Effect of Bear Garlic Addition on the Chemical Composition, Microbiological Quality, Antioxidant Capacity, and Degree of Proteolysis in Soft Rennet Cheeses Produced from Milk of Polish Red and Polish Holstein-Friesian Cows
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Basic Chemical Composition and Fatty Acid Profile
2.2. Microbiological Quality
2.3. Proteolysis
2.4. Antioxidant Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
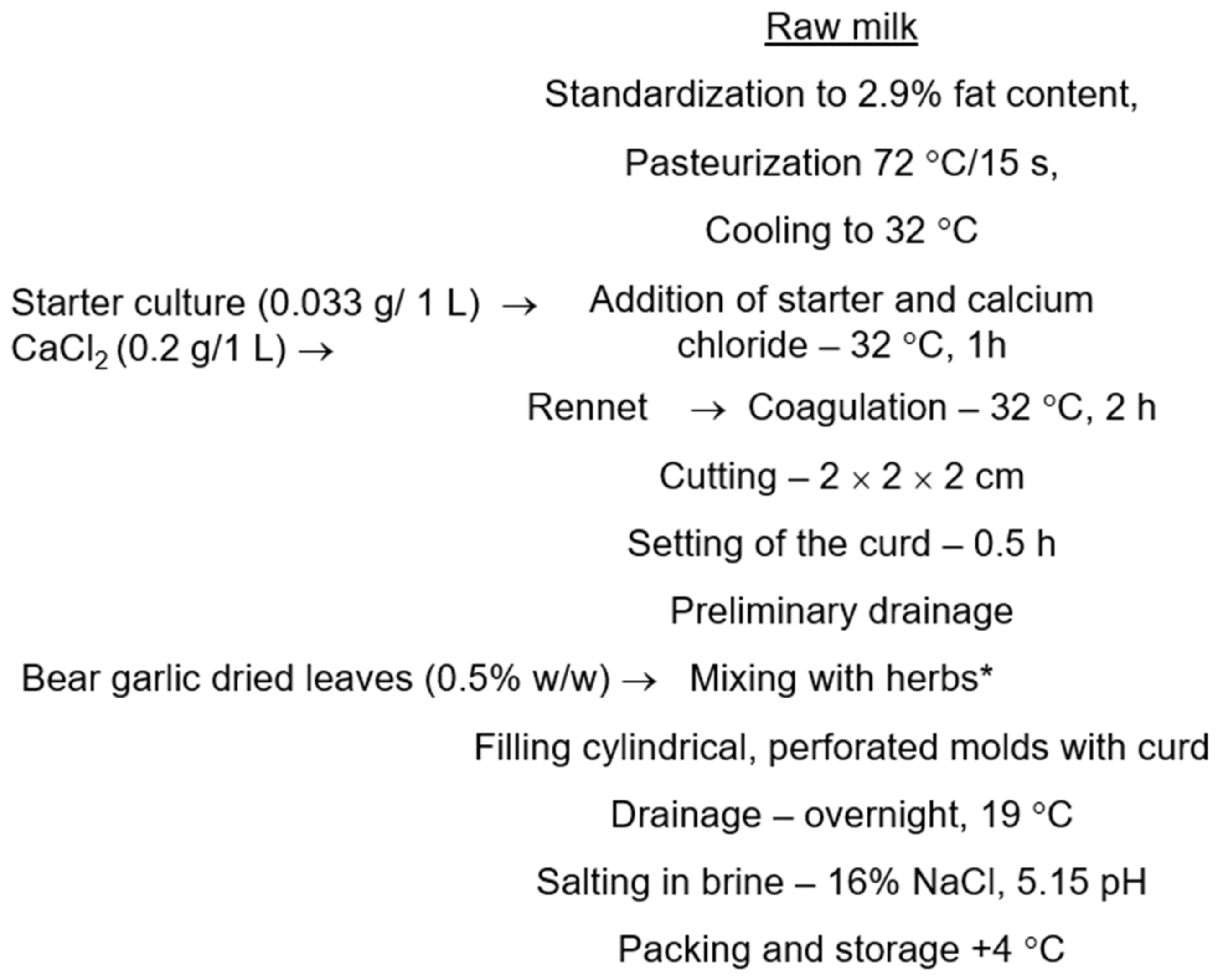
4.2. Cheese Production
4.3. Methods
4.3.1. Basic Chemical Composition
4.3.2. Determination of Fatty Acids Profile in Cheese
4.3.3. Antioxidant Activity
- Total phenolic content (TPC)
- Ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP)
- Scavenging activity against DPPH radical
4.3.4. Microbiological Study, pH and Water Activity
4.3.5. Proteolysis
- Free amino acids (FAA) analysis by HPLC method
- OPA assay
4.4. Study Arrangement and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Domagała, J.; Najgebauer-Lejko, D.; Walczycka, M. Traditional unfermented and fermented liquid milk products from the Malopolska Region. In Cultural Heritage—Possibilities for Land-Centered Societal Development. Environmental History; Hernik, J., Walczycka, M., Sankowski, E., Harris, B.J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 13, pp. 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akan, E.; Yerlikaya, O.; Akpinar, A.; Karagozlu, C.; Kinik, O.; Uysal, H.R. The effect of various herbs and packaging material on antioxidant activity and colour parameters of whey (Lor) cheese. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2021, 74, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupas, C.; Métoyer, B.; El Hatmi, H.; Adt, I.; Mahgoub, S.A.; Dumas, E. Plants: A natural solution to enhance raw milk cheese preservation? Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güler, Z. Profiles of organic acid and volatile compounds in acid-type cheeses containing herbs and spices (Surk cheese). Int. J. Food Prop. 2014, 17, 1379–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, S.M.; Youssef, A.M. Potential application of herbs and spices and their effects in functional dairy products. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Cai, Y.Z.; Brooks, J.D.; Corke, H. Potential application of spice and herb extracts as natural preservatives in cheese. J. Med. Food 2011, 14, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, S.; Kolniak-Ostek, J.; Oszmiański, J.; Wiśniewski, R. Comparison of phenolic content and antioxidant capacity of bear garlic (Allium ursinum L.) in different maturity stages. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e12921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zięć, G.; Topolska, K.; Łukasiewicz, M. North Carpathian herbs. Properties and application in food and folk medicine. In Indicators of Change in Cultural Heritage; Hernik, J., Król, K., Prus, B., Walczycka, M., Kao, R., Eds.; Publishing House of the University of Agriculture in Krakow: Krakow, Poland, 2021; pp. 155–169. [Google Scholar]
