Abstract
A novel series of twenty-five rhodamine-linked benzenesulfonamide derivatives (7a–u and 9a–d) were synthesized and screened for their inhibitory action against four physiologically relevant human (h) carbonic anhydrase (CA) isoforms, namely hCA I, hCA II, hCA IX, and hCA XII. All the synthesized molecules showed good to excellent inhibition against all the tested isoforms in the nanomolar range due to the presence of the sulfonamide as a zinc binding group. The target compounds were developed from indol-3-ylchalcone-linked benzenesulfonamide where the indol-3-ylchalcone moiety was replaced with rhodanine-linked aldehydes or isatins to improve the inhibition. Interestingly, the molecules were slightly more selective towards hCA IX and XII compared to hCA I and II. The most potent and efficient ones against hCA I were 7h (KI 22.4 nM) and 9d (KI 35.8 nM) compared to the standard drug AAZ (KI 250.0 nM), whereas in case of hCA II inhibition, the derivatives containing the isatin nucleus as a tail were preferred. Collectively, all compounds were endowed with better inhibition against hCA IX compared to AAZ (KI 25.8 nM) as well as strong potency against hCA XII. Finally, these newly synthesized molecules could be taken as potential leads for the development of isoform selective hCA IX and XII inhibitors.
1. Introduction
In recent years, studies of rhodanine (2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one) based molecules have been on the rise because of their wide spectrum of biological activities through different mechanisms of action, and they have become a very important group of heterocyclic compounds in drug discovery. Rhodanine consists of a five-membered ring with sulfide and amino groups at the first and third positions, respectively. The amino group could be responsible for interaction with the ligand binding site of target proteins through different types of interactions, such as hydrogen bonding as well as interactions with metal ions [1,2]. Rhodanine is mostly important in photochemistry, medicinal chemistry, biochemistry, and industry [3,4]. Several substituted rhodanine compounds have been investigated to evaluate their potential antidiabetic, anti-Alzheimer, anticancer, and antimicrobial activities [5,6]. Hence, the rhodanine structure, after different chemical modification and functionalization, could provide compounds with a broad range of biological activities [7,8,9,10].
Enzymes were usually targeted for drug discovery and development because of their vital role in many diseases. Therefore, researchers have focused on developing drug candidates that act as enzyme activators or inhibitors. Carbonic anhydrases (CAs, E.C.4.2.1.1) are metalloenzymes that play a major role in the reversible conversion of water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2) into a proton (H+) and bicarbonate anion (HCO3−). Eight different, genetically distinct CA families are known to date: α-, β-, γ-, δ-, ζ-, θ-, η-, and ι-, depending on their catalytic activity, localization in different organisms, and sensitivity to different classes of modulators [11,12,13,14,15,16]. The α-class, which consists of 16 isoforms, is the only one present in humans. CA isoenzymes regulate many physio-pathological and biochemical processes, such as pH homeostasis, acid-base regulation, calcification, gluconeogenesis, ureagenesis, bone resorption, and tumorigenicity. Therefore, CA inhibitors (CAIs) have been experimentally and clinically proposed as anti-epileptics, diuretics, anti-glaucoma, anti-microbial, or anti-cancer agents [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24].
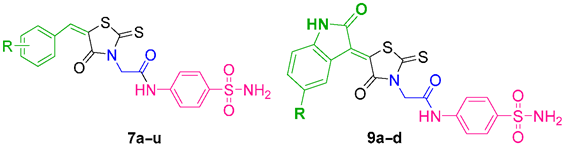
The synthesis of rhodanine derivatives and exploring their potential inhibitory actions against various diseases are popular areas of research. Unfortunately, few efforts have been made to investigate the potential of rhodanine derivatives as hCA inhibitors [7,8,9]. Hence, in the present study, we synthesized and investigated a novel series of benzenesulfonamide-linked rhodanine derivatives for their inhibitory effects on hCA isoenzymes. Moreover, to better explore the chemical space within this privileged scaffold and to take advantage of the good inhibitory potency displayed against hCA I, II, and XIII by indole-linked benzenesulfonamide derivatives [25,26,27,28,29], we designed our derivatives functionalizing the rhodanine nucleus with both aryl and isatin rings (tail approach) to orient the isoform selectivity against four different hCA isoforms. Hence, the target compound was developed from indol-3-ylchalcone-linked benzenesulfonamide (which was previously synthesized in our lab) where the indol-3-ylchalcone moiety was replaced with rhodanine-linked aldehydes or isatins (Figure 1) in order to keep the presence of a nitrogen in this portion of the scaffold constant or not constant.
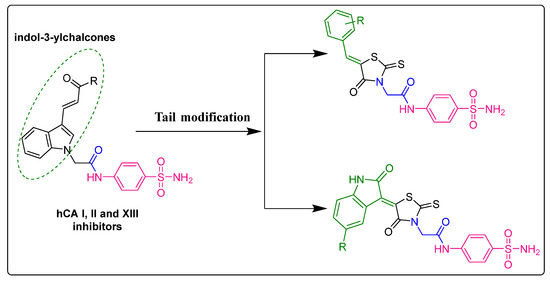
Figure 1.
