Realization of Rapid Large-Size 3D Printing Based on Full-Color Powder-Based 3DP Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effects of Z-Axial Height and Monolayer Area on Printing Time
2.2. Effects of Orientation on Printing Time
2.2.1. XYX Rotation Method
- (a)
- The change of Z-axial height value is observed when the digital model is rotated around X axis, and then the orientation with minimum z-axial height is found out in the angle range (0–180°).
- (b)
- Based on the orientation of digital model in step 1, it is rotated around Y axis, and obtaining the orientation with minimum Z-axial height in the angle range (0–180°).
- (c)
- Based on the orientation of digital model in step 2, repeating step 1.
2.2.2. Verification and Analysis
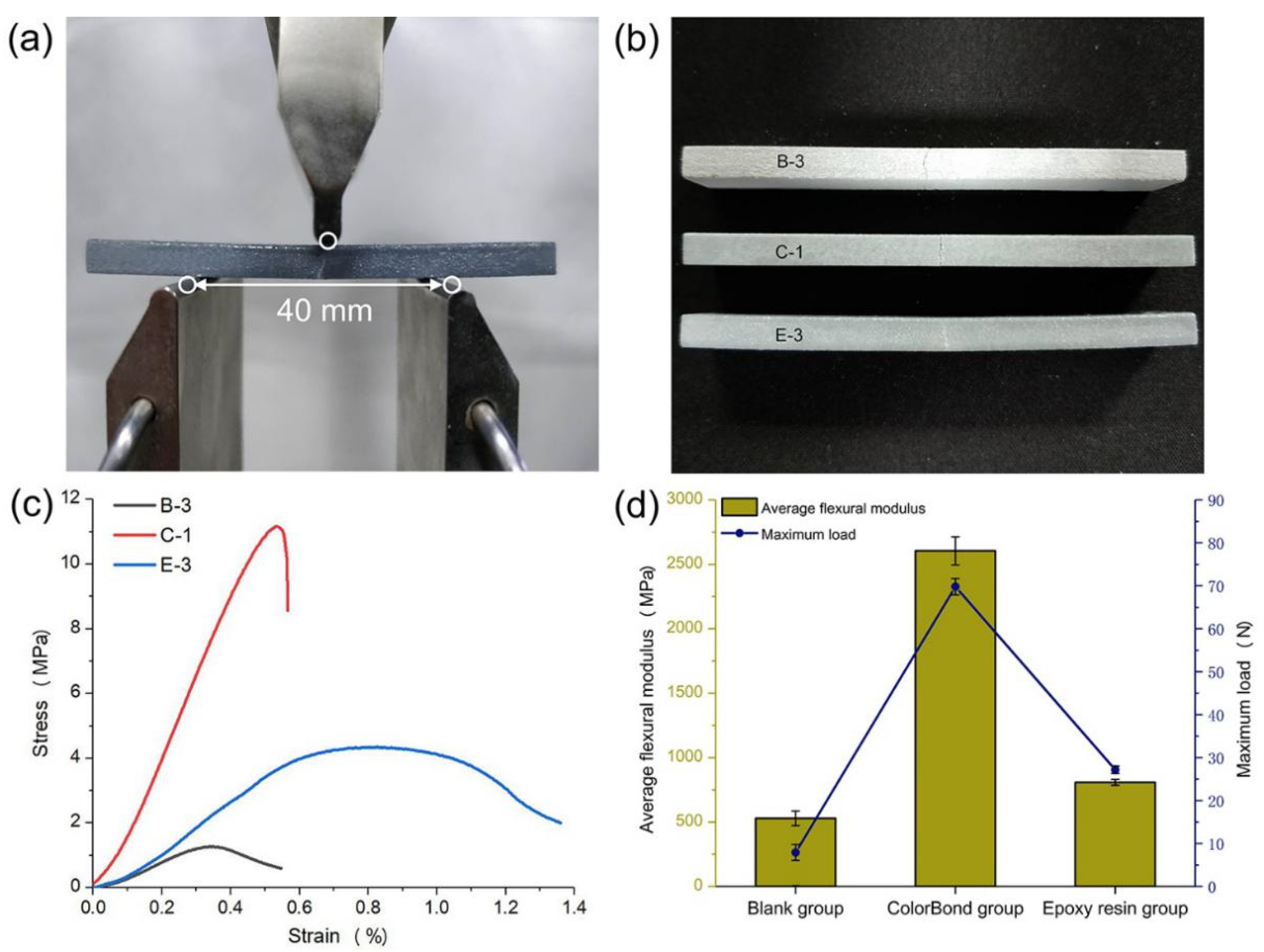
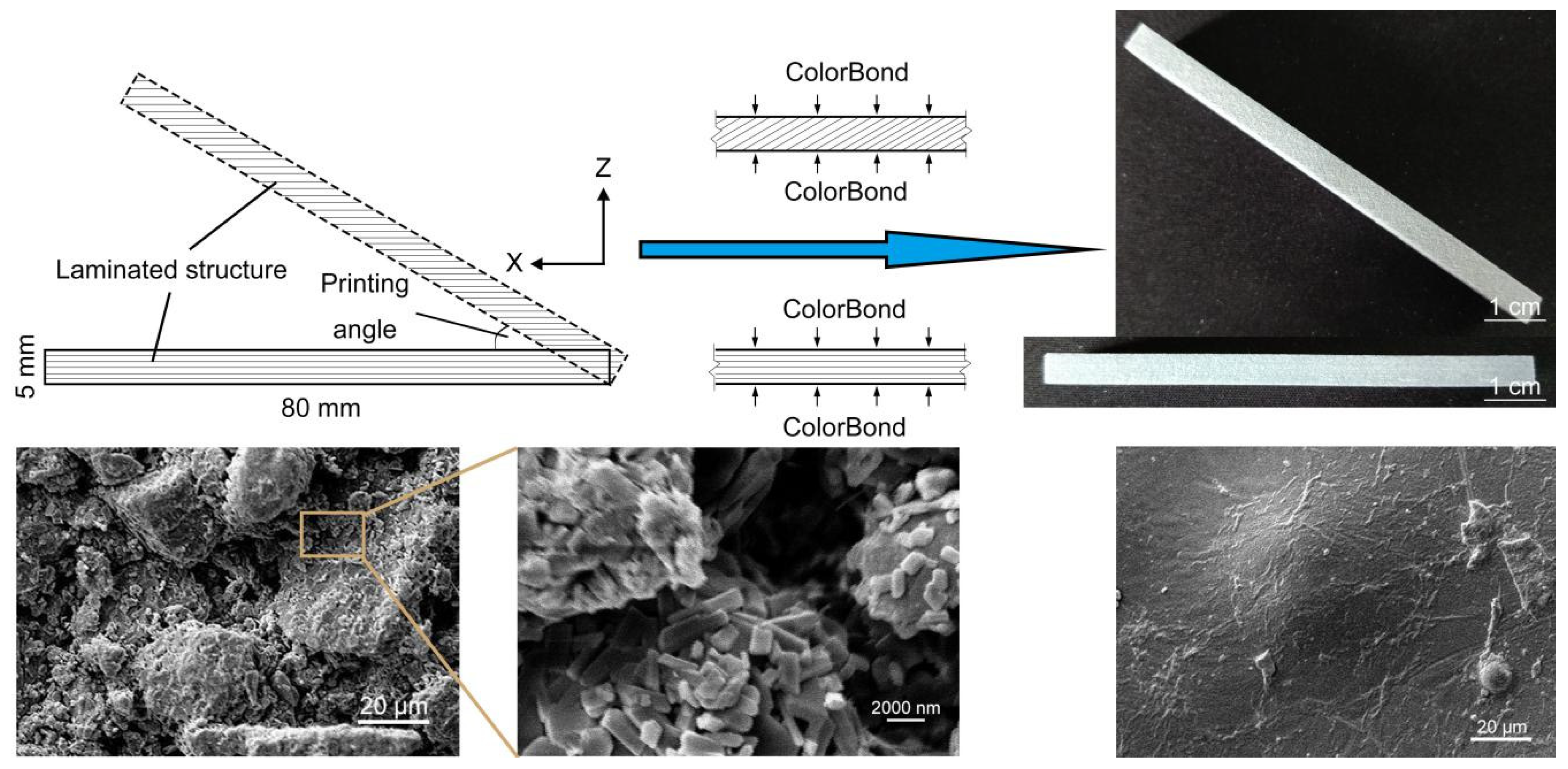
2.3. Effects of Impregnants on Mechanical Behavior
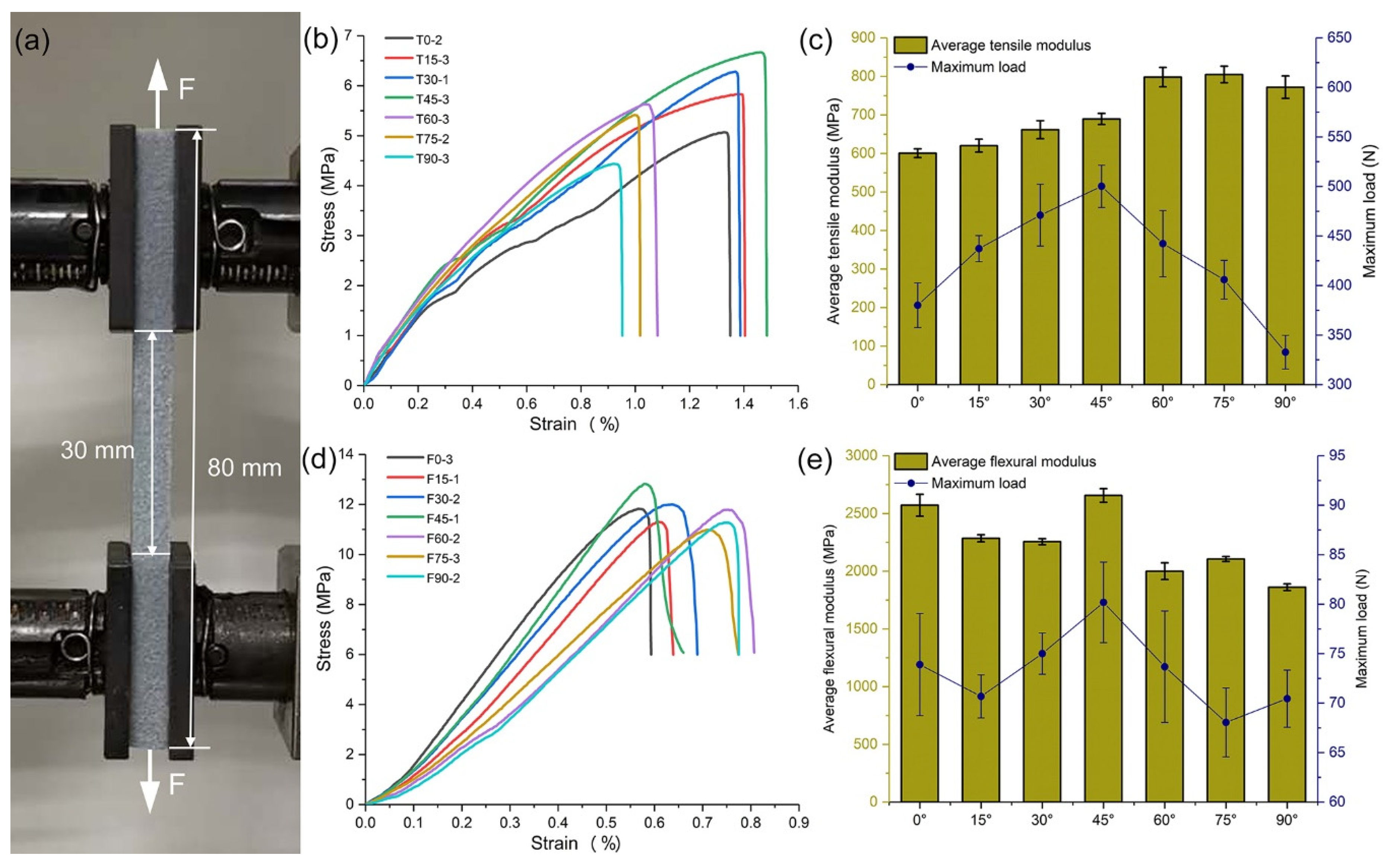
2.4. Mechanical Tests Based on Different Angles
