Recent Advances in the Stereoselective Total Synthesis of Natural Pyranones Having Long Side Chains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Stereoselective Total Syntheses
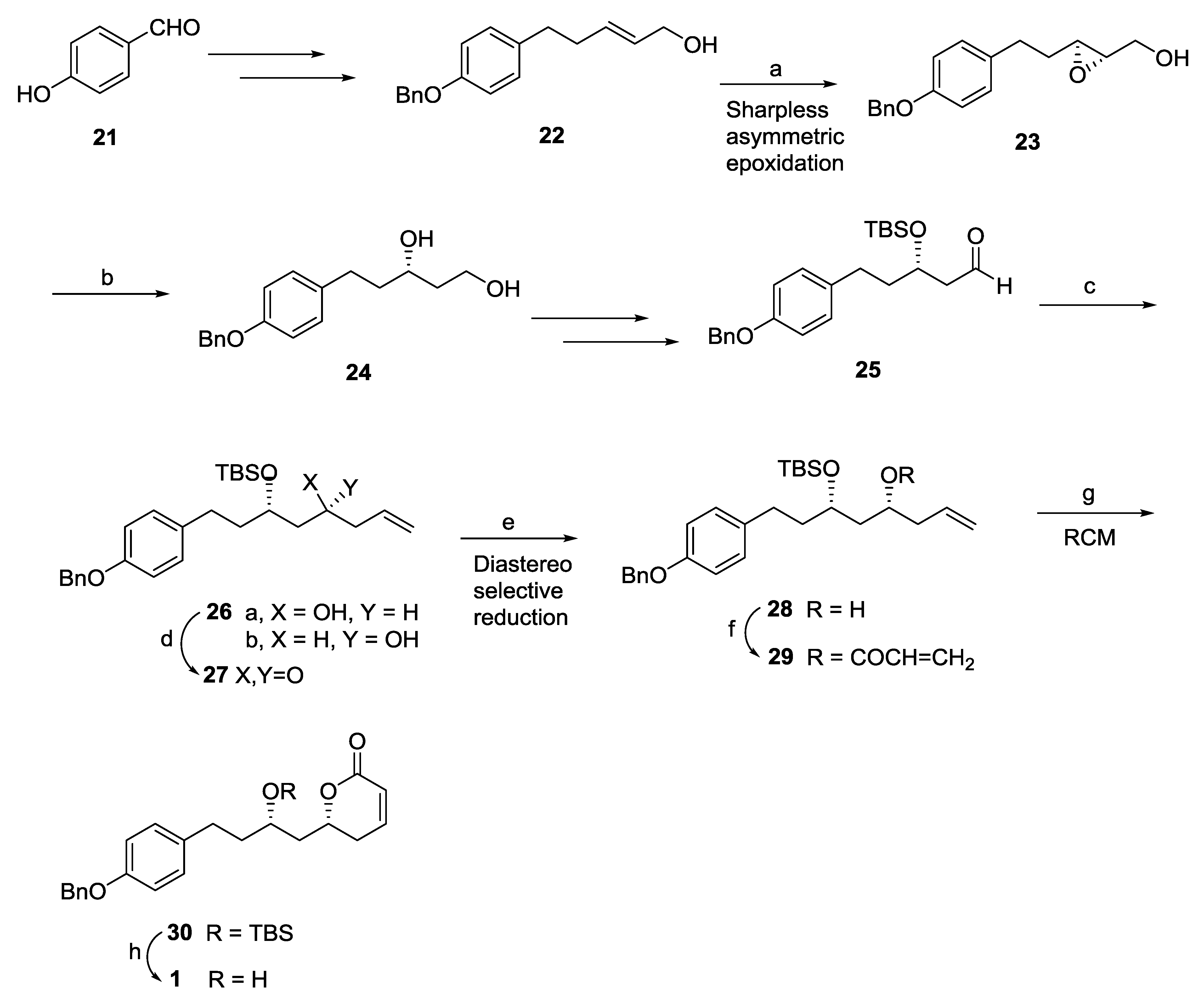
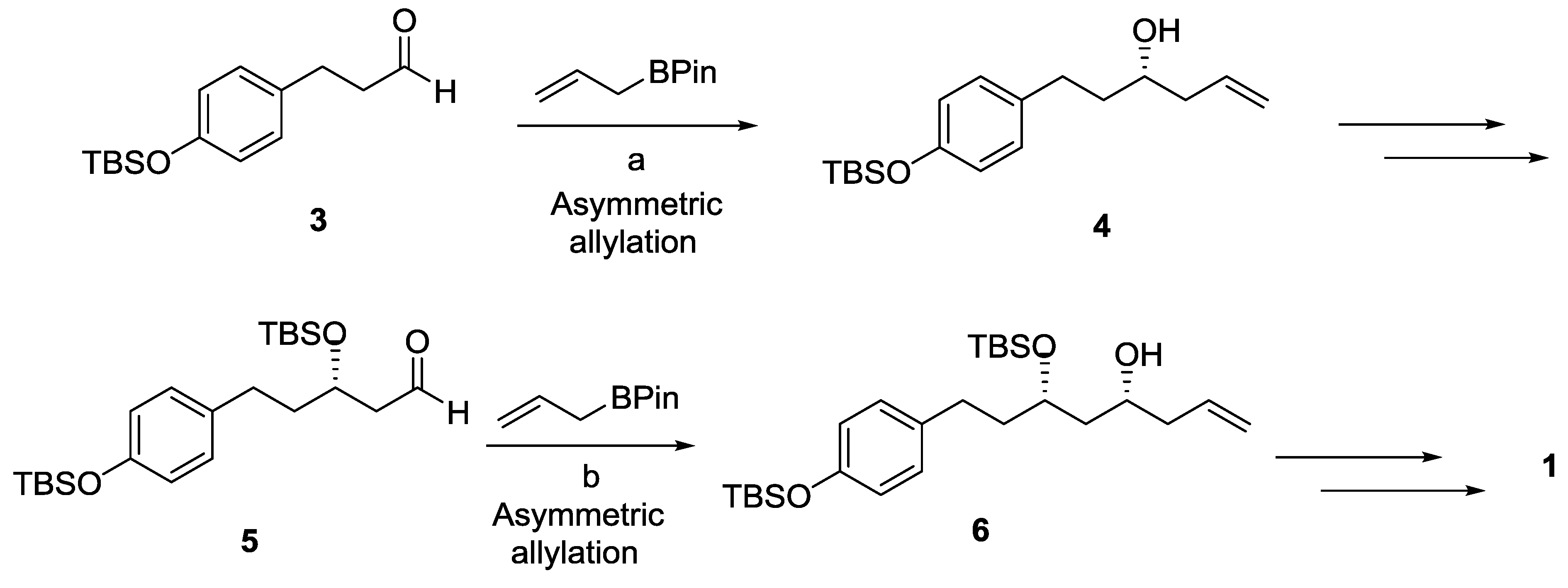
2.1. Dodoneine

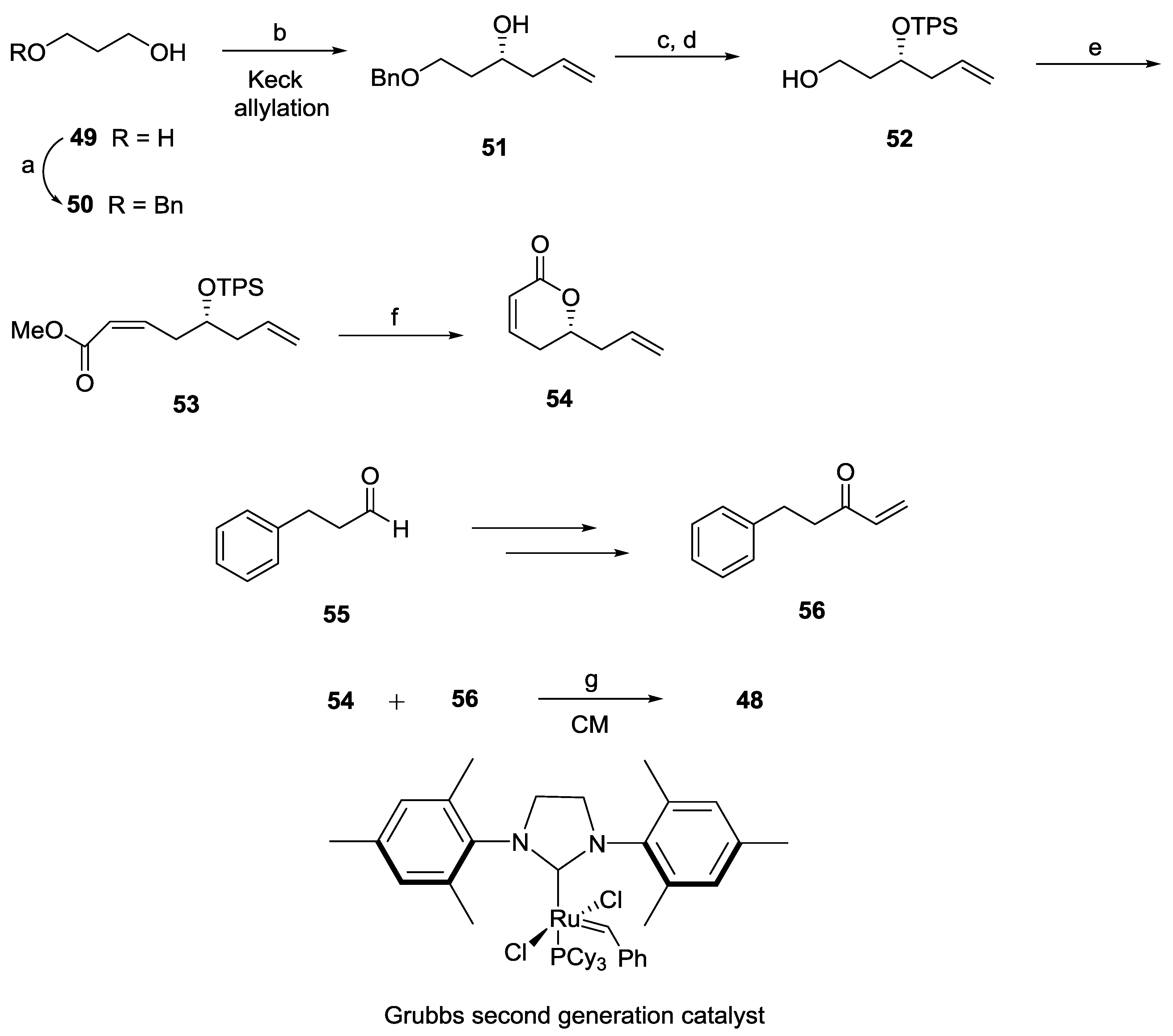
2.2. Rugulactone

2.3. Synargentolide A

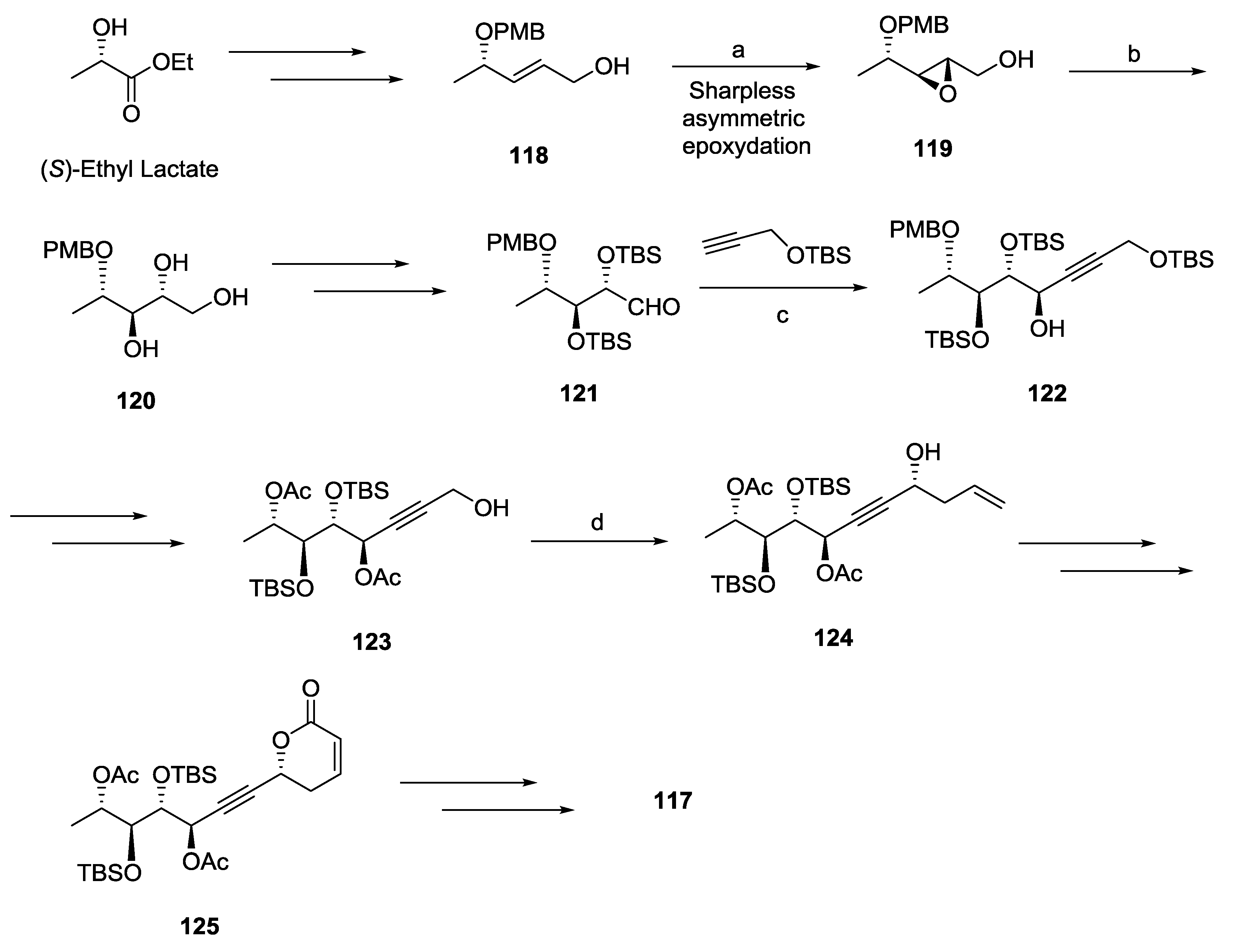
2.4. Synargentolide B

2.5. Synrotolide

2.6. Lippialactone

2.7. Spicigerolide

2.8. Cryptofolione

2.9. Passifloricin A

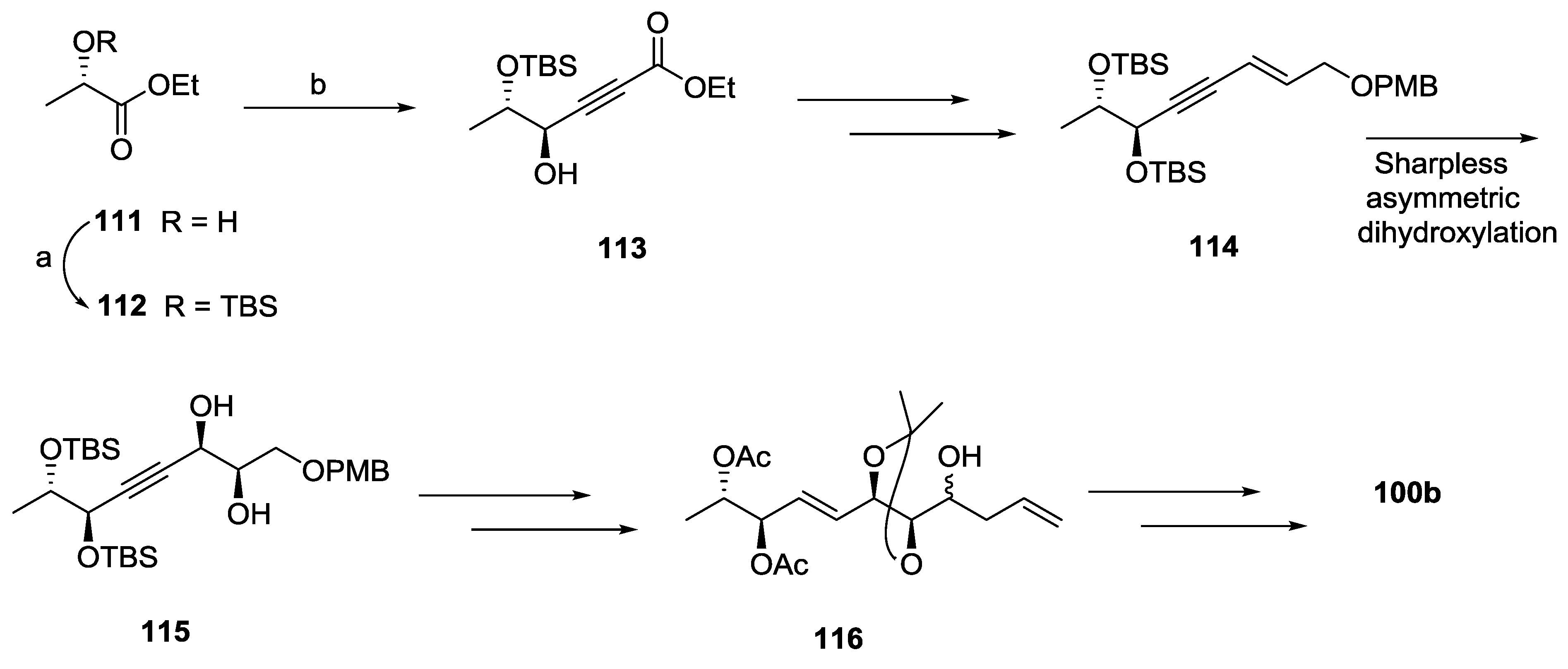
2.10. Strictifolione

3. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HF | Hydrofluoric acid | TsCl | Para-toluene sulfonyl chloride |
| TBS | tert-Butyldimethylsilyl | TESCl | Triethylsilyl Chloride |
| DIBAL-H | Diisobutylaluminium hydride | DET | N,N-Diethyltryptamine |
| DIPEA | N,N-Diisopropylethylamine | (S)-CBS | (S)-5,5-Diphenyl-2-methyl-3,4-propano-1,3,2-oxazaborolidine |
| PTSA | para-toluenesulfonic acid | NIS | N-Bromo scuccinimide |
| PPTS | Pyridinium p-toluenesulfonate | TBSOTf | Trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate |
| DIPT | Diisopropyltartrate | t-BuOK | Potassium tert-butoxide |
| TBHP | tert-Butylhydroperoxide | AcOH | Acetic acid |
| DMP | 2,2-Dimethoxypropane | LiAlH4 | Lithium aluminium hydride |
| TBSCl | tert-Butyldimethylsilyl chloride | Et3N | Triethyl amine |
| IBX | 2-Iodoxybenzoic acid | t-BuOH | tert-Butyl alcohol |
| BINOL | 1,1′-Bi-2-naphthol | NaBH4 | Sodium borohydride |
| Ti(iPrO)4 | Titanium isopropoxide | BnBr | Benzyl Bromide |
| PMB | 4-Methoxybenzyl | THF | Tetrahydrofuran |
| KHMDS | Potassium hexamethyldisilazide | CHCl3 | Chloroform |
| NF-kB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells | DMAP | 4-Dimethylaminopyridine |
| TBAI | tert-Butylammonium iodide | NaH | Sodium hydride |
| TBDPSCl | tert-Butyldiphenylsilyl chloride | NH4Cl | Ammonium chloride |
| NaHMDS | Sodium bis (trimethylsilyl) amide | NaIO4 | Sodium periodate |
| NADPH | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate | Ac | Acetyl |
| THP | Tetrahydropyran | TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
| TEMPO | (2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl)oxyl | MOMCl | Methoxymethyl chloride |
| TPP | Thiamine pyrophosphate |
References
- McGlacken, G.P.; Fairlamb, I.J.S. 2-Pyrone natural products and mimetics: Isolation, characterisation and biological activity. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouedraogo, M.; Carreyre, H.; Vandebrouck, C.; Bescond, J.; Raymond, G.; Guissou, I.-P.; Cognard, C.; Becq, F.; Potreau, D.; Cousson, A.; et al. Structure Elucidation of a Dihydropyranone from Tapinanthus dodoneifolius. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 2006–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meragelman, T.L.; Scudiero, D.A.; Davis, R.E.; Staudt, L.M.; McCloud, T.G.; Cardellina, J.H.; Shoemaker, R.H. Inhibitors of the NF-κB Activation Pathway from Cryptocarya rugulosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echeverri, F.; Arango, V.; Quiñones, W.; Torres, F.; Escobar, G.; Rosero, Y.; Archbold, R. Passifloricins, polyketides α-pyrones from Passiflora foetida resin. Phytochemistry 2001, 56, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereda-Miranda, R.; Fragoso-Serrano, M.; Cerda-García-Rojas, C.M. Application of molecular mechanics in the total stereochemical elucidation of spicigerolide, a cytotoxic 6-tetraacetyloxyheptenyl-5,6-dihydro-α-pyrone from Hyptis spicigera. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaplar, P.; Yılmazer, Ö.; Çağır, A. 6-Bicycloaryl substituted (S)- and (R)-5,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-ones: Asymmetric synthesis, and anti-proliferative properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, A.; Agrawal, V.; Shandilya, A.; Bisaria, V.S.; Sundar, D. Non-nucleosidic inhibition of Herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase: Mechanistic insights into the anti-herpetic mode of action of herbal drug withaferin A. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USUI, T. Actin- and Microtubule-Targeting Bioprobes: Their Binding Sites and Inhibitory Mechanisms. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McCracken, S.T.; Kaiser, M.; Boshoff, H.I.; Boyd, P.D.W.; Copp, B.R. Synthesis and antimalarial and antituberculosis activities of a series of natural and unnatural 4-methoxy-6-styryl-pyran-2-ones, dihydro analogues and photo-dimers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassa, T.; Kato, H.; Kajiura, H. Isolation and structure of pycnophorin, a novel diterpene α-pyrone with antimicrobial activity, produced by phytopathogenic macrophoma kuwatsukai. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986, 27, 2121–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalesse, M.; Christmann, M.; Bhatt, U.; Quitschalle, M.; Claus, E.; Saeed, A.; Burzlaff, A.; Kasper, C.; Haustedt, L.O.; Hofer, E.; et al. The Chemistry and Biology of Ratjadone. Chem. Bio. Chem. 2001, 2, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, J.A.; Carda, M.; Murga, J.; Falomir, E. Stereoselective syntheses of naturally occurring 5,6-dihydropyran-2-ones. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 2929–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucard, V.; Broustal, G.; Campagne, J.M. Synthetic Approaches to α,β-Unsaturated δ-Lactones and Lactols. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 2007, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, K.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Synthesis of 5,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-ones (microreview). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2016, 52, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson Cardona , G.; Winston Quiñones, F.; Fernando Echeverri, L. Leishmanicidal Activity of Passifloricin A and Derivatives. Molecules 2004, 9, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreyre, H.; Coustard, J.-M.; Carré, G.; Vandebrouck, C.; Bescond, J.; Ouédraogo, M.; Marrot, J.; Vullo, D.; Supuran, C.T.; Thibaudeau, S. Natural product hybrid and its superacid synthesized analogues: Dodoneine and its derivatives show selective inhibition of carbonic anhydrase isoforms I, III, XIII and XIV. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3790–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuccarese, M.F.; Wang, Y.; Beuning, P.J.; O’Doherty, G.A. Cryptocaryol Structure–Activity Relationship Study of Cancer Cell Cytotoxicity and Ability to Stabilize PDCD4. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubbs, R.H. Olefin-Metathesis Catalysts for the Preparation of Molecules and Materials (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3760–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreyre, H.; Carré, G.; Ouedraogo, M.; Vandebrouck, C.; Bescond, J.; Supuran, C.T.; Thibaudeau, S. Bioactive Natural Product and Superacid Chemistry for Lead Compound Identification: A Case Study of Selective hCA III and L-Type Ca2+ Current Inhibitors for Hypotensive Agent Discovery. Molecules 2017, 22, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carré, G.; Carreyre, H.; Ouedraogo, M.; Becq, F.; Bois, P.; Thibaudeau, S.; Vandebrouck, C.; Bescond, J. The hypotensive agent dodoneine inhibits L-type Ca2+ current with negative inotropic effect on rat heart. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 728, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Bercedo, P.; Falomir, E.; Murga, J.; Carda, M.; Marco, J.A. Stereoselective Synthesis of the Naturally Occurring 2-Pyranone Dodoneine. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 2008, 4015–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srihari, P.; Rajendar, G.; Srinivasa Rao, R.; Yadav, J.S. First stereoselective total synthesis of (+)-dodoneine. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 5590–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittoo, A.; Bellosta, V.; Cossy, J. Total synthesis of (+)-dodoneine. Synlett 2008, 2459–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Suneel, K.; Satyalakshmi, G.; Kumar, D.N. Stereoselective total synthesis of dodoneine. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2009, 20, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuppalapati, S.V.N.; Putapatri, S.R.; Kantevari, S. A formal enantioselective synthesis of (+)-dodoneine via cyclic sulfate methodology. Arkivoc 2009, 2009, 217–226. [Google Scholar]
- Sabitha, G.; Bhaskar, V.; Reddy, S.S.S.; Yadav, J.S. Total synthesis of (+)-dodoneine and its 6-epimer. Synthesis 2009, 2, 3285–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauniyar, V.; Hall, D.G. Rationally Improved Chiral Brønsted Acid for Catalytic Enantioselective Allylboration of Aldehydes with an Expanded Reagent Scope. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 4236–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnababu, B.; Reddy, S.P.; Rao, C.B.; Rajesh, K.; Venkateswarlu, Y. Stereoselective Total Synthesis of Dodoneine. Helv. Chim. Acta 2010, 93, 1960–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allais, F.; Ducrot, P.H. Stereoselective total synthesis of (+)-dodoneine. Synthesis 2010, 1649–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, G.E.; Covel, J.A.; Schiff, T.; Yu, T. Pyran Annulation: Asymmetric Synthesis of 2,6-Disubstituted-4-methylene Tetrahydropyrans. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimmins, M.T.; Chaudhary, K. Titanium Enolates of Thiazolidinethione Chiral Auxiliaries: Versatile Tools for Asymmetric Aldol Additions. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 775–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, K. Highly Selective Synthesis of Z-Unsaturated Esters by Using New Horner−Emmons Reagents, Ethyl (Diarylphosphono)acetates. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 1934–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsbury, J.S.; Harrity, J.P.A.; Bonitatebus, P.J.; Hoveyda, A.H. A Recyclable Ru-Based Metathesis Catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Still, W.C.; Gennari, C. Direct synthesis of Z-unsaturated esters. A useful modification of the horner-emmons olefination. Tetrahedron Lett. 1983, 24, 4405–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuki, T.; Sharpless, K.B. The first practical method for asymmetric epoxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 5974–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.C.; VanNieuwenhze, M.S.; Sharpless, K.B. Catalytic Asymmetric Dihydroxylation. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 2483–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaus, S.E.; Brandes, B.D.; Larrow, J.F.; Tokunaga, M.; Hansen, K.B.; Gould, A.E.; Furrow, M.E.; Jacobsen, E.N. Highly Selective Hydrolytic Kinetic Resolution of Terminal Epoxides Catalyzed by Chiral (salen)CoIII Complexes. Practical Synthesis of Enantioenriched Terminal Epoxides and 1,2-Diols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.K.; Shekhar, V.; Reddy, T.S.; Reddy, S.P.; Venkateswarlu, Y. Stereoselective first total synthesis of (R)-rugulactone. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2009, 20, 2315–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, D.K.; Das, P.P.; Sai Reddy, D.; Yadav, J.S. First total syntheses and absolute configuration of rugulactone and 6(R)-(4′-oxopent-2′-enyl)-5,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-one. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 5941–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrikos-Ergas, T.; Giannopoulos, V.; Smonou, I. An efficient chemoenzymatic approach towards the synthesis of rugulactone. Molecules 2018, 23, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.K.; Shekhar, V.; Prabhakar, P.; Chinna Babu, B.; Siddhardha, B.; Murthy, U.S.N.; Venkateswarlu, Y. Stereoselective synthesis and biological evaluation of (R)-rugulactone, (6R)-((4R)-hydroxy-6-phenyl-hex-2-enyl)-5,6-dihydro-pyran-2-one and its 4S epimer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 4657–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddipalli, G.; Venkataiah, M.; Fadnavis, N.W. Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of both enantiomers of rugulactone. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2010, 21, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allais, F.; Aouhansou, M.; Majira, A.; Ducrot, P.H. Asymmetric total synthesis of rugulactone, an α-pyrone from Cryptocarya rugulosa. Synthesis 2010, 2787–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Srinivas, Y.; Sudhakar, C.; Raghavendar Reddy, P. Stereoselective Total Synthesis of Rugulactone. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2011, 94, 1290–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, A.; Saikia, P.P.; Saikia, B.; Chaturvedi, D.; Barua, N.C. An improved stereoselective total synthesis of (R)-rugulactone. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 5133–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böse, D.; Fernández, E.; Pietruszka, J. Stereoselective Synthesis of Both Enantiomers of Rugulactone. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 3463–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, D.B.; Kanth, B.S.; Satyakumar, A.; Kamble, V.T.; Das, B. Simple Stereoselective Synthesis of Unsaturated Lactone Intermediates and Their Conversion into Natural Dihydropyranones and Their Enantiomers. Lett. Org. Chem. 2013, 10, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.; Singh, R. A Facile Stereoselective Total Synthesis of (R)-Rugulactone. ISRN Org. Chem. 2014, 2014, 767954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kii, S.; Maruoka, K. Practical approach for catalytic asymmetric allylation of aldehydes with a chiral bidentate titanium(IV) complex. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 1935–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cros, F.; Pelotier, B.; Piva, O. Regioselective Tandem Ring Closing/Cross Metathesis of 1,5-Hexadien-3-ol Derivatives: Application to the Total Synthesis of Rugulactone. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 2010, 5063–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collett, L.A.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Rivett, D.E.A. 5,6-Dihydro-α-pyrones from Syncolostemon argenteus. Phytochemistry 1998, 48, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fortanet, J.; Murga, J.; Carda, M.; Marco, J.A. Stereoselective synthesis of the published structure of synargentolide A and of one of its stereoisomers. Arkivoc 2005, 2005, 175–188. [Google Scholar]
