Protolysis and Complex Formation of Organophosphorus Compounds—Characterization by NMR-Controlled Titrations
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Developing Technical Setups for Automated NMR Titrations
1.2. Some Comments on Macroscopic Protolytic Equilibria—Dissociation and Stability Constants
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Phosphonic Acids
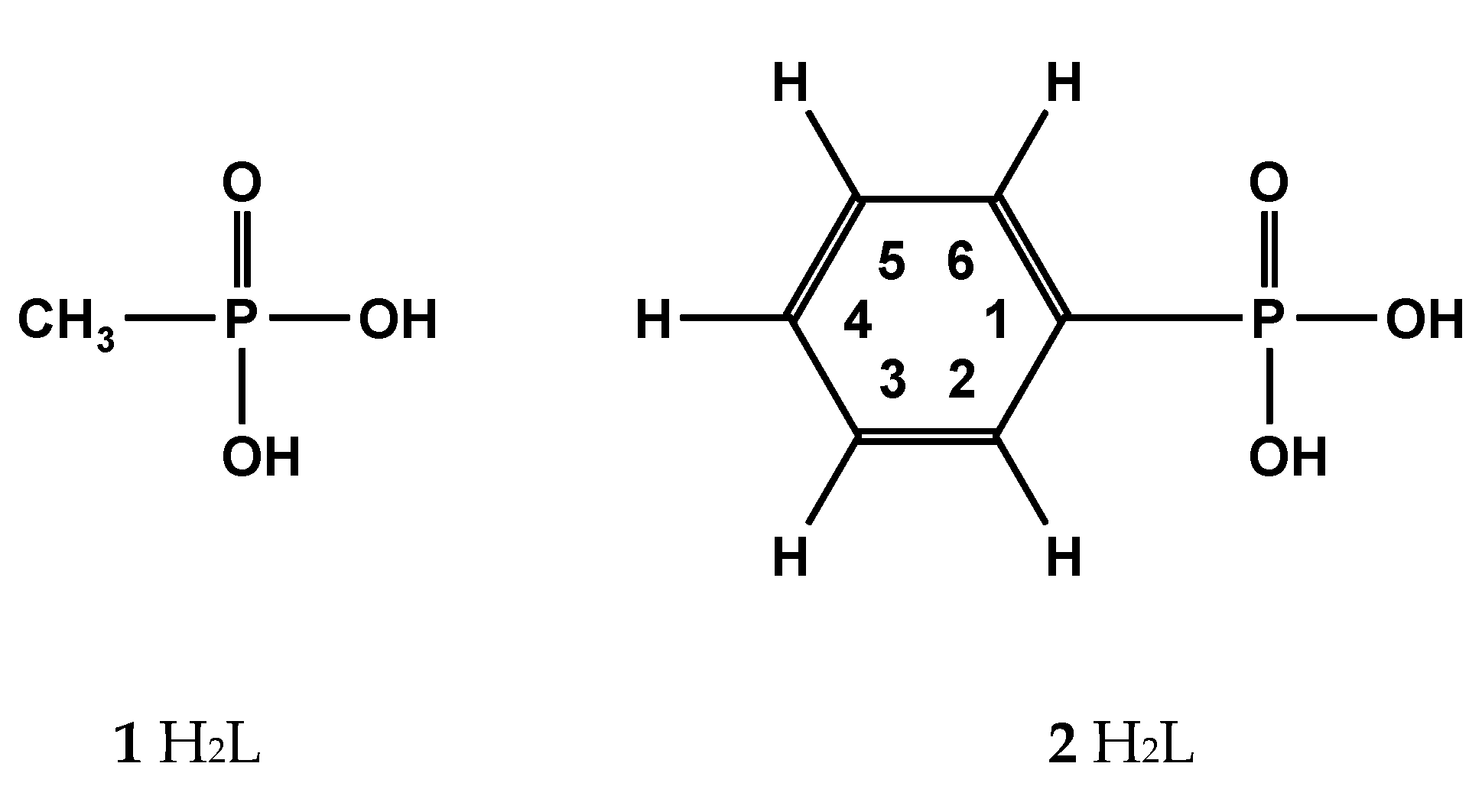
2.1.1. Methanephosphonic Acid 1
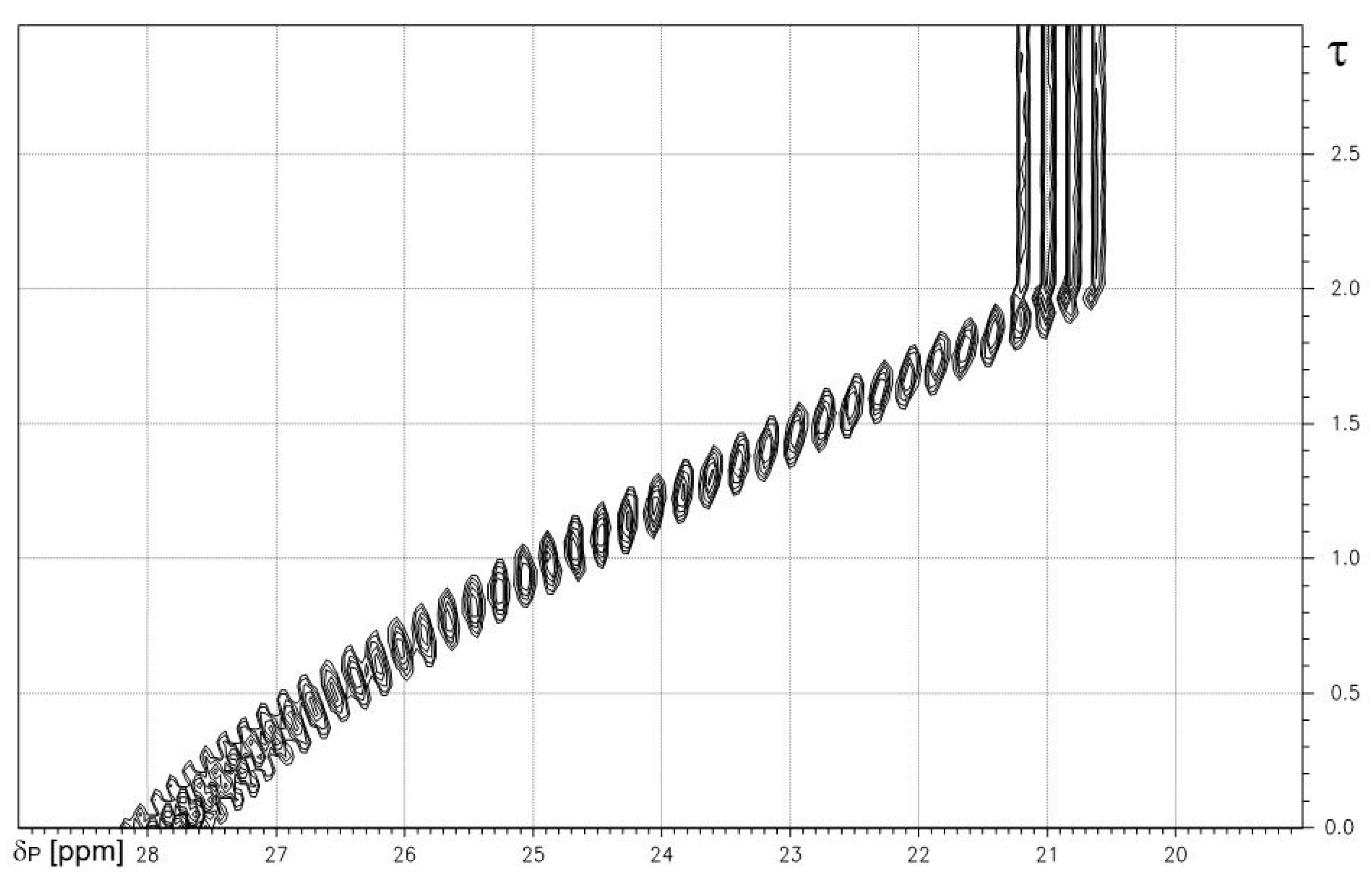
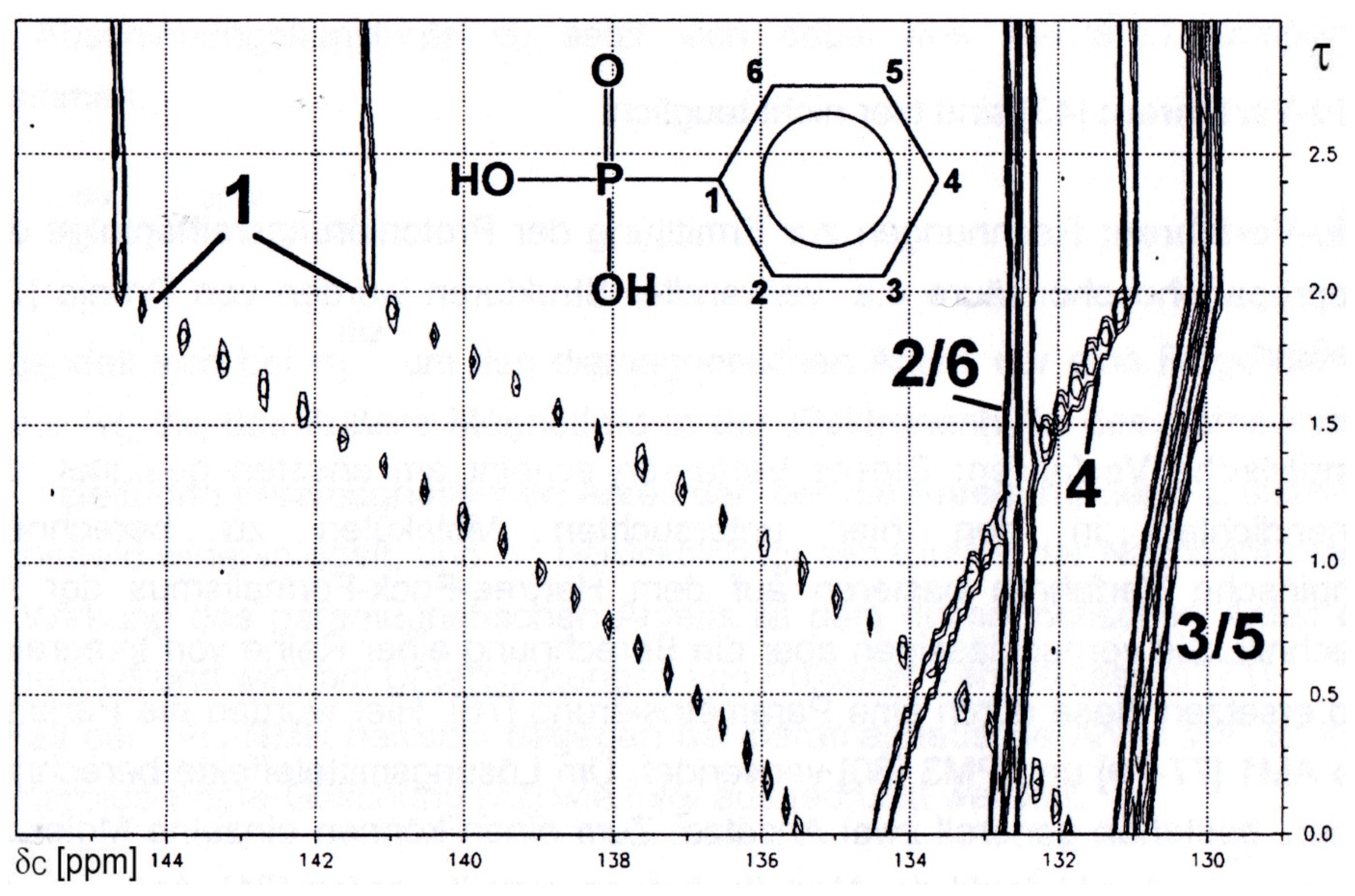
2.1.2. Phenylphosphonic Acid 2
2.2. Comparison of Aliphatic and Aromatic Aminophosphonic Acids
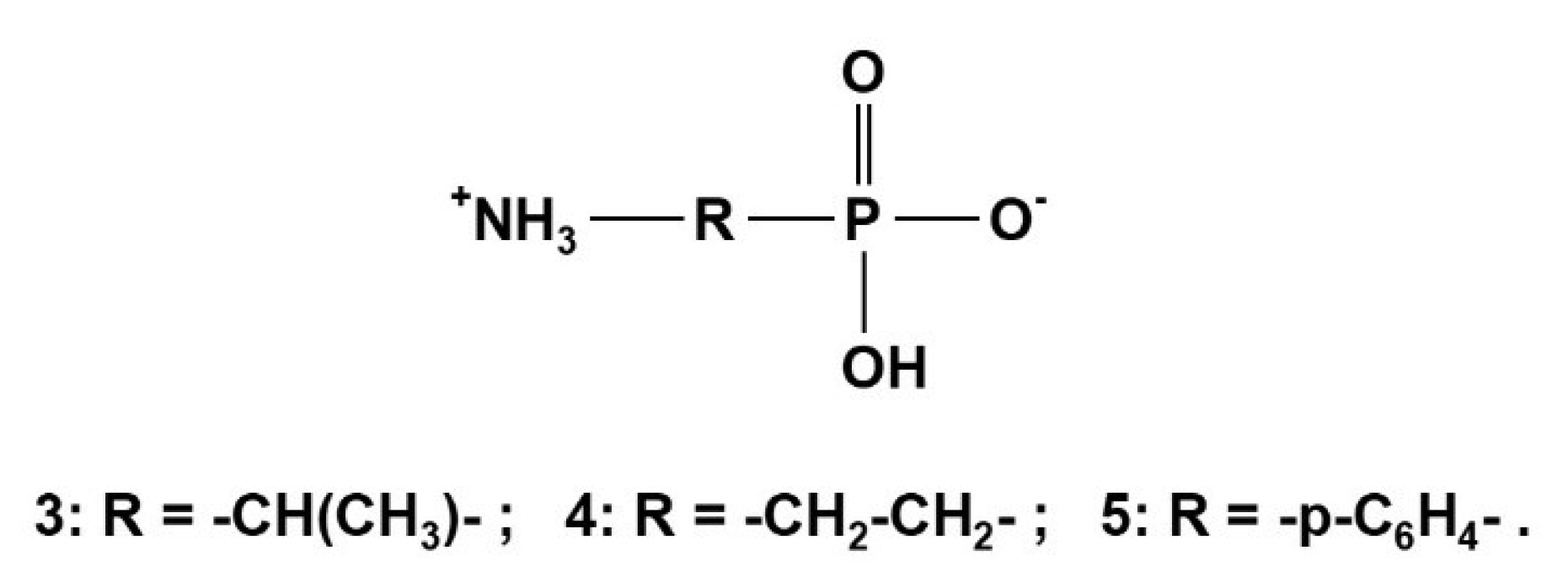
2.2.1. Aliphatic Aminophosphonic Acids
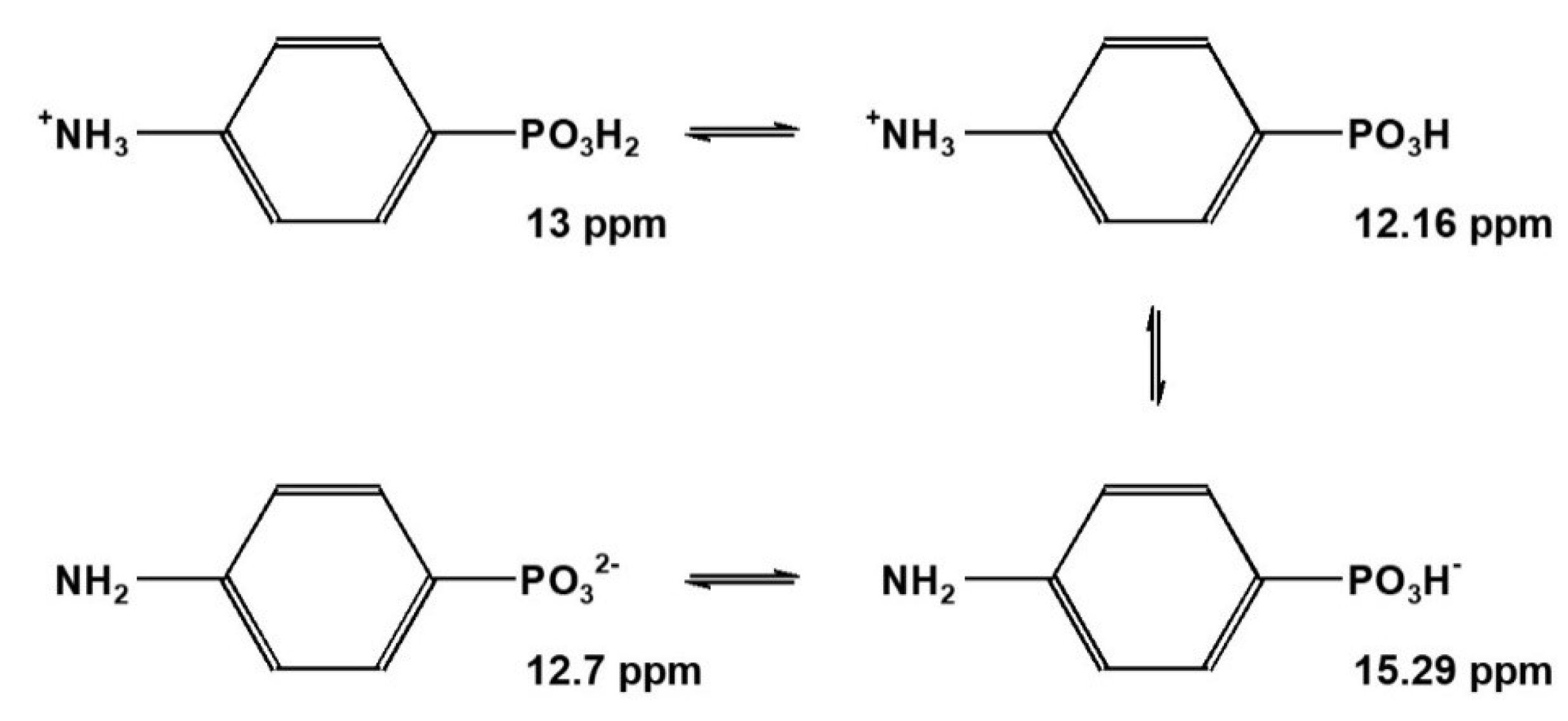
2.2.2. Aromatic p-Aminophenylphosphonic Acid 5
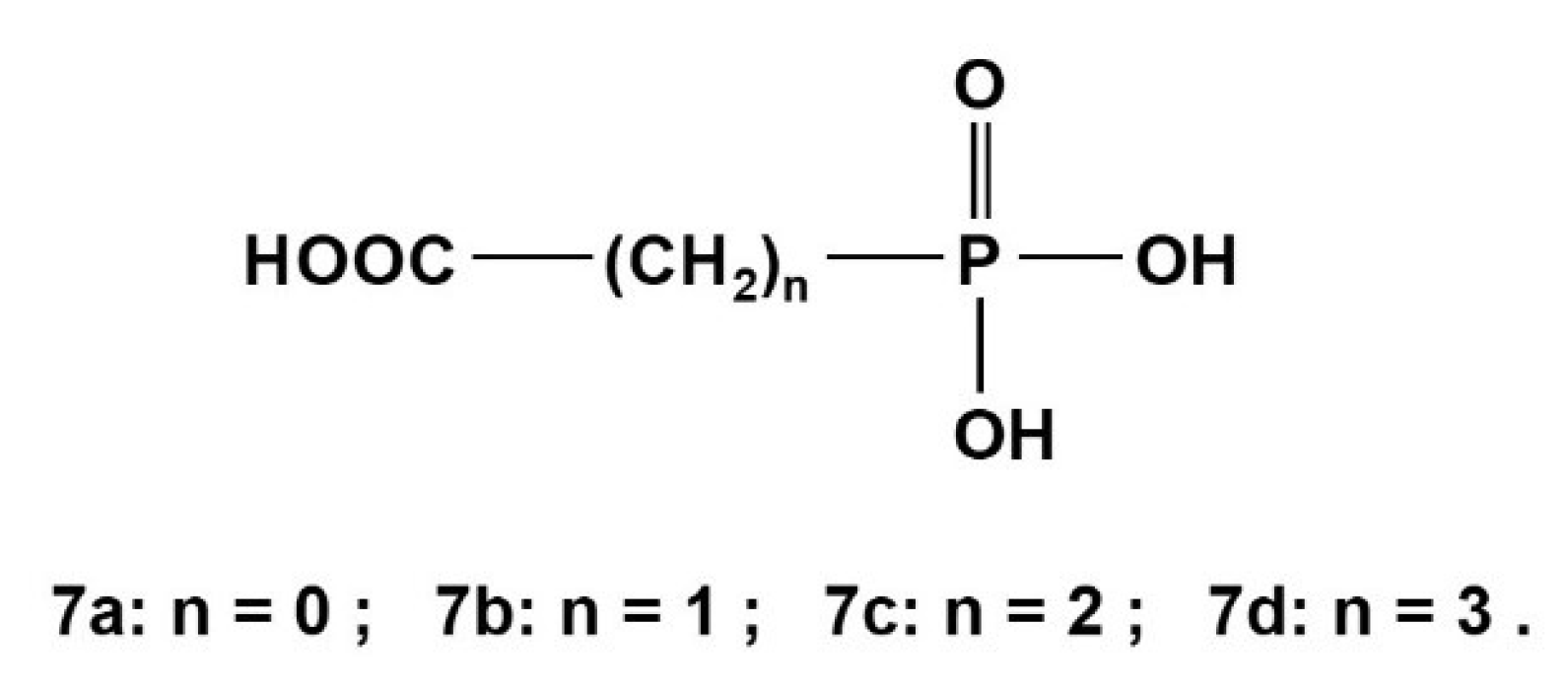
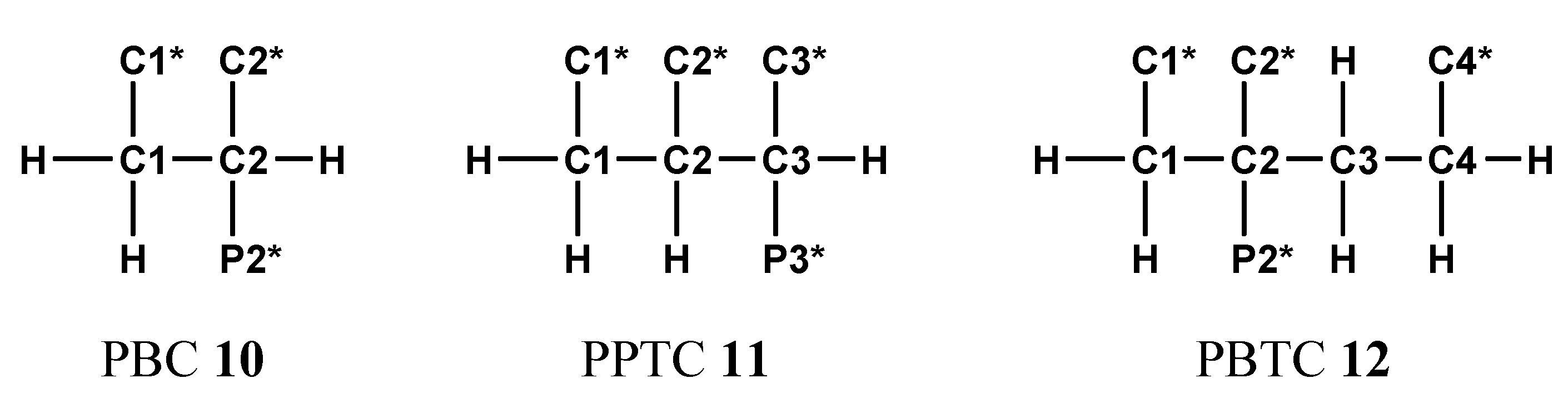
2.3. Phosphonocarboxylic Acids HOOC-(CH2)n-PO3H2 7a to 7d (n = 0 to 3)
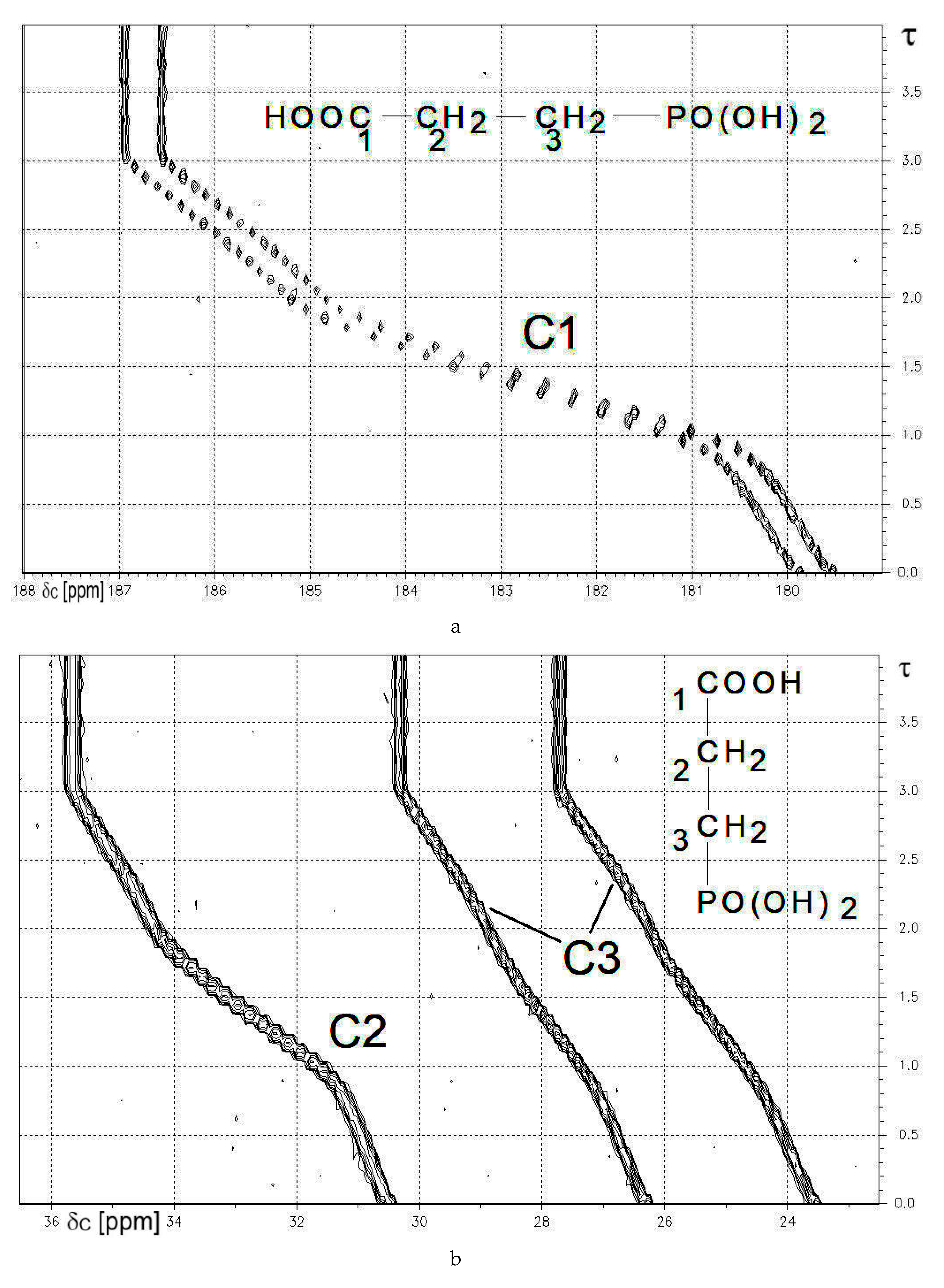
2.3.1. Compound 7c: 13C{1H}-NMR-Controlled Titration of 3-Phosphonopropionic Acid HOOC-CH2-CH2-PO3H2 7c.
2.3.2. 19. F-NMR-Controlled Retro Titrations of Lithium Salts LiOOC-CH2-nFn-PO3Li2 8a and 8b
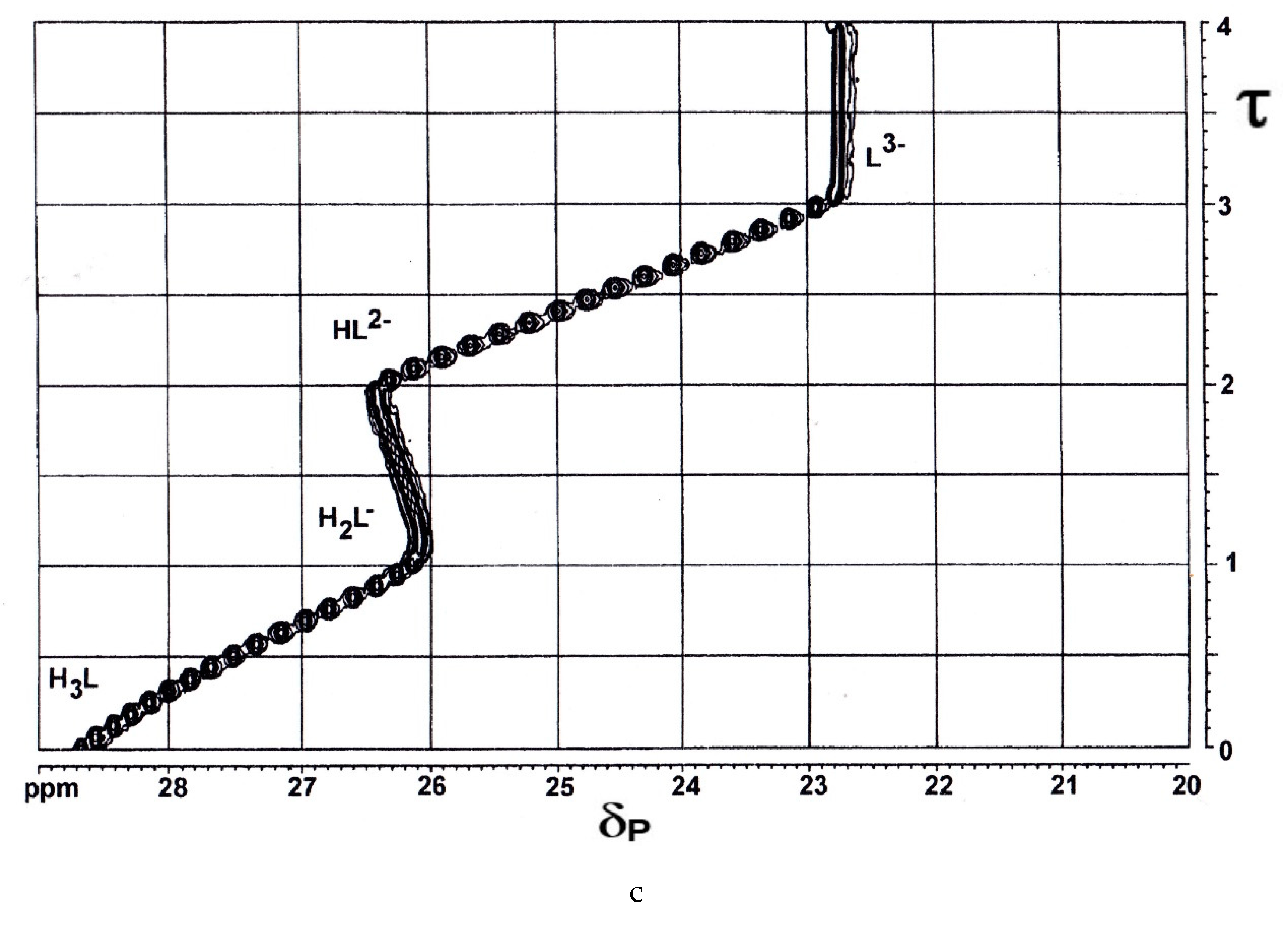
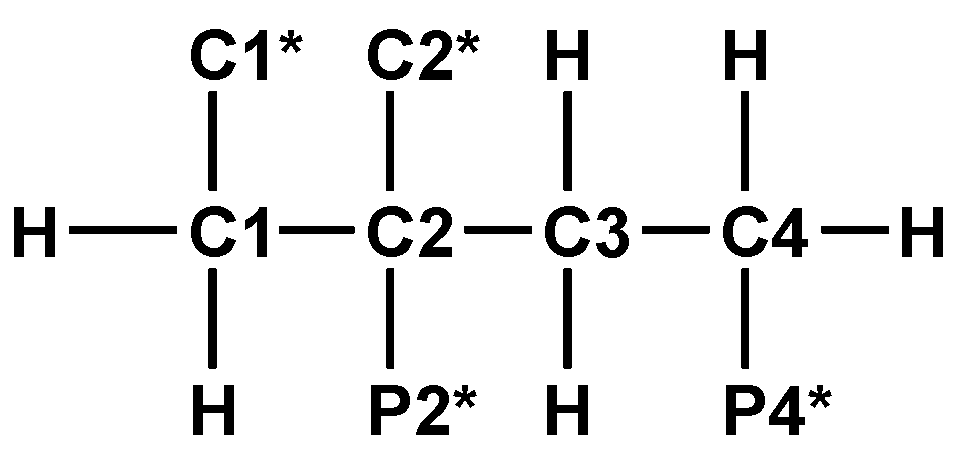
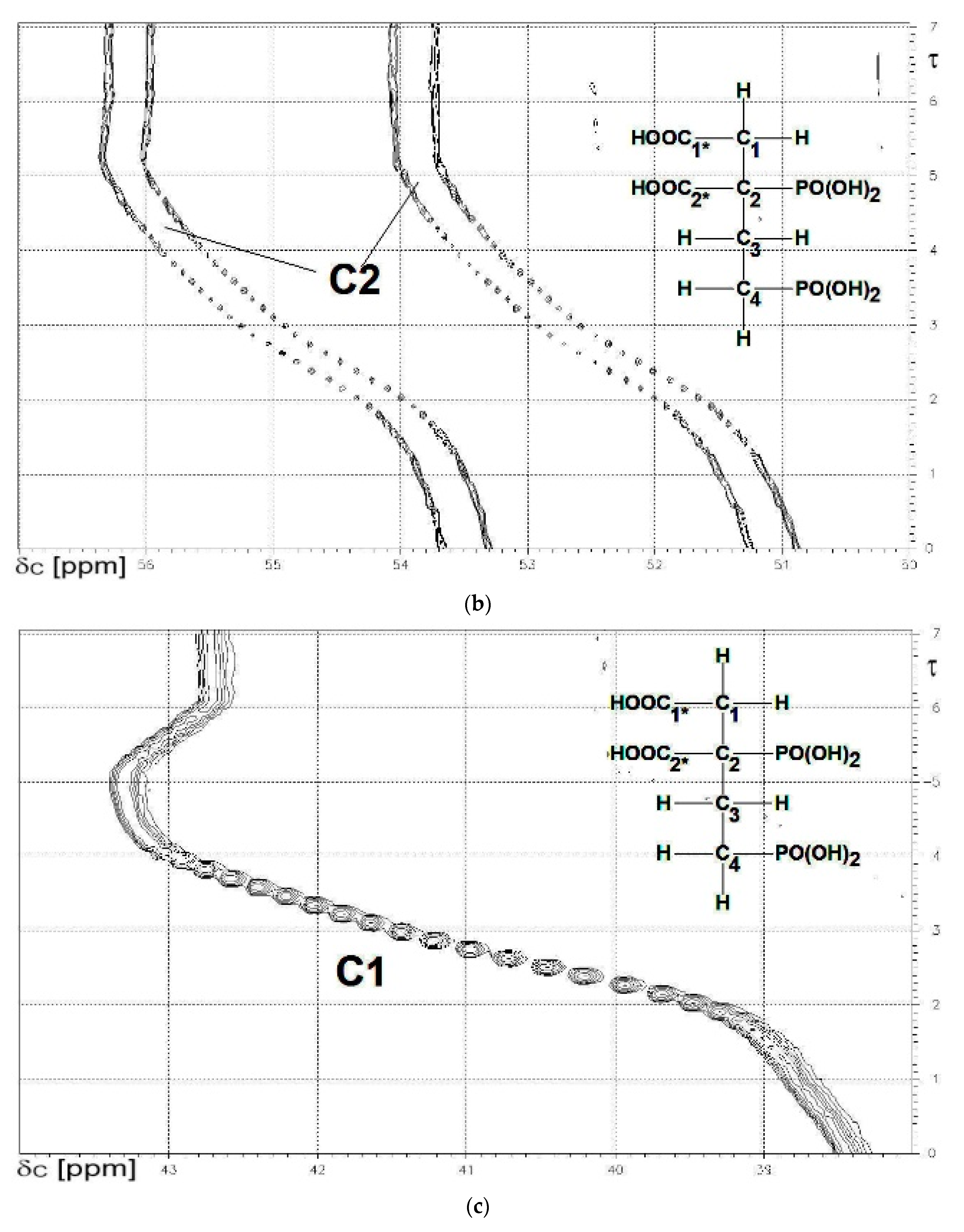
2.3.3. 2,4-Diphosphonobutane-1,2-Dicarboxylic Acid (DPBDC) 9
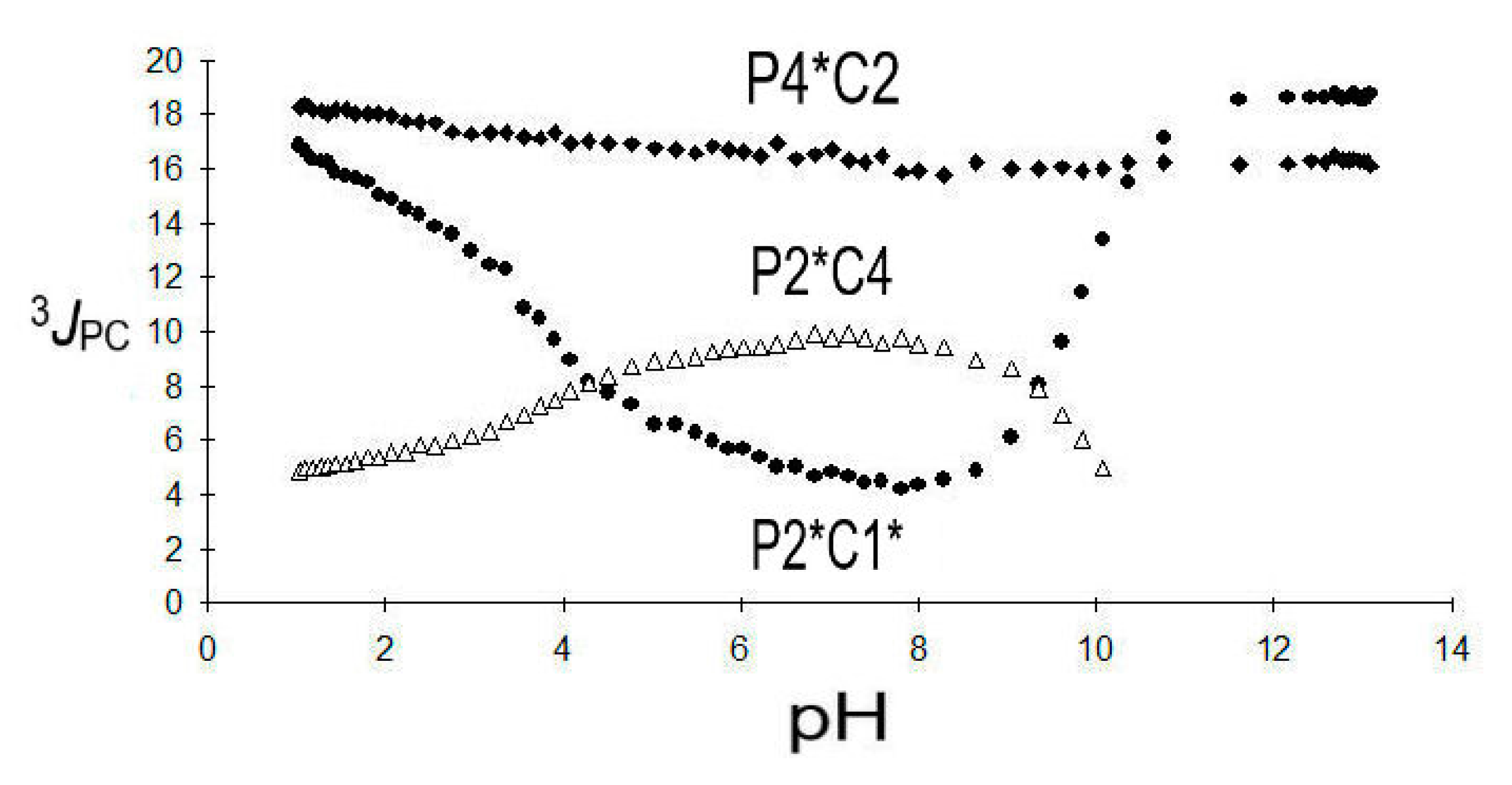
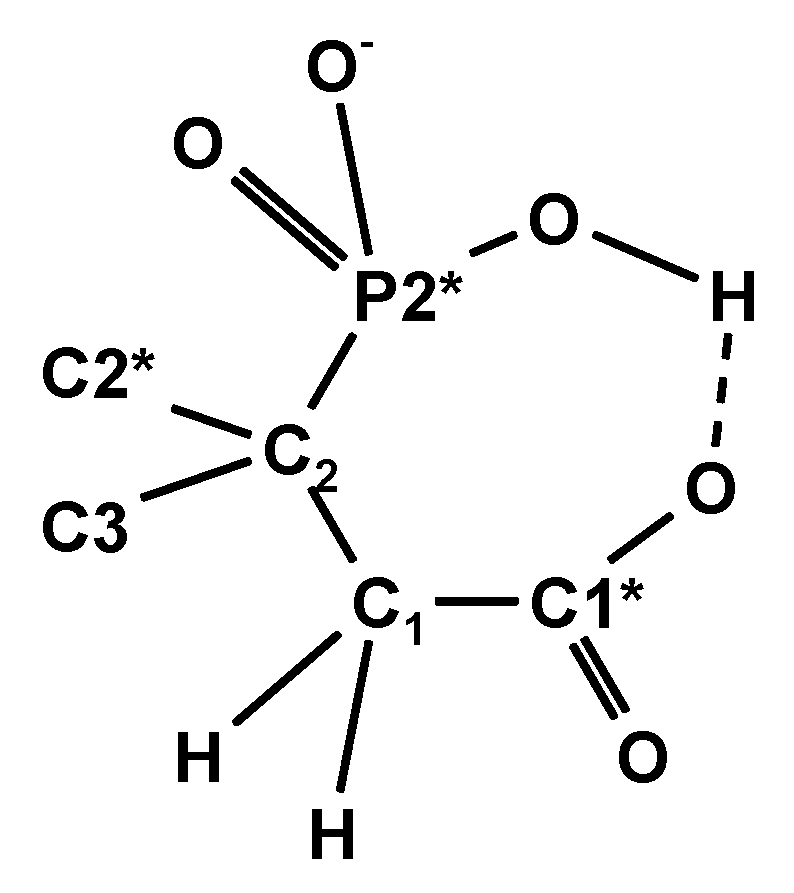
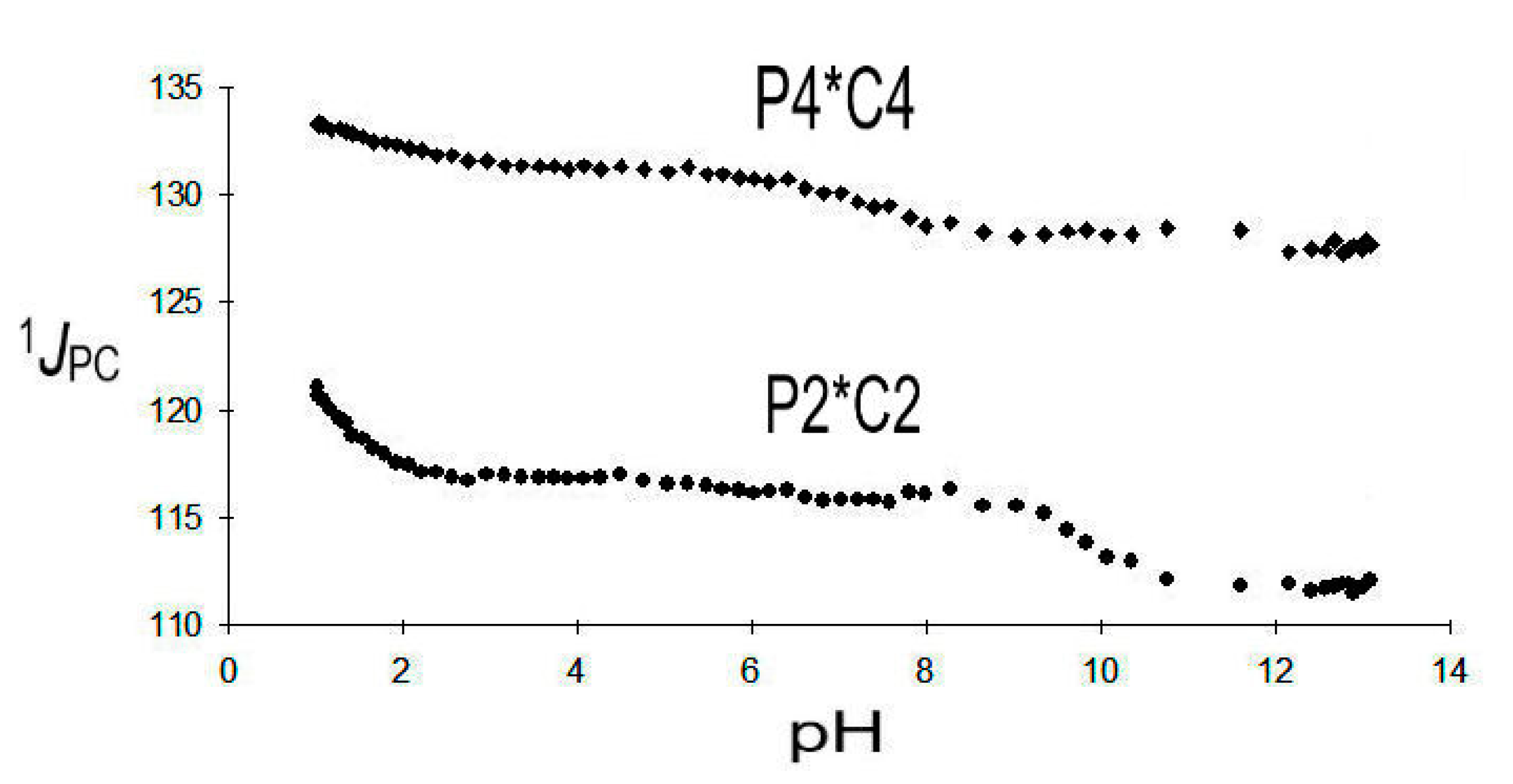
Some Comments on DPBDC 9