2.5. Related Performance Research of Adhesives
3. Materials and Methods
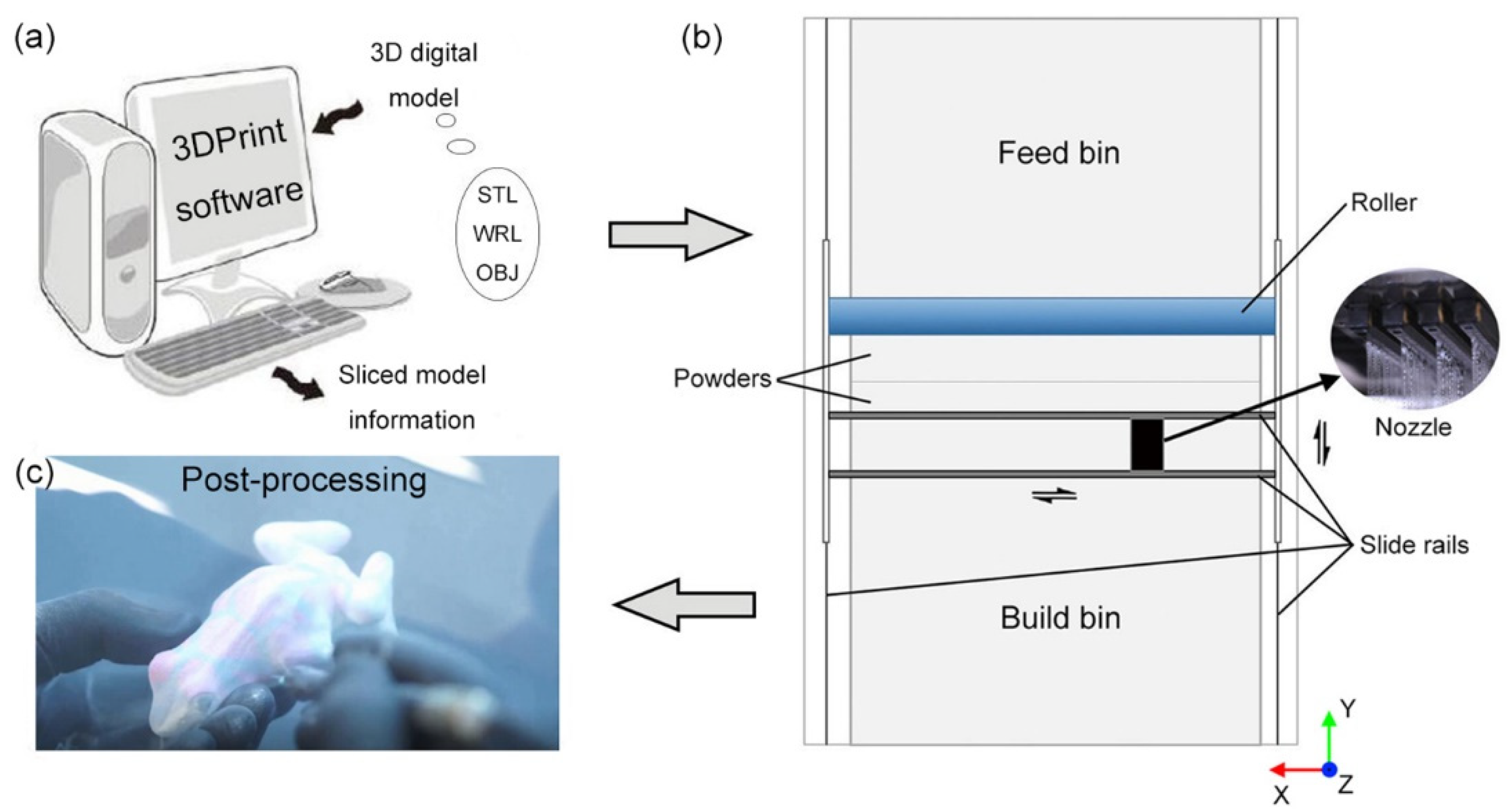
3.1. Materials and Equipment
- (a)
- The powder in feed bin is transported to build bin by the roller to build a substrate with smooth surface;
- (b)
- After paving a layer of powder on the substrate, the color binders are sprayed by nozzles onto the powder along X axis;
- (c)
- Repeating step b) until 3D models are formed;
- (d)
- Impregnation with epoxy resin for post-processing.
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Estimation and Reduction of Printing Time
3.2.2. Enhancement of Mechanical Properties
3.2.3. Selection of Adhesives
4. Conclusions
- (a)
- Digital models are placed with the XYX rotation method.
- (b)
- Models are split into several parts at an angle of 45° to Z axis according to the size and the capacity of build bin.
- (c)
- Following the printing and de-powdering processes, all parts are impregnated by ColorBond for about 20 s.