- Sobolewska, D.; Podolak, I.; Makowska-Wąs, J. Allium ursinum: Botanical, phytochemical and pharmacological overview. Phytochem. Rev. 2015, 14, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štajner, D.; Popović, B.M.; Čanadanović-Brunet, J.; Štajner, M. Antioxidant and scavenger activities of Allium ursinum. Fitoterapia 2008, 79, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MRiRW. Ser Podpuszczkowy z Leśną Nutą. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/rolnictwo/ser-podpuszczkowy-z-lesna-nuta (accessed on 19 October 2022).
- Gębczyński, P.; Bernaś, E.; Słupski, J. Usage of wild-growing plants as foodstuff. In Cultural Heritage—Possibilities for Land-Centered Societal Development; Hernik, J., Walczycka, M., Sankowski, E., Harris, B.J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanus, P.; Znamirowska, A.; Kuźniar, P. Zastosowanie dodatku jęczmienia (Hordeum vulgare) i czosnku niedźwiedziego (Allium ursinum) w technologii kefirów z mleka koziego (in Polish). In Przegląd wybranych zagadnień z zakresu przemysłu spożywczego. Monografia; Szala, M., Kropiwiec, K., Eds.; Wydawnictwo Naukowe TYGIEL Sp. z o.o.: Lublin, Poland, 2016; pp. 155–166. [Google Scholar]
- Coşkun, H.; Tunçtürk, Y. The effect of Allium sp. on the extension of lipolysis and proteolysis in Van herby cheese during maturation. Nahrung 2000, 44, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagdiç, O.; Simsek, B.; Küçüköner, E. Microbiological and physicochemical characteristics of Van herby cheese, a traditional Turkish dairy product. Milchwissenschaft 2003, 58, 382–385. [Google Scholar]
- Tarakçi, Z.; Coşkun, H.; Tunçtürk, Y. Some properties of fresh and ripened herby cheese, a traditional variety produced in Turkey. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 42, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Çelik, S.E.; Özyürek, M.; Altun, M.; Bektaşoğlu, B.; Güçlü, K.; Berker, K.I.; Ӧzgӧkҫe, F.; Apak’, R. Antioxidant capacities of herbal plants used in the manufacture of Van herby cheese: ‘Otlu peynir’. Int. J. Food Prop. 2008, 11, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerlikaya, O.; Akan, E.; Bayram, O.Y.; Karaman, A.D.; Kinik, O. The impact of medicinal and aromatic plant addition on antioxidant, total phenolic, antimicrobial activities, and microbiological quality of Mozzarella cheese. Int. Food Res. J. 2021, 28, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kose, S.; Ocak, E. Determination of antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of Herby cheese. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, A.; Tornambè, G.; Bellina, V.; De Pasquale, C.; Mazza, F.; Maniaci, G.; Di Grigoli, A. Effect of farming system and cheesemaking technology on the physicochemical characteristics, fatty acid profile, and sensory properties of Caciocavallo Palermitano cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 710–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwinczuk, Z.; Barlowska, J.; Chabuz, W.; Brodziak, A. Nutritional value and technological suitability of milk from cows of three Polish breeds included in the genetic resources conservation programme. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2012, 12, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P. An increase in the omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio increases the risk for obesity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Znamirowska, A.; Szajnar, K.; Rożek, P.; Kalicka, D.; Kuźniar, P.; Hanus, P.; Kotula, K.; Obirek, M.; Kluz, M. Effect of addition of wild garlic (Allium ursinum) on the quality of kefirs from sheep’s milk. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2017, 16, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, T.; Razavi, M.; Esmaeili Koutamehr, M. The effect of wild leek (Allium ampeloprasum) on growth and survival of Lactobacillus acidophilus and sensory properties in Iranian white cheese. Res. Innov. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 7, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, H. Microbiological and biochemical changes in herby cheese during ripening. Nahrung 1998, 42, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliguem, H.; Ben Hassine, D.; Ben Haj Said, L.; Ben Tekaya, I.; Rahmani, R.; Bellagha, S. Supplementation of double cream cheese with Allium roseum: Effects on quality improvement and shelf-life extension. Foods 2021, 10, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, A.; Mikhova, B.; Najdenski, H.; Tsvetkova, I.; Kostova, I. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of wild garlic Allium ursinum of Bulgarian origin. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dżugan, M.; Kordiaka, R.; Kočániová, M.; Wesołowska, M. Czosnek niedźwiedzi (Allium ursinum) jako uzupełnienie wiosennej diety (in Polish). In Właściwości produktów i surowców żywnościowych. Wybrane zagadnienia; Tarko, T., Duda-Chodak, A., Witczak, M., Najgebauer-Lejko, D., Eds.; Oddział Małopolski Polskiego Towarzystwa Technologów Żywności: Kraków, Poland, 2014; pp. 248–258. [Google Scholar]
- Stanisavljević, N.; Soković Bajić, S.; Jovanović, Ž.; Matić, I.; Tolinački, M.; Popović, D.; Popović, N.; Terzić-Vidojević, A.; Golić, N.; Beškoski, V.; et al. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activity of Allium ursinum and their associated microbiota during simulated in vitro digestion in the presence of food matrix. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 606616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, F.C.; Swaisgood, H.E.; Porter, D.H.; Catignani, G.L. Spectrophotometric assay using o-phthaldialdehyde for determination of proteolysis in milk and isolated milk proteins. J. Dairy Sci. 1983, 66, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, B.A. (Ed.) Microbiology and Biochemistry of Cheese and Fermented Milk; Blackie Academic & Professional: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, H.; Rhue, M.R.; Nishimura, T. Role of free amino acids and peptides in food taste. In Flavor Chemistry; Teranishi, R., Buttery, R.G., Shahidi, F., Eds.; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 158–174. [Google Scholar]
