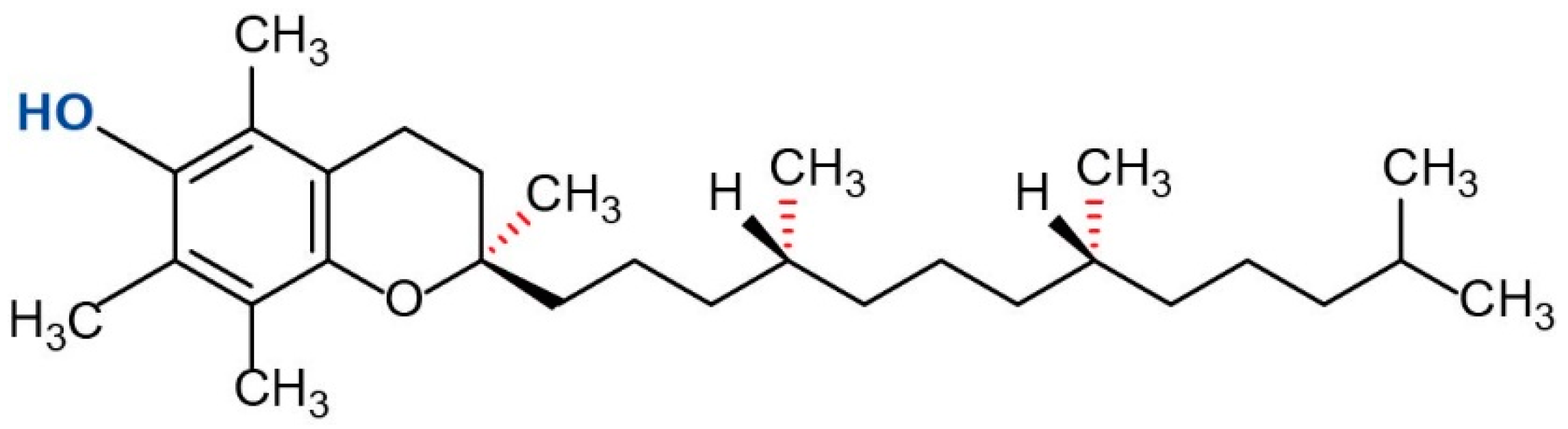
Effect of α-Tocopherol on the Physicochemical Properties of Sturgeon Surimi during Frozen Storage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effects of α-TOH on Total Viable Counts and pH of Sturgeon Surimi during Frozen Storage
2.2. Effects of α-TOH on the Water-Extractable Protein (WEP) and Salt-Extractable Protein (SEP) of Sturgeon Surimi during Frozen Storage
