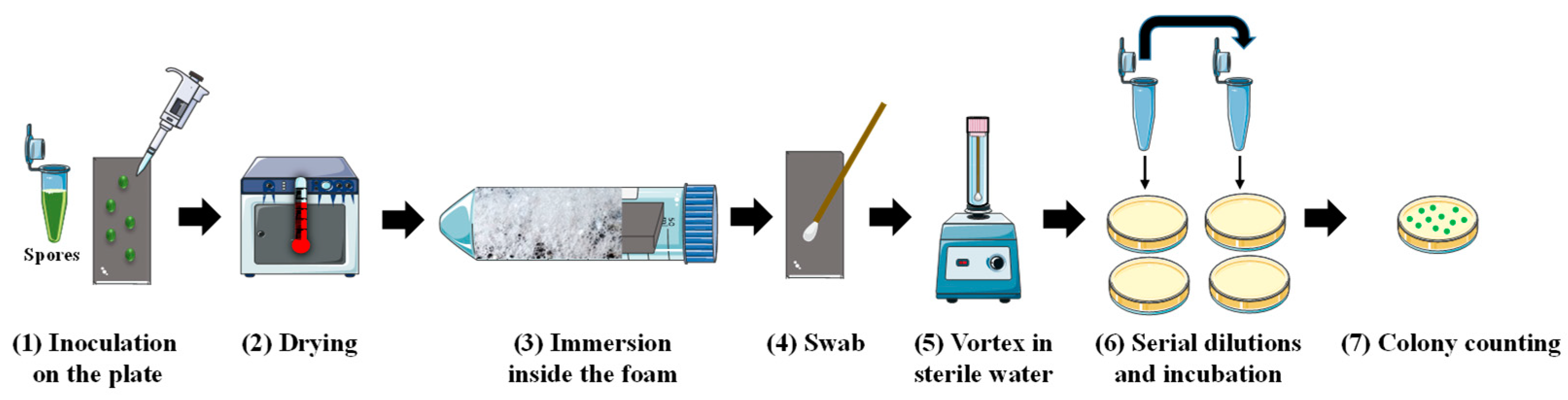
3.2.6. Production and Characterization of Foams for Spore Detachment
3.2.7. Viability of Spores
3.2.8. Spore Detachment Analysis
3.2.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Drakontis, C.E.; Amin, S. Biosurfactants: Formulations, Properties, and Applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 48, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfrum, S.; Marcus, J.; Touraud, D.; Kunz, W. A renaissance of soaps?—How to make clear and stable solutions at neutral pH and room temperature. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 236, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, J.S.; Naik, V.M.; Singhal, S.; Juvekar, V.A. Soap: The polymorphic genie of hierarchically structured soft condensed-matter products. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 6347–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, M. Pouchers Perfumes, Cosmetics and Soaps, Soap, 10th ed.; Butler, H., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 1993; pp. 453–465. [Google Scholar]
- Fameau, A.-L.; Gaillard, C.; Marion, D.; Bakan, B. Interfacial properties of functionalized assemblies of hydroxy-fatty acid salts isolated from fruit tomato peels. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameau, A.; Marangoni, A.G. Back to the future: Fatty acids, the green genie to design smart soft materials. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameau, A.-L.; Rogers, M.A. The curious case of 12-hydroxystearic acid — the Dr. Jekyll & Mr. Hyde of molecular gelators. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 45, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.-C.; Seo, E.-S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, K.-R.; Park, J.-B.; Oh, D.-K. Production of 10-hydroxystearic acid from oleic acid by whole cells of recombinant Escherichia coli containing oleate hydratase from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 158, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, E.-Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Yang, K.-M.; Joo, Y.-C.; Oh, D.-K.; Park, J.-B. Bioprocess engineering to produce 10-hydroxystearic acid from oleic acid by recombinant Escherichia coli expressing the oleate hydratase gene of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-X.; Pan, J.; Yu, H.-L.; Xu, J.-H. Enzymatic synthesis of 10-oxostearic acid in high space-time yield via cascade reaction of a new oleate hydratase and an alcohol dehydrogenase. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 306, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, S.; De Simeis, D.; Castagna, A.; Valentino, M. The fatty-acid hydratase activity of the most common probiotic microorganisms. Catalysts 2020, 10, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koritala, S.; Hou, C.T.; Hesseltine, C.W.; Bagby, M.O. Microbial conversion of oleic acid to 10-hydroxystearic acid. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1989, 32, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, S.; De Simeis, D. New insights on the baker’s yeast-mediated hydration of oleic acid: The bacterial contaminants of yeast are responsible for the stereoselective formation of (R)-10-hydroxystearic acid. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaro, F.; Boga, C.; De Zorzi, R.; Geremia, S.; Gigli, L.; Nitti, P.; Semeraro, S. (R)-10-Hydroxystearic Acid: Crystals vs. Organogel. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douliez, J.-P.; Gaillard, C.; Navailles, L.; Nallet, F. Novel lipid system forming hollow microtubes at high yields and concentration. Langmuir 2006, 22, 2942–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fameau, A.-L.; Houinsou-Houssou, B.; Novales, B.; Navailles, L.; Nallet, F.; Douliez, J.