Rationale to design the target compounds.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
The target molecules were designed using the tail approach as depicted in Scheme 1. The reactions involved the commercially available starting materials glycine (1) and chloroacetic acid (2). The intermediate 3, (2-(4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid) was obtained via the one-pot, three component condensation of glycine, chloroacetic acid, and carbon disulfide by using a method identified in past literature [30]. The rhodamine-containing intermediate 3 (2-(4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid) was then subjected to acid-amine coupling with sulfanilamide (4), according to a previously reported procedure [31], to produce intermediate 5, which was further functionalized through Knoevenagel condensation [32] with the appropriated carbonyl compound (benzaldehydes (6) and isatins (8)) to produce the target compounds 7a–u and 9a–d, respectively, in good to excellent yield.
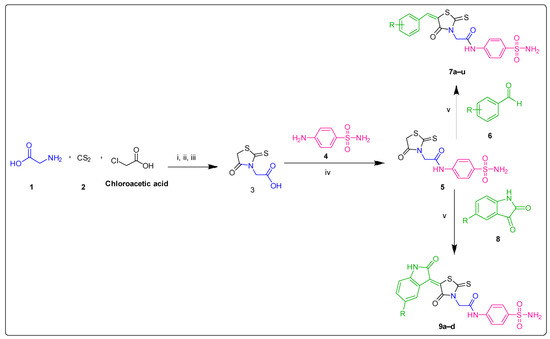
Scheme 1.
Reagent and conditions: (i) NaOH, EtOH, rt, 4–5 h; (ii) rt, 7–8 h; (iii) HCl, pH 1.0, rt, 2 h, 82%; (iv) EDCI, HOBt, DMF, rt; 7–8 h, 85%; (v) sodium acetate, acetic acid, EtOH, reflux, 4–5 h, 50–79%. For R substituents, please refer to Table 1.
2.2. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibition: Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) Studies
The inhibition data for the newly synthesized rhodanine-linked benzenesulfonamide derivatives were reported against two physiologically relevant cytosolic hCA I and hCA II and two tumor-associated transmembrane hCA IX and hCA XII while using acetazolamide (AAZ) as the standard drug, and the results were summarized in Table 1. All the isoenzymes belong to the human α-class of CAs. The following structure–activity relationships (SARs as reported in Figure 2) can be extrapolated as follows.

Table 1.
Inhibition of hCA isoforms I, II, IX, and XII with KI (nM) data for compounds 7a–u and 9a–d and acetazolamide (AAZ) as the standard inhibitor by means of the stopped-flow carbon dioxide assays.
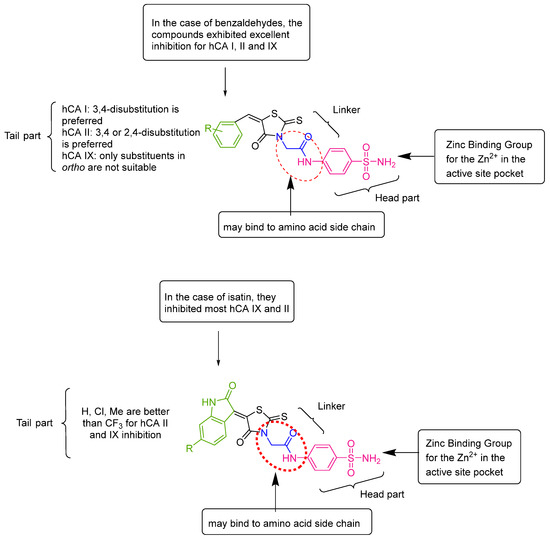
Figure 2.
Structure–activity relationships for the target compounds against carbonic anhydrase isoforms hCA I, II, IX, and XII.
All the molecules tested against the cytosolic isoform hCA I showed good to excellent inhibition in the nanomolar range. All the compounds showed inhibition with KI < 900 nM, except for 7c with KI > 1000 nM. Out of twenty-five molecules, fifteen showed excellent inhibition, with KI inferior to the reference drug AAZ (KI 250 nM). The most active compounds were 7h (KI 22.4 nM), which was 11 times more potent than AAZ, while 7k (78.6 nM), 7n (84.0 nM), 7s (77.9 nM), 7t (77.5 nM), 7u (70.6 nM), 9a (41.6 nM), 9b (92.2 nM), and 9d (35.8 nM) were also more potent compared to AAZ. It was also observed that both electron-withdrawing and electron-donating substituents on the aromatic portion (R) contributed to good inhibition. Isatin-based series was slightly better than aryl-substituted rhodanines towards this isoform.
The other physiologically dominant isoform hCA II, which is also known as the anti-glaucoma drug target, was inhibited by all the tested compounds in a good to excellent nanomolar range (4.3–954.2 nM) comparable to AAZ (12.1 nM). The most active compounds were 9a (4.3 nM, nearly three times better than AAZ), 9b (5.5 nM), 9d (5.2 nM), 7h (7.3 nM), 7k (12.7 nM), 7p (8.0 nM), 7t (9.6 nM), and 7u (8.9 nM). In this case, both the electron-withdrawing and electron-donating substituents on the aromatic ring (R) provided good inhibition. Compound 7c was also the least active within the series.
Excellent inhibitory activity was observed with all the synthesized compounds investigated in the low nanomolar range for the inhibition of the main tumor-associated transmembrane isozyme hCA IX. Four derivatives, namely 7b, 7l, 7m, and 7o, showed high hCA IX inhibitory activity, with KI ranging from 28.2 to 51.5 nM, which was comparable to AAZ, whereas the remaining 21 molecules showed better inhibition (4.2–23.6 nM) than AAZ (25.8 nM). The best hCA IX inhibitors, 7g (4.2 nM) and 9a (4.7 nM), were nearly six times better than the standard AAZ. Collectively, the trend was flat, indicating that these rhodanine-based derivatives represent a suitable template to design potent and selective hCA IX inhibitors.