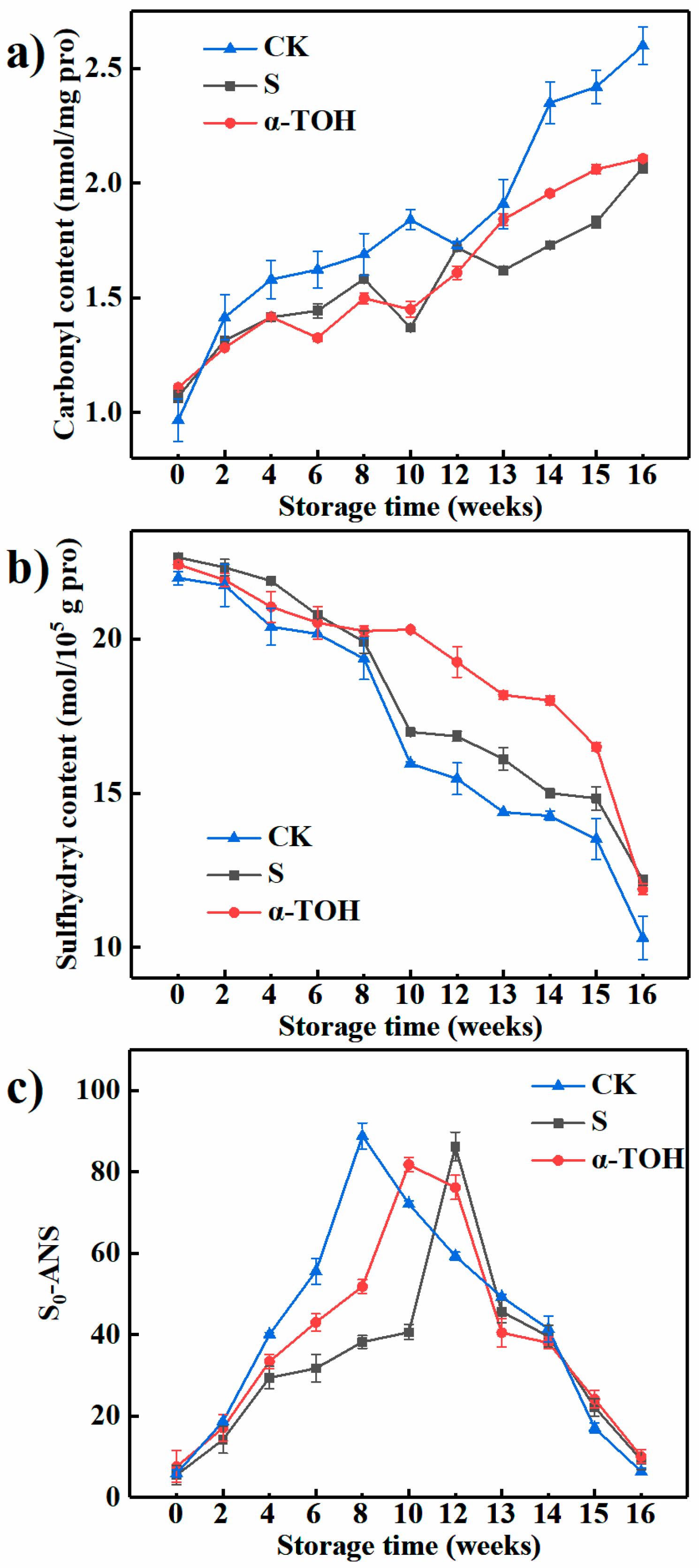
2.3. Effects of α-TOH on the Protein Carbonyls, Protein Total Sulfhydryl and Surface Hydrophobicity of Sturgeon Surimi during Frozen Storage
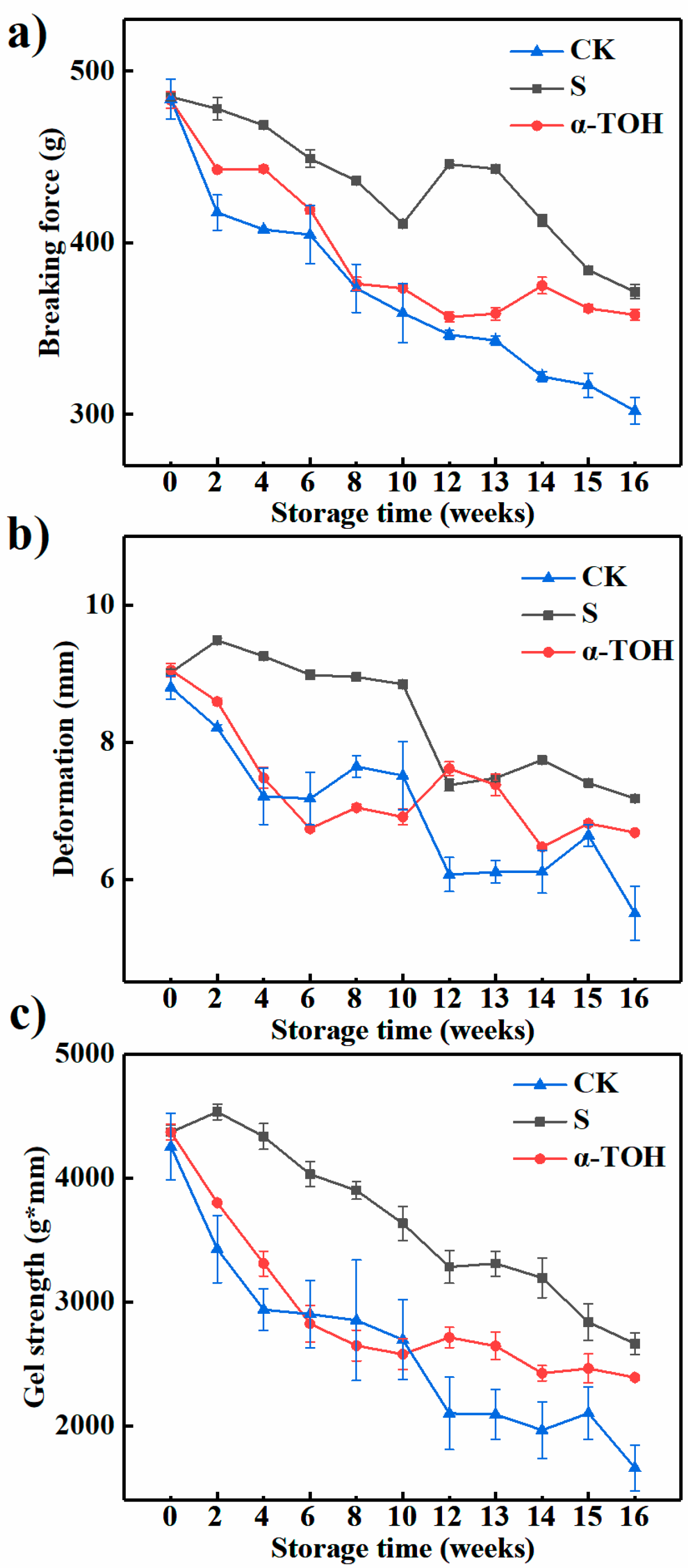
2.4. Effects of α-TOH on the Gel Properties of Sturgeon Surimi during Frozen Storage
2.5. Effects of α-TOH on Water Holding Capacity (WHC) and Whiteness of Sturgeon Surimi during Frozen Storage
