Synthesis of N-Substituted Iminosugar C-Glycosides and Evaluation as Promising α-Glucosidase Inhibitors
Abstract
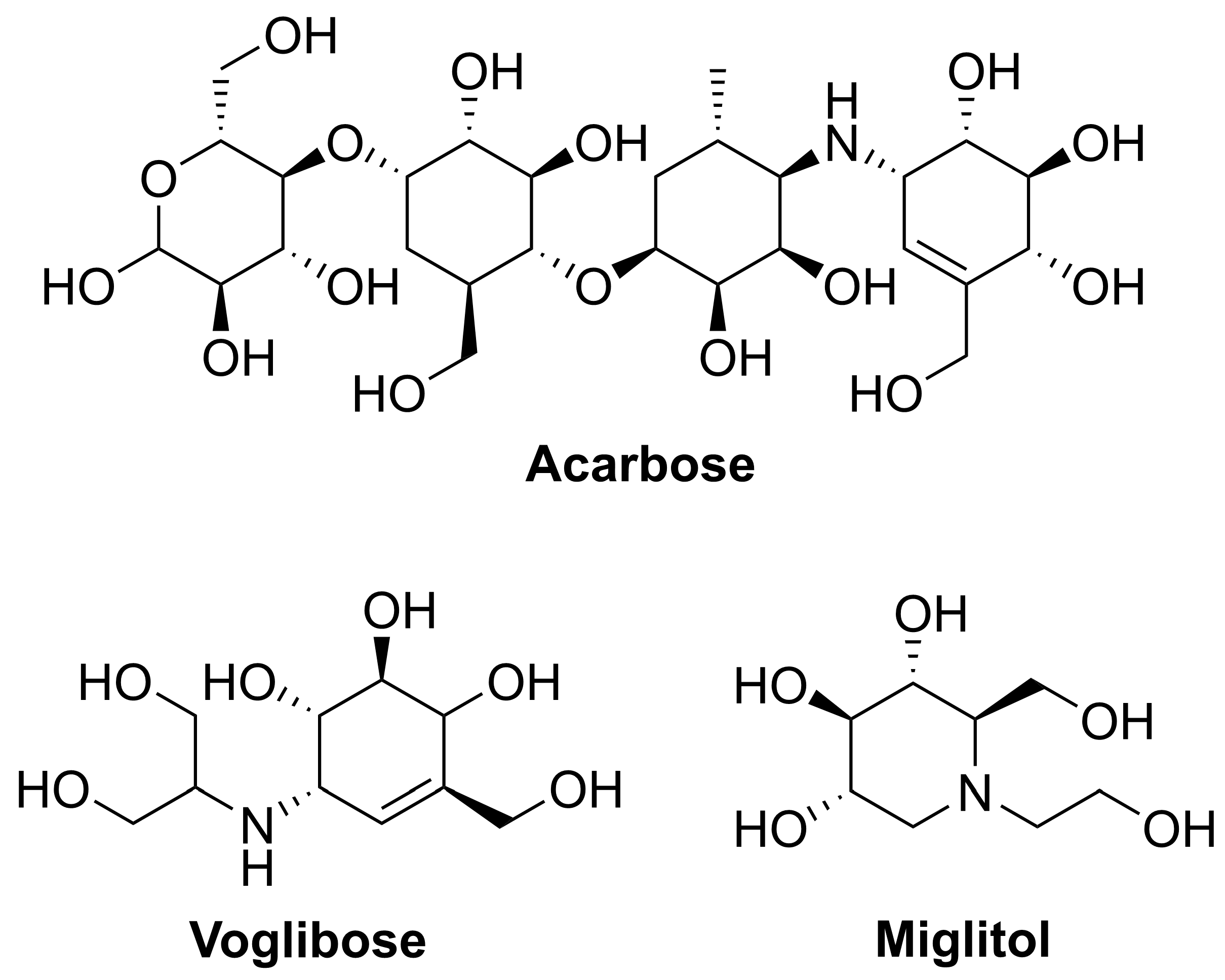