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Van Wazer, J.R.; Callis, C.F.; Shoolery, J.N.; Jones, R.C. Principles of Phosphorus Chemistry. II. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Measurements. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1956, 78, 5715–5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutchfield, M.M.; Callis, C.F.; Irani, R.R.; Roth, G.C. Phosphorus Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies of Ortho and Condensed Phosphate. Inorg. Chem. 1962, 1, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, R.; Roberts, J.D. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. 13C Spectra of Aliphatic Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylate Anions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1969, 91, 4504–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubel, P.-H.; Popov, A.I.J. Acid Properties of Some Phosphonocarboxylic Acids. Sol. Chem. 1979, 8, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, T.G.; Hall, R.J.; Harris, A.D.; Kimlin, H.A.; McMahon, I.J.N.M.R. Study of Acid-Base Equilibria of Aminoalkylphosphonic Acids, +NH3(CH2)nPO3H− (n = 1, 2, 3); Evidence for Cyclization in Solution. Austr. J. Chem. 1984, 37, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, T.G.; Hall, R.J.; McMahon, I.J. NMR Spectra of Iminobis(methylenebisphosphonic acid), HN(CH2PO3H2)2 and Related Ligands and of Their Complexes with Platinum(II). Inorg. Chem. 1985, 25, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K.; Araki, T.; Suzuki, T. Complex Formation of Amino Polyphosphonates. 