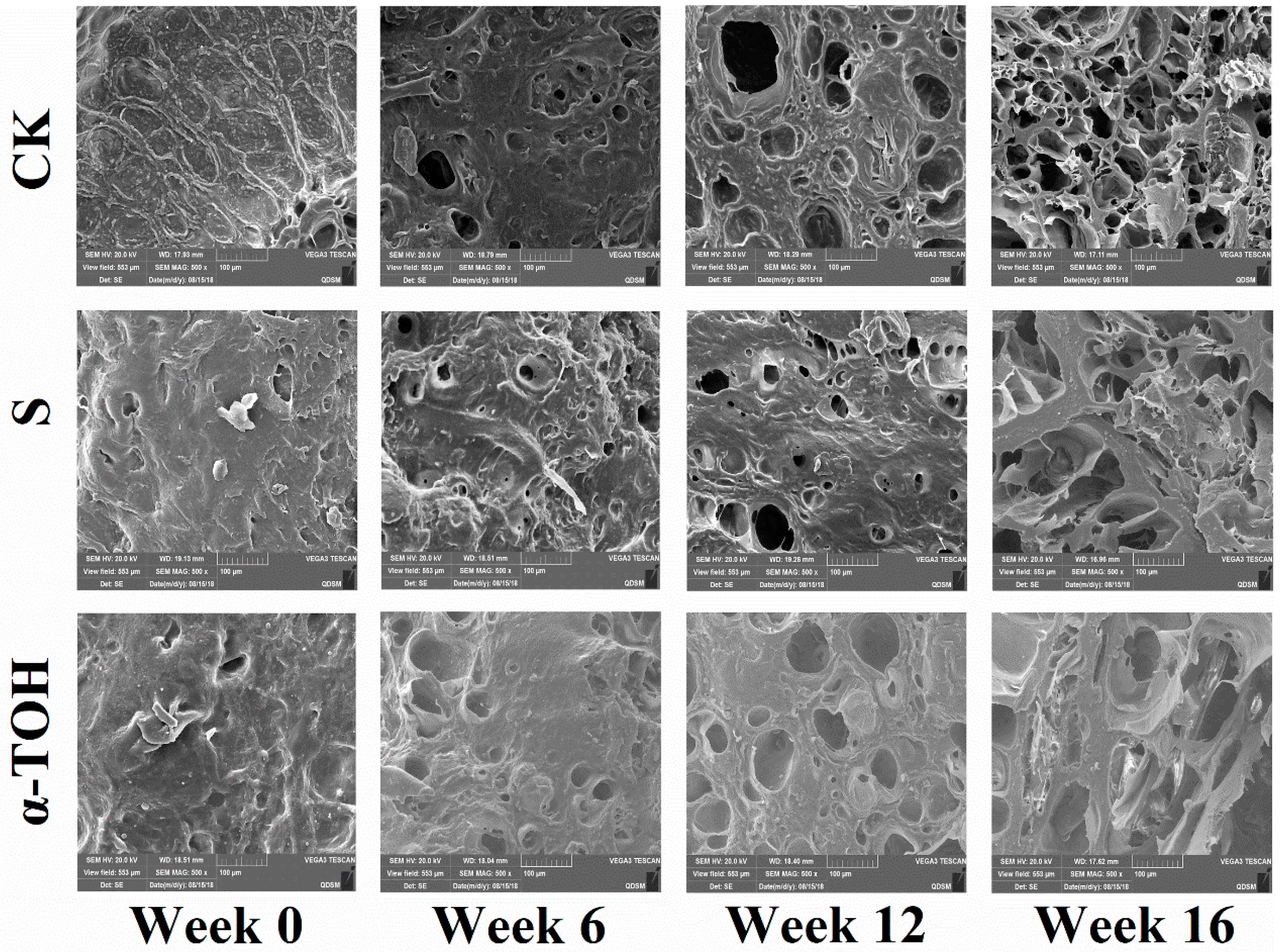
2.6. Effects of α-TOH on the Microstructure of Sturgeon Surimi during Frozen Storage
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of Sturgeon Surimi
3.3. Microbiological Growth and pH Analysis
3.4. Determination of Water-Extractable Protein (WEP) Content and Salt-Extractable Protein (SEP) Content
3.5. Determination of Protein Carbonyls, Protein Total Sulfhydryl and Surface Hydrophobicity
3.6. Sturgeon Surimi Gel Preparation
3.6.1. Determination of Gel Properties
3.6.2. Determination of Water-Holding Capacity and Whiteness
3.6.3. Microstructure of Surimi Gels
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salehi, H. Fish consumption. Available online: https://financialtribune.com/articles/people/42911/fish-consumption (accessed on 5 June 2016).
