Synthesis and AChE-Inhibitory Activity of New Benzimidazole Derivatives
Abstract
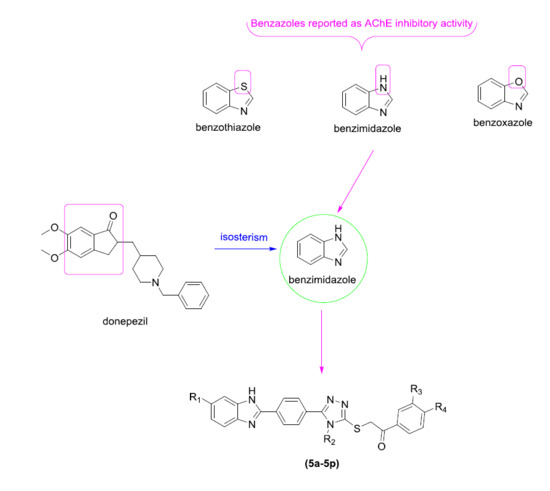
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
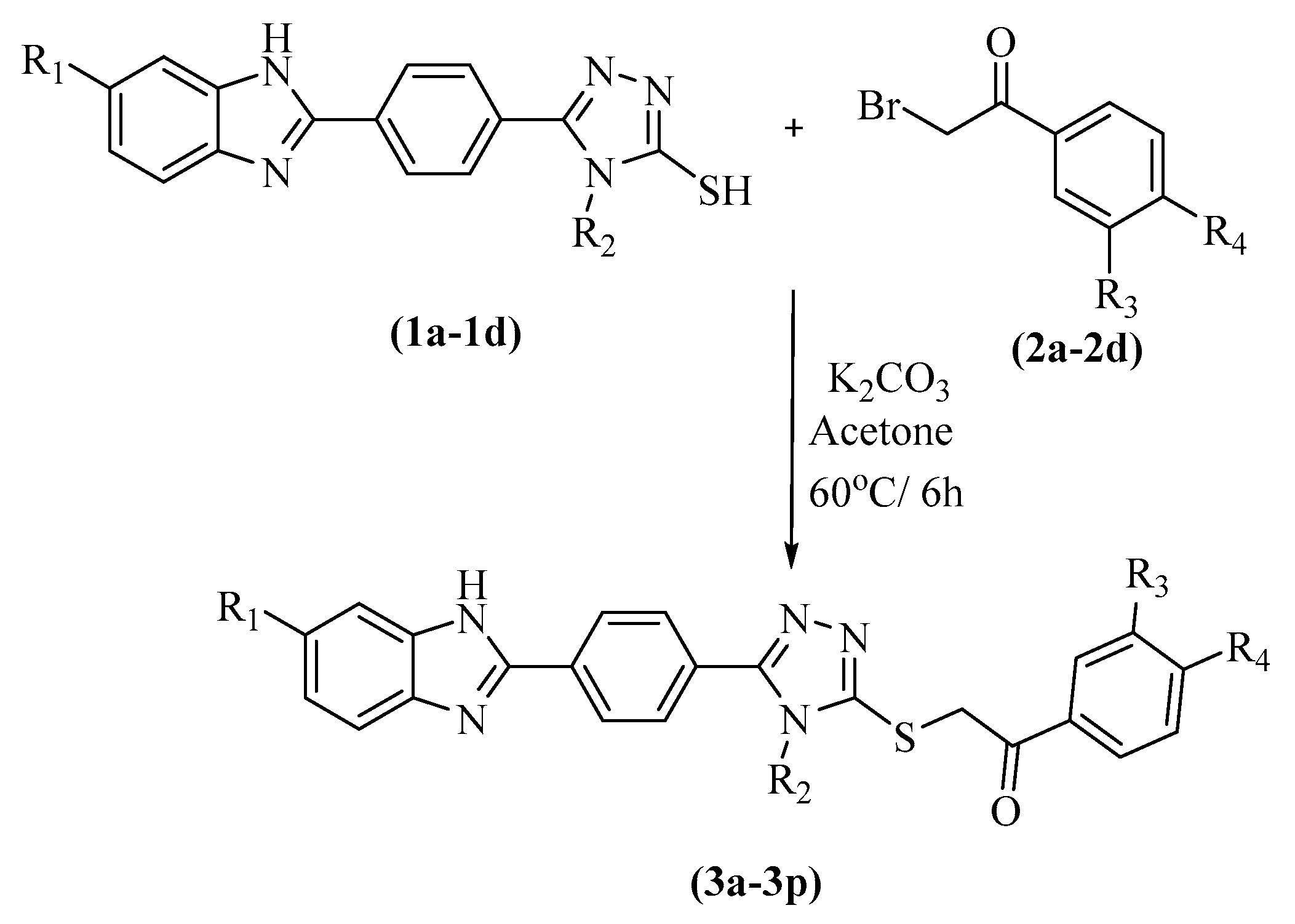
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Anticholinesterase Activity Assay
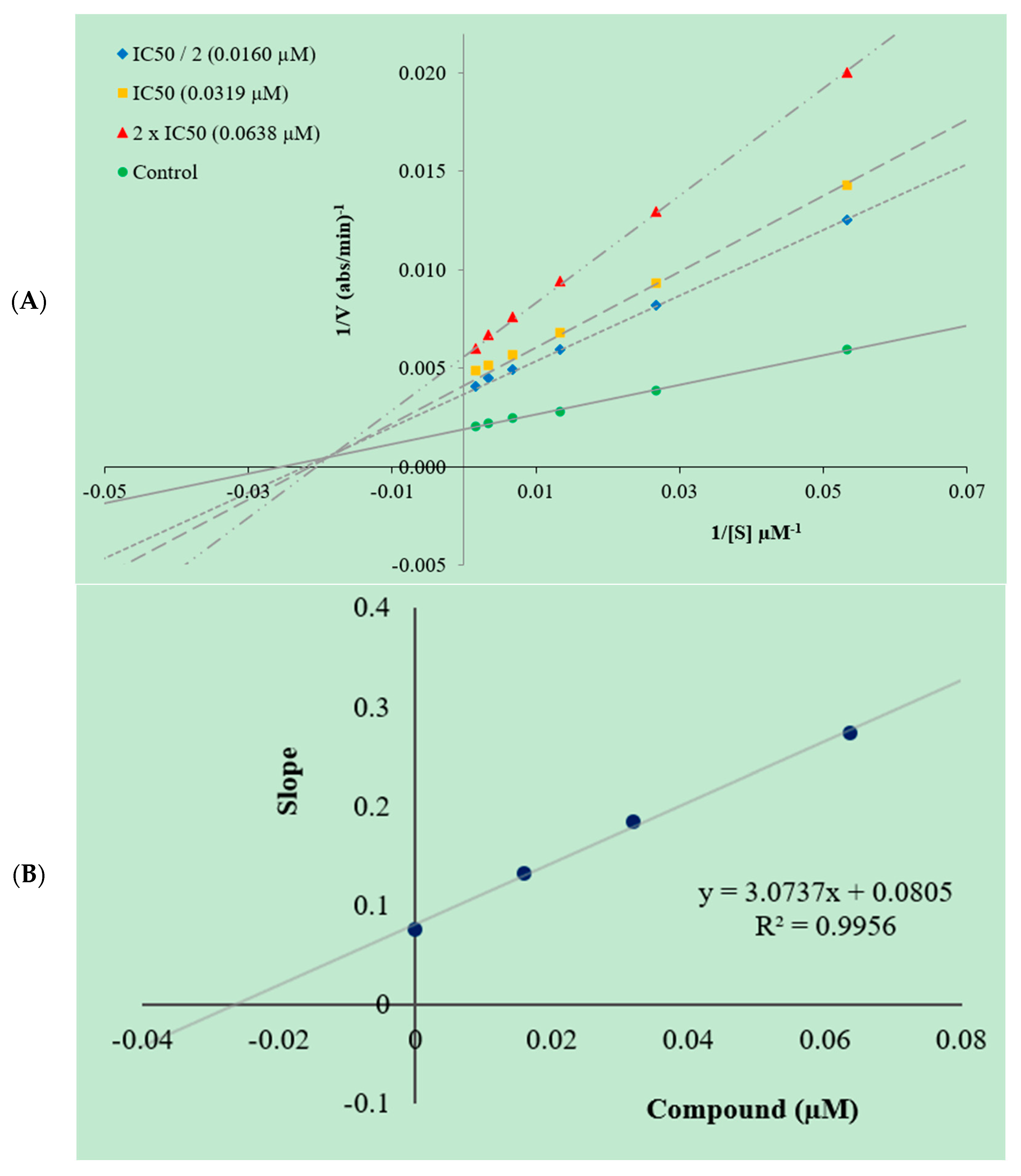
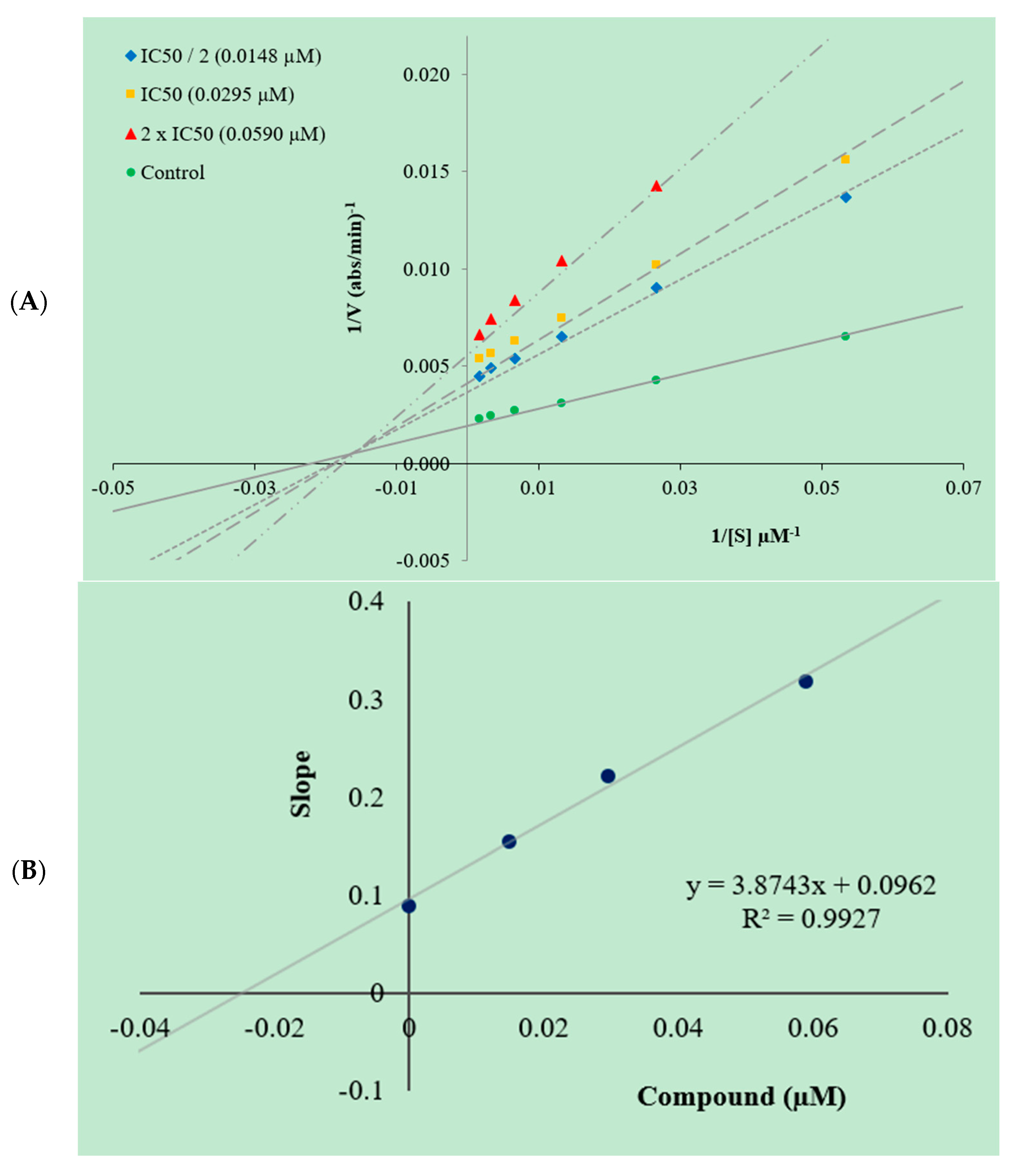
2.3. Enzyme Kinetic Studies
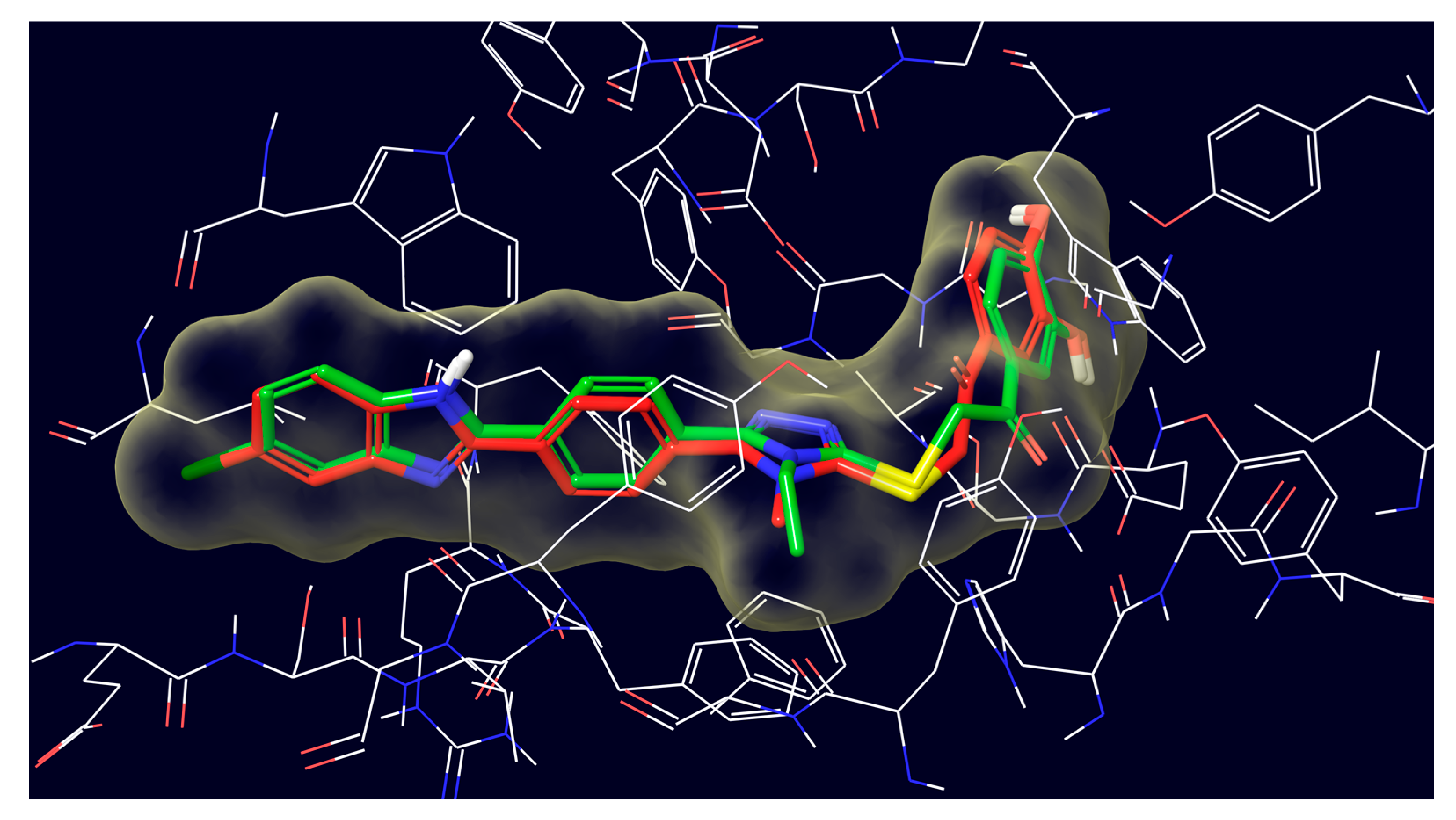
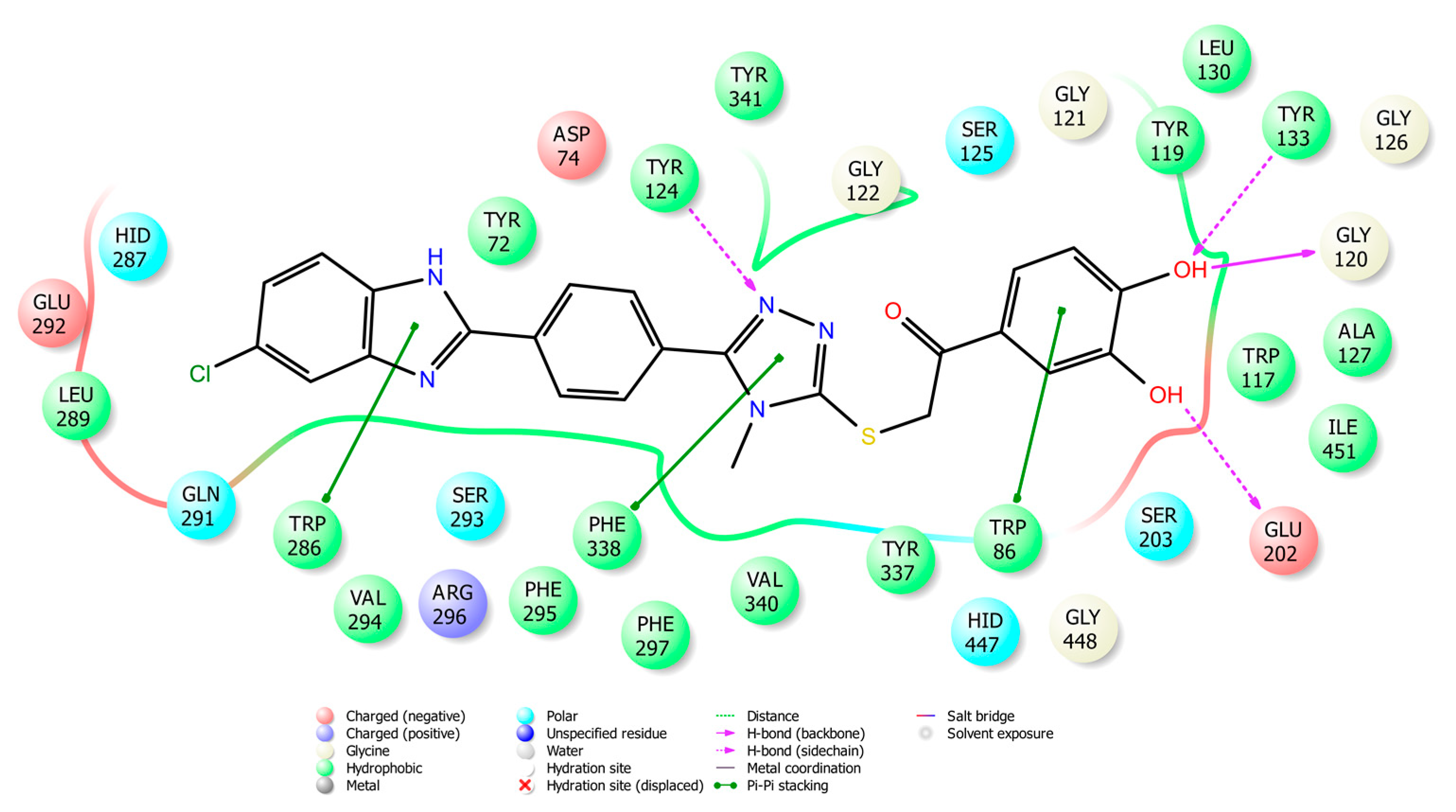
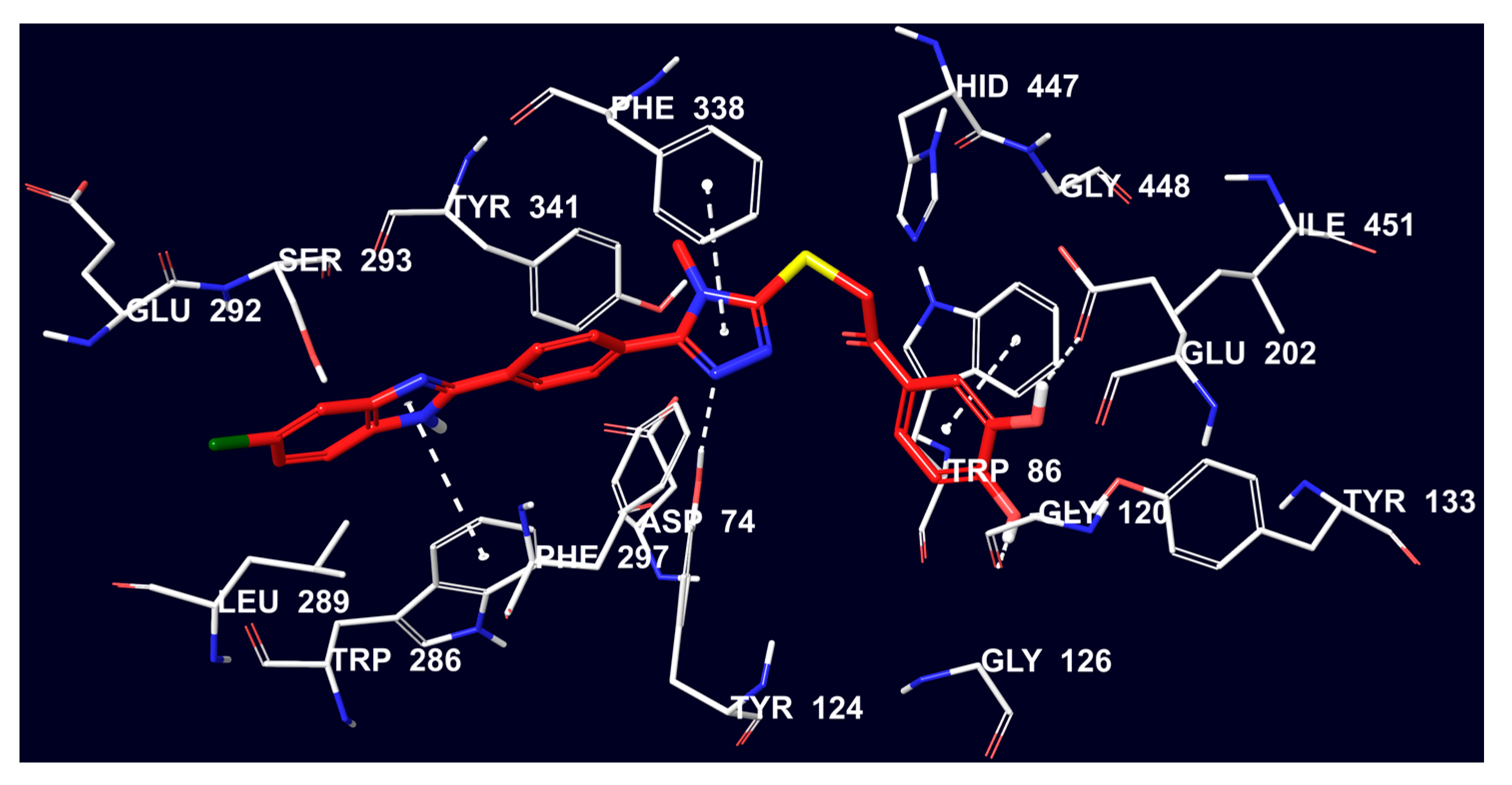
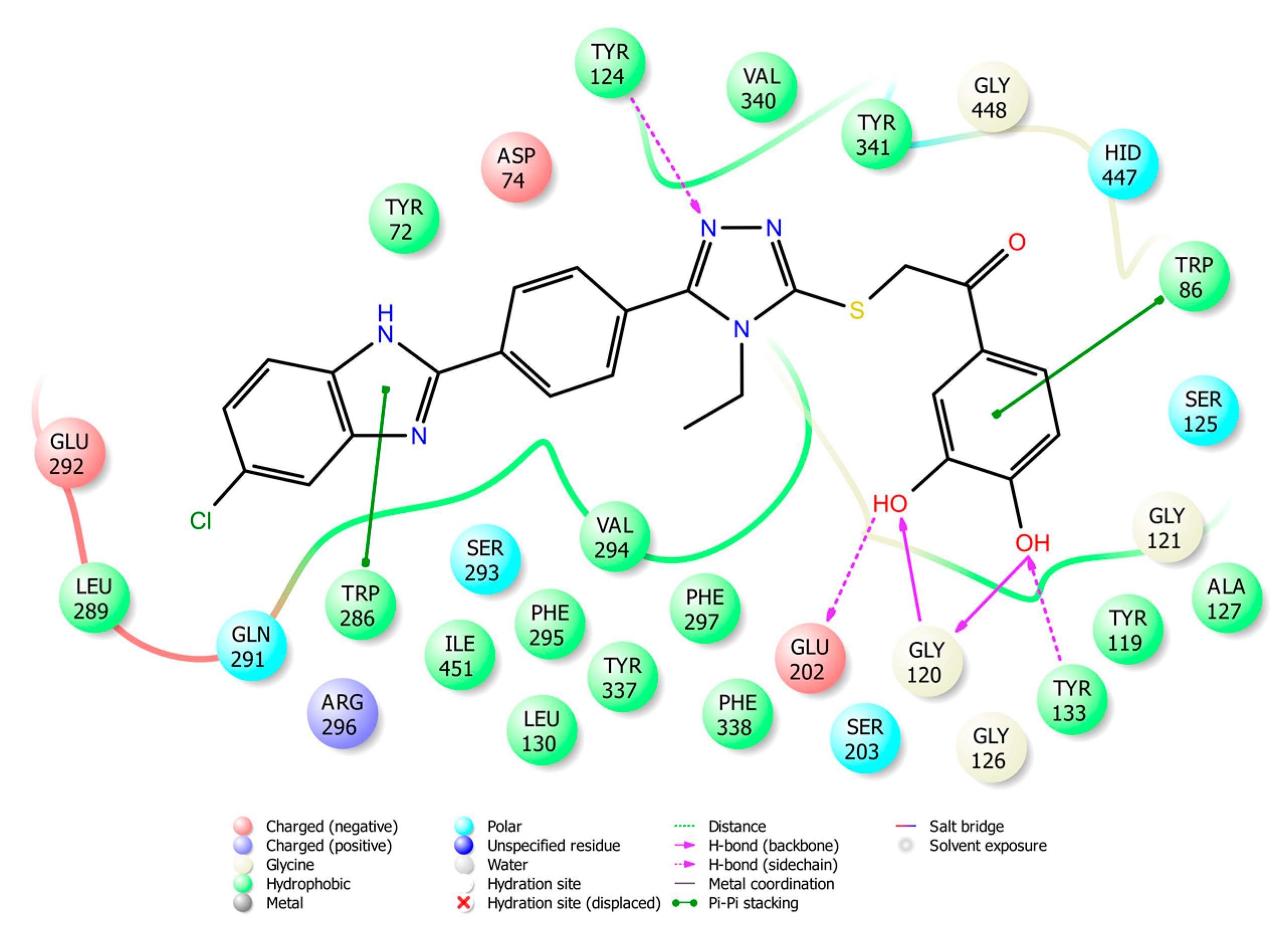
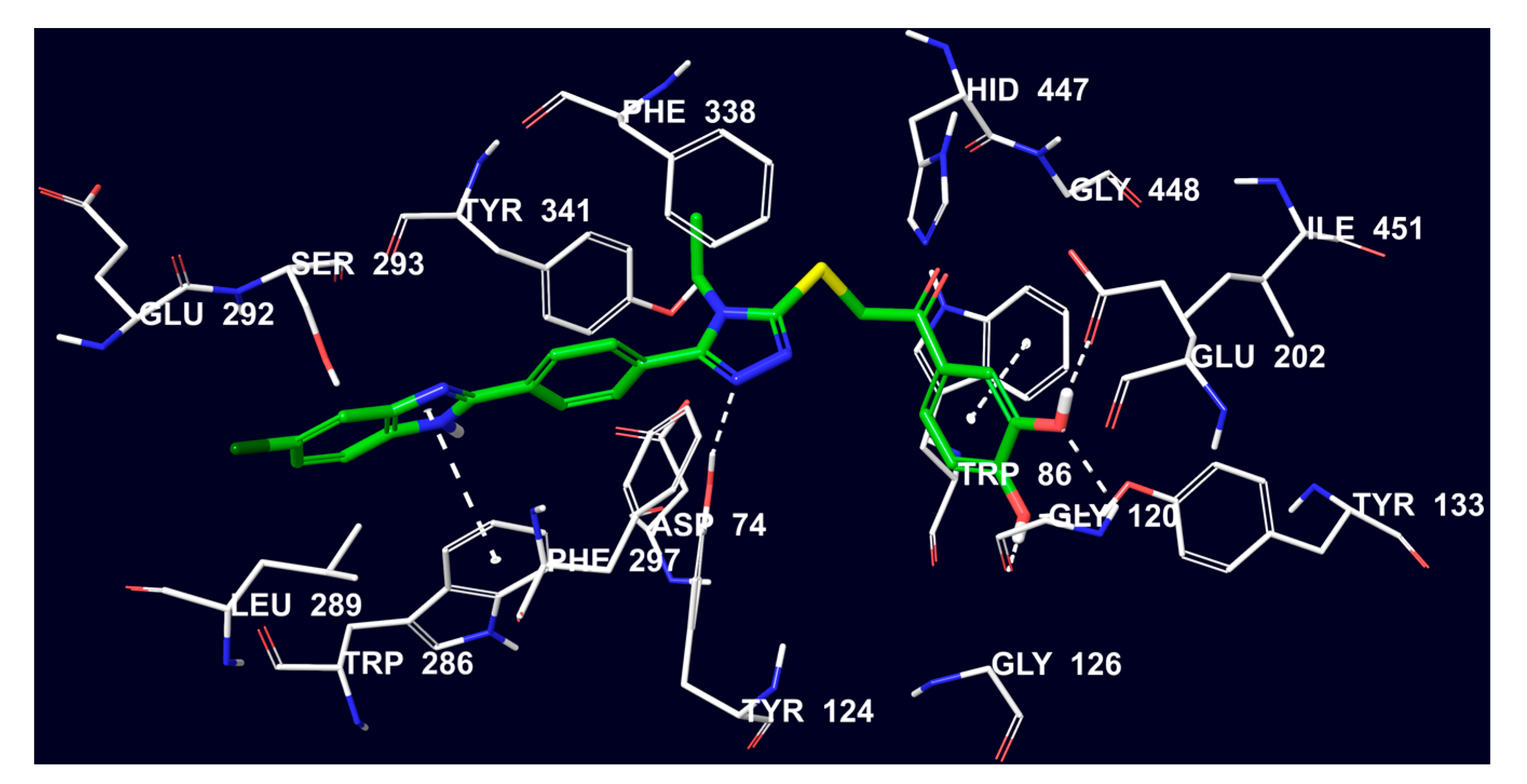
2.4. Molecular Docking Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. 5(6)-Chloro/fluoro-2-((4-methylcarboxylate)phenyl)-1H-benzimidazole
3.1.2. 4-(5(6)-Chloro/fluoro-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)benzohydrazide
3.1.3. N-methyl/ethyl-2-[4-(5(6)-chloro/fluoro-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)benzoyl]hydrazine-1-carbothioamide
3.1.4. 4-Methyl/Ethyl-5[4-5(6)-chloro/fluoro-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)phenyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thiol (1a–d)
3.1.5. 2-(4-(4-Methyl/ethyl-5-(2-(substitutedphenyl)-2-oxo-ethylthio)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3yl)-phenyl)-5(6)-chloro/fluoro-1H-benzimidazoles 3a–p
3.2. Anticholinesterase Activity Assay
3.3. Kinetic Studies of Enzyme Inhibition
3.4. Molecular Docking Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madav, Y.; Wairkar, S.; Prabhakar, B. Recent therapeutic strategies targeting beta amyloid and tauopathies in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2019, 146, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.H.; Karri, V.; Tay, N.W.R.; Chang, K.H.; Ah, H.Y.; Ng, P.Q.; Ho, H.S.; Keh, H.W.; Candasamy, M. Emerging pathways to neurodegeneration: Dissecting the critical molecular mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Chu, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Dai, C.; Huang, X.; Fang, L.; Ao, Q.; Huang, D. The neuroprotective effect of deep brain stimulation at nucleus basalis of Meynert in transgenic mice with Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmaoglu, S.; Yilmaz, A.O.; Polat, M.F.; Kaya, R.; Gulcin, İ.; Algul, O. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Tris-Chalcones as Potent Carbonic Anhydrase, Acetylcholinesterase, Butyrylcholinesterase and α-Glycosidase Inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 85, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Gabr, M.T. Multitarget therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease. Neural. Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pilipenko, V.; Narbute, K.; Beitnere, U.; Rumaks, J.; Pupure, J.; Jansone, B.; Klusa, V. Very low doses of muscimol and baclofen ameliorate cognitive deficits and regulate protein expression in the brain of a rat model of streptozocin-induced Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 818, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Anumala, U.R.; Heyny-von Haußen, R.; Hölzer, J.; Goetschy-Meyer, V.; Mall, G.; Hılger, I.; Czech, C.; Schmidt, B. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of trimethine cyanine dyes as fluorescent probes for the detection of tau fibrils in Alzheimer’s disease brain and olfactory epithelium. Chem. Med. Chem. 2013, 8, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, H.; Khan, A.; Vaibhav, K.; Khan, M.M.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, M.E.; Ahmad, A.; Tabassum, R.; Islam, F.; Safhi, M.M.; et al. Taurine ameliorates neurobehavioral, neurochemical and immunohistochemical changes in sporadic dementia of Alzheimer’s type (SDAT) caused by intracerebroventricular streptozotocin in rats. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 2181–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Gupta, S.K.; Ganeshpurkar, A.; Gutti, G.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Modi, G.; Singh, S.K. Development of Piperazinediones as dual inhibitor for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 150, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, A.; Zaib, S.; Ashraf, S.; Iftikhar, J.; Muddassar, M.; Zhang, K.Y.; Iqbal, J. Synthesis, cholinesterase inhibition and molecular modelling studies of coumarin linked thiourea derivatives. Bioorg. Chem. 2015, 63, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, Z.; Mahdavi, M.; Saeedi, M.; Karimpour-Razkenari, E.; Edraki, N.