-P. 12-Hydroxystearic acid lipid tubes under various experimental conditions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 341, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fameau, A.-L.; Cousin, F.; Saint-Jalmes, A. Morphological Transition in Fatty Acid Self-Assemblies: A Process Driven by the Interplay between the Chain-Melting and Surface-Melting Process of the Hydrogen Bonds. Langmuir 2017, 33, 12943–12951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameau, A.-L.; Ventureira, J.; Novales, B.; Douliez, J.-P. Foaming and emulsifying properties of fatty acids neutralized by tetrabutylammonium hydroxide. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 403, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameau, A.-L.; Saint-Jalmes, A. Yielding and flow of solutions of thermoresponsive surfactant tubes: Tuning macroscopic rheology by supramolecular assemblies. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 3622–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, K.S.; Rahaii, B.; Fuller, G.G. Surface rheological transitions in Langmuir monolayers of bi-competitive fatty acids. Langmuir 2002, 18, 6597–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollhardt, D.; Siegel, S.; Cadenhead, D.A. Effect of hydroxyl group position and system parameters on the features of hydroxystearic acid monolayers. Langmuir 2004, 20, 7670–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollhardt, D.; Siegel, S.; Cadenhead, D.A. Characteristic features of hydroxystearic acid monolayers at the air/water interface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17448–17456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameau, A.-L.; Saint-Jalmes, A.; Cousin, F.; Houinsou Houssou, B.; Novales, B.; Navailles, L.; Nallet, F.; Gaillard, C.; Boué, F.; Douliez, J.-P. Smart foams: Switching reversibly between ultrastable and unstable foams. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8264–8269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallet, F.; Laversanne, R.; Roux, D. Modelling X-ray or neutron scattering spectra of lyotropic lamellar phases: Interplay between form and structure factors. J. Phys. II 1993, 3, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, C.; Artzner, F.; Suchod, B.; Berthault, M.; Konovalov, O.; Pecaut, J.; Smilgies, D.; Renault, A. Two-and three-dimensional stacking of chiral alcohols. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 12778–12785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schad, T.; Preisig, N.; Blunk, D.; Piening, H.; Drenckhan, W.; Stubenrauch, C. Less is more: Unstable foams clean better than stable foams. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 590, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, T.; Krzewinski, F.; Yamakawa, N.; Lemy, C.; Hamiot, A.; Brunet, L.; Lacoste, A.-S.; Knirel, Y.; Guerardel, Y.; Faille, C. The sps genes encode an original legionaminic acid pathway required for crust assembly in Bacillus subtilis. MBio 2020, 11, e01153-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, T.; Roché, M.; Honorez, C.; Jumeau, M.; Balan, A.; Jedrzejczyk, C.; Drenckhan, W. Controlled foam generation using cyclic diphasic flows through a constriction. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2017, 96, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dari, C.; Dallagi, H.; Faille, C.; Dubois, T.; Lemy, C.; Deleplace, M.; Abdallah, M.; Gruescu, C.; Beaucé, J.; Benezech, T.; et al. Decontamination of Spores on Model Stainless-Steel Surface by Using Foams Based on Alkyl Polyglucosides. Molecules 2023, 28, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoda, J.; Sakai, T.; Inomata, Y. Liquid oil that flows in spaces of aqueous foam without defoaming. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 9438–9444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaka, A.; Sonoda, J.; Tajima, H.; Sakai, T. Dynamics of liquid oil that flows inside aqueous wet foam. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 9786–9791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensire, R.; Lorenceau, E. Stable oil-laden foams: Formation and evolution. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 247, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schad, T.; Preisig, N.; Drenckhan, W.; Stubenrauch, C. Foam-based cleaning of surfaces contaminated with mixtures of oil and soot. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2022, 25, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, R.; Rawlings, A.V.; Wandeler, E.; Jackson, E.; Trevisan, S.; Monneuse, J.; Bendik, I.; Massironi, M.; Imfeld, D. Bio-derived hydroxystearic acid ameliorates skin age spots and conspicuous pores. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2019, 41, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaillard, T.; Honorez, C.; Jumeau, M.; Elias, F.; Drenckhan, W. A simple technique for the automation of bubble size measurements. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 473, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallagi, H.; Faille, C.; Gruescu, C.; Aloui, F.; Benezech, T. Foam flow cleaning, an effective and environmentally friendly method for controlling the hygiene of closed surfaces contaminated with biofilms. Food Bioprod. Process. 2022, 136, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameau, A.-L.; Douliez, J.-P.; Boué, F.; Ott, F.; Cousin, F. Adsorption of multilamellar tubes with a temperature tunable diameter at the air/water interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 362, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameau, A.-L.; Lam, S.; Velev, O.D. Multi-stimuli responsive foams combining particles and self-assembling fatty acids. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 3874–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameau, A.-L.; Cousin, F.; Derrien, R.; Saint-Jalmes, A. Design of responsive foams with an adjustable temperature threshold of destabilization. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 3874–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Toquin, E.; Faure, S.; Orange, N.; Gas, F. New biocide foam containing hydrogen peroxide for the decontamination of vertical surface contaminated with Bacillus thuringiensis spores. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dari, C.; Cousin, F.; Le Coeur, C.; Dubois, T.; Benezech, T.; Saint-Jalmes, A.; Fameau, A.-L. Ultrastable and Responsive Foams Based on 10-Hydroxystearic Acid Soap for Spore Decontamination. Molecules 2023, 28, 4295. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114295
Dari C, Cousin F, Le Coeur C, Dubois T, Benezech T, Saint-Jalmes A, Fameau A-L. Ultrastable and Responsive Foams Based on 10-Hydroxystearic Acid Soap for Spore Decontamination. Molecules. 2023; 28(11):4295. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114295
Chicago/Turabian StyleDari, Carolina, Fabrice Cousin, Clemence Le Coeur, Thomas Dubois, Thierry Benezech, Arnaud Saint-Jalmes, and Anne-Laure Fameau. 2023. "Ultrastable and Responsive Foams Based on 10-Hydroxystearic Acid Soap for Spore Decontamination" Molecules 28, no. 11: 4295. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114295
APA StyleDari, C., Cousin, F., Le Coeur, C., Dubois, T., Benezech, T., Saint-Jalmes, A., & Fameau, A.-L. (2023). Ultrastable and Responsive Foams Based on 10-Hydroxystearic Acid Soap for Spore Decontamination. Molecules, 28(11), 4295. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114295






