Correlation Study of Biological Activity with Quercetin and Phenolics Content in Onion Extracts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
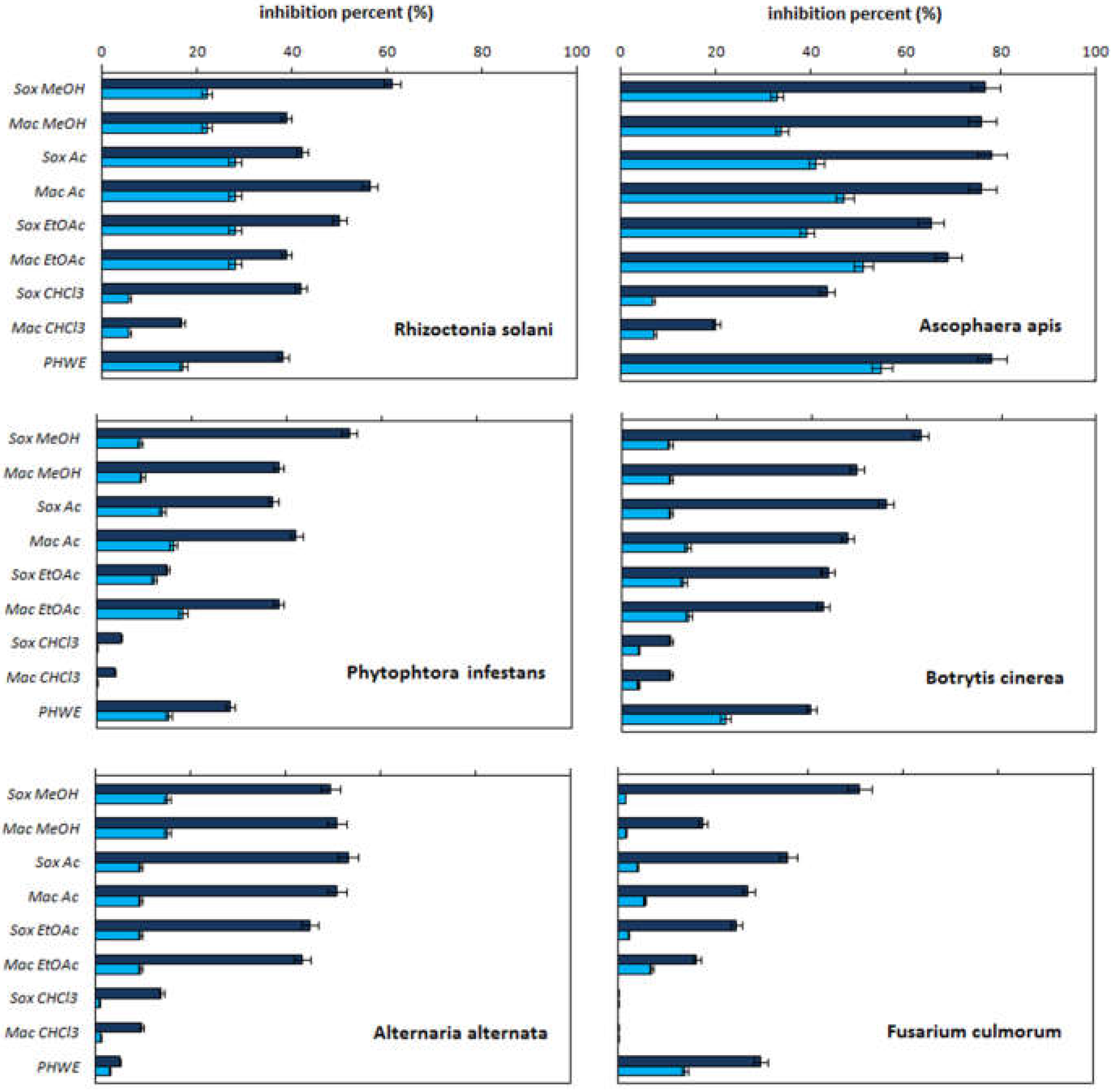
2.1. Antifungal Activity
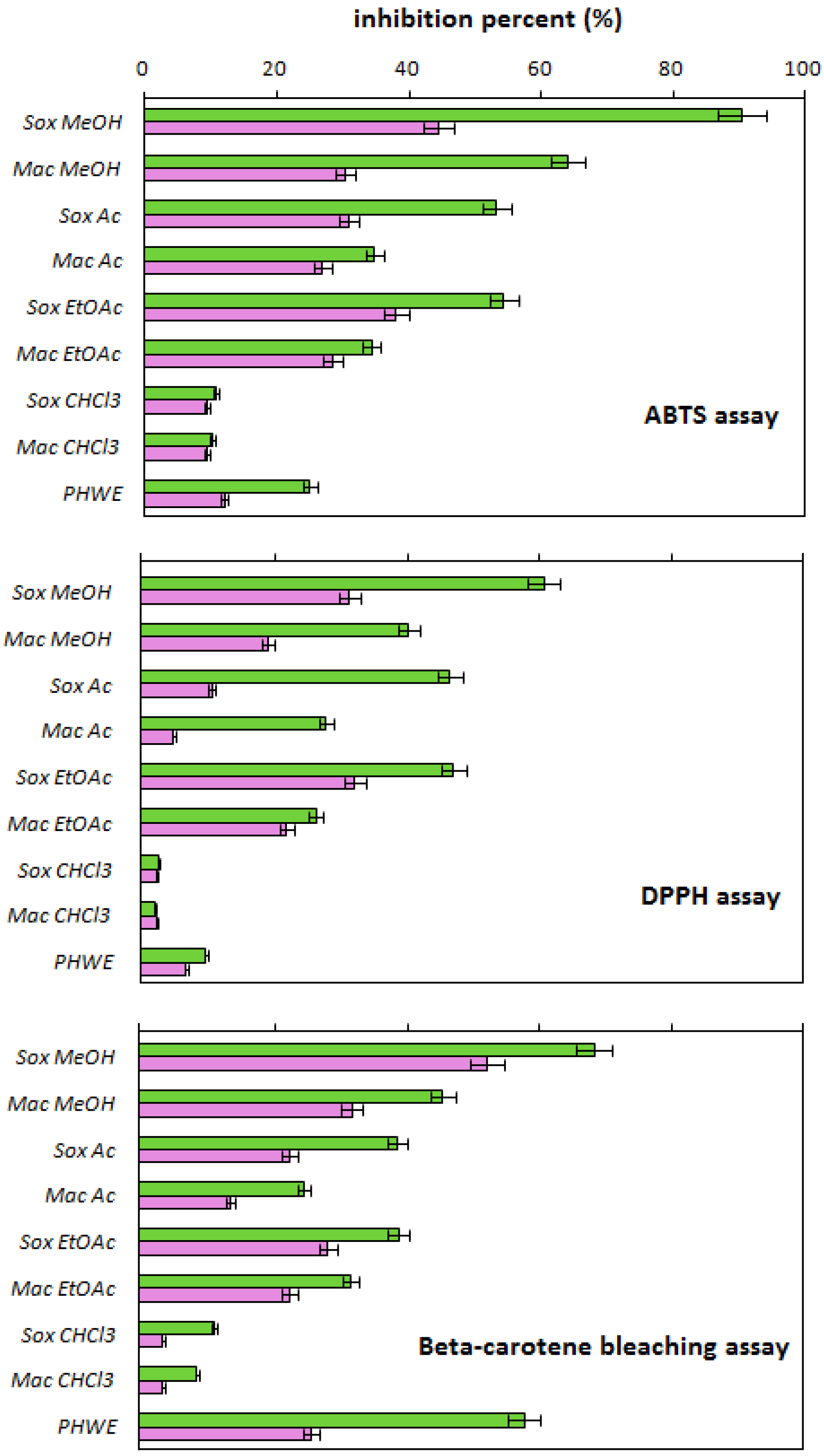
2.2. Antioxidant Activity
Correlation of Antioxidant Activity of Onion Extracts with the Temperature of PHWE Process and the Quercetin/Phenolics Content in the Extracts
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Pressurized Hot Water Extraction
3.3. Extraction in the Soxhlet Apparatus
3.4. Maceration
3.5. HPLC Analysis of Quercetin
3.6. Total Phenolics Content Measurement
3.7. Antioxidant Activity
3.7.1. β-Carotene Bleaching Assay
3.7.2. DPPH Method
3.7.3. ABTS Method
3.8. Antifungal Activity
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Wianowska, D.; Bryshten, I. New insights into vitamin K—From its natural sources through biological properties and chemical methods of quantitative determination. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, A.V.A.; Arulmoli, R.; Parasuraman, S. Overviews of biological importance of quercetin: A bioactive flavonoid. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2016, 10, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G.E.S.; Beshbishy, A.M.; Ikram, M.; Mulla, Z.S.; Abd El-Hack, M.; Taha, A.E.; Algammal, A.M.; Elewa, Y.H.A. The pharmacological activity, biochemical properties, and pharmacokinetics of the major natural polyphenolic flavonoid: Quercetin. Foods 2020, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimestad, R.; Fossen, T.; Molund Vågen, I. Onions: A source of unique dietary flavonoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 10067–10080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wianowska, D. Application of sea sand disruption method for HPLC determination of quercetin in plants. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wianowska, D.; Dawidowicz, A.L.; Bernacik, K.; Typek, R. Determining the true content of quercetin and its derivatives in plants. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Ko, E.Y.; Assefa, A.D.; Ha, S.; Nile, S.H.; Lee, E.T.; Park, S.W. Temperature-dependent studies on the total phenolics, flavonoids, antioxidant activities, and sugar content in six onion varieties. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sandahl, M.; Sjöberg, P.J.R.; Turner, C. Pressurised hot water extraction in continuous flow mode for thermolabile compounds: Extraction of polyphenols in red onions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wianowska, D.; Dawidowicz, A.L. Effect of water content in extraction mixture on the pressurized liquid extraction efficiency-stability of quercetin 4-glucoside during extraction from onions. J. AOAC Int. 2016, 99, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wianowska, D.; Olszowy-Tomczyk, M.; Garbaczewska, S. A Central Composite Design in increasing the quercetin content in the aqueous onion waste isolates with antifungal and antioxidant properties. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 248, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wianowska, D.; Garbaczewska, S.; Cieniecka-Roslonkiewicz, A.; Typek, R.; Dawidowicz, A.L. Chemical composition and antifungal activity of Chelidonium majus extracts–antagonistic action of chelerythrine and sanguinarine against Botrytis cinerea. Chem. Ecol. 2018, 34, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wianowska, D.; Garbaczewska, S.; Cieniecka-Roslonkiewicz, A.; Typek, R.; Kielczewska, A. Influence of the extraction conditions on the antifungal properties of walnut green husk isolates. Anal. Lett. 2020, 53, 1970–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauflihah, Y.M.; Gollavelii, G.; Ling, Y.-C. Correlation study of antioxidant activity with phenolic and flavonoid compounds in 12 Indonesian indigenous herbs. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmić, C.; Begić, S.; Mićić, V.; Petrović, Z.; Avdić, G. Effect of solvent and extraction condition on antioxidative activity of sage (Salvia officinalis L.) extracts obtained by maceration. Technol. Acta 2019, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszowy, M. What is responsible for antioxidant properties of polyphenolic compounds from plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 144, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwinienko, G.; Ingold, K.U. Solvent effects on the rates and mechanisms of reaction of phenols with free radicals. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawidowicz, A.L.; Olszowy, M. Depletion/protection of β-carotene in estimating antioxidant activity by β-carotene bleaching assay. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 7321–7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.H. Scales of solute hydrogen-bonding: Their construction and application to physicochemical and biochemical processes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1993, 22, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwinienko, G.; Ingold, K.U. Abnormal solvent effects on hydrogen atom abstraction. 