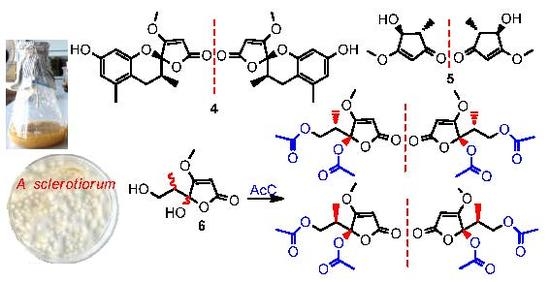
New Butenolides and Cyclopentenones from Saline Soil-Derived Fungus Aspergillus Sclerotiorum
Abstract
1. Introduction
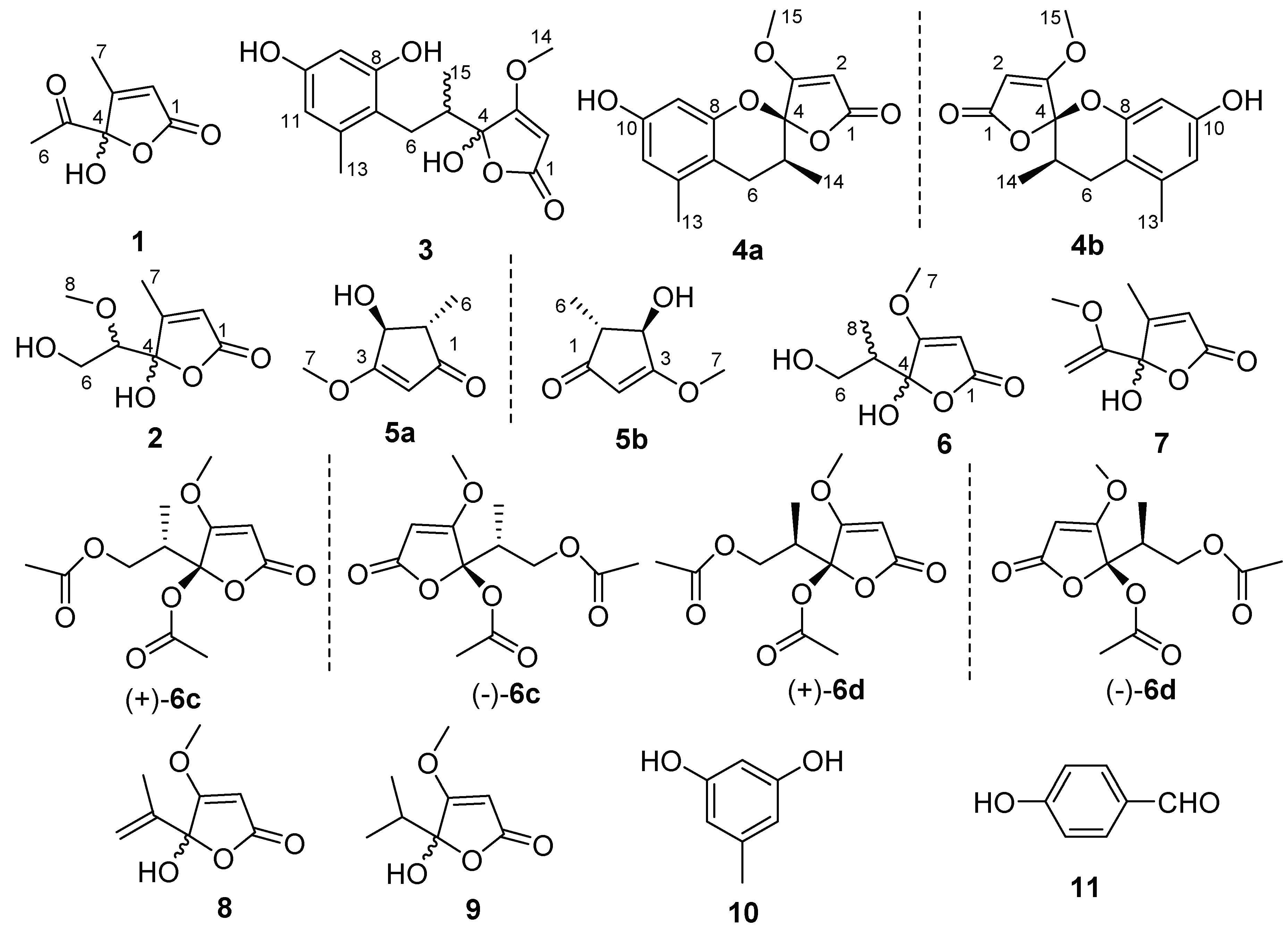
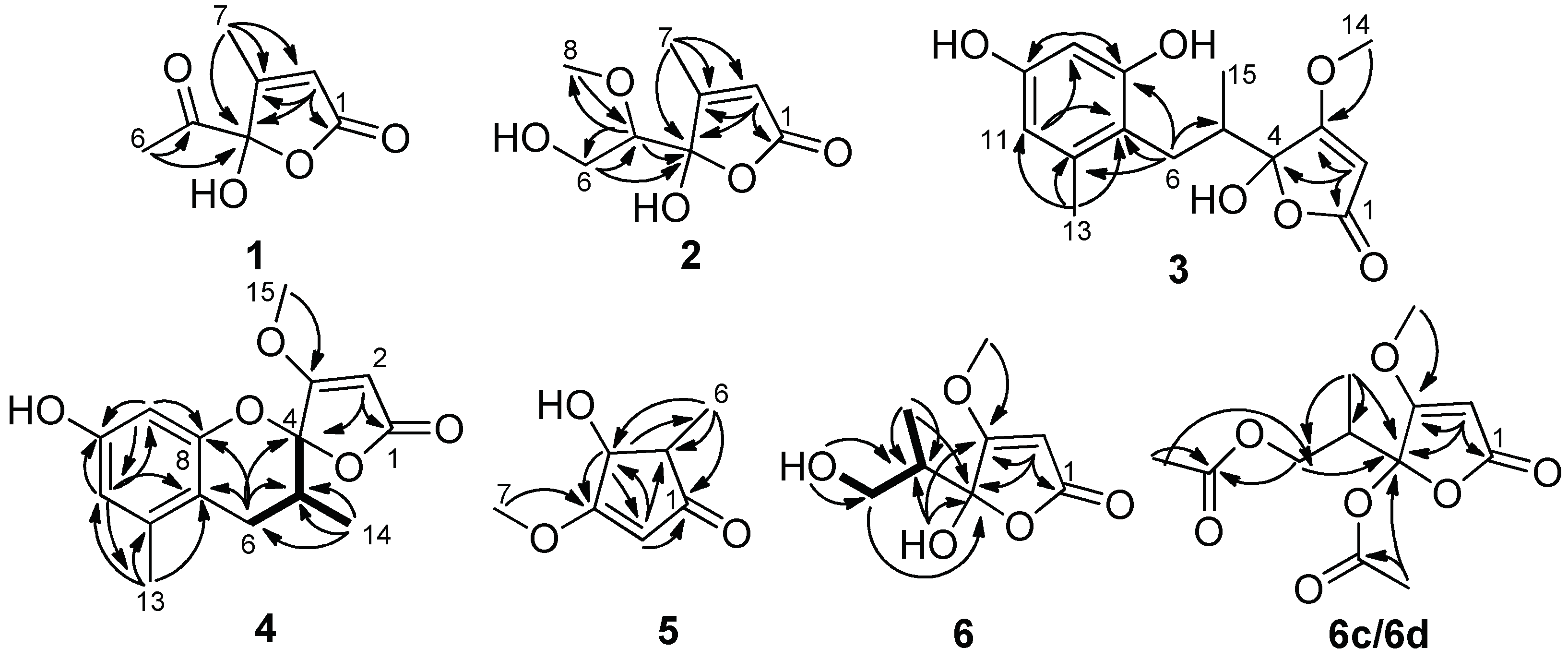
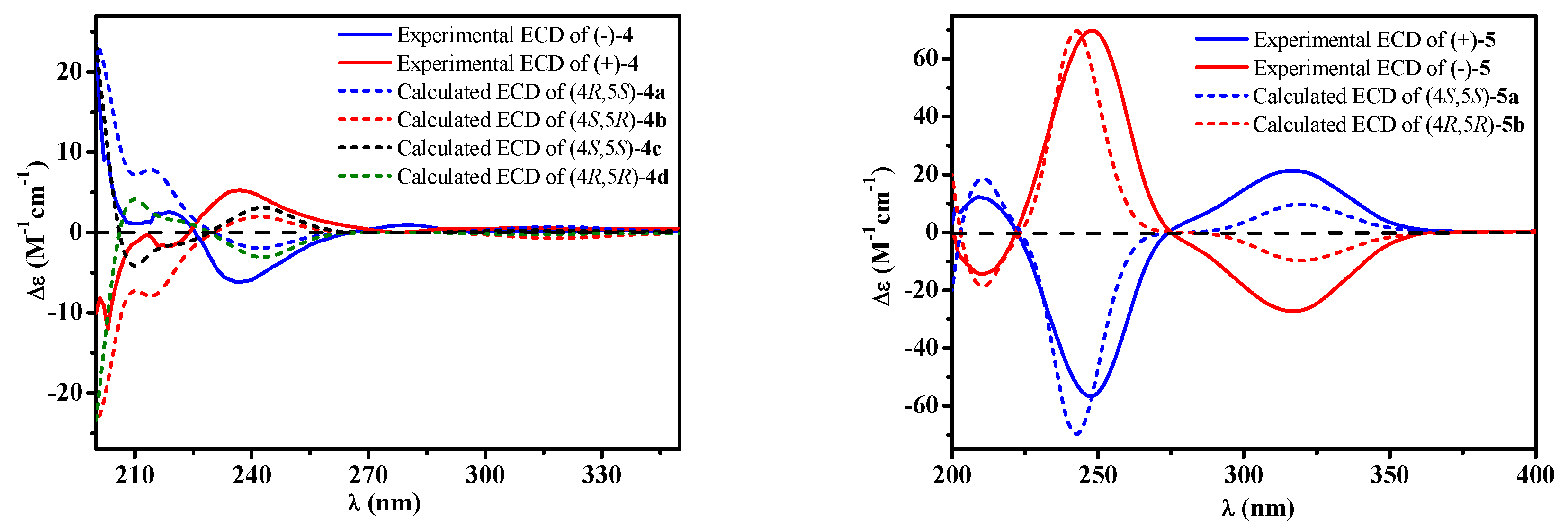
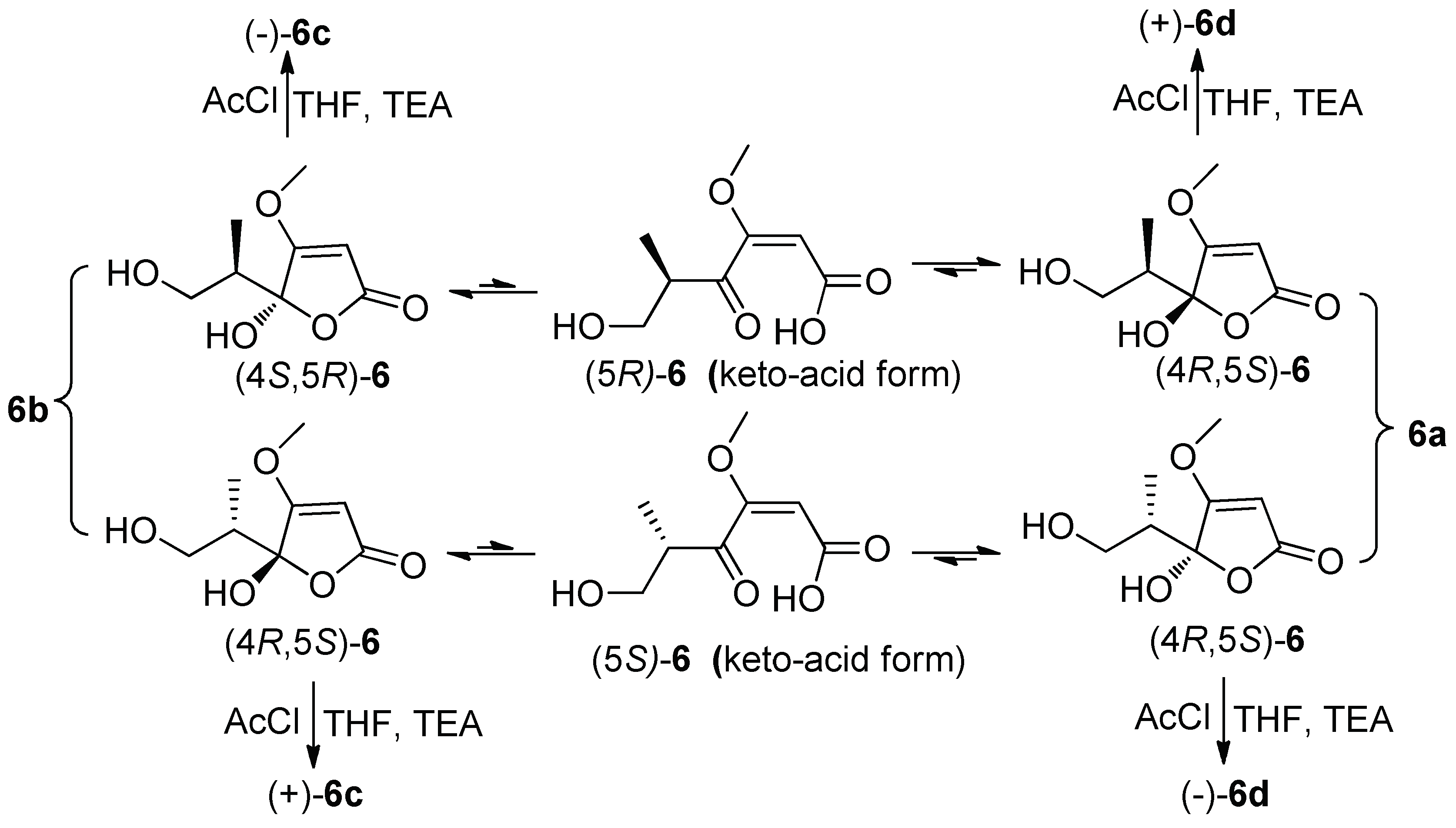
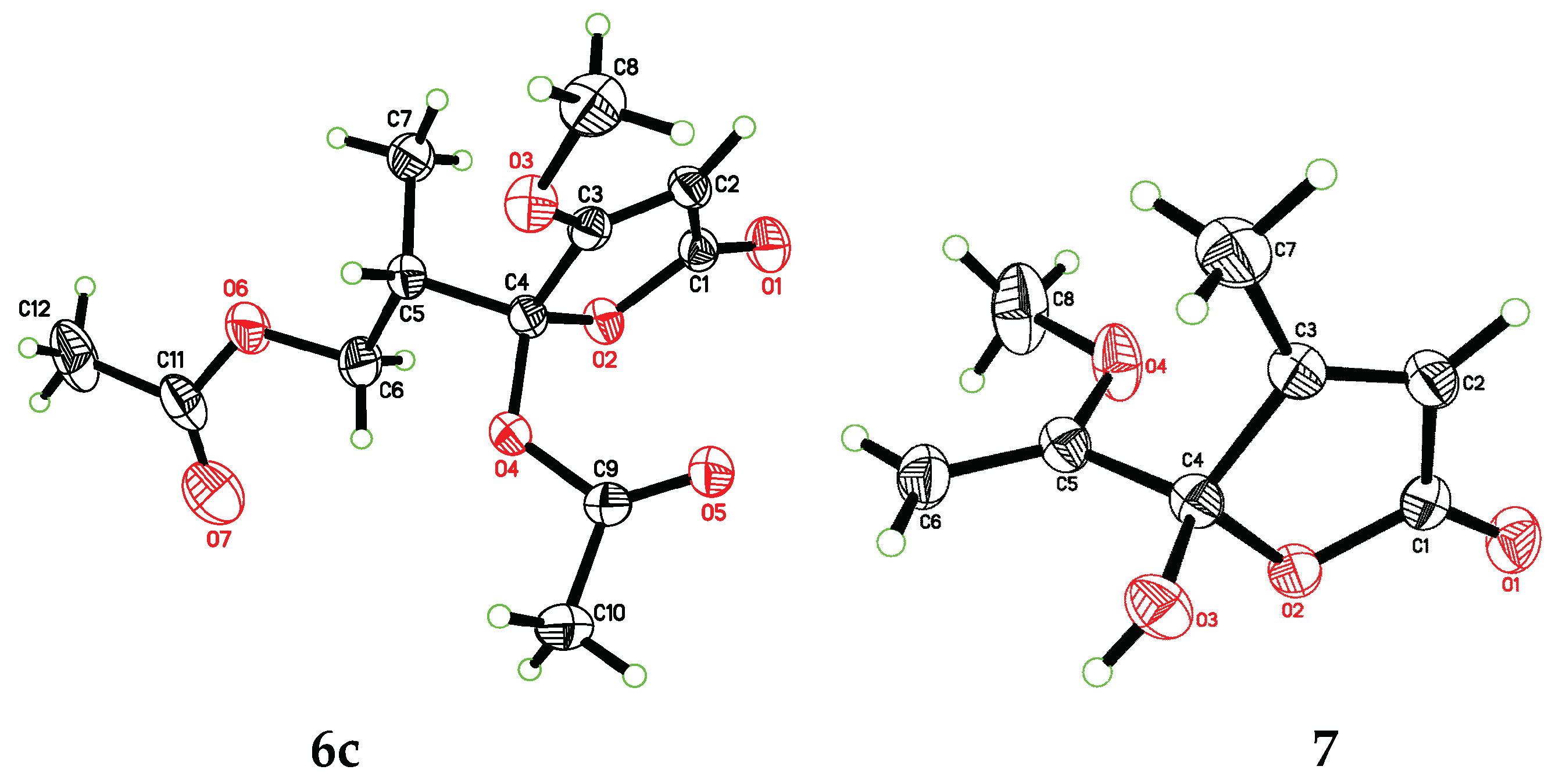
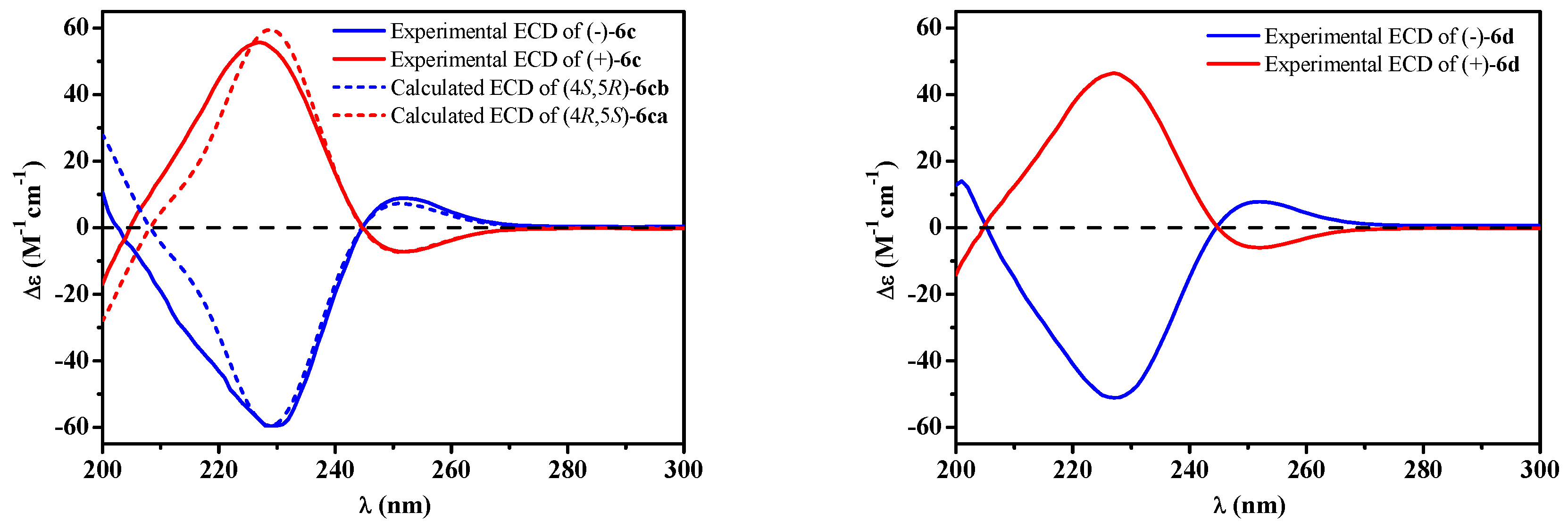
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Fungal Material
4.3. Fermentation and Extraction
4.4. Purification
4.5. Preparation and Isolation of (±)-6c and (±)-6d
4.6. Biological Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, J.W.