The other tumor-associated transmembrane isoenzyme hCA XII was also strongly inhibited by all the synthesized compounds, with KI ranging from 9.0 to 258.3 nM compared to AAZ (5.7 nM). The most active compounds were 7b (9.1 nM), 7e (9.6 nM), 7i (9.0 nM), 7o (9.5 nM), 7p (9.8 nM), 7r (9.6 nM), 7s (9.0 nM), and 7u (9.5 nM). Additionally, in this study, we could not register marked variations within the series in terms of inhibitory activity, despite isatin-based compounds seemingly being slightly more active.
The molecules displayed selectivity towards hCA IX and XII compared to hCA I and II. The structure–activity relationships (Figure 2) showed that regardless of whether the molecules bared electron-donating or electron-withdrawing groups, they exhibited good inhibition. However, it was also observed that the molecules with aryl rings (7a–u) or isatins (9a–d) showed good inhibition for specific isoforms.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
The target compounds were synthesized from commercially available reagents without further purification. The solvents were distilled and dried following standard methods as necessary prior to their use. All the air and moisture sensitive reactions were kept under inert conditions using clean and dried glassware and a syringe technique to transfer the solutions. The reactions were monitored via thin layer chromatography (TLC) using Merck silica gel 60F–254 plates. The synthesized molecules were purified by washing them with a mixture of 5–10% ethylacetate in hexane. The melting points were acquired using Stuart digital melting point apparatus (SMP 30) in open capillary tubes, and they were uncorrected. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR and 13C NMR) spectra were recorded using an Avance Bruker 500 MHz and 125 MHz spectrometer in DMSO-d6 as the solvent and tetramethylsilane (TMS) as the internal standard. Chemical shifts were represented as δ values in parts per million (ppm) and coupling constants (J) in Hz. Multiplicities were described as s (singlet), d (doublet), t (triplet), q (quartet), m (multiplet), and dd (doublet of doublets). HRMS were determined using the Agilent QTOF mass spectrometer 6540 series instrument, and they were performed via ESI techniques at 70 eV.
3.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 2-(4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic Acid (3)
Compound 3 was obtained from one-pot, three component condensation reaction, where glycine (2 g, 26.6 mmol) and sodium hydroxide (2.3 g, 58 mmol) were dissolved in 15 mL of ethanol followed by the dropwise addition of carbon disulfide (1.5 mL) with vigorous stirring at room temperature for 6 h. Chloroacetic acid (3 g, 31 mmol) was then added and stirring continued at room temperature for 5 h. The resultant reaction mixture was acidified with dilute HCl until pH 1.0 was achieved and stirring continued for 1 h. The progress of the reaction was checked using TLC. Twenty to thirty mL of water was then added, and the cyclized product was extracted in ethyl acetate, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and evaporated under vacuum. The residue was purified by washing it with a mixture of 5–10% ethylacetate in hexane to obtain compound 3 (4.2 g, 82%).
3.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 2-(4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (5)
1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDCI, 644 mg, 3.35 mmol) and 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBT, 453 mg, 3.35 mmol) were added to a stirring solution of 3 (500 mg, 2.6 mmol) in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), which was followed by the addition of 4-aminobenzenesulfonamide (481 mg, 2.7 mmol), and the mixture was stirred vigorously at room temperature for 8 h. The progress of the reaction was checked using TLC. Forty to fifty mL of water was added to the resultant reaction mixture. The mixture was stirred vigorously to form a brownish solid precipitate, which was filtered off and dried to afford compound 5 (0.8 g, 86%).
3.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Benzylidene/Oxoindolin-Containing Thioxothiazolidin-Linked Benzenesulfonamides (7a–u, 9a–d)
The appropriate benzaldehyde (6)/isatin (8) (0.23 mmol), sodium acetate (37 mg, 0.45 mmol), and glacial acetic acid (0.45 mmol) were added to a stirring solution of compound 5 (80 mg, 0.23 mmol) in ethanol and then refluxed for 4–6 h. The progress of the reaction was checked using TLC, and on completion, the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, followed by the addition of ice-cold water, and the precipitate was filtered off, washed with water, and then dried to afford the target compounds (7a–u/9a–d) in good to excellent yield (NMR data for intermediates and final compounds are reported as Supplementary Materials).
3.5. Characterization Data for New Compounds
2-(4-Oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid (3): light yellow solid, yield: 94%; mp: 264–268 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.22 (s, 1H), 4.94 (s, 2H), 3.57 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.6, 166.9, 164.2, 47.4, 44.2. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C5H5NO3S2 191.98 [M + H]+ found 191.097 [M + H]+.
2-(4-Oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (5): light brown solid, yield: 90%; mp: 294–296 °C; 1 H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.71 (s, 1H), 7.78 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.69 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.26 (s, 2H), 4.75 (s, 2H), 4.43 (s, 2H), 4.94 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 203.6, 174.4, 164.4, 141.7, 139.3, 127.3, 119.2, 47.0, 36.6. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C11H12N3O4S3 345.9990 [M + H]+ found 345.9997 [M + H]+.