- Tarakci, Z.; Temiz, H. A review of the chemical, biochemical and antimicrobial aspects of Turkish Otlu (herby) cheese. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2009, 62, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkaczewska, J.; Borawska-Dziadkiewicz, J.; Kulawik, P.; Duda, I.; Morawska, M.; Mickowska, B. The effects of hydrolysis condition on the antioxidant activity of protein hydrolysate from Cyprinus carpio skin gelatin. LWT 2020, 117, 108616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.M.; Fox, P.F. Effect of adding free amino acids to Cheddar cheese curd on proteolysis, flavour and texture development. Int. Dairy J. 1997, 7, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangia, N.P.; Murgia, M.A.; Garau, G.; Sanna, M.G.; Deiana, P. Influence of selected lab cultures on the evolution of free amino acids, free fatty acids and Fiore Sardo cheese microflora during the ripening. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrau, M.A.; Mangia, N.P.; Murgia, M.A.; Sanna, M.G.; Garau, G.; Leccis, L.; Caredda, M.; Deiana, P. Employment of autochthonous microflora in Pecorino Sardo cheese manufacturing and evolution of physicochemical parameters during ripening. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulikowska, A.; Kilcawley, K.N.; Doolan, I.A.; Alonso-Gomez, M.; Nongonierma, A.B.; Hannon, J.A.; Wilkinson, M.G. The impact of reduced sodium chloride content on Cheddar cheese quality. Int. Dairy J. 2013, 28, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gođevac, D.; Vujisić, L.; Mojović, M.; Ignjatović, A.; Spasojević, I.; Vajs, V. Evaluation of antioxidant capacity of Allium ursinum L. volatile oil and its effect on membrane fluidity. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivokapic, M.; Bradic, J.; Petkovic, A.; Popovic, M. Phytochemical and pharmacological properties of Allium ursinum. Serb. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2018, 22, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najgebauer-Lejko, D.; Sady, M.; Grega, T.; Walczycka, M. The impact of tea supplementation on microflora, pH and antioxidant capacity of yoghurt. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC; Horwitz, W.; Latimer, G. (Eds.) Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 18th ed.; AOAC: Arlington, VA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 3433:2008; Cheese—Determination of Fat Content—Van Gulik Method. International Organization Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- ISO 5943:2006; Cheese and Processed Cheese Products—Determination of Chloride Content—Potentiometric Titration Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Stanley, G.H.S. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledoux, M.; Chardigny, J.M.; Darbois, M.; Soustre, Y.; Sébédio, J.L.; Laloux, L. Fatty acid composition of French butters, with special emphasis on conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) isomers. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2005, 18, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, B.; Iasko, B.; David, L. Antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of some commercial fruit-flavoured yogurts. Stu. U. Babes-Bol. Chem. 2016, 61, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- PN-EN ISO 6887-5:2010; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Preparation of Test Samples, Initial Suspension and Decimal Dilutions for Microbiological Examination—Part 5: Specific Rules for the Preparation of Milk and Milk Products. International Organization Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- PN-EN ISO 4833-1:2013-12; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microorganisms—Part 1: Colony Count at 30 Degrees C by the Pour Plate Technique. International Organization Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- IDF Standard No 149A; Dairy Starter Cultures of Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB). Standard of Identity, International Dairy Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 1997.
- ISO 21527-2:2008; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Yeasts and Moulds—Part 2: Colony Count Technique in Products with Water Activity Less than or Equal to 0.95. International Organization Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- PN-ISO 4832:2007; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Coliforms—Colony-Count Technique. International Organization Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- ISO 18787:2017; Foodstuffs—Determination of Water Activity. International Organization Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
| Milk Source | TS | Lactose * | Fat | Protein | Ash |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PHF | 12.00 a ± 0.06 | 4.24 a ± 0.12 | 4.05 a ± 0.05 | 3.05 a ± 0.00 | 0.63 a ± 0.03 |
| PR | 12.72 b ± 0.13 | 4.05 a ± 0.05 | 4.53 a ± 0.12 | 3.47 b ± 0.06 | 0.73 b ± 0.01 |
| Variability Factor | TS | Fat | Protein | Ash | NaCl | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g/100 g) | (g/100 g TS) | ||||||
| PR | N | 41.80 a ± 1.17 | 22.30 a ± 0.83 | 53.36 a ± 1.48 | 18.48 a ± 1.13 | 2.2275 a ± 0.0225 | 0.48 a ± 0.02 |
| BG | 48.53 bc ± 1.52 | 22.75 a ± 1.39 | 46.88 a ± 2.45 | 21.23 ab ± 0.76 | 2.5675 a ± 0.1146 | 0.43 a ± 0.10 | |
| PHF | N | 46.48 b ± 0.63 | 24.75 a ± 1.05 | 53.35 a ± 2.86 | 18.78 a ± 0.80 | 2.3175 a ± 0.1368 | 0.63 a ± 0.07 |
| BG | 52.84 c ± 0.93 | 26.38 a ± 1.25 | 50.05 a ± 3.04 | 23.35 b ± 0.97 | 2.6250 a ± 0.1574 | 0.65 a ± 0.05 | |
| MS | * | * | ns | ns | ns | * | |
| ChT | * | ns | ns | * | * | ns | |
| MS × ChT | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| PR | PHF | Effect | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | BG | N | BG | MS | ChT | MS × ChT | |
| C4:0 | 2.12 a ± 0.01 | 1.83 a ± 0.12 | 1.62 a ± 0.54 | 1.96 a ± 0.05 | ns | ns | ns |
| C6:0 | 1.53 b ± 0.05 | 1.33 ab ± 0.08 | 1.20 a ± 0.05 | 1.11 a ± 0.03 | * | * | ns |
| C8:0 | 1.01 b ± 0.04 | 0.90 b ± 0.05 | 0.66 a ± 0.02 | 0.63 a ± 0.01 | * | ns | ns |
| C10:0 | 2.29 b ± 0.11 | 2.09 b ± 0.11 | 1.30 a ± 0.03 | 1.26 a ± 0.01 | * | ns | ns |