1. Potentiometric and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies of Nitrilotris(methylenephosphonate) Complexes of the Alkaline Earth-Metal Ions. Inorg. Chem. 1987, 26, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K.; Araki, T.; Suzuki, T.; Doi, K. Complex Formation of Amino Polyphosphonates. 1. Stability and Structure of Nitrilotris(methylenephosphonate) Complexes of the Divalent Transitions-Metal Ions in Aqueous Solution. Inorg. Chem. 1989, 28, 2687–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K.; Kanda, T.; Naganuma, Y.; Suzuki, T. Formation and Protonation of Aminopolyphosphonate Complexes of Alkaline-earth and Divalent Transition-metal Ions in Aqueous Solution. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1993, 17, 2558–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K.; Myagawa, T.; Sakaguchi, T.; Doi, K. Structure and Thermodynamic Properties of Aminopolyphosphonate Complexes of the Alkaline-earth Metal Ions. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1993, 24, 3777–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K.; Ichikawa, T.; Uehara, K. Eight-membered chelate-ring complexes of cobalt(III)-polyamine complexes of aminopolyphosphonates in aqueous solution. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1996, 14, 3077–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matczak-Jon, E.; Kurzak, B.; Kamecka, A.; Sawka-Dobrowolska, W.; Kafarski, P.; Lejjczak, B. Zink(II) complexes of phosphonic acid analogues of glutamic acid. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1996, 3455–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matczak-Jon, E.; Kurzak, B.; Kamecka, A.; Sawka-Dobrowolska, W.; Kafarski, P. Interactions of zinc(II), magnesium(II) and calcium(II) with iminodimethylenediphosphonic acids in aqueous solutions. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1999, 20, 3627–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohovec, J.; Kývala, M.; Vojtišek, P.; Hermann, P.; Lukeš, I. Synthesis, Crystal Structures, and Solution Properties of N-Methylene(phenyl)phosphinic Acid Derivatives of Cyclen and Cyclam. J. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, K.; Popov, A.; Rönkkömäki, H.; Lajunen, L.H.J.; Hannu-Kuure, M.; Vendilo, A.; Tsirul’nikova, N. 31P, 23Na and 133Cs NMR equilibrium study of iminobis(methylenephosphonic acid) complexes with alkali metals. Inorg. Chimica Acta 2002, 344, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, A.; Rönkkömäki, H.; Popov, K.; Lajunen, L.H.J.; Vendilo, A. 31P NMR protonation equilibria study of iminobis(methylenphosphonic) acid and its derivatives at high pH. Inorg. Chimica Acta 2003, 353, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohms, G.; Grossmann, G. Über die pH-Abhängigkeit der 31P- und 13C-NMR-Spektren von Cyclohexan-, Cyclohexen- und Benzenphosphonsäuren. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1987, 544, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönkömäki, H.; Jokisaari, H.; Lajunen, L.H. 31P NMR and Potentiometric Studies on the Protonation of Isopropyl Esters of Chlodronic Acid. Acta Chem. Scand. 