- (d)
- The impregnated parts are bonded by α-cyanoacrylate adhesive with the sizing of 25 mg/cm2.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, J.; Tari, M.J.; Hahn, H.T. Characterization of the laminated object manufacturing (LOM) process. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2000, 6, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yu, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhu, M.; Gao, Y. Large-size color models visualization under 3D paper-based printing. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2017, 23, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Meteyer, S.; Perry, N.; Zhao, Y.F. Energy consumption model of Binder-jetting additive manufacturing processes. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 7005–7015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.M.; Adewunmi, A.; Schek, R.M.; Flanagan, C.L.; Krebsbach, P.H.; Feinberg, S.E.; Hollister, S.J.; Das, S. Bone tissue engineering using polycaprolactone scaffolds fabricated via selective laser sintering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4817–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, V.; Scanlan, J.P.; Eres, M.H.; Martinez-Sykora, A.; Chinchapatnam, P. Cost-driven build orientation and bin packing of parts in Selective Laser Melting (SLM). Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 273, 334–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J. Liquid phase 3D printing for quickly manufacturing conductive metal objects with low melting point alloy ink. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2014, 57, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrimurthulu, K.; Pandey, P.M.; Reddy, N.V. Optimum part deposition orientation in fused deposition modeling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2004, 44, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Rivenson, Y.; Yardimci, N.T.; Veli, M.; Luo, Y.; Jarrahi, M.; Ozcan, A. All-optical machine learning using diffractive deep neural networks. Science 2018, 361, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Nian, Q.; Deng, B.; Jin, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Cheng, G.J. Three-dimensional printing of complex structures: Man made or toward nature? ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9710–9715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Y. 3D-printed biomimetic super-hydrophobic structure for microdroplet manipulation and oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchels, F.P.W.; Domingos, M.A.N.; Klein, T.J.; Malda, J.; Bartolo, P.J.; Hutmacher, D.W. Additive manufacturing of tissues and organs. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1079–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzik, G. Geometric accuracy of aircraft engine blade models constructed by means of the generative rapid prototyping methods FDM and SLA. Adv. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 34, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Yan, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, G. Paper-based 3D printing industrialization for customized wine packaging applications. In Proceedings of the NIP & Digital Fabrication Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 5–9 November 2017; Society for Imaging Science and Technology: Springfield, VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Melchels, F.P.W.; Jan, F.; Grijpma, D.W. A review on stereolithography and its applications in biomedical engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6121–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, B.G.; Bright, G.; Walker, A. A study on state of the art technology of laminated object manufacturing (LOM). In CAD/CAM, Proceedings of the Robotics and Factories of the Future, New Delhi, India, 6–8 January 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Olakanmi, E.O.; Cochrane, R.F.; Dalgarno, K.W. A review on selective laser sintering/melting (SLS/SLM) of aluminium alloy powders: Processing, microstructure, and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 74, 401–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, S.F.S.; Gharehkhani, S.; Mehrali, M.; Yarmand, H.; Metselaar, H.S.C.; Kadri, N.A.; Osman, N.A.A. A review on powder-based additive manufacturing for tissue engineering: Selective laser sintering and inkjet 3D printing. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mat. 2015, 16, 033502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligon, S.C.; Liska, R.; Stampfl, J.; Gurr, M.; Mülhaupt, R. Polymers for 3d printing and customized additive manufacturing. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10212–10290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espalin, D.; Muse, D.W.; Macdonald, E.; Wicker, R.B. 3D Printing multifunctionality: Structures with electronics. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2014, 72, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.Y.; Chua, C.K.; Dong, Z.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, D.Q.; Loh, L.E.; Sing, S.L. Review of selective laser melting: Materials and applications. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2015, 2, 041101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Meng, X.; Chen, J.F.; Ye, L. Mechanical properties of structures 3D printed with cementitious powders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 486–497. [Google Scholar]
- Stanic, M.; Lozo, B.; Svetec, D.G. Colorimetric properties and stability of 3D prints. Rapid Prototyping J. 2012, 18, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhu, M.; Xu, B.; Chen, G. Review on processes and color quality evaluation of color 3D printing. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2018, 24, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, E.M.; Haggerty, J.S.; Cima, M.J.; Williams, P.A. Three-dimensional Printing Techniques. U.S. Patent 5,204,055A, 20 April 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Mick, P.T.; Christoph, A.; Mainprize, J.G.; Symons, S.P.; Chen, J.M. Face validity study of an artificial temporal bone for simulation surgery. Otol. Neurotol. 2013, 34, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, K.; Potgieter, J.; Arif, K.; Archer, R. Opportunities and challenges for large scale 3D printing of complex parts. In Proceedings of the 2017 24th International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice (M2VIP), Auckland, New Zealand, 21–23 November 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- D-shape. Available online: https://d-shape.com (accessed on 25 January 2019).