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Khanavi, M.; Akbarzadeh, T. Novel tacrine-coumarin hybrids linked to 1, 2, 3-triazole as anti-Alzheimer’s compounds: In vitro and in vivo biological evaluation and docking study. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 83, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolet, Y.; Lockridge, O.; Masson, P.; Fontecilla-Camps, J.C.; Nachon, F. Crystal structure of human butyrylcholinesterase and of its complexes with substrate and products. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 41141–41147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallender, W.D.; Szegletes, T.; Rosenberry, T.L. Acetylthiocholine binds to Asp74 at the peripheral site of human acetylcholinesterase as the first step in the catalytic pathway. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 7753–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehfooz, H.; Saeed, A.; Sharma, A.; Albericio, F.; Larik, F.A.; Jabeen, F.; Channar, P.A.; Flörke, U. Dual Inhibition of AChE and BChE with the C-5 Substituted Derivative of Meldrum’s Acid: Synthesis, Structure Elucidation, and Molecular Docking Studies. Crystals 2017, 7, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, J.A.; Trujillo, J.G.; Quintana, D.; Jiménez, H.A.; Arellano, M.G.; Bahena, J.R.; Tamay, F.; Ciprés, F.J. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition by products generated in situ from the transformation of N-arylisomaleimides. Med. Chem. Res. 2018, 27, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Malpani, Y.R.; Lee, J.; Shin, J.S.; Han, S.B.; Jung, Y.S. Novel tacrine-pyridinium hybrid reactivators of organophosphorus-inhibited acetylcholinesterase: Synthesis, molecular docking, and in vitro reactivation study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 