(‒)-Cannabidiolic Acid, a Still Overlooked Bioactive Compound: An Introductory Review and Preliminary Research
Abstract
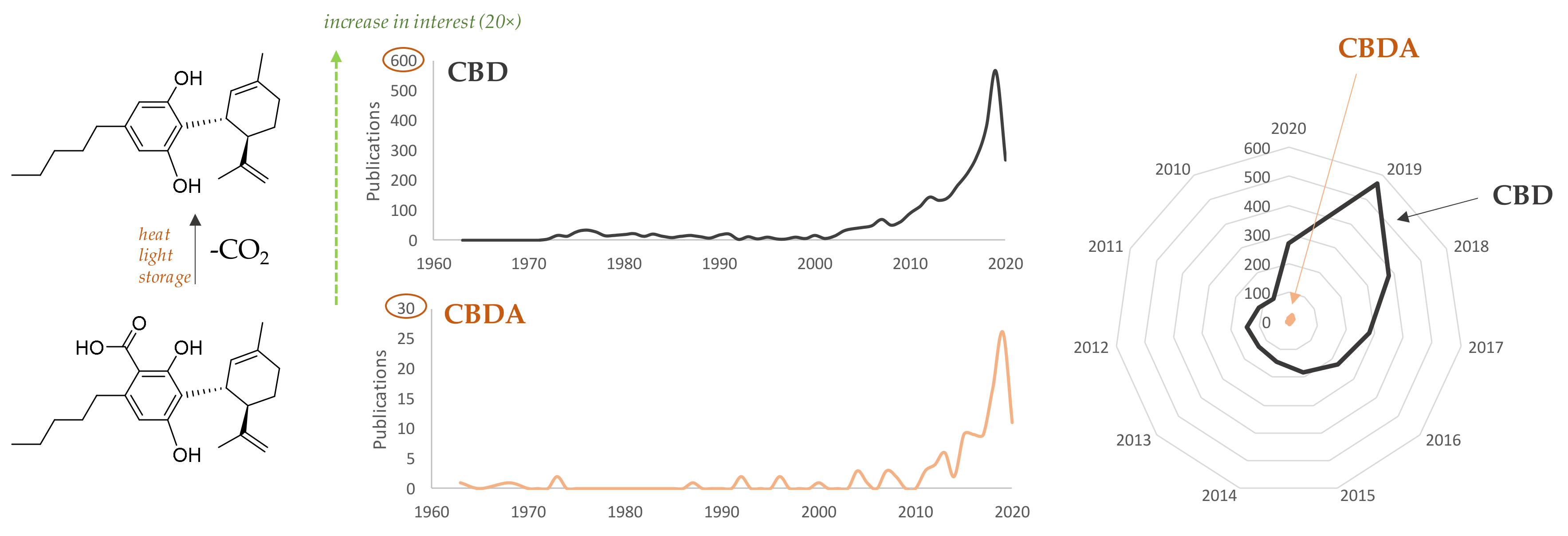
1. Introduction
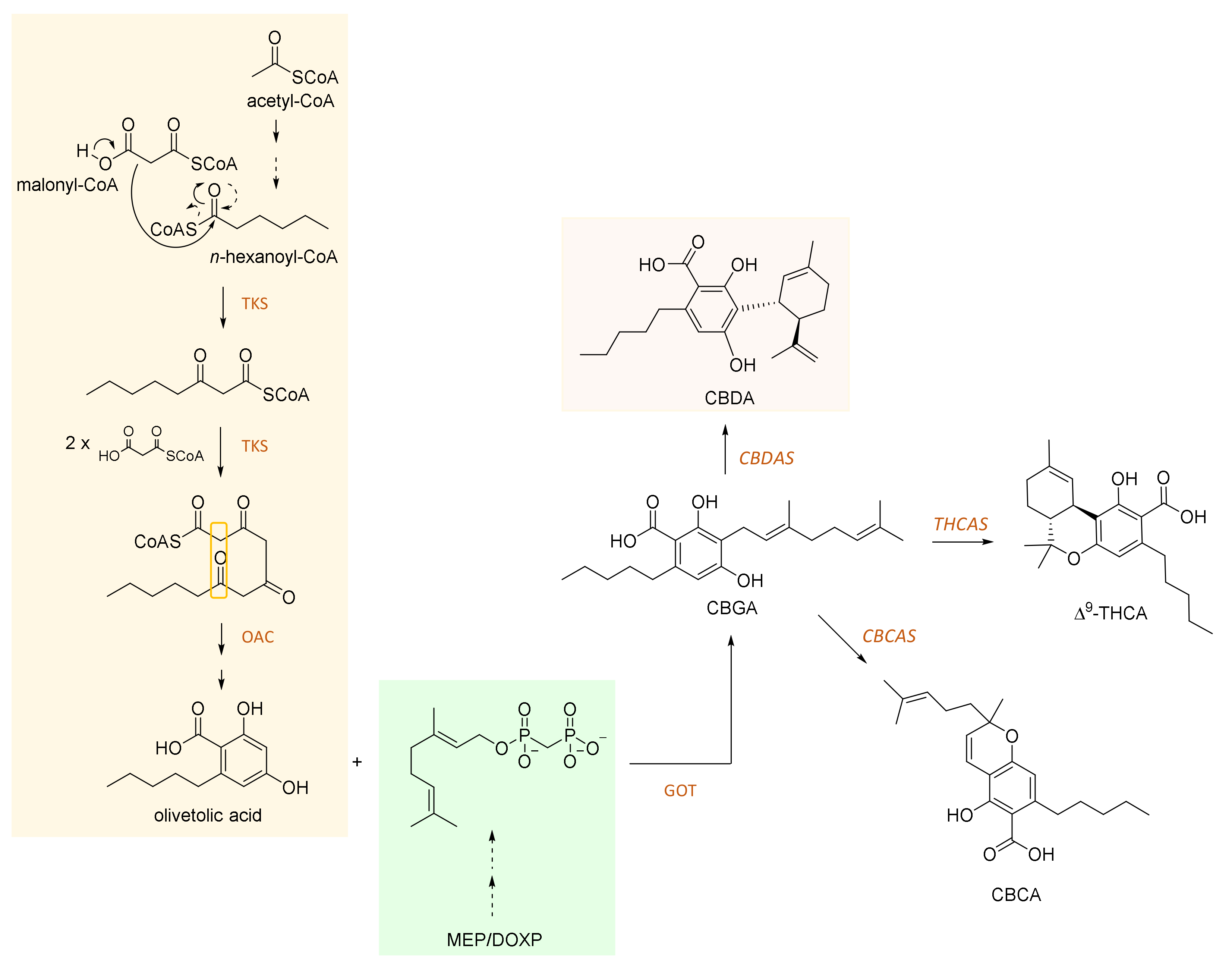
2. CBDA and Its Biosynthesis
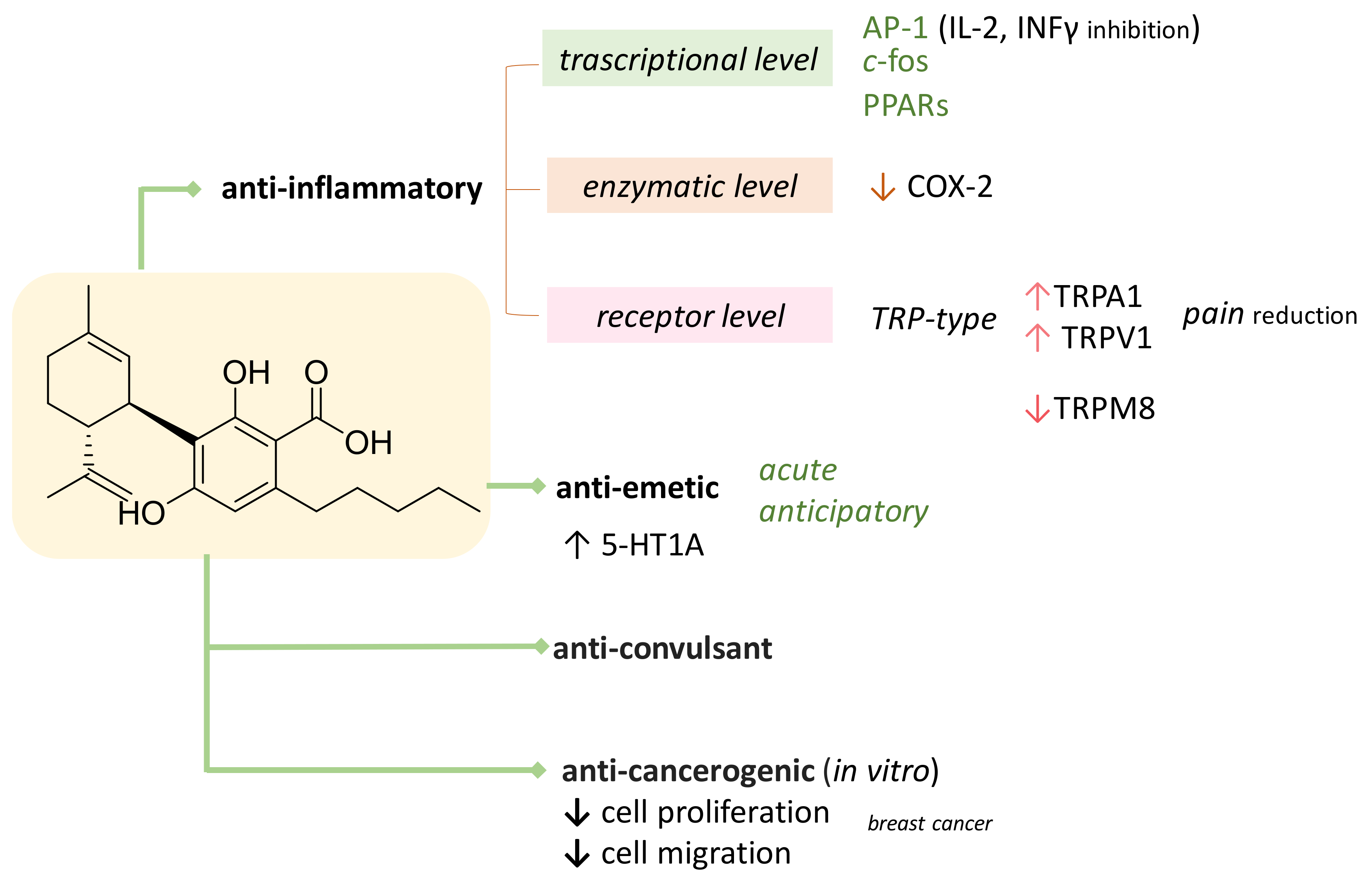
3. CBDA as Bioactive Compound
4. CBDA: The King Compound in Industrial Hemp and Its (By)-Products
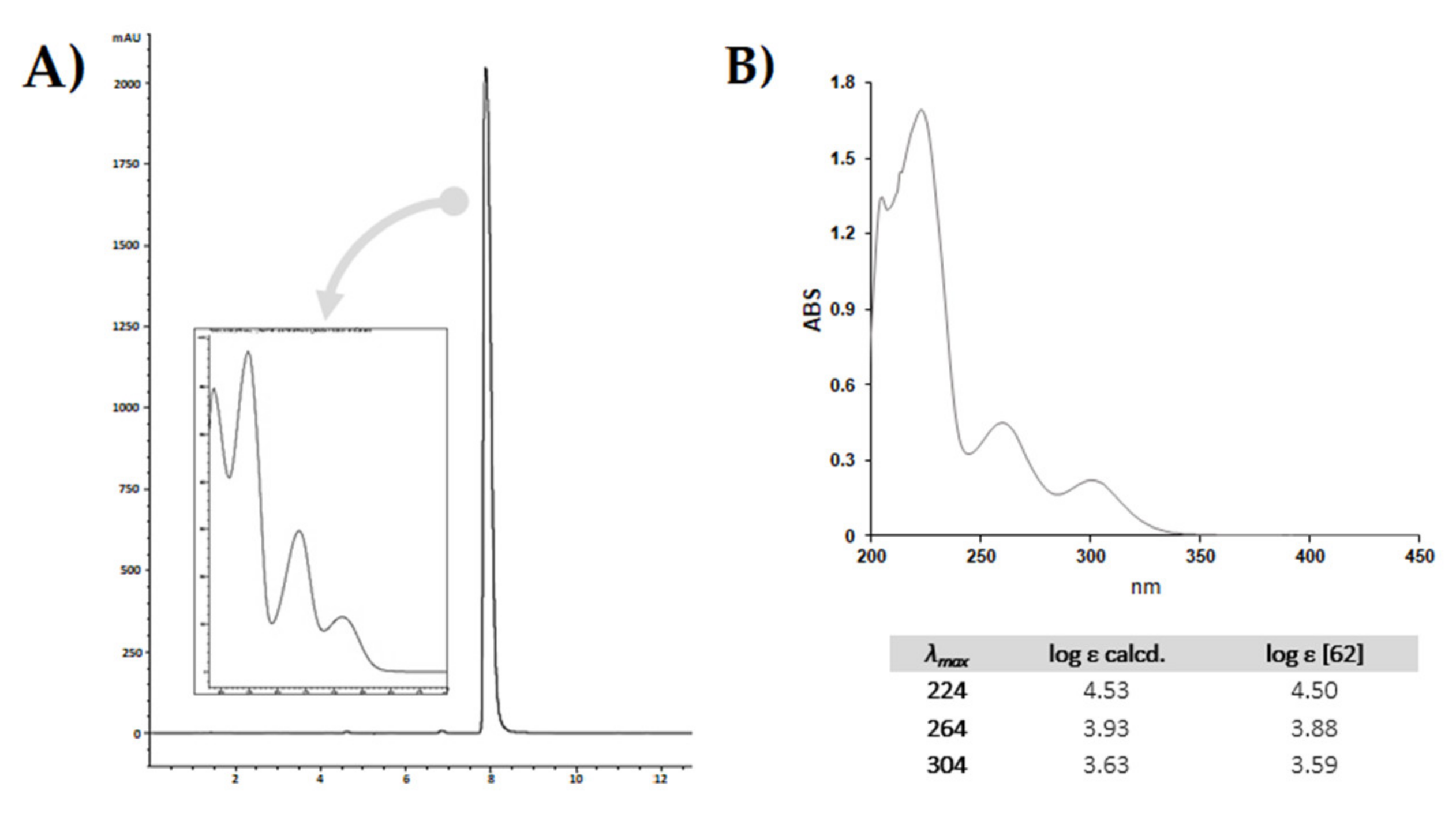
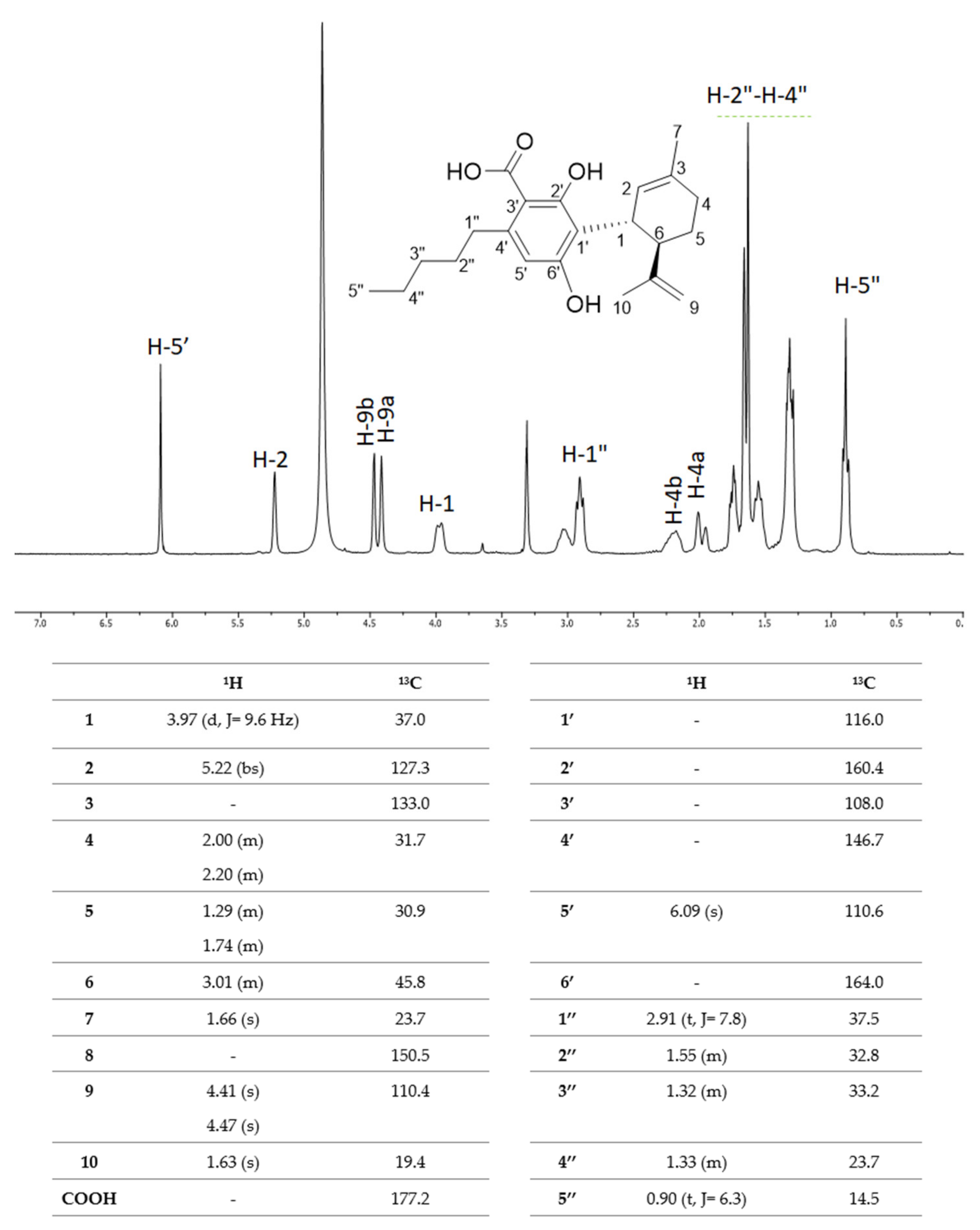
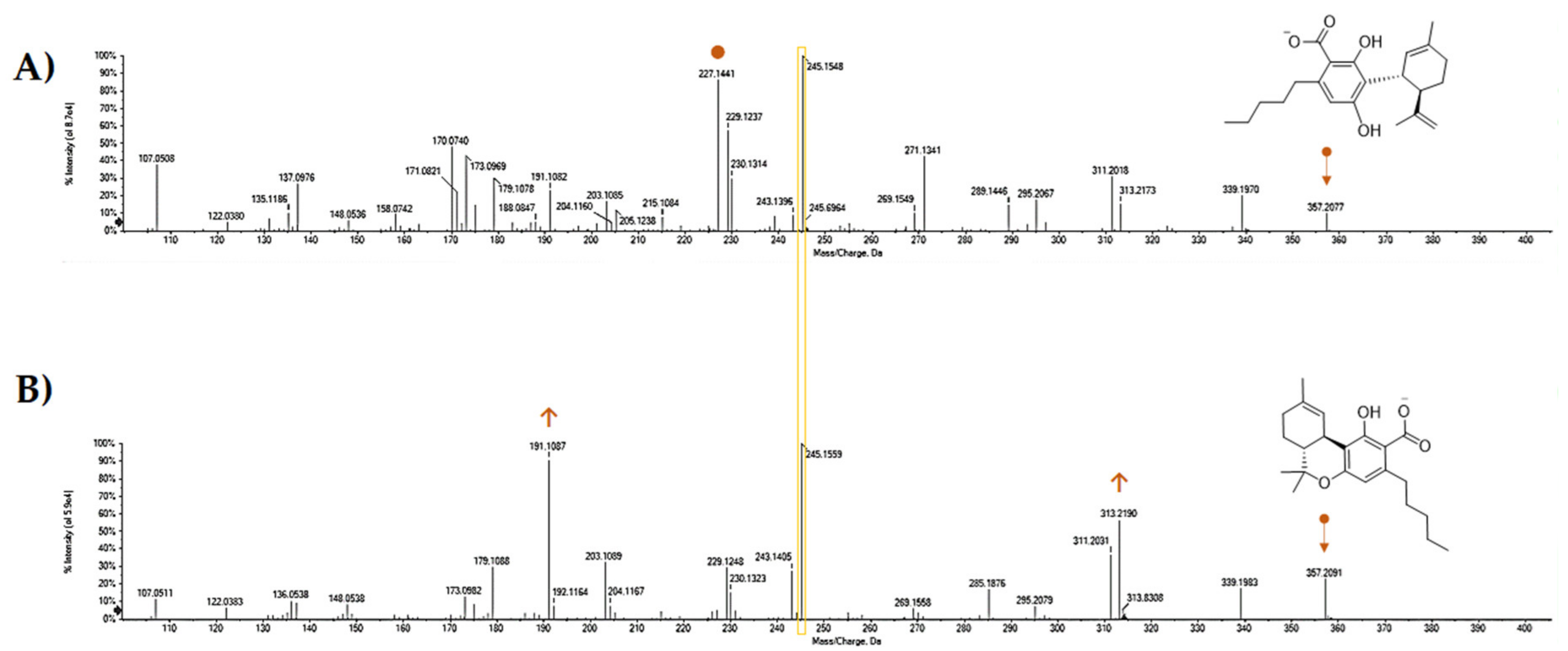
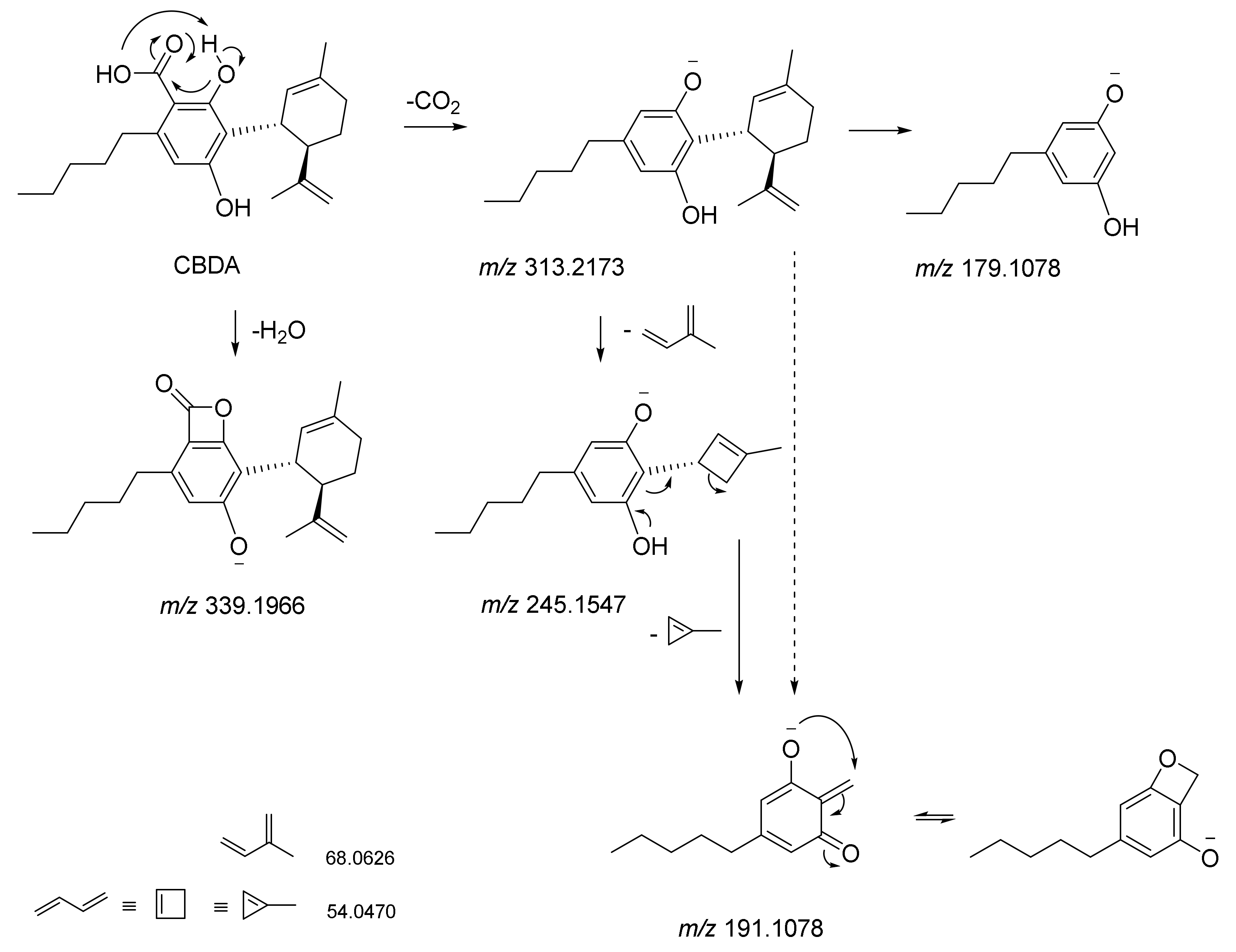
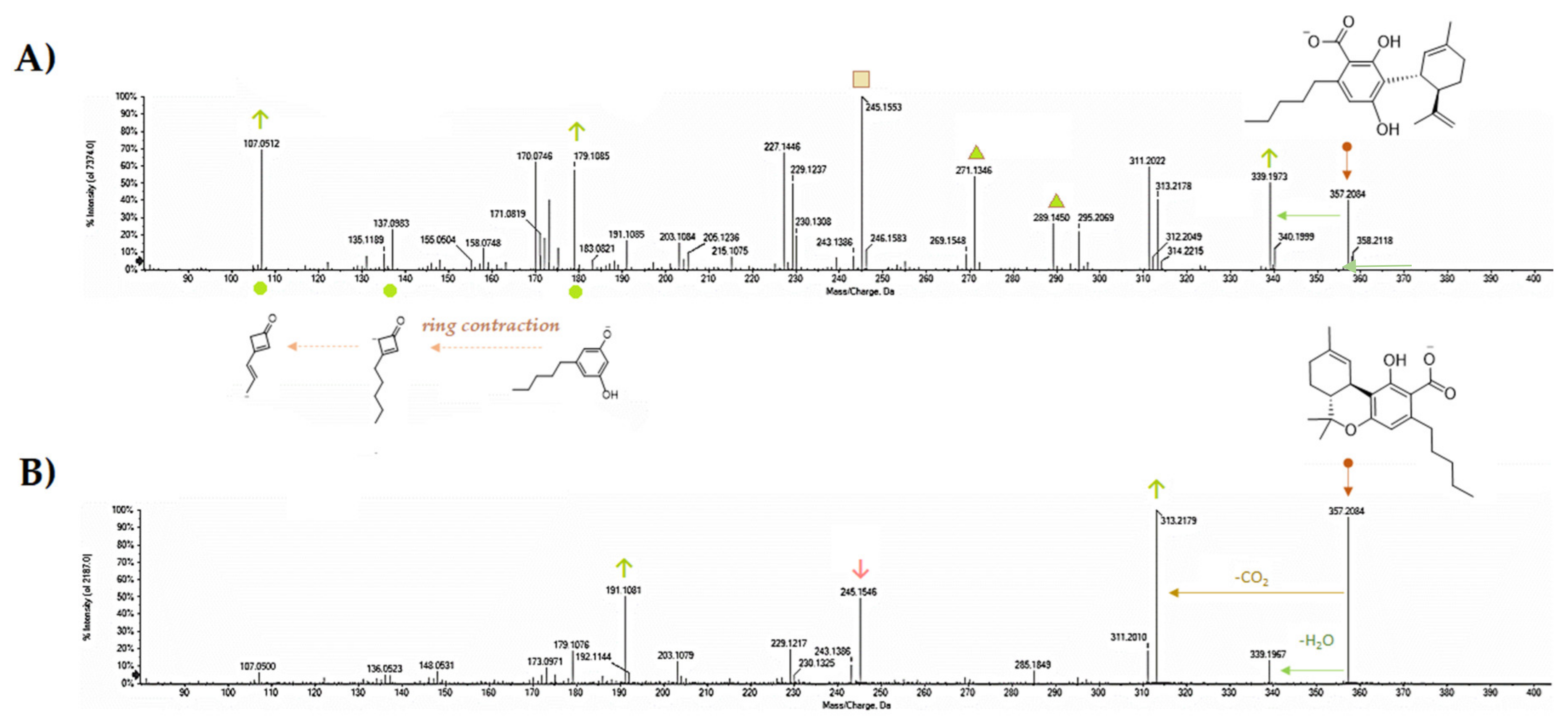
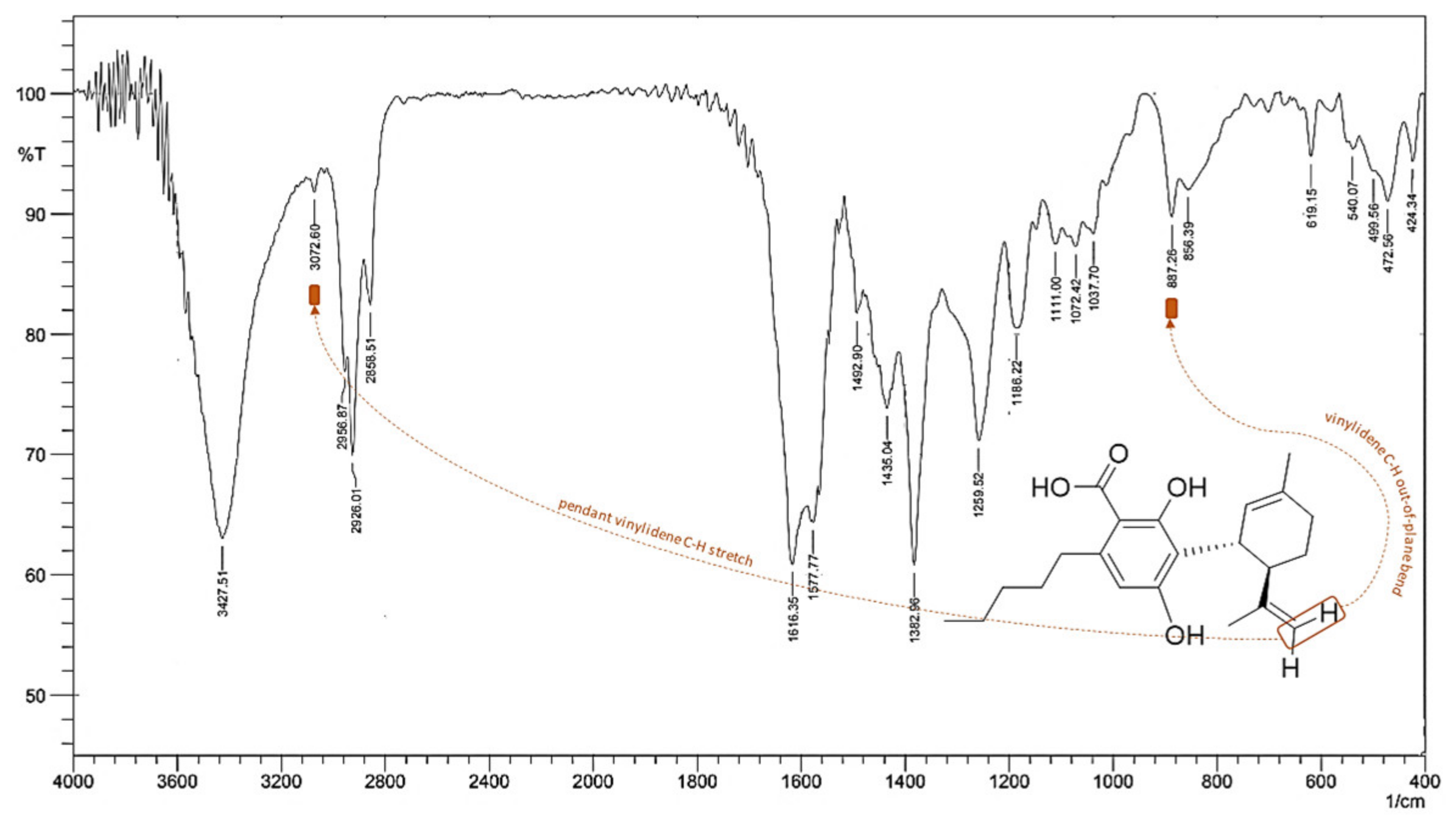
5. CBDA Isolation and Chemical Characterization from Hemp Pollen: Our New Goal
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faugno, S.; Piccolella, S.; Sannino, M.; Principio, L.; Crescente, G.; Baldi, G.M.; Fiorentino, N.; Pacifico, S. Can agronomic practices and cold-pressing extraction parameters affect phenols and polyphenols content in hempseed oils? Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 130, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moccia, S.; Siano, F.; Russo, G.L.; Volpe, M.G.; La Cara, F.; Pacifico, S.; Piccolella, S.; Picariello, G. Antiproliferative and antioxidant effect of polar hemp extracts (Cannabis sativa L., Fedora cv.) in human colorectal cell lines. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, E.; Crescente, G.; Formato, M.; Pecoraro, M.T.; Mallardo, M.; Piccolella, S.; Daniele, A.; Pacifico, S. Hempseed lignanamides rich-fraction: Chemical Investigation and cytotoxicity towards U-87 glioblastoma cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluttenhofer, C.; Yuan, L. Challenges towards revitalizing hemp: A multifaceted crop. Trends Plant. Sci. 2017, 22, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, S.; Jarocka-Karpowicz, I.; Skrzydlewska, E. Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties of cannabidiol. Antioxidants 2019, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizpurua-Olaizola, O.; Soydaner, U.; Öztürk, E.; Schibano, D.; Simsir, Y.; Navarro, P.; Etxebarria, N.; Usobiaga, A. Evolution of the cannabinoid and terpene content during the growth of Cannabis sativa plants from different chemotypes. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citti, C.; Pacchetti, B.; Vandelli, M.A.; Forni, F.; Cannazza, G. Analysis of cannabinoids in commercial hemp seed oil and decarboxylation kinetics studies of cannabidiolic acid (CBDA). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 149, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, C.M.; Hausman, J.F.; Guerriero, G. Cannabis sativa: The plant of the thousand and one molecules. Front. Plant. Sci. 2016, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taura, F.; Sirikantaramas, S.; Shoyama, Y.; Yoshikai, K.; Shoyama, Y.; Morimoto, S. Cannabidiolic-acid Synthase, the chemotype-determining enzyme in the fiber-type Cannabis sativa. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2929–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagne, S.J.; Stout, J.M.; Liu, E.; Boubakir, Z.; Clark, S.M.; Page, J.E. Identification of olivetolic acid cyclase from Cannabis sativa reveals a unique catalytic route to plant polyketides. Proc. Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012, 109, 12811–12816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onofri, C.; de Meijer, E.P.M.; Mandolino, G. Sequence heterogeneity of cannabidiolic-and tetrahydrocannabinolic acid-synthase in Cannabis sativa L. and its relationship with chemical phenotype. Phytochemistry 2015, 116, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, Â.; Hansen, E.H.; Kayser, O.; Carlsen, S.; Stehle, F. Designing microorganisms for heterologous biosynthesis of cannabinoids. FEMS Yeast Res. 2017, 17, fox037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zirpel, B.; Kayser, O.; Stehle, F. Elucidation of structure-function relationship of THCA and CBDA synthase from Cannabis sativa L. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 284, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stout, J.M.; Boubakir, Z.; Ambrose, S.J.; Purves, R.W.; Page, J.E. The hexanoyl-CoA Precursor for cannabinoid biosynthesis is formed by an acyl-activating enzyme in Cannabis sativa trichomes. Plantj. 2012, 71, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Matsui, T.; Kodama, T.; Mori, T.; Zhou, X.; Taura, F.; Noguchi, H.; Abe, I.; Morita, H. Structural basis for olivetolic acid formation by a polyketide cyclase from Cannabis sativa. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 1088–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.B. Cannabidiol claims and misconceptions. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisanti, S.; Malfitano, A.M.; Ciaglia, E.; Lamberti, A.; Ranieri, R.; Cuomo, G.; Abate, M.; Faggiana, G.; Proto, M.C.; Fiore, D.; et al. Cannabidiol: State of the art and new challenges for therapeutic applications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 175, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPartland, J.M.; Duncan, M.; Di Marzo, V.; Pertwee, R.G. Are cannabidiol and tetrahydrocannabivarin negative modulators of the endocannabinoid system? A systematic review. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 737–753. [Google Scholar]
