MEG Effects on Hydrolysis of Polyamide 66/Glass Fiber Composites and Mechanical Property Changes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Material
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Immersion in MEG Solution
2.4. Mechanical Properties
2.5. Hydrolysis (Molecular Structure Change) Observation
3. Results and Discussion
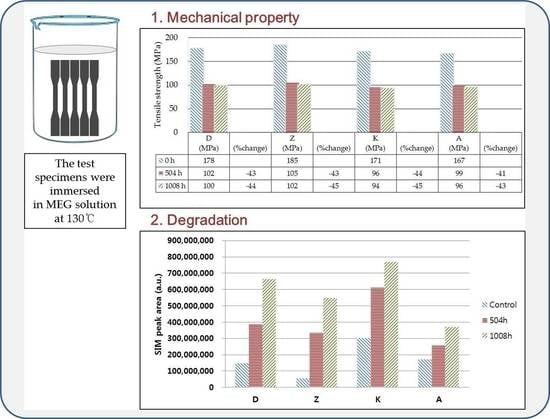
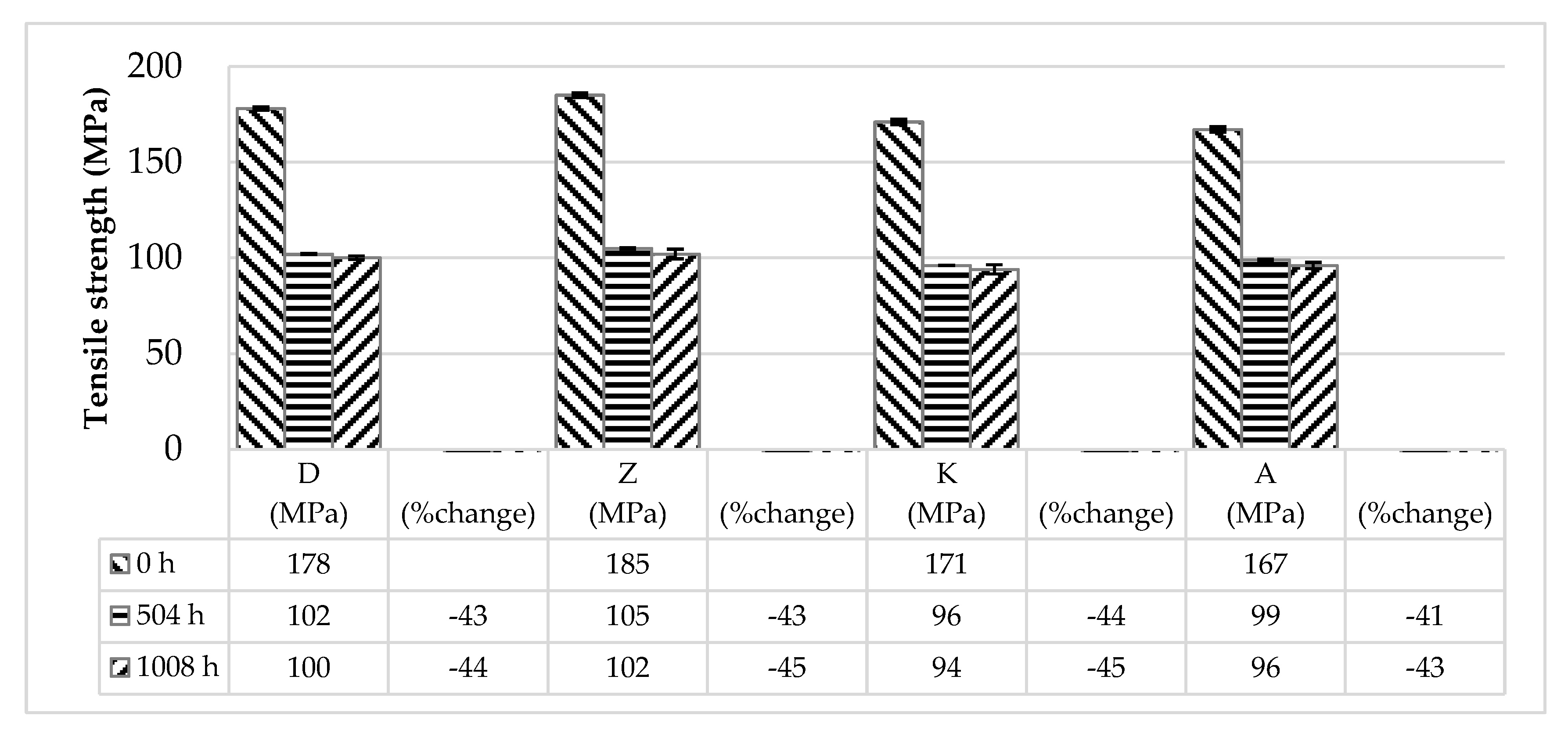
3.1. Changes in Mechanical Properties After Immersion in MEG
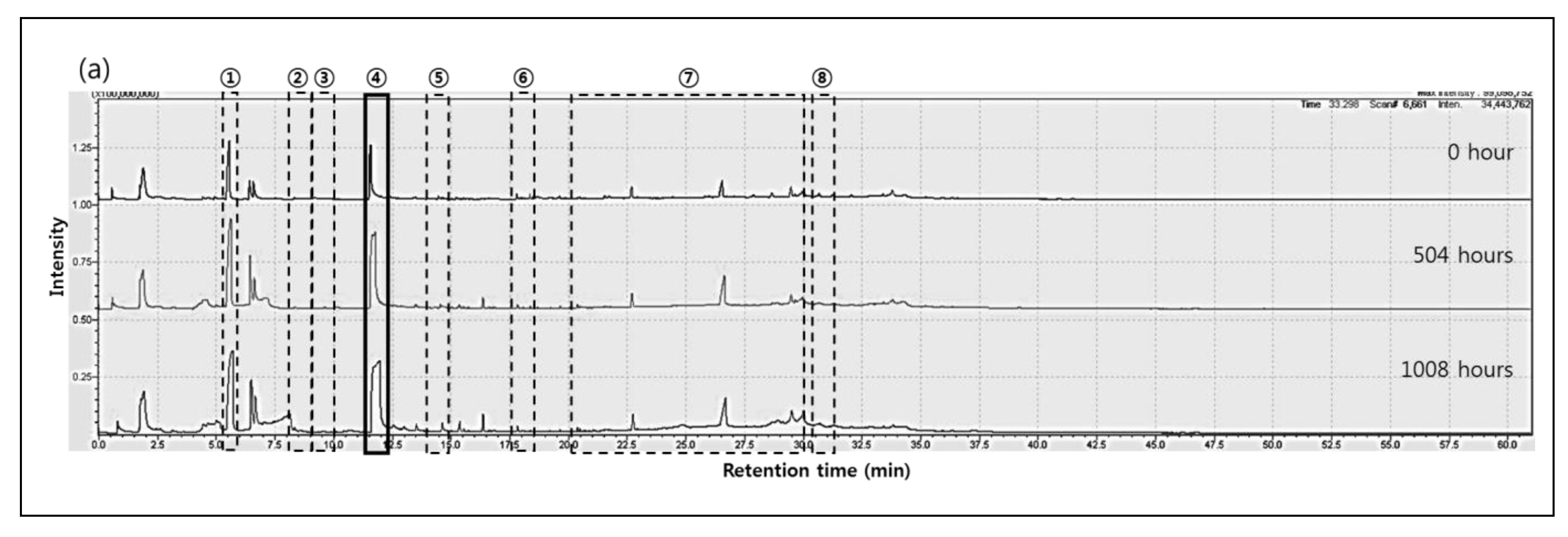
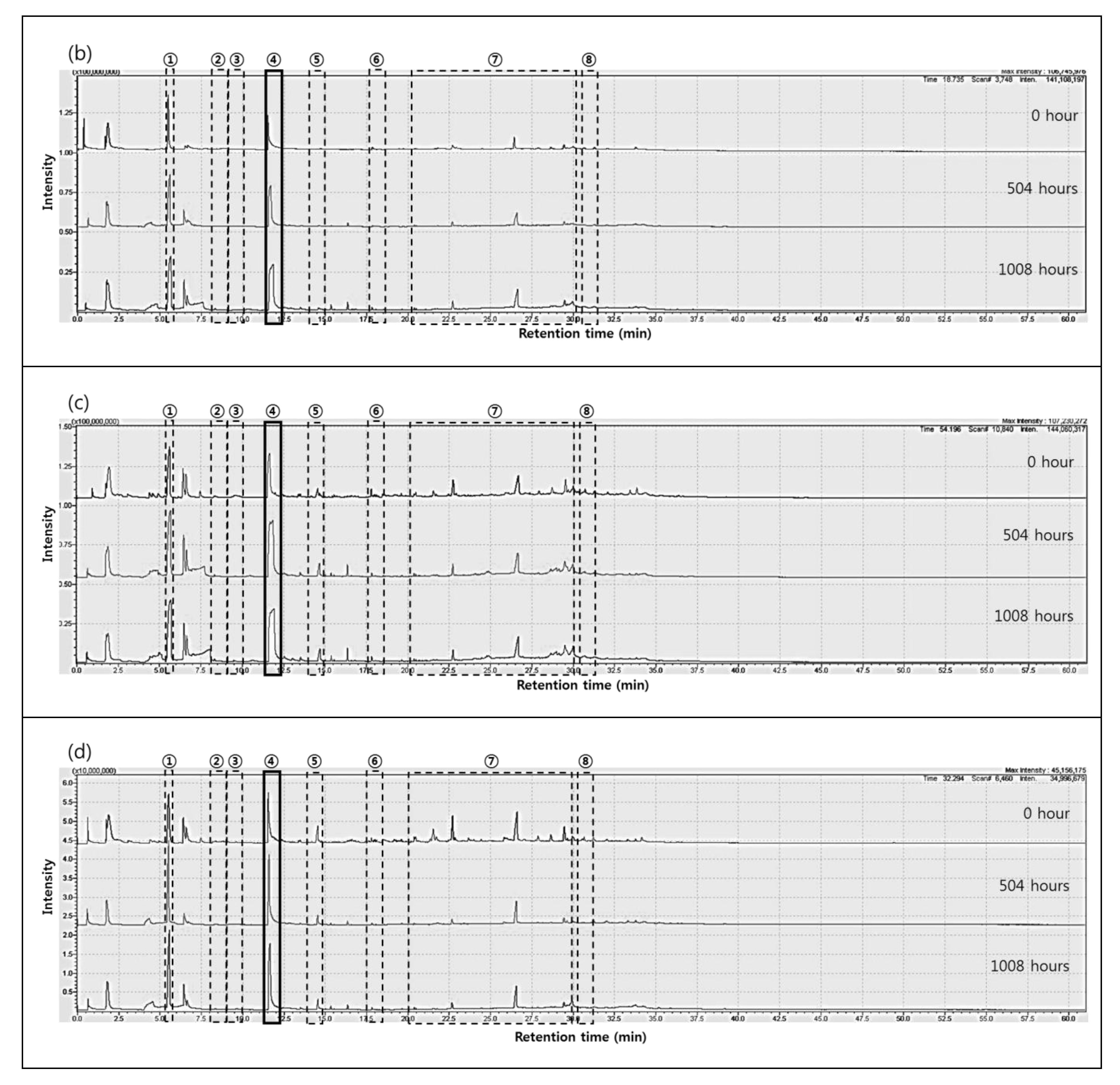
3.2. Py-GC/MS Observation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forsström, D.; Terselius, B. Thermo oxidative stability of polyamide 6 films I. Mechanical and chemical characterization. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2000, 67, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrer, J. Automotive light-weighting pushed. Rubber World 2015, 252, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Carothers, W.H.; Berchet, G.J. Studies on polymerization and ring formation. VIII. Amides from ε-aminocaproic acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1930, 52, 5289–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.Y.; Weon, J.I. Characterization of thermal degradation of polymide 66 composite: Relationship between lifetime prediction and activation energy. Polymer 2012, 36, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, W.N.; Kwon, I.H.; Lim, S.H.; Ko, M.B.; Choe, C.R. Effects of processing conditions of injection molding on the microstructure of long fiber reinforced nylon composites. Polymer 1999, 23, 681–689. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, B.S.; Woo, D.J.; Suh, M.H.; Lee, S.H. A study on the ternary GF/PA/PP composites manufactured by using pre-impregnated glass fiber. Polymer 2000, 24, 701–712. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, B.J.; Hay, J.N. Thermal degradation of nylon polymers. Polym. Int. 2000, 49, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, C.H.; Pearce, E.M.; Bulkin, B.J. FT–IR spectroscopic study on the thermal and thermal oxidative degradation of nylons. J. Polym. Sci. 1987, 25, 2409–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiaku, U.S.; Hamada, H.; Mizoguchi, M.; Chow, W.S.; Mohd Ishak, Z.A. The effect of ambient moisture and temperature conditions on the mechanical properties of glass fiber/carbon fiber/nylon 6 sandwich hybrid composites consisting of skin-core morphologies. Polym. Compos. 