- Noman, A.; Xu, Y.; AL-Bukhaiti, W.Q.; Abed, S.M.; Ali, A.H.; Ramadhan, A.H.; Xia, W. Influence of enzymatic hydrolysis conditions on the degree of hydrolysis and functional properties of protein hydrolysate obtained from Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis) by using papain enzyme. Process Biochem. 2018, 67, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2014; FAO Fisheries Department, Fishery Information, Data and Statistics Unit: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Boscari, E.; Vitulo, N.; Ludwig, A.; Caruso, C.; Mugue, N.S.; Suciu, R.; Congiu, L. Fast genetic identification of the beluga sturgeon and its sought-after caviar to stem illegal trade. Food Control 2017, 75, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falahatkar, B. Nutritional requirements of the Siberian sturgeon: An updated synthesis. In the siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii, Brandt, 1869) Volume 1-Biology. Springer. Cham. 2018, 207–228. [Google Scholar]
- Bueno, M.; Resconi, V.C.; Campo, M.M.; Cacho, J.; Ferreira, V.; Escudero, A. Effect of freezing method and frozen storage duration on odor-active compounds and sensory perception of lamb. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, X.; Bin, Z.; Lu-Kai, M.; Ji-Peng, S. Cryoprotective effects of trehalose, alginate, and its oligosaccharide on quality of cooked-shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) during frozen storage. J. Food Process Preserv. 2017, 41, e12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FRYE, T. Activity of vitamin E and related chain-breaking phenolic antioxidants in vitro. J. Am. Chern. Soc. 1981, 103, 6472. [Google Scholar]
- Rigotti, A. Absorption, transport, and tissue delivery of vitamin E. Mol. Aspects Med. 2007, 28, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descalzo, A.M.; Sancho, A.M. A review of natural antioxidants and their effects on oxidative status, odor and quality of fresh beef produced in Argentina. Meat Sci. 2008, 79, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, Z.; Yuan, F.; Lin, H.; Pavase, T.R. Effects of brown seaweed polyphenols, α-tocopherol, and ascorbic acid on protein oxidation and textural properties of fish mince (Pagrosomus major) during frozen storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Sun, J.; Liu, D.; Fu, M.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y. The preservative effects of chitosan film incorporated with thinned young apple polyphenols on the quality of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) fillets during cold storage: Correlation between the preservative effects and the active properties of the film. Food Packaging Shelf 2018, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Microorganisms in Foods. 2. Sampling for Microbiological Analysis: Principles and Specific Applications; University of Toronto Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1986; pp. 1–293.
- Pan, L.; Lin, C.; Zhang, G.; Mu, G.; Yang, X. The effect of pre-process and transport strategies on survival, microbiologic, and physiologic of patinopecten yessoensis. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, P.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Ren, L.; Jin, R.; Xue, J.; Dai, Z. Effect of cryogenic immersion freezing on quality changes of vacuum-packed bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) during frozen storage. J. Food Process Preserv. 2018, 42, e13640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periago, M.J.; Ayala, M.D.; López-Albors, O.; Abdel, I.; Martinez, C.; García-Alcázar, A.; Gil, F. Muscle cellularity and flesh quality of wild and farmed sea bass, dicentrarchus labrax L. Aquaculture 2005, 249, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Liao, L.; Qiao, Y.; Xiong, G.; Li, D.; Wang, C.; Shi, L. The effects of vacuum package combined with tea polyphenols (V+ TP) treatment on quality enhancement of weever (Micropterus salmoides) stored at 0 °C and 4 °C. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 91, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultin, H.O.; Feng, Y.; Stanley, D.W. A re-examination of muscle protein solubility. J. Muscle Foods 1995, 6, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eymard, S.; Carcouët, E.; Rochet, M.J.; Dumay, J.; Chopin, C.; Genot, C. Development of lipid oxidation during manufacturing of horse mackerel surimi. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 1750–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Wang, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhu, B.; Luo, Y. Quality changes and predictive models of radial basis function neural networks for brined common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fillets during frozen storage. Food Chem. 2016, 201, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auh, J.H.; Lee, H.G.; Kim, J.W.; Yoon, H.S.; Park, K.H. Highly concentrated branched oligosaccharides as cryoprotectant for surimi. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Zhou, B.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, M. Protective effect of perilla (Perilla frutescens) leaf essential oil on the quality of a surimi-based food. J. Food Process Preserv. 2018, 42, e13540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, R.L.; Garland, D.; Oliver, C.N.; Amici, A.; Climent, I.; Lenz, A.G.; Stadtman, E.R. Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 186, 464–478. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B.; Han, J.; He, X. The influence of superchilling and cryoprotectants on protein oxidation and structural changes in the myofibrillar proteins of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) surimi. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.S.; Endo, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Moku, M.; Kawaguchi, K. Denaturation of myofibrillar protein in myctophid fish during refrigeration and freezing storage. Fish. Sci. 1997, 63, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, Q.; Xiong, S.; Fu, Y.; Chen, L. Effects of high intensity ultrasound on structural and physicochemical properties of myosin from silver carp. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 37, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; You, J.; Xiong, S.; Yin, T. Short-term frozen storage enhances cross-linking that was induced by transglutaminase in surimi gels from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). Food Chem. 2018, 257, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, A.; Lin, L.; Liang, Y.; Benjakul, S.; Shi, X.; Liu, X. Physicochemical properties of natural actomyosin from threadfin bream (Nemipterus spp.) induced by high hydrostatic pressure. Food Chem. 2014, 156, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Thongkaew, C.; Tanaka, M. Comparative study on physicochemical changes of muscle proteins from some tropical fish during frozen storage. Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sych, J.; Lacroix, C.; Adambounou, L.T.; Castaigne, F. Cryoprotective effects of lactitol, palatinit and polydextrose® on cod surimi proteins during frozen storage. J. Food Sci. 1990, 55, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhu, B.; Luo, Y. Changes in chemical interactions and gel properties of heat-induced surimi gels from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) fillets during setting and heating: Effects of different washing solutions. Food Hydrocolloid. 2018, 75, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Thongkaew, C.; Tanaka, M. Effect of frozen storage on chemical and gel-forming properties of fish commonly used for surimi production in Thailand. Food Hydrocolloid. 2005, 19, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, S.; Fawthrop, S.A.; Howell, N.K. Electron spin resonance (ESR) study on free radical transfer in fish lipid–protein interaction. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.Z.; Yang, S.; Wu, G. Free radicals, antioxidants, and nutrition. Nutrition 2002, 18, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuraida, I.; Raharjo, S.; Hastuti, P.; Indrati, R. Effect of Setting Condition on the Gel Properties of Surimi from Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 18, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, H.W.; Hogden, C.G. The biuret reaction in the determination of serum proteins. 1. A study of the conditions necessary for the production of a stable color which bears a quantitative relationship to the protein concentration. J. Biol. Chem. 1940, 135, 707–725. [Google Scholar]