- Blessing, E.M.; Steenkamp, M.M.; Manzanares, J.; Marmar, C.R. Cannabidiol as a potential treatment for anxiety disorders. Neurotherapeutics. 2015, 12, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.J.; Freeman, T.P.; Schafer, G.L.; Curran, H.V. Cannabidiol attenuates the appetitive effects of Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in humans smoking their chosen cannabis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010, 35, 1879–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Fierro, A.; Pessoa-Mahana, C.D. Cannabidiol binding and negative allosteric modulation at the cannabinoid type 1 receptor in the presence of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol: An in silico study. PLoS ONE. 2019, 14, e0220025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philpott, H.T.; OʼBrien, M.; McDougall, J.J. Attenuation of early phase inflammation by cannabidiol prevents pain and nerve damage in rat osteoarthritis. Pain. 2017, 158, 2442–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusho, C.A.; Court, T. Cannabidiol: A brief review of its therapeutic and pharmacologic efficacy in the management of joint disease. Cureus. 2020, 12, e7375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, R.S.; Batista, J., Jr.; Viana, R.B.; Baetas, A.C.; Orestes, E.; Andrade, M.A.; Honório, K.M.; da Silva, A.B. Understanding the molecular aspects of tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol as antioxidants. Molecules. 2013, 18, 12663–12674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Hu, F.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S. Cannabidiol attenuates OGD/R-induced damage by enhancing mitochondrial bioenergetics and modulating glucose metabolism via pentose-phosphate pathway in hippocampal neurons. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Giagnoni, G.; Franke, C.; Trovato, A.E.; Colleoni, M. Vanilloid TRPV1 receptor mediates the antihyperalgesic effect of the nonpsychoactive cannabinoid, cannabidiol, in a rat model of acute inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogno, T.; Hanus, L.; De Petrocellis, L.; Tchilibon, S.; Ponde, D.E.; Brandi, I.; Moriello, A.S.; Davis, J.B.; Mechoulam, R.; Di Marzo, V. Molecular targets for cannabidiol and its synthetic analogues: Effect on vanilloid VR1 receptors and on the cellular uptake and enzymatic hydrolysis of anandamide. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestro, S.; Mammana, S.; Cavalli, E.