In Situ SABRE Hyperpolarization with Earth’s Field NMR Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
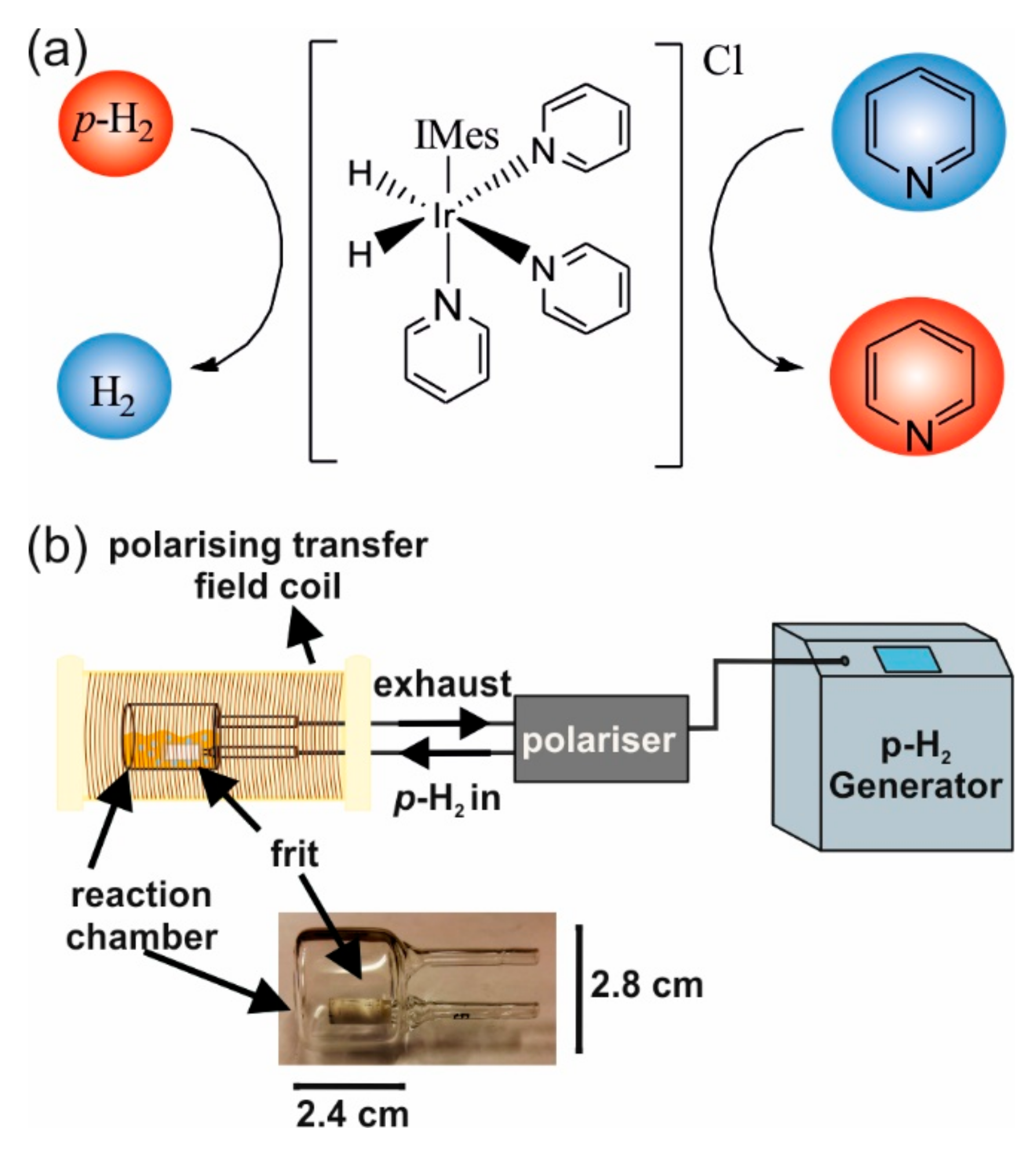
2.1. In Situ SABRE Hyperpolarization with H-EFNMR Detection
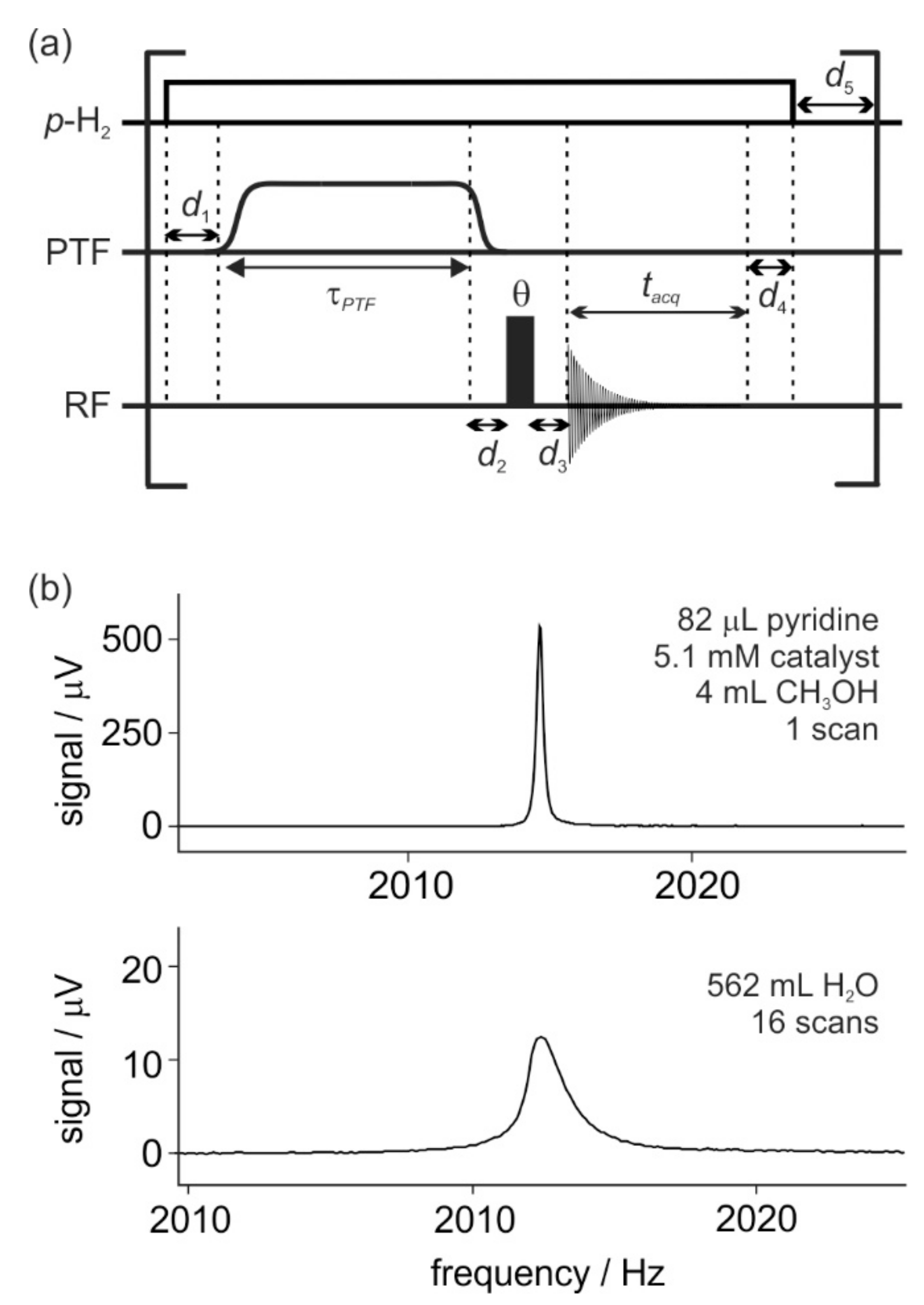
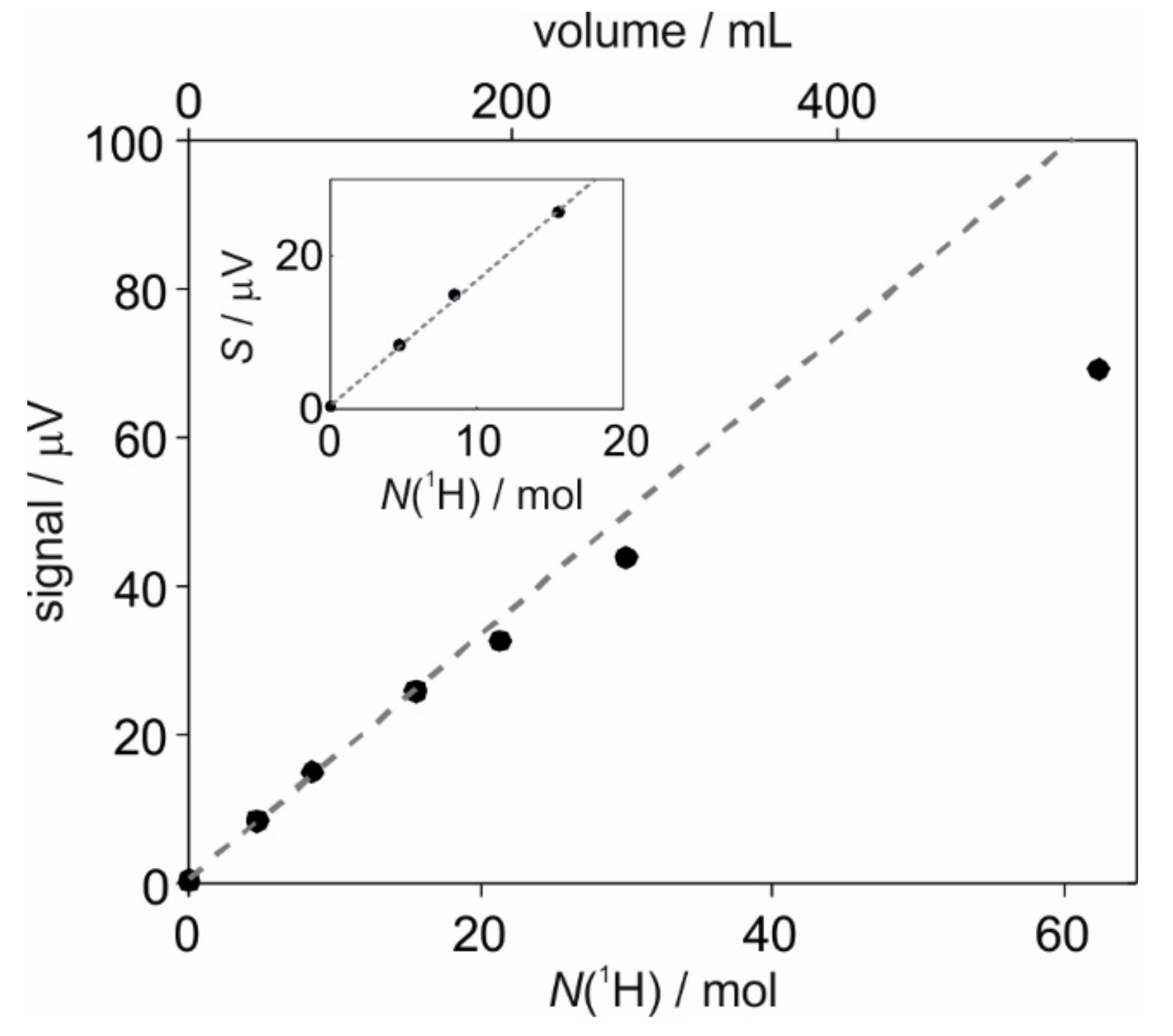
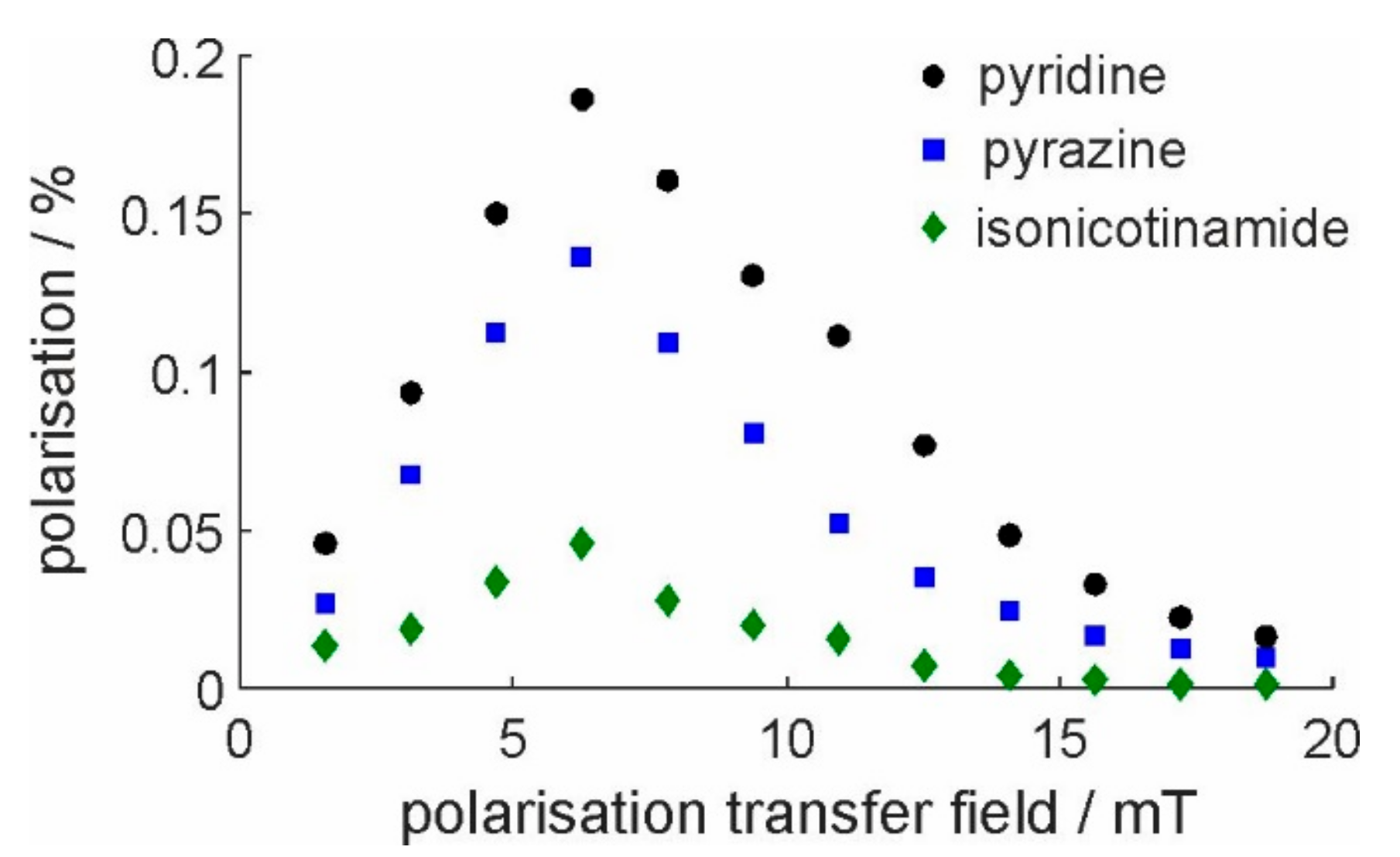
2.2. Calibration of SABRE Hyperpolarization with H-EFNMR Detection
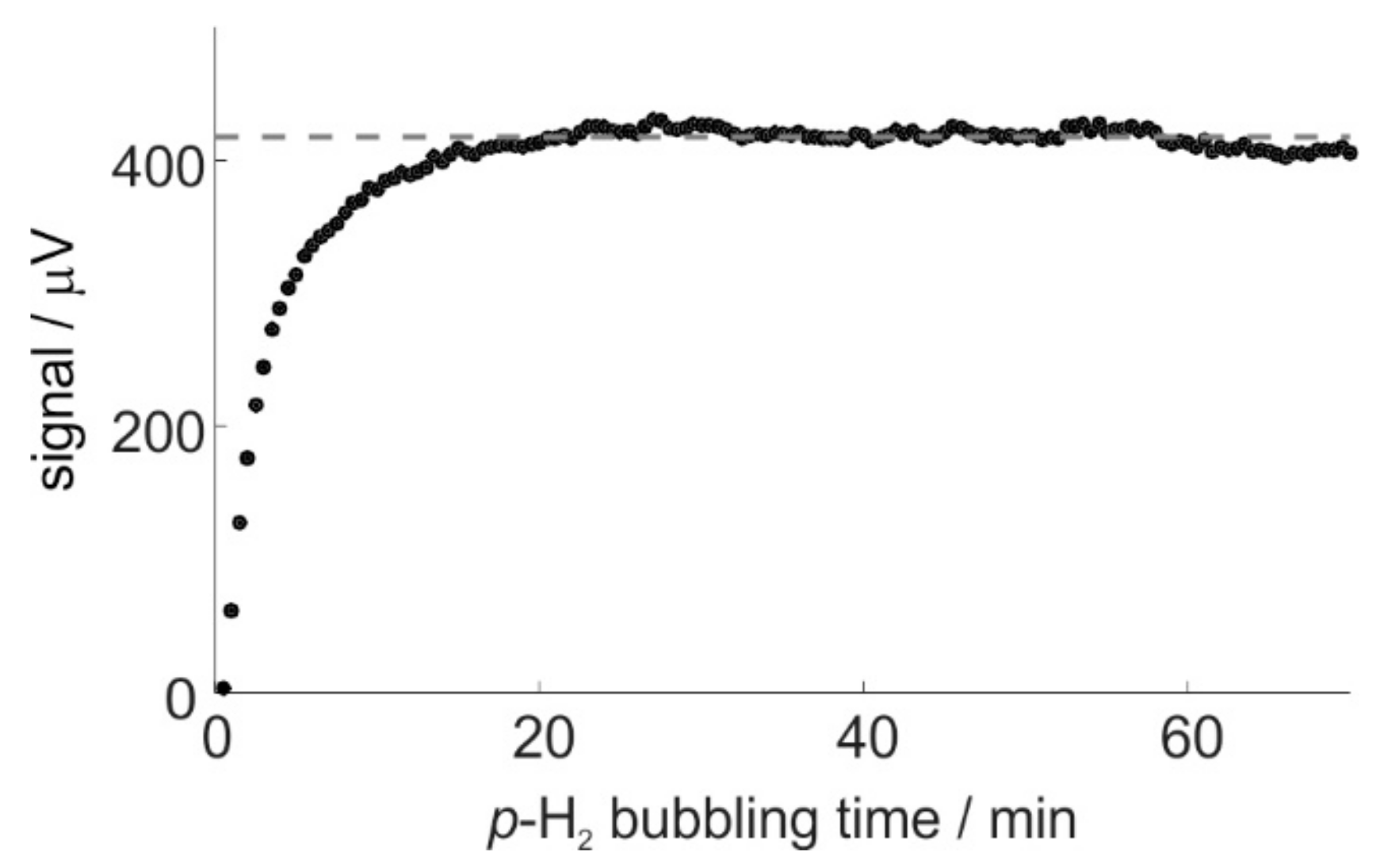
2.3. Catalyst Activation and SABRE Signal Reproducibility
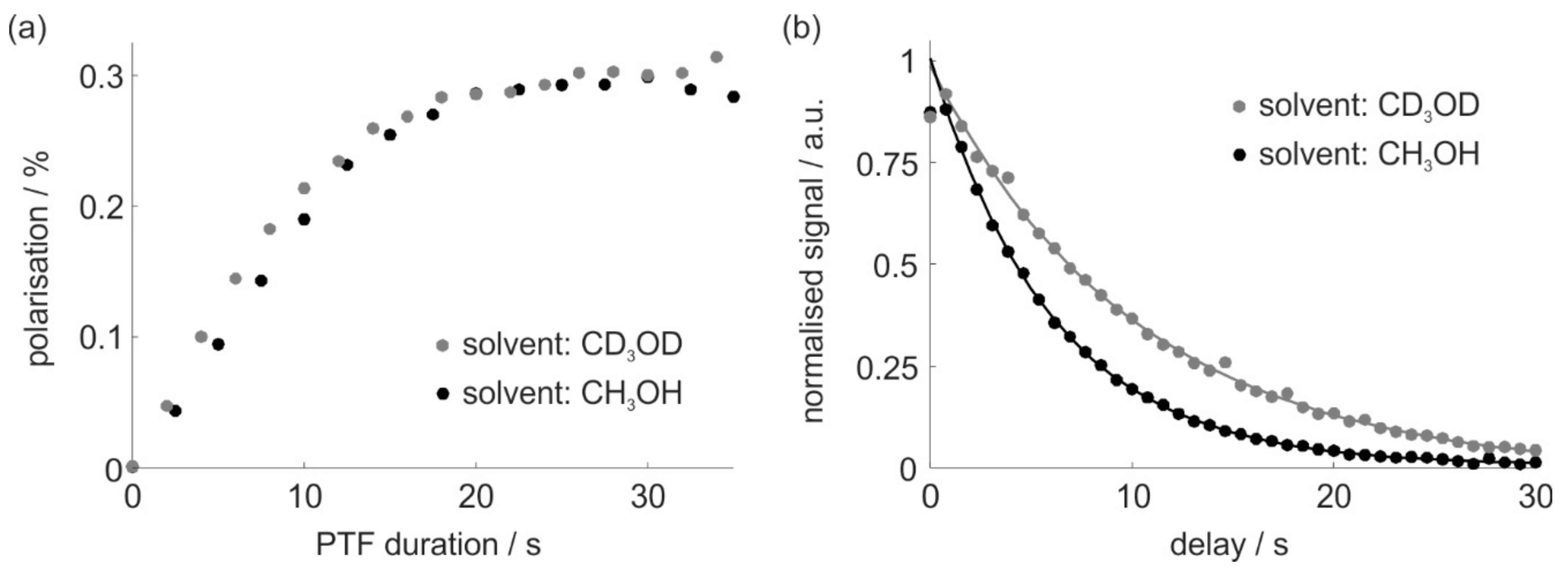
2.4. SABRE Polarization Build-Up and Decay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Preparation
3.2. Parahydrogen Generation and Control
3.3. SABRE Hyperpolarization and EFNMR Detection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nikolaou, P.; Goodson, B.M.; Chekmenev, E.Y. NMR hyperpolarization techniques for biomedicine. Chem. -A Eur. J. 2015, 21, 3156–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halse, M.E. Perspectives for hyperpolarization in compact NMR. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 83, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, C.; Schroder, L. NMR of hyperpolarized probes. NMR Biomed. 2013, 26, 788–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Okuno, Y.; Cavagnero, S. Sensitivity enhancement in solution NMR: Emerging ideas and new frontiers. J. Magn. Reson. 2014, 241, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bentum, J.; van Meerten, B.; Sharma, M.; Kentgens, A. Perspectives on dnp-enhanced NMR spectroscopy in solutions. J. Magn. Reson. 2016, 264, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barskiy, D.A.; Coffey, A.M.; Nikolaou, P.; Mikhaylov, D.M.; Goodson, B.M.; Branca, R.T.; Lu, G.J.; Shapiro, M.G.; Telkki, V.V.; Zhivonitko, V.V.; et al. NMR hyperpolarization techniques of gases. Chem. A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 