SERS Detection of the Anti-Epileptic Drug Perampanel in Human Saliva
Abstract
1. Introduction
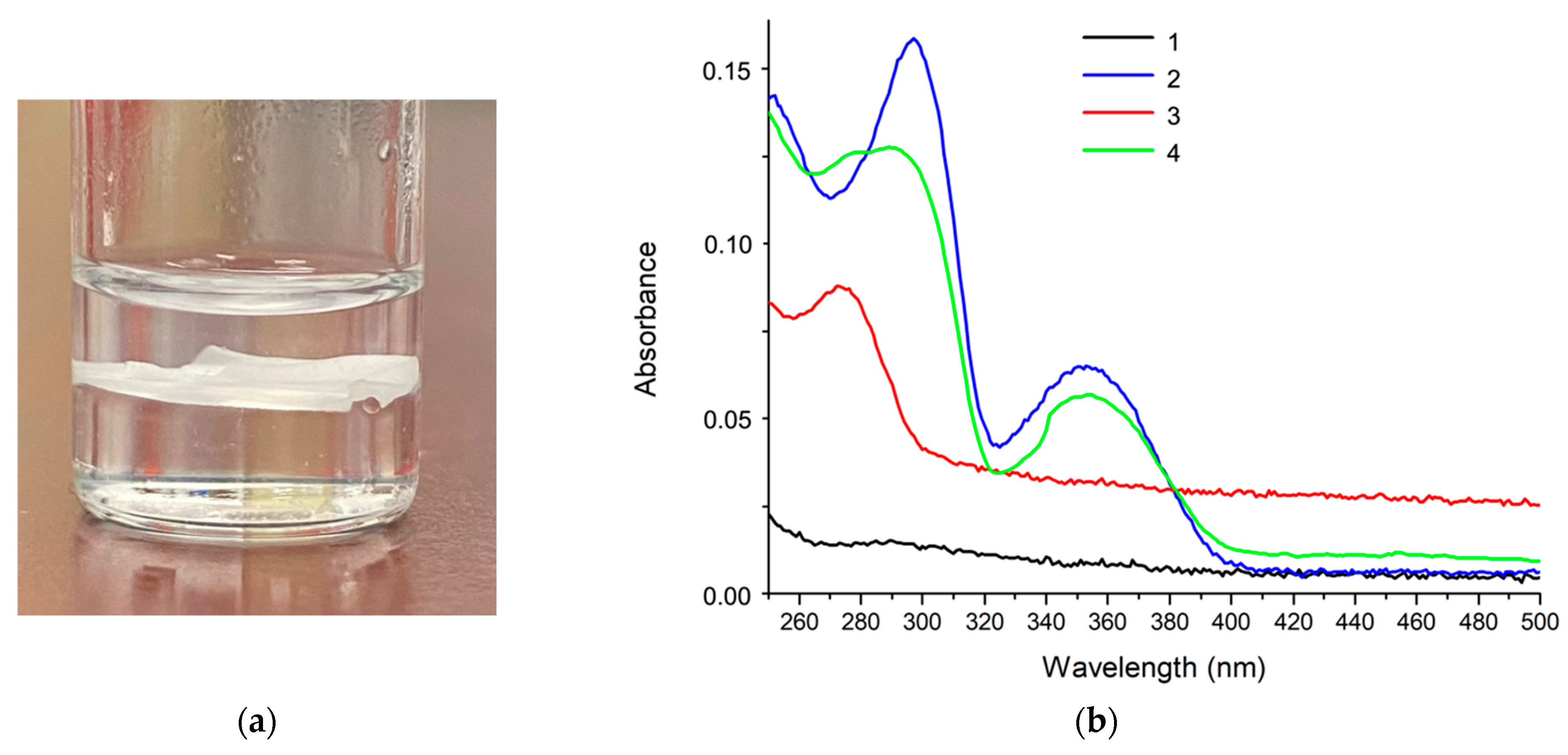
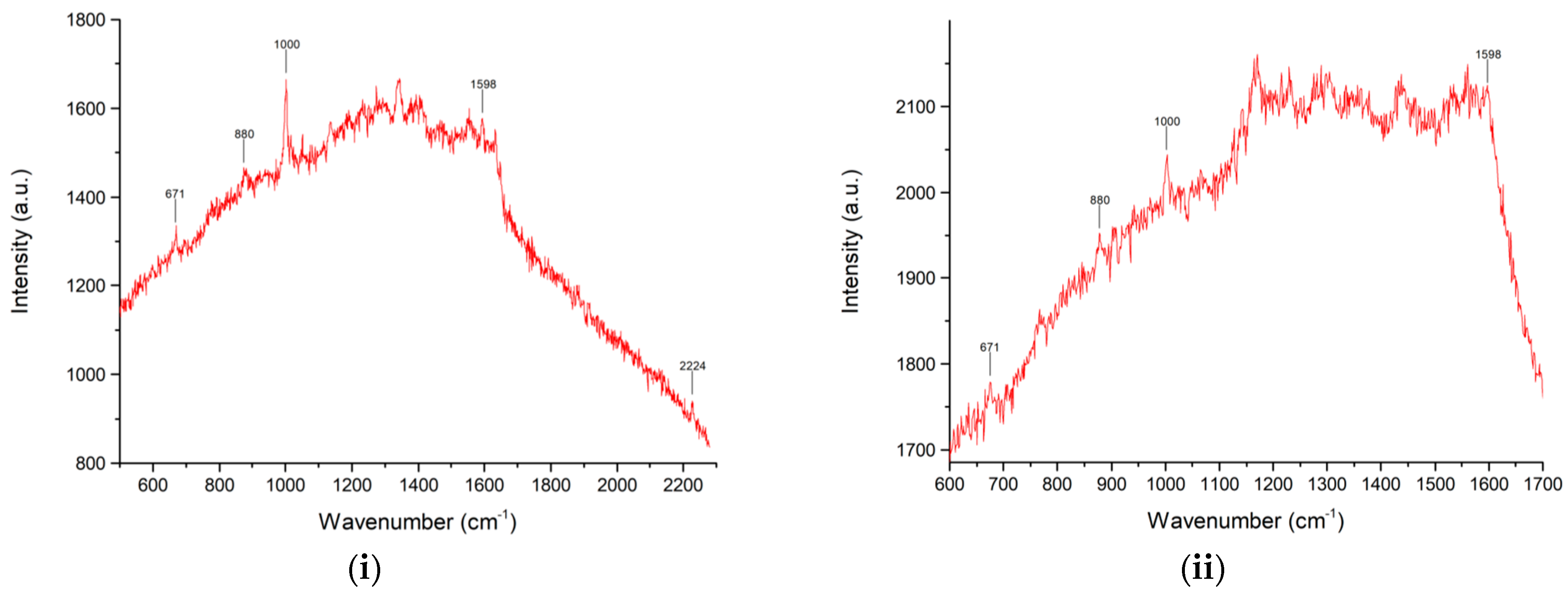
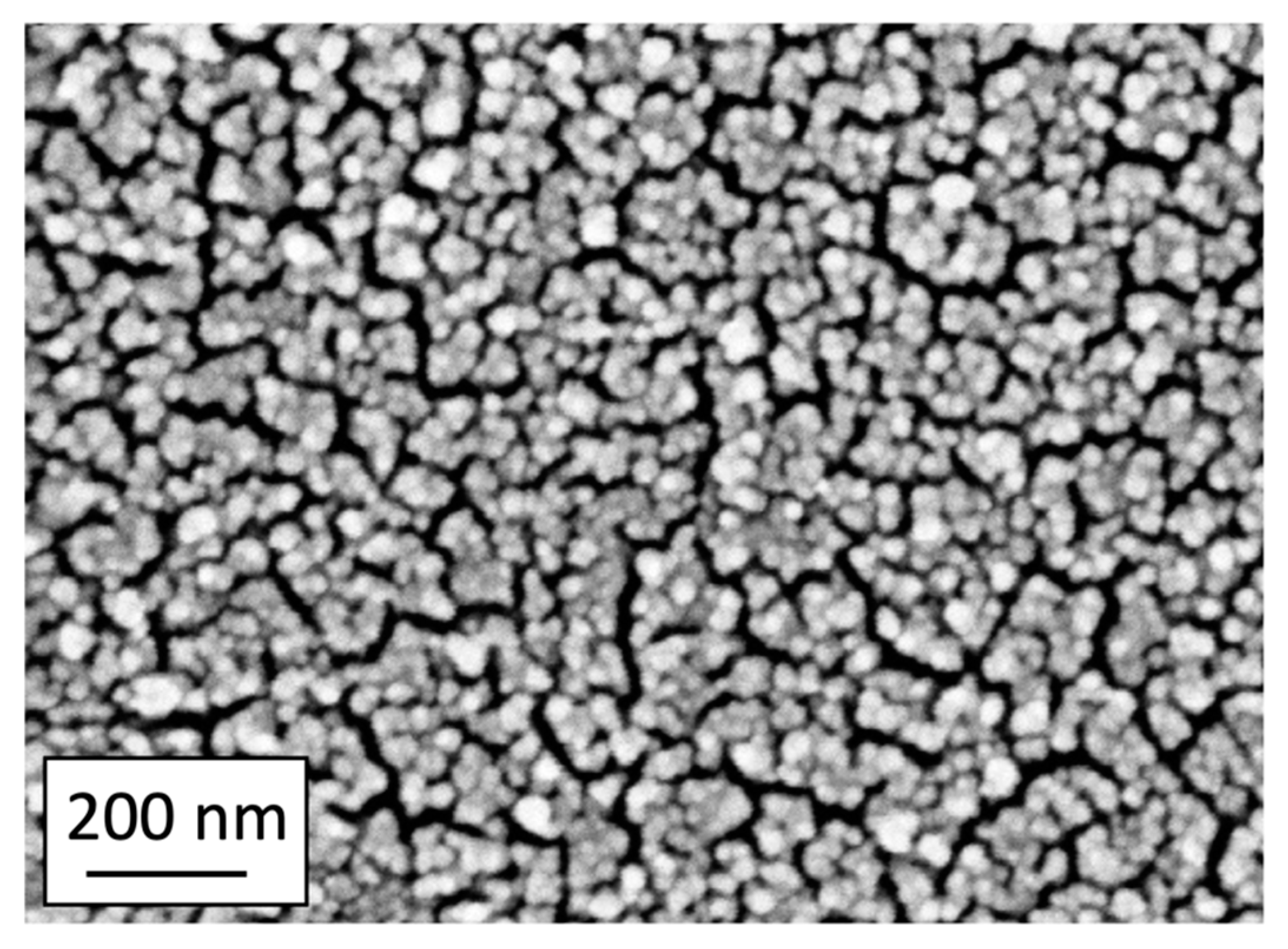
2. Results and Discussion
3. Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Robertson, J.; Hatton, C.; Emerson, E.; Baines, S. Prevalence of epilepsy among people with intellectual disabilities: A systematic review. Seizure 2015, 29, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.S.; Lee, M.H. Overview of therapeutic drug monitoring. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2009, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasowski, M.D.; McMillin, G.A. Advances in anti-epileptic drug testing. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 436, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistaffa, M. SERS Assessment of Carbamazepine in Methanol, Chloroform and Patient Samples Using Au Sensors with Optimized Surface Nanostructure. Master’s Thesis, Politecnico di Milano, Milano, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, N.R.; Ossi, P.M.; Trusso, S. Driving electromagnetic field enhancements in tailored gold surface nanostructures: Optical properties and macroscale simulations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 466, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.X.; Rodriguez, R.S.; Haynes, C.L.; Ozaki, Y.; Zhao, B. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2021, 1, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilot, R.; Signorini, R.; Durante, C.; Orian, L.; Bhamidipati, M.; Fabris, L. A review on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Biosensors 2019, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandri, I.; Lombardi, J.R. Enhanced Raman Scattering with Dielectrics. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14921–14981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoleo, A.; Rossi, C.; Poggi, G.; Rossi, M.; Meneghetti, M.; Baglioni, P. Spotting aged dyes on paper with SERS. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 24070–24076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Zhang, Q.; Xia, X.; Li, C.; Hei Ho, W.K.H.; Yan, J.; Huang, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, P.; Yi, C.; et al. A CRISPR-Cas12a integrated SERS nanoplatform with chimeric DNA/RNA hairpin guide for ultrasensitive nucleic acid detection. Theranostics 2022, 12, 5914–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Ho, W.K.H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Yan, J.; Yang, H.; Hao, J.; Wong, S.H.D.; Yang, M. Magnetic-Responsive Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Platform with Tunable Hot Spot for Ultrasensitive Virus Nucleic Acid Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 4714–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, C.; Li, A.; Li, X.; Lu, Z.; Wang, T. Detection of Exhaled Volatile Organic Compounds Improved by Hollow Nanocages of Layered Double Hydroxide on Ag Nanowires. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 16523–16527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, X.; Su, B.; Liu, C.; Song, Q.; Luo, D.; Mo, G.; Wang, T. Selective Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering for Quantitative Detection of Lung Cancer Biomarkers in Superparticle@MOF Structure. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1702275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, N.R.; Lucotti, A.; Tommasini, M.; Neri, F.; Trusso, S.; Ossi, P.M. SERS detection and DFT calculation of 2-naphthalene thiol adsorbed on Ag and Au probes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 237, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworska, A.; Fornasaro, S.; Sergo, V.; Bonifacio, A. Potential of Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) in Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM). A critical review. Biosensors 2016, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panikar, S.S.; Ramírez-García, G.; Sidhik, S.; Lopez-Luke, T.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, C.; Ciapara, I.H.; Castillo, P.S.; Camacho-Villegas, T.; De la Rosa, E. Ultrasensitive SERS Substrate for Label-Free Therapeutic-Drug Monitoring of Paclitaxel and Cyclophosphamide in Blood Serum. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 2100–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasini, M.; Zanchi, C.; Lucotti, A.; Bombelli, A.; Villa, N.S.; Casazza, M.; Ciusani, E.; de Grazia, U.; Santoro, M.; Fazio, E.; et al. Laser-Synthesized SERS Substrates as Sensors