- Buswell, R.A.; Soar, R.C.; Gibb, A.G.; Thorpe, A. Freeform construction: Mega-scale rapid manufacturing for construction. Automat. Constr. 2007, 16, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, B.; Paul, S.C.; Mohamed, N.A.N.; Tay, Y.W.D.; Tan, M.J. Measurement of tensile bond strength of 3D printed geopolymer mortar. Measurement. 2018, 113, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, G.J.; Williams, R.; Purnell, P.; Farahi, E. 3D Printing of cement composites. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2010, 109, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorndran, E.; Klarner, M.; Klammert, U.; Grover, L.M.; Patel, S.; Barralet, J.E.; Gbureck, U. 3D powder printing of β-tricalcium phosphate ceramics using different strategies. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, B67–B71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeil, P.; Sungwook, C.; Gyeorye, L.; Dusu, K. Printing time/material usage estimation of 3-d printer using digital printing method. Korean J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2017, 22, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Ganganath, N.; Cheng, C.T.; Fok, K.Y.; Chi, K.T. Trajectory planning for 3d printing: A revisit to traveling salesman problem. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Control, New York, NY, USA, 7–11 December 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J. Study on optimization of 3D printing parameters. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 392, 062050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Haihong, Z.; Xiang, W. Visual threshold analysis of printing color. Guangdong Print. 