2005, 26, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallés-Lluch, A.; Camacho, W.; Ribes-Greus, A.; Karlsson, S. Influence of water on the viscoelastic behavior of recycled nylon 6,6. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 85, 2211–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Desai, S.M.; Pathak, G. Thermal decomposition kinetics of photooxidized nylon 66. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 2146–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, M.A.; McAuley, K.B.; Marchildon, E.K.; Cunningham, M.F. Thermal degradation kinetics of nylon 66: Experimental study and comparison with model predictions. Macromol. React. Eng. 2007, 1, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchik, S.V.; Weil, E.D.; Lewin, M. Thermal decomposition of aliphatic nylons. Polym. Int. 1999, 48, 532–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alothman, Z.A.; Alam, M.M.; Naushad, M. Heavy toxic metal ion exchange kinetics: Validation of ion exchange process on composite cation exchanger nylon 6,6 Zr(IV) phosphate. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 956–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.H.; Koh, J.S. Mechanical properties and morphology of polyamide 6/maleated polypropylene blends. J. Korean Ind. Eng. Chem. 1999, 10, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, B.Y.; Ha, M.H.; Han, D.H. Morphological, rheological, and mechanical properties of polyamide 6/polypropylene blends compatibilized by electron-beam irradiation in the presence of a reactive agent. Materials 2016, 9, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viers, B.D. Nylon6,6. In Polymer Data Handbook; Mark, J.E., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999; ISBN 0195107896. [Google Scholar]
- White, J.L.; Kim, K.J. Thermoplastic and Rubber Compounds Technology and Physical Chemistry; Carl Hanser Verlag: Munich, Germany, 2008; ISBN 1569904073. [Google Scholar]
- Watt, W.; Perov, B.V. Strong Fibres; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; ISBN 0444875050. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.K.; Kennel, E.; Kim, K.J. Polymer Nanocomposites Handbook; Taylor & Francis, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 9780849397776. [Google Scholar]
