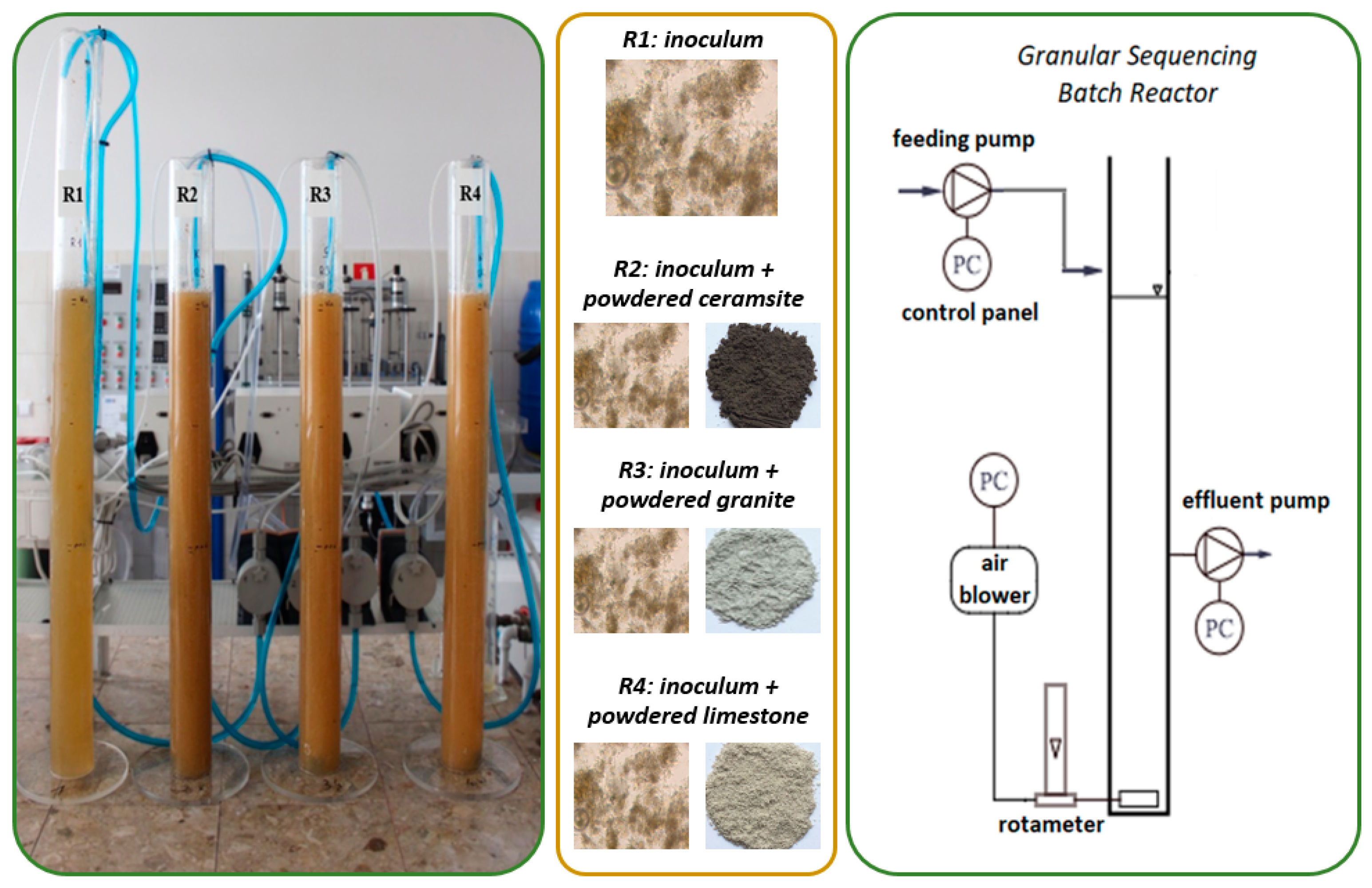
The Impact of Different Powdered Mineral Materials on Selected Properties of Aerobic Granular Sludge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
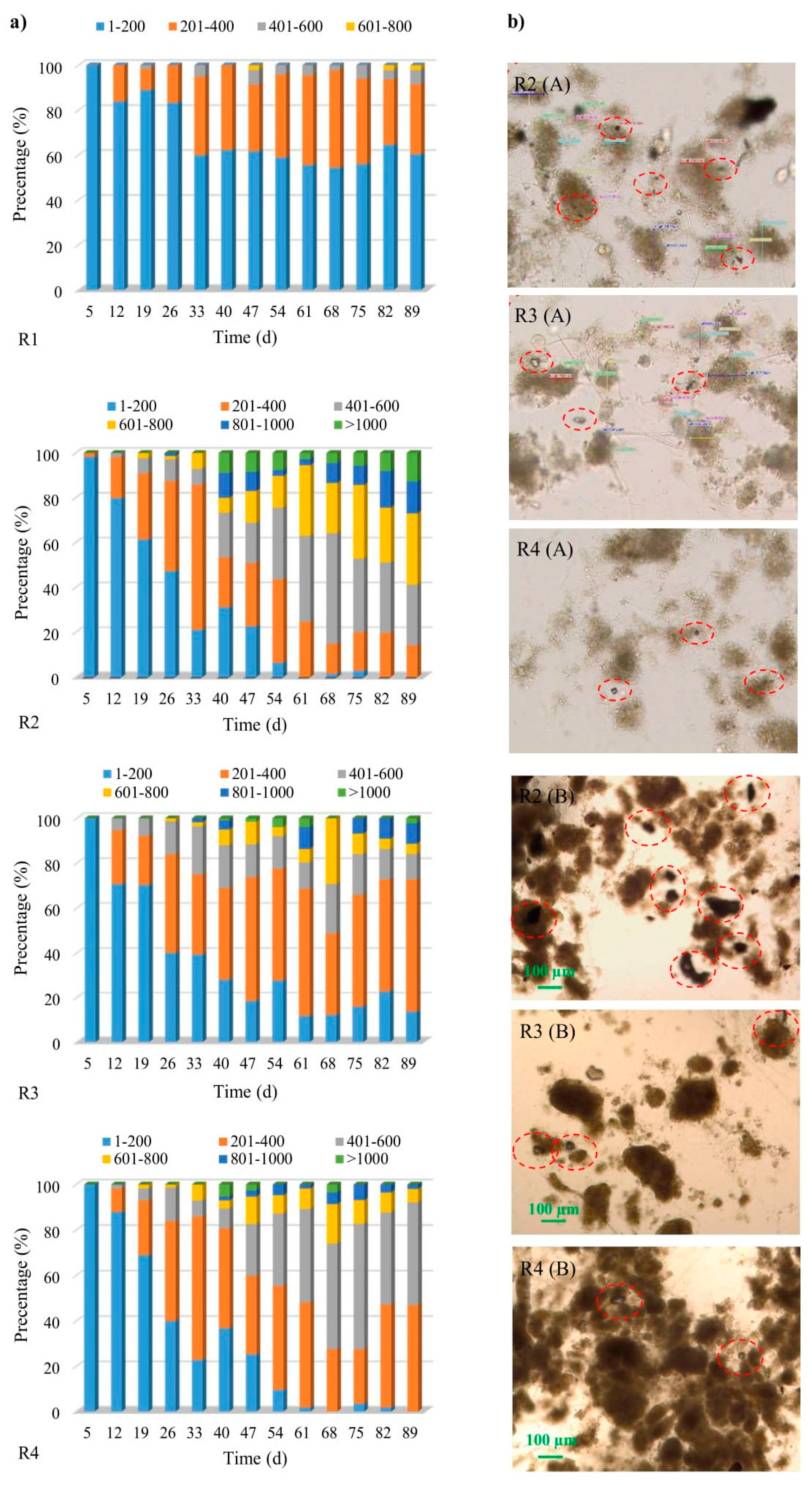
2.1. Selected Physical Properties of Biomass
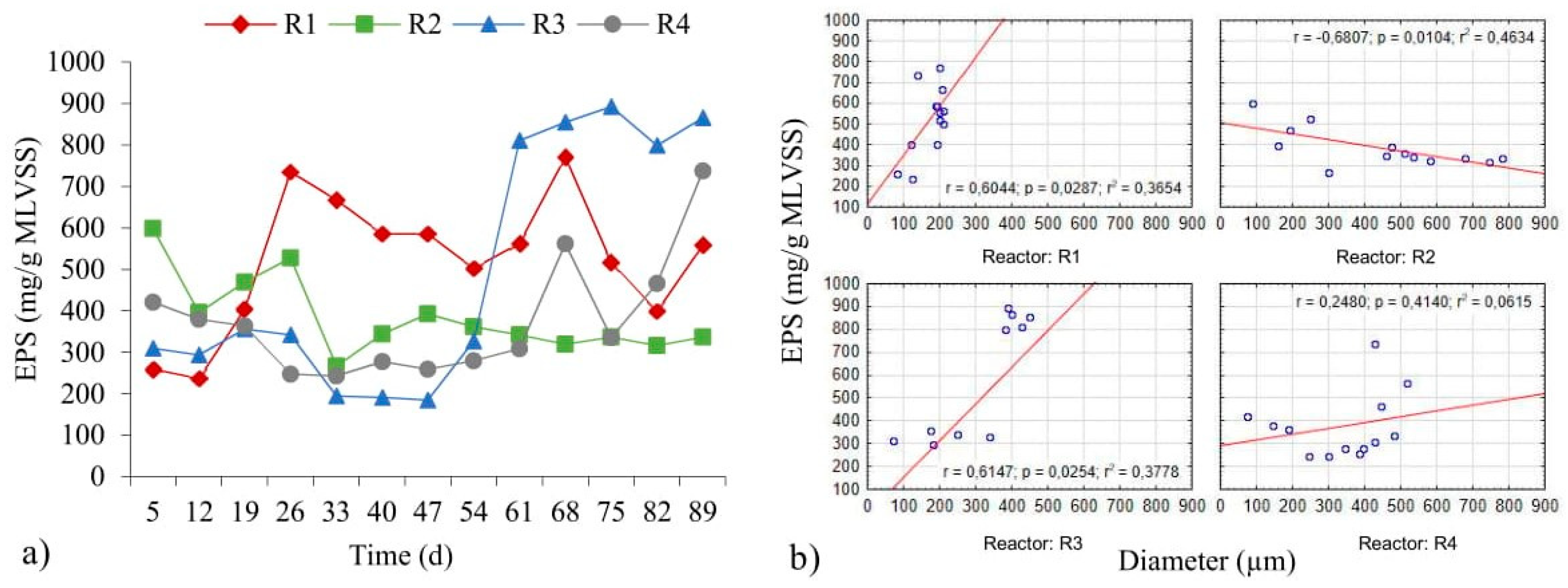
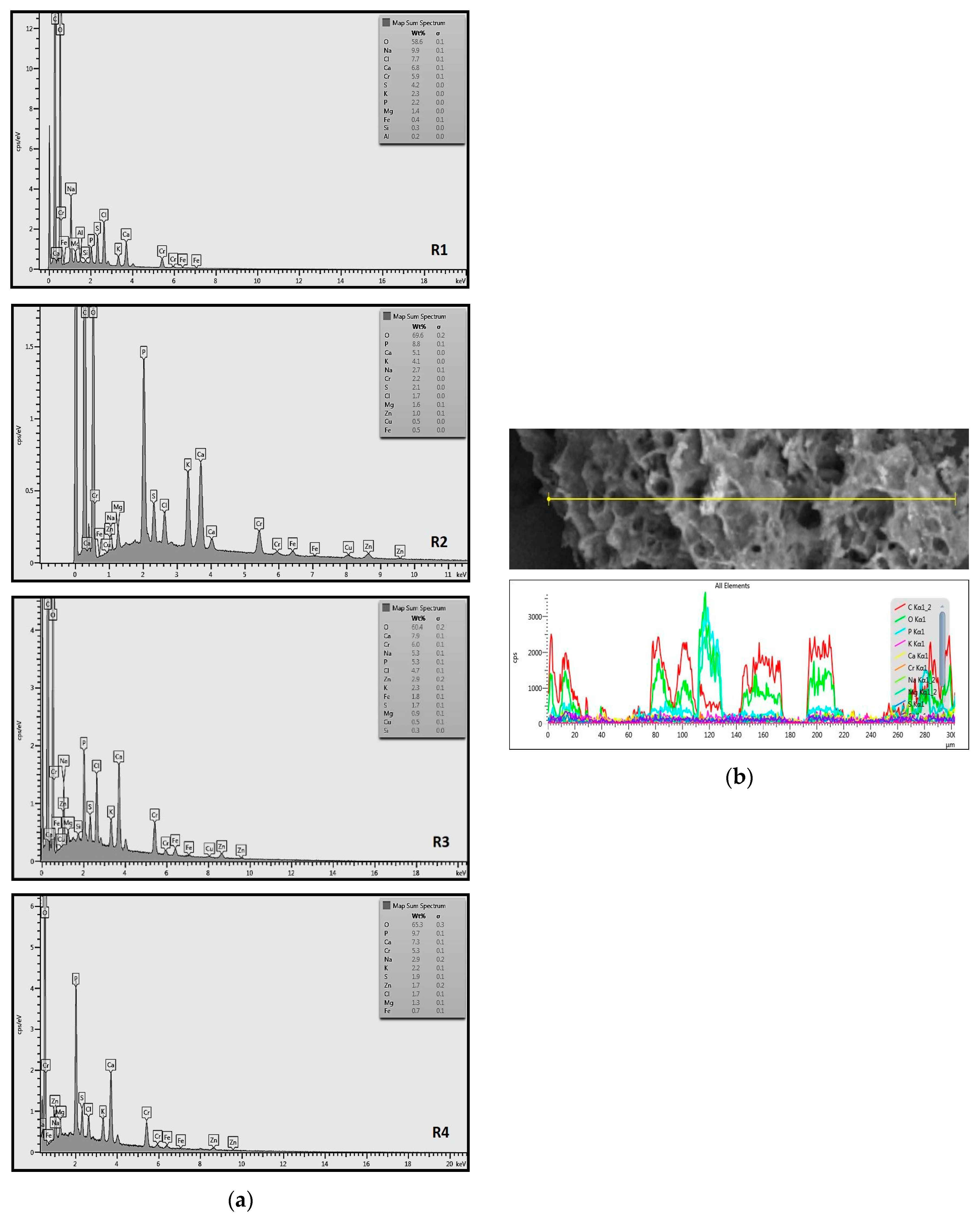
2.2. Selected Chemical Properties of Biomass
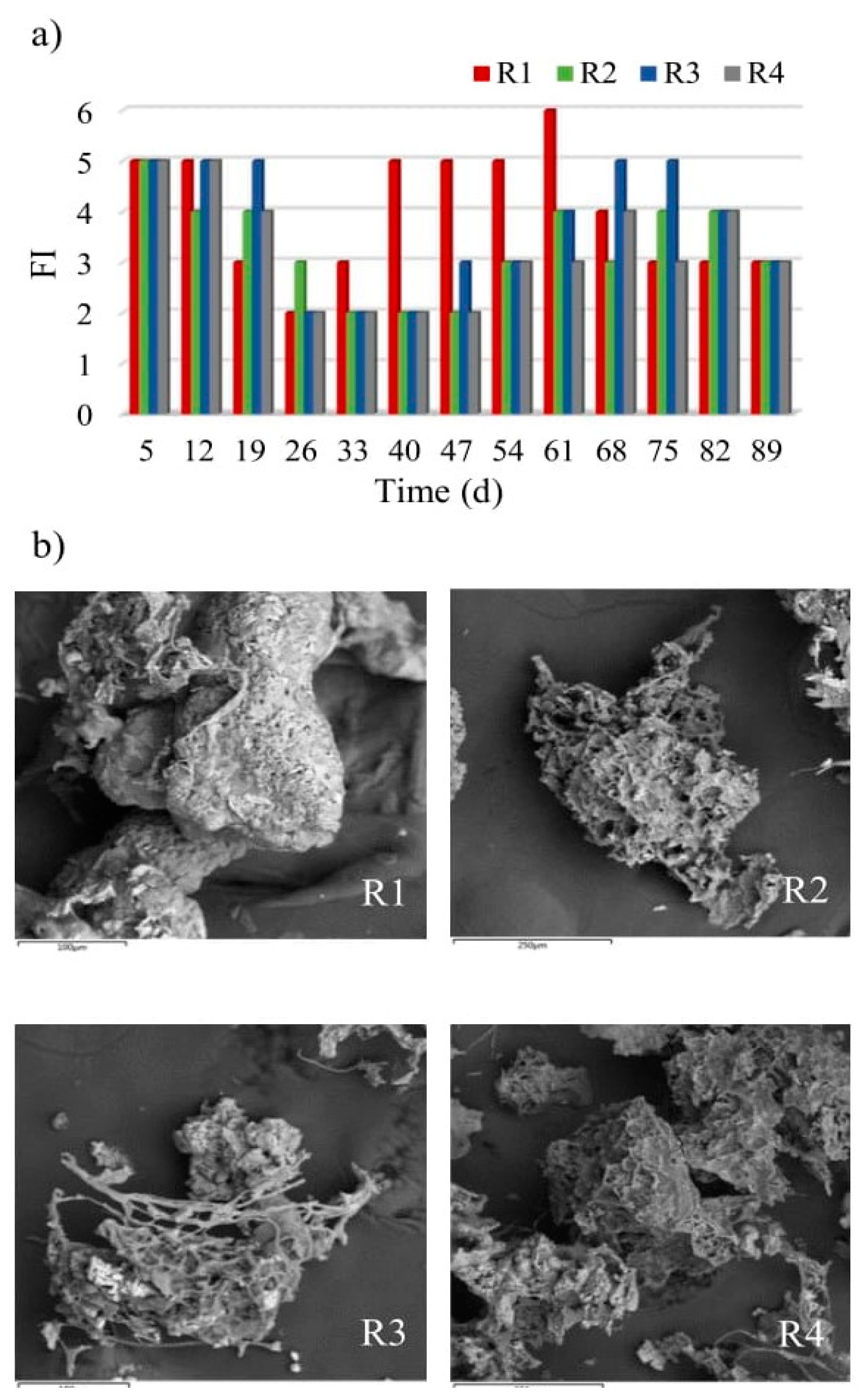
2.3. Biological Properties of Biomass
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reactor Set-up and Operation
3.2. Analytical Method
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Babko, R.; Jaromin-Gleń, K.; Łagód, G.; Pawłowska, M.; Pawłowski, A. Effect of Drilling Mud Addition on Activated Sludge and Processes in Sequencing Batch Reactors. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 1490–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masłoń, A.; Tomaszek, J.A.; Zamorska, J.; Zdeb, M.; Piech, A.; Opaliński, I.; Jurczyk, Ł. The Impact of Powdered Keramsite on Activated Sludge and Wastewater Treatment in a Sequencing Batch Reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 237, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielowski, K.; Czekański, A.; Leśniańska, A. Using Data Mining to Predict Sludgeand Filamentous Microorganism Sedimentation. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 3105–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Liu, L.; Liang, H.; Wu, W.-M. Aerobic Granular Sludge: Characterization, Mechanism of Granulation and Application to Wastewater Treatment. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2011, 31, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnota, J.; Tomaszek, J.A.; Miąsik, M.; Zdeb, M. Aerobic Granular Sludge—Factors Affecting the Granulation Process in the Sequencing Batch Reactors. JCEEA 2013, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilén, B.-M.; Liébana, R.; Persson, F.; Modin, O.; Hermansson, M. The Mechanisms of Granulation of Activated Sludge in Wastewater Treatment, its Optimization, and Impact on Effluent Quality. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 5005–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, L.; Svardal, K.; Krampe, J. Comparison of Aerobic Granulation in SBR and Continuous-Flow Plants. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnota, J.; Masłoń, A. Biogranulation and Physical Properties of Aerobic Granules in Reactors at Low Organic Loading Rate and with Powdered Ceramsite Added. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franca, R.D.G.; Pinheiro, H.M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Lourenço, N.D. Stability of Aerobic Granules During Long-Term Bioreactor Operation. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 228–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kreuk, M.K.; Kishida, N.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Aerobic Granular Sludge—State of the Art. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verawaty, M.; Pijuan, M.; Yuan, Z.; Bond, P.L. Determining the Mechanisms for Aerobic Granulation from Mixed Seed of Floccular and Crushed Granules in Activated Sludge Wastewater Treatment. Water Res. 2012, 46, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Tay, J.-H. Characteristics and Stability of Aerobic Granules Cultivated with Different Starvation Time. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Kiran Kumar Reddy, G. Aerobic Granular Sludge Technology: Mechanisms of Granulation and Biotechnological Applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1128–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kończak, B. The Role Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Formation and Activity Mechanisms of Granular Sludge under Aerobic Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, The Silesian University of Technology, Gliwice, Poland, 2011; pp. 1–148. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Song, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; He, Q.; Zhang, W.; Song, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, H. Simultaneous Nitrification, Denitrification and Phosphorus Removal in An Aerobic Granular Sludge Sequencing Batch Reactor with High Dissolved Oxygen: Effects of Carbon to Nitrogen Ratios. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Song, Y.; Yu, H.; Zeng, P.; Liu, R. Fractionation and Characterization of Dissolved Extracellular and Intracellular Products Derived from Floccular Sludge and Aerobic Granules. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 123, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, N.D. Treatment of High-Strength Organic Wastewater Using an Aerobic Granular System with Baffled Membrane Bioreactor AIT Thesis. Master’s Thesis, Asian Institute of Technology, Bangkok, Thailand, 2006; pp. 1–119. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.-G.; Gai, L.-H.; Zhao, L.-J.; Fan, M.-H.; Gong, W.-X.; Gao, B.-Y.; Ma, Y. Aerobic Granules for Low-Strength Wastewater Treatment: Formation, Structure, and Microbial Community. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 2009, 84, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa Rollemberg, S.L.; Mendes Barros, A.R.; Milen Firmino, P.I.; Bezerra dos Santos, A. Aerobic Granular Sludge: Cultivation Parameters and Removal Mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnota, J.; Masłoń, A.; Zdeb, M. Powdered Keramsite as Unconventional Method of AGS Technology Support in GSBR Reactor with Minimum-Optimum OLR. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 44, 00024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Ji, M.; Li, G.; Qin, F. Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC) Addition for Enhancement of Aerobically Grown Microbial Granules Treating Landfill Leachate. IEEE Xplore 2010, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.J.; Li, X.Y.; Yu, H.G. Aerobic Sludge Granulation Facilitated by Activated Carbon for Partial Nitrification Treatment of Ammonia-Rich Wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 218, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Chen, T.; Ma, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhuo, W. Accelerating Aerobic Sludge Granulation by Adding Dry Sewage Sludge Micropowder in Sequencing Batch Reactors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 10056–10065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.J.; Li, X.Y.; Yu, H.Q. Granular Activated Carbon for Aerobic Sludge Granulation in a Bioreactor with a Low-Strength Wastewater Influent. Sep. Purify Technol. 