1998, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, P.; Huson, D.; Parraman, C.; Stanić, M. 3D printing in colour: Technical evaluation and creative applications. In Proceedings of the Impact 6 international printmaking conference, Bristol, UK, 16–19 September 2009; Impact: Bristol, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Yuan, J.; Chen, G. Color reproduction accuracy promotion of 3D-Printed surfaces based on microscopic image analysis. Int. J. Pattern. Recogn. 2020, 34, 2054004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.R.; Cui, G.H.; Rigg, B. The development of the CIE 2000 colour-difference formula: CIEDE2000. Color. Res. Appl. 2001, 26, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples are available from the authors. |

| Exp. A (Effects of Z-Axial Height on Printing Time) | Exp. B (Effects of Monolayer Area on Printing Time) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Parameters | Z-Axial Height (cm) | Basal Area (cm2) | Cuboids | Cylinders | ||||||
| Basal Area (cm2) | Z-Axial Height (cm) | Printing Time (min) | No. | Side Length (cm) | Time (min) | No. | Radius (cm) | Time (min) | |||
| A1 | 100 | 2 | 65 | 2 | 100 | B11 | 10.00 | 65 | B21 | 5.64 | 68 |
| A2 | 4 | 131 | 200 | B12 | 14.14 | 83 | B22 | 7.98 | 86 | ||
| A3 | 6 | 196 | 300 | B13 | 17.32 | 94 | B23 | 9.77 | 102 | ||
| A4 | 8 | 262 | 400 | B14 | 20.00 | 105 | B24 | 11.28 | 113 | ||
| A5 | 10 | 327 | 500 | B15 | 22.36 | 118 | B25 | 12.62 | 126 | ||
| A6 | 12 | 392 | 600 | B16 | 24.49 | 126 | B26 | 13.82 | 135 | ||
| A7 | 14 | 452 | 700 | B17 | 26.46 | 138 | B27 | 14.93 | 150 | ||
| A8 | 16 | 517 | 800 | B18 | 28.28 | 148 | B28 | 15.96 | 163 | ||
| A9 | 18 | 582 | 900 | B19 | 30.00 | 159 | B29 | 16.93 | 174 | ||
| A10 | 20 | 648 | 1000 | B10 | 31.62 | 167 | B20 | 17.84 | 184 | ||
| Specimens | Standard Primitives | Compound Objects | Body Objects | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  | 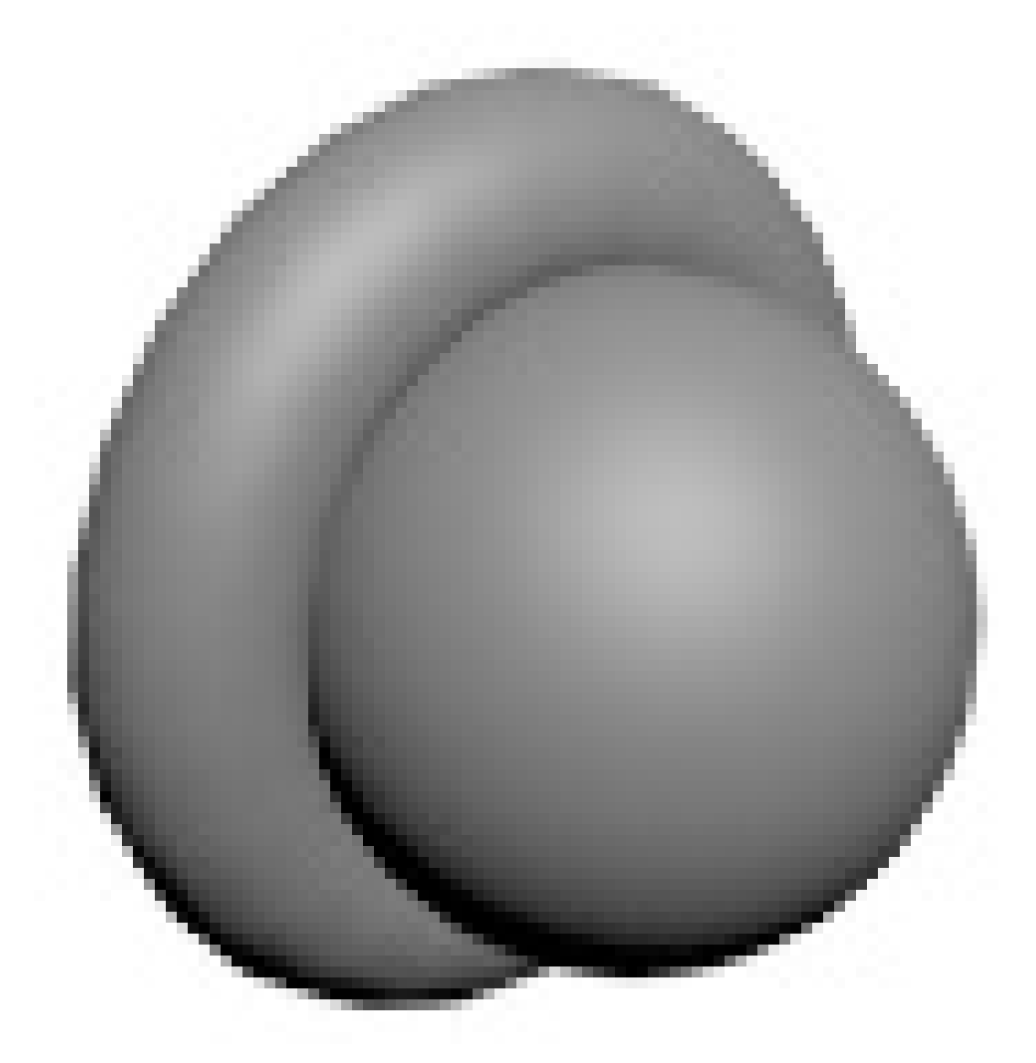 |  | 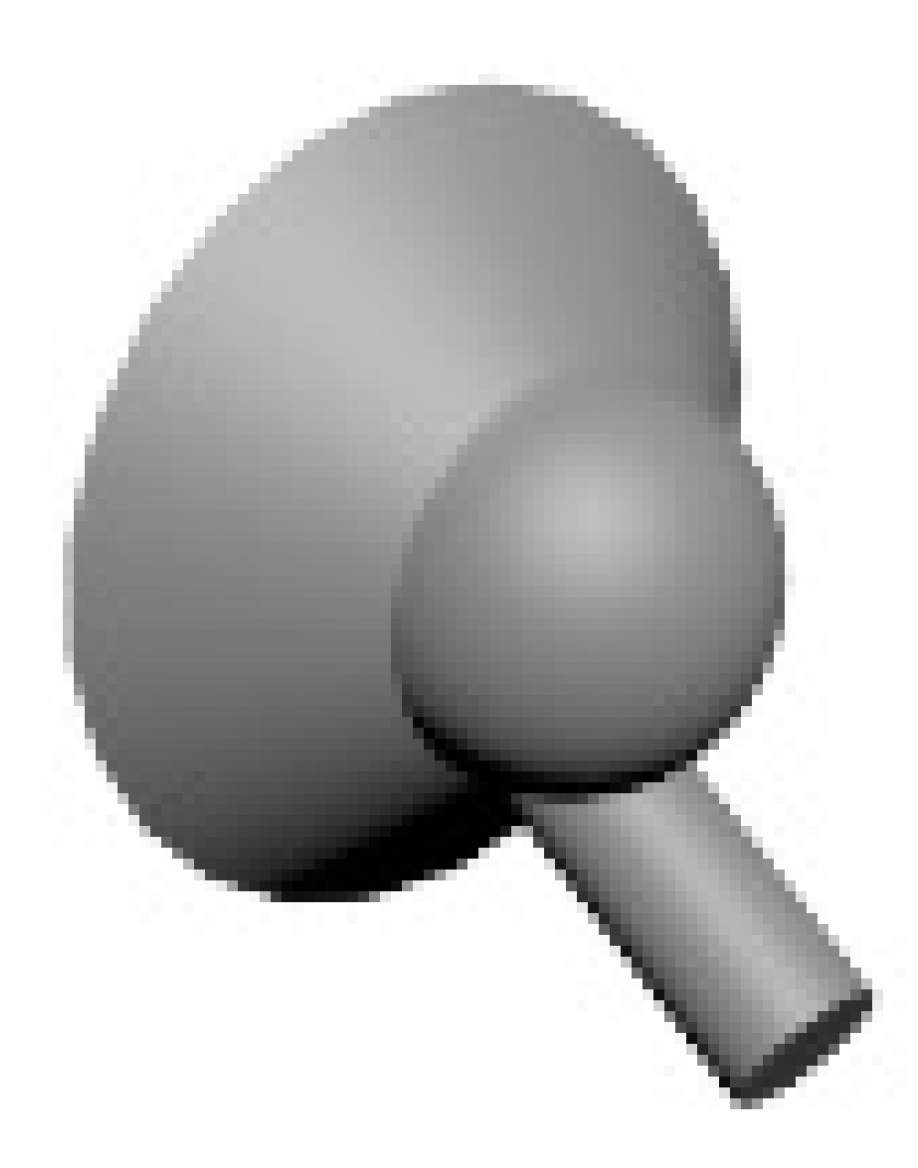 |  |  |  | 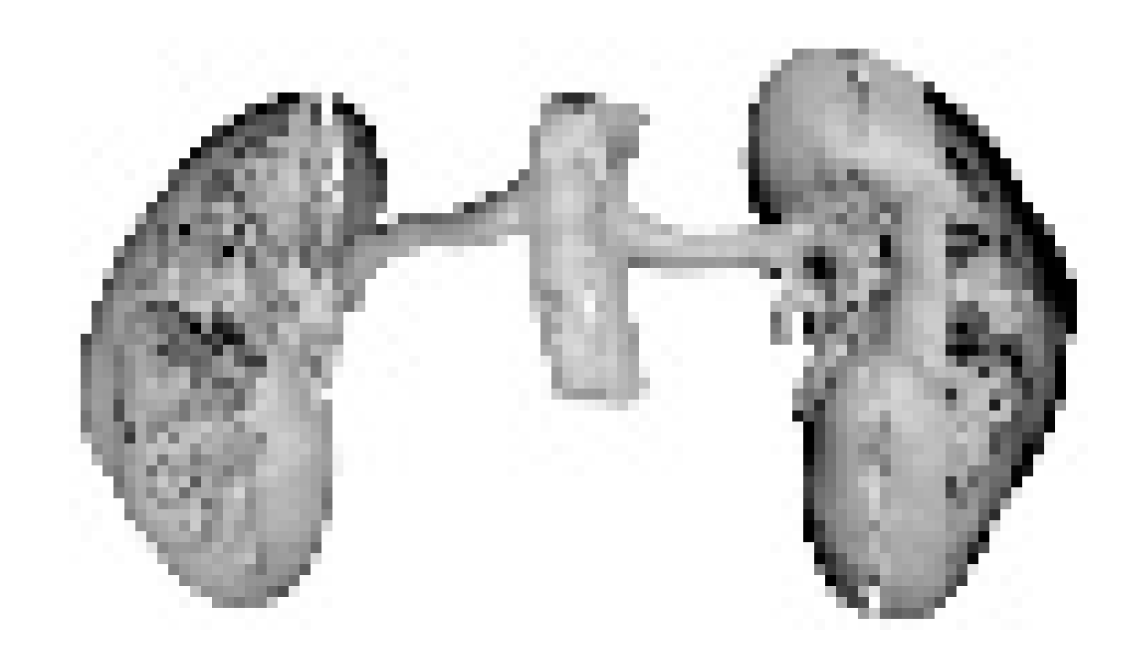 | |