toward Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, C.; MacMillan, D.; McCardle, C.; Smith, W.E. Quantitative analysis of mitoxantrone by surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 3160–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Mao, S.; Lin, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, N. Research Progress of Raman Spectroscopy and Raman Imaging in Pharmaceutical Analysis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossi, P.M.; Neri, F.; Santo, N.; Trusso, S. Noble metal nanoparticles produced by nanosecond laser ablation. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 104, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danhof, M.; Breimer, D.D. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in Saliva. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1978, 3, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsalos, P.N.; Berry, D.J. Therapeutic drug monitoring of antiepileptic drugs by use of saliva. Ther. Drug Monit. 2013, 35, 4–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, E.; Lamster, I.B. The Diagnostic Applications of Saliva—A Review. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2002, 13, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Moon, J.; Shin, Y.W.; Lee, S.T.; Jung, K.H.; Park, K.I.; Jung, K.Y.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.; Yu, K.S.; et al. Usefulness of saliva for perampanel therapeutic drug monitoring. Epilepsia 2020, 61, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidal, B.E.; Ferry, J.; Majid, O.; Hussein, Z. Concentration–effect relationships with perampanel in patients with pharmacoresistant partial-onset seizures. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meirinho, S.; Rodrigues, M.; Fortuna, A.; Falcão, A.; Alves, G. Liquid chromatographic methods for determination of the new antiepileptic drugs stiripentol, retigabine, rufinamide and perampanel: A comprehensive and critical review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2021, 11, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrelli, A.; Villa, N.S.; Lucotti, A.; Dellasega, D.; Ossi, P.M.; Tommasini, M. Sensing the Anti-Epileptic Drug Perampanel with Paper-Based Spinning SERS Substrates. Molecules 2022, 27, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virkler, K.; Lednev, I.K. Forensic body fluid identification: The Raman spectroscopic signature of saliva. Analyst 2010, 135, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekha, P.; Aruna, P.; Brindha, E.; Koteeswaran, D.; Baludavid, M.; Ganesan, S. Near-infrared Raman spectroscopic characterization of salivary metabolites in the discrimination of normal from oral premalignant and malignant conditions. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2016, 47, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittings, S.; Turnbull, N.; Henry, B.; Roberts, C.J.; Gershkovich, P. Characterisation of human saliva as a platform for oral dissolution medium development. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 91, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, N.S. Development of a SERS Technique for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring: Case Study on Perampanel. Master’s Thesis, Politecnico di Milano, Milano, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Agha-Hosseini, F.; Dizgah, I.M.; Amirkhani, S. The composition of unstimulated whole saliva of healthy dental students. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2006, 7, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Liao, X.; Li, Y.; Cao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Cassidy, D.P. Sensitive detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with gold colloid coupled chloride ion SERS sensor. Analyst 2019, 144, 6698–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fycompa Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.fycompa.com/-/media/Files/Fycompa/Fycompa_Prescribing_Information.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2023).
- Perampanel, Item No. 23003. Available online: https://www.caymanchem.com/product/23003/perampanel (accessed on 20 April 2023).
- Zanchi, C.; Lucotti, A.; Tommasini, M.; Pistaffa, M.; Giuliani, L.; Trusso, S.; Ossi, P.M. Pulsed laser deposition of gold thin films with long-range spatial uniform SERS activity. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Proc. 2019, 125, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

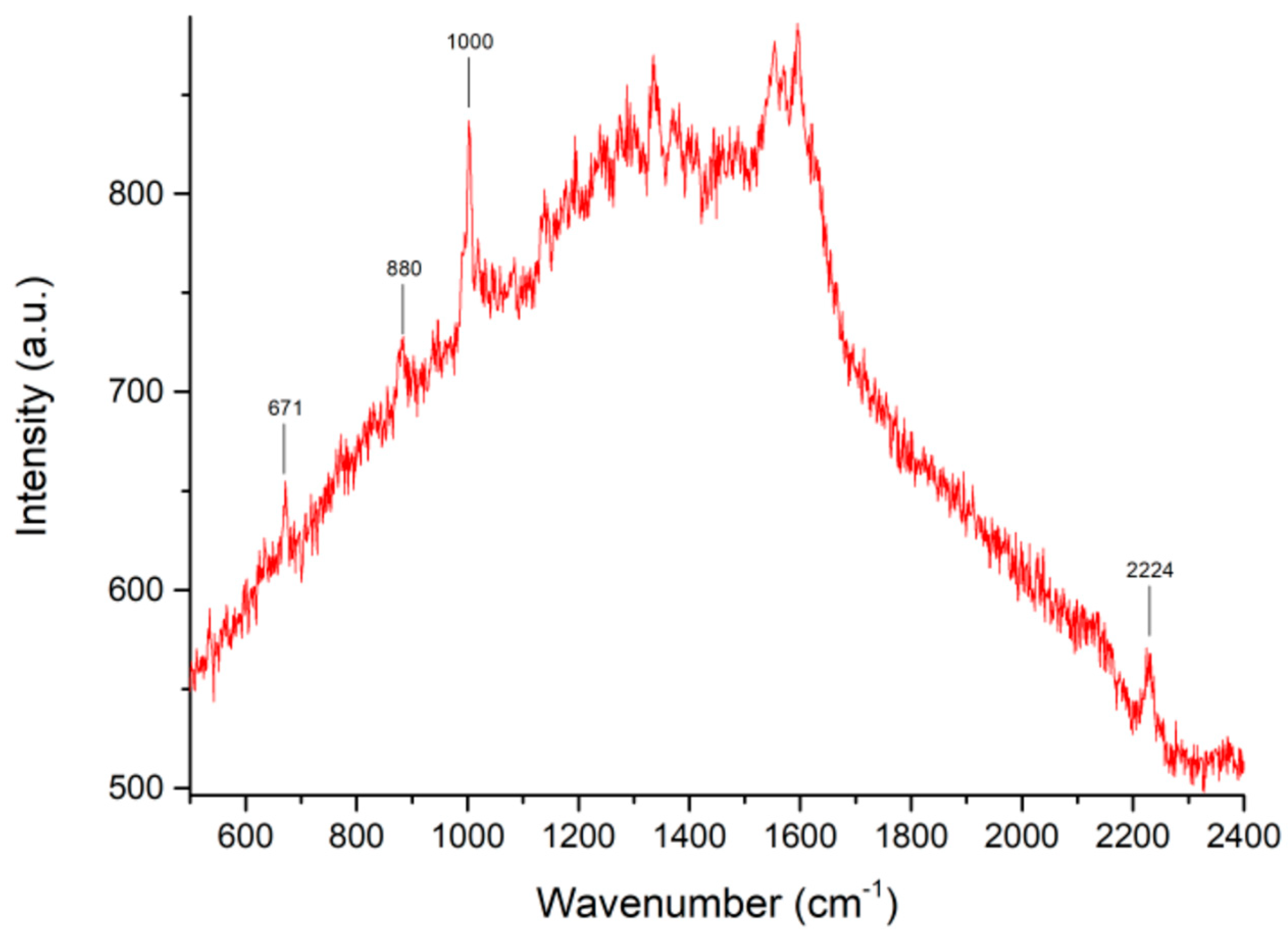
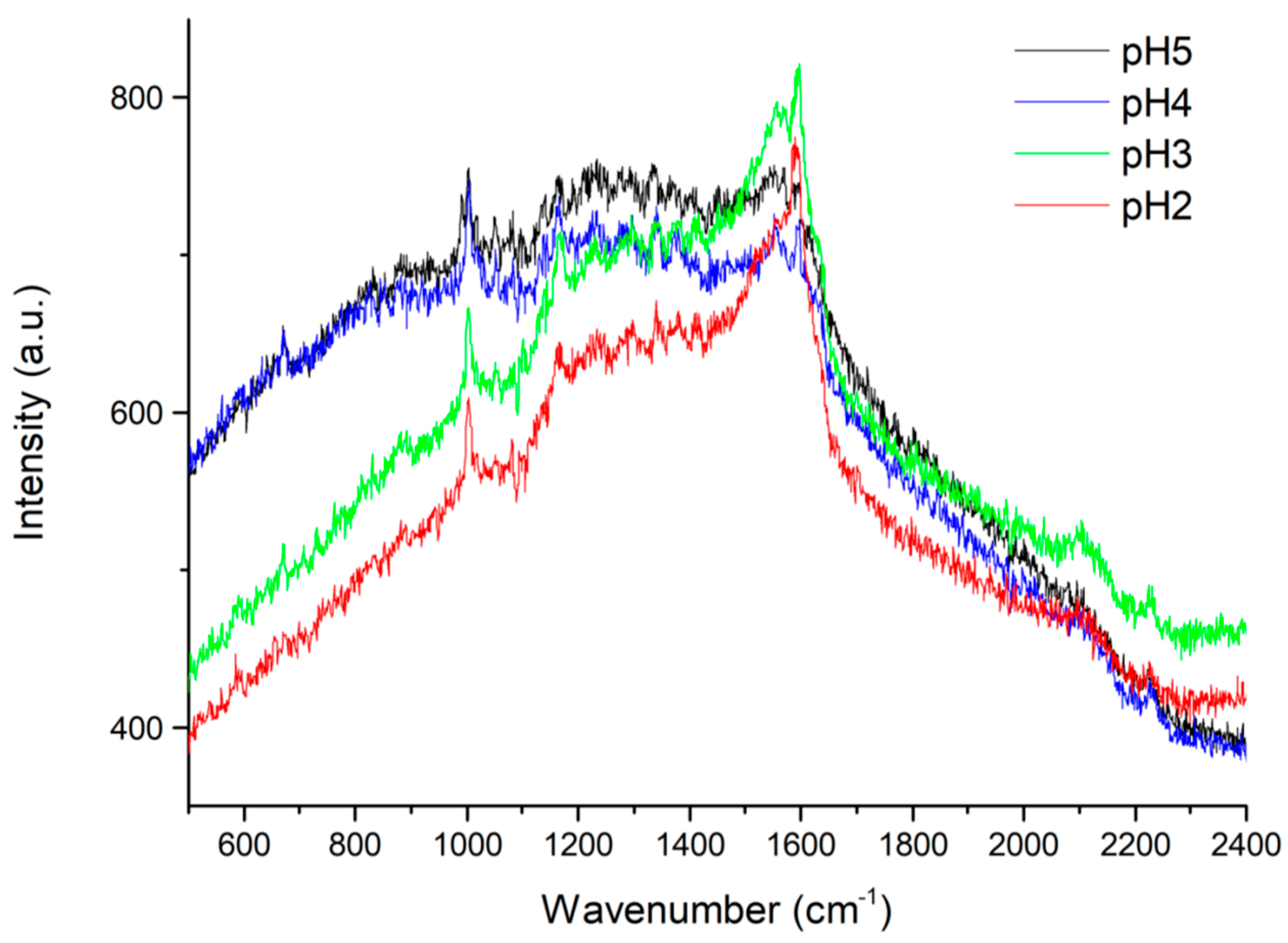
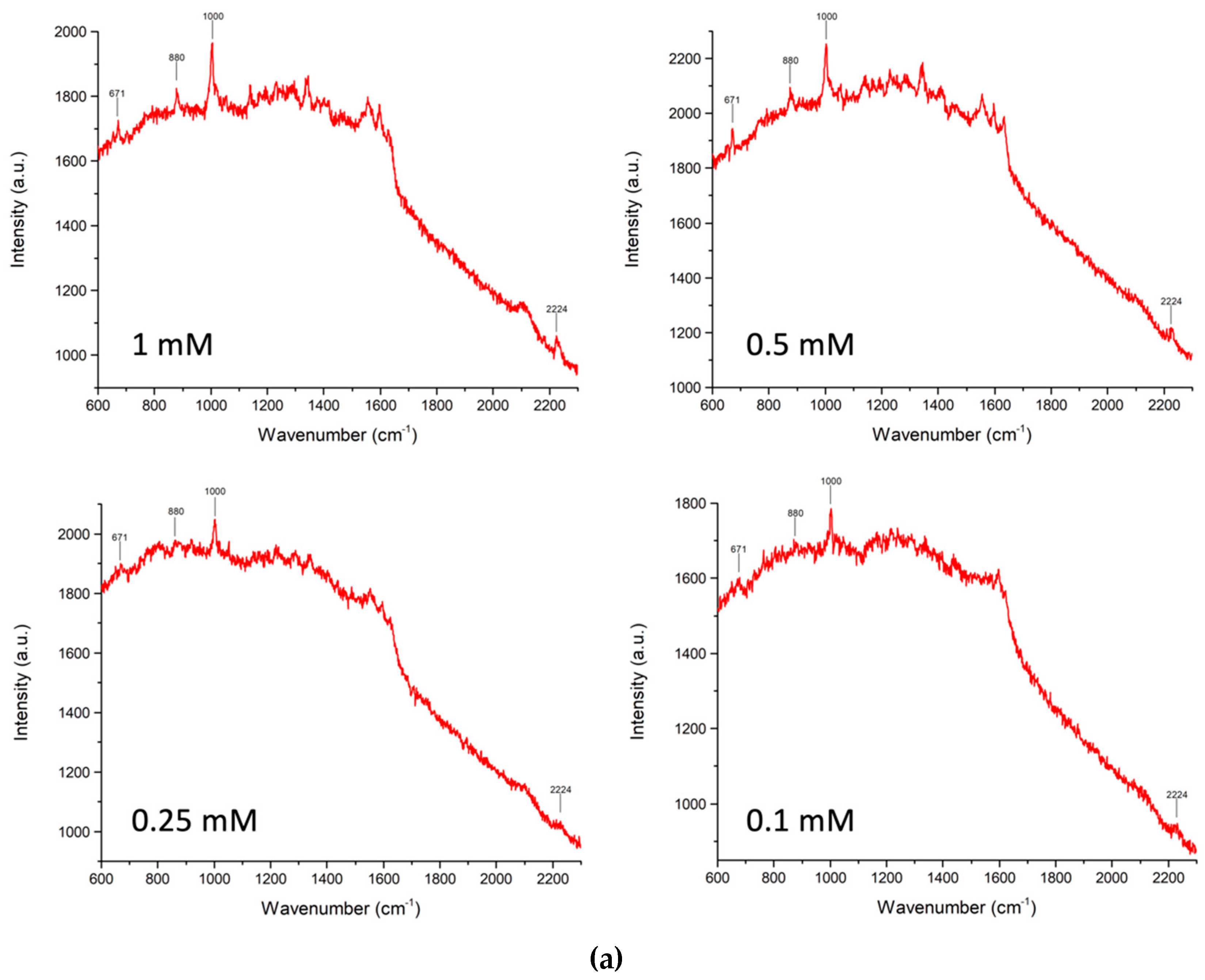
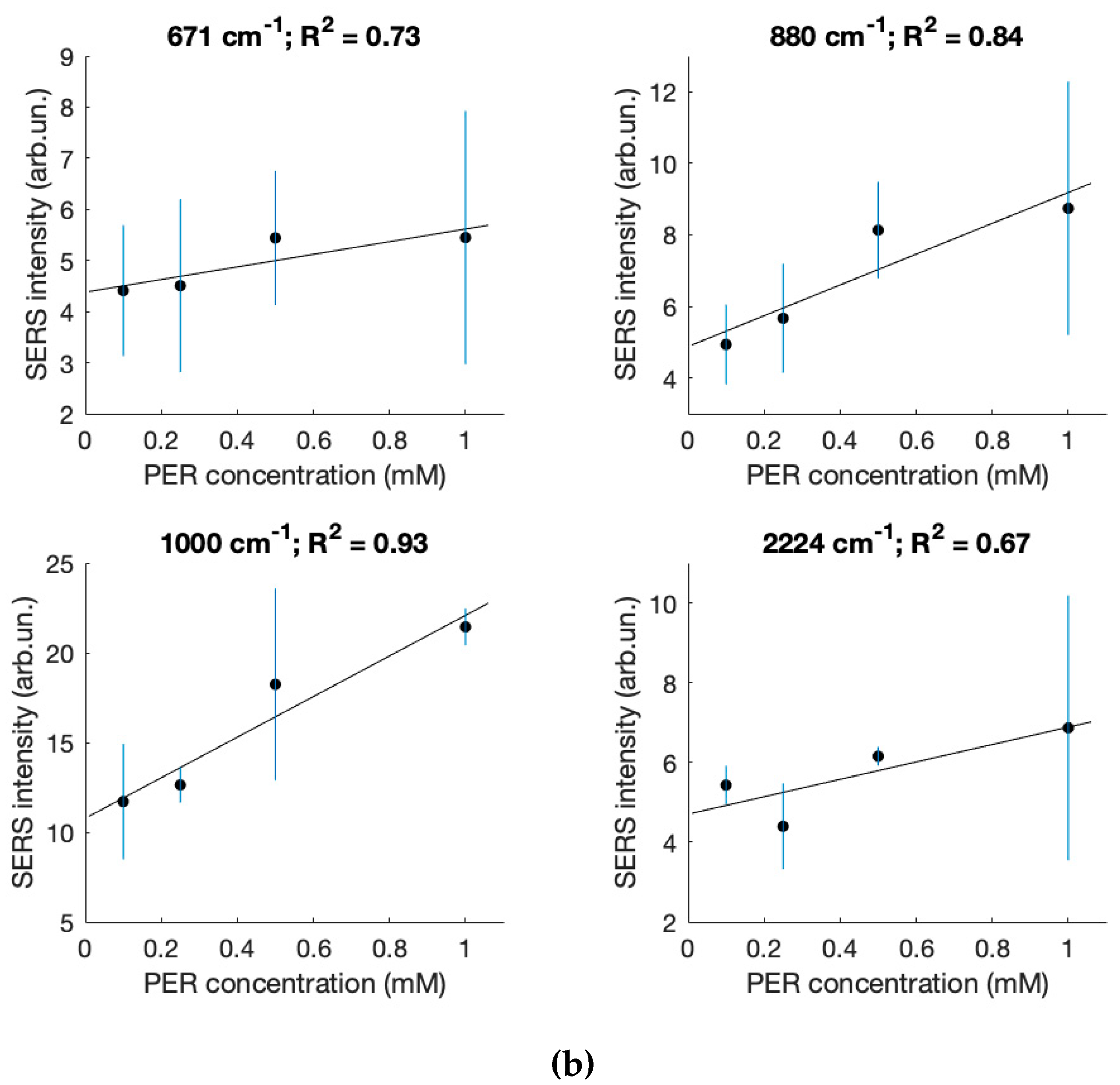

| Sample Composition (Volume Ratios: Saliva/Solution A) | pH |  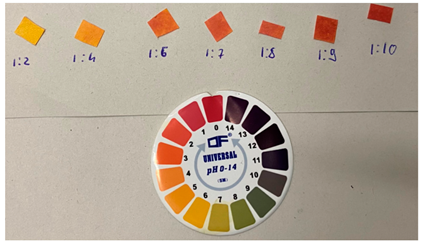 |