1993, 47, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, K.; Niskanen, E.; Rönkkömäki, H.; Lajunen, L.H.J. 31P NMR Study of organophosphonate protonation equilibrium at high pH. New J. Chem. 1999, 23, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szakács, Z.; Hägele, G. Accurate determination of low pK values by 1H NMR titration. Talanta 2004, 62, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szakács, Z.; Hägele, G.; Tyka, R. 1H/31P NMR pH indicator series to eliminate the glass electrode in NMR spectroscopic pKa determinations. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 522, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, K.; Rönkkömäki, H.; Lajunen, L.H. Guidelines for The NMR Measurements for Determination of High And Low pKa Values. Pure Appl. Chem. 2006, 78, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesinowski, J.P.; Sunberg, R.J.; Benedict, J.J. pH Control and Rapid Mixing in Spinning NMR Samples. J. Magn. Res. 1982, 47, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, J.; Henriksson, U.; Klason, T. A 205 TL NMR Titration Study of the Complex Formation between Tl(I) and Cl- in Aqueous Solution. Acta Chem. Scand. 1986, A40, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, W. Gravity-driven pH adjustment for site-specific protein pKa measurement by solution-state NMR. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2017, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägele, G.; Grzonka, M.; Kropp, H.-W.; Ollig, J.; Spiegl, H. Phosphonic and phosphinic acids: Monitoring protolytic and complex formation equilibria by titration dependent stopped-flow-NMR-techniques. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon 1993, 77, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägele, G.; Varbanov, S.; Ollig, J.; Kropp, H.