- Le Gac, P.-Y.; Fayolle, B. Impact of fillers (short glass fibers and rubber) on the hydrolysis-induced embrittlement of polyamide 6.6. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2018, 153, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullekom, R.V.; Joachimi, D.; Karbach, A.; Persigehl, P.; De Bock, M. Molding Compositions and Their Use. U.S. Patent 20050043443, 24 February 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Joachimi, D.; Schlte, H.; Littek, W.; Kadelka, J. Highly Viscous Polyamide for Use in Extrusion Blow Molding. U.S. Patent 20030092822, 15 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.M.; Kim, K.J. Effects of moisture and temperature on recrystallization and mechanical property improvement of PA66/GF composite. Polymer 2015, 39, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Pei, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, H.; Cheng, F.; Ma, J. Brittle–ductile transition in PP/EPDM blends: Effect of notch radius. Polymer 2003, 44, 3125–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, S.C.; Li, W.D.; Li, R.K.Y. Impact toughening behaviour of quaternary PP/HDPE/EPDM/EP blends. Eur. Polym. J. 1998, 34, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, K.J. Measurement of degree of hydrolysis of a PA66/GF composite using a py-GC/MS analysis. Elastom. Compos. 2017, 52, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissi, E. Entropic control of chemiluminescent reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 3386–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaupart, N.; Serpe, G.; Verdu, J. Molecular weight distribution and mass changes during polyamide hydrolysis. Polymer 1998, 39, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.H.; Turnbull, D. Molecular transport in liquids and glasses. J. Chem. Phys. 1959, 31, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumins, C.A.; Kwei, T.K. Free volume and other Theories. In Diffusion in Polymers; Crank, J., Park, G.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1968; ISBN 0121970507. [Google Scholar]
- Moy, P.; Karasz, F.E. Epoxy-water interactions. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1980, 20, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merdas, I.; Thominette, F.; Tcharkhtchi, A.; Verdu, J. Factors governing water absorption by composite matrices. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puffr, R.; Šebenda, J. On the structure and properties of polyamides. XXVII. The mechanism of water sorption in polyamides. J. Polym. Sci. Part C Polym. Symp. 1967, 16, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razumovskii, L.P.; Markin, V.S.; Zaikov, G.Y. Sorption of water by aliphatic polyamides. Review. Polym. Sci. USSR 1985, 27, 751–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, X.; Verdu, J. Humid Ageing of Organic Matrix Composites. In Durability of Composites in a Marine Environment; Davies, P., Rajapakse, Y.D.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 208, ISBN 9401779767. [Google Scholar]