| saliva | 6–7 | |
| 1:2 | 5 | |
| 1:4 | 4 | |
| 1:6 | 3 | |
| 1:7 | 3 | |
| 1:8 | 2–3 | |
| 1:9 | ca. 2 | |
| 1:10 | 2 | |
| Acidic solution A | 2 |
| PER Solution in MeOH (μL, Either 10−2 or 10−3 M) | Saliva (μL) | Acidic Solution B (μL) | Final PER Concentration (M) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 (10−2 M) | 90 | 0.6 | 10−3 | 4 |
| 100 (10−3 M) | 100 | 1 | 5 × 10−4 | 4 |
| 50 (10−3 M) | 150 | 1.1 | 2.5 × 10−4 | 4 |
| 20 (10−3 M) | 180 | 1.2 | 10−4 | 4 |
| c (mM) | 671 cm−1 | 880 cm−1 | 1000 cm−1 | 2224 cm−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 2.6 | 5.9 | 21 | 7.8 | |
| 6.5 | 7.2 | 20.3 | 3.1 | ||
| 7.7 | 13.4 | 22.4 | 9.2 | ||
| 6.1 | 9.1 | 22 | 9.1 | ||
| 4.3 | 8.1 | 21.5 | 5.2 | ||
| 5.4 | 8.7 | 21.4 | 6.9 | average | |
| 2 | 2.9 | 0.8 | 2.7 | st. dev. | |
| 0.5 | 4.5 | 9.6 | 25 | 6.3 | |
| 7.1 | 7.8 | 16.7 | 5.8 | ||
| 5.5 | 7.6 | 18.4 | 6.3 | ||
| 5.4 | 6.9 | 13.1 | 6.2 | ||
| 4.7 | 8.9 | 17.9 | 6.1 | ||
| 5.4 | 8.1 | 18.2 | 6.2 | average | |
| 1.1 | 1.1 | 4.3 | 0.2 | st. dev. | |
| 0.25 | 3.5 | 6.4 | 11.4 | 5.4 | |
| 5.2 | 7.3 | 12.7 | 4.8 | ||
| 6.6 | 5.6 | 13.6 | 4.7 | ||
| 3.7 | 4.1 | 12.7 | 4 | ||
| 3.6 | 5 | 12.7 | 3.2 | ||
| 4.5 | 5.7 | 12.6 | 4.4 | average | |
| 1.4 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.9 | st. dev. | |
| 0.1 | 3.5 | 4.4 | 12.2 | 5.5 | |
| 6.1 | 5.8 | 15.9 | 5.7 | ||
| 3.8 | 5.7 | 11.2 | 5.9 | ||
| 4.1 | 5.1 | 9.3 | 5.2 | ||
| 4.5 | 3.7 | 10 | 4.9 | ||
| 4.4 | 4.9 | 11.7 | 5.4 | average | |
