UV-Cured Antibacterial Hydrogels Based on PEG and Monodisperse Heterofunctional Bis-MPA Dendrimers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Instruments and Methods
2.2.1. NMR Spectroscopy
2.2.2. MALDI-MS
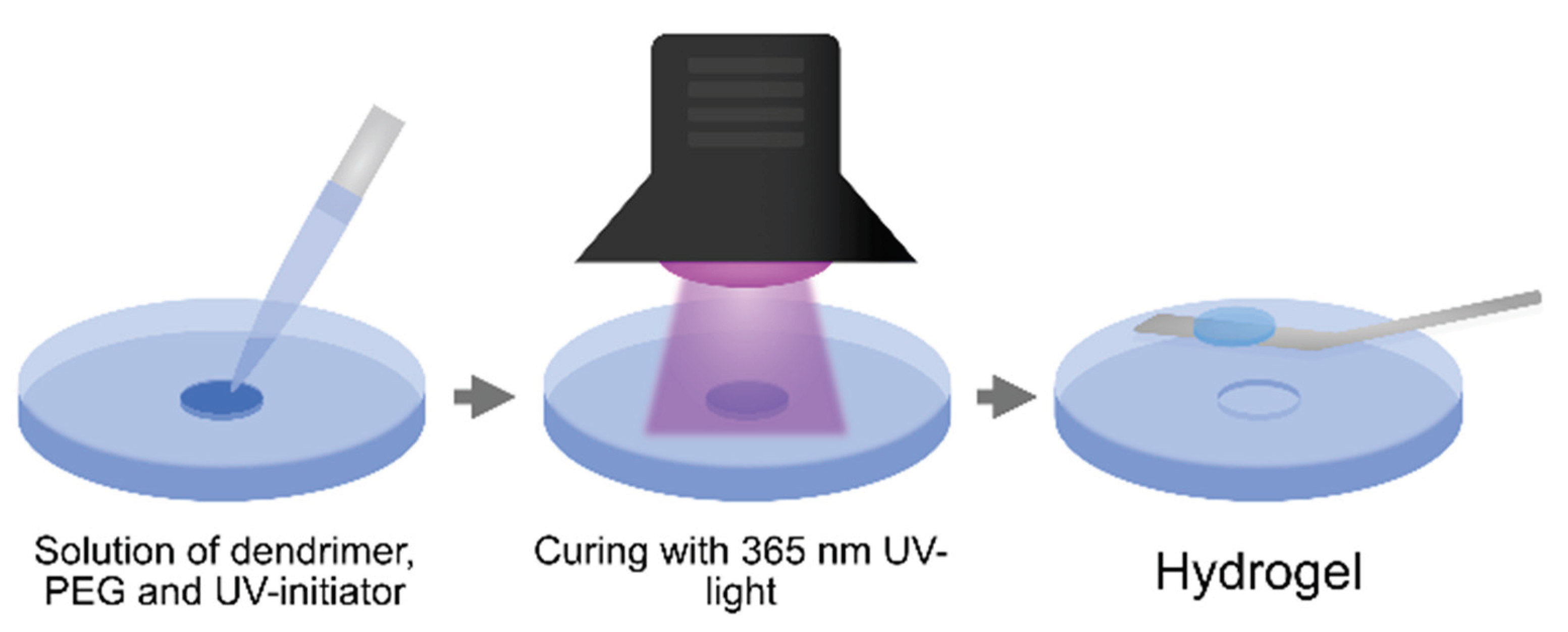
2.2.3. Gel Curing
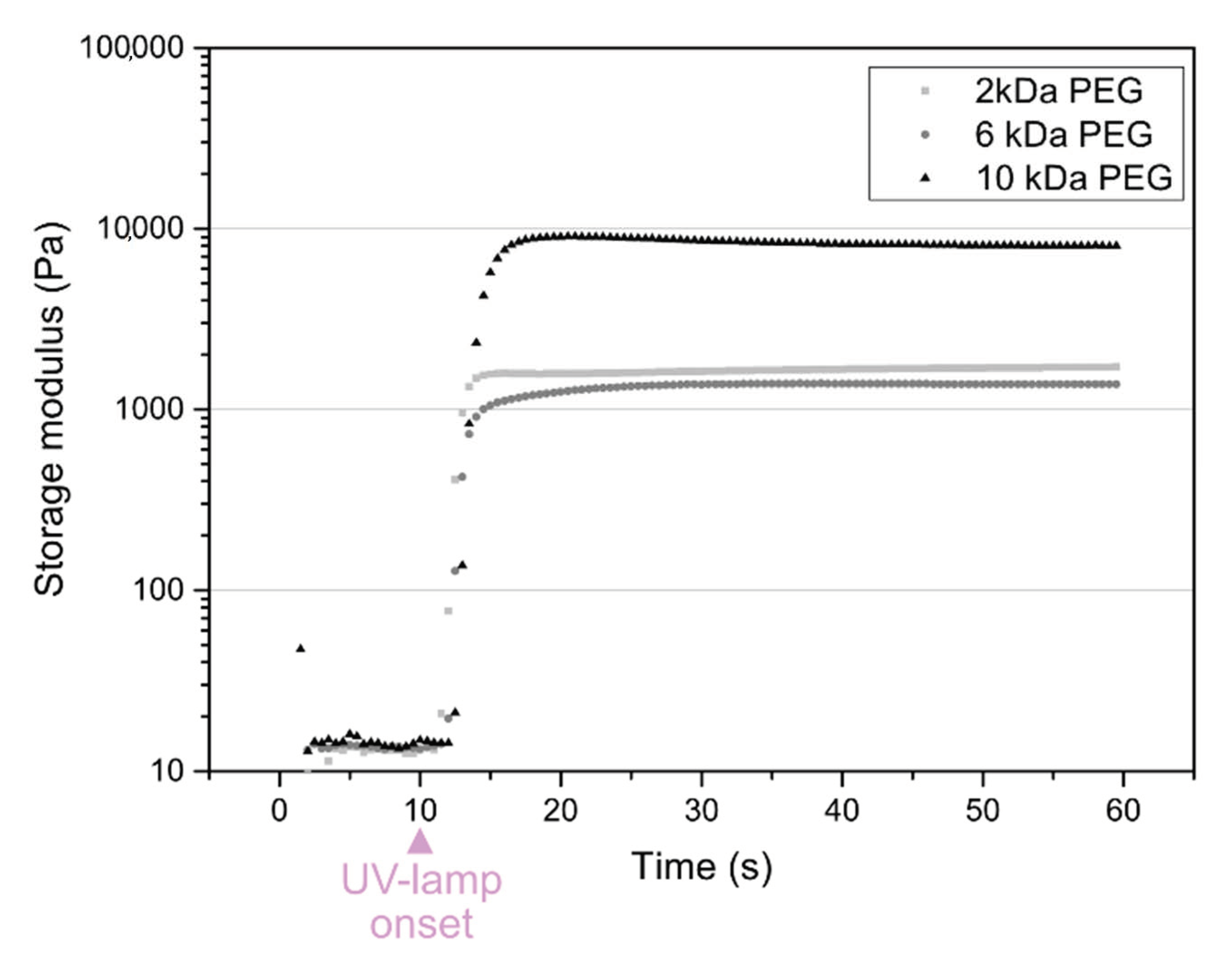
2.2.4. Rheology
2.2.5. Cell Experiments
2.2.6. Bacterial Experiments
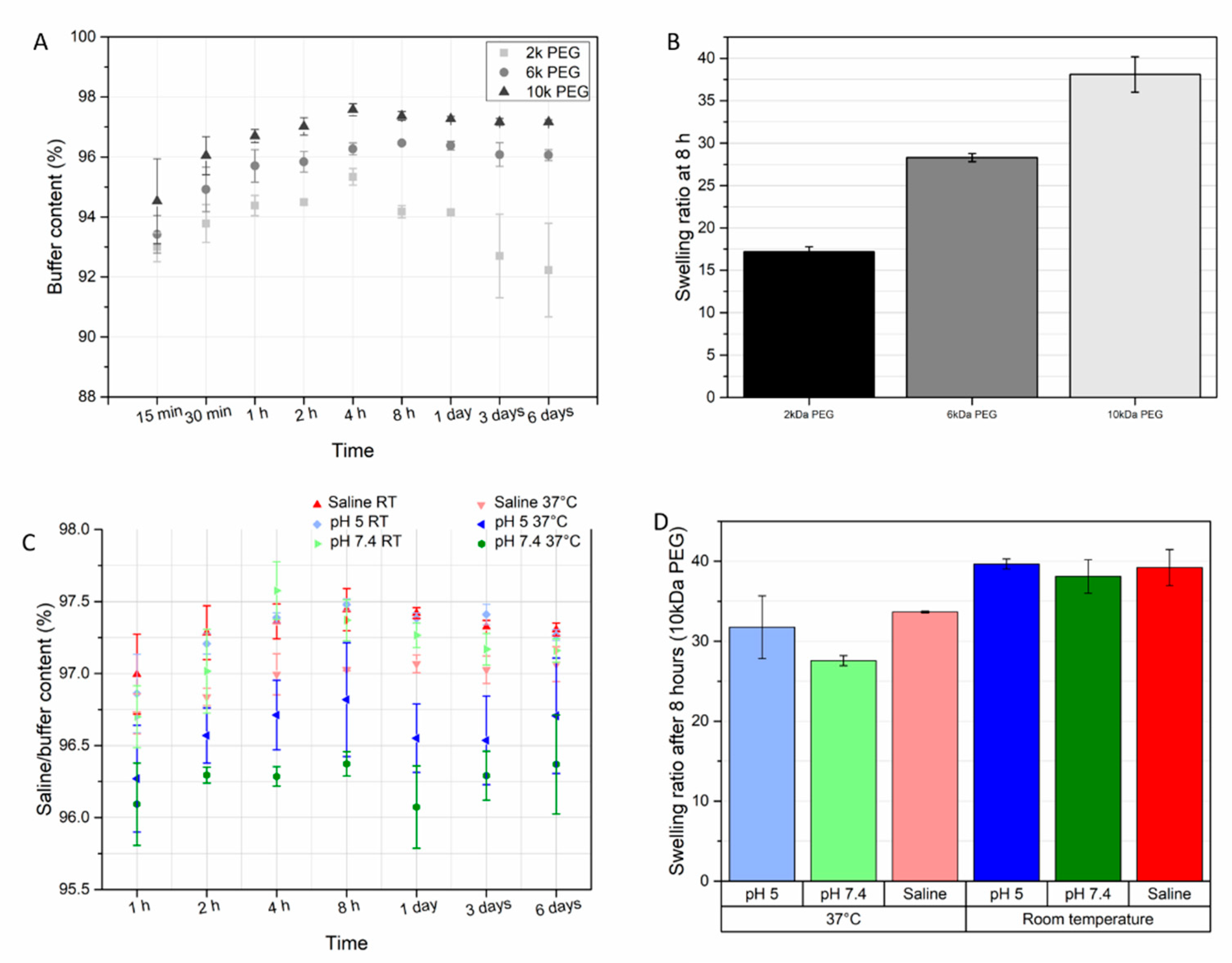
2.2.7. Swelling
2.2.8. Gel Fraction
3. Results and Discussion
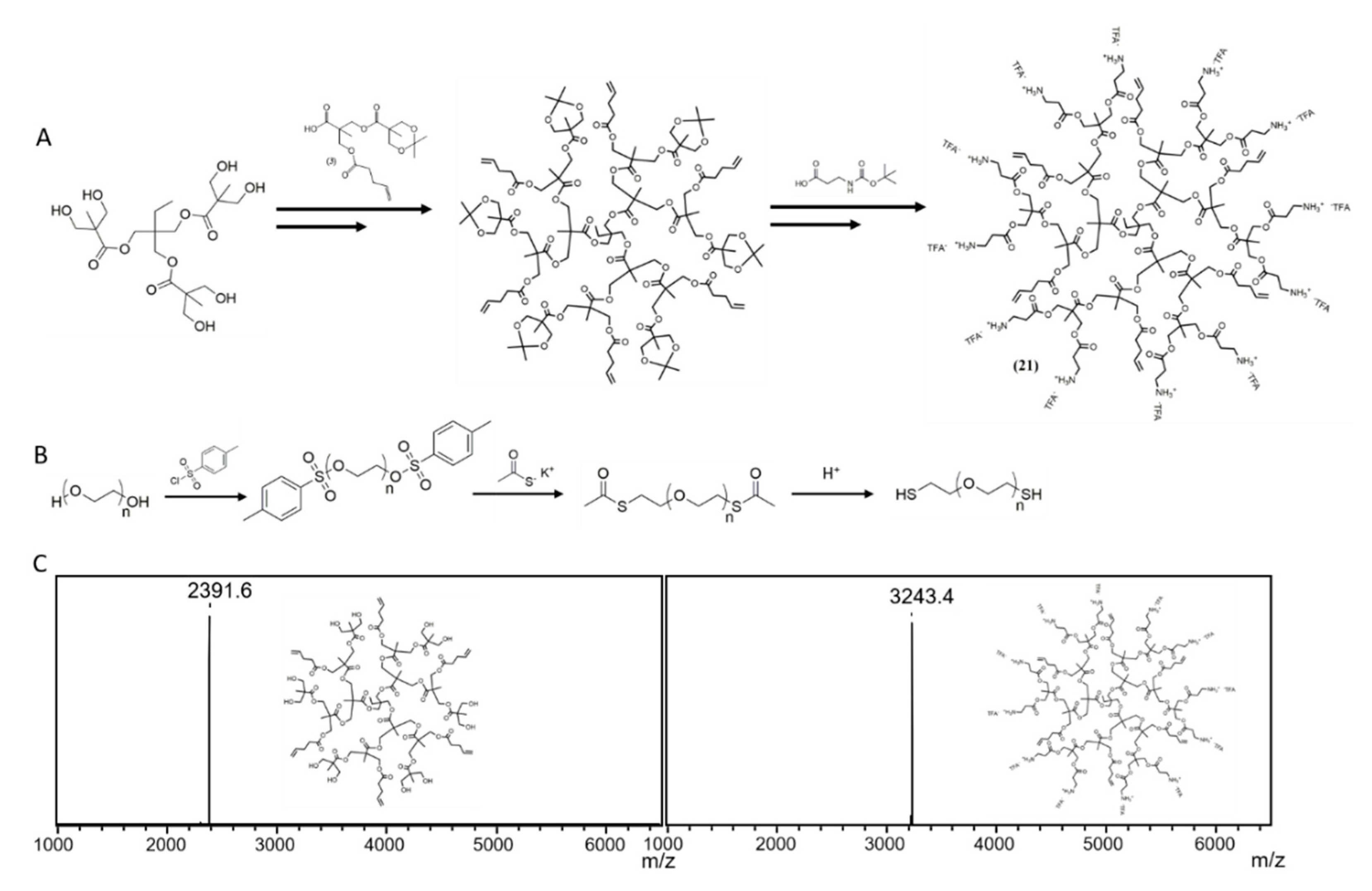
3.1. Synthesis of Dendrimers and PEGs
3.2. Formulation and Curing of Hydrogels
3.3. Swelling of Hydrogels
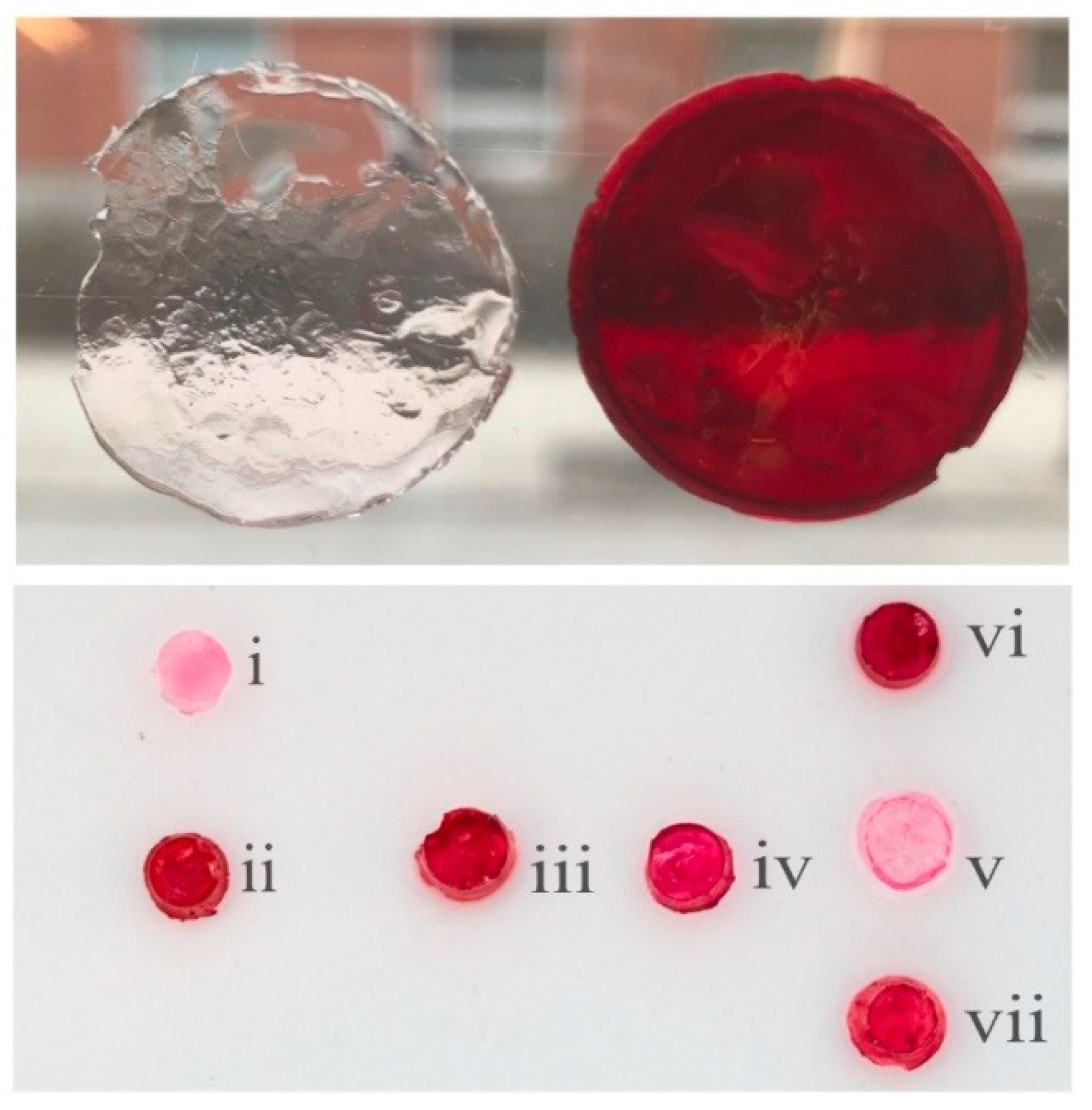
3.4. Post-Functionalization of Hydrogels with the NHS-Ester of Disperse Red 13
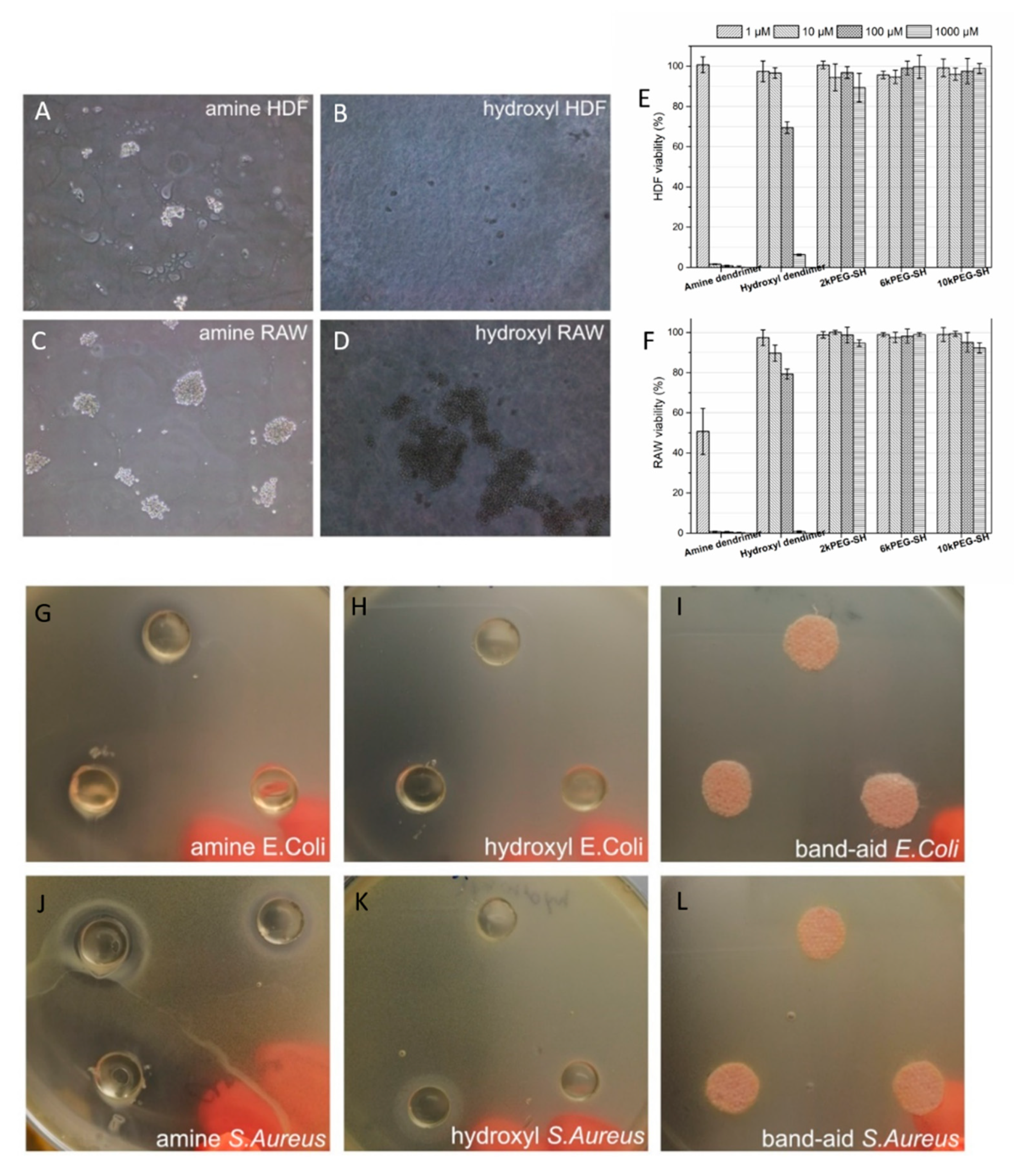
3.5. Biocompatibility and Antibacterial Activity of Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization and applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichterle, O.; Lim, D. Hydrophilic gels for biological use. Nature 1960, 185, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, C. Absorbent Product Containing a Hydrocolloidal Composition. U.S. Patent 3670731A, 20 June 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Phadke, A.; Zhang, C.; Arman, B.; Hsu, C.