725–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovtunov, K.V.; Pokochueva, E.V.; Salnikov, O.G.; Cousin, S.F.; Kurzbach, D.; Vuichoud, B.; Jannin, S.; Chekmenev, E.Y.; Goodson, B.M.; Barskiy, D.A.; et al. Hyperpolarized NMR spectroscopy: d-dnp, PHIP, and SABRE techniques. Chem. Asian J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, R.A.; Adams, R.W.; Duckett, S.B.; Mewis, R.E.; Williamson, D.C.; Green, G.G.R. The theory and practice of hyperpolarization in magnetic resonance using parahydrogen. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2012, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natterer, J.; Bargon, J. Parahydrogen induced polarization. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 1997, 31, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, C.R.; Weitekamp, D.P. Transformation of symmetrization order to nuclear-spin magnetization by chemical-reaction and nuclear-magnetic-resonance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 57, 2645–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenschmid, T.C.; Kirss, R.U.; Deutsch, P.P.; Hommeltoft, S.I.; Eisenberg, R.; Bargon, J.; Lawler, R.G.; Balch, A.L. Para hydrogen induced polarization in hydrogenation reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 8089–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, C.R.; Weitekamp, D.P. Para-hydrogen and synthesis allow dramatically enhanced nuclear alignment. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 5541–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravica, M.G.; Weitekamp, D.P. Net NMR alignment by adiabatic transport of para-hydrogen addition-products to high magnetic-field. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1988, 145, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckett, S.B.; Sleigh, C.J. Applications of the parahydrogen phenomenon: A chemical perspective. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 1999, 34, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckett, S.B.; Mewis, R.E. Application of parahydrogen induced polarization techniques in NMR spectroscopy and imaging. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golman, K.; Axelsson, O.; Johannesson, H.; Mansson, S.; Olofsson, C.; Petersson, J.S. Parahydrogen-induced polarization in imaging: Subsecond C-13 angiography. Magn. Reson. Med. 2001, 46, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viale, A.; Reineri, F.; Santelia, D.; Cerutti, E.; Ellena, S.; Gobetto, R.; Aime, S. Hyperpolarized agents for advanced MRI investigations. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 53, 604–617. [Google Scholar]
- Reineri, F.; Viale, A.; Ellena, S.; Boi, T.; Daniele, V.; Gobetto, R.; Aime, S. Use of labile precursors for the generation of hyperpolarized molecules from hydrogenation with parahydrogen and aqueous-phase extraction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7350–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamans, B.C.; Andreychenko, A.; Heerschap, A.; Wijmenga, S.S.; Tessari, M. NMR at earth’s magnetic field using para-hydrogen induced polarization. J. Magn. Reson. 2011, 212, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddell, K.W.; Coffey, A.M.; Chekmenev, E.Y. In situ detection of PHIP at 48 mt: Demonstration using a centrally controlled polarizer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theis, T.; Ganssle, P.; Kervern, G.; Knappe, S.; Kitching, J.; Ledbetter, M.P.; Budker, D.; Pines, A. Parahydrogen-enhanced zero-field nuclear magnetic resonance. Nat. Phys. 2011, 7, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.C.; Kervern, G.; Theis, T.; Ledbetter, M.P.; Ganssle, P.J.; Blanchard, J.W.; Budker, D.; Pines, A. Parahydrogen-induced polarization at zero magnetic field. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 138, 234201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colell, J.; Turschmann, P.; Gloggler, S.; Schleker, P.; Theis, T.; Ledbetter, M.; Budker, D.; Pines, A.; Blumich, B.; Appelt, S. Fundamental aspects of parahydrogen enhanced low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 137602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, R.W.; Aguilar, J.A.; Atkinson, K.D.; Cowley, M.J.; Elliott, P.I.P.; Duckett, S.B.; Green, G.G.R.; Khazal, I.G.; Lopez-Serrano, J.; Williamson, D.C. Reversible interactions with para-hydrogen enhance NMR sensitivity by polarization transfer. Science 2009, 323, 1708–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayner, P.J.; Duckett, S.B. Signal amplification by reversible exchange (SABRE): From discovery to diagnosis. Angew. Chem. (Int. Ed. Engl.) 2018, 57, 6742–6753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mewis, R.E.; Atkinson, K.D.; Cowley, M.J.; Duckett, S.B.; Green, G.G.R.; Green, R.A.; Highton, L.A.R.; Kilgour, D.; Lloyd, L.S.; Lohman, J.A.B.; et al. Probing signal amplification by reversible exchange using an NMR flow system. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2014, 52, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoevener, J.-B.; Schwaderlapp, N.; Lickert, T.; Duckett, S.B.; Mewis, R.E.; Highton, L.A.R.; Kenny, S.M.; Green, G.G.R.; Leibfritz, D.; Korvink, J.G.; et al. A hyperpolarized equilibrium for magnetic resonance. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2946. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmkuhl, S.; Wiese, M.; Schubert, L.; Held, M.; Kuppers, M.; Wessling, M.; Blumich, B. Continuous hyperpolarization with parahydrogen in a membrane reactor. J. Magn. Reson. 2018, 291, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štěpánek, P.; Sanchez-Perez, C.; Telkki, V.-V.; Zhivonitko, V.V.; Kantola, A.M. High-throughput continuous-flow system for SABRE hyperpolarization. J. Magn. Reson. 2019, 300, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravdivtsev, A.N.; Yurkovskaya, A.V.; Vieth, H.M.; Ivanov, K.L. Spin mixing at level anti-crossings in the rotating frame makes high-field SABRE feasible. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 24672–24675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovedo, P.; Knecht, S.; Baumlisberger, T.; Cremer, A.L.; Duckett, S.B.; Mewis, R.E.; Green, G.G.R.; Burns, M.; Rayner, P.J.; Leibfritz, D.; et al. Molecular MRI in the Earth’s magnetic field using continuous hyperpolarization of a biomolecule in water. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 5670–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barskiy, D.A.; Kovtunov, K.V.; Koptyug, I.V.; He, P.; Groome, K.A.; Best, Q.A.; Shi, F.; Goodson, B.M.; Shchepin, R.V.; Truong, M.L.; et al. In situ and ex situ low-field NMR spectroscopy and MRI endowed by SABRE hyperpolarization. Chemphyschem 2014, 15, 4100–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckenmaier, K.; Rudolph, M.; Back, C.; Misztal, T.; Bommerich, U.; Fehling, P.; Koelle, D.; Kleiner, R.; Mayer, H.A.; Scheffler, K.; et al. Squid-based detection of ultra-low-field multinuclear NMR of substances hyperpolarized using signal amplification by reversible exchange. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckenmaier, K.; Rudolph, M.; Fehling, P.; Steffen, T.; Back, C.; Bernard, R.; Pohmann, R.; Bernarding, J.; Kleiner, R.; Koelle, D.; et al. Mutual benefit achieved by combining ultralow-field magnetic resonance and hyperpolarizing techniques. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 125103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Jeong, K.; Shim, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Min, S.; Chae, H.; Namgoong, S.K.; Kim, K. Squid-based ultralow-field MRI of a hyperpolarized material using signal amplification by reversible exchange. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theis, T.; Ledbetter, M.P.; Kervern, G.; Blanchard, J.W.; Ganssle, P.J.; Butler, M.C.; Shin, H.D.; Budker, D.; Pines, A. Zero-field NMR enhanced by parahydrogen in reversible exchange. