Ageritin—The Ribotoxin-like Protein from Poplar Mushroom (Cyclocybe aegerita) Sensitizes Primary Glioblastoma Cells to Conventional Temozolomide Chemotherapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
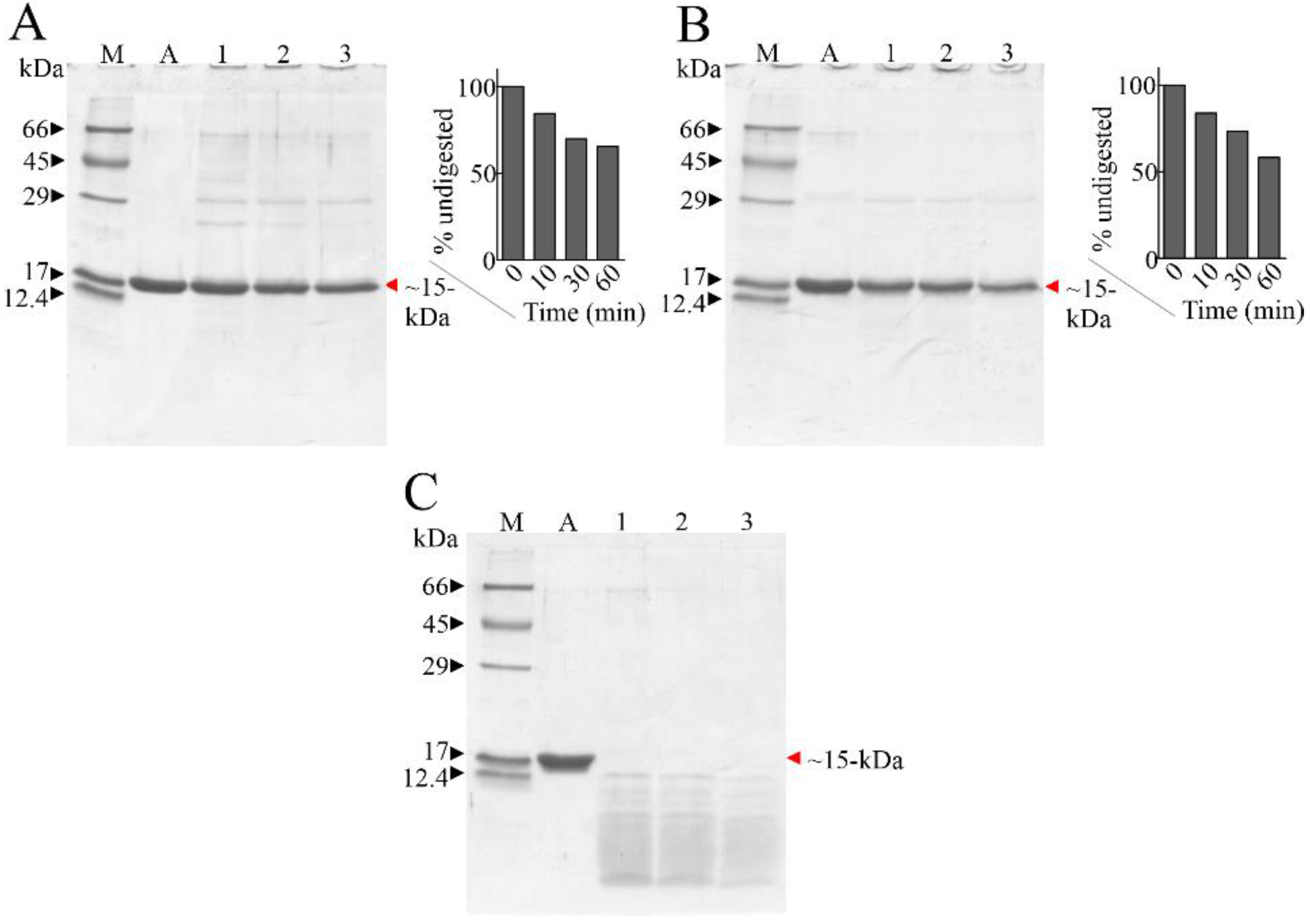
2.1. Susceptibility of Ageritin to Proteolysis
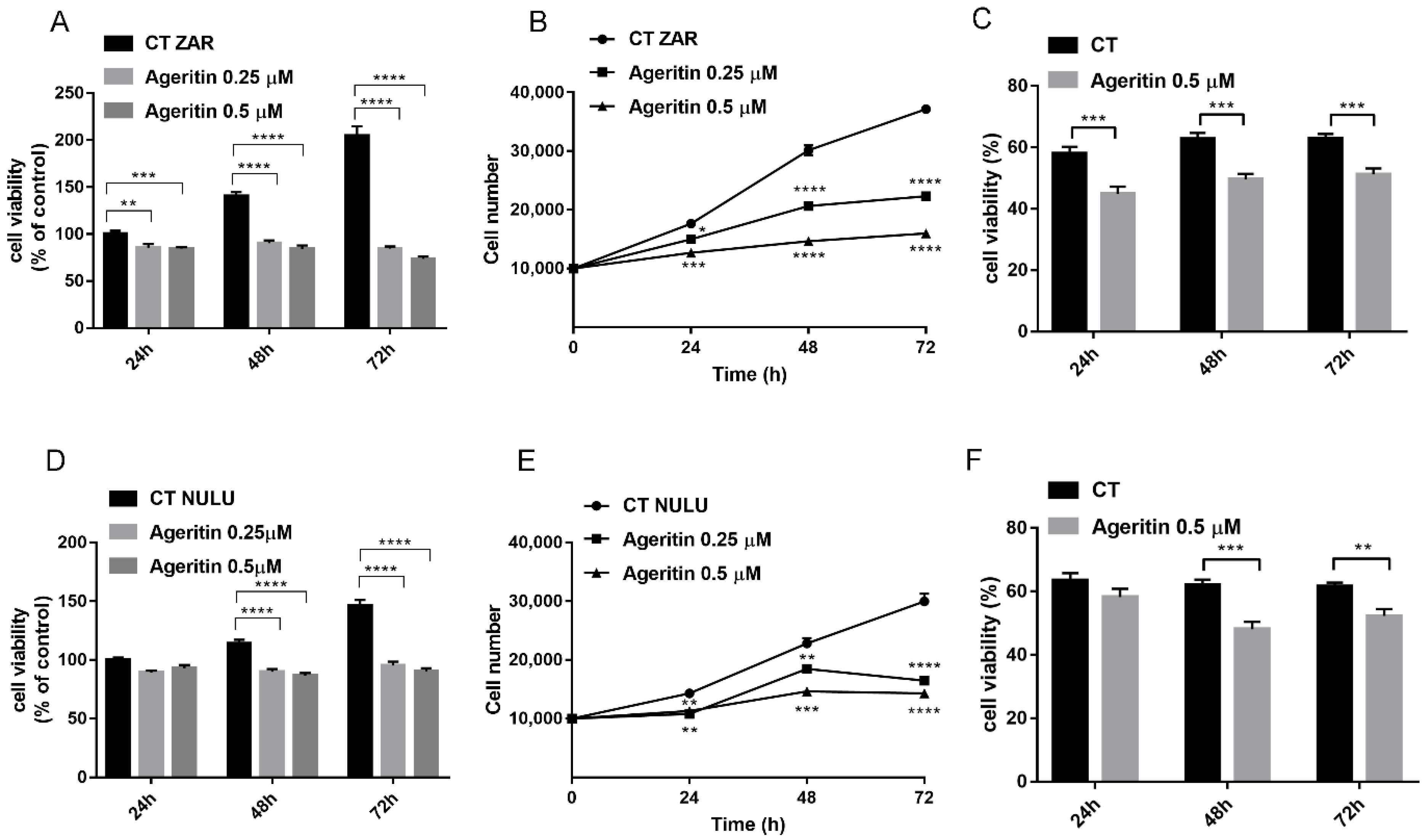
2.2. Cytotoxicity of Ageritin on Patient-Derived Glioblastoma Cell Lines NULU and ZAR
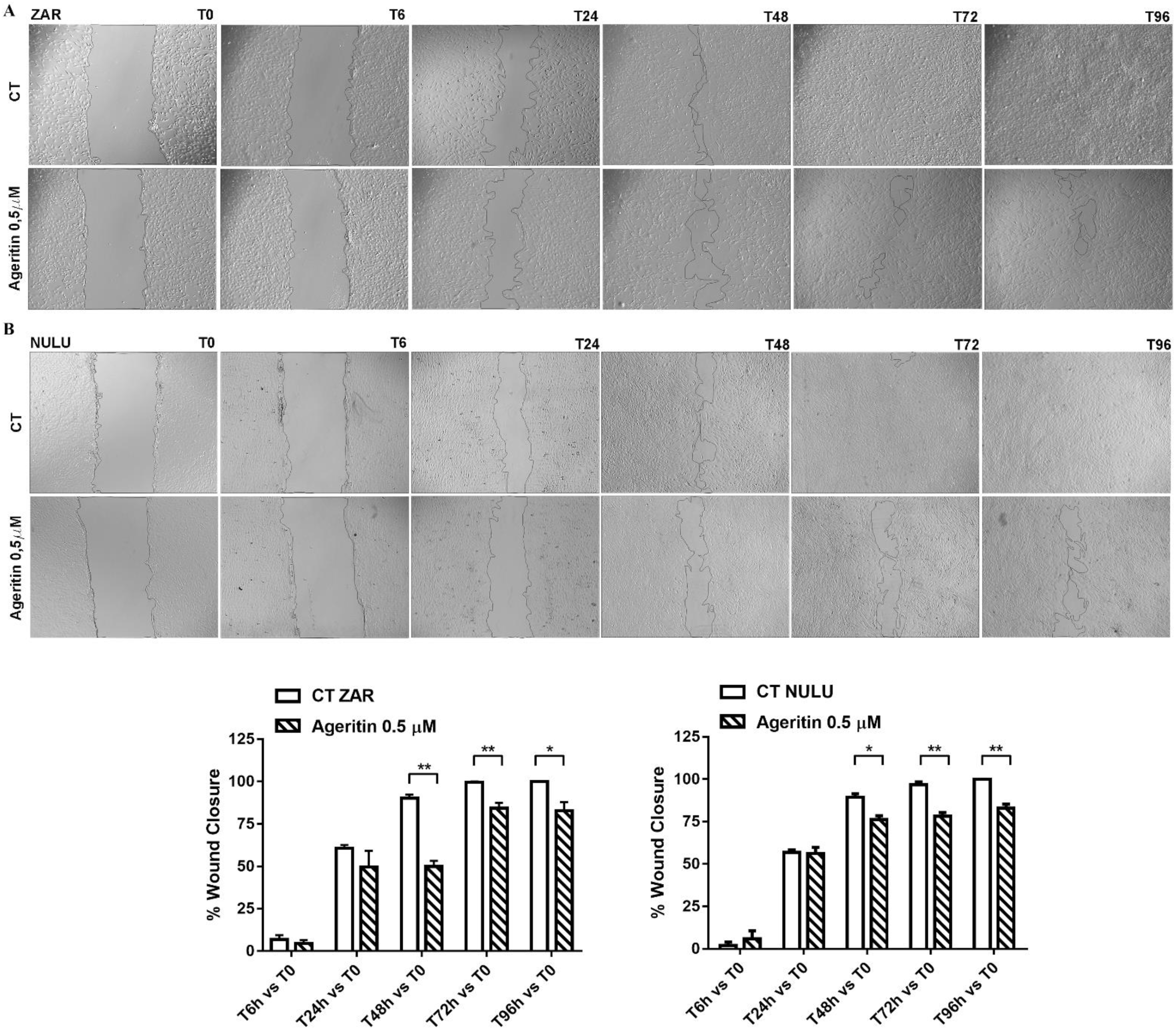
2.3. Effect of Ageritin on Cell Migration and Invasion
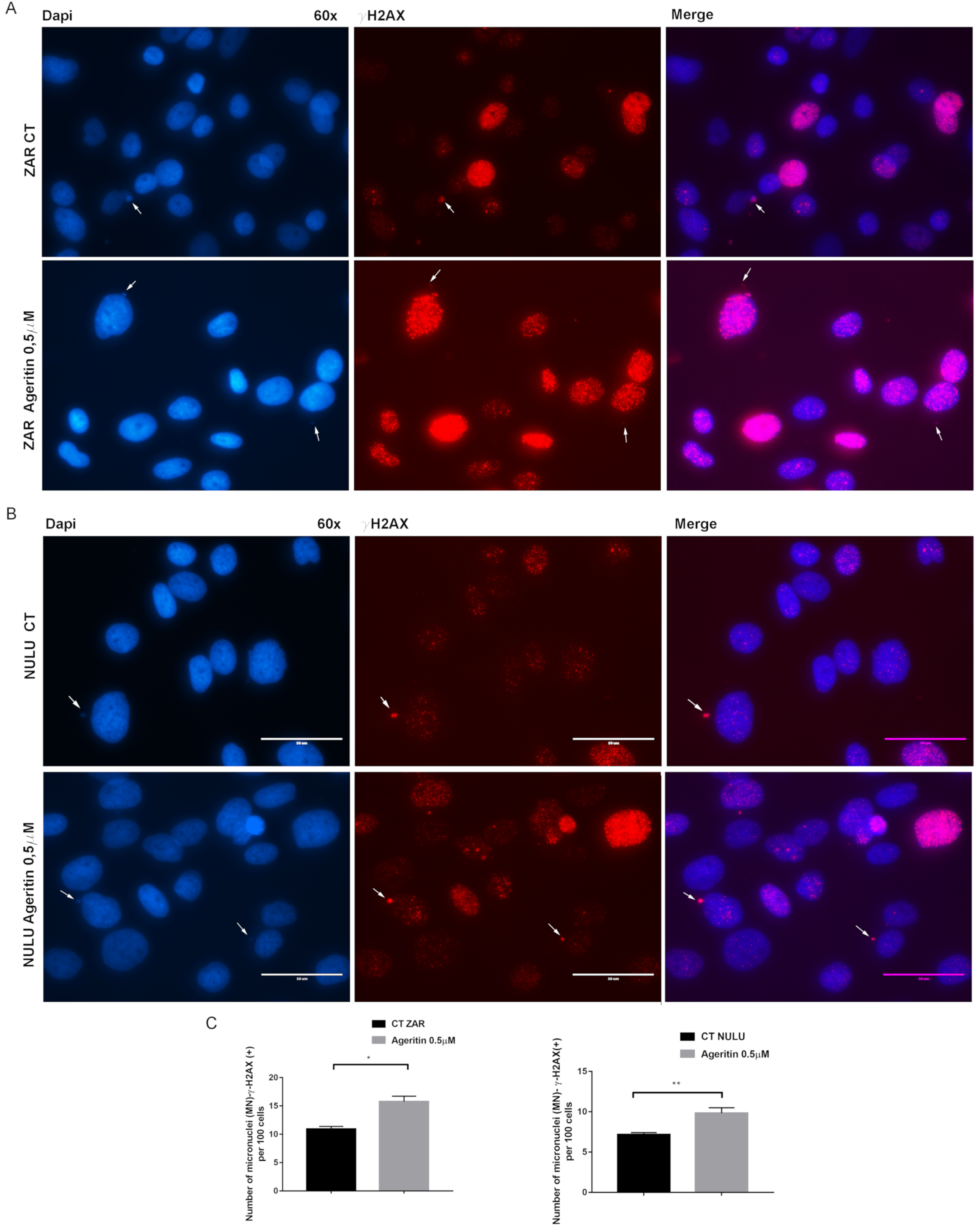
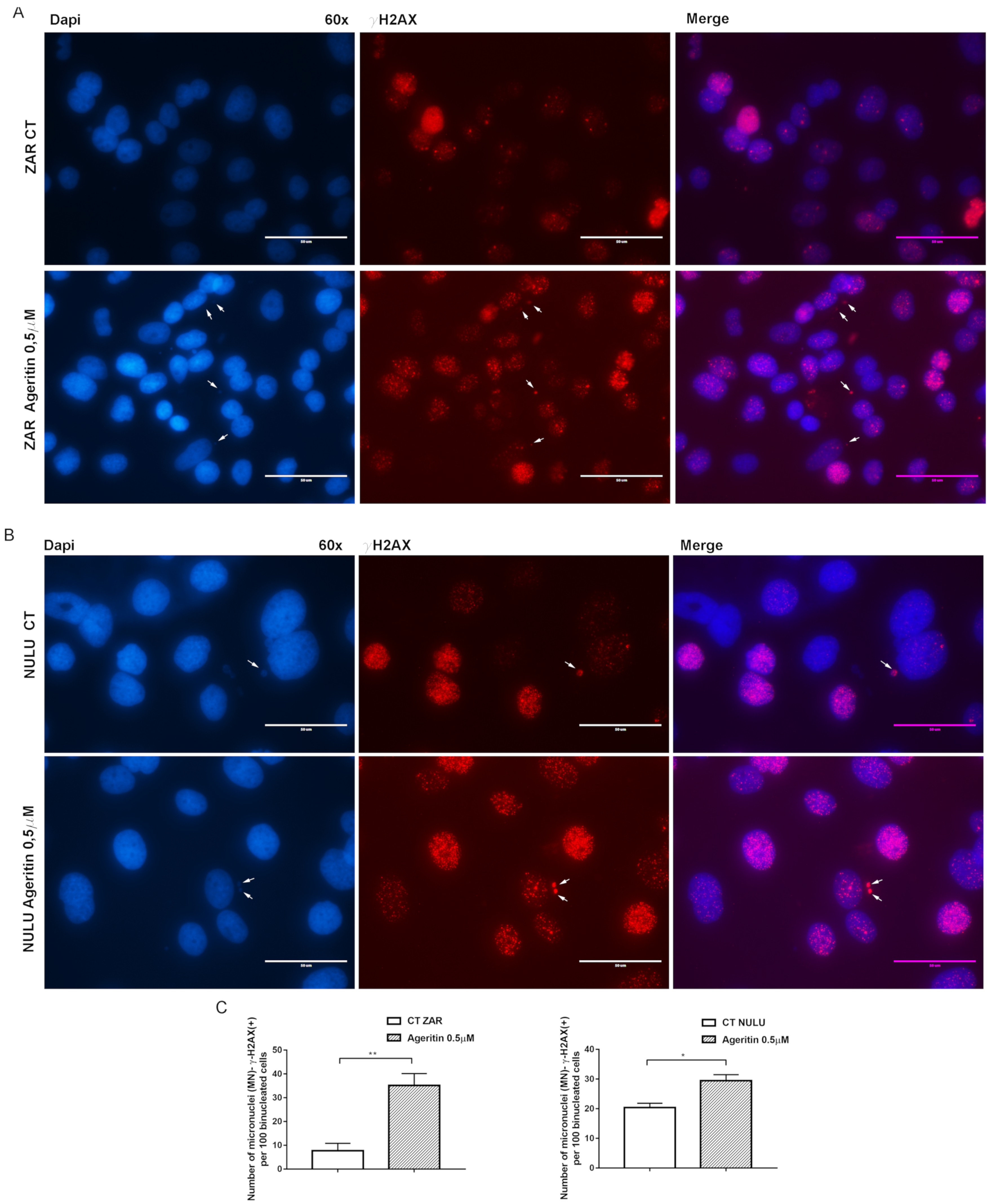
2.4. Ageritin-Induced Genotoxicity Evaluable as Increase in γ-H2AX (+) Micronuclei
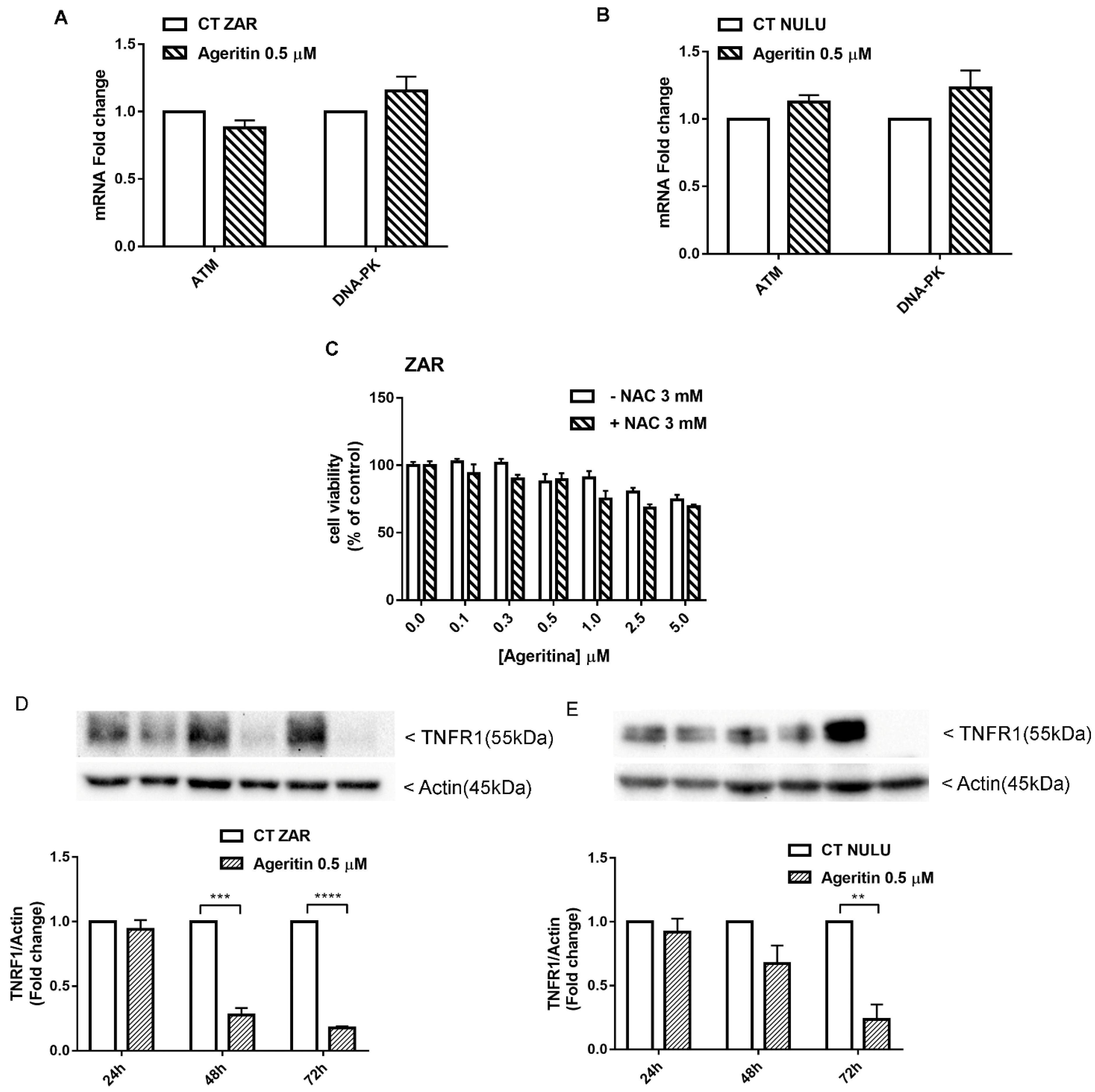
2.5. Transcriptional Deregulation Analysis of DNA Repair Enzyme Ataxia-Telangiectasia-Mutated ATM and DNA-Dependent Protein Kinase (DNA-PK) in Ageritin-Treated Glioblastoma Cells
2.6. Potential Role of Ageritin in Oxidative Stress and Deregulation of Tumour Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 (TNFR1)
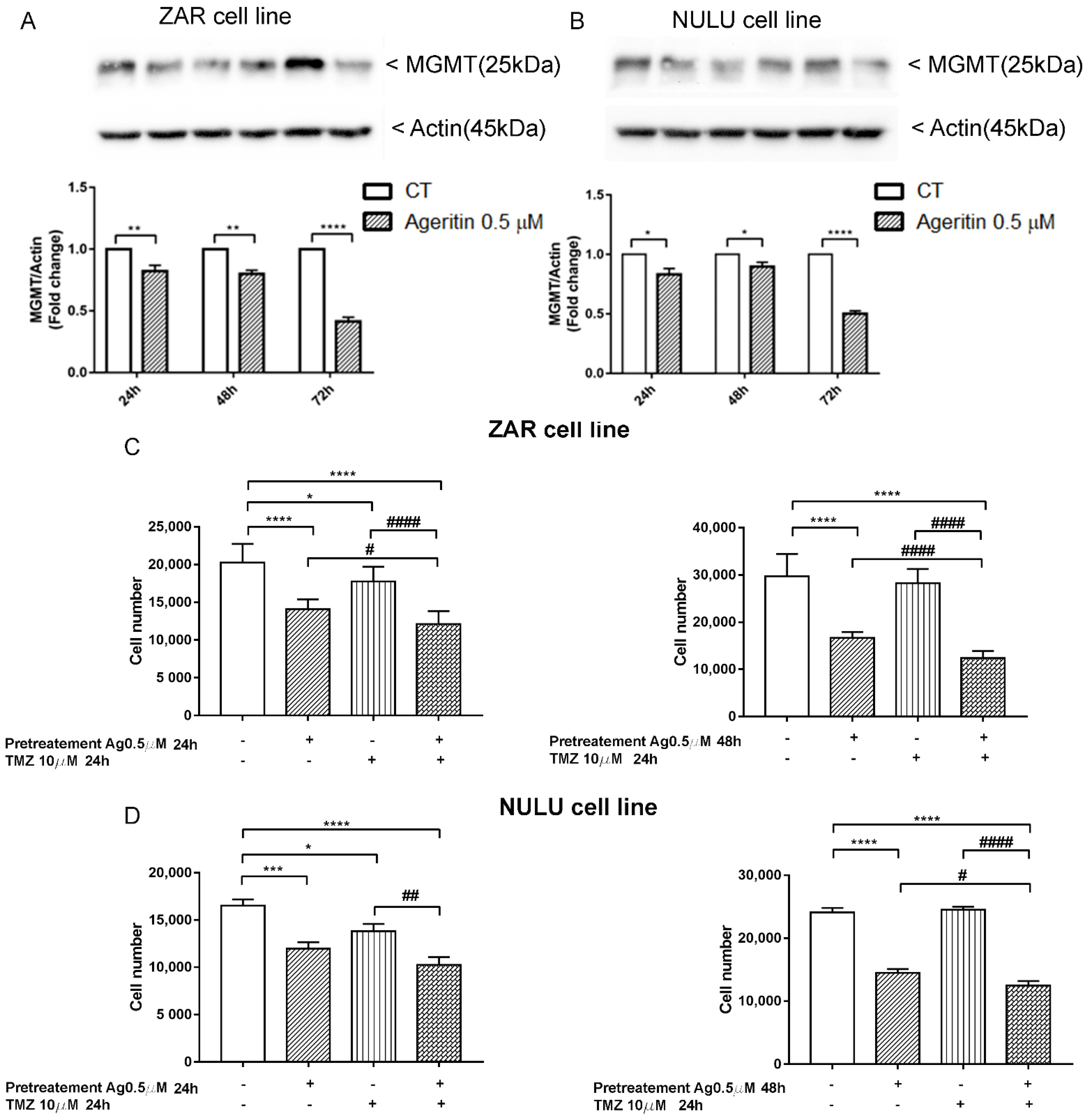
2.7. The inhibition of MGMT Protein Expression and Sensitization of Primary Glioblastoma Cells Lines to TMZ after Ageritin Pre-Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Purification of Ageritin
4.3. In Vitro Proteolytic Digestion
4.4. Cell Cultures
4.5. Cytotoxicity Test and IC50 Values
4.6. Growth Curve and Cell Proliferation Assay by Trypan Blue
4.7. Wound Healing Assay
4.8. Immunofluorescence for Micronuclei (MN)-γ-H2AX (+)
4.9. Cytochalasin B Micronucleus Assay
4.10. Real-Time PCR for DNA Damage Repair Enzymes ATM and DNA-PK