- Jellinek, H.H.G.; Dunkle, S.R. Degradation and Stabilization of Polymers; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1983; ISBN 0444422161. [Google Scholar]
- Sombatsompop, N.; Chaochanchaikul, K. Effect of moisture content on mechanical properties, thermal and structural stability and extrudate texture of poly(vinyl chloride)/wood sawdust composites. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimschuessel, H.K. Relationships on the effect of water on glass transition temperature and young’s modulus of nylon 6. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. Ed. 1978, 16, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, M. Moisture absorption and its influence on the tensile properties of glass-fibre reinforced polyamide 6,6. Polym. Polym. Compos. 1994, 2, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Jacques, B.; Werth, M.; Merdas, I.; Thominette, F.; Verdu, J. Hydrolytic ageing of polyamide 11. 1. Hydrolysis kinetics in water. Polymer 2002, 43, 6439–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J.L. Structure–property relationships in glass-reinforced polyamide, Part 3: Effects of hydrolysis ageing on the dimensional stability and performance of short glass–fiber-reinforced polyamide 66. Polym. Compos. 2007, 28, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, M.I. Nylon Plastics Handbook; Hanser/Gardner: New York, NY, USA, 1995; ISBN 1569901899. [Google Scholar]
- Lasagabaster, A.; Abad, M.J.; Barral, L.; Ares, A. FTIR study on the nature of water sorbed in polypropylene (PP)/ethylene alcohol vinyl (EVOH) films. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 3121–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, E.S.; Poulsen, L.; Ogilby, P.R. Mechanism of the temperature-dependent degradation of polyamide 66 films exposed to water. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1977–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Wang, J.; Tsuru, T. Gas transport properties of interfacially polymerized polyamide composite membranes under different pre-treatments and temperatures. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 449, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Hagiwara, H.; Yanagishita, H.; Ito, K.; Tsuru, T. Structural characterization of thin-film polyamide reverse osmosis membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Wang, J.; Tsuru, T. Application of interfacially polymerized polyamide composite membranes to isopropanol dehydration: Effect of membrane pre-treatment and temperature. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J.L. The influence of fibre length, diameter and concentration on the impact performance of long glass-fibre reinforced polyamide 6,6. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattimer, R.P. Direct analysis of polypropylene compounds by thermal desorption and pyrolysis—Mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1993, 26, 65–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaudo, G.; Puglisi, C. Thermal degradation mechanisms in condensation polymers. In Developments in Polymer Degradation; Grassie, N., Ed.; Applied Science: London, UK, 1987; Volume 7, ISBN 9401080321. [Google Scholar]
- Montaudo, G.; Puglisi, C. Thermal degradation of condensation polymers. In Comprehensive Polymer Science; Allen, G., Aggarwal, S.L., Russo, S., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1992; ISBN 0080370713. [Google Scholar]
- Dussel, H.-J.; Rosen, H.; Hummel, D.O. Feldionen-und Elektronenstoß-Massenspektrometrie von Polymeren und Copolymeren, 5. Aliphatische und aromatische Polyamide und Polyimide. Makromol. Chem. 1976, 177, 2343–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, H.; Nagaya, T.; Sugimura, Y.; Tsuge, S. Studies on thermal degradation of aliphatic polyamides by pyrolysis-glass capillary chromatography. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 1982, 4, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornsby, P.R.; Wang, J.; Rothon, R.; Jackson, G.; Wilkinson, G.; Cossick, K. Thermal decomposition behaviour of polyamide fire-retardant compositions containing magnesium hydroxide filler. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1996, 51, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKerron, D.H.; Gordon, R.P. Minor products from the pyrolysis of thin films of poly(hexamethylene adipamide). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1985, 12, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaudo, G.; Lattimer, R.P. Mass Spectrometry of Polymers; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; Washington, DC, USA, 2001; ISBN 0849331277. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |



| D | Z | K | A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA66 (wt%) | 66.78 (± 0.61) | 68.81 (± 0.41) | 66.24 (± 0.88) | 66.92 (± 0.54) |