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
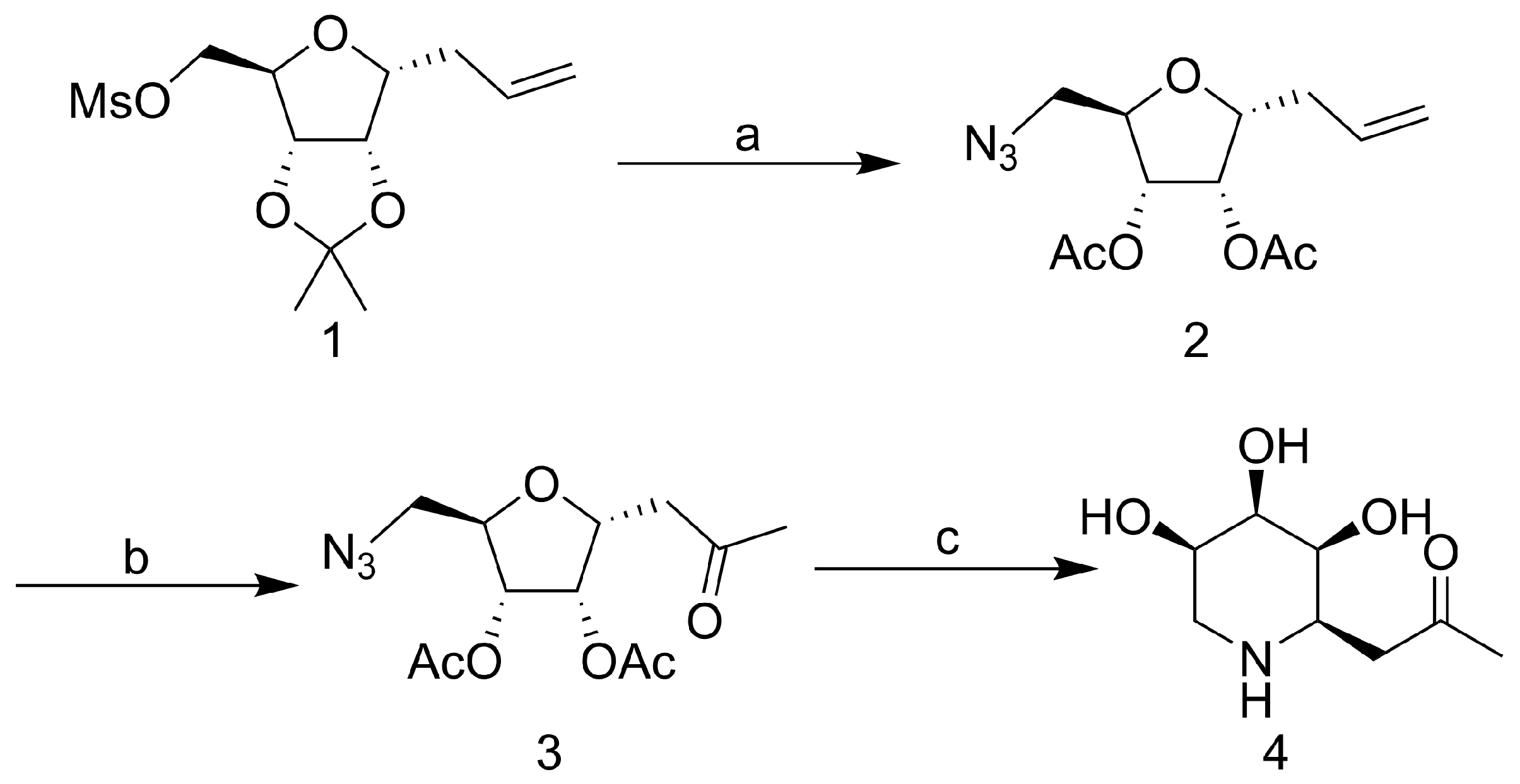
2.1. Synthesis of Iminosugar C-Glycosides
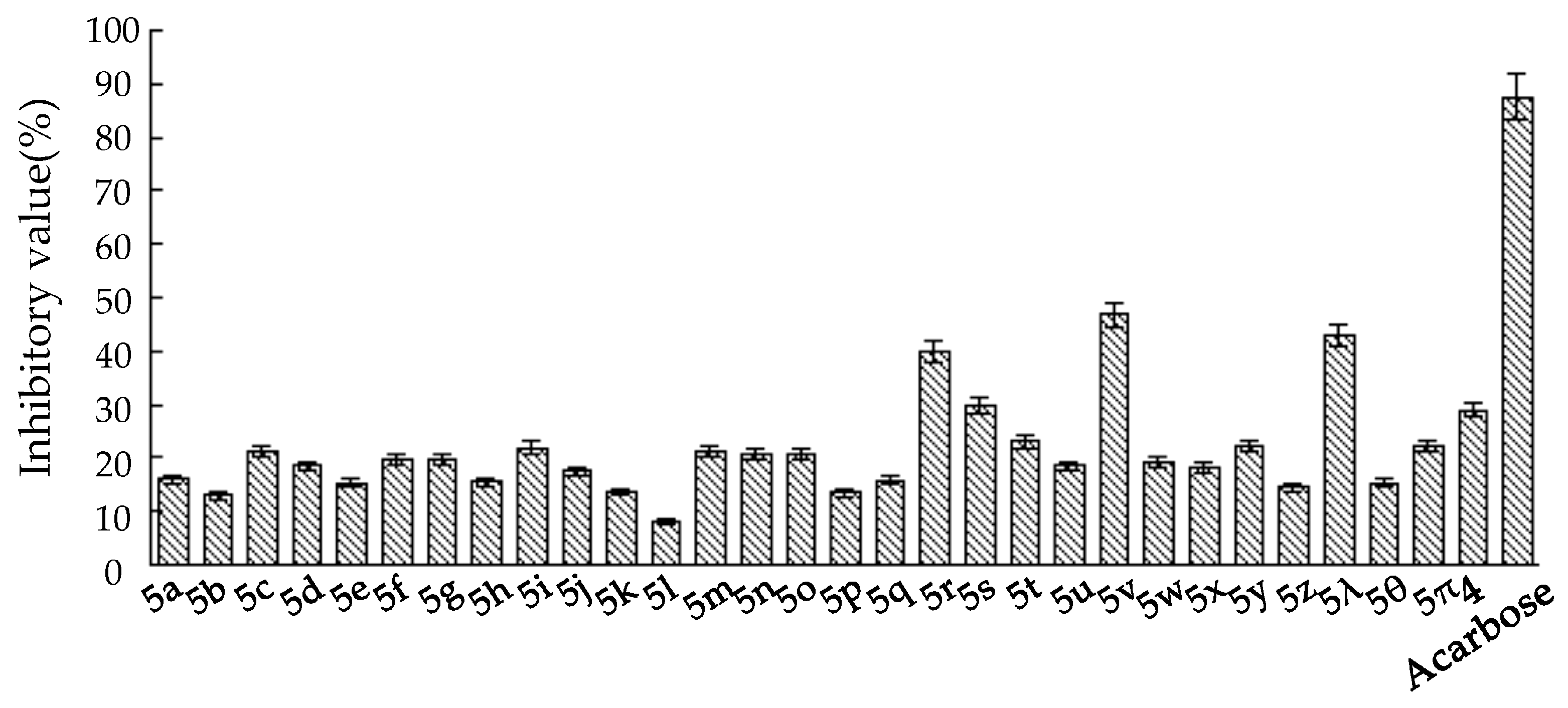