2. Resolution of the curcumin antioxidant controversy. The role of Sequential Proton Loss Electron Transfer. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 5888–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beesk, N.; Perner, H.; Schwarz, D.; George, E.; Kroh, L.W.; Rogn, S. Distribution of quercetin-3,4′-O-diglucoside, quercetin-4′-O-monoglucoside, and quercetin in different parts of onion bulb (Allium cepa L.) influenced by genotype. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.C.; Jalil, A.M.M.; Ismail, A. Phenolic and theobromine contents of commercial dark, milk and white chocolates on the Malaysian market. Molecules 2009, 14, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawidowicz, A.L.; Wianowska, D.; Olszowy, M. On practical problems in estimation of antioxidant activity of compounds by DPPH method (Problems in estimation of antioxidant activity). Food Chem. 2012, 131, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenadis, N.; Wang, L.-F.; Tsimidou, M.; Zhang, H.-Y. Estimation of scavenging activity of phenolic compounds using the ABTS(●+) assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 4669–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Extractant Type | Extraction Method | Quercetin Content [mg/g] | Quercetin Concentration * [mg/mL] | Total Phenolics Content [mg GAEs/g] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHCl3 | Mac | 3.05 ± 0.11 | 0.031 ± 0.001 | 57.2 ± 8.21 |
| Sox | 2.56 ± 0.38 | 0.026 ± 0.004 | 57.6 ± 5.32 | |
| EtOAc | Mac | 457 ± 3.75 | 4.570 ± 0.037 | 674 ± 9.60 |
| Sox | 276 ± 0.71 | 2.760 ± 0.071 | 551 ± 9.23 | |
| MeOH | Mac | 390 ± 1.98 | 3.90 ± 0.020 | 655 ± 8.12 |
| Sox | 303 ± 1.27 | 3.03 ± 0.013 | 630 ± 2.82 | |
| Ac | Mac | 147 ± 0.57 | 1.47 ± 0.006 | 414 ± 9.90 |
| Sox | 139 ± 0.92 | 1.39 ± 0.009 | 486 ± 4.05 | |
| Water | PHWE | 187 ± 1.16 | 1.87 ± 0.001 | 456 ± 5.48 |
| Onion Variety | PHWE Temp. [°C] | Inedible Part | Edible Part | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin Amount | Phenolics Amount | Quercetin Amount | Phenolics Amount | ||
| White onion | 50 | 1.81 ± 0.05 | 19.8 ±0.21 | 3.22 ± 0.14 | 11.7 ± 0.22 |
| 75 | 5.62 ±0.14 | 60.9 ± 3.15 | 3.53 ± 0.21 | 17.4 ± 0.55 | |
| 100 | 16.33 ±0.52 | 48.6 ± 2.85 | 3.63 ± 0.17 | 29.9 ± 1.24 | |
| 125 | 40.28 ±3.21 | 81.7 ± 3.47 | 3.61 ± 0.42 | 33.0 ± 1.23 | |