| T1 (min) | 630 | 628 | 554 | 743 | 534 | 656 | 547 | 384 | 576 | 337 |
| T2 (min) | 223 | 434 | 320 | 602 | 183 | 508 | 316 | 377 | 382 | 251 |
| (T1-T2)/T1 (%) | 64.6 | 30.9 | 42.2 | 19.0 | 65.7 | 22.6 | 42.2 | 1.8 | 33.7 | 25.5 |
| Adhesives | Width of Bonded Gap (μm) | Tensile Test | Flexural Test | Chromatic Aberration (ΔE, NBS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Modulus (MPa) | Fracture Location | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Flexural Modulus (MPa) | |||
| Vegetable glue | 52 | 1.43 | 317.58 | A | 0.53 | 430.52 | 5.52 |
| Sodium silicate | 22.7 | 1.16 | 209.53 | A | 0.68 | 477.92 | 3.98 |
| Double component epoxy resin | 24.7 | 4.64 | 598.55 | A | 8.48 | 1786.74 | 1.78 |
| α-cyanoacrylate | 15.3 | 6.58 | 786.33 | N | 13.57 | 2052.22 | 1.57 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, C. Realization of Rapid Large-Size 3D Printing Based on Full-Color Powder-Based 3DP Technique. Molecules 2020, 25, 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092037
Chen G, Wang X, Chen H, Chen C. Realization of Rapid Large-Size 3D Printing Based on Full-Color Powder-Based 3DP Technique. Molecules. 2020; 25(9):2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092037
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Guangxue, Xiaochun Wang, Haozhi Chen, and Chen Chen. 2020. "Realization of Rapid Large-Size 3D Printing Based on Full-Color Powder-Based 3DP Technique" Molecules 25, no. 9: 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092037
APA StyleChen, G., Wang, X., Chen, H., & Chen, C. (2020). Realization of Rapid Large-Size 3D Printing Based on Full-Color Powder-Based 3DP Technique. Molecules, 25(9), 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092037