| Target | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
| ATM | 5′-TTTACCTAACTGTGAGCTGTCTCCAT-3′ | 5′-ACTTCCGTAAGGCATCGTAACAC-3′ |
| DNA-PK | 5′-CCAGCTCTCACGCTCTGATATG-3′ | 5′-CAAACGCATGCCCAAAGTC-3′ |
| GAPDH | 5′-GGTGAAGGTCGGAGTCAA-3′ | 5′-CATGTAGTTGAGGTCAATGAA-3′ |
4.11. Western Blot Analysis
4.12. Involvement of Oxidative Stress in Ageritin-Mediated Signals
4.13. Sensitivity Response of Patient-Derived Glioblastoma Cells to TMZ, after Pre-Treatment with Ageritin
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Endo, Y.; Wool, I.G. The site of action of alpha-sarcin on eukaryotic ribosomes. The sequence at the alpha-sarcin cleavage site in 28 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 9054–9060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragucci, S.; Landi, N.; Russo, R.; Valletta, M.; Pedone, P.V.; Chambery, A.; Di Maro, A. Ageritin from Pioppino Mushroom: The Prototype of Ribotoxin-Like Proteins, a Novel Family of Specific Ribonucleases in Edible Mushrooms. Toxins 2021, 13, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, N.; Pacifico, S.; Ragucci, S.; Iglesias, R.; Piccolella, S.; Amici, A.; Di Giuseppe, A.M.A.; Di Maro, A. Purification, characterization and cytotoxicity assessment of Ageritin: The first ribotoxin from the basidiomycete mushroom Agrocybe aegerita. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragucci, S.; Landi, N.; Russo, R.; Valletta, M.; Citores, L.; Iglesias, R.; Pedone, P.V.; Pizzo, E.; Di Maro, A. Effect of an additional N-terminal methionyl residue on enzymatic and antifungal activities of Ageritin purified from Agrocybe aegerita fruiting