| 150 | 37.3 ± 2.98 | 83.6 ± 2.98 | 3.59 ± 0.27 | 23.0 ± 1.06 | |
| 175 | 28.5 ± 1.57 | 94.6 ± 3.46 | 3.48 ± 0.14 | 24.9 ± 0.98 | |
| Red onion | 50 | 5.11 ± 0.13 | 61.7 ± 3.17 | 0.55 ± 0.09 | 2.34 ± 0.04 |
| 75 | 9.97 ± 0.21 | 60.4 ± 2.85 | 2.35 ± 0.15 | 7.58 ± 0.05 | |
| 100 | 23.0 ± 1.54 | 75.6 ± 3.63 | 3.49 ± 0.22 | 28.7 ± 1.54 | |
| 125 | 31.0 ± 1.26 | 89.6 ± 3.47 | 3.57 ± 0.18 | 32.6 ± 0.95 | |
| 150 | 34.0 ± 0.98 | 97.2 ± 3.05 | 2.85 ± 0.13 | 18.3 ± 0.86 | |
| 175 | 30.0 ± 1.12 | 119 ± 0.26 | 2.43 ± 0.06 | 17.4 ± 0.44 | |
| Onion Variety/Part | AA Method | CCs for Quercetin | CCs for Phenolics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | RHO | R | RHO | ||
| White/inedible scales | ABTS | 0.714 * | 0.874 | 0.866 | 0.825 |
| DPPH | 0.565 * | 0.643 | 0.808 | 0.585 | |
| Beta-carotene | 0.641 * | 0.837 | 0.827 | 0.655 | |
| White/edible entry | ABTS | 0.842 | 0.071 * | 0.820 | 0.270 * |
| DPPH | 0.816 | 0.110 * | 0.875 | 0.532 * | |
| Beta-carotene | 0.860 | 0.800 | 0.950 | 0.760 | |
| Red/inedible scales | ABTS | 0.951 | −0.217 * | 0.961 | −0.424 * |
| DPPH | 0.856 | 0.364 * | 0.908 | 0.294 * | |
| Beta-carotene | 0.990 | 0.517 * | 0.833 | 0.650 | |
| Red/edible entry | ABTS | 0.948 | 0.829 | 0.933 | 0.956 |
| DPPH | 0.942 | 0.789 | 0.841 | 0.901 | |
| Beta-carotene | 0.758 * | 0.669 | 0.610 * | 0.524 * | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olszowy-Tomczyk, M.; Garbaczewska, S.; Wianowska, D. Correlation Study of Biological Activity with Quercetin and Phenolics Content in Onion Extracts. Molecules 2022, 27, 8164. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238164
Olszowy-Tomczyk M, Garbaczewska S, Wianowska D. Correlation Study of Biological Activity with Quercetin and Phenolics Content in Onion Extracts. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8164. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238164
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlszowy-Tomczyk, Małgorzata, Sylwia Garbaczewska, and Dorota Wianowska. 2022. "Correlation Study of Biological Activity with Quercetin and Phenolics Content in Onion Extracts" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8164. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238164
APA StyleOlszowy-Tomczyk, M., Garbaczewska, S., & Wianowska, D. (2022). Correlation Study of Biological Activity with Quercetin and Phenolics Content in Onion Extracts. Molecules, 27(23), 8164. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238164