3784–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkay, Ü.D.; Can, Ö.D.; Sağlık, B.N.; Cevik, U.A.; Levent, S.; Özkay, Y.; Ilgın, S.; Atlı, Ö. Design, synthesis, and AChE inhibitory activity of new benzothiazole–piperazines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5387–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, H.; Demirtas, A.; Ucar, G.; Taslimi, P.; Gulcin, I. Synthesis of Mannich bases by two different methods and evaluation of their acetylcholine esterase and carbonic anhydrase inhibitory activities. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2017, 14, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.M.; Barreiro, E.J. Bioisosterism: A useful strategy for molecular modification and drug design. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patani, G.A.; LaVoie, E.J. Bioisosterism: A rational approach in drug design. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 3147–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havrylyuk, D.; Heidary, D.K.; Nease, L.; Parkin, S.; Glazer, E.C. Photochemical Properties and Structure-Activity Relationships of RuII Complexes with Pyridylbenzazole Ligands as Promising Anticancer Agents. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 12, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiremathad, A.; Keri, R.S.; Esteves, A.R.; Cardoso, S.M.; Chaves, S.; Santos, M.A. Novel Tacrine-Hydroxyphenylbenzimidazole hybrids as potential multitarget drug candidates for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 148, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, N.; Mirjalili, B.B.F.; Nadri, H.; Abdolahi, Z.; Forootanfar, H.; Samzadeh-Kermani, A.; Küçükkılınç, T.T.; Ayazgok, B.; Emami, S.; Haririan, I.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new N-benzylpyridinium-based benzoheterocycles as potential anti-Alzheimer’s agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 83, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, M.V.; Castro, H.C.; Abreu, P.A. Molecular Modeling of Benzimidazole Derivatives: A Promising Series of GluN2B Selective NMDA Receptor Antagonists. Curr. Drug Therapy 2018, 13, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, S.; Tatheer, A. 4-Acetamidobenzaldehyde derivatives as biological active candidates; synthesis, anti-oxidant, Anti-Alzheimer and DNA binding studies. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2018, 15, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan-Zitouni, G.; Hussein, W.; Saglik, B.N.; Baysal, M.; Kaplancikli, Z.A. Fighting Against Alzheimer’s Disease: Synthesis of New Pyrazoline and Benzothiazole Derivatives as New Acetylcholinesterase and MAO Inhibitors. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2018, 15, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, S.; Hiremathad, A.; Tomás, D.; Keri, R.S.; Piemontese, L.; Santos, M.A. Exploring the chelating capacity of 2-hydroxyphenyl-benzimidazole based hybrids with multi-target ability as anti-Alzheimer’s agents. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 16503–16515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouramiri, B.; Moghimi, S.; Mahdavi, M.; Nadri, H.; Moradi, A.; Tavakolinejad-Kermani, E.; Firoozpour, L.; Asadipour, A.; Foroumadi, A. Synthesis and anticholinesterase activity of new substituted benzo [d] oxazole-based derivatives. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 89, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarıkaya, G.; Çoban, G.; Parlar, S.; Tarikogullari, A.H.; Armagan, G.; Erdoğan, M.A.; Alptüzün, V.; Alpan, A.S. Multifunctional cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease: Synthesis, biological evaluations, and docking studies of o/p-propoxyphenylsubstituted-1H-benzimidazole derivatives. Arch. Pharm. 2018, 351, 1800076. [Google Scholar]
- Unsal-Tan, O.; Ozadali-Sari, K.; Ayazgok, B.; Küçükkılınç, T.T.; Balkan, A. Novel 2-Arylbenzimidazole derivatives as multi-targeting agents to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 1506–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozadali-Sari, K.; Küçükkılınç, T.T.; Ayazgok, B.; Balkan, A.; Unsal-Tan, O. Novel multi-targeted agents for Alzheimer’s disease: Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular modeling of novel 2-[4-(4-substitutedpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] benzimidazoles. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 72, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpan, A.S.; Parlar, S.; Carlino, L.; Tarikogullari, A.H.; Alptüzün, V.; Güneş, H.S. Synthesis, biological activity and molecular modeling studies on 1H-benzimidazole derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 4928–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaburun, A.Ç.; Kaya Çavuşoğlu, B.; Acar Çevik, U.; Osmaniye, D.; Sağlık, B.N.; Levent, S.; Özkay, Y.; Atlı, Ö.; Koparal, A.S.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. Synthesis and Antifungal Potential of Some Novel Benzimidazole-1,3,4-Oxadiazole Compounds. Molecules 2019, 24, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaca Gençer, H.; Acar Çevik, U.; Levent, S.; Sağlık, B.N.; Korkut, B.; Özkay, Y.; Ilgın, S.; Öztürk, Y. New Benzimidazole-1,2,4-Triazole Hybrid Compounds: Synthesis, Anticandidal Activity and Cytotoxicity Evaluation. Molecules 2017, 22, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, Ö.D.; Osmaniye, D.; Demir Özkay, Ü.; Sağlık, B.N.; Levent, S.; Ilgın, S.; Baysal, M.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. MAO enzymes inhibitory activity of new benzimidazole derivatives including hydrazone and propargyl side chains. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 131, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, J.; Rudolph, M.J.; Burshteyn, F.; Cassidy, M.S.; Gary, E.N.; Love, J.; Height, J.J. Structures of human acetylcholinesterase in complex with pharmacologically important ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10282–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sağlık, B.N.; Ilgın, S.; Özkay, Y. Synthesis of new donepezil analogues and investigation of their effects on cholinesterase enzymes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 124, 1026–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, W.; Sağlık, B.N.; Levent, S.; Korkut, B.; Ilgın, S.