bodies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglivo, I.; Ragucci, S.; D’Incecco, P.; Landi, N.; Russo, R.; Faoro, F.; Pedone, P.V.; Di Maro, A. Gene Organization, Expression, and Localization of Ribotoxin-Like Protein Ageritin in Fruiting Body and Mycelium of Agrocybe aegerita. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, A.; García-Ortega, L.; Moreira, M.; Ragucci, S.; Landi, N.; Di Maro, A.; Berisio, R. Binding and enzymatic properties of Ageritin, a fungal ribotoxin with novel zinc-dependent function. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, A.; García-Ortega, L.; Ragucci, S.; Russo, R.; Landi, N.; Berisio, R.; Di Maro, A. Structural and enzymatic properties of Ageritin, a novel metal-dependent ribotoxin-like protein with antitumor activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 2888–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, N.; Ragucci, S.; Russo, R.; Pedone, P.V.; Chambery, A.; Di Maro, A. Structural insights into nucleotide and protein sequence of Ageritin: A novel prototype of fungal ribotoxin. J. Biochem. 2019, 165, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyrov, A.; Azevedo, S.; Herzog, R.; Vogt, E.; Arzt, S.; Lüthy, P.; Müller, P.; Rühl, M.; Hennicke, F.; Künzler, M. Heterologous Production and Functional Characterization of Ageritin, a Novel Type of Ribotoxin Highly Expressed during Fruiting of the Edible Mushroom Agrocybe aegerita. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01549-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citores, L.; Ragucci, S.; Ferreras, J.M.; Di Maro, A.; Iglesias, R. Ageritin, a Ribotoxin from Poplar Mushroom (Agrocybe aegerita) with Defensive and Antiproliferative Activities. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampitella, E.; Landi, N.; Oliva, R.; Gaglione, R.; Bosso, A.; De Lise, F.; Ragucci, S.; Arciello, A.; Petraccone, L.; Pizzo, E.; et al. Toxicity and membrane perturbation properties of the ribotoxin-like protein Ageritin. J. Biochem. 2021, 170, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, N.; Ragucci, S.; Russo, R.; Valletta, M.; Pizzo, E.; Ferreras, J.M.; Di Maro, A. The ribotoxin-like protein Ostreatin from Pleurotus ostreatus fruiting bodies: Confirmation of a novel ribonuclease family expressed in basidiomycetes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, N.; Ragucci, S.; Culurciello, R.; Russo, R.; Valletta, M.; Pedone, P.V.; Pizzo, E.; Di Maro, A. Ribotoxin-like proteins from Boletus edulis: Structural properties, cytotoxicity and in vitro digestibility. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragucci, S.; Pacifico, S.; Ruocco, M.R.; Crescente, G.; Nasso, R.; Simonetti, M.; Masullo, M.; Piccolella, S.; Pedone, P.V.; Landi, N.; et al. Ageritin from poplar mushrooms: Scale-up purification and cytotoxicity towards undifferentiated and differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6342–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanif, F.; Muzaffar, K.; Perveen, K.; Malhi, S.M.; Simjee Sh, U. Glioblastoma Multiforme: A Review of its Epidemiology and Pathogenesis through Clinical Presentation and Treatment. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2017, 18, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.I.; Mason, W.P. Temozolomide: The evidence for its therapeutic efficacy in malignant astrocytomas. Core Evid. 2010, 4, 93–111. [Google Scholar]
