Does the Metabolome of Wild-like Dendrobium officinale of Different Origins Have Regional Differences?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Habitat Survey
2.2. Data Evaluation
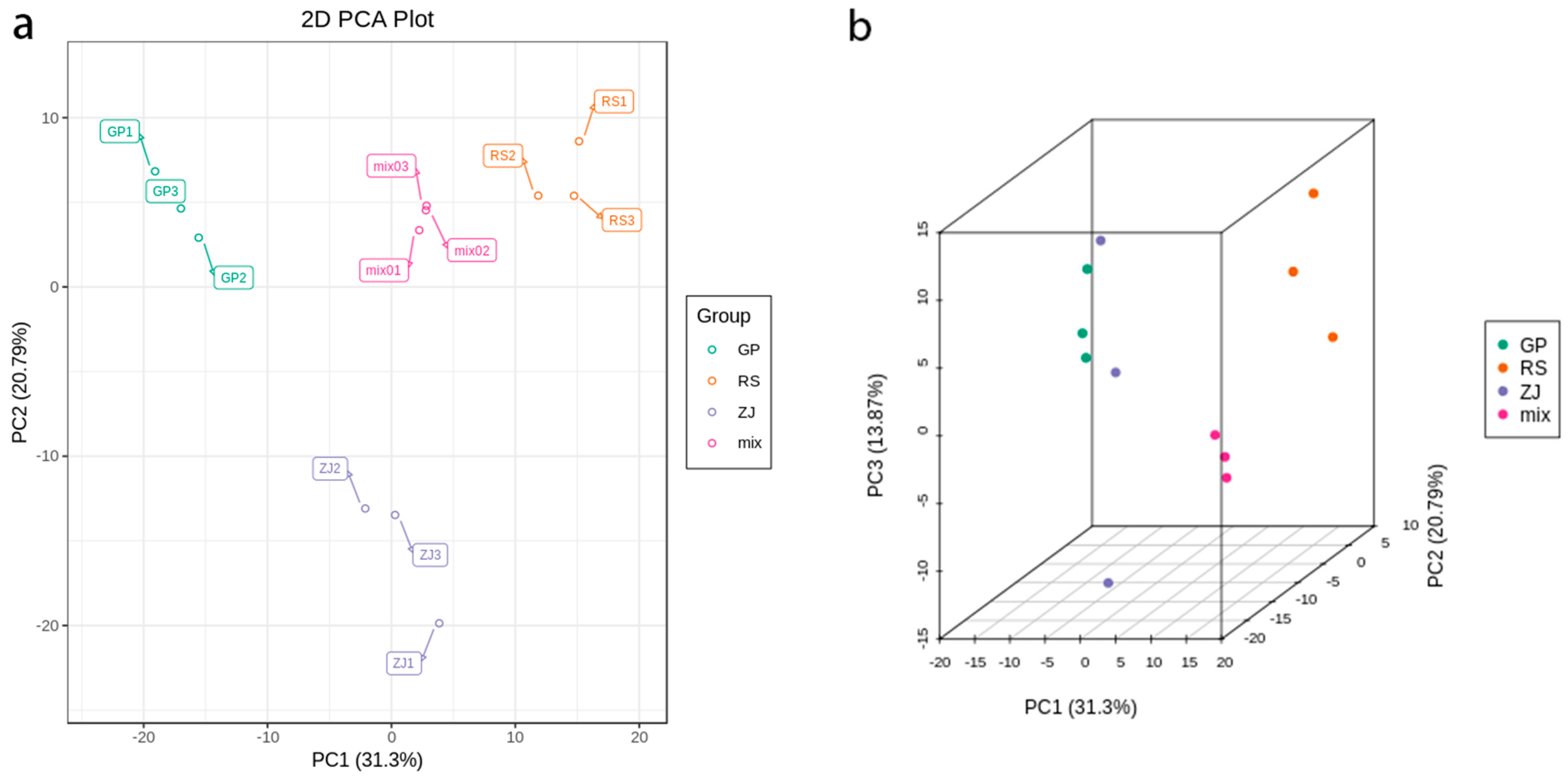
2.3. Principal Component Analysis
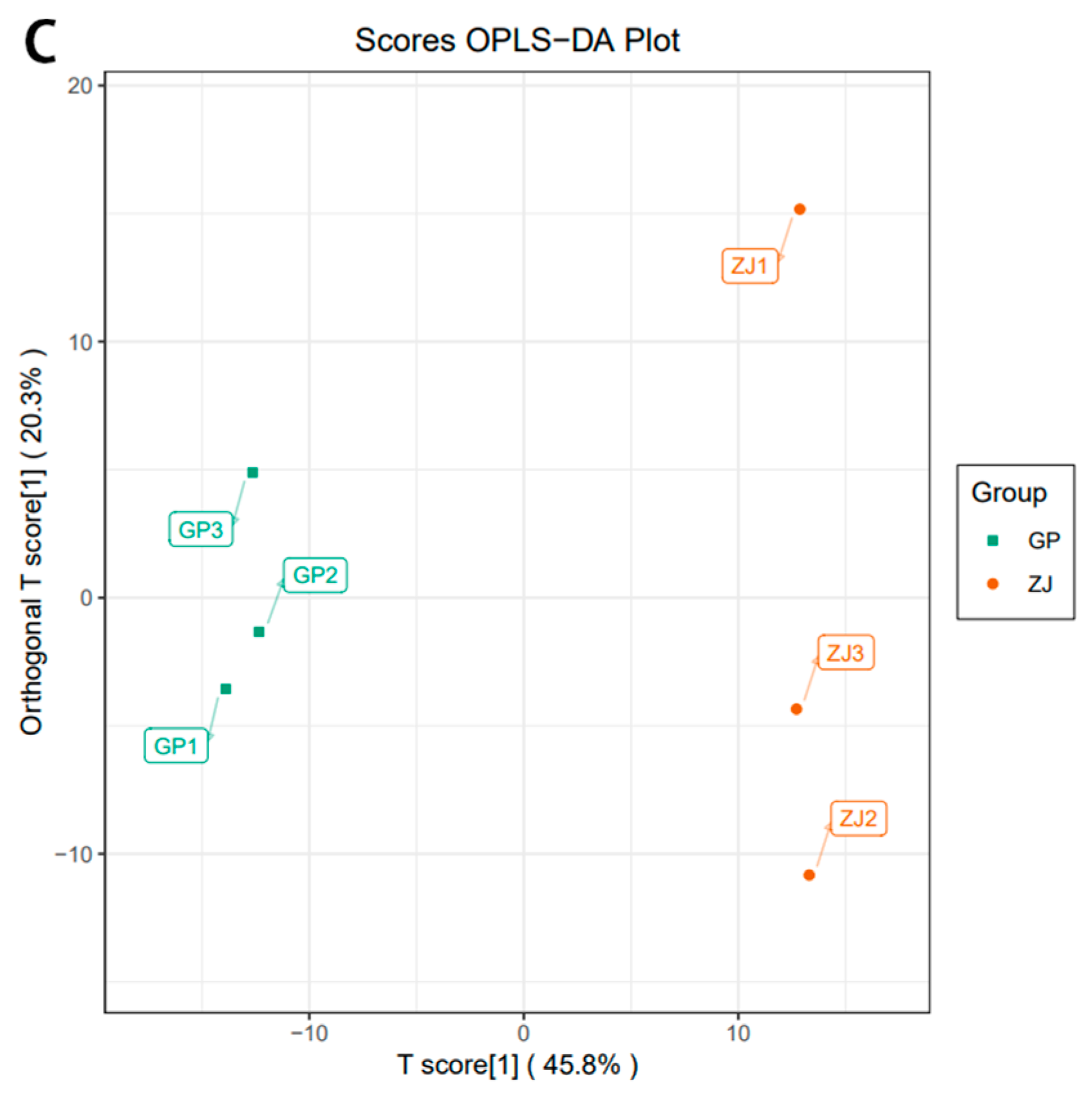
2.4. Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis
2.5. Widely Targeted Metabolomics Profiling
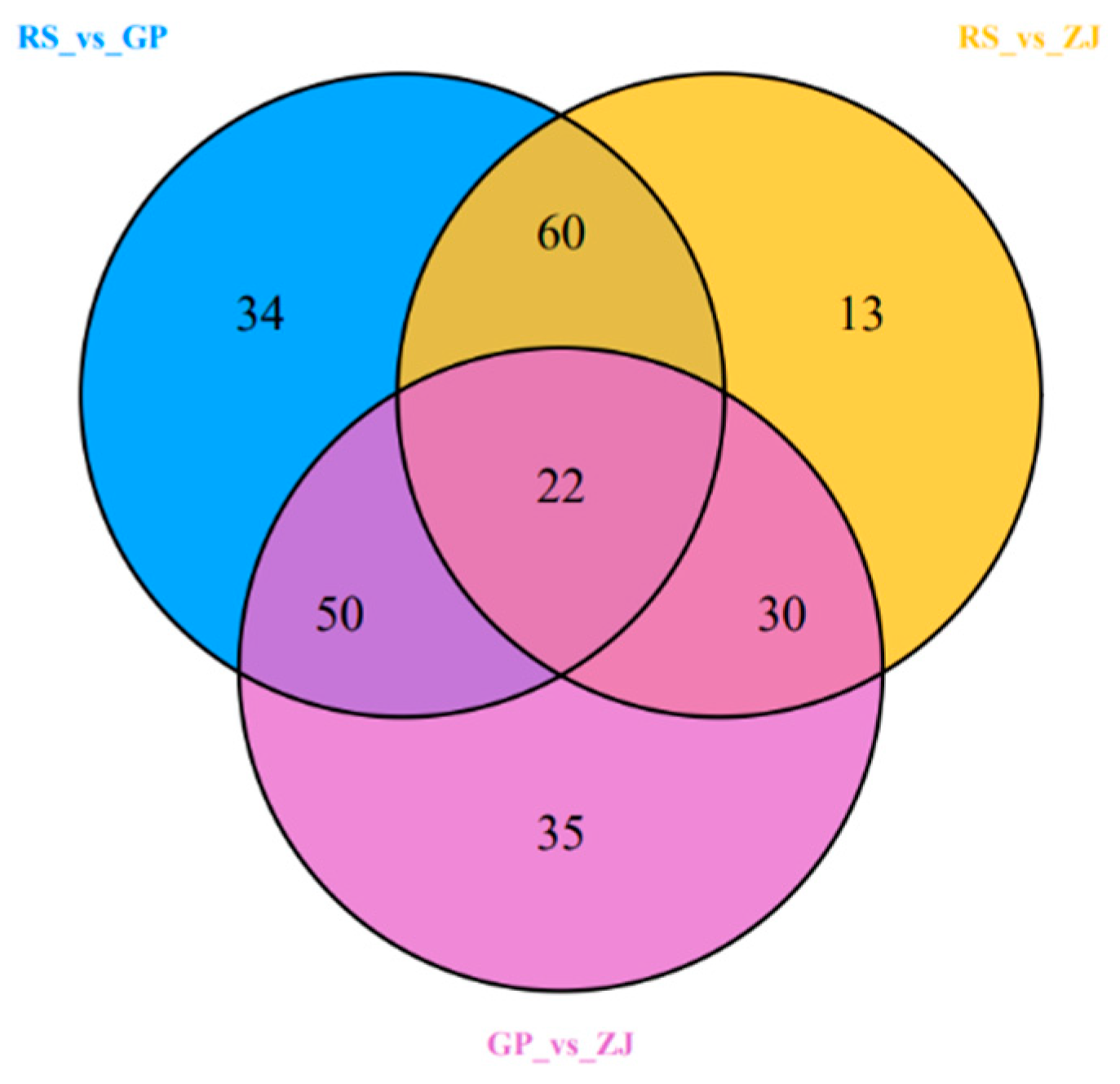
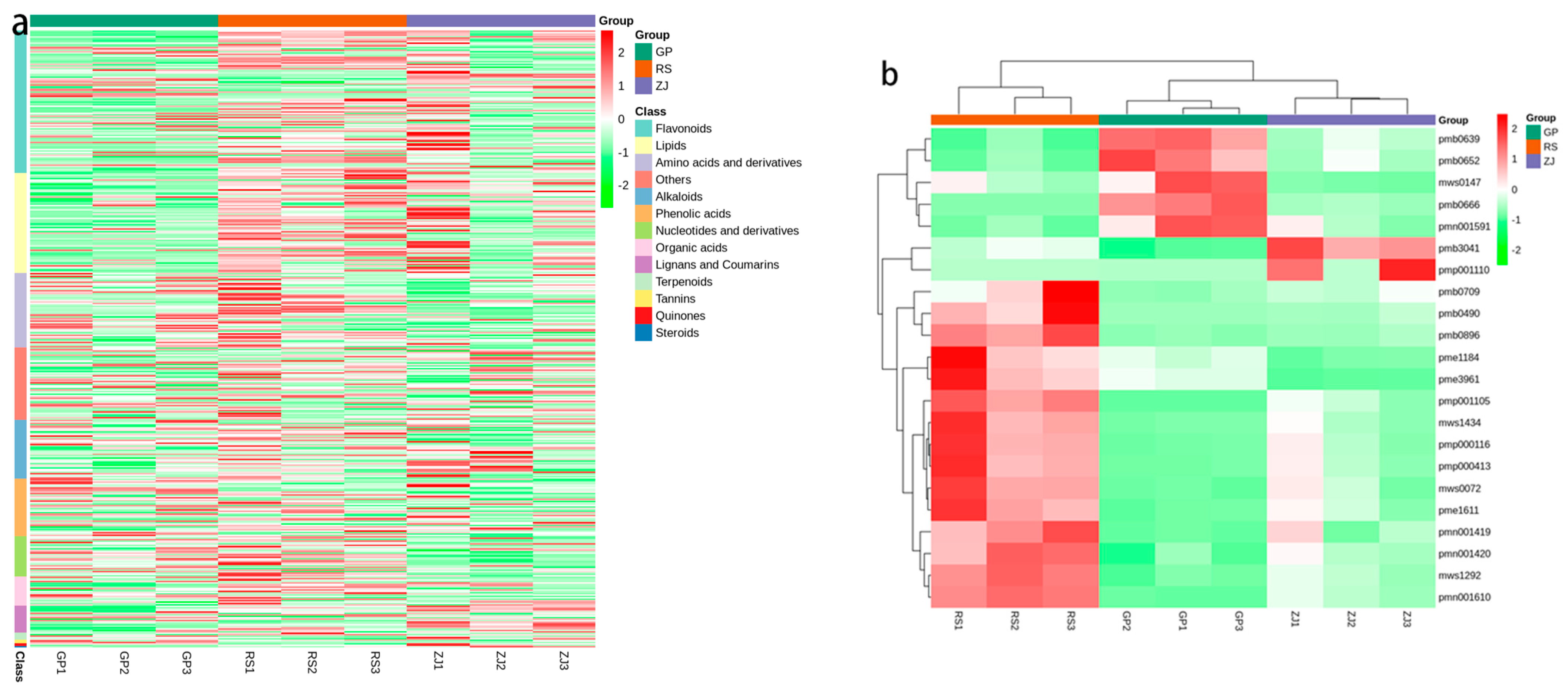
2.6. Identification of Differential Metabolites
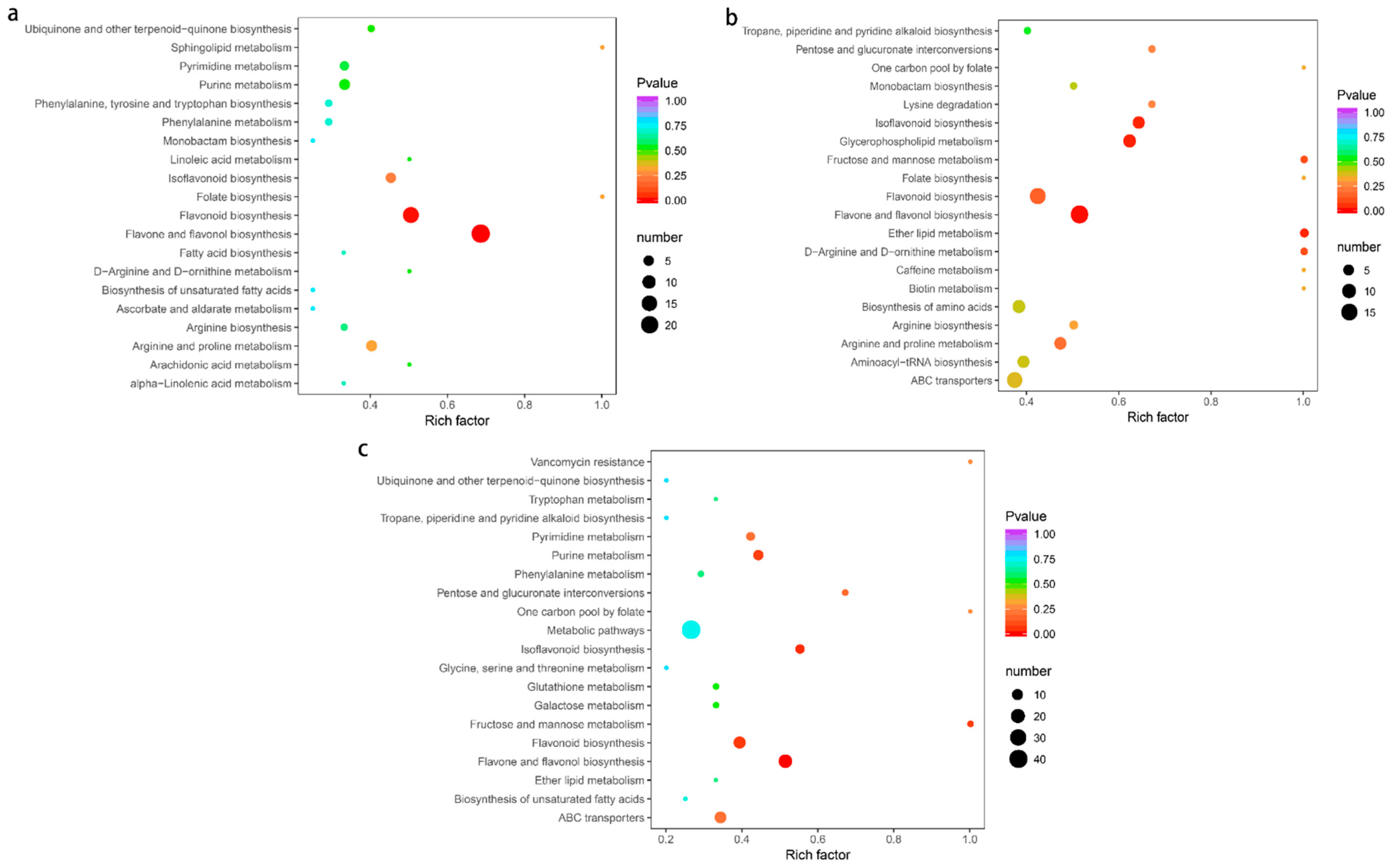
2.7. Pathway Enrichment Analysis of Differential Metabolites
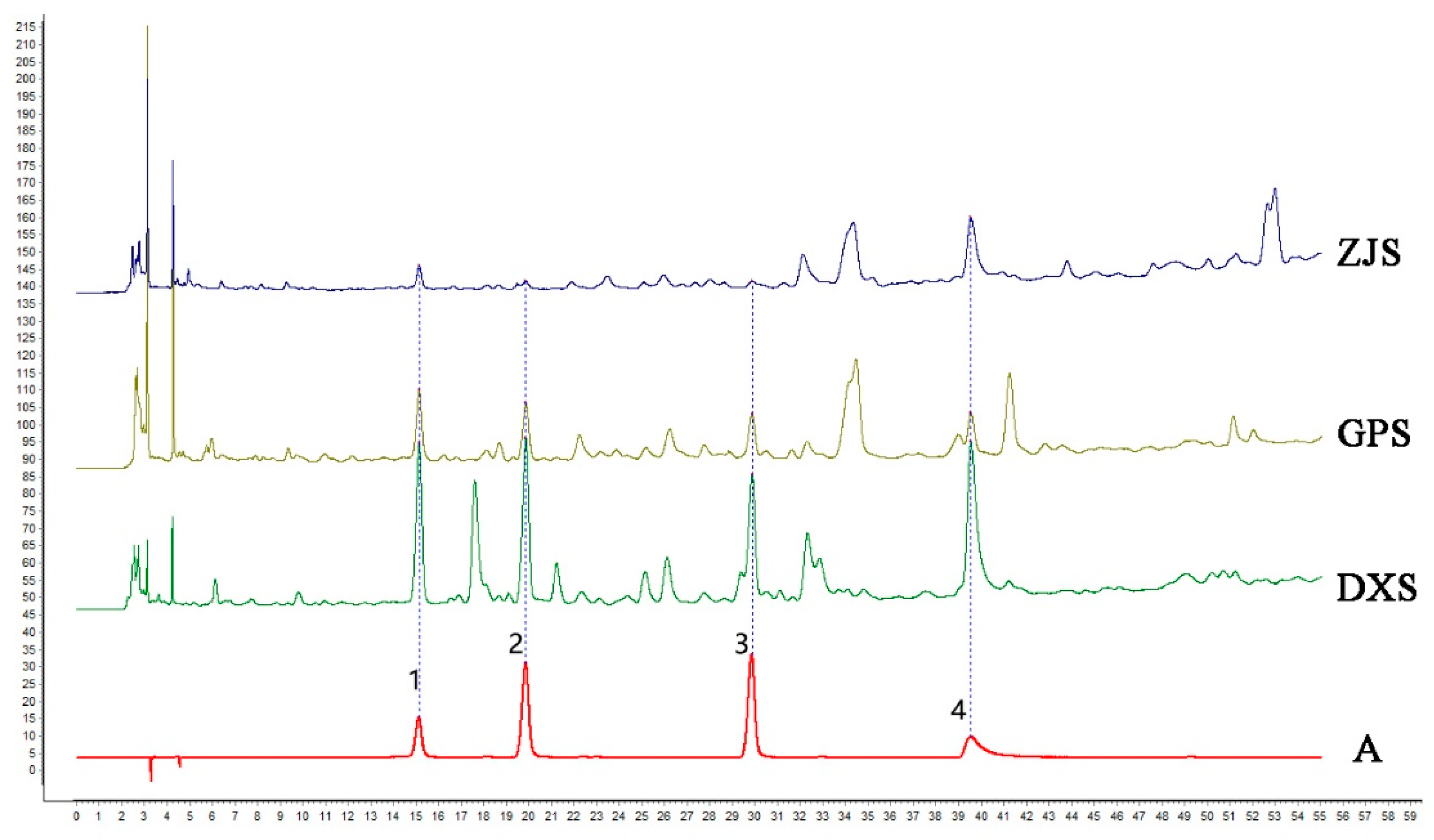
2.8. Quantitative and Qualitative HPLC Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Sample Preparation and Extraction
4.3. UPLC-ESI-MS/MS
4.4. ESI-Q TRAP-MS/MS Analysis
4.5. Metabolic Profiling of D. officinale Stems
4.6. Data Analysis
4.7. HPLC Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis Conditions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teixeira, D.S.J.; Ng, T.B. The medicinal and pharmaceutical importance of Dendrobium species. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 2227–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Zhao, T.; Sheng, Y.; Zheng, T.; Fu, L.; Zhang, Y. Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo:A Review on Its Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Industrialization. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 7436259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, T.B.; Liu, J.; Wong, J.H.; Ye, X.; Wing, S.S.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, K.Y. Review of research on Dendrobium, a prized folk medicine. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.G.; Schuiteman, A.; Li, D.Z.; Huang, W.C.; Chung, S.W.; Li, J.W.; Zhou, H.L.; Jin, W.T.; Lai, Y.J.; Li, Z.Y.; et al. Molecular systematics of Dendrobium (Orchidaceae, Dendrobieae) from mainland Asia based on plastid and nuclear sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Dang, P.P.; Zhao, Z.; Yuan, L.C.; Zhou, Z.H.; Wolf, D.; Luo, Y.B. An assessment of the Chinese medicinal Dendrobium industry: Supply, demand and sustainability. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 229, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, J.; Yu, Q.; Song, X.S.; Shao, W. Artificial cultivation modes for Dendrobium officinale. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013, 38, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Luo, Y. Breakthrough in key science and technologies in Dendrobium catenatum industry. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2017, 42, 2223–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroslakova, I.; Pedrussio, S.; Wolfram, E. Direct Coupling of HPTLC with MALDI-TOF MS for Qualitative Detection of Flavonoids on Phytochemical Fingerprints. Phytochem. Anal. 2016, 27, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujak, R.; Struck-Lewicka, W.; Markuszewski, M.J.; Kaliszan, R. Metabolomics for laboratory diagnostics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 113, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lains, I.; Gantner, M.; Murinello, S.; Lasky-Su, J.A.; Miller, J.W.; Friedlander, M.; Husain, D. Metabolomics in the study of retinal health and disease. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2019, 69, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angamuthu, S.; Ramaswamy, C.R.; Thangaswamy, S.; Sadhasivam, D.R.; Nallaswamy, V.D.; Subramanian, R.; Ganesan, R.; Raju, A. Metabolic Annotation, Interactions and Characterization of Natural Products of Mango (Mangifera indica L.): 1h Nmr Based Chemical Metabolomics Profiling. Process Biochem. 2021, 2018, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, C.; Qi, Y.; Song, F.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S. Fingerprint analysis of Radix Aconiti using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization/ tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-ESI/MS) combined with stoichiometry. Talanta 2013, 103, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, J.; Simirgiotis, M.J.; Lima, B.; Paredes, J.D.; Villegas, G.C.; Gamarra-Luques, C.; Borquez, J.; Luna, L.; Wendel, G.H.; Maria, A.O.; et al. Antioxidant, Gastroprotective, Cytotoxic