Changes of Physicochemical, Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity during the Brewing Process of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
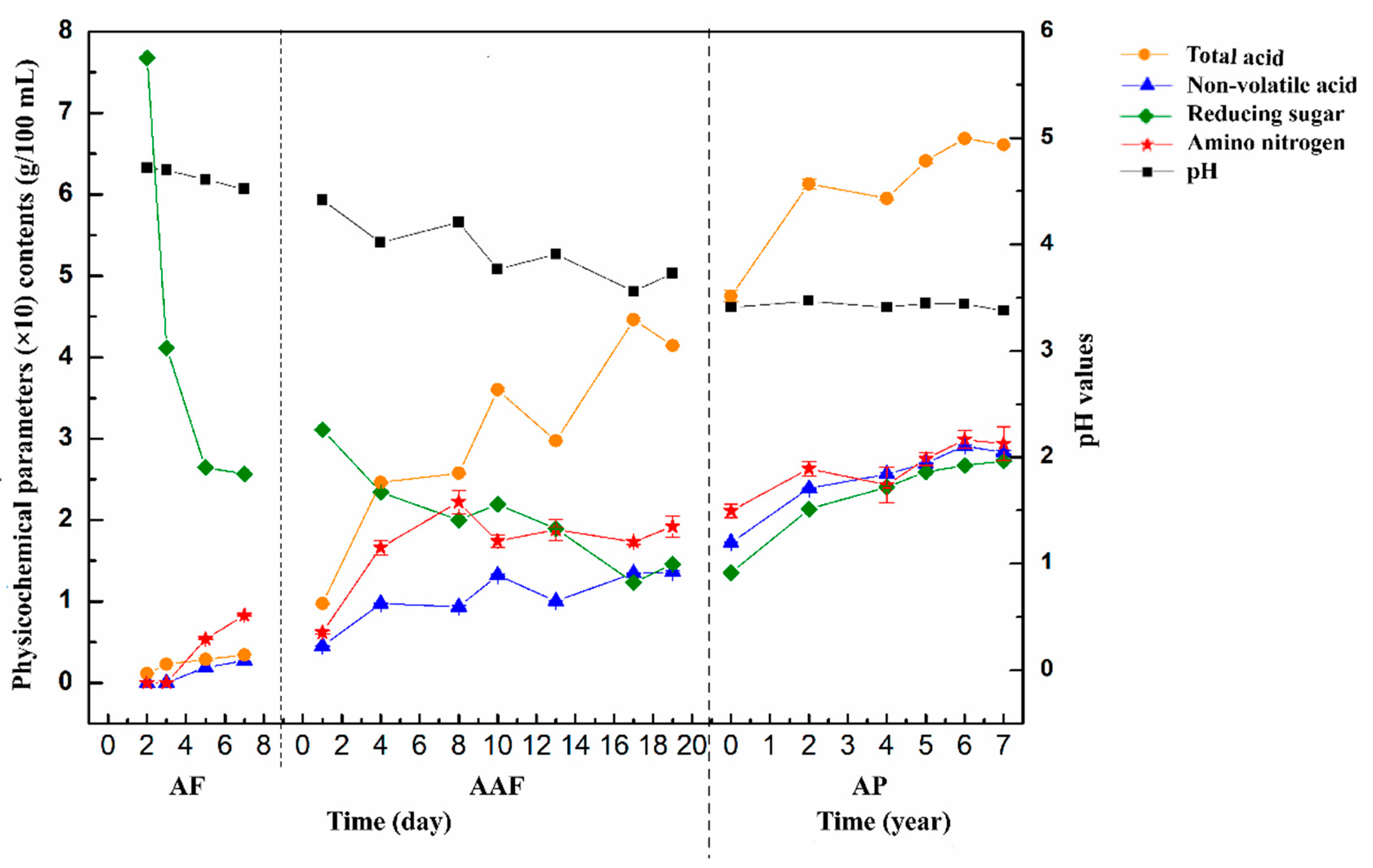
2.1. Changes in Physicochemical Parameters during the Brewing Process of ZAV
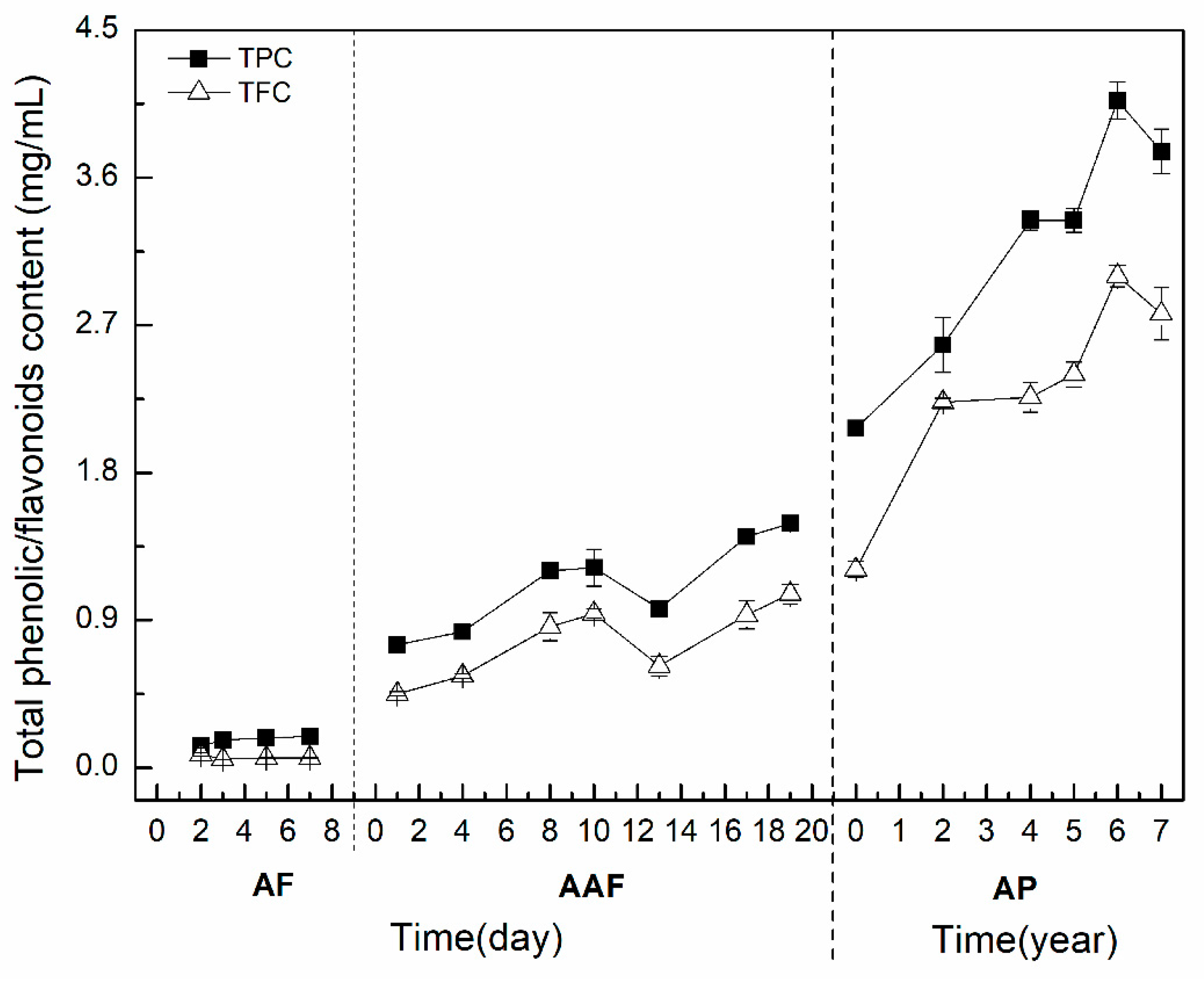
2.2. Alteration of TPC and TFC during the Brewing Process of ZAV
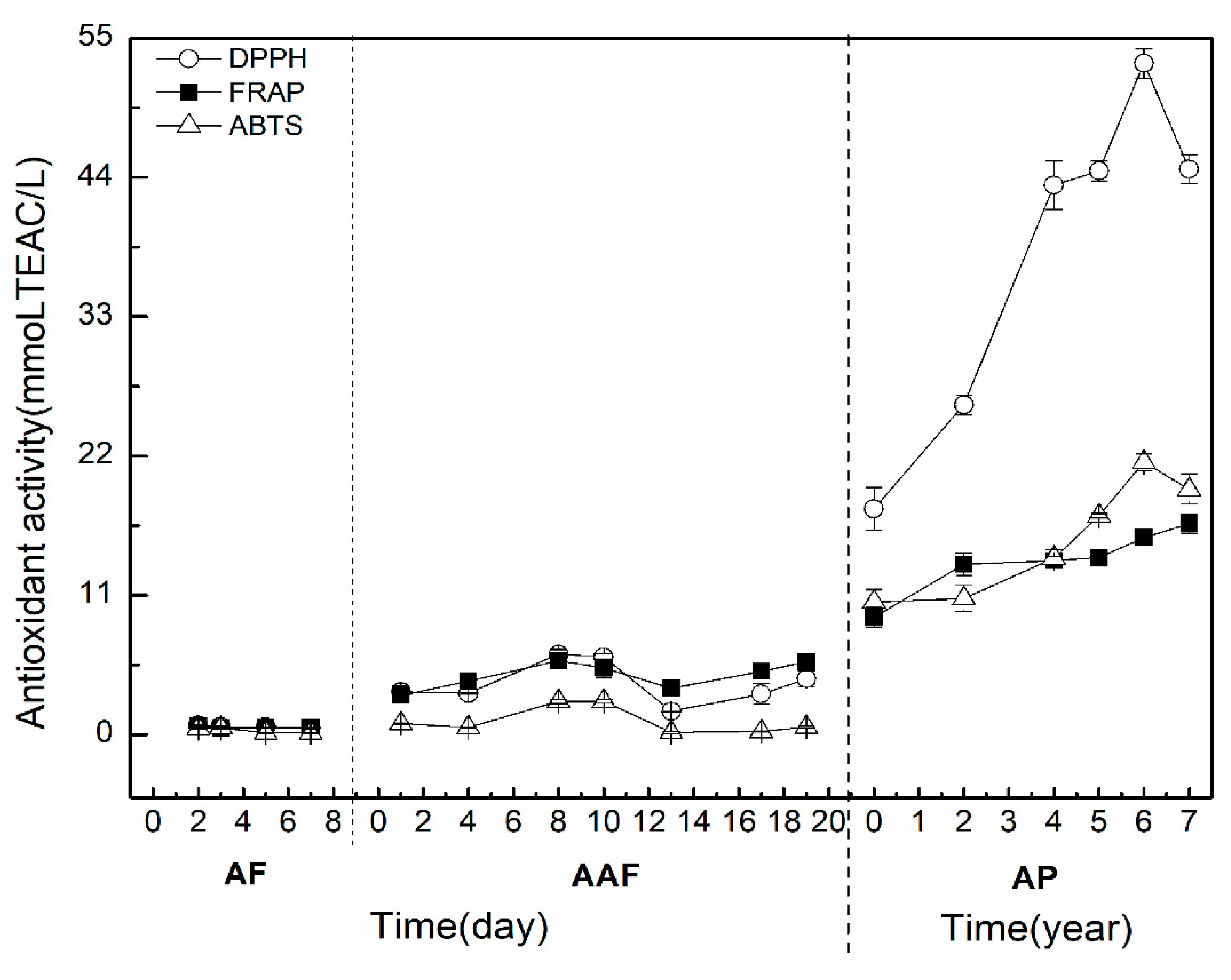
2.3. TAA and its Correlation with TPC and TFC during the Brewing Process of ZAV
2.4. Variation of Phenolic Compound Contents during the AP of ZAV
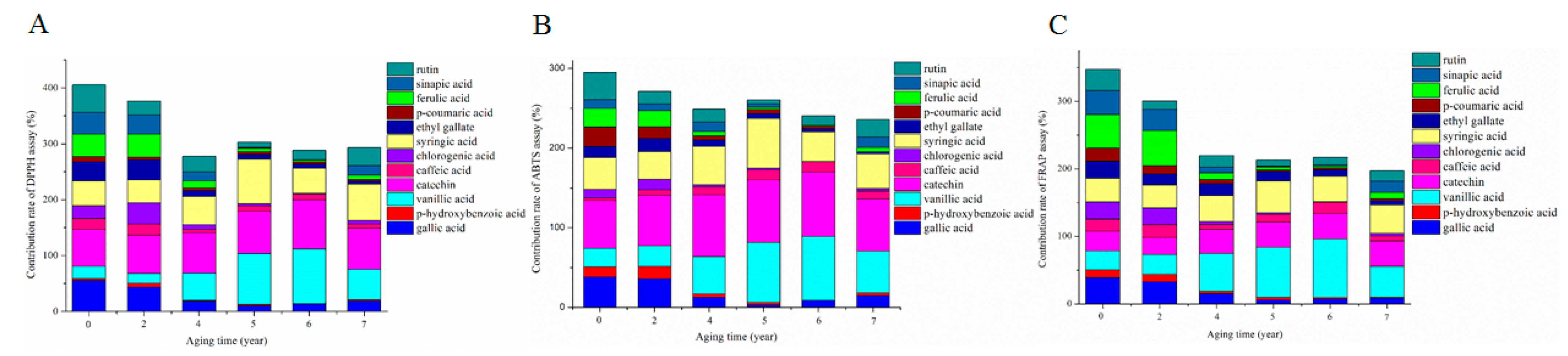
2.5. Antioxidant Contribution of Phenolic Compounds during the AP of ZAV
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples and Reagents
3.2. Detection of the Physicochemical Parameters
3.3. Measurement of TPC and TFC
3.4. Determination of TAA
3.5. Identification of Phenolic Compositions
3.6. Determination of High Molecular Weight Melanoidins
3.7. Analysis of Antioxidant Contribution of Phenolic Compounds in Mixed Solution
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ZAV | Zhenjiang aromatic vinegar |
| ABTS | 2,2’-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) |
| DPPH | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| FRAP | ferric reducing antioxidant power |
| HPLC | high performance liquid chromatography |
| TPC | total phenolic content |
| TFC | total flavonoid content |
| TAA | total antioxidant activity |
| TEAC | Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity |
| AF | alcohol fermentation |
| AAF | acetic acid fermentation |
| AP | aging process |
References
- Solieri, L.; Giudici, P. Vinegars of the World; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sáizabajo, M.J.; Gonzálezsáiz, J.M.; Pizarro, C. Near infrared spectroscopy and pattern recognition methods applied to the classification of vinegar according to raw material and elaboration process. J. Near Infrared Spec. 2004, 12, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daglia, M.; Amoroso, A.; Rossi, D.; Mascherpa, D.; Maga, G. Identification and quantification of α-dicarbonyl compounds in balsamic and traditional balsamic vinegars and their cytotoxicity against human cells. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2013, 31, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, T.M.; Oliveira, D.N.D.; Ferreira, M.S.; Catharino, R.R. High-throughput analysis by SP-LDI-MS for fast identification of adulterations in commercial balsamic vinegars. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 838, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrera, R.R.; Lobo, A.P.; Alonso, J.J.M. Effect of cider maturation on the chemical and sensory characteristics of fresh cider spirits. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishidai, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Torikai, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Ishihara, N.; Mori, H.; Ohigashi, H. Kurosu, a traditional vinegar produced from unpolished rice, suppresses lipid peroxidation in vitro and in mouse skin. Biosci., Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.B.; Li, Y.X.; Shi, J.Y.; Huang, X.W.; Zhao, J.W. Traditional Vinegars Identification by Colorimetric Sensor. Procedia Chem. 2012, 6, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xu, Q.; Chen, J.; Lu, Z.; Xia, R.; Li, G.; Ma, Y. Ligustrazine formation in Zhenjiang aromatic vinegar: Changes during fermentation and storing process. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gan, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yin, L.; Cheng, Y. Effect of laboratory-scale decoction on the antioxidative activity of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar: The contribution of melanoidins. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Han, Y. Analysis of bacterial diversity during acetic acid fermentation of Tianjin duliu aged vinegar by 454 pyrosequencing. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 71, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Lu, Z.; Shi, J.; Ma, Y. Monitoring the microbial community during solid-state acetic acid fermentation of Zhenjiang aromatic vinegar. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Tao, W.; Ao, Z. Antioxidant activity of vinegar melanoidins. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Tian, J.J.; Ge, H.F.; Liu, R.H.; Xiao, J.B. Effects of tetramethylpyrazine from Chinese black vinegar on antioxidant and hypolipidemia activities in HepG2 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 109, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Jo, Y.; Chung, N.; Gu, S.Y.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kwon, J.H. Physicochemical qualities and flavor patterns of traditional Chinese vinegars manufactured by different fermentation methods and aging periods. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2017, 22, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, Y.; Chen, F.S. Free phenolic acids in Shanxi aged vinegar: Changes during aging and synergistic antioxidant activities. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.M.; Wang, X.Y.; Tian, C.R.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, B.S.; Song, X.Z.; Zhang, J. Characterization of organic acids and phenolic compounds of cereal vinegars and fruit vinegars in China. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2016, 41, e12937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice-Evans, C.A. Antioxidant properties of phenolic compounds. Trends Plant Sci. 1997, 2, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Thind, T.S.; Singh, B.; Arora, S. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation by extracts/subfractions of chickrassy (Chukrasia tabularis A. Juss.). Naturwissenschaften 2009, 96, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, I.; Caliskan, O.; Tornuk, F.; Ozcanc, N.; Yalcin, H.; Baslar, M.; Sagdic, O. Antioxidant, antimicrobial, mineral, volatile, physicochemical and microbiological characteristics of traditional home-made Turkish vinegars. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verzelloni, E.; Tagliazucchi, D.; Conte, A. Relationship between the antioxidant properties and the phenolic and flavonoid content in traditional balsamic vinegar. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.L.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, X.L.; Xia, T.; Wang, M. Antioxidant activity of Chinese Shanxi aged vinegar and its correlation with polyphenols and flavonoids during the brewing process. J Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2479–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porgal, E.; Büyüktuncel, E. Determination of phenolic composition and antioxidant capacity of native red wines by high performance liquid chromatography and spectrophotometric methods. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Yao, J.; Zhang, J.; Duan, W.; Zhang, B.; Xie, X.; Wang, M. Evaluation of nutritional compositions, bioactive compounds, and antioxidant activities of Shanxi aged vinegars during the aging process. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 2638–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benabdallah, A.; Rahmoune, C.; Boumendjel, M.; Aissi, O.; Messaoud, C. Total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of six wild mentha species (Lamiaceae) from northeast of Algeria. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, T.; Giudici, P.; Chen, F. Vinegar functions on health: Constituents, sources, and formation mechanisms. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 1124–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazuch, C.M.; Siepmann, F.B.; Canan, C.; Colla, E. Vinegar: Functional aspects. Científica 2015, 43, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plessi, M.; Bertelli, D.; Miglietta, F. Extraction and identification by GC-MS of phenolic acids in traditional balsamic vinegar from Modena. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, S.; Toydemir, G.; Boyacioglu, D.; Beekwilder, J.; Capanoglu, E. Fruit antioxidants during vinegar processing: Changes in content and in vitro bio-accessibility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharchoufi, S.; Gomez, J.; Lasanta, C.; Castro, R.; Sainz, F.; Hamdi, M. Benchmarking laboratory-scale pomegranate vinegar against commercial wine vinegars: Antioxidant activity and chemical composition. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4749–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliazucchi, D.; Verzelloni, E.; Conte, A. Antioxidant properties of traditional balsamic vinegar and boiled must model systems. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 227, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalou, S.; Hatzidimitriou, E.; Papadopoulou, M.; Kontogianni, V.G.; Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Gerothanassis, I.P.; Tsimidou, M.Z. Beyond traditional balsamic vinegar: Compositional and sensorial characteristics of industrial balsamic vinegars and regulatory requirements. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 43, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, P.M.; Chillo, S.; Giudici, P.; Nobile, M.A.D. Measuring rheological properties for applications in quality assessment of traditional balsamic vinegar: Description and preliminary evaluation of a model. J. Food Eng. 2007, 80, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.W.; Lazim, A.M.; Fazry, S.; Zaki, U.K.H.H.; Lim, S.J. Varieties, production, composition and health benefits of vinegars: A review. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesfaye, W.; Lourdes Morales, M.; Garcı´a-Parı´lla, M.C.; Troncoso, A.M. Evolution of phenolic compounds during an experimental aging in wood of sherry vinegar. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7053–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, F.; Li, P.; Pan, Q.; Huang, w. Determination of red wine flavonoids by HPLC and effect of aging. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoji, Y.; Tamura, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Nanda, K.; Nishidai, S.; Nishikawa, Y.; Ishihara, N.; Ohigashi, H. Isolation and identification of DPPH radical scavenging compounds in Kurosu (Japanese unpolished rice vinegar). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 6501–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülçin, I. Antioxidant activity of food constituents: An overview. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 345–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastante, M.J.C.; Guerrero, E.D.; Mejías, R.C.; Marín, R.N.; Dodero, M.C.R.; Barroso, C.G. Study of the polyphenolic composition and antioxidant activity of new sherry vinegar-derived products by maceration with fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11814–11820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Correlation of volatile and nonvolatile components with the total antioxidant capacity of tartary buckwheat vinegar: Influence of the thermal processing. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelli, D.; Maietti, A.; Papotti, G.; Tedeschi, P.; Bonetti, G.; Graziosi, R.; Plessi, M. Antioxidant activity, phenolic compounds, and NMR characterization of balsamic and traditional balsamic vinegar of Modena. Food Anal. Method. 2015, 8, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verzelloni, E.; Tagliazucchi, D.; Conte, A. Contribution of melanoidins to the antioxidant activity of traditional balsamic vinegar during aging. J. Food Biochem. 2010, 34, 1061–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourvellec, C.L.; Renard, C.M. Interactions between phenolic compounds and macromolecules: Quantification methods and mechanisms. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 213–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindon, K.; Carew, A.; Mierczynskavasilev, A.; Kassara, S.; Kerslake, F.; Smith, P.A. Characterization of macromolecular complexes in red wine: Composition, molecular mass distribution and particle size. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.M.; Castro, R.; Rodriguez, M.C.; Guillén, D.A.; Barroso, C.G. Study of the antioxidant power of brandies and vinegars derived from sherry wines and correlation with their content in polyphenols. Food Res. Int. 2004, 7, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Song, H.; Ren, C.; Li, Z.G. Key aroma compounds in Shanxi aged tartary buckwheat vinegar and changes during its thermal processing. Flavour Fragrance, J. 2011, 27, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Marta, M.; Cristina, D.A. Melanoidins as a potential functional food ingredient. Curr. Opin. in Food Sci. 2017, 14, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, V.L.