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Use of cannabidiol in the treatment of epilepsy: Efficacy and security in clinical trials. Molecules. 2019, 24, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, E.M.; Bolognini, D.; Limebeer, C.L.; Cascio, M.G.; Anavi-Goffer, S.; Fletcher, P.J.; Mechoulam, R.; Pertwee, R.G.; Parker, L.A. Cannabidiol, a non-psychotropic component of cannabis, attenuates vomiting and nausea-like behaviour via indirect agonism of 5-HT(1A) somatodendritic autoreceptors in the dorsal raphe nucleus. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 2620–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokoena, R.D.; George, P.B.; Abrahamse, H. Enhancing breast cancer treatment using a combination of cannabidiol and gold nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammell, D.C.; Zhang, L.P.; Ma, F.; Abshire, S.M.; McIlwrath, S.L.; Stinchcomb, A.L.; Westlund, K.N. Transdermal cannabidiol reduces inflammation and pain-related behaviours in a rat model of arthritis. Eur J. Pain. 2016, 20, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirikoc, S.; Priola, S.A.; Marella, M.; Zsürger, N.; Chabry, J. Nonpsychoactive cannabidiol prevents prion accumulation and protects neurons against prion toxicity. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 9537–9544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oláh, A.; Markovics, A.; Szabó-Papp, J.; Szabó, P.T.; Stott, C.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Bíró, T. Differential effectiveness of selected non-psychotropic phytocannabinoids on human sebocyte functions implicates their introduction in dry/seborrheic skin and acne treatment. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, S.; Misawa, K.; Yamamoto, I.; Watanabe, K. Cannabidiolic acid as a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory component in cannabis. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2008, 36, 1917–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Petrocellis, L.; Vellani, V.; Schiano-Moriello, A.; Marini, P.; Magherini, P.C.; Orlando, P.; Di Marzo, V. Plant-derived cannabinoids modulate the activity of transient receptor potential channels of ankyrin type-1 and melastatin type-8. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 325, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognini, D.; Rock, E.M.; Cluny, N.L.; Cascio, M.G.; Limebeer, C.L.; Duncan, M.; Stott, C.G.; Javid, F.A.; Parker, L.A.; Pertwee, R.G. Cannabidiolic acid prevents vomiting in Suncus murinus and nausea-induced behaviour in rats by enhancing 5-HT1A receptor activation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 