2011, 80, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhao, H.; Hu, M.; Yu, H.; Xu, X.; Vidonish, J. Granular Activated Carbon as Nucleating Agent for Aerobic Sludge Granulation: Effect of GAC Size on Velocity Field Differences (GAC versus flocs) and Aggregation Behavior. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Qin, L.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Chen, J.; You, J.; Shen, Y.; Chen, H. Effect of Granular Activated Carbon on the Aerobic Granulation of Sludge and its Mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 236, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Tu, Q.; Su, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; He, Q. Formation, Extracellular Polymeric Substances, and Structural Stability of Aerobic Granules Enhanced by Granular Activated Carbon. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6123–6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Chen, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y. ZnCl2 Modified Biochar Derived from Aerobic Granular Sludge for Developed Microporosity and Enhanced Adsorption to Tetracycline. Biores. Technol. 2020, 297, 122381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Xue, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, L.; Wei, Q.; Du, B. Enhanced Aerobic Granulation and Nitrogen Removal by the Addition of Zeolite Powder in A Sequencing Batch Reactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9235–9243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, B.X.; Visvanathan, C.; Spérandio, M.; Aim, R.B. Fouling Characterization in Aerobic Granulation Coupled Baffled Membrane Separation Unit. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 318, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, B.X.; Visvanathan, C.; Aim, R.B. Characterization of Aerobic Granular Sludge at Various Organic Loading Rates. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.L.; Zhang, S.L.; Zou, Z.C.; Wang, H.Y. Enhanced Formation of Aerobic Granular Sludge with Yellow Earth as Nucleating Agent in a Sequencing Batch Reactor. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrojo, B. Advanced Systems for Biological Treatment of High Nitrogen—Loaded Wastewater. Ph.D. Thesis, University Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2007; pp. 1–312. [Google Scholar]