Activities and UHPLC PDA-Q Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry Identification of Metabolites in Baccharis grisebachii Decoction. Molecules 2019, 24, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zhang, W.; Li, H. Application of metabolomics for unveiling the therapeutic role of traditional Chinese medicine in metabolic diseases. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 242, 112057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yan, H.; Chen, J.; Xie, H.; Peng, L.; Xie, T.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Shan, J. Application of metabolomics in viral pneumonia treatment with traditional Chinese medicine. Chin. Med. 2019, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, J.; Ghebrezadik, H.; Hylands, P.J. Metabolomic quality control of commercial Asian ginseng, and cultivated and wild American ginseng using (1)H NMR and multi-step PCA. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 114, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.S.; Liu, Y.R.; Lv, Y.; Duan, J.A.; Chen, S.Z.; Sun, J.; Song, Z.X.; Wu, X.M.; Liu, L. Quality markers of animal medicinal materials: Correlative analysis of musk reveals distinct metabolic changes induced by multiple factors. Phytomedicine 2018, 44, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomase, V.; Changbhale, S.; Patil, S.; Kale, K. Metabolomics. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, W.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, B.; Seo, J.H.; Seo, Y.H.; Lee, S.; Jeong, C.H.; Lee, S. Hair Metabolomics in Animal Studies and Clinical Settings. Molecules 2019, 24, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, H.; Yang, J.; Song, G.; Wen, D.; Liu, W.; Jin, M.; Wang, Q.; Du, Y.; Sun, Q.; et al. A high-throughput metabolomics approach for the comprehensive differentiation of four Pulsatilla Adans herbs combined with a nontargeted bidirectional screen for rapid identification of triterpenoid saponins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 2071–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Liao, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; An, R.; Zeng, Q.; Li, X. A