(E)-2-(5-Benzylidene-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)-acetamide (7a): yellow solid, yield: 68%; mp: 260–262 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.81 (s, 1H), 7.93 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.73–7.70 (m, 4H), 7.58 (dt, J = 8.3, 6.8 Hz, 3H), 7.29 (s, 2H), 4.94 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 194.1, 167.1, 164.3, 141.7, 139.3, 134.2, 133.3, 131.7, 131.2, 130.1, 127.3, 122.6, 119.3, 47.3. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C18H15N3NaO4S3 456.0122 [M + Na]+ found 456.0144 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(5-(4-Chlorobenzylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7b): yellow solid, yield: 54%; mp: 270–272 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.78 (s, 1H), 7.92 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (t, J = 8.6 Hz, 4H), 7.66 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.26 (s, 2H), 4.94 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.7, 167.0, 164.2, 141.7, 139.4, 136.3, 132.8, 132.2, 130.1, 127.3, 123.3, 119.3, 47.3. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C18H14ClN3O4S3 467.9913 [M + H]+ found 467.1735 [M + H]+.
(E)-2-(4-Oxo-2-thioxo-5-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzylidene)thiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7c): yellow solid, yield: 64%; mp: 296–298 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.80 (s, 1H), 7.96 (s, 1H), 7.85 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.28 (s, 2H), 4.95 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.8, 167.0, 164.2, 150.1, 141.7, 139.4, 133.3, 132.5, 127.3, 123.7, 122.2, 119.3, 47.3. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C19H14F3N3NaO5S3 539.9945 [M + Na]+ found 539.998 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(5-(2-Fluorobenzylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7d): yellow solid, yield: 55%; mp: 230–232 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.83 (s, 1H), 7.87 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 7.66 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.45 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.30 (s, 2H), 4.95 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.5, 166.8, 164.2, 148.9, 141.6, 139.4, 136.3, 134.9, 131.7, 131.6, 127.3, 125.7, 125.5, 119.3, 47.4. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C18H14FN3NaO4S3 474.0028 [M + Na]+ found 474.0048 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(4-Oxo-2-thioxo-5-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)thiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7e): yellow solid, yield: 60%; mp: 291–293 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.82 (s, 1H), 8.01 (s, 1H), 7.93 (q, J = 8.7 Hz, 4H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.29 (s, 2H), 4.95 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.7, 166.9, 164.2, 141.6, 139.4, 137.2, 132.2, 131.6, 130.8, 130.5, 127.3, 126.8, 126.7, 125.6, 125.3, 123.2, 119.3, 47.3. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C19H14F3N3NaO4S3 523.9996 [M + Na]+ found 523.9992 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(5-(4-(Allyloxy)benzylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7f): yellow solid, yield: 58%; mp: 262–264 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.80 (s, 1H), 7.88 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 7.67 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 7.29 (s, 2H), 7.17 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 6.07 (ddt, J = 17.2, 10.5, 5.3 Hz, 1H), 5.46–5.41 (m, 1H), 5.31 (dd, J = 10.5, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 4.93 (s, 2H), 4.71–4.69 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.8, 167.1, 164.3, 161.1, 141.7, 139.3, 134.4, 133.5, 127.3, 126.0, 119.3, 118.5, 116.3, 69.0, 47.2. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C21H19N3NaO5S3 512.0385 [M + Na]+ found 512.0371 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(4-Oxo-2-thioxo-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzylidene)thiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7g): yellow solid, yield: 56%; mp: 290–292 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.81 (s, 1H), 7.87 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 7.29 (s, 2H), 7.02 (s, 2H), 4.95 (s, 2H), 3.88 (s, 6H), 3.77 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.8, 167.0, 164.3, 153.8, 141.7, 140.6, 139.3, 134.6, 128.8, 127.3, 121.4, 119.2, 108.7, 60.7, 56.6, 47.3. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C21H21N3NaO7S3 546.0439 [M + Na]+ found 546.8308 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(5-(3-Ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7h): yellow solid, yield: 52%; mp: 278–280 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.80 (s, 1H), 10.16 (s, 1H), 7.82 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.71 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.29 (s, 2H), 7.24 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (dd, J = 8.4, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.00 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 4.93 (s, 2H), 4.12 (q, J = 6.9 Hz, 2H), 1.39 (t, J = 6.9 Hz, 3H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.8, 167.1, 164.3, 151.2, 147.8, 141.7, 139.3, 135.3, 127.3, 125.9, 124.8, 119.3, 118.0, 117.0, 116.2, 64.4, 47.2, 15.1. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C20H19N3NaO6S3 516.0334 [M + Na]+ found 516.0321 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(5-(4-Cyanobenzylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7i): yellow solid, yield: 56%; mp: 308–310 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.82 (s, 1H), 8.03 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.98 (s, 1H), 7.88 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.30 (s, 2H), 4.95 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 198.3, 171.6, 168.9, 146.4, 144.1, 142.4, 138.4, 136.6, 136.3, 132.1, 130.9, 123.9, 123.5, 117.8, 52.1. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C19H14N4NaO4S3 481.0075 [M + Na]+ found 481.0072 [M + Na]+..