- Beun, J.J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Heijnen, J.J. Aerobic Granulation in A Sequencing Batch Airlift Reactor. Water Res. 2002, 36, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezotti, M.; Lippel, G.; Bassin, J.P. Advanced Biological Processes for Wastewater Treatment: Emerging, Consolidated Technologies and Introduction to Molecular Techniques; Springer Nature: Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 2011; pp. 1–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudan, C.; Filali, A.; Lefebvre, D.; Spérandio, M.; Girbal-Neuhauser, E. Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) from Aerobic Granular Sludges: Extraction, Fractionation, and Anionic Properties. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 1685–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusanowska, P.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I.; Korsak, E. Extracellular Polymers Content in Aerobic Granular Sludge. In Interdisciplinary Problems in Environmental Protection and Engineering; Wiśniewski, J., Kutyłowska, M., Trusz-Zdybek, A., Eds.; Publishing House of the Wroclaw University of Technology: Wrocław, Poland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, G.; Li, A.; Li, X.; Yu, H. Effects of Seed Sludge Properties and Selective Biomass Discharge on Aerobic Sludge Granulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Wang, L.; Su, H. Role and Influence of Extracellular Polymeric Substances on the Preparation of Aerobic Granular Sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 173, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, R.; Corsino, S.F.; Torregrossa, M.; Di Bella, G. The Role of Extracellular Polymeric Substances on Aerobic Granulation with Stepwise Increase of Salinity. Sep. Puryf. Technol. 2018, 195, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mañas, A.; Biscans, B.; Spérandio, M. Biologically Induced Phosphorus Precipitation in Aerobic Granular Sludge Process. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3776–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Rusanowska, P.; Głowacka, K. Operation Mode and External Carbon Dose as Determining Factors in Elemental Composition and Morphology of Aerobic Granules. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2016, 42, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Toh, S.; Tay, J.; Moy, B.; Ivanov, V.; Tay, S. Size-effect on the Physical Characteristics of the Aerobic Granule in a SBR. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2003, 60, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.M.; Unz, R.F. Filamentous Sulfur Bacteria of Activated Sludge: Characterization of Thiothrix, Beggiatoa, and Eikelboom Type 021N Strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiałkowska, E.; Fyda, J.; Pajdak-Stós, A.; Więckowski, K. Activated Sludge. Biology and Microscopic Analysis, 2nd ed.; Seidel-Przywecki: Warszawa, Poland, 2010. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Bernat, K.; Zielińska, M.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I.; Łata, A. Changes in Dehydrogenase Activity of Activated Sludge in Sequencing Batch Reactor under Constant Aeration. Czas. Tech. 2007, 2, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Miksch, K. Physiological Activity of Microorganisms in the Activated Sludge Process. Sci. J. Sil. Univ. Technol. Ser. Environ. Eng. 1983, 24, 1–80. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.-L.; Tay, J.-H.; Liu, Y.; Tiong-Lee Tay, S. Ca2+ Augmentation for Enhancement of Aerobically Grown Microbial Granules in Sludge Blanket Reactors. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, T.-T.; Liu, L.; Sheng, G.-P.; Liu, X.-W.; Yu, H.-Q.; Zhang, M.-C.; Zhu, J.-R. Calcium Spatial Distribution in Aerobic Granules and its Effects on Granule Structure, Strength and Bioactivity. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3343–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Bishop, P.L.; Kinkle, B.K. Comparison of Extraction Methods for Quantifying Extracellular Polymers in Biofilms. Wat. Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, G.H.; Jørgensen, P.E.; Henze, M. Characterization of Functional Microorganism Groups and Substrate in Activated Sludge and Wastewater by AUR, NUR and OUR. Wat. Sci. Technol. 1992, 25, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, M.; Bernat, K.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I. Respirometric Activity of Activated Sludge in Sequencing Batch Reactor Depending on Substrate and Dissolved Oxygen Concentration. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2012, 38, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds not are available from the authors. |

| Parameter | Units | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLVSS | (g MLVSS/L) | 1.49 ± 0.36 | 4.12 ± 0.71 | 3.38 ± 1.93 | 3.94 ± 1.39 |
| MLSS | (g MLSS/L) | 2.28 ± 0.41 | 5.24 ± 0.78 | 4.46 ± 2.14 | 5.07 ± 1.54 |
| SVI5 | (mL/g) | 156.27 ± 88.9 | 51.07 ± 22.9 | 81.71 ± 54.1 | 43.47 ± 29.3 |
| SVI30 | (mL/g) | 96.6 ± 38.2 | 39.8 ± 8.6 | 55.5 ± 27.4 | 32.8 ± 10.7 |
| SVI5/SVI30 | (-) | 1.6 ± 0.3 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 0.4 |
| SV | (m/h) | 4.0 ± 0.4 | 15.4 ± 6.1 | 10.7 ± 2.9 | 13.1 ± 4.4 |
| Parameter | Units | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average diameter | (µm) | 200.2 | 783.1 | 399.0 | 430.0 |
| MLVSS | (g MLVSS/L) | 1.64 | 3.34 | 1.27 | 1.55 |
| MLSS | (g MLSS/L) | 2.39 | 4.23 | 1.98 | 2.30 |
| Density of granules | (g MLVSS/Lgranules) | 14.61 | 37.26 | 16.69 | 21.45 |
| Number of granules* | (-) | 8∙107 | 1.1∙106 | 6.9∙106 | 5.2∙106 |
| Specific surface area of the granules* | (m2/m3) | 3369** | 687 | 1145*** | 1010*** |
| Reactor | Element | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium | Phosphorus | Magnesium | |
| R1 | 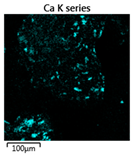 | 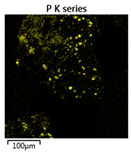 | 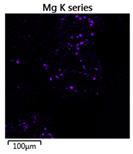 |
| R2 | 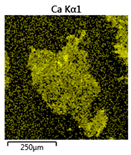 | 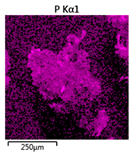 | |
| R3 | 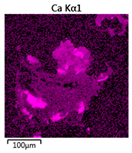 |  | 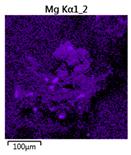 |
| R4 | 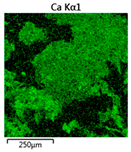 | 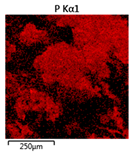 | 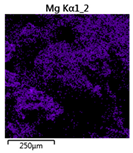 |