-W. Aminomethylphosphine Oxides: Synthesis, Dissociation and Stability Constants, 31P{1H}-NMR-controlled Titration. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chemie 1994, 620, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägele, G. 31P NMR controlled titrations of Phosphorus-Containing Acids and Bases in Protolysis and Complex Formation. In Phosphorus-31 NMR Spectral Properties in Compound Characterization and Structural Analysis; Quin, L.D., Verkade, J.G., Eds.; VCH Publishers: New York, NJ, USA, 1994; Chapter 30; pp. 395–409. [Google Scholar]
- Hägele, G.; Ollig, J. NMR-controlled titrations of phosphorus containing acids and bases. Comput. Chem. 1995, 19, 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Ahrendt, C.; Hägele, G. The Photo-T-Concept: Hard- and software combination for the determination of macroscopic and microscopic dissociation constants. Comput. Chem. 1995, 19, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägele, G.; Szakács, Z.; Ollig, J.; Hermens, S.; Pfaff, C. NMR-Controlled Titrations: Characterizing Aminophosphonates and Related Structures. Heteroat. Chem. 2000, 11, 562–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägele, G.; Grzonka, M.; Peters, J.; Spiegl, H.; Kropp, H.W.; Ollig, J.; Hermens, S.; Augner, S.; Uhlemann, C.; Pfaff, C.; et al. NMR-Controlled Titrations—Principles and Progress: Monitoring Protonation and Complex Formation Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions. Available online: https://www.theresonance.com/nmr-controlled-titration-download-the-paper/ (accessed on 2 September 2019).
