Molecular Dynamics Insight into the CO2 Flooding Mechanism in Wedge-Shaped Pores
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
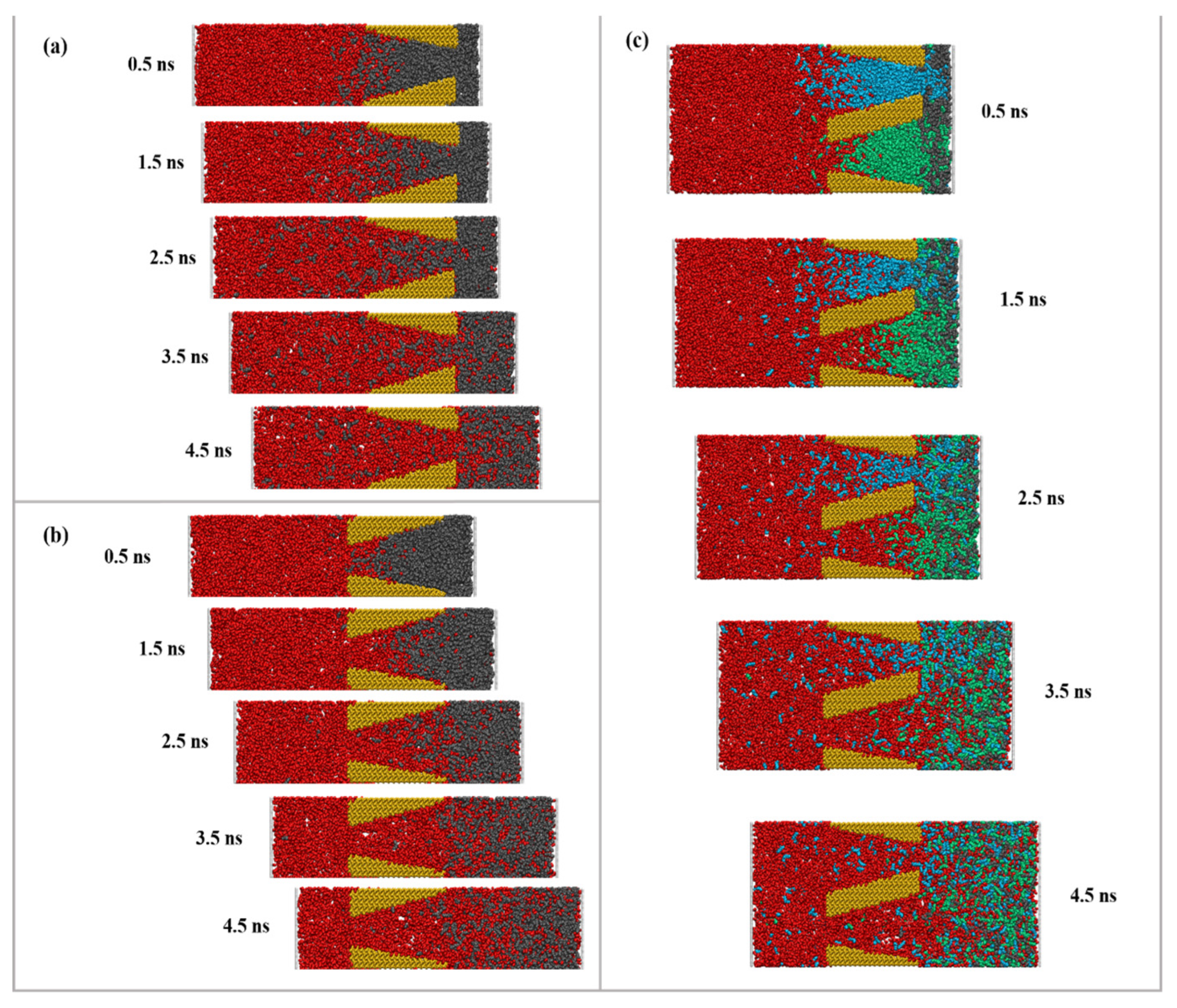
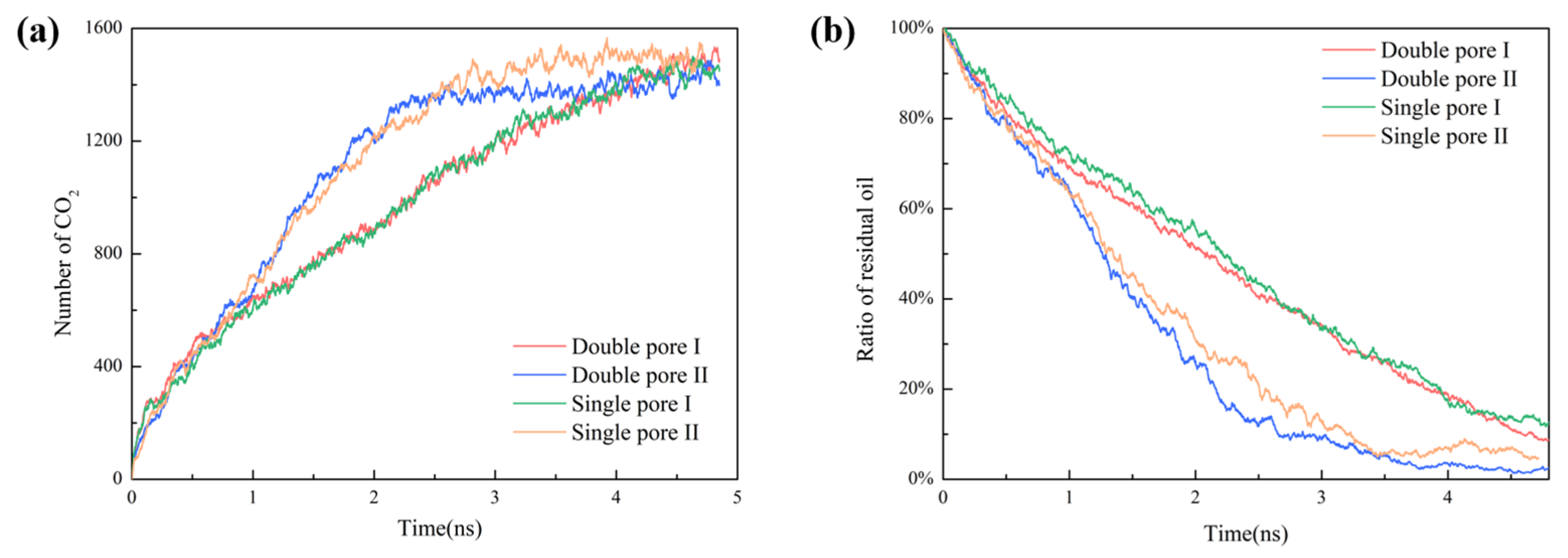
2.1. CO2 Flooding Process
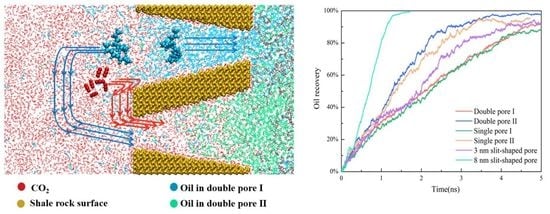
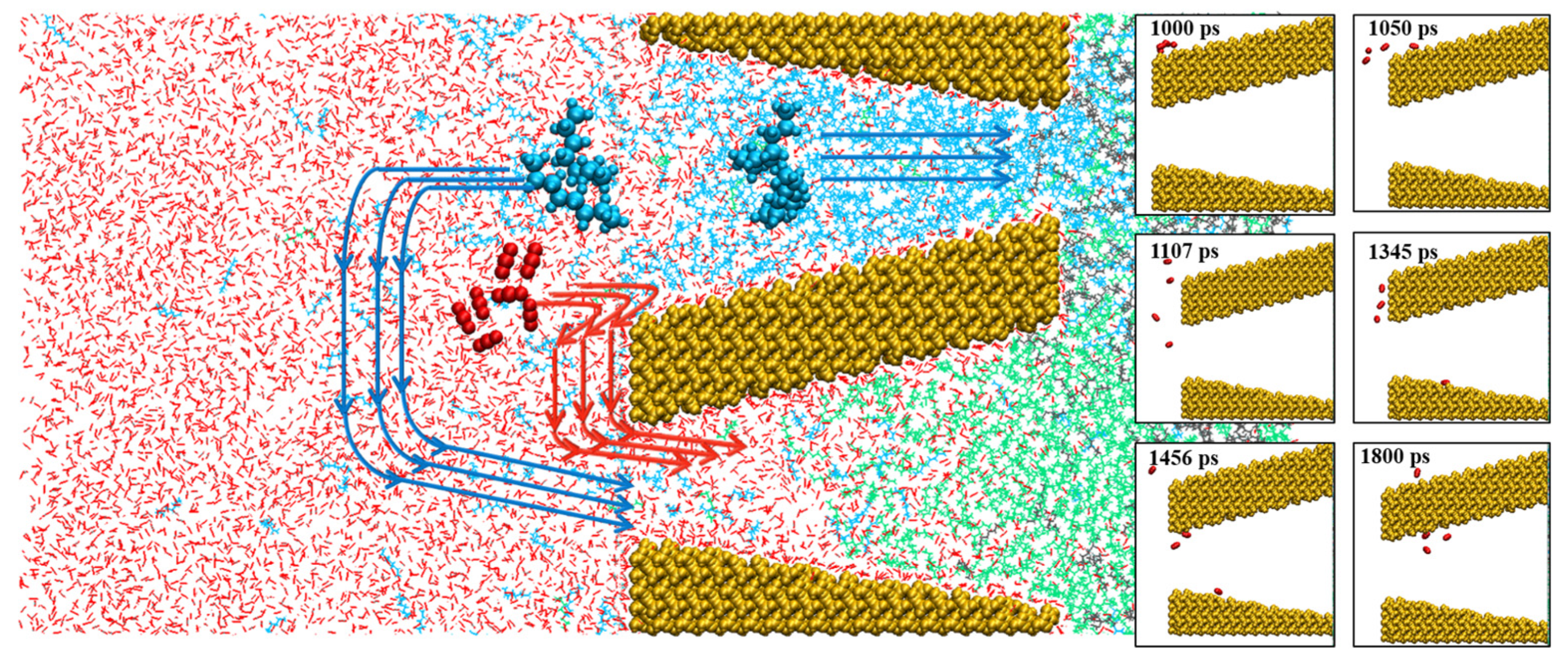
2.2. Oil/CO2 Inter-Pore Migration Mechanism
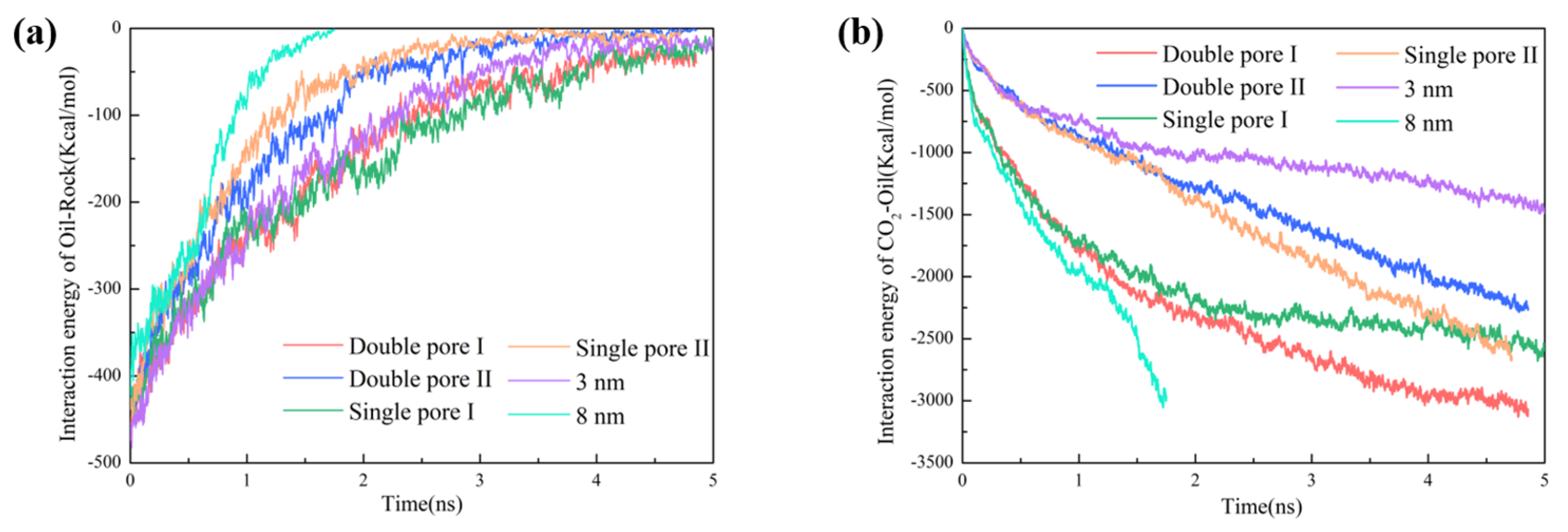
2.3. Interaction
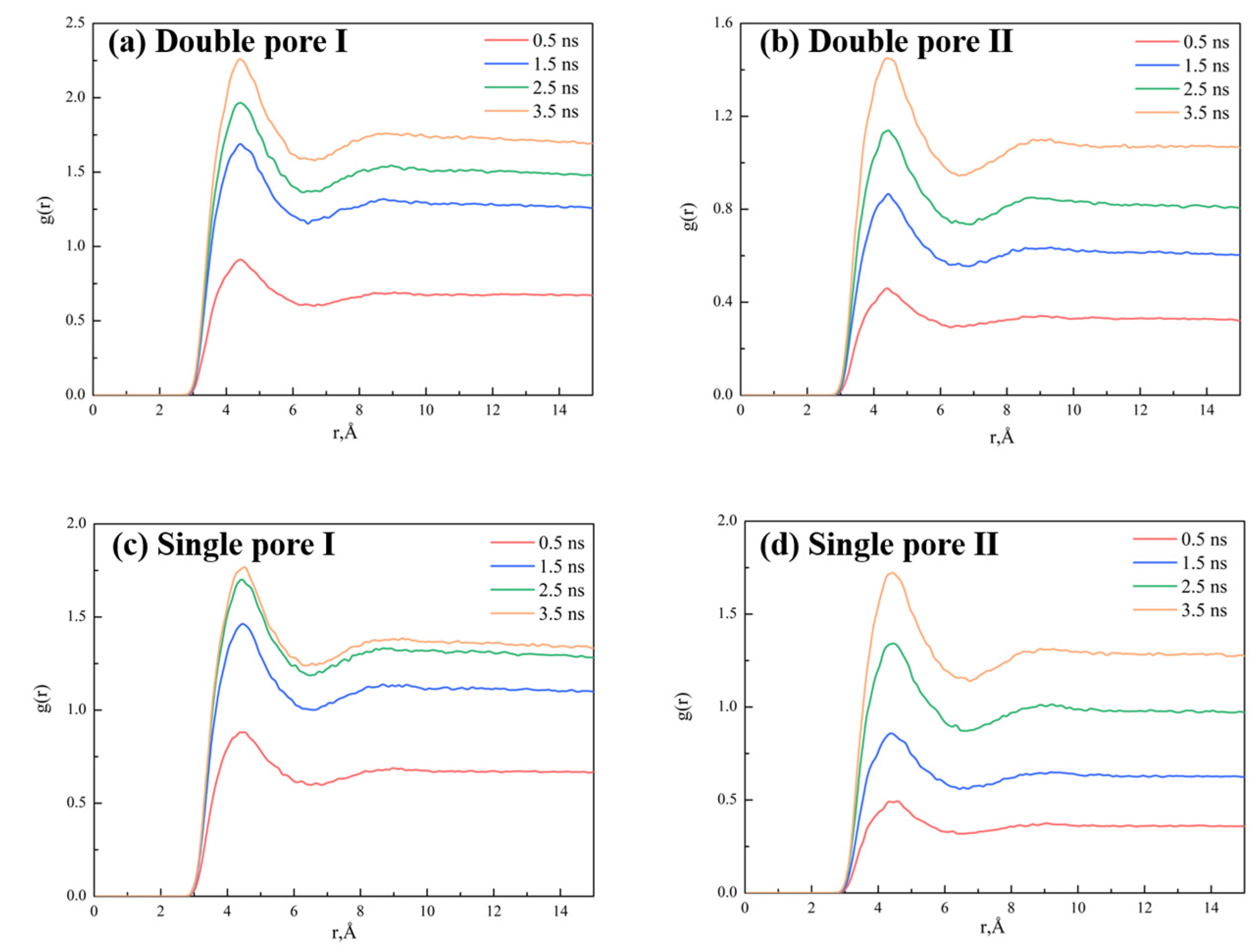
2.4. Effect of Pore Shape on CO2–Oil Miscibility
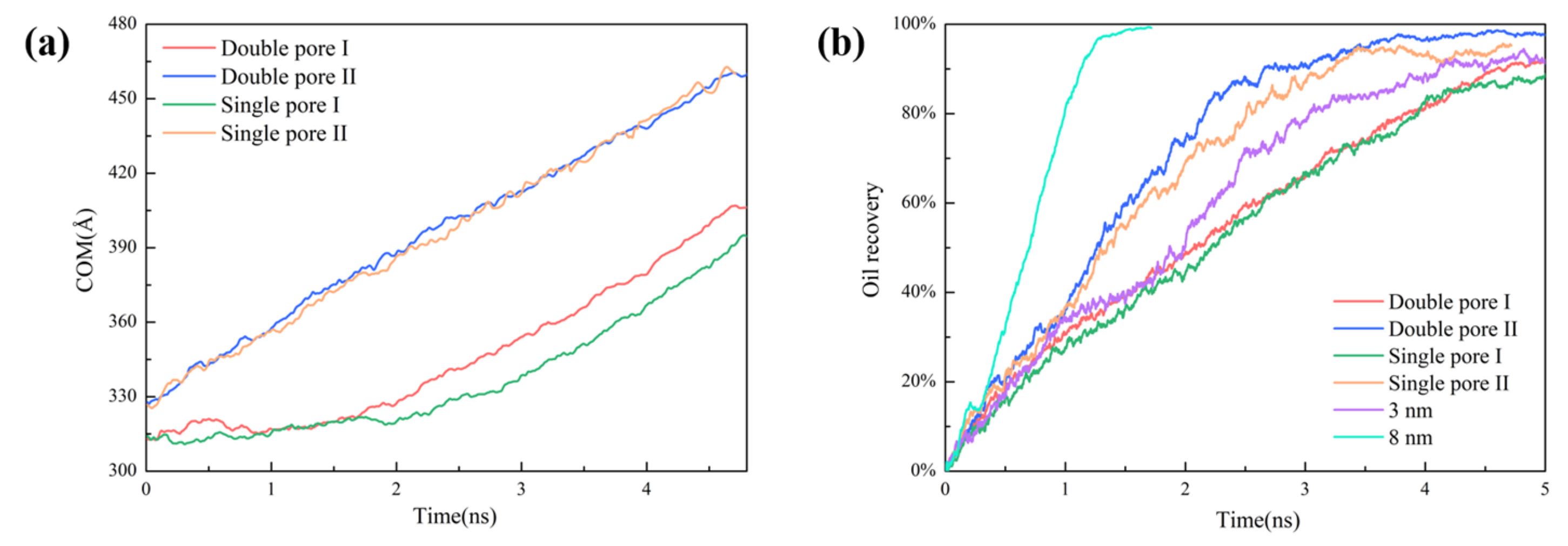
2.5. Effect of Wedge-Shaped Pore on Oil Recovery
3. Models and Methodology
3.1. Modeling
3.2. Simulation Details
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haider, W.H. Estimates of total oil & gas reserves in the world, future of oil and gas companies and smart investments by E & P companies in renewable energy sources for future energy needs. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, 13–15 January 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimi, D. The greenhouse gas effects of increased US oil and gas production. Energy Transit. 2020, 4, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, I.V. Prospects for the development of the oil and gas industry in the regional and global economy. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2018, 8, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, R.G.; Reed, R.M.; Ruppel, S.C.; Hammes, U. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores. AAPG Bull. 2012, 96, 1071–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, M.; Tong, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, B.; Xie, Y.; Yang, L. Assessment of global unconventional oil and gas resources. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2016, 43, 925–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfi, M.; Barrufet, M.; Killough, J. Effect of pore sizes on composition distribution and enhance recovery from liquid shale—Molecular sieving in low permeability reservoirs. Fuel 2019, 235, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Hou, J.; Li, H.A.