2.2. α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Assays
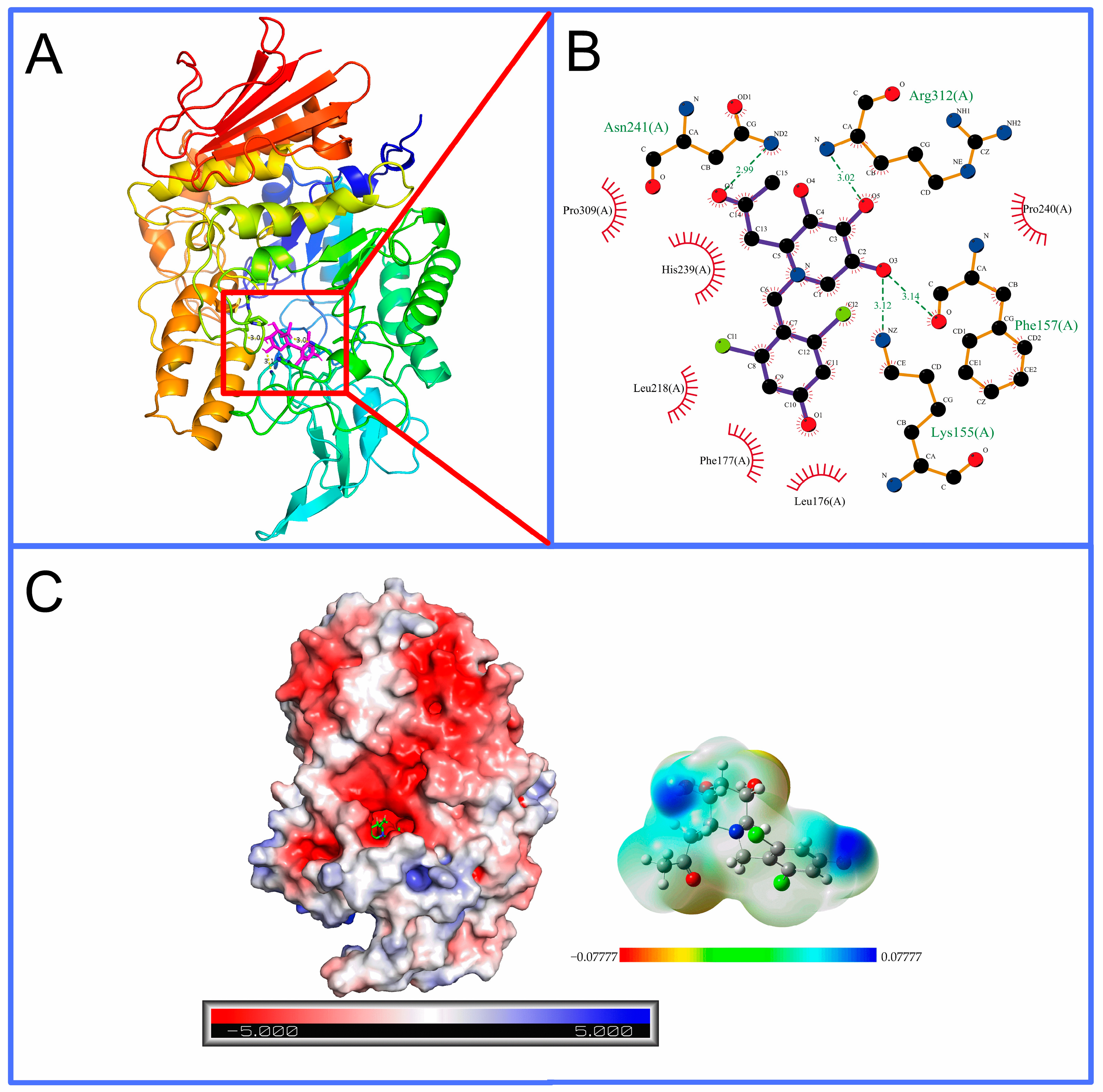
2.3. Homology Modeling and Molecular Docking
2.4. In Silico Analysis
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General Procedures
3.1.2. Synthetic Procedures
3.2. α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 16 February 2022).