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Molecules 2018, 23, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tok, F.; Koçyiğit Kaymakçıoğlu, B.; Sağlık, B.N.; Levent, S.; Özkay, Y.; Kaplancıklı, Z.A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new pyrazolone Schiff bases as monoamine oxidase and cholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 84, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 3a–p are available from the authors. |
| Compounds | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | –Cl | –CH3 | - | - | 81 |
| 1b | –Cl | –C2H5 | - | - | 78 |
| 1d | –F | –CH3 | - | - | 77 |
| 1c | –F | –C2H5 | - | - | 75 |
| 3a | –Cl | –CH3 | –H | –CN | 84 |
| 3b | –Cl | –CH3 | –H | –Br | 82 |
| 3c | –Cl | –CH3 | –H | –CH3 | 79 |
| 3d | –Cl | –CH3 | –OH | –OH | 76 |
| 3e | –Cl | –C2H5 | –H | –CN | 81 |
| 3f | –Cl | –C2H5 | –H | –Br | 80 |
| 3g | –Cl | –C2H5 | –H | –CH3 | 74 |
| 3h | –Cl | –C2H5 | –OH | –OH | 83 |
| 3i | –F | –CH3 | –H | –CN | 76 |
| 3j | –F | –CH3 | –H | –Br | 73 |
| 3k | –F | –CH3 | –H | –CH3 | 71 |
| 3l | –F | –CH3 | –OH | –OH | 77 |
| 3m | –F | –C2H5 | –H | –CN | 70 |
| 3n | –F | –C2H5 | –H | –Br | 73 |
| 3o | –F | –C2H5 | –H | –CH3 | 82 |
| 3p | –F | –C2H5 | –OH | –OH | 81 |
| Compounds | % Inhibition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AChE | BChE | |||
| 10−3 M | 10−4 M | 10−3 M | 10−4 M | |
| 3a | 68.18 ± 1.05 | 47.26 ± 0.62 | 40.28 ± 0.98 | 25.13 ± 0.56 |
| 3b | 44.20 ± 0.87 | 26.18 ± 0.63 | 28.15 ± 0.97 | 18.42 ± 0.88 |
| 3c | 39.18 ± 0.71 | 17.89 ± 0.54 | 26.11 ± 0.74 | 20.21 ± 0.61 |
| 3d | 98.55 ± 1.17 | 93.99 ± 1.10 | 51.19 ± 0.99 | 38.12 ± 0.41 |
| 3e | 77.29 ± 1.06 | 41.22 ± 0.84 | 38.22 ± 0.63 | 22.41 ± 0.47 |
| 3f | 47.22 ± 0.67 | 24.08 ± 0.48 | 29.15 ± 0.59 | 17.88 ± 0.40 |
| 3g | 37.20 ± 0.68 | 18.33 ± 0.38 | 31.89 ± 0.99 | 24.75 ± 0.95 |
| 3h | 98.25 ± 1.12 | 94.55 ± 1.08 | 61.26 ± 0.90 | 35.20 ± 0.42 |
| 3i | 61.22 ± 1.02 | 38.28 ± 0.67 | 43.51 ± 0.78 | 18.49 ± 0.50 |
| 3j | 48.51 ± 0.88 | 18.39 ± 0.60 | 29.64 ± 0.87 | 21.44 ± 0.70 |
| 3k | 42.29 ± 0.71 | 27.88 ± 0.67 | 36.17 ± 0.93 | 21.16 ± 0.97 |
| 3l | 94.58 ± 1.74 | 83.20 ± 1.13 | 55.43 ± 0.47 | 29.88 ± 0.38 |
| 3m | 59.03 ± 0.88 | 39.26 ± 0.46 | 48.11 ± 0.38 | 20.66 ± 0.45 |