(E)-2-(5-(3-Methoxybenzylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7j): yellow solid, yield: 52%; mp: 258–260 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.80 (s, 1H), 7.90 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 7.51 (t, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (s, 2H), 7.26 (dd, J = 4.3, 2.3 Hz, 2H), 7.14 (dd, J = 8.3, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 4.94 (s, 2H), 3.84 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 194.0, 167.0, 164.2, 160.2, 141.7, 139.3, 134.7, 134.2, 131.2, 127.3, 123.0, 122.9, 119.3, 117.7, 116.4, 55.8, 47.3. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C19H17N3NaO5S3 486.0219 [M + Na]+ found 486.0228 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(5-(4-Methoxybenzylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7k): yellow solid, yield: 55%; mp: 275–277 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.81 (s, 1H), 7.88 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.68 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.29 (s, 2H), 7.16 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 4.94 (s, 2H), 3.87 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.9, 167.2, 164.3, 162.2, 141.7, 139.3, 134.4, 133.6, 127.3, 125.9, 119.3, 119.2, 115.7, 115.0, 56.1, 47.3. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C19H17N3NaO5S3 486.0219 [M + Na]+ found 486.0222 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(5-(4-Isopropylbenzylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7l): yellow solid, yield: 56%; mp: 268–270 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.80 (s, 1H), 7.89 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 7.71 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 7.64 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.48 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.29 (s, 2H), 4.94 (s, 2H), 2.98 (dt, J = 13.7, 6.9 Hz, 1H), 1.24 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 6H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 194.0, 167.1, 164.3, 152.8, 141.7, 139.3, 134.3, 131.5, 131.1, 128.1, 127.3, 121.4, 119.3, 47.2, 33.9, 23.9. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C21H21N3NaO4S3 498.0592 [M + Na]+ found 498.0626 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(4-Oxo-5-(3-phenoxybenzylidene)-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7m): yellow solid, yield: 52%; mp: 287–289 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.79 (s, 1H), 7.91 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.71 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.60 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.46 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H), 7.29 (s, 3H), 7.23 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.12 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 4.93 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.8, 166.9, 164.2, 158.1, 156.2, 141.7, 139.3, 135.2, 133.5, 131.7, 130.7, 127.3, 125.7, 124.7, 123.5, 121.3, 120.2, 119.7, 119.3, 47.3. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C24H19N3NaO5S3 548.0385 [M + Na]+ found 548.0387 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(5-(3,4-Dimethoxybenzylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7n): yellow solid, yield: 63%; mp: 288–290 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.79 (s, 1H), 7.87 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.32 (d, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H), 7.28 (s, 3H), 7.19 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 4.94 (s, 2H), 3.86 (s, 6H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.8, 167.1, 164.3, 152.1, 149.6, 141.7, 139.3, 134.8, 127.3, 126.1, 125.5, 119.4, 119.3, 114.3, 112.8, 56.3, 56.1, 47.3. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C20H19N3NaO6S3 516.0334 [M + Na]+ found 516.0312 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(4-Oxo-2-thioxo-5-(2,4,5-trimethoxybenzylidene)thiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7o): yellow solid, yield: 59%; mp: 288–290 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.79 (s, 1H), 7.97 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.71 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.28 (s, 2H), 6.99 (s, 1H), 6.84 (s, 1H), 4.92 (s, 2H), 3.96 (s, 3H), 3.93 (s, 3H), 3.81 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 194.2, 167.3, 164.4, 155.3, 154.4, 143.7, 141.7, 139.3, 130.2, 127.3, 119.3, 118.5, 113.2, 112.9, 98.1, 56.9, 56.6, 56.5, 47.2. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C21H21N3NaO7S3 546.0439 [M + Na]+ found 546.0451 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(5-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7p): yellow solid, yield: 60%; mp: 275–277 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.78 (s, 1H), 7.96 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.71 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 7.47 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 7.28 (s, 2H), 6.76 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 6.74 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 4.92 (s, 2H), 3.95 (s, 3H), 3.89 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 194.4, 167.3, 164.6, 164.4, 160.6, 141.7, 139.3, 132.7, 129.8, 127.3, 119.3, 118.8, 114.7, 107.7, 99.2, 56.5, 56.3, 47.2. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C20H19N3NaO5S3 500.0385 [M + Na]+ found 500.0369 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(4-Oxo-2-thioxo-5-(2,4,6-trimethoxybenzylidene)thiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7q): orange solid, yield: 56%; mp: 273–275 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.77 (s, 1H), 8.04 (s, 1H), 7.78 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.71 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.28 (s, 2H), 6.37 (s, 2H), 4.90 (s, 2H), 3.93 (s, 6H), 3.90 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 195.7, 167.8, 165.9, 164.5, 160.6, 141.8, 139.3, 128.1, 127.3, 119.5, 119.2, 104.0, 91.7, 56.4, 56.4, 47.2. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C21H21N3NaO7S3 546.0439 [M + Na]+ found 546.0428 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(5-(3,4-Difluorobenzylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7r): yellow solid, yield: 52%; mp: 274–276 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.82 (s, 1H), 7.91 (s, 1H), 7.87–7.82 (m, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.71 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.69–7.64 (m, 1H), 7.57 (s, 1H), 7.30 (s, 2H), 4.94 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 198.4, 171.7, 169.0, 157.0, 156.9, 156.0, 155.9, 155.0, 154.0, 153.9, 146.4, 144.1, 136.7, 135.9, 132.9, 132.9, 132.8, 132.1, 132.0, 128.7, 125.3, 125.2, 124.1, 124.0, 52.1. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C18H13F2N3NaO4S3 491.9934 [M + Na]+ found 491.9921 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(5-(3-Nitrobenzylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7s): orange solid, yield: 55%; mp: 295–297 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.81 (s, 1H), 8.57 (s, 1H), 8.36 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 1H), 8.11 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 2H), 7.88 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 7.28 (s, 2H), 4.96 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.4, 166.8, 164.2, 148.9, 141.6, 139.4, 136.3, 134.9, 131.7, 131.6, 127.3, 125.7, 125.5, 119.3, 47.4. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C18H14N4NaO6S3 500.9973 [M + Na]+ found500.9985 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(5-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7t): orange solid, yield: 59%; mp: 291–293 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.81 (s, 1H), 9.63 (s, 1H), 7.83 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.29 (s, 2H), 6.99 (s, 2H), 4.94 (s, 2H), 3.87 (s, 6H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.7, 167.1, 164.3, 148.9, 141.7, 140.2, 139.3, 135.5, 127.3, 123.7, 119.3, 118.4, 109.3, 56.6, 49.1. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C20H19N3NaO7S3 532.0283 [M + Na]+ found 532.0274 [M + Na]+.