| C12:0 | 2.75 b ± 0.13 | 2.61 b ± 0.09 | 1.53 a ± 0.02 | 1.53 a ± 0.02 | * | ns | ns |
| C13:0 | 0.08 b ± 0.00 | 0.07 b ± 0.01 | 0.06 ab ± 0.00 | 0.05 a ± 0.01 | * | * | ns |
| C14:0 | 10.18 b ± 0.19 | 9.95 b ± 0.10 | 6.74 a ± 0.03 | 6.75 a ± 0.10 | * | ns | ns |
| C15:0 | 1.27 a ± 0.01 | 1.26 a ± 0.00 | 1.08 a ± 0.05 | 1.10 a ± 0.06 | * | ns | ns |
| C16:0 | 28.92 a ± 0.43 | 29.39 a ± 0.32 | 28.41 a ± 0.78 | 28.63 a ± 0.59 | ns | ns | ns |
| C17:0 | 0.68 a ± 0.01 | 0.70 a ± 0.02 | 0.66 a ± 0.02 | 0.63 a ± 0.03 | ns | ns | ns |
| C18:0 | 12.86 a ± 0.29 | 13.29 a ± 0.14 | 14.38 b ± 0.25 | 14.53 b ± 0.26 | * | ns | ns |
| C20:0 | 2.07 a ± 0.20 | 1.60 a ± 0.50 | 1.44 a ± 0.16 | 1.43 a ± 0.14 | ns | ns | ns |
| Σ SFA | 65.85 b ± 0.09 | 65.04 b ± 0.57 | 59.08 a ± 0.71 | 59.60 a ± 0.59 | * | ns | ns |
| C10:1 | 0.26 b ± 0.01 | 0.23 b ± 0.01 | 0.14 a ± 0.00 | 0.13 a ± 0.01 | * | ns | ns |
| C14:1 | 0.61 a ± 0.02 | 0.85 b ± 0.00 | 0.56 a ± 0.05 | 0.59 a ± 0.02 | * | * | * |
| C16:1 (n-9) | 0.29 a ± 0.01 | 0.26 a ± 0.00 | 0.24 a ± 0.02 | 0.18 a ± 0.06 | ns | ns | ns |
| C16:1 (n-7) | 1.82 a ± 0.06 | 1.86 a ± 0.05 | 1.90 a ± 0.01 | 1.88 a ± 0.01 | ns | ns | ns |
| C17:1 | 0.22 a ± 0.01 | 0.22 a ± 0.00 | 0.32 a ± 0.06 | 0.26 a ± 0.02 | ns | ns | ns |
| C18:1 (cis-11) | 6.57 b ± 1.30 | 5.12 ab ± 0.46 | 3.25 a ± 0.57 | 3.96 ab ± 0.55 | * | ns | ns |
| C18:1 (n-9) | 21.26 a ± 1.34 | 22.92 a ± 0.63 | 31.71 b ± 0.52 | 30.73 b ± 0.35 | * | ns | ns |
| Σ MUFA | 30.95 a ± 0.10 | 31.45 a ± 0.23 | 38.12 b ± 0.40 | 37.74 b ± 0.34 | * | ns | ns |
| C18:2 (trans-9,12; n-6) | 0.31 b ± 0.04 | 0.22 b ± 0.02 | 0.07 a ± 0.01 | 0.09 a ± 0.03 | * | ns | ns |
| C18:2 (n-6) | 1.49 a ± 0.03 | 1.53 a ± 0.03 | 2.03 b ± 0.13 | 1.84 ab ± 0.09 | * | ns | ns |
| C18:3 (n-6) | 0.00 a ± 0.00 | 0.35 a ± 0.35 | 0.02 a ± 0.01 | 0.09 a ± 0.08 | ns | ns | ns |
| C18:3 (n-3) | 1.21 b ± 0.05 | 1.33 b ± 0.12 | 0.47 a ± 0.14 | 0.64 a ± 0.11 | * | ns | ns |
| n-6/n-3 | 1.49 a ± 0.06 | 1.55 a ± 0.11 | 5.73 b ± 1.40 | 3.53 b ± 0.56 | * | ns | ns |
| CLA | 0.13 a ± 0.01 | 0.10 a ± 0.04 | 0.18 a ± 0.03 | 0.15 a ± 0.03 | ns | ns | ns |
| Σ PUFA | 3.14 a ± 0.04 | 3.52 a ± 0.43 | 2.78 a ± 0.31 | 2.65 a ± 0.27 | ns | ns | ns |
| Cheese Type: | N | BG | Statistical Effects | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storage Time: | 0 w | 2 w | 0 w | 2 w | |||
| TABC (log cfu/g) | Milk type: | PR | 9.26 b ± 0.07 | 8.64 ab ± 0.22 | 9.21 b ± 0.10 | 9.05 ab ± 0.02 | MS—*; ChT—ns; S—* MS × ChT—ns MS × S—ns ChT × S—* MS × ChT × S—ns |
| PHF | 8.90 ab ± 0.13 | 8.33 a ± 0.27 | 8.72 ab ± 0.09 | 8.67 ab ± 0.05 | |||
| Lactococcus (log cfu/g) | Milk type: | PR | 9.00 a ± 0.01 | 8.48 a ± 0.15 | 8.92 a ± 0.04 | 8.78 a ± 0.06 | MS—*; ChT—ns; S—ns MS × ChT—ns MS × S—ns ChT × S—ns MS × ChT × S—ns |
| PHF | 8.31 a ± 0.59 | 7.79 a ± 0.15 | 8.09 a ± 0.53 | 8.39 a ± 0.08 | |||
| Yeasts (log cfu/g) | Milk type: | PR | 0.00 a ± 0.00 | 4.22 a ± 0.93 | 0.00 a ± 0.00 | 1.22 a ± 1.22 | MS—ns; ChT—ns; S—ns MS × ChT—ns MS × S—ns ChT × S—ns MS × ChT × S—ns |