- Oliva, M.A.; Staffieri, S.; Castaldo, S.; Giangaspero, F.; Esposito, V.; Arcella, A. Characterization of primary glioma cell lines derived from the patients according to 2016 CNS tumour WHO classification and comparison with their parental tumours. J. Neurooncol. 2021, 151, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santanché, S.; Bellelli, A.; Brunori, M. The unusual stability of saporin, a candidate for the synthesis of immunotoxins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 234, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, W.; Reiser, G. Trypsin and trypsin-like proteases in the brain: Proteolysis and cellular functions. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klegeris, A.; McGeer, P.L. Chymotrypsin-like proteases contribute to human monocytic THP-1 cell as well as human microglial neurotoxicity. Glia 2005, 51, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohiuddin, I.S.; Kang, M.H. DNA-PK as an Emerging Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.H.; Oh, D.Y. ATM in DNA repair in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 203, 107391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Wang, W.; Guo, H.; Sun, Z.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Tischfield, J.A.; Gong, Y.; Shao, C. Oxidative stress preferentially induces a subtype of micronuclei and mediates the genomic instability caused by p53 dysfunction. Mutat. Res. 2014, 770, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, C.J.; Sharpe, Z.; Alemara, S.; Mackenzie, S.; Liu, G.; Abdallah, B.; Horne, S.; Regan, S.; Heng, H.H. Micronuclei