| 1 | 0.9 | 2.6 | 0.4 | st. dev. |
| 10−3 M PER in MeOH (μL) | Saliva (μL) | PER Concentration at Step 1 (M) | PER Concentration at Step 6 (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | |||
| 80 | 1920 | 4 × 10−5 | 10−5 |
| 64 | 1936 | 3.2 × 10−5 | 8 × 10−6 |
| 48 | 1942 | 2.4 × 10−5 | 6 × 10−6 |
| 40 | 1960 | 2 × 10−5 | 5 × 10−6 |
| 16 | 1984 | 8 × 10−6 | 2 × 10−6 |
| (b) | |||
| 20 | 480 | 4 × 10−5 | 10−5 |
| 16 | 484 | 3.2 × 10−5 | 8 × 10−6 |
| 12 | 488 | 2.4 × 10−5 | 6 × 10−6 |
| 10 | 490 | 2 × 10−5 | 5 × 10−6 |
| 4 | 496 | 8 × 10−6 | 2 × 10−6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tommasini, M.; Lucotti, A.; Stefani, L.; Trusso, S.; Ossi, P.M. SERS Detection of the Anti-Epileptic Drug Perampanel in Human Saliva. Molecules 2023, 28, 4309. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114309
Tommasini M, Lucotti A, Stefani L, Trusso S, Ossi PM. SERS Detection of the Anti-Epileptic Drug Perampanel in Human Saliva. Molecules. 2023; 28(11):4309. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114309
Chicago/Turabian StyleTommasini, Matteo, Andrea Lucotti, Luca Stefani, Sebastiano Trusso, and Paolo M. Ossi. 2023. "SERS Detection of the Anti-Epileptic Drug Perampanel in Human Saliva" Molecules 28, no. 11: 4309. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114309
APA StyleTommasini, M., Lucotti, A., Stefani, L., Trusso, S., & Ossi, P. M. (2023). SERS Detection of the Anti-Epileptic Drug Perampanel in Human Saliva. Molecules, 28(11), 4309. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114309