(E)-2-(5-(4-Nitrobenzylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (7u): yellow solid, yield: 57%; mp: 258–260 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.86 (s, 1H), 8.39 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 8.04 (s, 1H), 7.97 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.30 (s, 2H), 4.96 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 193.6, 166.9, 164.2, 148.3, 141.6, 139.4, 139.4, 132.1, 131.3, 127.3, 126.8, 124.9, 119.3, 47.4. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C18H14N4NaO6S3 500.9973 [M + Na]+ found 500.9985 [M + Na]+.
(Z)-2-(4-Oxo-5-(2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (9a): orange solid, yield: 76%; mp: 230–233 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.34 (s, 1H), 10.82 (s, 1H), 8.79 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.74–7.71 (m, 2H), 7.45 (dd, J = 11.1, 4.3 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (s, 2H), 7.10 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 6.99 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 4.99 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 198.2, 168.4, 166.9, 164.3, 145.5, 141.7, 139.4, 134.0, 130.3, 128.4, 127.3, 126.7, 122.8, 120.2, 119.4, 111.4, 47.0. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C19H14N4NaO5S3 497.0024 [M + Na]+ found 497.0019 [M + Na]+.
(Z)-2-(5-(5-Methyl-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (9b): orange solid, yield: 79%; mp: 259–261 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.13 (s, 1H), 10.81 (s, 1H), 8.45 (t, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H), 7.81–7.77 (m, 2H), 7.73–7.70 (m, 2H), 7.28 (s, 2H), 7.07 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.7 Hz, 1H), 6.90 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 4.99 (s, 2H), 3.77 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 198.3, 168.4, 167.0, 164.3, 155.2, 141.6, 139.4, 139.4, 130.5, 127.3, 127.1, 120.8, 120.0, 119.4, 113.7, 111.9, 56.1, 47.0. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C20H16N4NaO5S3 511.0181 [M + Na]+ found 511.0201 [M + Na]+.
(Z)-2-(4-Oxo-5-(2-oxo-5-(trifluoromethyl)indolin-3-ylidene)-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (9c): brown solid, yield: 73%; mp: 246–248 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.53 (s, 1H), 10.82 (s, 1H), 8.78 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.28 (s, 2H), 7.09 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 5.00 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 197.8, 168.4, 167.2, 164.2, 144.4, 141.6, 139.4, 132.7, 127.3, 126.7, 125.4, 121.0, 119.4, 112.4, 47.1. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C20H13F3N4NaO5S3 564.9898 [M + Na]+ found 564.9867 [M + Na]+.
(Z)-2-(5-(5-Chloro-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)acetamide (9d): orange solid, yield: 78%; mp: 251–253 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.49 (s, 1H), 10.84 (s, 1H), 8.81 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.72 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.52 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (s, 2H), 7.02 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 5.00 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 197.8, 168.2, 167.1, 164.2, 144.1, 141.6, 139.4, 133.1, 132.2, 127.5, 127.3, 126.6, 125.4, 121.5, 119.4, 112.8, 47.0. HRMS (ESI-QTOF): m/z calculated for C19H13ClN4NaO5S3 530.9634 [M + Na]+ found 530.9647 [M + Na]+.
3.6. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibition Assay
An SX.18MV-R Applied Photophysics (Oxford, UK) stopped-flow instrument was used to assay the inhibition of various CA isozymes [33]. Phenol Red (at a concentration of 0.2 mM) was used as an indicator, working at an absorbance maximum of 557 nm with 10 mM Hepes (pH 7.4) as a buffer and 10 mM NaClO4 to maintain constant ionic strength (this anion was not inhibitory in the used concentration), following the CA-catalyzed CO2 hydration reaction for a period of 5–10 s. Saturated CO2 solutions in water at 25 °C were used as substrate. Stock solutions of inhibitors were prepared at a concentration of 10 mM (in DMSO-water 1:1, v/v) with dilutions up to 0.01 nM done with the assay buffer mentioned above. At least seven different inhibitor concentrations were used to measure the inhibition constant. Inhibitor and enzyme solutions were preincubated together for 10 min at room temperature prior to assay to allow for the formation of the E-I complex. Triplicate experiments were done for each inhibitor concentration, and the values reported throughout the paper were the means of these results. The inhibition constants were obtained via non-linear, least-squares methods using the Cheng–Prusoff equation, as reported earlier [34], and they represented the means of at least three different determinations. All CA isozymes used in this study were recombinant proteins obtained by our group, as reported earlier, and their concentrations in the assay system were 5–12 nM [35,36,37].