| PHF | 2.37 a ± 1.13 | 3.32 a ± 0.17 | 1.52 a ± 1.52 | 1.95 a ± 1.95 | |||
| pH | Milk type: | PR | 4.66 a ± 0.05 | 4.51 a ± 0.02 | 4.52 a ± 0.01 | 4.60 a ± 0.03 | MS—ns; ChT—ns; S—ns MS × ChT—ns MS × S—ns ChT × S—ns MS × ChT × S—* |
| PHF | 4.49 a ± 0.10 | 4.78 a ± 0.19 | 4.62 a ± 0.05 | 4.43 a ± 0.10 | |||
| Water activity | Milk type: | PR | 0.924 a ± 0.002 | 0.951 a ± 0.015 | 0.932 a ± 0.011 | 0.946 a ± 0.021 | MS—ns; ChT—ns; S—ns MS × ChT—ns MS × S—ns ChT × S—ns MS × ChT × S—ns |
| PHF | 0.945 a ± 0.013 | 0.944 a ± 0.010 | 0.938 a ± 0.010 | 0.938 a ± 0.011 | |||
| PR | PHF | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAA | N | BG | N | BG | ||||
| (mg/kg) | 0 w | 2 w | 0 w | 2 w | 0 w | 2 w | 0 w | 2 w |
| ASP | 11.12 a ± 2.92 | 15.94 ab ± 4.92 | 12.88 ab ± 3.80 | 16.14 ab ± 3.35 | 18.35 ab ± 4.47 | 26.51 abc ± 7.01 | 36.77 bc ± 7.28 | 46.35 c ± 6.52 |
| SER | 2.00 a ± 0.41 | 3.08 a ± 0.86 | 5.10 a ± 1.72 | 11.17 a ± 1.33 | 4.99 a ± 2.39 | 6.88 a ± 2.87 | 21.29 ab ± 9.38 | 32.29 b ± 6.66 |
| GLU | 31.10 a ± 4.49 | 40.30 a ± 7.83 | 46.60 a ± 11.42 | 57.90 ab ± 7.63 | 92.30 ab ± 10.00 | 157.80 bc ± 36.80 | 160.40 bc ± 30.69 | 201.80 c ± 41.12 |
| GLY | 0.48 a ± 0.04 | 0.58 a ± 0.03 | 1.34 a ± 0.19 | 2.58 ab ± 0.51 | 3.08 ab ± 0.80 | 4.37 ab ± 0.76 | 7.10 b ± 2.29 | 12.88 c ± 1.14 |
| HIS | 2.25 a ± 0.28 | 3.25 a ± 0.62 | 5.47 a ± 1.29 | 15.18 a ± 2.76 | 6.59 a ± 1.45 | 7.81 a ± 1.13 | 34.03 ab ± 9.51 | 57.02 b ± 22.21 |
| ARG | 1.62 a ± 0.31 | 2.25 a ± 0.49 | 4.35 a ± 1.32 | 11.60 ab ± 1.82 | 7.78 a ± 1.02 | 19.14 ab ± 6.34 | 26.00 ab ± 10.94 | 45.17 b ± 17.82 |
| THR | 16.81 a ± 4.06 | 23.69 ab ± 6.70 | 12.73 a ± 3.62 | 16.84 a ± 2.65 | 14.57 a ± 1.31 | 28.52 ab ± 3.06 | 29.74 ab ± 5.19 | 43.52 b ± 7.38 |
| PRO | 52.03 a ± 11.54 | 68.18 a ± 16.22 | 49.89 a ± 5.30 | 62.39 a ± 8.54 | 63.48 a ± 2.25 | 77.68 a ± 2.78 | 50.72 a ± 9.99 | 84.77 a ± 3.21 |
| ALA | 7.66 a ± 0.74 | 10.95 ab ± 1.76 | 11.55 ab ± 2.95 | 14.05 abc ± 2.36 | 10.21 ab ± 2.83 | 21.24 abc ± 7.14 | 34.16 bc ± 7.31 | 39.52 c ± 10.45 |
| TYR | 11.31 a ± 1.54 | 15.54 ab ± 2.81 | 18.42 ab ± 3.79 | 26.88 ab ± 3.64 | 27.12 ab ± 8.05 | 48.35 ab ± 18.48 | 62.12 ab ± 20.79 | 73.93 b ± 20.65 |
| VAL | 5.33 a ± 0.84 | 7.06 a ± 1.38 | 18.71 ab ± 3.42 | 23.38 ab ± 3.10 | 11.71 a ± 2.15 | 17.60 ab ± 4.00 | 56.97 bc ± 13.62 | 67.61 c ± 19.80 |
| MET | 0.86 a ± 0.08 | 1.21 a ± 0.17 | 4.68 a ± 1.71 | 10.45 a ± 2.29 | 3.72 a ± 0.80 | 7.07 a ± 1.75 | 42.62 b ± 7.46 | 50.83 b ± 7.18 |
| LYS | 18.70 a ± 5.81 | 26.60 ab ± 9.32 | 31.40 ab ± 10.91 | 46.20 ab ± 11.49 | 47.92 ab ± 5.48 | 66.96 ab ± 7.08 | 113.24 bc ± 26.90 | 156.56 c ± 41.62 |
| ILE | 2.15 a ± 0.32 | 3.00 a ± 0.55 | 12.63 a ± 3.86 | 16.63 a ± 2.40 | 9.21 a ± 3.41 | 17.69 a ± 6.74 | 50.29 b ± 10.05 | 64.73 b ± 10.69 |
| LEU | 4.06 a ± 0.71 | 5.60 a ± 1.08 | 25.50 a ± 6.27 | 50.78 ab ± 9.31 | 15.72 a ± 4.75 | 24.79 a ± 6.49 | 91.54 ab ± 28.89 | 132.80 b ± 42.06 |
| PHE | 3.66 a ± 0.60 | 4.99 a ± 0.77 | 17.91 ab ± 2.77 | 38.75 b ± 4.35 | 20.01 ab ± 5.65 | 28.38 ab ± 7.51 | 16.94 ab ± 6.52 | 29.91 ab ± 12.56 |