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3987–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, A.M.; Shchepin, R.V.; Truong, M.L.; Wilkens, K.; Pham, W.; Chekmenev, E.Y. Open-source automated parahydrogen hyperpolarizer for molecular imaging using C-13 metabolic contrast agents. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8279–8288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, A.M.; Shchepin, R.V.; Feng, B.B.; Colon, R.D.; Wilkens, K.; Waddell, K.W.; Chekmenev, E.Y. A pulse programmable parahydrogen polarizer using a tunable electromagnet and dual channel NMR spectrometer. J. Magn. Reson. 2017, 284, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, M.J.; Adams, R.W.; Atkinson, K.D.; Cockett, M.C.R.; Duckett, S.B.; Green, G.G.R.; Lohman, J.A.B.; Kerssebaum, R.; Kilgour, D.; Mewis, R.E. Iridium n-heterocyclic carbene complexes as efficient catalysts for magnetization transfer from para-hydrogen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6134–6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.W.; Duckett, S.B.; Green, R.A.; Williamson, D.C.; Green, G.G.R. A theoretical basis for spontaneous polarization transfer in non-hydrogenative parahydrogen-induced polarization. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 131, 194505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theis, T.; Truong, M.L.; Coffey, A.M.; Shchepin, R.V.; Waddell, K.W.; Shi, F.; Goodson, B.M.; Warren, W.S.; Chekmenev, E.Y. Microtesla SABRE enables 10% nitrogen-15 nuclear spin polarization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1404–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pravdivtsev, A.N.; Yurkovskaya, A.V.; Vieth, H.-M.; Ivanov, K.L.; Kaptein, R. Level anti-crossings are a key factor for understanding para-hydrogen-induced hyperpolarization in SABRE experiments. Chemphyschem 2013, 14, 3327–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, L.S.; Adams, R.W.; Bernstein, M.; Coombes, S.; Duckett, S.B.; Green, G.G.R.; Lewis, R.J.; Mewis, R.E.; Sleigh, C.J. Utilization