Nicotinic Antagonist UFR2709 Inhibits Nicotine Reward and Decreases Anxiety in Zebrafish
Abstract
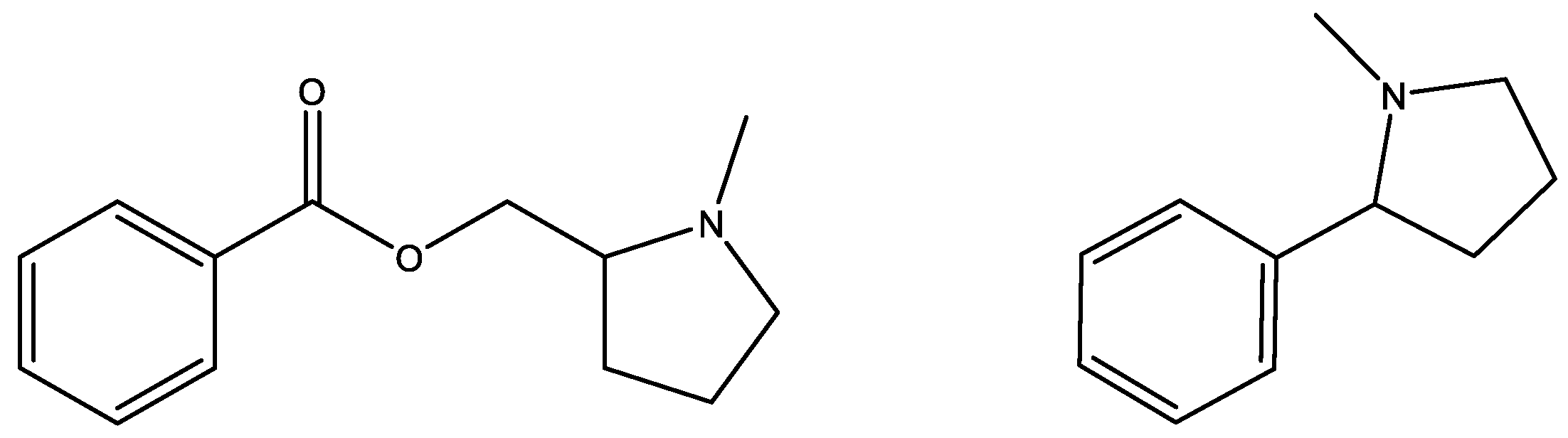
1. Introduction
2. Results
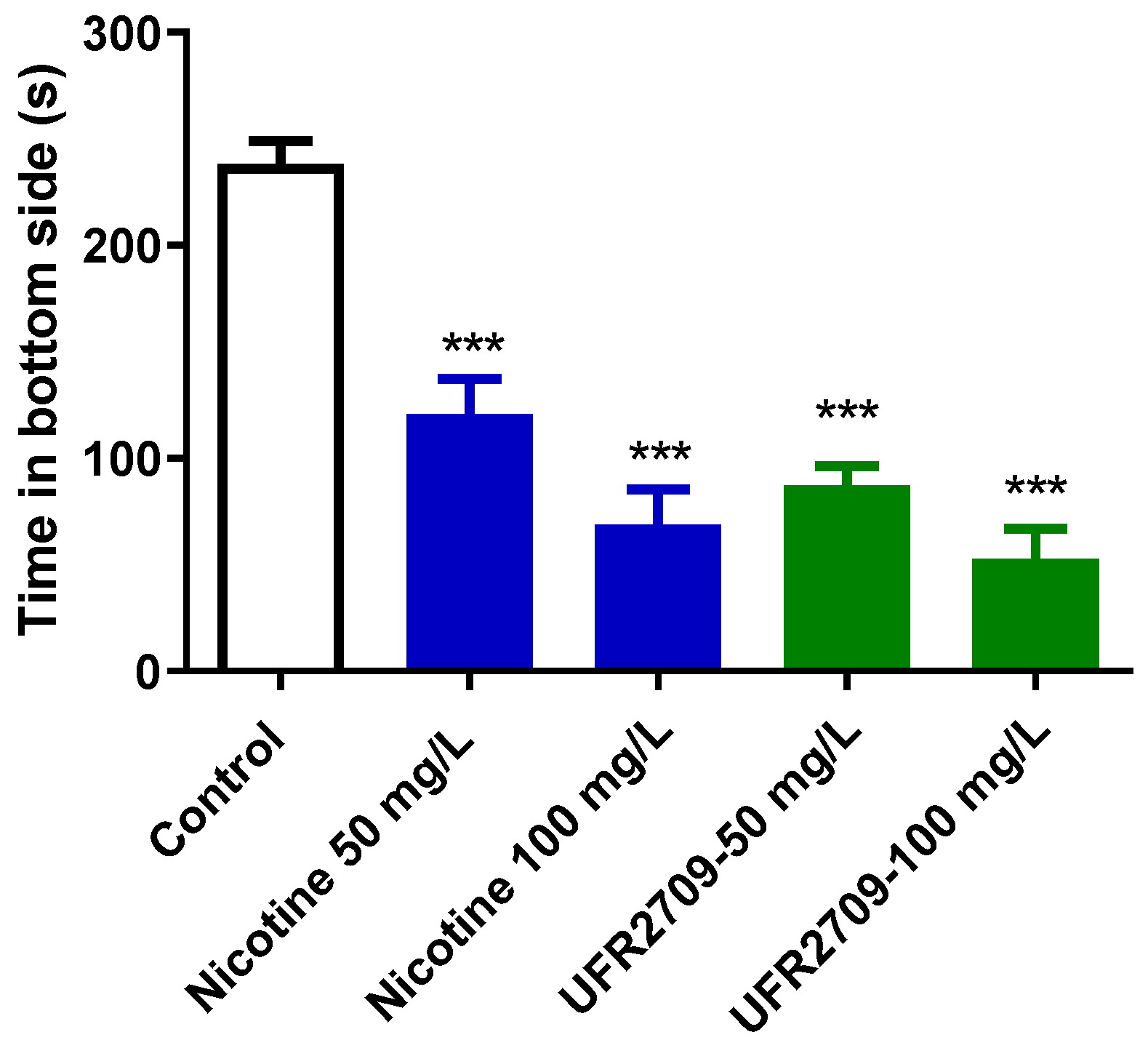
2.1. Effects of Nicotine and UFR2709 on the Novel Tank Diving Test (NTT)
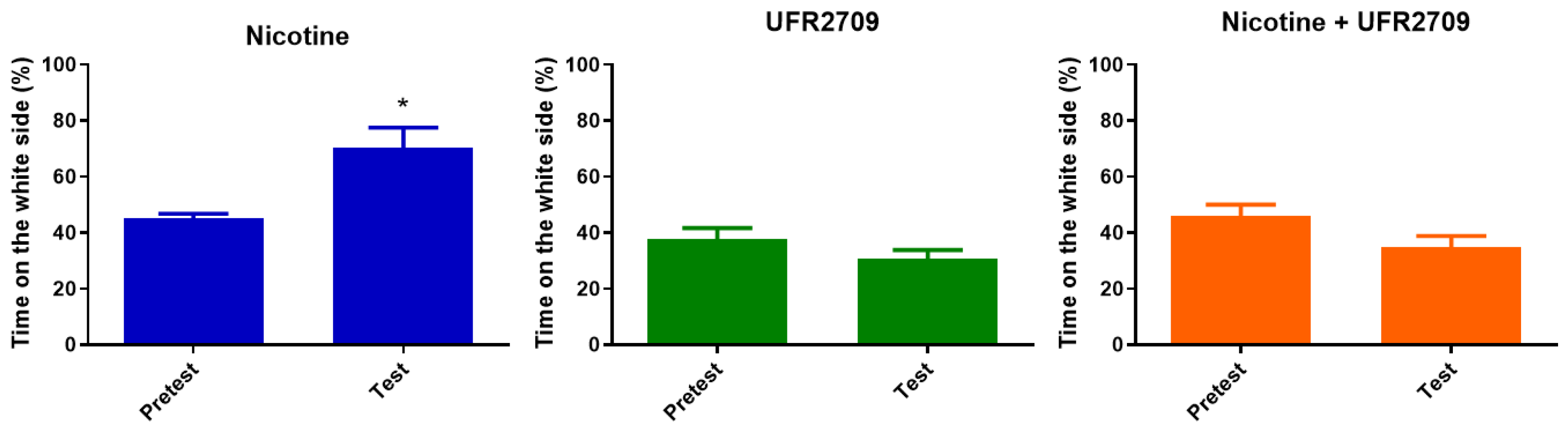
2.2. Effects of Nicotine and UFR2709 on Conditioned Place Preference (CPP)
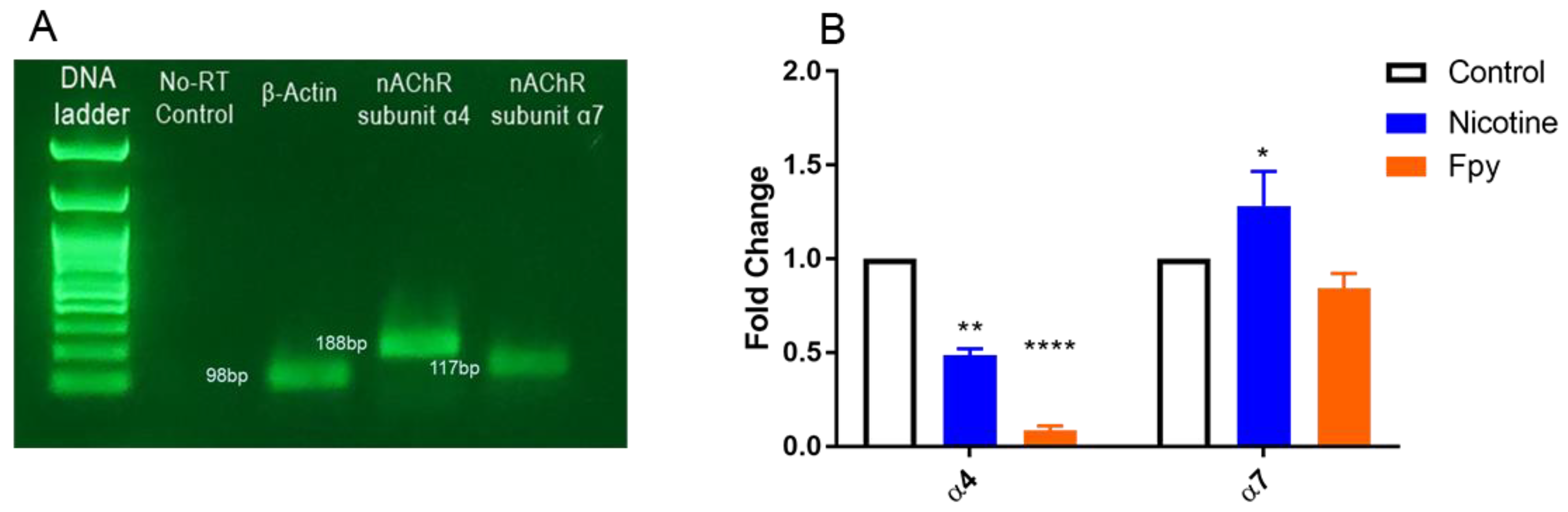
2.3. Gene Expression of α4 and α7 nACh Receptor Subunits in Adult Zebrafish Brain
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Drugs
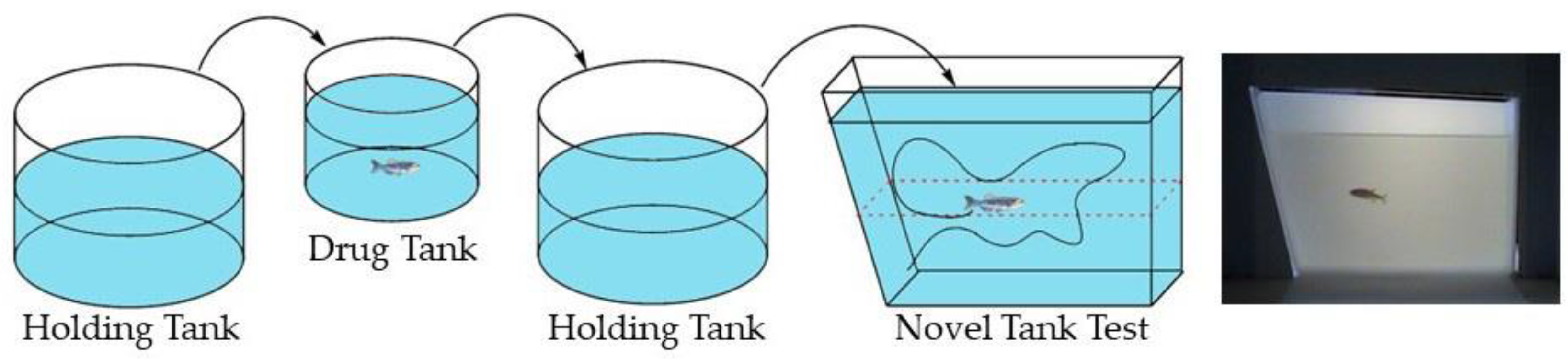
4.3. Novel Tank Test
4.4. Conditioned Place Preference
4.5. Reverse Transcription and quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meyers, J.R. Zebrafish: Development of a Vertebrate Model Organism. Curr. Protoc. Essent. Lab. Tech. 2018, 16, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlai, R.; Lahav, M.; Guo, S.; Rosenthal, A. Drinks like a fish: Zebra fish (Danio rerio) as a behavior genetic model to study alcohol effects. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2000, 67, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, R.J.; Bergner, C.L.; Hart, P.C.; Cachat, J.M.; Canavello, P.R.; Elegante, M.F.; Elkhayat, S.I.; Bartels, B.K.; Tien, A.K.; Tien, D.H.; et al. Understanding behavioral and physiological phenotypes of stress and anxiety in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.D.; Bencan, Z.; Cerutti, D.T. Anxiolytic effects of nicotine in zebrafish. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 90, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, H.A.; Sigstad, C.; Scalzo, F.M. Effects of dizocilpine (MK-801) on circling behavior, swimming activity, and place preference in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2004, 26, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvan, M.J.; Loucks, E.; Weber, D.N.; Williams, F.E. Ethanol effects on the developing zebrafish: Neurobehavior and skeletal morphogenesis. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2004, 26, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, F.E.; White, D.; Messer, W.S. A simple spatial alternation task for assessing memory function in zebrafish. Behav. Processes 2002, 58, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturriaga-Vásquez, P.; Osorio, F.; Riquelme, S.; Castro, S.; Herzog, R. Zebrafish: A Model for Behavioral Pharmacology. Farmacol. Chile 2012, 5, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- van Staden, C.; de Brouwer, G.; Botha, T.L.; Finger-Baier, K.; Brand, S.J.; Wolmarans, D. Dopaminergic and serotonergic modulation of social reward appraisal in zebrafish (Danio rerio) under circumstances of motivational conflict: Towards a screening test for anti-compulsive drug action. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 379, 112393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bencan, Z.; Sledge, D.; Levin, E.D. Buspirone, chlordiazepoxide and diazepam effects in a zebrafish model of anxiety. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2009, 94, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, T.; Fontana, B.D.; Müller, T.E.; Bertoncello, K.T.; Canzian, J.; Rosemberg, D.B. Nicotine prevents anxiety-like behavioral responses in zebrafish. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 94, 109655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, A.; Wu, N.; Cachat, J.; Hart, P.; Gaikwad, S.; Wong, K.; Utterback, E.; Gilder, T.; Kyzar, E.; Newman, A.; et al. Pharmacological modulation of anxiety-like phenotypes in adult zebrafish behavioral models. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninkovic, J.; Bally-Cuif, L. The zebrafish as a model system for assessing the reinforcing properties of drugs of abuse. Methods 2006, 39, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faillace, M.P.; Pisera-Fuster, A.; Bernabeu, R. Evaluation of the rewarding properties of nicotine and caffeine by implementation of a five-choice conditioned place preference task in zebrafish. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 84, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panula, P.; Chen, Y.-C.; Priyadarshini, M.; Kudo, H.; Semenova, S.; Sundvik, M.; Sallinen, V. The comparative neuroanatomy and neurochemistry of zebrafish CNS systems of relevance to human neuropsychiatric diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 40, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rink, E.; Wullimann, M.F. Connections of the ventral telencephalon and tyrosine hydroxylase distribution in the zebrafish brain (Danio rerio) lead to identification of an ascending dopaminergic system in a teleost. Brain Res. Bull. 2002, 57, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.; Kannan, R.R. Zebrafish: An emerging real-time model system to study Alzheimer’s disease and neurospecific drug discovery. Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.M.; Collier, A.D.; Meshalkina, D.A.; Kysil, E.V.; Khatsko, S.L.; Kolesnikova, T.; Morzherin, Y.Y.; Warnick, J.E.; Kalueff, A.V.; Echevarria, D.J. Zebrafish models in neuropsychopharmacology and CNS drug discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1925–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, R.A. Neurobiology of addiction. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1996, 6, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Wise, R.A.; Baler, R. The dopamine motive system: Implications for drug and food addiction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, E.Y.-M.; Munro, A. Effects of dopaminergic drugs on locomotor activity in teleost fish of the genus Oreochromis (Cichlidae): Involvement of the telencephalon. Physiol. Behav. 1998, 64, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rink, E.; Wullimann, M.F. The teleostean (zebrafish) dopaminergic system ascending to the subpallium (striatum) is located in the basal diencephalon (posterior tuberculum). Brain Res. 2001, 889, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, P.; Lau, B.; Guo, S. Conditioned place preference behavior in zebrafish. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedikian, X.; Faillace, M.P.; Bernabeu, R. Behavioral and Molecular Analysis of Nicotine-Conditioned Place Preference in Zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darland, T.; Dowling, J.E. Behavioral screening for cocaine sensitivity in mutagenized zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11691–11696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, P.; Berberoglu, M.A.; Guo, S. Preference for ethanol in zebrafish following a single exposure. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 217, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisera-Fuster, A.; Rocco, L.; Faillace, M.P.; Bernabeu, R. Sensitization-dependent nicotine place preference in the adult zebrafish. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 92, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisera-Fuster, A.; Faillace, M.P.; Bernabeu, R. Pre-Exposure to Nicotine with Nocturnal Abstinence Induces Epigenetic Changes that Potentiate Nicotine Preference. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 1828–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braida, D.; Ponzoni, L.; Moretti, M.; Viani, P.; Pallavicini, M.; Bolchi, C.; Appiani, R.; Bavo, F.; Gotti, C.; Sala, M. Behavioural and pharmacological profiles of zebrafish administrated pyrrolidinyl benzodioxanes and prolinol aryl ethers with high affinity for heteromeric nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Molina, C.; Ortiz-severin, J.; Osorio, F.; Quiroz, G.; Reyes-parada, M.; Varas, R.; Moya, P.R.; Iturriaga-Vásquez, P. Effects of selective α4 β2 Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) ligands on the behaviour of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) in the novel tank diving task. Rev. Farmacol. Chile 2015, 8, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gotti, C.; Zoli, M.; Clementi, F. Brain nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: Native subtypes and their relevance. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, E.X.; Pereira, E.F.R.; Alkondon, M.; Rogers, S.W. Mammalian Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors: From Structure to Function. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 73–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, V.C.; Arnsten, A.F.T.; Wang, M. Involvement of Nicotinic Receptors in Working Memory Function; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Papke, R.L.; Brunzell, D.H.; De Biasi, M. Cholinergic Receptors and Addiction; Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbon, A.; Boyer, L.; Auquier, P.; Boucekine, M.; Barrow, V.; Lançon, C.; Fond, G. Anxiolytic consumption is associated with tobacco smoking and severe nicotine dependence. Results from the national French medical students (BOURBON) study. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 94, 109645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.E.; Loiacono, R.E. Nicotine regulates alpha7 nicotinic receptor subunit mRNA: Implications for nicotine dependence. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, C.D.; Lu, Q.; Johnson, P.M.; Marks, M.J.; Kenny, P.J. Habenular α5 nicotinic receptor subunit signalling controls nicotine intake. Nature 2011, 471, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wonnacott, S. The paradox of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor upregulation by nicotine. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1990, 11, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govind, A.P.; Vezina, P.; Green, W.N. Nicotine-induced upregulation of nicotinic receptors: Underlying mechanisms and relevance to nicotine addiction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz, G.; Sotomayor-Zárate, R.; González-Gutierrez, J.P.; Viscarra, F.; Moraga, F.; Bermudez, I.; Reyes-Parada, M.; Quintanilla, M.E.; Lagos, D.; Rivera-Meza, M.; et al. UFR2709, a Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Antagonist, Decreases Ethanol Intake in Alcohol-Preferring Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brioni, J.D.; O’Neill, A.B.; Kim, D.J.B.; Decker, M.W. Nicotinic receptor agonists exhibit anxiolytic-like effects on the elevated plus-maze test. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 238, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targowska-Duda, K.M.; Budzynska, B.; Michalak, A.; Jozwiak, K.; Biala, G.; Arias, H.R. 3-Furan-2-yl-N-p-tolyl-acrylamide, a highly selective positive allosteric modulator of α7 nicotinic receptors, produces anxiolytic-like activity in mice. J. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 33, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, B.; Pearson, L.; Buccafusco, J. Effect of the use-dependent, nicotinic receptor antagonist BTMPS in the forced swim test and elevated plus maze after cocaine discontinuation in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 474, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagen, Z.M.; Mitchum, R.; Vezina, P.; McGehee, D.S. Enhanced Nicotinic Receptor Function and Drug Abuse Vulnerability. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 8771–8778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zirger, J.M.; Beattie, C.E.; McKay, D.B.; Thomas Boyd, R. Cloning and expression of zebrafish neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Gene Expr. Patterns 2003, 3, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, K.M.; Nakkula, R.; Zirger, J.M.; Beattie, C.E.; Boyd, R.T. Cloning and spatiotemporal expression of zebrafish neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha 6 and alpha 4 subunit RNAs. Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faundez-Parraguez, M.; Farias-Rabelo, N.; Gonzalez-Gutierrez, J.P.; Etcheverry-Berrios, A.; Alzate-Morales, J.; Adasme-Carreño, F.; Varas, R.; Bermudez, I.; Iturriaga-Vasquez, P. Neonicotinic analogues: Selective antagonists for α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compound UFR2709 are available from the authors. |

| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| β-Actin (NM_131031.1) | CGAACGACCAACCTAAACCTC | ACCTCCCTTTCCAGTTTCCG |
| nAChR subunit α4 (NM_001048063.1) | CATGCCCATGCGGAAGAAAG | TCGTTCCACTCCTGCTTCAC |
| nAChR subunit α7 (NM_201219.2) | TGCTGCCTATGGAGTGTGTC | CGTGAGTGAGTGGGTGTCAT |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viscarra, F.; González-Gutierrez, J.; Esparza, E.; Figueroa, C.; Paillali, P.; Hödar-Salazar, M.; Cespedes, C.; Quiroz, G.; Sotomayor-Zárate, R.; Reyes-Parada, M.; et al. Nicotinic Antagonist UFR2709 Inhibits Nicotine Reward and Decreases Anxiety in Zebrafish. Molecules 2020, 25, 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25132998
Viscarra F, González-Gutierrez J, Esparza E, Figueroa C, Paillali P, Hödar-Salazar M, Cespedes C, Quiroz G, Sotomayor-Zárate R, Reyes-Parada M, et al. Nicotinic Antagonist UFR2709 Inhibits Nicotine Reward and Decreases Anxiety in Zebrafish. Molecules. 2020; 25(13):2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25132998
Chicago/Turabian StyleViscarra, Franco, Juan González-Gutierrez, Erica Esparza, Carla Figueroa, Pablo Paillali, Martin Hödar-Salazar, Camilo Cespedes, Gabriel Quiroz, Ramón Sotomayor-Zárate, Miguel Reyes-Parada, and et al. 2020. "Nicotinic Antagonist UFR2709 Inhibits Nicotine Reward and Decreases Anxiety in Zebrafish" Molecules 25, no. 13: 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25132998
APA StyleViscarra, F., González-Gutierrez, J., Esparza, E., Figueroa, C., Paillali, P., Hödar-Salazar, M., Cespedes, C., Quiroz, G., Sotomayor-Zárate, R., Reyes-Parada, M., Bermúdez, I., & Iturriaga-Vásquez, P. (2020). Nicotinic Antagonist UFR2709 Inhibits Nicotine Reward and Decreases Anxiety in Zebrafish. Molecules, 25(13), 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25132998