| 3n | 49.27 ± 0.55 | 30.21 ± 0.49 | 27.10 ± 0.53 | 18.77 ± 0.42 |
| 3o | 28.06 ± 0.33 | 19.22 ± 0.30 | 25.99 ± 0.38 | 20.08 ± 0.46 |
| 3p | 87.26 ± 1.17 | 81.25 ± 1.88 | 53.19 ± 0.46 | 31.44 ± 0.38 |
| Donepezil | 99.42 ± 1.85 | 97.26 ± 1.24 | - | - |
| Tacrine | - | - | 98.52 ± 1.66 | 95.50 ± 1.74 |
| Compounds | % Inhibition of AChE | AChE IC50 (nM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10−5 M | 10−6 M | 10−7 M | 10−8 M | 10−9 M | ||
| 3d | 87.26 ± 1.28 | 78.85 ± 1.19 | 67.18 ± 0.92 | 45.32 ± 0.82 | 15.75 ± 0.48 | 31.9 ± 0.1 |
| 3h | 90.23 ± 1.03 | 81.25 ± 1.08 | 65.32 ± 0.97 | 44.28 ± 0.71 | 17.20 ± 0.58 | 29.5 ± 1.2 |
| 3l | 73.18 ± 1.17 | 68.20 ± 0.97 | 48.11 ± 0.61 | 32.29 ± 0.58 | 18.77 ± 0.37 | 169.4 ± 7.2 |
| 3p | 77.48 ± 1.98 | 71.62 ± 1.08 | 47.83 ± 0.97 | 39.33 ± 0.67 | 15.47 ± 0.64 | 139.9 ± 5.1 |
| Donepezil | 94.11 ± 1.71 | 90.17 ± 1.02 | 75.65 ± 1.15 | 35.74 ± 0.58 | 17.89 ± 0.42 | 21.8 ± 0.9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acar Cevik, U.; Saglik, B.N.; Levent, S.; Osmaniye, D.; Kaya Cavuşoglu, B.; Ozkay, Y.; Kaplancikli, Z.A. Synthesis and AChE-Inhibitory Activity of New Benzimidazole Derivatives. Molecules 2019, 24, 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050861
Acar Cevik U, Saglik BN, Levent S, Osmaniye D, Kaya Cavuşoglu B, Ozkay Y, Kaplancikli ZA. Synthesis and AChE-Inhibitory Activity of New Benzimidazole Derivatives. Molecules. 2019; 24(5):861. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050861
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcar Cevik, Ulviye, Begüm Nurpelin Saglik, Serkan Levent, Derya Osmaniye, Betul Kaya Cavuşoglu, Yusuf Ozkay, and Zafer Asim Kaplancikli. 2019. "Synthesis and AChE-Inhibitory Activity of New Benzimidazole Derivatives" Molecules 24, no. 5: 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050861
APA StyleAcar Cevik, U., Saglik, B. N., Levent, S., Osmaniye, D., Kaya Cavuşoglu, B., Ozkay, Y., & Kaplancikli, Z. A. (2019). Synthesis and AChE-Inhibitory Activity of New Benzimidazole Derivatives. Molecules, 24(5), 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050861