- Sabitha, G.; Gopal, P.; Reddy, C.N.; Yadav, J.S. Stereoselective synthesis of the published structure of synargentolide A and of one of its stereoisomers. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 6298–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, A.; Balakrishna, M.; Reddy, P.V.; Faazil, S. An efficient synthesis of synargentolide A from d-mannitol. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2010, 21, 2517–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.R.; Penchalaiah, K. Stereoselective total synthesis of (+)-synargentolide A. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2010, 21, 2853–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Balasubramanyam, P.; Veeranjaneyulu, B.; Chinna Reddy, G. An Efficient Stereoselective Total Synthesis of Synargentolide A and Its Epimer. Helv. Chim. Acta 2011, 94, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabitha, G.; Reddy, S.S.S.; Raju, A.; Yadav, J.S. A concise stereoselective total synthesis of synargentolide a from 3,4,6-Tri-o-acetyl-d-glucal. Synthesis 2011, 1279–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.S.; Thirupathaiah, B.; Singh, V.K.; Ravishashidhar, V. Total synthesis of (+)-synargentolide A. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2012, 23, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, D.; Reichenbach, L.F. Asymmetric synthesis of synargentolide A and its 3-epimer using the RAMP-hydrazone methodology. Synthesis 2013, 45, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-González, F.; Suárez-Ortiz, G.A.; Fragoso-Serrano, M.; Cerda-García-Rojas, C.M.; Pereda-Miranda, R. DFT 1H–1H coupling constants in the conformational analysis and stereoisomeric differentiation of 6-heptenyl-2H-pyran-2-ones: Configurational reassignment of synargentolide A. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2015, 53, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.R.; Gutala, P. Total Synthesis and Determination of the Absolute Configuration of 5,6-Dihydro-α-pyrone Natural Product Synargentolide B. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 3313–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereda-Miranda, R.; García, M.; Delgado, G. Structure and stereochemistry of four α-pyrones from Hyptis oblongifolia. Phytochemistry 1990, 29, 2971–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabitha, G.; Shankaraiah, K.; Yadav, J.S. Tandem Ring-Closing/Cross-Metathesis Approach for the Synthesis of Synargentolide B and Its Stereoisomers. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2013, 4870–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konda, S.; Bhaskar, K.; Nagarapu, L.; Akkewar, D.M. A convenient approach to total synthesis of synargentolide-B from l-ascorbic acid and d-ribose. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 3087–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Du, Y. Chiron approach for the total synthesis of (+)-synargentolide B. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 6443–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Qiao, J.; Liu, Y.; He, P.; Du, Y. Stereoselective synthesis of (−)-synargentolide B. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaraswamy, G.; Raghu, N.; Jayaprakash, N.; Ankamma, K. A concise diastereoselective synthesis of 5′-epi synargentolide-B. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 5472–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramulu, U.; Rajaram, S.; Ramesh, D.; Suresh Babu, K. Total synthesis of synargentolide B. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2015, 26, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies Coleman, M.T.; English, R.B.; Rivett, D.E.A. Synrotolide, an α-pyrone from Syncolostemon rotundifolius. Phytochemistry 1987, 26, 1497–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srihari, P.; Prem Kumar, B.; Subbarayudu, K.; Yadav, J.S. A convergent approach for the total synthesis of (−)-synrotolide diacetate. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 6977–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, P.R.; Reddy, P.S. Stereoselective total synthesis of (−)-synrotolide diacetate from d-ribose. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 3995–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabitha, G.; Rao, A.S.; Sandeep, A.; Yadav, J.S. The First Stereoselective Total Synthesis of (–)-Synrotolide. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 2014, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabitha, G.; Rao, A.S.; Sandeep, A.; Latha, B.M.; Reddy, D.V. Total synthesis of (−)-synrotolide and the evaluation of its antiproliferative activity. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2014, 25, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludere, M.T.; van Ree, T.; Vleggaar, R. Isolation and relative stereochemistry of lippialactone, a new antimalarial compound from Lippia javanica. Fitoterapia 2013, 86, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, P.R.; Nomula, R.; Kunde, R. First total synthesis of lippialactone and its C9 epimer. Synthesis 2014, 46, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowravaram, S.; Karra, P.; Sudina, P. Stereoselective total synthesis of lippialactone. Reports Org. Chem. 2015, 5, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Falomir, E.; Murga, J.; Carda, M.; Marco, J.A. Stereoselective synthesis of spicigerolide. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falomir, E.; Murga, J.; Ruiz, P.; Carda, M.; Marco, J.A.; Pereda-Miranda, R.; Fragoso-Serrano, M.; Cerda-García-Rojas, C.M. Stereoselective Synthesis and Determination of the Cytotoxic Properties of Spicigerolide and Three of Its Stereoisomers. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 5672–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georges, Y.; Ariza, X.; Garcia, J. Stereoselective Synthesis of (−)-Spicigerolide. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabitha, G.; Reddy, C.N.; Raju, A.; Yadav, J.S. Stereoselective total synthesis of the cytotoxic lactone (−)-spicigerolide. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2011, 22, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, N.K.; Carreira, E.M. A Simple, Mild, Catalytic, Enantioselective Addition of Terminal Acetylenes to Aldehydes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 9687–9688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, A.; Duthaler, R.O.; Marti, R.; Rihs, G.; Rothe-Streit, P.; Schwarzenbach, F. Enantioselective syntheses with titanium carbohydrate complexes. Part 7. Enantioselective allyltitanation of aldehydes with cyclopentadienyldialkoxyallyltitanium complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 2321–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, E.J.; Helal, C.J. Reduction of Carbonyl Compounds with Chiral Oxazaborolidine Catalysts: A New Paradigm for Enantioselective Catalysis and a Powerful New Synthetic Method. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 1986–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba Reddy, B.V.; Veerabhadra Reddy, V.; Praneeth, K. Stereoselective total synthesis of (+)-boronolide, (+)-anamarine, 8-epi-spicegerolide. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 1398–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehlapelo, B.M.; Drewes, S.E.; Scott-Shaw, R. A 6-substituted 5,6-dihydro-α-pyrone from two species of Cryptocarya. Phytochemistry 1994, 37, 847–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalheiro, A.J.; Yoshida, M. 6-[ω-arylalkenyl]-5,6-dihydro-α-pyrones from Cryptocarya moschata (Lauraceae). Phytochemistry 2000, 53, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, Y.; Aikawa, K.; Irie, R.; Katsuki, T. Asymmetric synthesis of cryptofolione and determination of its absolute configuration. Heterocycles 2005, 66, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabitha, G.; Reddy, S.S.S.; Reddy, D.V.; Bhaskar, V.; Yadav, J.S. Stereoselective approaches to the total synthesis of (6R,4′S, 6′R)-cryptofolione. Synthesis 2010, 3453–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Nagendra, S.; Ravindra Reddy, C. Stereoselective total synthesis of (+)-cryptofolione and (+)-goniothalamin. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2011, 22, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.N.; Meshram, H.M. Total synthesis of (−)-diospongin A and (+)-cryptofolione via asymmetric aldol reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.; Ganganna, B.; Bhunia, D. First stereoselective total synthesis of cryptomoscatone D2 and syntheses of (5R,7S)-kurzilactone and (+)-cryptofolione by an asymmetric acetate aldol approach. Synthesis 2012, 44, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, N.; Yang, Q.; Huang, S.; Wang, X. A concise and straightforward approach to total synthesis of (+)-Strictifolione and formal synthesis of Cryptofolione via a unified strategy. Synth. Commun. 2019, 49, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagendra, S.; Krishna Reddy, V.; Das, B. Stereoselective Synthesis of the Non-Lactonic Portion of (Z)-Cryptofolione and Approaches towards Its Conversion to (Z)-Cryptofolione. Helv. Chim. Acta 2015, 98, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fortanet, J.; Murga, J.; Carda, M.; Marco, J.A. On the Structure of Passifloricin A: Asymmetric Synthesis of the δ-Lactones of (2Z,5S,7R,9S,11S)- and (2Z,5R,7R,9S,11S)-Tetrahydroxyhexacos-2-enoic Acid. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 1447–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murga, J.; García-Fortanet, J.; Carda, M.; Marco, J.A. Asymmetric synthesis of passifloricin A: A correction in structure. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 7909–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murga, J.; García-Fortanet, J.; Carda, M.; Marco, J.A. Stereoselective Synthesis of the Antiprotozoal Lactone Passifloricin A and Seven Isomers Thereof. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 7277–7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, D.P.; Moura-Letts, G.; Pohlman, M. Solution-Phase Mixture Synthesis with Fluorous Tagging En Route: Total Synthesis of an Eight-Member Stereoisomer Library of Passifloricins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2423–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.; Rambabu, C.; Reddy, A.S. Asymmetric synthesis of (+)-passifloricin A and its 6-epimer. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 4476–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabitha, G.; Prasad, M.N.; Shankaraiah, K.; Reddy, N.M.; Yadav, J.S. Convergent synthesis of passifloricin a via a prins cyclisation and olefin cross-metathesis approach. Synthesis 2010, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arundale, E.; Mikeska, L.A. The Olefin-Aldehyde Condensation. The Prins Reaction. Chem. Rev. 1952, 51, 505–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.R.; Veeranjaneyulu, B.; Nagendra, S.; Das, B. Stereoselective Total Synthesis of Passifloricin A. Helv. Chim. Acta 2013, 96, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliawaty, L.D.; Kitajima, M.; Takayama, H.; Achmad, S.A.; Aimi, N. A 6-substituted-5,6-dihydro-2-pyrone from Cryptocarya strictifolia. Phytochemistry 2000, 54, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabitha, G.; Fatima, N.; Gopal, P.; Reddy, C.N.; Yadav, J.S. Stereoselective total synthesis of (+)-strictifolione and (6R)-6-[(4R,6R)-4,6-dihydroxy-10-phenyldec-1-enyl]-5,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-one by Prins reaction and olefin cross-metathesis. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2009, 20, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Veeranjaneyulu, B.; Balasubramanyam, P.; Srilatha, M. Stereoselective total synthesis of (+)-strictifolione and (6R)-6[(E,4R,6R)-4,6-dihydro-10-phenyl-1-decenyl)-5,6-dihydro-2H-2-pyrone. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2010, 21, 2762–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Gupta, P. Hydrolytic kinetic resolution as an emerging tool in the synthesis of bioactive molecules. Synlett 2009, 1367–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Pandey, M.; Gupta, P.; Naidu, S.V.; Dhavale, D.D. Enantio- and Diastereocontrolled Total Synthesis of (+)-Strictifolione. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 2010, 6993–7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadigaonkar, S.; Koli, M.R.; Gamre, S.S.; Choudhary, M.K.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Sharma, A. A chemoenzymatic asymmetric synthesis of (+)-strictifolione. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2012, 23, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, S.; Venukadasula, P.K.M.; Hanson, P.R. An Efficient, Modular Approach for the Synthesis of (+)-Strictifolione and a Related Natural Product. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tang, S.; Xie, X.; Wang, X.; He, L.; Xu, K.; She, X. Concise Total Syntheses of (+)-Strictifolione and (6R)-6-[(4R,6R)-4,6-Dihydroxy-10-phenyldec-1-enyl]-5,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-one. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 8234–8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Laxminarayana, K.; Krishnaiah, M.; Kumar, D.N. Stereoselective total synthesis of a potent natural antifungal compound (6S)-5,6,dihydro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-6-phenyl hexyl]-2H-pyran-2-one. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 6396–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, D.B.; Kanth, B.S.; Srilatha, M.; Das, B. First stereoselective total synthesis of naturally occurring (6R)-6-(4-Oxopentyl)-5,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-one and Its (6S)-enantiomer. Synthesis 2012, 44, 469–473. [Google Scholar]
- Chinna Reddy, G.; Balasubramanyam, P.; Salvanna, N.; Sreenivasulu Reddy, T.; Das, B. The first stereoselective total synthesis of (Z)-cryptomoscatone D2, a natural G2 checkpoint inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 2415–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.R.; Lingaiah, M.; Das, B. Stereoselective Total Synthesis of psiAβ—A Sporogenic Psi Factor from Aspergillus nidulans 1. Synlett 2014, 25, 975–976. [Google Scholar]
- Raghavendar Reddy, P.; Das, B. Stereoselective Total Synthesis of Crassalactone A, a Natural Cytotoxic Styryl Lactone. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2015, 98, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

































© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avula, S.K.; Das, B.; Csuk, R.; Al-Rawahi, A.; Al-Harrasi, A. Recent Advances in the Stereoselective Total Synthesis of Natural Pyranones Having Long Side Chains. Molecules 2020, 25, 1905. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081905
Avula SK, Das B, Csuk R, Al-Rawahi A, Al-Harrasi A. Recent Advances in the Stereoselective Total Synthesis of Natural Pyranones Having Long Side Chains. Molecules. 2020; 25(8):1905. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081905
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvula, Satya Kumar, Biswanath Das, Rene Csuk, Ahmed Al-Rawahi, and Ahmed Al-Harrasi. 2020. "Recent Advances in the Stereoselective Total Synthesis of Natural Pyranones Having Long Side Chains" Molecules 25, no. 8: 1905. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081905
APA StyleAvula, S. K., Das, B., Csuk, R., Al-Rawahi, A., & Al-Harrasi, A. (2020). Recent Advances in the Stereoselective Total Synthesis of Natural Pyranones Having Long Side Chains. Molecules, 25(8), 1905. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081905