4. Conclusions
The present research work explained the design and synthesis of novel benzenesulfonamide-linked rhodanine derivatives (7a–u, 9a–d) as crucial and selective human carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. All the tested hCA isoforms (I, II, IX, XII) were affected by the newly synthesized molecules in variable degrees of inhibition. All the molecules showed excellent inhibition in the nanomolar range. However, the selectivity was more pronounced towards hCA IX and XII. The most potent and efficient compounds against hCA I were 7h (22.4 nM) and 9d (35.8 nM) compared to standard AAZ (250.0 nM), whereas in the case of hCA II, the isatin derivatives 9a (4.3 nM), 9b (5.5 nM), and 9d (5.2 nM) exhibited excellent potency compared to standard AAZ (12.1 nM). The compounds which showed the best inhibition against isoform hCA IX were 7g (4.2 nM) and 9a (4.7 nM) compared to standard AAZ (25.8 nM). Conversely, for hCA XII, all the compounds exhibited moderate potencies, and the best among them were 7i (9.0 nM) and 7s (9.0 nM) compared to standard AAZ (5.7 nM). It was also noticed that both aryls and isatins with electron-donating and electron-withdrawing groups showed good inhibition potencies. From the results obtained in the present study, it is concluded that these newly synthesized benzenesulfonamide-linked rhodanine derivatives are very interesting lead molecules for the design and synthesis of isoform selective inhibitors of tumor-associated isoforms.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules27228028/s1, Figures S1–S54: 1H and 13C NMR spectra of intermediates and final compounds.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A., V.M.Y. and C.T.S.; methodology, S.C., V.M.Y. and A.A.; synthesis and characterization, B.S., A.K., P.S., V.S.M. and K.K.C.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A., V.M.Y. and A.A.; writing—review and editing, S.C. and C.T.S.; funding acquisition, B.S., A.K., P.S., V.S.M. and K.K.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was partially funded by intramural grants to S.C. (FAR2021).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available within the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors B.S., A.K., P.S., V.S.M., and K.K.C. are thankful to the Department of Pharmaceuticals, the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers, and the Government of India, New Delhi for the award of NIPER fellowship.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds are available from the authors upon request.
References
- Krátký, M.; Štěpánková, Š.; Vorčáková, K.; Vinšová, J. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of novel rhodanine derivatives as potential cholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorg Chem. 2016, 68, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.B.; Kumari, P.; Ravi, V. Scope of Selective Heterocycles from Organic and Pharmaceutical Perspective: Recent Advances in the Biological Importance of Rhodanine Derivatives; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; Chapter 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mermer, A. The Importance of Rhodanine Scaffold in Medicinal Chemistry: A Comprehensive Overview. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 738–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Zarei, M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Babapoor, A.; Amani, A.M. A conceptual review of rhodanine: Current applications of antiviral drugs, anticancer and antimicrobial activities. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 1132–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepański, J.; Tuszewska, H.; Trotsko, N. Anticancer Profile of Rhodanines: Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) and Molecular Targets-A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddila, S.; Gorle, S.; Jonnalagadda, S.B. Drug screening of rhodanine derivatives for antibacterial activity. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayindir, S.; Caglayan, C.; Karaman, M.; Gülcin, İ. The green synthesis and molecular docking of novel N-substituted rhodanines as effective inhibitors for carbonic anhydrase and acetylcholinesterase enzymes. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 90, 103096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminskyy, D.; Kryshchyshyn, A.; Lesyk, R. Recent developments with rhodanine as a scaffold for drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 1233–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermer, A.; Demirbas, N.; Colak, A.; Demir, E.A.; Kulabas, N.; Demirbas, A. One-pot, Four-Component Green Synthesis, Carbonic Anhydrase II Inhibition and Docking Studies of 5-Arylidenerhodanines. Chem. Select. 2018, 3, 12234–12242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.J.; Bin Ahmad Kamar, A.K.D.; Fung, G.T.; Liang, C.T.; Avupati, V.R. Review of anticancer potentials and structure-activity relationships (SAR) of rhodanine derivatives. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, B.; Sahoo, S.K.; Singh, P.; Angeli, A.; Yaddanapudi, V.M.; Supuran, C.T.; Arifuddin, M. Exploration of 2-phenylquinoline-4-carboxamide linked benzene sulfonamide derivatives as isoform selective inhibitors of transmembrane human carbonic anhydrases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 234, 114247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. Anti-infective carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: A patent and literature review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, P.; Vermelho, A.B.; Scozzafava, A.; Parkkila, S.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. Anion inhibition studies of the α-carbonic anhydrase from the protozoan pathogen Trypanosoma cruzi, the causative agent of Chagas disease. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 4472–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Prete, S.; Vullo, D.; Fisher, G.M.; Andrews, K.T.; Poulsen, S.A.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. Discovery of a new family of carbonic anhydrases in the malaria pathogen Plasmodium falciparum--the η-carbonic anhydrases. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 4389–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. The η-class carbonic anhydrases as drug targets for antimalarial agents. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güzel-Akdemir, Ö.; Akdemir, A.; Pan, P.; Vermelho, A.B.; Parkkila, S.; Scozzafava, A.