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z. Technical and economic feasibility of a novel heavy oil recovery method: Geothermal energy assisted heavy oil recovery. Energy 2019, 181, 853–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakkoli, O.; Kamyab, H.; Shariati, M.; Mohamed, A.M.; Junin, R. Effect of nanoparticles on the performance of polymer/surfactant flooding for enhanced oil recovery: A review. Fuel 2022, 312, 122867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Hao, Y.; Zhan, S.; Wang, W.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. Experimental study on microscopic mechanisms and displacement efficiency of N2 flooding in deep-buried clastic reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, X. Enhanced oil recovery by CO2–CH4 flooding in low permeability and rhythmic hydrocarbon reservoir. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 12849–12853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Ju, B.; Chen, Y.; Luo, X.; Petro, X. Laboratory investigation of CO2 flooding. In Proceedings of the Nigeria Annual International Conference and Exhibition, Abuja, Nigeria, 2–4 August 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S. Enhanced oil recovery-an overview. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. Rev. De L’ifp 2008, 63, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, X.; Tao, Z.; Wang, S.; Fan, J.; Feng, Q.; Xue, Q. The miscible behaviors and mechanism of CO2/CH4/C3H8/N2 and crude oil in nanoslits: A molecular dynamics simulation study. Fuel 2021, 304, 121461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedini, A.; Torabi, F. Oil Recovery Performance of Immiscible and Miscible CO2 Huff -and -Puff Processes. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhang, H.; Wei, G.; Liu, D.; Li, C.; Yang, F.; Yao, B. Experimental Study on the Effective Viscosity of Unstable CO2 Flooding Produced Fluid with the Energy Dissipation Method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 59, 1308–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Lun, Z.; Lv, C.; Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D. Effect of Contact Time and GasComponent on Interfacial Tension of CO2/Crude Oil Systemby Pendant Drop Method. J. Spectrosc. 2015, 2015, 285891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Shen, P.; Liao, X.; Li, F.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Z. Potential evaluation of CO2 EOR and sequestration in Yanchang oilfield. J. Energy Inst. 2016, 89, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritsen, M.G.; Durlofsky, L.J. Modeling fluid flow in oil reservoirs. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2005, 37, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, X.; Lai, F.; Gao, X.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, N.; Luo, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, S.; Luo, X.; et al. Characteristics and Genetic Mechanism of Pore Throat Structure of Shale Oil Reservoir in Saline Lake—A Case Study of Shale Oil of the Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin. Energies 2021, 14, 8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Balhoff, M.T.; Mohanty, K.K. Simulation of fracture-to-fracture gas injection in an oil-rich shale. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Houston, TX, USA, 28–30 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Q.; Liu, C.; Awan, R.S.; Yang, X.; Lu, Z.; Li, G.; Wu, Y.; Feng, D.; Ran, Y. Comparison of Pore Size Distribution, Heterogeneity and Occurrence Characteristics of Movable Fluids of Tight Oil Reservoirs Formed in Different Sedimentary Environments: A Case Study of the Chang 7 Member of Ordos Basin, China. Nat. Resour. Res. 2022, 31, 415–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Pang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z.; He, Z.; Qin, Z.; Fan, X. A