of SABRE-derived hyperpolarization to detect low-concentration analytes via 1d and 2d NMR methods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 12904–12907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, P.M.; John, R.O.; Parrott, A.J.; Rayner, P.J.; Iali, W.; Nordon, A.; Halse, M.E.; Duckett, S.B. Quantification of hyperpolarization efficiency in SABRE and SABRE-relay enhanced NMR spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 26362–26371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, P.M.; Parrott, A.J.; Semenova, O.; Nordon, A.; Duckett, S.B.; Halse, M.E. SABRE hyperpolarization enables high-sensitivity 1H and 13C benchtop NMR spectroscopy. Analyst 2018, 143, 3442–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, K.M.; Mewis, R.E.; Olaru, A.M.; Green, G.G.R.; Fairlamb, I.J.S.; Duckett, S.B. Investigating pyridazine and phthalazine exchange in a series of iridium complexes in order to define their role in the catalytic transfer of magnetization from para-hydrogen. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 3981–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, L.S.; Asghar, A.; Burns, M.J.; Charlton, A.; Coombes, S.; Cowley, M.J.; Dear, G.J.; Duckett, S.B.; Genov, G.R.; Green, G.G.R.; et al. Hyperpolarization through reversible interactions with parahydrogen. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 3544–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, P.J.; Burns, M.J.; Olaru, A.M.; Norcott, P.; Fekete, M.; Green, G.G.R.; Highton, L.A.R.; Mewis, R.E.; Duckett, S.B. Delivering strong 1H nuclear hyperpolarization levels and long magnetic lifetimes through signal amplification by reversible exchange. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3188–E3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barskiy, D.A.; Shchepin, R.V.; Tanner, C.P.N.; Colell, J.F.P.; Goodson, B.M.; Theis, T.; Warren, W.S.; Chekmenev, E.Y. The absence of quadrupolar nuclei facilitates efficient C-13 hyperpolarization via reversible exchange with parahydrogen. Chemphyschem 2017, 18, 1493–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducker, E.B.; Kuhn, L.T.; Munnemann, K.; Griesinger, C. Similarity of SABRE field dependence in chemically different substrates. J. Magn. Reson. 2012, 214, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |
| Volume/mL | T2*/s | S0/µV | Scorr/µV |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | - | 0.38 | 0.38 |
| 42 | 0.410 ± 0.013 | 7.90 | 8.40 |
| 76 | 0.350 ± 0.008 | 13.9 | 15.0 |
| 140 | 0.245 ± 0.003 | 23.3 | 25.8 |
| 192 | 0.225 ± 0.003 | 29.2 | 32.6 |
| 270 | 0.219 ± 0.003 | 39.1 | 43.8 |
| 270 | 0.197 ± 0.003 | 60.9 | 69.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hill-Casey, F.; Sakho, A.; Mohammed, A.; Rossetto, M.; Ahwal, F.; Duckett, S.B.; John, R.O.; Richardson, P.M.; Virgo, R.; Halse, M.E. In Situ SABRE Hyperpolarization with Earth’s Field NMR Detection. Molecules 2019, 24, 4126. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224126
Hill-Casey F, Sakho A, Mohammed A, Rossetto M, Ahwal F, Duckett SB, John RO, Richardson PM, Virgo R, Halse ME. In Situ SABRE Hyperpolarization with Earth’s Field NMR Detection. Molecules. 2019; 24(22):4126. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224126
Chicago/Turabian StyleHill-Casey, Fraser, Aminata Sakho, Ahmed Mohammed, Matheus Rossetto, Fadi Ahwal, Simon B. Duckett, Richard O. John, Peter M. Richardson, Robin Virgo, and Meghan E. Halse. 2019. "In Situ SABRE Hyperpolarization with Earth’s Field NMR Detection" Molecules 24, no. 22: 4126. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224126
APA StyleHill-Casey, F., Sakho, A., Mohammed, A., Rossetto, M., Ahwal, F., Duckett, S. B., John, R. O., Richardson, P. M., Virgo, R., & Halse, M. E. (2019). In Situ SABRE Hyperpolarization with Earth’s Field NMR Detection. Molecules, 24(22), 4126. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224126