-C.; Mashelkar, R.A.; Lele, A.K.; Tauber, M.J.; Arya, G.; Varghese, S. Rapid self-healing hydrogels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4383–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Namata, F.; Erlandsson, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wågberg, L.; Malkoch, M. Self-assembled polyester dendrimer/cellulose nanofibril hydrogels with extraordinary antibacterial activity. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuta, T.; Takashima, Y.; Nakahata, M.; Otsubo, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Harada, A. Preorganized hydrogel: Self-healing properties of supramolecular hydrogels formed by polymerization of host-guest-monomers that contain cyclodextrins and hydrophobic guest groups. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2849–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.-Y.; Wu, J.; Moochhala, S.M.; Tan, M.-H.; Lu, J. Development of a chitosan-based wound dressing with improved hemostatic and antimicrobial properties. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4323–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Lin, Q.; Gong, P.; Ma, L.; Yang, S. A novel wound dressing based on Ag/graphene polymer hydrogel: Effectively kill bacteria and accelerate wound healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3933–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, H.; Guo, B.; Dong, R.; Qiu, Y.; Ma, P.X. Antibacterial anti-oxidant electroactive injectable hydrogel as self-healing wound dressing with hemostasis and adhesiveness for cutaneous wound healing. Biomaterials 2017, 122, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Lüchow, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Fortuin, L.; Mohanty, S.; Brauner, A.; Malkoch, M. Nanogel encapsulated hydrogels as advanced wound dressings for the controlled delivery of antibiotics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2006453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczynska, M.D.; Villa-Camacho, J.C.; Ghobril, C.; Perez-Viloria, M.; Tevis, K.M.; Blessing, W.A.; Nazarian, A.; Rodriguez, E.K.; Grinstaff, M.W. On-demand dissolution of a dendritic hydrogel-based dressing for second-degree burn wounds through thiol-thioester exchange reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9984–9987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Bae, Y.H.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, S.W. Biodegradable block copolymers as injectable drug-delivery systems. Nature 1997, 388, 860–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, N.; Ramay, H.R.; Gunn, J.; Matsen, F.A.; Zhang, M. PEG-grafted chitosan as an injectable thermosensitive hydrogel for sustained protein release. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-C.; Wu, Y.-C.; Mi, F.-L.; Lin, Y.-H.; Yu, L.-C.; Sung, H.-W. A novel pH-sensitive hydrogel composed of N, O-carboxymethyl chitosan and alginate cross-linked by genipin for protein drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2004, 96, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutolf, M.P.; Lauer-Fields, J.L.; Schmoekel, H.G.; Metters, A.T.; Weber, F.E.; Fields, G.B.; Hubbell, J.A. Synthetic matrix metalloproteinase-sensitive hydrogels for the conduction of tissue regeneration: Engineering cell-invasion characteristics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.USA 2003, 100, 5413–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Chu, C.R.; Payne, K.A.; Marra, K.G. Injectable in situ forming biodegradable chitosan—Hyaluronic acid based hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2499–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J. Bioactive modification of poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogels for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4639–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihre, H.; Hult, A.; Söderlind, E. Synthesis, characterization and 1H NMR self-diffusion studies of dendritic aliphatic polyesters based on 2, 2-bis (hydroxymethyl) propionic acid and 1, 1, 1-tris (hydroxyphenyl) ethane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 6388–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliu, N.; Walter, M.V.; Montañez, M.I.; Kunzmann, A.; Hult, A.; Nyström, A.; Malkoch, M.; Fadeel, B. Stability and biocompatibility of a library of polyester dendrimers in comparison to polyamidoamine dendrimers. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1970–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gallego, S.; Hult, D.; Olsson, J.V.; Malkoch, M. Fluoride-promoted esterification with imidazolide-activated compounds: A modular and sustainable approach to dendrimers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2416–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Plackett, B. Why big pharma has abandoned antibiotics. Nature 2020, 586, S50–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenström, P.; Hjorth, E.; Zhang, Y.; Andrén, O.C.; Guette-Marquet, S.; Schultzberg, M.; Malkoch, M. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of monodisperse amino-functional polyester dendrimers with rapid degradability and antibacterial properties. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 4323–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyle, C.E.; Bowman, C.N. Thiolene click chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 1540–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbanks, B.D.; Schwartz, M.P.; Bowman, C.N.; Anseth, K.S. Photoinitiated polymerization of PEG-diacrylate with lithium phenyl-2, 4, 6-trimethylbenzoylphosphinate: Polymerization rate and cytocompatibility. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6702–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon-Chemin, L.; Buisine, E.; Yardley, V.; Kohler, S.; Debreu, M.-A.; Landry, V.; Sergheraert, C.; Croft, S.L.; Krauth-Siegel, R.L.; Davioud-Charvet, E. 2-and 3-substituted 1, 4-naphthoquinone derivatives as subversive substrates of trypanothione reductase and lipoamide dehydrogenase from trypanosoma c ruzi: Synthesis and correlation between redox cycling activities and in vitro cytotoxicity. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 548–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, M.; Wilems, T.; Hahn, M.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E. Compositional control of poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogel modulus independent of mesh size. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2011, 98, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temenoff, J.S.; Athanasiou, K.A.; Lebaron, R.G.; Mikos, A.G. Effect of poly (ethylene glycol) molecular weight on tensile and swelling properties of oligo (poly (ethylene glycol) fumarate) hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 59, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimi-Kenari, H.; Mollaie, F.; Dashtimoghadam, E.; Imani, M.; Nyström, B. Effects of chain length of the cross-linking agent on rheological and swelling characteristics of dextran hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, C.K.; Kerstein, M.D. Overview of wound healing in a moist environment. Am. J. Surg. 1994, 167, S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Yu, Y. Lipid bilayer disruption induced by amphiphilic Janus nanoparticles: The non-monotonic effect of charged lipids. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertazzi, L.; Gherardini, L.; Brondi, M.; Sulis Sato, S.; Bifone, A.; Pizzorusso, T.; Ratto, G.M.; Bardi, G. In vivo distribution and toxicity of PAMAM dendrimers in the central nervous system depend on their surface chemistry. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad-Villar, E.M.; Etter, S.F.; Thiel, M.A.; Hauser, P.C. Determination of chlorhexidine digluconate and polyhexamethylene biguanide in eye drops by capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 561, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stenström, P.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hutchinson, D.; García-Gallego, S.; Malkoch, M. UV-Cured Antibacterial Hydrogels Based on PEG and Monodisperse Heterofunctional Bis-MPA Dendrimers. Molecules 2021, 26, 2364. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082364
Stenström P, Fan Y, Zhang Y, Hutchinson D, García-Gallego S, Malkoch M. UV-Cured Antibacterial Hydrogels Based on PEG and Monodisperse Heterofunctional Bis-MPA Dendrimers. Molecules. 2021; 26(8):2364. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082364
Chicago/Turabian StyleStenström, Patrik, Yanmiao Fan, Yuning Zhang, Daniel Hutchinson, Sandra García-Gallego, and Michael Malkoch. 2021. "UV-Cured Antibacterial Hydrogels Based on PEG and Monodisperse Heterofunctional Bis-MPA Dendrimers" Molecules 26, no. 8: 2364. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082364
APA StyleStenström, P., Fan, Y., Zhang, Y., Hutchinson, D., García-Gallego, S., & Malkoch, M. (2021). UV-Cured Antibacterial Hydrogels Based on PEG and Monodisperse Heterofunctional Bis-MPA Dendrimers. Molecules, 26(8), 2364. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082364