Widely Metabolomic Analysis Revealed Metabolic Alterations of Epimedium Pubescens Leaves at Different Growth Stages. Molecules 2019, 25, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Zuo, J.; Zhang, H.; Zu, M.; Yu, M.; Liu, S. Transcriptome and metabolome profiling unveil the accumulation of flavonoids in Dendrobium officinale. Genomics 2022, 114, 110324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Ji, Y.; Li, S.; Lu, L.; Tian, M.; Yang, W.; Li, H. Extensive Metabolic Profiles of Leaves and Stems from the Medicinal Plant Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo. Metabolites 2019, 9, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, S.; Yu, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, W.; Chen, W.; Yun, Y.; Chen, H. Comparative Metabolomic Analysis of Dendrobium officinale under Different Cultivation Substrates. Metabolites 2020, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tu, H.; Wan, J.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Luo, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H. Spatio-temporal distribution and natural variation of metabolites in citrus fruits. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slamova, K.; Kapesova, J.; Valentova, K. “Sweet Flavonoids”: Glycosidase-Catalyzed Modifications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostetler, G.L.; Ralston, R.A.; Schwartz, S.J. Flavones: Food Sources, Bioavailability, Metabolism, and Bioactivity. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, M.; Yang, B. Structure, bioactivity, and synthesis of methylated flavonoids. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1398, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, Y.; Souza, M.; Souza, M. Sulphated Flavonoids: Biosynthesis, Structures, and Biological Activities. Molecules 2018, 23, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Alseekh, S.; Fernie, A.R.; Luo, J. The Structure and Function of Major Plant Metabolite Modifications. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 899–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Luo, Y.; Lei, Z.; Wei, G. UHPLC-ESI-MS analysis of purified flavonoids fraction from stem of Dendrobium denneaum Paxt. and its preliminary study in Inducing apoptosis of HepG2 cells. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 8936307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Liang, J.; Si, J.; Wu, S. Dendrobium officinale leaves as a new antioxidant source. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 37, 400–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.M.; Wu, L.S.; Si, J.P.; Liu, J.J.; Yu, Z.X.; Wang, H.C.; Zhang, M.; Rong, S. Screening of meaningful endophytic fungi in Dendrobium officinale based on polysaccharides and flavonoids. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2016, 41, 2208–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Y.; Yang, Z.; Ji, X.; An, W.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S.; He, L.; Lai, X.; Huang, S.; Zheng, X. Comparative analysis of transcriptome and metabolome uncovers the metabolic differences between Dendrobium officinale protocorms and mature stems. All Life 2020, 13, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Fan, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Effect of drying methods on physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of Dendrobium officinale. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Han, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Kuang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Yang, Y.; Pang, K.; Yang, S.; Qin, J.; et al. Comparison of metabolomics of Dendrobium officinale in different habitats by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2020, 89, 10400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Kuo, H.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Tsai, M.Y. Current Advances in the Biological Activity of Polysaccharides in Dendrobium with Intriguing Therapeutic Potential. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 1663–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Qi, J.; Du, D.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, X. Current advances of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides in dermatology: A literature review. Pharm. Biol. 2020, 58, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Ko, C.H.; Siu, W.S.; Li, L.F.; Han, X.Q.; Yang, L.; Bik-San, L.C.; Hu, J.M.; Leung, P.C. Polysaccharides of Dendrobium officinale Kimura & Migo protect gastric mucosal cell against oxidative damage-induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 208, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xing, S.; Tao, S.; Liu, C.; Wei, G.; Yuan, Y.; Lei, Z. Structural characterization of polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale and their effects on apoptosis of HeLa cell line. Molecules 2018, 23, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Gui, S.; Huang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Shun, Q.; Huang, K.; Tao, S.; Wei, G. Characteristic Fingerprint Analysis of Dendrobium Huoshanense by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2016, 18, 3802-08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.Y.; Ma, J.; Kong, X.X.; Wang, X.F.; Li, S.S.; Qi, X.L.; Yan, Y.H.; Cheng, J.; Liu, Q.; Jin, W.; et al. Sodium rutin ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology by enhancing microglial amyloid-beta clearance. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Ren, Z.; Du, B.; Xing, S.; Huang, S.; Li, Y.; Lei, Z.; Li, D.; Chen, H.; Huang, Y.; et al. Structure Identification of ViceninII Extracted from Dendrobium officinale and the Reversal of TGF-beta1-Induced Epithelial (-) Mesenchymal Transition in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells through TGF-beta/Smad and PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2019, 24, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Liu, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Ren, F. Partial characterization and immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharides from the stem of Dendrobium officinale (Tiepishihu) in vitro. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Liao, X.; Zhou, C.J.; Hu, L.; Wei, G.; Huang, Y.C.; Lei, Z.X.; Ren, Z.R.; Liu, Z.X.; Liu, Z.H. Identification of C-glycosyl flavones and quality assessment in Dendrobium nobile. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 35, e9012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.Y.; Xie, Z.S.; Huang, Y.C.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, C.J.; Wang, Y.W.; Wei, G. HPLC Characteristic Spectrum Optimization of Flavonoid Glycosides on Dendrobium officinale and Characteristics Analysis of Different Provenances. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2019, 25, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Li, R.; Ren, L.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Ma, D.; Luo, Y. A comparative metabolomics study of flavonoids in sweet potato with different flesh colors (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam). Food Chem. 2018, 260, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gong, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, S.; Xiong, L.; Luo, J. A novel integrated method for large-scale detection, identification, and quantification of widely targeted metabolites: Application in the study of rice metabolomics. Mol. Plant. 2013, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Group | Average Pearson’s Correlation Coefficients * |
|---|---|
| GP vs. GP | 0.94421 |
| RS vs. RS | 0.97132 |
| ZJ vs. ZJ | 0.95574 |
| GP vs. RS | 0.83320 |
| RS vs. ZJ | 0.92307 |
| ZJ vs. GP | 0.82796 |
| Class | Number of Compounds | Class | Number of Compounds |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids | 102 | Others | 20 |
| Lipids | 72 | Lignans and Coumarins | 19 |
| Amino acids and their derivatives | 53 | Vitamins | 7 |
| Alkaloids | 42 | Terpenoids | 5 |
| Phenolic acids | 41 | Proanthocyanidins | 2 |
| Nucleotides and derivatives | 29 | Quinones | 2 |
| Carbohydrates and Alcohols | 25 | Tannins | 1 |
| Organic acid | 21 | Steroids | 1 |
| Compounds | Class |
|---|---|
| Kaempferol-3-neohesperidoside-7-glucoside | Flavonoids |
| Apigenin-6-C-β-D-xyloside-8-C-β-Darabinoside | Flavonoids |
| Apigenin 5-O-glucoside | Flavonoids |
| Isoschaftoside | Flavonoids |
| Isovitexin | Flavonoids |
| 8-C-Hexosyl-apigenin O-hexosyl-O-hexoside | Flavonoids |
| C-Hexosyl-apigenin O-pentoside | Flavonoids |
| 6-C-Hexosyl-apigenin O-sinapoylhexoside | Flavonoids |
| Quercetin 7-O-malonylhexosyl-hexoside | Flavonoids |