| CYS | 1.00 a ± 0.11 | 1.17 a ± 0.12 | 2.03 a ± 0.63 | 3.36 b ± 1.36 | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Total FAA | 172.11 a ± 33.44 | 232.79 a ± 53.09 | 281.15 ab ± 62.62 | 424.27 ab ± 51.43 | 356.80 ab ± 44.43 | 560.83 ab ± 101.54 | 825.24 bc ± 177.55 | 1145.93 c ± 240.70 |
| OPA(mM GLY/g) | 4.89 a ± 2.34 | 7.16 a ± 3.42 | 8.22 a ± 0.55 | 18.75 b ± 1.01 | 9.39 a ± 0.66 | 23.80 b ± 1.27 | 10.19 a ± 0.03 | 32.19 c ± 1.09 |
| Cheese Type: | N | BG | Statistical Effects | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storage Time: | 0 w | 2 w | 0 w | 2 w | |||
| TPC (mg GAE) | Milk type: | PR | 48.00 ab ± 8.27 | 45.95 ab ± 8.22 | 95.88 ab ± 21.93 | 82.01 ab ± 17.87 | MS—ns; ChT—*; S—ns MS × ChT—ns MS × S—ns ChT × S—ns MS × ChT × S—ns |
| PHF | 26.34 a ± 10.18 | 17.52 ab ± 4.41 | 67.71 ab ± 22.75 | 124.80 b ± 40.95 | |||
| ARP (mM TE) | Milk type: | PR | 0.012 a ± 0.001 | 0.025 abc ± 0.003 | 0.019 ab ± 0.003 | 0.038 c ± 0.003 | MS—ns; ChT—*; S—* MS × ChT—ns MS × S—* ChT × S—ns MS × ChT × S—ns |
| PHF | 0.017 ab ± 0.003 | 0.016 ab ± 0.003 | 0.029 bc ± 0.003 | 0.023 ab ± 0.005 | |||
| FRAP (mM Fe2+) | Milk type: | PR | 0.038 a ± 0.001 | 0.035 a ± 0.003 | 0.051 a ± 0.003 | 0.048 a ± 0.006 | MS—*; ChT—ns; S—ns MS × ChT—ns MS × S—ns ChT × S—ns MS × ChT × S—ns |
| PHF | 0.079 a ± 0.052 | 0.111 a ± 0.054 | 0.156 a ± 0.088 | 0.167 a ± 0.076 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Najgebauer-Lejko, D.; Pluta-Kubica, A.; Domagała, J.; Turek, K.; Duda, I.; Golian, J. Effect of Bear Garlic Addition on the Chemical Composition, Microbiological Quality, Antioxidant Capacity, and Degree of Proteolysis in Soft Rennet Cheeses Produced from Milk of Polish Red and Polish Holstein-Friesian Cows. Molecules 2022, 27, 8930. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248930
Najgebauer-Lejko D, Pluta-Kubica A, Domagała J, Turek K, Duda I, Golian J. Effect of Bear Garlic Addition on the Chemical Composition, Microbiological Quality, Antioxidant Capacity, and Degree of Proteolysis in Soft Rennet Cheeses Produced from Milk of Polish Red and Polish Holstein-Friesian Cows. Molecules. 2022; 27(24):8930. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248930
Chicago/Turabian StyleNajgebauer-Lejko, Dorota, Agnieszka Pluta-Kubica, Jacek Domagała, Katarzyna Turek, Iwona Duda, and Jozef Golian. 2022. "Effect of Bear Garlic Addition on the Chemical Composition, Microbiological Quality, Antioxidant Capacity, and Degree of Proteolysis in Soft Rennet Cheeses Produced from Milk of Polish Red and Polish Holstein-Friesian Cows" Molecules 27, no. 24: 8930. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248930
APA StyleNajgebauer-Lejko, D., Pluta-Kubica, A., Domagała, J., Turek, K., Duda, I., & Golian, J. (2022). Effect of Bear Garlic Addition on the Chemical Composition, Microbiological Quality, Antioxidant Capacity, and Degree of Proteolysis in Soft Rennet Cheeses Produced from Milk of Polish Red and Polish Holstein-Friesian Cows. Molecules, 27(24), 8930. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248930