1456–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertwee, R.G.; Rock, E.M.; Guenther, K.; Limebeer, C.L.; Stevenson, L.A.; Haj, C.; Smoum, R.; Parker, L.A.; Mechoulam, R. Cannabidiolic acid methyl ester, a stable synthetic analogue of cannabidiolic acid, can produce 5-HT1A receptor-mediated suppression of nausea and anxiety in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Rodríguez, E.; Arankowsky-Sandoval, G.; Pertwee, R.G.; Parker, L.; Mechoulam, R. Sleep and neurochemical modulation by cannabidiolic acid methyl ester in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 155, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Linher-Melville, K.; Niazmand, M.J.; Sharma, M.; Shahid, A.; Zhu, K.L.; Parzei, N.; Sidhu, J.; Haj, C.; Mechoulam, R. An evaluation of the anti-hyperalgesic effects of cannabidiolic acid-methyl ester in a preclinical model of peripheral neuropathic pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, E.M.; Limebeer, C.L.; Parker, L.A. Effect of cannabidiolic acid and ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol on carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia and edema in a rodent model of inflammatory pain. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 3259–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, E.M.; Parker, L.A. Effect of low doses of cannabidiolic acid and ondansetron on LiCl-induced conditioned gaping (a model of nausea-induced behaviour) in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.L.; Low, I.K.; Banister, S.D.; McGregor, I.S.; Arnold, J.C. Pharmacokinetics of phytocannabinoid acids and anticonvulsant effect of cannabidiolic acid in a mouse model of Dravet syndrome. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 3047–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadal, X.; Del Río, C.; Casano, S.; Palomares, B.; Ferreiro-Vera, C.; Navarrete, C.; Sánchez-Carnerero, C.; Cantarero, I.; Bellido, M.L.; Meyer, S.; et al. Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid is a potent PPARγ agonist with neuroprotective activity. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 4263–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, K.A.; Shah, S.; Dalgleish, A.G.; Liu, W.M. Enhancing the activity of cannabidiol and other cannabinoids in vitro through modifications to drug combinations and treatment schedules. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 4373–4380. [Google Scholar]