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. A class of sulfonamides with strong inhibitory action against the α-carbonic anhydrase from Trypanosoma cruzi. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 5773–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechederra, R.L.; Waheed, A.; Sly, W.S.; Supuran, C.T.; Minteer, S.D. Effect of sulfonamides as carbonic anhydrase VA and VB inhibitors on mitochondrial metabolic energy conversion. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 1544–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.C.; Chafe, S.C.; Supuran, C.T.; Dedhar, S. Cancer Therapeutic Targeting of Hypoxia Induced Carbonic Anhydrase IX: From Bench to Bedside. Cancers 2022, 14, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, S.; Uysal, T.K.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T.; Ozensoy Guler, O. Is carbonic anhydrase inhibition useful as a complementary therapy of Covid-19 infection? J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, M.; McKenna, R. Update on carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: A patent review (2008–2011). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2012, 22, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touisni, N.; Maresca, A.; McDonald, P.C.; Lou, Y.; Scozzafava, A.; Dedhar, S.; Winum, J.Y.; Supuran, C.T. Glycosyl coumarin carbonic anhydrase IX and XII inhibitors strongly attenuate the growth of primary breast tumors. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 8271–8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Carta, F. Antiobesity carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: A literature and patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabrizi, F.; Mincione, F.; Somma, T.; Scozzafava, G.; Galassi, F.; Masini, E.; Impagnatiello, F.; Supuran, C.T. A new approach to antiglaucoma drugs: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors with or without NO donating moieties. Mechanism of action and preliminary pharmacology. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appetecchia, F.; Consalvi, S.; Berrino, E.; Gallorini, M.; Granese, A.; Campestre, C.; Carradori, S.; Biava, M.; Poce, G. A Novel Class of Dual-Acting DCH-CORMs Counteracts Oxidative Stress-Induced Inflammation in Human Primary Tenocytes. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Purnachander Yadav, P.; Swain, B.; Thacker, P.S.; Angeli, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Arifuddin, M. Discovery of a novel series of indolylchalcone-benzenesulfonamide hybrids acting as selective carbonic anhydrase II inhibitors. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 108, 104647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Sridhar Goud, N.; Swain, B.; Kumar Sahoo, S.; Choli, A.; Angeli, A.; Singh Kushwah, B.; Madhavi Yaddanapudi, V.; Supuran, C.T.; Arifuddin, M. Synthesis of a new series of quinoline/pyridine indole-3-sulfonamide hybrids as selective carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 70, 128809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkamhawy, A.; Woo, J.; Nada, H.; Angeli, A.; Bedair, T.M.; Supuran, C.T.; Lee, K. Identification of Novel and Potent Indole-Based Benzenesulfonamides as Selective Human Carbonic Anhydrase II Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, In Vitro, and In Silico Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Choli, A.; Swain, B.; Angeli, A.; Sahoo, S.K.; Yaddanapudi, V.M.; Supuran, C.T.; Arifuddin, M. Design and development of novel series of indole-3-sulfonamide ureido derivatives as selective carbonic anhydrase II inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. 2022, 355, e2100333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir-Yazıcı, K.; Bua, S.; Akgüneş, N.M.; Akdemir, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Güzel-Akdemir, Ö. Indole-Based Hydrazones Containing A Sulfonamide Moiety as Selective Inhibitors of Tumor-Associated Human Carbonic Anhydrase Isoforms IX and XII. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żeslawska, E.; Nitek, W.; Tejchman, W. The Synthesis and Crystal Structures of the Homologues of Epalrestat. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2015, 45, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negah, S.; Mehdi, K.; Mohsen, A.; Amirhossein, S.; Hamid, N.; Alireza, M.; Saeed, E.; Ebrahim, S.M.; Alireza, F.; Abbas, S. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 5-benzylidenerhodanine-3-acetic acid derivatives as AChE and 15-LOX inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 389–395. [Google Scholar]
- Bourahla, K.; Guihéneuf, S.; Limanton, E.; Paquin, L.; Le Guével, R.; Charlier, T.; Rahmouni, M.; Durieu, E.; Lozach, O.; Carreaux, F.; et al. Design and Microwave Synthesis of New (5Z) 5-Arylidene-2-thioxo-1,3-thiazolinidin-4-one and (5Z) 2-Amino-5-arylidene-1,3-thiazol-4(5H)-one as New Inhibitors of Protein Kinase DYRK1A. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifah, R.G. The carbon dioxide hydration activity of carbonic anhydrase. I. Stop-flow kinetic studies on the native human isoenzymes B and C. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 2561–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, F.; Carradori, S.; Ronca, R.; Rezzola, S.; Filiberti, S.; Carta, F.; Turati, M.; Supuran, C.T. Benzenesulfonamides with different rigidity-conferring linkers as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: An insight into the antiproliferative effect on glioblastoma, pancreatic, and breast cancer cells. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2022, 37, 1857–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güzel-Akdemir, Ö.; Demir-Yazıcı, K.; Vullo, D.; Supuran, C.T.; Akdemir, A. New Pyridinium Salt Derivatives of 2-(Hydrazinocarbonyl)-3-phenyl-1H-indole-5-sulfonamide as Selective Inhibitors of Tumour-Related Human Carbonic Anhydrase Isoforms IX and XII. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 2637–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T.; Clare, B.W. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors—Part 57: Quantum chemical QSAR of a group of 1,3,4-thiadiazole- and 1,3,4-thiadiazoline disulfonamides with carbonic anhydrase inhibitory properties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 34, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, F.; Supuran, C.T.; Scozzafava, A. Sulfonamides and their isosters as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 1149–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).