| GF (wt%) | 31.52 (± 0.76) | 29.25 (± 0.38) | 30.35 (± 0.18) | 30.78 (± 0.39) |
| Additive (wt%) | 1.71 (± 0.15) | 1.95 (± 0.03) | 3.41 (± 0.7) | 2.30 (± 0.15) |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) [5 mm/min] | Tensile Modulus (MPa) [5 mm/min] | Tensile Elongation (%) [5 mm/min] | Impact Strength (kJ/m2) [unnotched] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | Before | 178 | 9551 | 3.1 | 66.04 |
| After | 100 | 5099 | 4.3 | 69.42 | |
| % change rate | −44 | −47 | +40 | +5 | |
| Z | Before | 185 | 9494 | 3.5 | 76.62 |
| After | 102 | 4646 | 4.4 | 73.97 | |
| % change rate | −45 | −51 | +28 | −3 | |
| K | Before | 171 | 9078 | 2.9 | 61.09 |
| After | 94 | 5022 | 3.5 | 67.76 | |
| % change rate | −45 | −45 | +23 | +11 | |
| A | Before | 167 | 9039 | 3.3 | 77.2 |
| After | 96 | 4561 | 5.4 | 88.43 | |
| % change rate | −43 | −50 | +63 | +15 | |
| Region | Retention Time (min) | Product | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| ① | 5.5 | Cyclopentanone | 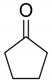 |
| ② | 8.6 | 2-N-Hexylaziridine | 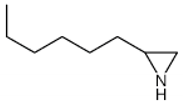 |
| ③ | 9.5 | 1-Decanol |  |
| ④ | 11.6 | 1,6-Hexanediamine |  |
| ⑤ | 13.4 | 3-None-1-ol | 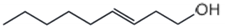 |
| 13.5 | Adiponitrile | 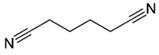 | |
| ⑥ | 17.8 | 1-Methyl-3-formlindole | 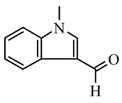 |
| ⑦ | 21.5 22.7 25.9 26.6 28.7 29.5 30.0 31.3 | 2-Azacyclotridecanone | 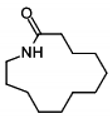 |
| ⑧ | 30.7 | Hexadecanenitrile |  |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, K.-J. MEG Effects on Hydrolysis of Polyamide 66/Glass Fiber Composites and Mechanical Property Changes. Molecules 2019, 24, 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040755
Lee J-Y, Kim K-J. MEG Effects on Hydrolysis of Polyamide 66/Glass Fiber Composites and Mechanical Property Changes. Molecules. 2019; 24(4):755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040755
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jong-Young, and Kwang-Jea Kim. 2019. "MEG Effects on Hydrolysis of Polyamide 66/Glass Fiber Composites and Mechanical Property Changes" Molecules 24, no. 4: 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040755
APA StyleLee, J.-Y., & Kim, K.-J. (2019). MEG Effects on Hydrolysis of Polyamide 66/Glass Fiber Composites and Mechanical Property Changes. Molecules, 24(4), 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040755