- IDF Diabetes Atlas | Tenth Edition. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/ (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Dhameja, M.; Gupta, P. Synthetic. Heterocyclic Candidates as Promising α-Glucosidase Inhibitors: An Overview. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 176, 343–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minks, J.A. Theoretical Framework to Guide a Study for Exploring the Impact of Established and Potential Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Appl. Nurs. Res. 2020, 53, 151267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derosa, G.; Maffioli, P. Efficacy and Safety Profile Evaluation of Acarbose Alone and in Association With Other Antidiabetic Drugs: A Systematic Review. Clin. Ther. 2012, 34, 1221–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rines, A.K.; Sharabi, K.; Tavares, C.D.J.; Puigserver, P. Targeting Hepatic Glucose Metabolism in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 786–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A.J. Is There a Role for α-Glucosidase Inhibitors in the Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus? Drugs 2003, 63, 933–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derosa, G.; Maffioli, P. Mini-Special Issue Paper Management of Diabetic Patients with Hypoglycemic Agents α-Glucosidase Inhibitors and Their Use in Clinical Practice. Arch. Med. Sci. 2012, 8, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.R.; Standl, E.; Tong, N.; Shah, P.; Kalra, S.; Rathod, R. Therapeutic Potential of α-Glucosidase Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Evidence-Based Review. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2015, 16, 1959–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosak, C.; Mertes, G. Critical Evaluation of the Role of Acarbose in the Treatment of Diabetes: Patient Considerations. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2012, 5, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sels, J.P.J.; Huijberts, M.S.; Wolffenbuttel, B.H. Miglitol, a New α-Glucosidase Inhibitor. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2005, 1, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, M.; Hadjiakhondi, A.; Mohammad Nabavi, S.; Manayi, A. Heterocyclic Compounds: Effective α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase Inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Javaid, K.; Wadood, A.; Jamal, A.; Batool, F.; Fazal-ur-Rehman, S.; Basha, F.Z.; Choudhary, M.I. In Vitro α-Glucosidase Inhibition by Non-Sugar Based Triazoles of Dibenzoazepine, Their Structure-Activity Relationship, and Molecular Docking. Med. Chem. 2017, 13, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Francis, S.; Dutta, D.; Gupta, V.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, J.Y.; Tash, J.S.; Schönbrunn, E.; Georg, G.I. Synthesis and Evaluation of Eight- and Four-Membered Iminosugar Analogues as Inhibitors of Testicular Ceramide-Specific Glucosyltransferase, Testicular β-Glucosidase 2, and Other Glycosidases. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 3082–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wadood, A.; Ghufran, M.; Khan, A.; Azam, S.S.; Jelani, M.; Uddin, R. Selective Glycosidase Inhibitors: A Patent Review (2012–Present). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, Y.; Igarashi, Y.; Ichikawa, M.; Suhara, Y. 1-N-Iminosugars: Potent and Selective Inhibitors of β-Glycosidases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 3007–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Hirokami, Y.; Kinami, K.; Tsuji, Y.; Miyawaki, S.; Adachi, I.; Hollinshead, J.; Nash, R.J.; Kiappes, J.L.; Zitzmann, N.; et al. Isolation and SAR Studies of Bicyclic Iminosugars from Castanospermum Australe as Glycosidase Inhibitors. Phytochemistry 2015, 111, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, R.J.; Bartholomew, B.; Penkova, Y.B.; Rotondo, D.; Yamasaka, F.; Stafford, G.P.; Jenkinson, S.F.; Fleet, G.W.J. Iminosugar IdoBR1 Isolated from Cucumber Cucumis Sativus Reduces Inflammatory Activity. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 16263–16271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrodnigg, T.M.; Steiner, A.J.; Ueberbacher, B.J. Natural and Synthetic Iminosugars as Carbohydrate Processing Enzyme Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy. Anticancer. Agents Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.N.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.H.; Ye, X.S. A Versatile Approach to N-Alkylated 1,4-Dideoxy-1,4-Imino-D-Arabinitols and 1,4-Dideoxy-1,4-Imino-L-Xylitols. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 2001–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compain, P. Iminosugar C-Glycosides: Synthesis and Biological Activity. In Iminosugars; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; pp. 63–86. ISBN 9780470517437. [Google Scholar]
- Butters, T.D.; Dwek, R.A.; Platt, F.M. Inhibition of Glycosphingolipid Biosynthesis: Application to Lysosomal Storage Disorders. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 4683–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Luo, H.; Ma, X.; Zou, W.; Shao, H. Stereoselective Synthesis of a Series of New N-Alkyl-3-Hydroxypiperidine Derivatives Containing a Hemiketal. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 4834–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Kawabata, J. α-Glucosidase Inhibition of 6-Hydroxyflavones. Part 3: Synthesis and Evaluation of 2,3,4-Trihydroxybenzoyl-Containing Flavonoid Analogs and 6-Aminoflavones as α-Glucosidase Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, T.; Doi, U.; Osawa, T. Inhibitory Activity of Corn-Derived Bisamide Compounds against α-Glucosidase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 51, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Kawabata, J. 2-Aminoresorcinol Is a Potent α-Glucosidase Inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 812–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; De Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology Modelling of Protein Structures and Complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienert, S.; Waterhouse, A.; De Beer, T.A.P.; Tauriello, G.; Studer, G.; Bordoli, L.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL Repository—New Features and Functionality. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D313–D319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C.; Schwede, T. Automated Comparative Protein Structure Modeling with SWISS-MODEL and Swiss-PdbViewer: A Historical Perspective. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, S162–S173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studer, G.; Rempfer, C.; Waterhouse, A.M.; Gumienny, R.; Haas, J.; Schwede, T. QMEANDisCo—Distance Constraints Applied on Model Quality Estimation. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, M.; Kiefer, F.; Biasini, M.; Bordoli, L.; Schwede, T. Modeling Protein Quaternary Structure of Homo- and Hetero-Oligomers beyond Binary Interactions by Homology. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Miyake, H.; Kusunoki, M.; Osaki, S. Steric Hindrance by 2 Amino Acid Residues Determines the Substrate Specificity of Isomaltase from Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 112, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti Correlation-Energy Formula into a Functional of the Electron Density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional Thermochemistry. III. The Role of Exact Exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Revision, C.01. Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. Software News and Update AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function Efficient Optimization and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, A.C.; Laskowski, R.A.; Thornton, J.M. LIGPLOT: A Program to Generate Schematic Diagrams of Protein-Ligand Interactions. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1995, 8, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarter, J.D.; Withers, S.G. Unequivocal Identification of Asp-214 as the Catalytic Nucleophile of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae α-Glucosidase Using 5-Fluoro Glycosyl Fluorides. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 6889–6894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A Free Web Tool to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics, Drug- Likeness and Medicinal Chemistry Friendliness of Small Molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Li, W.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, J.; Wu, Z.; Liu, G.; Lee, P.W.; Tang, Y. AdmetSAR: A Comprehensive Source and Free Tool for Assessment of Chemical ADMET Properties. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 3099–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and Computational Approaches to Estimate Solubility and Permeability in Drug Discovery and Development Settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A.K.; Viswanadhan, V.N.; Wendoloski, J.J. A Knowledge-Based Approach in Designing Combinatorial or Medicinal Chemistry Libraries for Drug Discovery. 1. A Qualitative and Quantitative Characterization of Known Drug Databases. J. Comb. Chem. 1999, 1, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kopple, K.D. Molecular Properties That Influence the Oral Bioavailability of Drug Candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, W.J.; Merz, K.M.; Baldwin, J.J. Prediction of Drug Absorption Using Multivariate Statistics. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 3867–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muegge, I.; Heald, S.L.; Brittelli, D. Simple Selection Criteria for Drug-like Chemical Matter. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 1841–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, L.; Yang, H. ADMET-Score—A Comprehensive Scoring Function for Evaluation of Chemical Drug-Likeness. Med. Chem. Commun. 2019, 10, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parida, S.K.; Jaiswal, S.; Singh, P.; Murarka, S. Multicomponent Synthesis of Biologically Relevant S-Aryl Dithiocarbamates Using Diaryliodonium Salts. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 6401–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
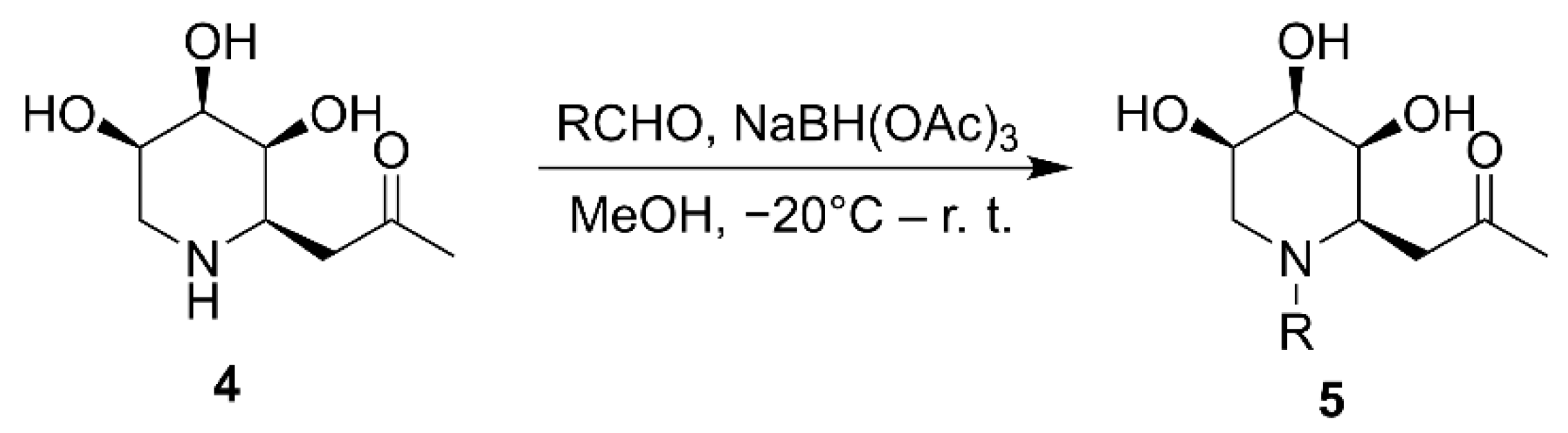

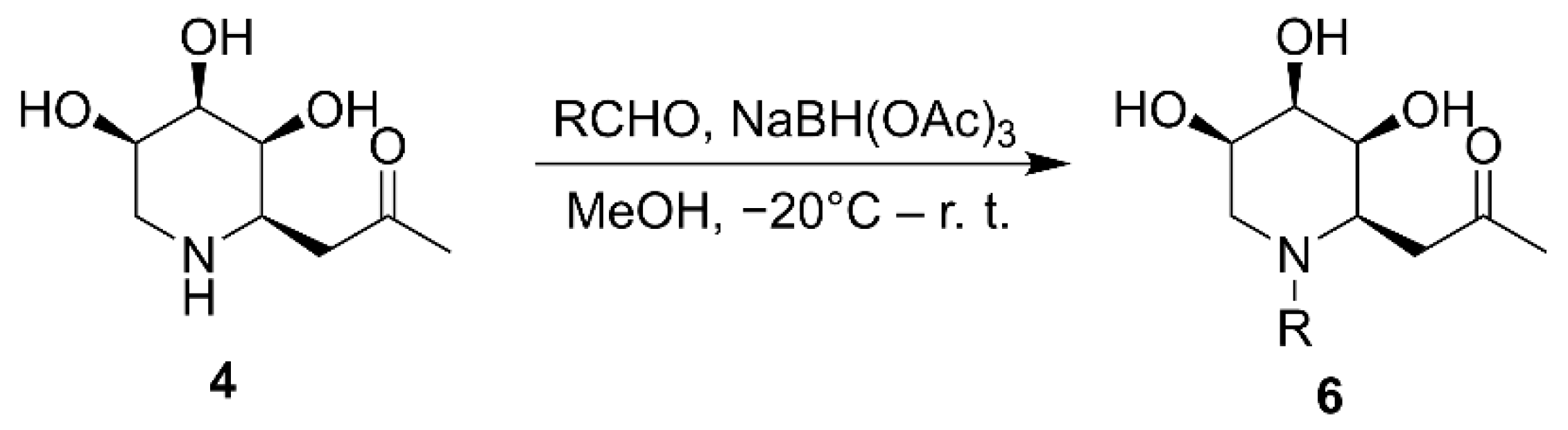


 | ||||
| Reducing Agent | Temperature | Solvent | Time | Yield |
| NaBH3CN | r. t. | MeOH | 8 h | N. R. |
| NaBH3CN | 0 °C | MeOH | 8 h | N. R. |
| NaBH3CN | −40 °C | MeOH | 8 h | N. R. |
| NaBH3CN | −78 °C | MeOH | 8 h | N. R. |
| NaBH3CN | −20 °C–r. t. | HOAc, MeOH | 8 h | N. R. |
| NaBH(OAc)3 | 0 °C–r. t. | MeOH | 3 h | 67% |
| NaBH(OAc)3 | −20 °C–r. t. | MeOH | 3 h | 93% |