| Parameter, Units | Powdered Granite (PG) | Powdered Ceramsite (PK) | Powdered Limestone (PL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sphericity | low sphericity | low sphericity | high sphericity |
| Diameter: d10; d50; d90, µm | 3.194; 26.817; 100.470 | 3.643; 24.110; 85.279 | 1.865; 33.915; 189.720 |
| Apparent density, g/cm3 | 2.6197 | 2.6182 | 2.1949 |
| Specific surface area, m2/g | 1.792 | 5.183 | 1.760 |
| Chemical composition, mg/g | Ca: 13.89; Mg: 1.46; Fe: 10.28; Si: 326.28 | Ca: 75.90; Mg: 21.61; Fe: 45.15; Si: 216.30 | Ca: 691.04; Mg: 4.61; Fe: 1.68; Si: 5.58 |
| Substance leaching, µg/g | Ca: 50.34; Mg: 2.38; Fe: 1.25; Si: 50.98 | Ca: 451.65; Mg: 97.87; Fe: 0.50; Si: 23.01 | Ca: 87.75; Mg: 12.67; Fe: 0.21; Si: 7.00 |
| Settling velocity, m/h | approx. 12.0 | approx. 9.0 | approx. 12.0 |
| Parameter | Units | Component | Average | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | mg O2/L | glucose | 717.1 | 62.6 | 615.0 | 785.0 |
| TP | mg P/L | KH2PO4 | 9.73 | 1.05 | 8.55 | 11.6 |
| TN | mg N/L | NH4Cl | 44.0 | 3.0 | 40.3 | 50.3 |
| COD/TP ratio | - | - | 74.9 | 12.8 | 53.8 | 89.7 |
| COD/TN ratio | - | - | 16.3 | 1.6 | 13.8 | 18.7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czarnota, J.; Masłoń, A.; Zdeb, M.; Łagód, G. The Impact of Different Powdered Mineral Materials on Selected Properties of Aerobic Granular Sludge. Molecules 2020, 25, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020386
Czarnota J, Masłoń A, Zdeb M, Łagód G. The Impact of Different Powdered Mineral Materials on Selected Properties of Aerobic Granular Sludge. Molecules. 2020; 25(2):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020386
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzarnota, Joanna, Adam Masłoń, Monika Zdeb, and Grzegorz Łagód. 2020. "The Impact of Different Powdered Mineral Materials on Selected Properties of Aerobic Granular Sludge" Molecules 25, no. 2: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020386
APA StyleCzarnota, J., Masłoń, A., Zdeb, M., & Łagód, G. (2020). The Impact of Different Powdered Mineral Materials on Selected Properties of Aerobic Granular Sludge. Molecules, 25(2), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020386








