Chromo-Fluorogenic Detection of Soman and Its Simulant by Thiourea-Based Rhodamine Probe
Abstract
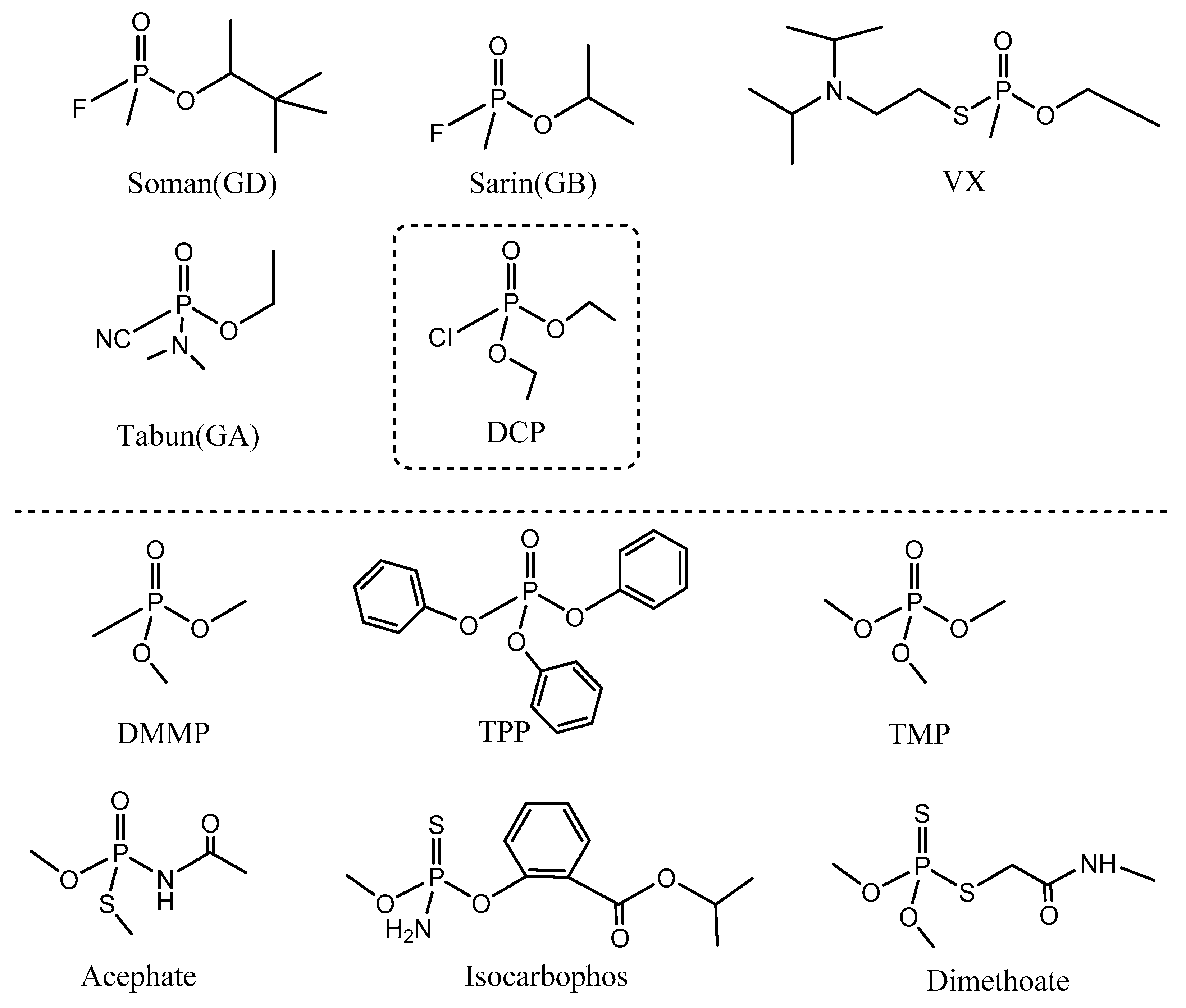
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
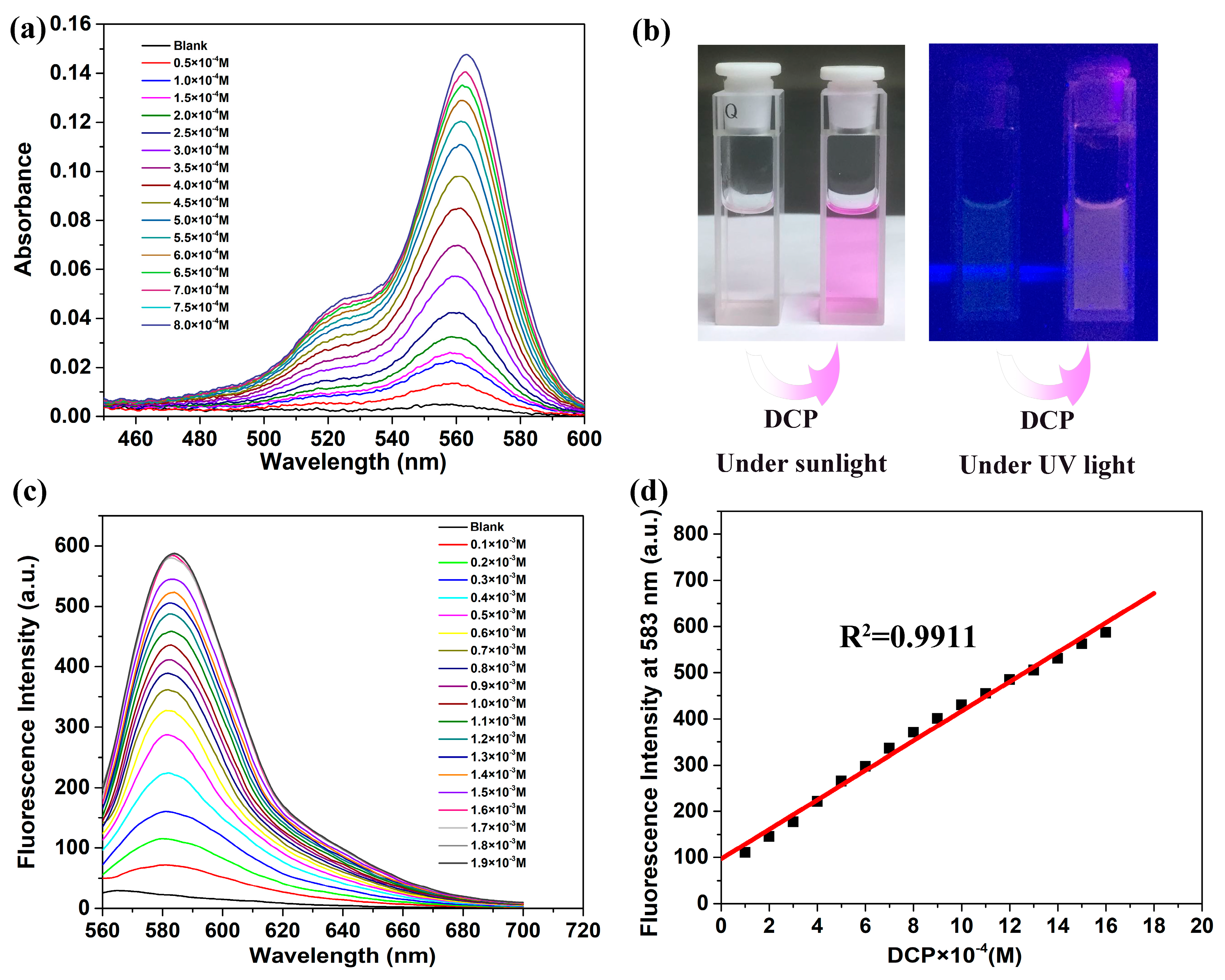
2.1. Spectroscopic Properties
2.2. Reaction Kinetics Study
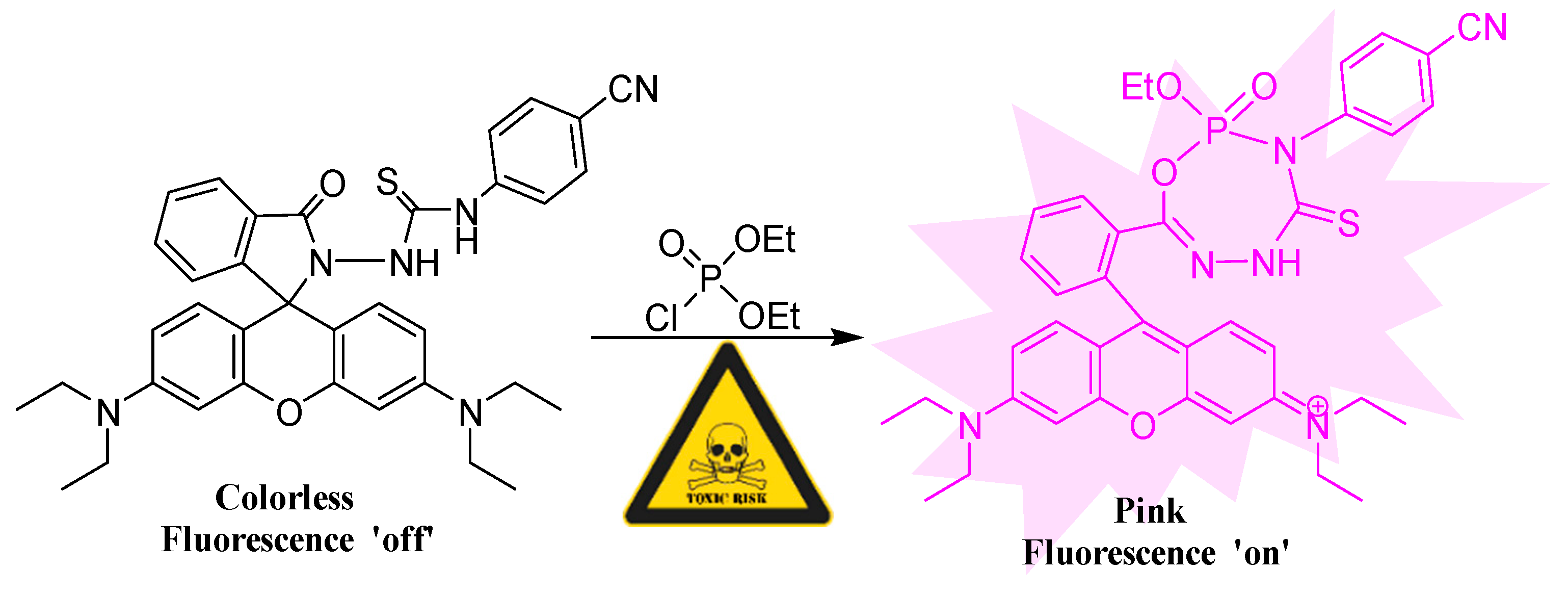
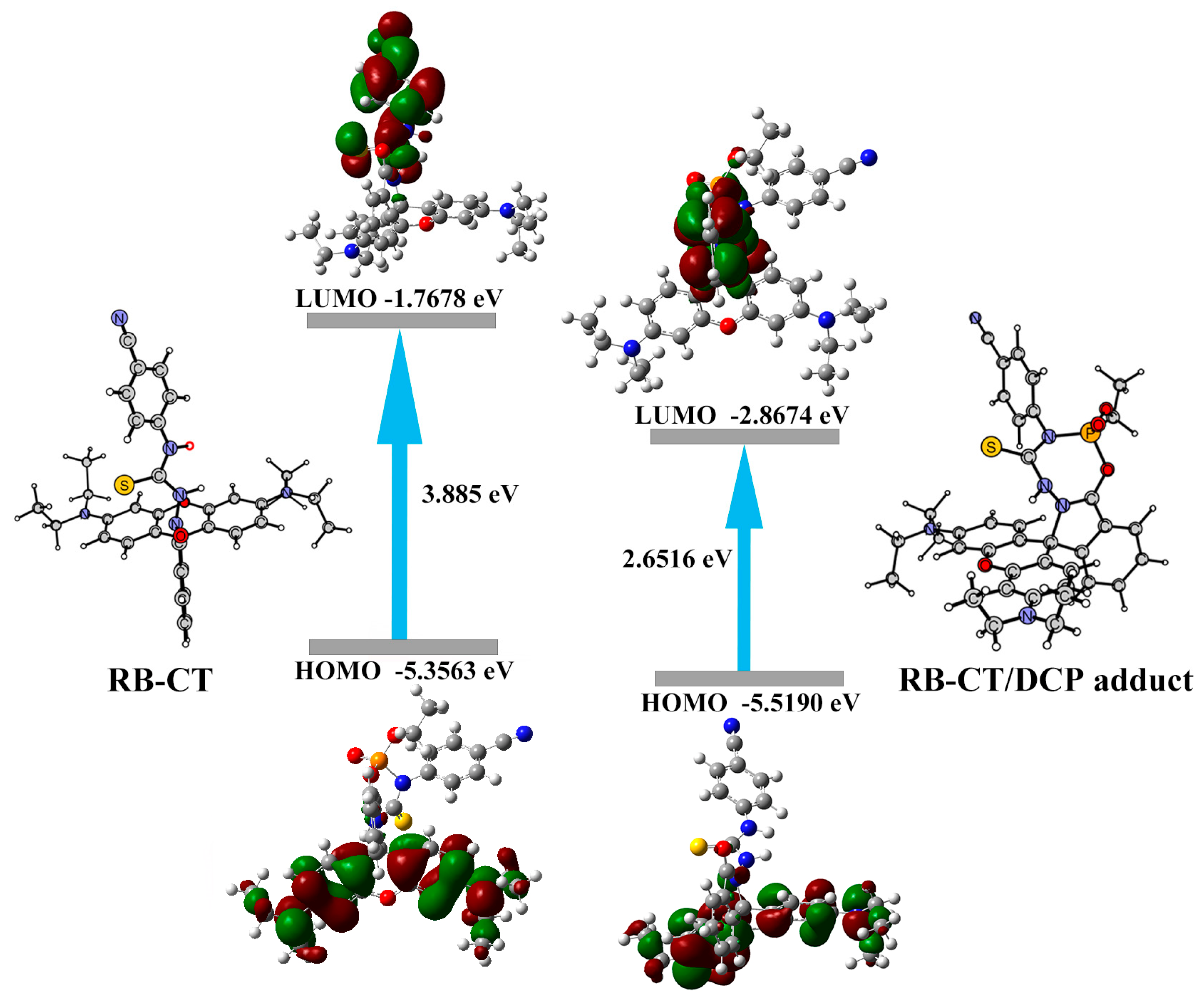
2.3. Mechanism Study
2.4. Interferents
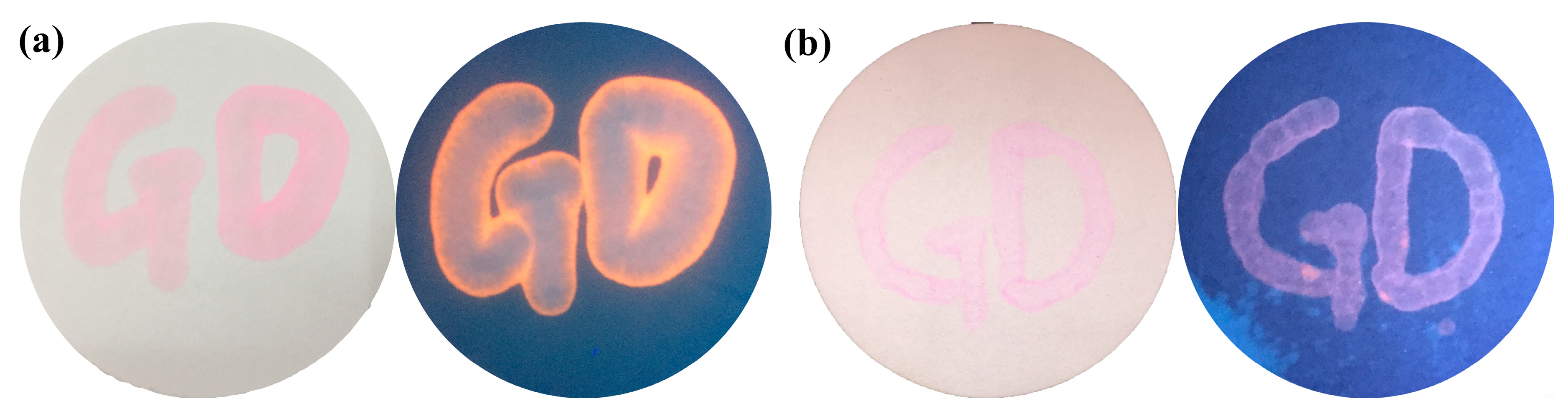
2.5. Practical Application toward Real Nerve Agent
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Measurements
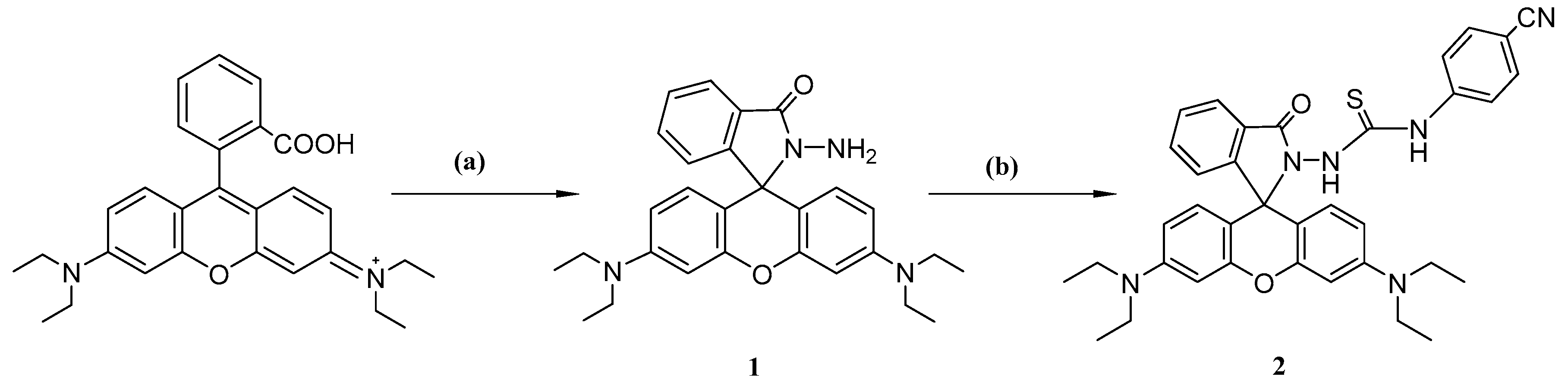
3.3. Synthetic Procedures
3.4. Reaction Kinetics Study
3.5. Computational Methods
3.6. Interferents
3.7. The Preparation of Test Kits of Real Nerve Agents in Liquid and Gas Phase
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szinicz, L. History of chemical and biological warfare agents. Toxicology 2005, 214, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunderson, C.H.; Lehmann, C.R.; Sidell, F.R.; Jabbari, B. Nerve agents: A review. Neurology 1992, 42, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Yang, Y. A concise colorimetric and fluorimetric probe for sarin related threats designed via the "covalent-assembly" approach. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6594–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.J.; Pishko, M.V.; Simonian, A.L.; Wild, J.R. Poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel-encapsulated fluorophore-enzyme conjugates for direct detection of organophosphorus neurotoxins. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 4909–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, A.J.; Berberich, J.A.; Drevon, G.F.; Koepsel, R.R. Biomaterials for mediation of chemical and biological warfare agents. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 5, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Cho, B.; Sohn, H. Detection of nerve agent stimulants based on photoluminescent porous silicon interferometer. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorribes-Soriano, A.; de la Guardia, M.; Esteve-Turrillas, F.A.; Armenta, S. Trace analysis by ion mobility spectrometry: From conventional to smart sample preconcentration methods. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1026, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresova, E.; Tomecek, D.; Fitl, P.; Vlcek, J.; Novotny, M.; Fiser, L.; Havlova, S.; Hozak, P.; Tudor, A.; Glennon, T.; et al. Textile chemiresistors with sensitive layers based on polymer ionic liquids: Applicability for detection of toxic gases and chemical warfare agents. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2018, 266, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.P.; Kimble, K.W.; Asher, S.A. Photonic crystal sensor for organophosphate nerve agents utilizing the organophosphorus hydrolase enzyme. Anal. Bioanal Chem. 2007, 389, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Liu, Z.; Du, X.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, D. Analytical application of poly{methyl[3-(2-hydroxy-3,4-difluoro)phenyl]propyl siloxane} as a QCM coating for DMMP detection. Talanta 2008, 76, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittle, J.D.; Fisher, B.P.; Esparza, A.J.; Morey, A.M.; Iacono, S.T. Sensing Chemical Warfare Agent Simulants via Photonic Crystals of the Morpho didius Butterfly. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 8301–8307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, K.S.; Mazumder, A.; Goud, D.R.; Dubey, D.K. A simplistic designing of molecularly imprinted polymers for derivative of nerve agents marker using P-31{H-1}NMR. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 98, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda Kumar, D.; Satija, J.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Mukherjee, A. Acetylcholinesterase-based inhibition screening through in situ synthesis of gold nanoparticles: Application for detection of nerve agent simulant. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costero, A.M.; Parra, M.; Gil, S.; Gotor, R.; Mancini, P.M.E.; Martinez-Manez, R.; Sancenon, F.; Royo, S. Chromo-fluorogenic detection of nerve-agent mimics using triggered cyclization reactions in push-pull dyes. Chem. Asian J. 2010, 5, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goud, D.R.; Pardasani, D.; Tak, V.; Dubey, D.K. A highly selective visual detection of tabun mimic diethyl cyanophosphate (DCNP): effective discrimination of DCNP from other nerve agent mimics. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 24645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba-Bon, A.; Costero, A.M.; Gil, S.; Martinez-Manez, R.; Sancenon, F. Selective chromo-fluorogenic detection of DFP (a Sarin and Soman mimic) and DCNP (a Tabun mimic) with a unique probe based on a boron dipyrromethene (BODIPY) dye. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 8745–8751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Jang, Y.J.; Lee, D.; Kim, B.-S.; Churchill, D.G. Real nerve agent study assessing pyridyl reactivity: Selective fluorogenic and colorimetric detection of Soman and simulant. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2017, 238, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Maiti, K.; Mondal, S.; Pramanik, A.K.; Guria, U.N.; Uddin, M.R.; Mandal, S.; Mandal, D.; Mahapatra, A.K. A chromogenic and ratiometric fluorogenic probe for rapid detection of a nerve agent simulant DCP based on a hybrid hydroxynaphthalene-hemicyanine dye. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 5959–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.-C.; Li, C.; Song, Q.-H. Selective and visual detection of a nerve agent mimic by phosphorylation and protonation of quinolin oximes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 7337–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royo, S.; Costero, A.M.; Parra, M.; Gil, S.; Martinez-Manez, R.; Sancenon, F. Chromogenic, specific detection of the nerve-agent mimic DCNP (a tabun mimic). Chemistry 2011, 17, 6931–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, L.; Sayed, S.E.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Costero, A.M.; Gil, S.; Gaviña, P.; Sancenón, F. Acetylcholinesterase-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles That Open in the Presence of Diisopropylfluorophosphate (a Sarin or Soman Simulant). Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 5548–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, H.S.; Ghosh, A.; Das, S.; Maiti, P.K.; Maitra, S.; Mandal, S.; Sahoo, P. Visualisation of DCP, a nerve agent mimic, in Catfish brain by a simple chemosensor. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wu, D.; Yoon, J. Recent Advances in the Development of Chromophore-Based Chemosensors for Nerve Agents and Phosgene. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royo, S.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F.; Costero, A.M.; Parra, M.; Gil, S. Chromogenic and fluorogenic reagents for chemical warfare nerve agents’ detection. Chem. Commun. 2007, 4839–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, S.; Pascual, L.; Agostini, A.; Martinez-Manez, R.; Sancenon, F.; Costero, A.M.; Parra, M.; Gil, S. A Chromogenic Probe for the Selective Recognition of Sarin and Soman Mimic DFP. ChemistryOpen 2014, 3, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.J.; Wang, Y.-W.; Senge, M.O.; Peng, Y. Sensitive fluorescence on-off probes for the fast detection of a chemical warfare agent mimic. J. Hazard Mater. 2018, 342, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.; Lee, M.; Seo, H.O.; Song, S.G.; Kim, K.S.; Park, C.H.; Kim, I.H.; Kim, Y.D.; Song, C. Structural Effect of Thioureas on the Detection of Chemical Warfare Agent Simulants. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Rana, H.; Raviraju, G.; Garg, P.; Baghel, A.; Gupta, A.K. Chromogenic and fluorogenic multianalyte detection with a tuned receptor: refining selectivity for toxic anions and nerve agents. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 59648–59656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.K.; Keunjeong Yook, A.; Tae, J. A Rhodamine-Based Fluorescent and Colorimetric Chemodosimeter for the Rapid Detection of Hg2+ Ions in Aqueous Media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 16760–16761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, S.; Manna, A.; Paul, S. Rapid ‘naked eye’ response of DCP, a nerve agent simulant: from molecules to low-cost devices for both liquid and vapour phase detection. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 21984–21988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, H.-S.; Angupillai, S.; Son, Y.-A. Prompt liquid-phase visual detection and low-cost vapor-phase detection of DCP, a chemical warfare agent mimic. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2016, 235, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramette, R.W.; Sandell, E.B. Rhodamine B Equilibria. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1956, 78, 4872–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotor, R.; Gaviña, P.; Ochando, L.E.; Chulvi, K.; Lorente, A.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Costero, A.M. BODIPY dyes functionalized with 2-(2-dimethylaminophenyl)ethanol moieties as selective OFF–ON fluorescent chemodosimeters for the nerve agent mimics DCNP and DFP. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 15975–15982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-F.; Guo, X.-Q.; Zhao, Y.-B. Development of a novel rhodamine-type fluorescent probe to determine peroxynitrite. Talanta 2002, 57, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision D. 01; Gaussian. Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. A new mixing of Hartree–Fock and local density-functional theories. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehre, W.J.; Ditchfield, R.; Pople, J.A. Self—Consistent Molecular Orbital Methods. XII. Further Extensions of Gaussian—Type Basis Sets for Use in Molecular Orbital Studies of Organic Molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 56, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francl, M.M.; Pietro, W.J.; Hehre, W.J.; Binkley, J.S.; Gordon, M.S.; DeFrees, D.J.; Pople, J.A. Self-consistent molecular orbital methods. XXIII. A polarization-type basis set for second-row elements. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 77, 3654–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauernschmitt, R.; Ahlrichs, R. Treatment of electronic excitations within the adiabatic approximation of time dependent density functional theory. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1996, 256, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, W.W.; Wiberg, K.B.; Frisch, M.J. Solvent effects. 3. Tautomeric Equilibria of Formamide and 2-pyridone in the Gas Phase and Solution: an ab Initio SCRF Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, O.A.; Land, W.H., Jr.; Wang, J. Targeting Chemical and Biological Warfare Agents at the Molecular Level. Electroanalysis 2003, 15, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of compounds 1–2 are available from the authors. |