and Genome Chaos: Changing the System Inheritance. Genes 2019, 10, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fenech, M.; Morley, A.A. Measurement of micronuclei in lymphocytes. Mutat. Res. 1985, 147, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, B.K.; Zimmer, D.M.; Mazurek, J.H.; Trzos, R.J.; Harbach, P.R.; Shu, V.S.; Johnson, M.A. Comparative genotoxicity of adriamycin and menogarol, two anthracycline antitumor agents. Cancer Res. 1983, 43, 5293–5297. [Google Scholar]
- Jagetia, G.C.; Nayak, V. Effect of doxorubicin on cell survival and micronuclei formation in HeLa cells exposed to different doses of gamma-radiation. Strahlenther. Onkol. Organ. Dtsch. Rontgengesellschaft. 2000, 176, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydemir, N.; Bilaloğlu, R. Genotoxicity of two anticancer drugs, gemcitabine and topotecan, in mouse bone marrow in vivo. Mutat. Res. 2003, 537, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, N.G.; Castro, M.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Gil, O.M.; Toscano-Rico, J.M.; Rueff, J. DNA-PK inhibitor wortmannin enhances DNA damage induced by bleomycin in V79 Chinese hamster cells. Teratog. Carcinog. Mutagenesis 2002, 22, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagetia, G.C.; Adiga, S.K. Correlation between cell survival and micronuclei formation in V79 cells treated with vindesine before exposure to different doses of gamma-radiation. Mutat. Res. 2000, 448, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, H.; Dostert, C.; Mak, T.W.; Brenner, D. TNF and ROS Crosstalk in Inflammation. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, E.D.; Cook, J.P.; Day, P.J.; Smith, D.C.; Roberts, L.M.; Lord, J.M. The low lysine content of ricin A chain reduces the risk of proteolytic degradation after translocation from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cytosol. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 3405–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamburino, R.; Pizzo, E.; Sarcinelli, C.; Poerio, E.; Tedeschi, F.; Ficca, A.G.; Parente, A.; Di Maro, A. Enhanced cytotoxic activity of a bifunctional chimeric protein containing a type 1 ribosome-inactivating protein and a serine protease inhibitor. Biochimie 2012, 94, 1990–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strebhardt, K.; Ullrich, A. Paul Ehrlich’s magic bullet concept: 100 years of progress. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maro, A.; Terracciano, I.; Sticco, L.; Fiandra, L.; Ruocco, M.; Corrado, G.; Parente, A.; Rao, R. Purification and characterization of a viral chitinase active against plant pathogens and herbivores from transgenic tobacco. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 147, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, R.; Ragucci, S.; Castaldo, S.; Oliva, M.A.; Landi, N.; Pedone, P.V.; Arcella, A.; Di Maro, A. Cytotoxicity Effect of Quinoin, Type 1 Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from Quinoa Seeds, on Glioblastoma Cells. Toxins 2021, 13, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, R.; Oliva, M.A.; Staffieri, S.; Castaldo, S.; Giangaspero, F.; Arcella, A. Implication of Lactucopicrin in