| Compound | IC50 (µM) | Compound | IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5r | 12.0 | 6d | 2.4 |
| 5λ | 7.4 | 6e | 0.9 |
| 5θ | >20.0 | 6f | >20.0 |
| 5π | >20.0 | 6g | >20.0 |
| 6a | 5.6 | 6h | >20.0 |
| 6b | 5.3 | 6i | 5.5 |
| 6c | 3.3 | 4 | >20.0 |
| Acarbose | 2.0 |
| Compound Name | MW (g/mol) | nAtoms | nRings | nCarbon | nHetero Atoms | RB | HBA | HBD | MR | TPSA (Å sqr) | XlogP | WlogP | MlogP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5r | 313.78 | 41 | 2 | 15 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 83.26 | 81.00 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.40 |
| 5λ | 295.33 | 42 | 2 | 15 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 80.27 | 101.23 | −0.96 | −0.89 * | −0.66 |
| 5θ | 295.33 | 42 | 2 | 15 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 80.27 | 101.23 | −0.96 | −0.89 * | −0.66 |
| 5π | 295.33 | 42 | 2 | 15 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 80.27 | 101.23 | −0.96 | −0.89 * | −0.66 |
| 6a | 329.78 | 42 | 2 | 15 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 85.28 | 101.23 | −0.33 | −0.24 | −0.14 |
| 6b | 374.23 | 42 | 2 | 15 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 87.97 | 101.23 | −0.26 | −0.13 | −0.02 |
| 6c | 313.32 | 42 | 2 | 15 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 4 | 80.23 | 101.23 | −0.86 | −0.34 | −0.27 |
| 6d | 329.78 | 42 | 2 | 15 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 85.28 | 101.23 | −0.33 | −0.24 | −0.14 |
| 6e | 364.22 | 42 | 2 | 15 | 8 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 90.29 | 101.23 | 0.30 | 0.41 | 0.37 |
| 6f | 325.36 | 46 | 2 | 16 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 86.76 | 110.46 | −0.98 | −0.89 * | −0.94 |
| 6g | 339.38 | 49 | 2 | 17 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 91.57 | 110.46 | −0.62 | −0.50 * | −0.70 |
| 6h | 325.36 | 46 | 2 | 16 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 86.76 | 110.46 | −0.98 | −0.89 * | −0.94 |
| 6i | 453.12 | 42 | 2 | 15 | 8 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 95.67 | 101.23 | 0.43 | 0.63 | 0.61 |
| Compound Name | Human Intestinal Absorption | Caco-2 Permeability | Blood Brain Barrier | Carcinogenicity | Ames Mutagenesis | Acute Oral Toxicity | Average Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6d | 0.9666 | 0.6029 | 0.9472 | 0.8429 | 0.5900 | 0.6726 | 0.7704 |
| 6e | 0.9666 | 0.6770 | 0.9472 | 0.8429 | 0.6500 | 0.6726 | 0.7927 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Tang, S.; Zhang, G.; Pan, Y.; Jiao, W.; Shao, H. Synthesis of N-Substituted Iminosugar C-Glycosides and Evaluation as Promising α-Glucosidase Inhibitors. Molecules 2022, 27, 5517. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175517
Wang H, Tang S, Zhang G, Pan Y, Jiao W, Shao H. Synthesis of N-Substituted Iminosugar C-Glycosides and Evaluation as Promising α-Glucosidase Inhibitors. Molecules. 2022; 27(17):5517. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175517
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haibo, Senling Tang, Guoqing Zhang, Yang Pan, Wei Jiao, and Huawu Shao. 2022. "Synthesis of N-Substituted Iminosugar C-Glycosides and Evaluation as Promising α-Glucosidase Inhibitors" Molecules 27, no. 17: 5517. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175517
APA StyleWang, H., Tang, S., Zhang, G., Pan, Y., Jiao, W., & Shao, H. (2022). Synthesis of N-Substituted Iminosugar C-Glycosides and Evaluation as Promising α-Glucosidase Inhibitors. Molecules, 27(17), 5517. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175517