review on pore structure characterization in tight sandstones. Earth Sci. Rev. 2018, 177, 436–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Lu, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, B. Classifying multiscale pores and investigating their relationship with porosity and permeability in tight sandstone gas reservoirs. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 9188–9200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Xiong, W.; Lang, X.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H. Quantitative analysis of nano-scale pore structures of broad sense shale oil reservoirs using atomic force microscopy. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2021, 39, 1839–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, W. Effect of microscopic pore-throat heterogeneity on gas-phase percolation capacity of tight sandstone reservoirs. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 12399–12416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Yan, Y.; Dai, C.; Zhang, J. Oil extraction mechanism in CO2 flooding from rough surface: Molecular dynamics simulation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 494, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Mo, T.; Wei, Y.; Guo, Z.; Feng, G. Molecular insight into oil displacement by CO2 flooding on rough silica surface. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2022, 181, 105507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedghi, M.; Piri, M.; Goual, L. Molecular dynamics of wetting layer formation and forced water invasion in angular nanopores with mixed wettability. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 141, 194703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Chen, S.; Pu, X.; Yan, J. Characteristics and controlling factors of shale oil reservoir spaces in the Bohai Bay Basin. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2020, 94, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashin, A.A.; El-Naby, A.A. Petrophysical, seismic structural and facies analysis of the Miocene reservoirs of East Morgan oil field, Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 3481–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J. How the oil recovery in deep oil reservoirs is affected by injected gas types: A molecular dynamics simulation study. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 231, 116286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Xie, Q.; Wei, X. Research on the application of molecular simulation technology in enhanced oil-gas recovery engineering. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 233, 01124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xue, Q.; Zhu, L.; Jin, Y.; Wu, T.; Guo, Q.; Zheng, H.; Lu, S. How to select an optimal surfactant molecule to speed up the oil-detachment from solid surface: A computational simulation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 147, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Liu, B.; Shen, Y.; Dai, C.; Zhang, J. Oil detachment mechanism in CO2 flooding from silica surface: Molecular dynamics simulation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 16, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, X.; Xiao, H.; Zheng, T. Microscopic production characteristics of tight oil in the nanopores of different CO2-affected areas from molecular dynamics simulations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 306, 122607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Sun, B.; He, J. Displacement mechanism of oil in shale inorganic nanopores by supercritical carbon dioxide from molecular dynamics simulations. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Javadpour, F.; Feng, Q. Molecular dynamics simulations of oil transport through inorganic nanopores in shale. Fuel 2016, 171, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, A.A.; Fenter, P.; Kubicki, J.D.; Wesolowski, D.J.; Cummings, P.T. Simulations of the quartz (1011)/water interface: A comparison of classical force fields, ab initio molecular dynamics, and X-ray reflectivity experiments. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 2076–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, A.A.; Wesolowski, D.J.; Cummings, P.T. Investigating the quartz (1010)/water interface using classical and ab initio molecular dynamics. Langmuir 2011, 27, 8700–8709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koretsky, C.M.; Sverjensky, D.A.; Sahai, N. A model of surface site types on oxide and silicate minerals based on crystal chemistry; implications for site types and densities, multi-site adsorption, surface infrared spectroscopy, and dissolution kinetics. Am. J. Sci. 1998, 298, 349–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosé, S. A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Maxwell, D.S.; Tirado-Rives, J. Development and testing of the OPLS all-atom force field on conformational energetics and properties of organic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11225–11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.G.; Yung, K.H. Carbon dioxide’s liquid-vapor coexistence curve and critical properties as predicted by a simple molecular model. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 12021–12024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headen, T.F.; Boek, E.S. Molecular dynamics simulations of asphaltene aggregation in supercritical carbon dioxide with and without limonene. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cygan, R.T.; Liang, J.J.; Kalinichev, A.G. Molecular models of hydroxide, oxyhydroxide, and clay phases and the development of a general force field. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toukmaji, A.Y.; Board, J.A., Jr. Ewald summation techniques in perspective: A survey. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1996, 95, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nymand, T.M.; Linse, P. Ewald summation and reaction field methods for potentials with atomic charges, dipoles, and polarizabilities. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 112, 6152–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ding, B.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J. Molecular insight into the miscible mechanism of CO2/C10 in bulk phase and nanoslits. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 141, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Mi, J.G.; Chan, K.Y. Comparison of different mixing rules for prediction of density and residual internal energy of binary and ternary Lennard–Jones mixtures. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2001, 178, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Lyu, W.; Ji, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Fang, H.; Yue, X.; Wei, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. Molecular Dynamics Insight into the CO2 Flooding Mechanism in Wedge-Shaped Pores. Molecules 2023, 28, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010188
Wang L, Lyu W, Ji Z, Wang L, Liu S, Fang H, Yue X, Wei S, Liu S, Wang Z, et al. Molecular Dynamics Insight into the CO2 Flooding Mechanism in Wedge-Shaped Pores. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010188
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lu, Weifeng Lyu, Zemin Ji, Lu Wang, Sen Liu, Hongxu Fang, Xiaokun Yue, Shuxian Wei, Siyuan Liu, Zhaojie Wang, and et al. 2023. "Molecular Dynamics Insight into the CO2 Flooding Mechanism in Wedge-Shaped Pores" Molecules 28, no. 1: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010188
APA StyleWang, L., Lyu, W., Ji, Z., Wang, L., Liu, S., Fang, H., Yue, X., Wei, S., Liu, S., Wang, Z., & Lu, X. (2023). Molecular Dynamics Insight into the CO2 Flooding Mechanism in Wedge-Shaped Pores. Molecules, 28(1), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010188