- Pfaff, C.G. Softwareentwicklung zur Auswertung und Visualisierung Kernresonanzspektroskopisch Kontrollierter Titrationen. Ph.D. Thesis, Heinrich-Heine-Universität, Düsseldorf, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, M.; Siegfried, L.; Kaden, T.A. pH-metric and NMR studies of complexation of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ with diazacrown ethers having dangling phosphonate groups. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2000, 24, 4664–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabenstein, D.L.; Sayer, T.L. Determination of Microscopic Acid Dissociation Constants by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1976, 48, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szakacs, Z.; Kraszni, M.; Noszal, B. Determination of microscopic acid-base parameters from NMR-pH titrations. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1428–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szakacs, Z. NMR-Titrationen und neue Auswertekonzepte zur Aufklärung der Mikroskopischen Dissoziation und der pH-abhängigen Konformation von Biorelevanten Phophinsäuren und Carnosinderivaten. Ph.D. Thesis, Heinrich-Heine-Universität, Düsseldorf, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kývala, M.; Lukeš, I. Chemometrics 95. In Book of Abstracts, Proceedings of the 4th International Chemometrics Conference of the Czech Chemical Society, Pardubice, Czech Republic, 3–7 July 1995; University of Pardubice: Pardubice, Czech Republic, 1995; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Augner, S.; Kehler, J.; Szakács, Z.; Breuer, E.; Hägele, G. Ring-chain tautomerism and protolytic equilibria of 3-hydroxy-3-phosphonoisobenzo-furanone studied by 1H-, 13C-, and 31P-NMR-controlled titrations. New J. Chem. 2008, 32, 1608–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augner, S. Neue Entwicklungen zur Durchführung automatisierter NMR-Kontrollierter Titrationen von Phosphon- und Phosphinsäuren. Ph.D. Thesis, Heinrich-Heine-Universität, Düsseldorf, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kropp, H.-W.; Hägele, G. Unpublished results from my student Kropp. Interested readers may contact G. Hägele. Unpublished work. 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lindner, A. 1-Phosphonopropan-1,2,3-tricarbonsäure—NMR- und Konformationsanalytische Untersuchungen. Ph.D. Thesis, Heinrich-Heine-Universität, Düsseldorf, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hägele, G. NMR-controlled titrations characterizing organophosphorus compounds. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2019, 194, 361–363. [Google Scholar]
- Ollig, J. Untersuchungen zur Titrationsabhängigen Kernresonanzspektroskopie. Ph.D. Thesis, Heinrich-Heine-Universität, Düsseldorf, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Robitaille, P.-M.L.; Robitaille, P.A.; Brown, G.G., Jr.; Brown, G.G. An Analysis of the pH-Dependent Chemical-Shift Behavior of Phosphorus-Containing Metabolites. J. Magn. Res. 1991, 91, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, K.; Rönkkömäki, H.; Lajunen, L.J.J. Critical evaluation of stability constants of phosphonic acids. Pure Appl. Chem. 2001, 73, 1641–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.; Alex, A.; Beck, B.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Gedeck, P.; Horn, A.H.C.; Hutter, M.; Martin, B.; Rauhut, G.; Sauer, W.; et al. VAMP 4.4; Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg: Erlangen, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak, M.; Nowogrocky, G. Acidites et complexes des acides (alkyl- et aminoalkyl-) phosphoniques—I: Determination potentiometrique des constantes d’acidite par affinement multiparametrique: Prise en compte de l’impurete carbonate. Talanta 1979, 26, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, M.S.; Abbott, E.H. Metal complexes of biologically occurring aminophosphonic acids. J. Coord. Chem. 1978, 8, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Balla, J.; Nagy, G.; Kozzlowski, H.; Kowalik, J. Complexes of aminophosphonates. I. Transition metal complexes of aminophosphonic acid analogues of α-alanine, β-alanine, phenylalanine and tyrosine. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1987, 138, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropp, H.-W.; Hägele, G. Analytische und NMR-spektroskopische Untersuchungen an Organophosphorsäuren. Unpublished work.
- Burton, D.J.; Sprague, L.G.; Pietrzyk, D.J.; Edelmuth, S.H. A Facile Synthesis of Difluorophosphonoacetic Acid. J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 3437–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, A. Computereinsatz in der Analytischen Chemie zur Untersuchung von Protolyse- und Komplexbildungs-Gleichgewichten am Beispiel der Phosphonocarbonsäuren. Ph.D. Thesis, Heinrich-Heine-Universität, Düsseldorf, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Rabenstein, D.L.; Sayer, T.L. Carbon-13 Chemical Shift parameters for Amines, Carboxylic Acids, and Amino Acids. J. Magn. Res. 1978, 24, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Examples | NMR | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Phosphonic acids | ||
| CH3P(O)(OH)2 | 31P{1H} | |
| LiOOC-CH2-P(O)(OLi)2 | 31P{1H} | 1) |
| (HO)2(O)P-CH2-CH2-P(O)(OH)2 | 13C{1H} | |
| CH3-C(OH)[P(O)(OH)2]2, HEDP, etidronic acid | 31P{1H} | |
| NH2-CH2-CH2-C(OH)(P(O)(OH)2)2, pamidronic acid | 31P{1H} | |
| HOOC-CH2-CH(COOH)-CH(COOH)-P(O)(OH)2, PPTC | 31P{1H} | |
| Phosphinic acids | ||
| (CH3)2P(O)OH | 31P{1H} | |
| HOOC-CH2-CH2-P(CH3)(O)OH | 13C{1H}, 1H | 2) |
| HO(O)(CH3)P-CH2-CH2-P(CH3)(O)OH | 13C{1H} | |
| HO(O)(CH3)P-CH2-CH2-C(H)(NH2)COOH | 1H | 2, 3) |
| Carboxylic acids | ||
| CH3COOH | 13C{1H} | |
| CH(CH3)2-CH2-CH(NH2)-C(O)-NH-CH(CH3)-COOH, peptide Leu-Ala | 13C{1H} | |
| CH2=CF-CH2-C(CH3)(NH2)-COOH | 19F |
| 1 in H2O | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | 13C{1H} | 31P{1H} | 31P | 31P{1H} | ||
| Exp. | a) | b) | c) | d) | ||
| Species | δC | 1JPC | δP | δP | 2JPH | δP |
| [ppm] | [Hz] | [ppm] | [ppm] | [Hz] | [ppm] | |
| H2L | 14.27 | 135.92 | 33.03 | 33.03 | −17.65 | 31.76 |
| HL− | 15.53 | 133.82 | 24.79 | 24.79 | −16.52 | 24.94 |
| L2− | 16.61 | 129.95 | 21.08 | 21.08 | −15.52 | 20.94 |
| Gradients | δC | 1JPC | δP | δP | 2JPH | δP |
| Δ1 | 1.26 | −2.10 | −8.24 | −8.24 | 1.13 | |
| Δ2 | 1.08 | −3.87 | −3.71 | −3.71 | 1.00 | |
| pKi | ||||||
| pK1 | 2.27 | 2.06 | 2.00 | 2.33 | ||
| pK2 | 7.85 | 7.66 | 7.68 | 7.78 | ||
| Phenylphosphonic Acid 2 | ||
|---|---|---|
| vs. TMAOH | vs. NaOH | |
| a) | b) | |
| δP(H2L) | 18.39 | 17.77 |
| δP(HL−) | 13.77 | 13.75 |
| δP(L2−) | 11.69 | 11.72 |
| Δ1 | −4.62 | −4.02 |
| Δ2 | −2.08 | −2.03 |
| pK1 | 1.74 | 1.86 |
| pK2 | 7.28 | 7.16 |
| δC and nJPC for Species | Gradients | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | H2L | HL− | L2− | Δ1 | Δ2 |
| δC C1 | 133.66 | 138.15 | 143.83 | +4.48 | +5.69 |
| δC C2/6 | 133.68 | 133.45 | 133.43 | −0.24 | −0.02 |
| δC C3/5 | 131.99 | 131.59 | 130.95 | −0.40 | −0.64 |
| δC C4 | 135.66 | 134.03 | 131.98 | −1.58 | −2.06 |
| 1JPC | 183.48 | 177.02 | 167.32 | −6.46 | −9.70 |
| 2JPC | 10.51 | 9.72 | 8.79 | −0.79 | −0.93 |
| 3JPC | 14.84 | 13.90 | 12.65 | −0.94 | −1.25 |
| 4JPC | 3.08 | 2.91 | 2.74 | −0.17 | −0.17 |
| Dissociation Species | ||
|---|---|---|
| Macroscopic | Microscopic | |
| H3L+ | +NH3-R-PO3H2 | |
| H2L | +NH3-R-PO3H− | NH2-R-PO3H2 |