| Tricin O-saccharic acid | Flavonoids |
| Isohemiphloin | Flavonoids |
| Apigenin-8-C-glucoside | Flavonoids |
| Genistein 8-C-glucoside | Flavonoids |
| 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid | Organic acids |
| 3-Hydroxy-3-methyl butyric acid | Organic acids |
| N’-Feruloyl putrescine | Alkaloids |
| N-p-Coumaroyl putrescine | Alkaloids |
| Deoxyguanosine | Nucleotides and derivatives |
| Deoxyadenosine | Nucleotides and derivatives |
| 1-O-[(E)-p-Cumaroyl]-β-D-glucopyranose | Phenolic acids |
| 1-O-[(E)-Caffeoyl]-β-D-glucopyranose | Phenolic acids |
| Rutundic acid | Terpenoids |
| Components | Linear Equations | R2 | Repeatability RSD (%) | Precision RSD (%) | Stability RSD (%) (n = 7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rutin | 0.9997 | 2.46 | 2.69 | 2.41 | |
| Vicenin I | 0.9999 | 2.01 | 2.94 | 2.71 | |
| Vicenin II | 0.9998 | 2.04 | 0.97 | 1.32 | |
| Vicenin III | 0.9999 | 2.45 | 2.03 | 2.52 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, Q.; Liu, C.; Wu, Z.; Ni, C.; Li, J.; Huang, C.; Wang, H.; Wei, G. Does the Metabolome of Wild-like Dendrobium officinale of Different Origins Have Regional Differences? Molecules 2022, 27, 7024. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27207024
Lan Q, Liu C, Wu Z, Ni C, Li J, Huang C, Wang H, Wei G. Does the Metabolome of Wild-like Dendrobium officinale of Different Origins Have Regional Differences? Molecules. 2022; 27(20):7024. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27207024
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Qiqian, Chenxing Liu, Zhanghua Wu, Chen Ni, Jinyan Li, Chunlei Huang, Huan Wang, and Gang Wei. 2022. "Does the Metabolome of Wild-like Dendrobium officinale of Different Origins Have Regional Differences?" Molecules 27, no. 20: 7024. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27207024
APA StyleLan, Q., Liu, C., Wu, Z., Ni, C., Li, J., Huang, C., Wang, H., & Wei, G. (2022). Does the Metabolome of Wild-like Dendrobium officinale of Different Origins Have Regional Differences? Molecules, 27(20), 7024. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27207024