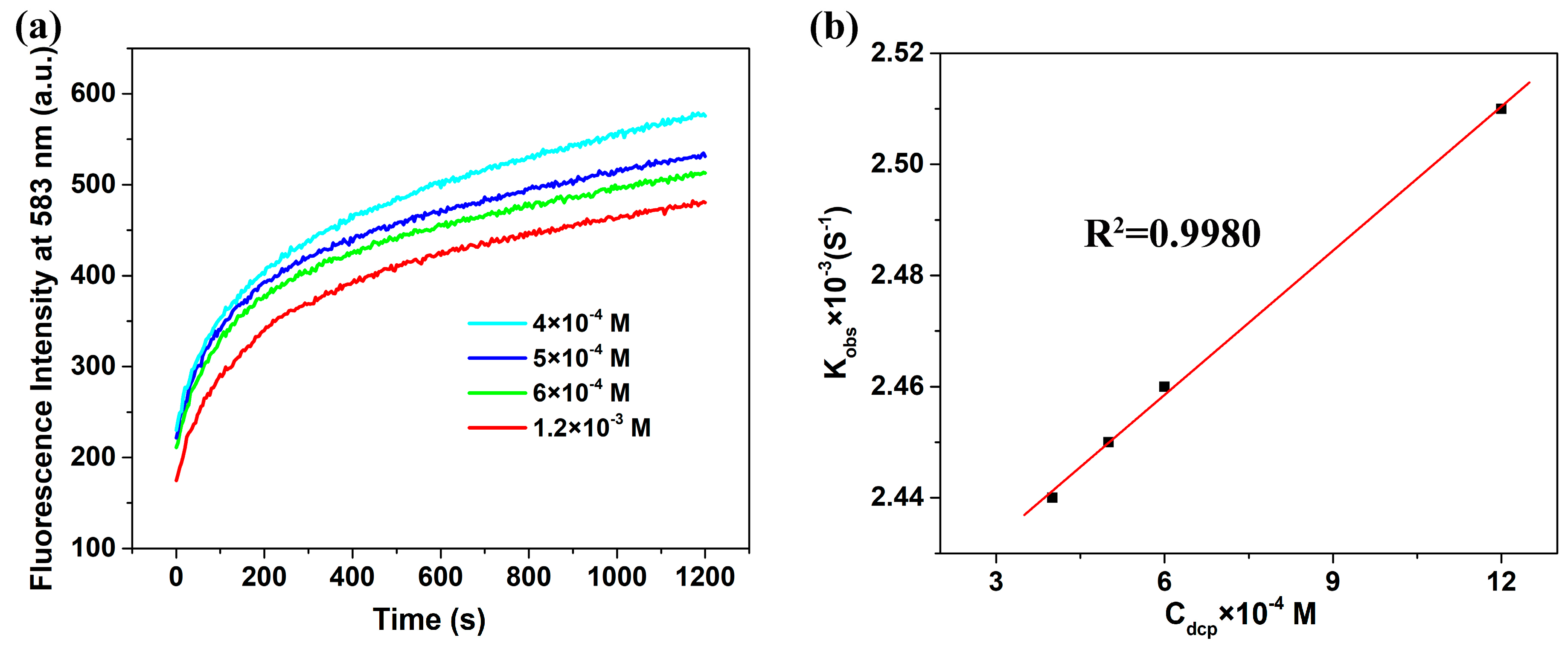

| The Concentrations of DCP | 4 × 10−4 | 5 × 10−4 | 6 × 10−4 | 1.2 × 10−3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kobs (s−1) | 0.00244 | 0.00245 | 0.00246 | 0.00251 |
| t1/2 (s) | 284 | 283 | 282 | 276 |
| k (M−2 S−1) | 8.645 × 10−6 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, W.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Zhong, J.; Zhao, C. Chromo-Fluorogenic Detection of Soman and Its Simulant by Thiourea-Based Rhodamine Probe. Molecules 2019, 24, 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050827
Li S, Zheng Y, Chen W, Zheng M, Zheng H, Zhang Z, Cui Y, Zhong J, Zhao C. Chromo-Fluorogenic Detection of Soman and Its Simulant by Thiourea-Based Rhodamine Probe. Molecules. 2019; 24(5):827. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050827
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shengsong, Yongchao Zheng, Weiqiang Chen, Meiling Zheng, He Zheng, Zhe Zhang, Yan Cui, Jinyi Zhong, and Chonglin Zhao. 2019. "Chromo-Fluorogenic Detection of Soman and Its Simulant by Thiourea-Based Rhodamine Probe" Molecules 24, no. 5: 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050827
APA StyleLi, S., Zheng, Y., Chen, W., Zheng, M., Zheng, H., Zhang, Z., Cui, Y., Zhong, J., & Zhao, C. (2019). Chromo-Fluorogenic Detection of Soman and Its Simulant by Thiourea-Based Rhodamine Probe. Molecules, 24(5), 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050827