Autophagy, Cell Cycle Arrest and Oxidative Stress to Inhibit U87Mg Glioblastoma Cell Growth. Molecules 2020, 25, 5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rotondo, R.; Ragucci, S.; Castaldo, S.; Landi, N.; Oliva, M.A.; Pedone, P.V.; Di Maro, A.; Arcella, A. Ageritin—The Ribotoxin-like Protein from Poplar Mushroom (Cyclocybe aegerita) Sensitizes Primary Glioblastoma Cells to Conventional Temozolomide Chemotherapy. Molecules 2022, 27, 2385. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27082385
Rotondo R, Ragucci S, Castaldo S, Landi N, Oliva MA, Pedone PV, Di Maro A, Arcella A. Ageritin—The Ribotoxin-like Protein from Poplar Mushroom (Cyclocybe aegerita) Sensitizes Primary Glioblastoma Cells to Conventional Temozolomide Chemotherapy. Molecules. 2022; 27(8):2385. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27082385
Chicago/Turabian StyleRotondo, Rossella, Sara Ragucci, Salvatore Castaldo, Nicola Landi, Maria Antonietta Oliva, Paolo V. Pedone, Antimo Di Maro, and Antonietta Arcella. 2022. "Ageritin—The Ribotoxin-like Protein from Poplar Mushroom (Cyclocybe aegerita) Sensitizes Primary Glioblastoma Cells to Conventional Temozolomide Chemotherapy" Molecules 27, no. 8: 2385. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27082385
APA StyleRotondo, R., Ragucci, S., Castaldo, S., Landi, N., Oliva, M. A., Pedone, P. V., Di Maro, A., & Arcella, A. (2022). Ageritin—The Ribotoxin-like Protein from Poplar Mushroom (Cyclocybe aegerita) Sensitizes Primary Glioblastoma Cells to Conventional Temozolomide Chemotherapy. Molecules, 27(8), 2385. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27082385