- De Petrocellis, L.; Ligresti, A.; Schiano Moriello, A.; Iappelli, M.; Verde, R.; Stott, C.G.; Cristino, L.; Orlando, P.; Di Marzo, V. Non-THC cannabinoids inhibit prostate carcinoma growth in vitro and in vivo: Pro-apoptotic effects and underlying mechanisms. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 79–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, S.; Okajima, S.; Miyoshi, H.; Yoshida, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Okada, T.; Amamoto, T.; Watanabe, K.; Omiecinski, C.J.; Aramaki, H. Cannabidiolic acid, a major cannabinoid in fiber-type cannabis, is an inhibitor of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell migration. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 214, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Takeda, S.; Okazaki, H.; Watanabe, K.; Takiguchi, M.; Aramaki, H. Cannabidiolic acid-mediated interference with AP-1 transcriptional activity in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, S.; Okazaki, H.; Ikeda, E.; Abe, S.; Yoshioka, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Aramaki, H. Down-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) by cannabidiolic acid in human breast cancer cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 39, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirao-Suzuki, M.; Takeda, S.; Koga, T.; Takiguchi, M.; Toda, A. Cannabidiolic Acid dampens the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells: Possible implication of the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor β/δ abrogation. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 45, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desa, S.; Osman, A.; Hyslop, R. In Silico assessment of drug-like properties of phytocannabinoids in Cannabis sativa. Educ. J.S.M.T. 2017, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, P.; Jagerovic, N. Antitumor cannabinoid chemotypes: Structural insights. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhaak, L.R.; Felth, J.; Karlsson, P.C.; Rafter, J.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Bohlin, L. Evaluation of the cyclooxygenase inhibiting effects of six major cannabinoids isolated from Cannabis sativa. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellati, F.; Brighenti, V.; Sperlea, J.; Marchetti, L.; Bertelli, D.; Benvenuti, S. New methods for the comprehensive analysis of bioactive compounds in Cannabis sativa L. (hemp). Molecules 2018, 23, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brighenti, V.; Pellati, F.; Steinbach, M.; Maran, D.; Benvenuti, S. Development of a new extraction technique and HPLC method for the analysis of non-psychoactive cannabinoids in fibre-type Cannabis sativa L. (Hemp). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 143, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorini, D.; Molle, A.; Nabissi, M.; Santini, G.; Benelli, G.; Maggi, F. Valorizing industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) by-products: Cannabidiol enrichment in the inflorescence essential oil optimizing sample pre-treatment prior to distillation. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 128, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, W.; Gul, S.W.; Radwan, M.M.; Wanas, A.S.; Mehmedic, Z.; Khan, I.I.; ElSohly, M.A. Determination of 11 cannabinoids in biomass and extracts of different varieties of Cannabis using high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Aoac Int. 2015, 98, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudge, E.M.; Murch, S.J.; Brown, P.N. Leaner and greener analysis of cannabinoids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 3153–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, J.R.; Petrakis, E.A.; Angelis, A.; Halabalaki, M.; Bonn, G.K.; Stuppner, H.; Skaltsounis, L.A. Rapid isolation of acidic cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa L. using pH-zone-refining centrifugal partition chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1599, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazekamp, A.; Simons, R.; Peltenburg-Looman, A.; Sengers, M.; van Zweden, R.; Verpoorte, R. Preparative isolation of cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa by Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2004, 27, 2421–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, M.R.; el-Mounajjed, D. Isolation of two constituents (Cannabidiolic Acid and Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) from Cannabis Sativa, L. by preparative thin layer chromatography. Ann. Pharm. Fr. 1973, 31, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, S.A.; ElSohly, M.A.; Sultana, G.N.N.; Mehmedic, Z.; Hossain, C.F.; Chandra, S. Flavonoid Glycosides and cannabinoids from the pollen of Cannabis sativa L. Phytochem. Anal. 2005, 16, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazekamp, A.; Peltenburg, A.; Verpoorte, R.; Giroud, C. Chromatographic and spectroscopic data of cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa L. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2005, 28, 2361–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Hazekamp, A.; Peltenburg-Looman, A.M.; Frédérich, M.; Erkelens, C.; Lefeber, A.W.; Verpoorte, R. NMR assignments of the major cannabinoids and cannabiflavonoids isolated from flowers of Cannabis sativa. Phytochem Anal. 2004, 15, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, P.; Futoran, K.; Lewitus, G.M.; Mukha, D.; Benami, M.; Shlomi, T.; Meiri, D. A new ESI-LC/MS approach for comprehensive metabolic profiling of phytocannabinoids in Cannabis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citti, C.; Linciano, P.; Panseri, S.; Vezzalini, F.; Forni, F.; Vandelli, M.A.; Cannazza, G. Cannabinoid Profiling of Hemp seed oil by Liquid Chromatography coupled to High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Front. Plant. Sci. 2019, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsohly, A.M.; Slade, D. Chemical constituents of marijuana: The complex mixture of natural cannabinoids. Life Sci. 2005, 78, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Canonical smile CCCCCC1=CC(=C(C(=C1C(=O)O)O)C2C=C(CCC2C(=C)C)C)O | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW (≤500)* | HBA (≤10)* | HBD (≤5)* | cLogP (≤5)* | TPSA, A2 (≤140*; ≤60#) | NRTOB (≤10)* |
| 358.48 | 4 | 3 | 6.43 | 77.75 | 7 |
| Good oral absorption*, Completely absorbed# | |||||
| GPCR ligand | Ion channel modulator | Kinase inhibitor | Nuclear receptor ligand | Protease inhibitor | Enzyme inhibitor |
| −0.39 | −0.05 | −0.74 | −0.30 | −0.63 | −0.09 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Formato, M.; Crescente, G.; Scognamiglio, M.; Fiorentino, A.; Pecoraro, M.T.; Piccolella, S.; Catauro, M.; Pacifico, S. (‒)-Cannabidiolic Acid, a Still Overlooked Bioactive Compound: An Introductory Review and Preliminary Research. Molecules 2020, 25, 2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112638
Formato M, Crescente G, Scognamiglio M, Fiorentino A, Pecoraro MT, Piccolella S, Catauro M, Pacifico S. (‒)-Cannabidiolic Acid, a Still Overlooked Bioactive Compound: An Introductory Review and Preliminary Research. Molecules. 2020; 25(11):2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112638
Chicago/Turabian StyleFormato, Marialuisa, Giuseppina Crescente, Monica Scognamiglio, Antonio Fiorentino, Maria Tommasina Pecoraro, Simona Piccolella, Michelina Catauro, and Severina Pacifico. 2020. "(‒)-Cannabidiolic Acid, a Still Overlooked Bioactive Compound: An Introductory Review and Preliminary Research" Molecules 25, no. 11: 2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112638
APA StyleFormato, M., Crescente, G., Scognamiglio, M., Fiorentino, A., Pecoraro, M. T., Piccolella, S., Catauro, M., & Pacifico, S. (2020). (‒)-Cannabidiolic Acid, a Still Overlooked Bioactive Compound: An Introductory Review and Preliminary Research. Molecules, 25(11), 2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25112638