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Method. Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of Zhenjiang aromatic vinegars during the brewing process are available from the authors. |

| Correlation Matrix | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPC | TFC | DPPH Assay | FRAP Assay | ABTS Assay | |
| TPC | 1 | 0.986 ** | 0.954 ** | 0.987 ** | 0.952 ** |
| TFC | 1 | 0.951 ** | 0.989 ** | 0.951 ** | |
| DPPH assay | 1 | 0.935 ** | 0.979 ** | ||
| FRAP assay | 1 | 0.944 ** | |||
| ABTS assay | 1 | ||||
| Alcohol Fermentation (AF) Samples | Acetic Acid Fermentation (AAF) Samples | Aging Process (AP) Samples |
|---|---|---|
| 2 days | 1 day | 0 year |
| 3 days | 4 days | 2 years |
| 5 days | 8 days | 4 years |
| 7 days | 10 days | 5 years |
| 13 days | 6 years | |
| 17 days | 7 years | |
| 19 days |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, W.; Xia, T.; Zhang, B.; Li, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, C.; Song, J.; Wang, M. Changes of Physicochemical, Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity during the Brewing Process of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar. Molecules 2019, 24, 3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213935
Duan W, Xia T, Zhang B, Li S, Zhang C, Zhao C, Song J, Wang M. Changes of Physicochemical, Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity during the Brewing Process of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar. Molecules. 2019; 24(21):3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213935
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Wenhui, Ting Xia, Bo Zhang, Shaopeng Li, Chenwei Zhang, Chaoya Zhao, Jia Song, and Min Wang. 2019. "Changes of Physicochemical, Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity during the Brewing Process of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar" Molecules 24, no. 21: 3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213935
APA StyleDuan, W., Xia, T., Zhang, B., Li, S., Zhang, C., Zhao, C., Song, J., & Wang, M. (2019). Changes of Physicochemical, Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity during the Brewing Process of Zhenjiang Aromatic Vinegar. Molecules, 24(21), 3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213935