| HL− | +NH3-R-PO32− | NH2-R-PO3H− |
| L2− | NH2-R-PO32− | |
| 3 | 4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13C{1H} a | 31P{1H} b | Pot. c | 13C{1H} d | 31P{1H} e | 31P{1H} f | Pot. g | |
| NaOH | NaOH | NaOH | NaOH | TMAOH | NaOH | TMAOH | |
| pK1 | 0.70 | 0.31 | 0.3 | 1.02 | 1.22 | 1.26 | 1.14 |
| pK2 | 5.72 | 5.63 | 5.58 | 6.38 | 6.23 | 6.24 | 6.34 |
| pK3 | 10.64 | 10.21 | 10.28 | 11.50 | 11.06 | 11.08 | 11.06 |
| 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31P{1H} a | 31P{1H} b | 31P{1H} a | 31P{1H} c | |
| Species | δP | δP | δP | δP |
| H3L+ | 15 * | 22.9 | 23.4 | 13 * |
| H2L | 14.92 | 19.29 | 19.36 | 12.16 |
| HL− | 13.08 | 16.80 | 16.81 | 15.29 |
| L2− | 22.25 | 19.39 | 19.72 | 12.70 |
| Gradients | ||||
| Δ1 | −0.08 | −3.61 | −4.04 | −0.84 |
| Δ2 | −1.84 | −2.49 | −2.55 | +3.13 |
| Δ3 | +9.17 | +2.59 | +3.91 | −2.59 |
| 3 in H2O | 4 in H2O | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | δC(C1) | 1JPC | δC(C2) | δC(C1) | 1JPC | δC(C2) |
| H3L+ | 46.80 | 151.5 | 16.0 | 27.50 | 137.4 | 37.09 |
| H2L | 47.70 | 143.8 | 16.43 | 28.73 | 131.4 | 38.22 |
| HL− | 49.07 | 134.5 | 17.23 | 29.47 | 124.8 | 39.28 |
| L2− | 48.15 | 138.0 | 19.79 | 35.45 | 126.5 | 39.76 |
| Gradients | ||||||
| Δ1 | +0.9 | −8.7 | +0.43 | +1.23 | −6.0 | +1.13 |
| Δ2 | +1.37 | +9.3 | +0.80 | +0.74 | −6.6 | +1.04 |
| Δ3 | −0.92 | +3.5 | +2.55 | +5.98 | +1.3 | +0.47 |
| 5 | 2 | 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pK1 | 0.44 | 1.88 | 4.68 |
| pK2 | 3.95 | 7.15 | |
| pK3 | 7.56 |
| HOOC-(CH2)n-PO3H2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7a | 7a [4] | 7b | 7c | 7c [4] | 7d | |
| n = 0 a | n = 0 | n = 1 b | n = 2 b | n = 2 | n = 3 b | |
| pK1 | 0.78 | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 1.22 ± 0.166 | 2.58 ± 0.013 | 2.26 ± 0.04 | 2.276 ± 0.006 |
| pK2 | 3.60 | 3.59 ± 0.02 | 4.942 ± 0.004 | 4.633 ± 0.004 | 4.63 ± 0.02 | 4.776 ± 0.004 |
| pK3 | 7.57 | 7.56 ± 0.02 | 8.099 ± 0.003 | 7.738 ± 0.003 | 7.75 ± 0.02 | 7.969 ± 0.003 |
| (a) | ||||||||||
| 7 | n | Species | δC(C1) | δC(C2) | δC(C3) | δC(C4) | 1JPC | 2JPC | 3JPC | 4JPC |
| a | 0 | H3L | 176.8 | 246.6 | ||||||
| H2L− | 178.7 | 236.7 | ||||||||
| HL2− | 181.8 | 231.8 | ||||||||
| L3− | 187.3 | 220.0 | ||||||||
| b | 1 | H3L | 172.91 | 37.68 | 128.6 | n. r. | ||||
| H2L− | 175.44 | 39.30 | 117.8 | n. r. | ||||||
| HL2− | 178.85 | 41.64 | 119.2 | n. r. | ||||||
| L3− | 181.74 | 43.50 | 112.6 | n. r. | ||||||
| c | 2 | H3L | 179.25 | 30.09 | 24.51 | 138.5 | 3.6 | 17.3 | ||
| H2L− | 180.68 | 31.40 | 25.91 | 135.1 | 3.2 | 17.8 | ||||
| HL2− | 185.01 | 34.27 | 27.50 | 133.0 | 4.1 | 18.7 | ||||
| L3− | 186.71 | 35.61 | 28.99 | 130.3 | 3.6 | 19.8 | ||||
| d | 3 | H3L | 180.38 | 36.67 | 20.44 | 28.19 | 135.2 | 4.0 | 17.4 | n. r. |
| H2L− | 181.12 | 37.46 | 21.58 | 29.74 | 133.5 | 3.8 | 17.2 | n. r. | ||
| HL2− | 185.86 | 41.45 | 23.13 | 30.46 | 132.5 | 3.9 | 17.7 | n. r. | ||
| L3− | 186.41 | 42.01 | 24.08 | 31.92 | 130.1 | 3.4 | 17.9 | n. r. | ||
| (b) | ||||||||||
| 7 | n | Gradients | δC(C1) | δC(C2) | δC(C3) | δC(C4) | 1JPC | 2JPC | 3JPC | |
| a | 0 | Δ1 | +1.9 | −9.9 | ||||||
| Δ2 | +3.1 | −4.9 | ||||||||
| Δ3 | +5.5 | −11.8 | ||||||||
| b | 1 | Δ1 | +2.53 | +1.62 | −10.8 | |||||
| Δ2 | +3.41 | +2.34 | +1.4 | |||||||
| Δ3 | +2.89 | +1.86 | −6.6 | |||||||
| c | 2 | Δ1 | +1.43 | +1.31 | +1.40 | −3.4 | −0.3 | 0.5 | ||
| Δ2 | +4.33 | +2.87 | +1.59 | −2.1 | 0.9 | 0.9 | ||||
| Δ3 | +1.70 | +1.34 | +1.49 | −2.7 | −0.5 | 1.1 | ||||
| d | 3 | Δ1 | +0.74 | +0.79 | +1.14 | 1.56 | −1.7 | −0.2 | −0.2 | |
| Δ2 | +4.74 | +3.99 | +1.55 | 0.72 | −1.0 | 0.1 | 0.5 | |||
| Δ3 | +0.55 | +0.56 | +0.95 | 1.46 | −2.4 | −0.5 | 0.2 | |||
| Shifts | δP | Error |
|---|---|---|
| H3L | 29.93 | ±0.25 |
| H2L− | 24.56 | ±0.02 |
| HL2− | 25.88 | ±0.01 |
| L3− | 22.06 | ±0.01 |
| Gradients | ||
| Δ1 | −5.37 | |
| Δ2 | +1.32 | |
| Δ3 | −3.82 |
| HOOC-CH2-nFn-PO3H2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 8c n = 1 | 8d n = 2 | ||
| [44] | [44] | [52] | |
| pK1 | 1.05 | 0.52 | 1.30 |
| pK2 | 3.43 | 2.22 | 1.95 |
| pK3 | 7.08 | 6.36 | 6.16 |
| HOOC-CH2-nFn-PO3H2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8c | 8d | 8c | 8d | |
| n = 1 | n = 2 | n = 1 | n = 2 | |
| 19F | 19F | |||
| Species | δF | δF | 2JPF | 2JPF |
| H3L | −38.27 | 44.24 | 67.8 | 76.5 |
| H2L− | −38.72 | 50.24 | 65.5 | 88.6 |
| HL2− | −29.31 | 53.05 | 70.3 | 92.8 |
| L3− | −27.15 | 55.24 | 63.4 | 82.0 |
| Gradients | ||||
| Δ1 | −0.45 | +6.00 | −2.3 | +12.1 |
| Δ2 | −9.41 | +2.81 | +4.8 | +4.2 |
| Δ3 | −8.16 | +2.19 | −6.9 | −10.8 |
| 13C{1H} NMR [44] | Potentiometric [44] | Potentiometric [53] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pK1 | 1.07 | 0.6 | 1.806 ± 0.066 |
| pK2 | 2.73 | 2.42 | 2.250 ± 0.021 |
| pK3 | 4.82 | 4.32 | 4.078 ± 0.005 |
| pK4 | 7.05 | 6.46 | 6.562 ± 0.004 |
| pK5 | 8.95 | 8.18 | 8.664 ± 0.006 |
| pK6 | 11.62 | 10.75 | 12.839 ± 0.007 |
| CTitrand | 0.262 (DPBDC) * | 0.0050 (DPBDC) * | 0.01119 (DPBDC) * |
| CTitrator | 3.986 (NaOH) * | 0.0975 (NaOH) * | 0.09863 (TMAOH) * |
| CIon buffer | 0 | 0.1 (NaCl) * | 0.09863 (TMANO3) * |
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C1* | C2* | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | δC | δC | 1JPC | 3JPC | δC | δC | 1JPC | 3JPC | δC | 3JPC | δC |
| H6L | 38.29 | 52.19 | 124.2 | 18.4 | 27.26 | 25.11 | 134.0 | 4.7 | 177.23 | 17.5 | 177.53 |
| H5L− | 38.70 | 52.42 | 116.8 | 18.2 | 27.51 | 25.56 | 132.4 | 5.1 | 177.82 | 15.9 | 178.66 |
| H4L2− | 39.38 | 52.98 | 116.9 | 17.3 | 29.09 | 26.34 | 131.3 | 6.3 | 178.85 | 12.5 | 179.18 |
| H3L3− | 41.78 | 54.06 | 116.7 | 16.8 | 30.95 | 26.15 | 131.3 | 9.0 | 181.69 | 6.4 | 180.70 |
| H2L4− | 43.28 | 54.66 | 115.9 | 16.6 | 29.98 | 26.54 | 130.3 | 9.9 | 183.46 | 4.3 | 181.53 |
| HL5− | 43.26 | 55.04 | 115.8 | 15.9 | 30.99 | 27.51 | 128.3 | 9.4 | 184.08 | 5.3 | 182.53 |
| L6− | 42.70 | 55.01 | 111.7 | 16.3 | 29.87 | 28.65 | 127.7 | - | 184.82 | 18.9 | 186.15 |
| Gradients | |||||||||||
| Δ1 | +0.41 | +0.23 | −7.4 | −0.2 | +0.25 | +0.45 | −1.6 | +0.4 | +0.59 | −1.6 | +1.13 |
| Δ2 | +0.68 | +0.56 | +0.1 | −0.9 | +1.58 | +0.78 | −1.1 | +1.2 | +1.03 | −3.4 | +0.52 |
| Δ3 | +1.40 | +1.08 | −0.2 | −0.5 | +1.86 | −0.19 | 0.0 | +2.7 | +2.84 | −6.1 | +1.52 |
| Δ4 | +1.50 | +0.60 | −0.8 | −0.2 | −0.97 | +0.39 | −1.0 | +0.9 | +1.77 | −2.1 | +0.83 |
| Δ5 | −0.02 | +0.38 | −0.1 | −0.7 | +1.01 | +0.97 | −2.0 | −0.5 | +0.62 | +1.0 | +1.00 |
| Δ6 | −0.56 | −0.03 | −4.1 | +0.4 | −1.12 | +1.14 | −0.6 | - | +0.74 | +13.6 | +3.62 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hägele, G. Protolysis and Complex Formation of Organophosphorus Compounds—Characterization by NMR-Controlled Titrations. Molecules 2019, 24, 3238. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183238
Hägele G. Protolysis and Complex Formation of Organophosphorus Compounds—Characterization by NMR-Controlled Titrations. Molecules. 2019; 24(18):3238. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183238
Chicago/Turabian StyleHägele, Gerhard. 2019. "Protolysis and Complex Formation of Organophosphorus Compounds—Characterization by NMR-Controlled Titrations" Molecules 24, no. 18: 3238. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183238
APA StyleHägele, G. (2019). Protolysis and Complex Formation of Organophosphorus Compounds—Characterization by NMR-Controlled Titrations. Molecules, 24(18), 3238. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183238