- Soyer, A.; Özalp, B.; Dalmış, Ü.; Bilgin, V. Effects of freezing temperature and duration of frozen storage on lipid and protein oxidation in chicken meat. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Seymour, T.A.; Morrissey, M.T.; An, H. Physicochemical changes in pacific whiting muscle proteins during iced storage. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gani, A.; Benjakul, S. Impact of virgin coconut oil nanoemulsion on properties of croaker surimi gel. Food Hydrocolloid. 2018, 82, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanier, T.C. Measurement of surimi composition and functional properties. Surimi Technol. 1992, 123–163. [Google Scholar]
- Himonides, A.T.; Taylor, K.D.A.; Knowles, M.J. The improved whitening of cod and haddock flaps using hydrogen peroxide. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |


| Storage Time (week) | Water Holding Capacity (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | S | α-TOH | |
| 0 | 84.51 ± 0.006 a,A | 85.11 ± 0.002 a,A | 84.80 ± 0.030 a,A |
| 2 | 83.21 ± 0.005 a,b,B | 84.90 ± 0.007 a,A | 84.46 ± 0.003 a,A |
| 4 | 82.23 ± 0.023 a,b,c,B | 84.61 ± 0.010 a,A | 84.05 ± 0.008 a,A |
| 6 | 80.52 ± 0.018 b,c,d,B | 84.57 ± 0.011 a,A | 83.51 ± 0.018 b,A |
| 8 | 80.44 ± 0.009 c,d,C | 84.33 ± 0.004 a,A | 82.93 ± 0.021 b,c,B |
| 10 | 79.06 ± 0.000 d,e,C | 83.64 ± 0.010 a,A | 81.76 ± 0.013 b,c,B |
| 12 | 78.60 ± 0.008 d,e,B | 81.97 ± 0.022 a,b,A | 81.53 ± 0.012 b,c,A |
| 13 | 78.48 ± 0.015 d,e,C | 81.70 ± 0.014 b,c,A | 80.44 ± 0.019 b,c,B |
| 14 | 77.32 ± 0.011 e,f,C | 81.10 ± 0.053 b,c,A | 79.51 ± 0.004 b,c,d,B |
| 15 | 76.71 ± 0.010 e,f,C | 80.11 ± 0.008 c,d,A | 78.90 ± 0.016 c,d,B |
| 16 | 73.54 ± 0.008 f,C | 79.64 ± 0.003 d,A | 78.75 ± 0.017 d,B |
| Storage Time (week) | Whiteness | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | S | α-TOH | |
| 0 | 72.75 ± 0.324 a,A | 72.67 ± 0.357 a,A | 73.09 ± 0.605 a,A |
| 2 | 71.16 ± 0.308 a,b,B | 72.55 ± 0.871 a,A | 72.78 ± 1.162 a,b,A |
| 4 | 71.18 ± 0.543 a,b,c,B | 71.72 ± 0.478 a,B | 72.42 ± 1.400 a,b,c,A |
| 6 | 71.02 ± 0.609 a,b,c,d,B | 71.82 ± 0.672 a,A | 72.40 ± 0.290 a,b,c,A |
| 8 | 70.73 ± 0.322 a,b,c,d,C | 71.66 ± 0.255 a,B | 72.23 ± 0.020 a,b,c,A |
| 10 | 70.52 ± 0.485 a,b,c,d,C | 71.61 ± 1.258 a,B | 72.09 ± 0.777 a,b,c,A |
| 12 | 70.26 ± 1.099 b,c,d,B | 71.21 ± 0.476 a,b,A | 71.92 ± 0.900 a,b,c,A |
| 13 | 70.02 ± 0.156 c,d,B | 71.38 ± 0.715 a,b,A | 71.87 ± 0.520 a,b,c,A |
| 14 | 69.76 ± 0.358 c,d,C | 70.83 ± 0.556 a,b,B | 71.72 ± 0.541 a,b,c,A |
| 15 | 69.61 ± 0.747 d,B | 69.78 ± 0.425 b,c,B | 71.27 ± 1.875 b,c,A |
| 16 | 67.39 ± 1.049 e,C | 68.83 ± 0.932 c,B | 70.94 ± 0.113 c,A |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, S.; Feng, G.; Cui, W.; Gao, R.; Bai, F.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, M. Effect of α-Tocopherol on the Physicochemical Properties of Sturgeon Surimi during Frozen Storage. Molecules 2019, 24, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040710
Tang S, Feng G, Cui W, Gao R, Bai F, Wang J, Zhao Y, Zeng M. Effect of α-Tocopherol on the Physicochemical Properties of Sturgeon Surimi during Frozen Storage. Molecules. 2019; 24(4):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040710
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Shuwei, Guangxin Feng, Wenxuan Cui, Ruichang Gao, Fan Bai, Jinlin Wang, Yuanhui Zhao, and Mingyong Zeng. 2019. "Effect of α-Tocopherol on the Physicochemical Properties of Sturgeon Surimi during Frozen Storage" Molecules 24, no. 4: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040710
APA StyleTang, S., Feng, G., Cui, W., Gao, R., Bai, F., Wang, J., Zhao, Y., & Zeng, M. (2019). Effect of α-Tocopherol on the Physicochemical Properties of Sturgeon Surimi during Frozen Storage. Molecules, 24(4), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040710