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.J.; Gu, Q.Q.; Li, D.H. The cytotoxics secondary metabolites from South China Sea derived fungus Aspergillus sclertoiorum XJW-56. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2014, 33, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Motohashi, K.; Inaba, S.; Takagi, M.; Shin-ya, K. JBIR-15, a new aspochracin derivative, isolated from a sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum Huber Sp080903f04. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 1898–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Phainuphong, P.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Saithong, S.; Phongpaichit, S.; Bowornwiriyapan, K.; Muanprasat, C.; Srimaroeng, C.; Duangjai, A.; Sakayaroj, J. Lovastatin analogues from the soil-derived fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PSU-RSPG178. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phainuphong, P.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Tadpetch, K.; Sukpondma, Y.; Saithong, S.; Phongpaichit, S.; Preedanon, S.; Sakayaroj, J. γ-Butenolide and furanone derivatives from the soil-derived fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PSU-RSPG178. Phytochemistry 2017, 137, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Zhu, H.; Hong, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Zhu, W. Novel cyclic hexapeptides from marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5262–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hong, K.; Liu, P.; Zhu, W. Cyclic tripeptides from the halotolerant fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, A.C.; Joshi, B.K.; Gloer, J.B.; Wicklow, D.T.; Dowd, P.F. New cyclic peptide and bisindolyl benzenoid metabolites from the sclerotia of Aspergillus sclerotiorum. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, A.C.; Gloer, J.B.; Wicklow, D.T.; Dowdw, P.F. Sclerotiamide: a new member of the paraherquamide class with potent antiinsectan activity from the sclerotia of Aspergillus sclerotiorum. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micetich, R.G.; Macdona, J.C. Metabolites of Aspergillus sclerotiorum Huber. J. Chem. Soc. 1964, 1507–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, J.; Kevei, E.; Rinyu, E.; Téren, J.; Kozakiewicz, Z. Ochratoxin production by Aspergillus species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 4461–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Nong, X.-H.; Qi, S.-H. New furanone derivatives and alkaloids from the co-culture of marine-derived fungi Aspergillus sclerotiorum and Penicillium citrinum. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1600327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q. Spatial and environmental effects on plant communities in the Yellow River Delta, Eastern China. J. For. Res. 2009, 20, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Zong, S.; Lu, Z. Effect of organic materials on the chemical properties of saline soil in the Yellow River Delta of China. Front. Earth Sci. 2015, 9, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, J. Saline-alkali land in the Yellow River Delta: amelioration zonation based on GIS. J. Geogr. Sci. 2001, 11, 313–320. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, P.; Liu, P.; Qu, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, W. α-Pyrones and diketopiperazine derivatives from the marine-derived actinomycete Nocardiopsis dassonvillei HR10-5. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2219–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Z.; Ma, L.Y.; Liu, D.S.; Huang, Y.L.; Wang, C.H.; Shi, S.S.; Pan, X.H.; Song, X.D.; Zhu, R.X. Peniciketals A−C, new spiroketals from saline soil derived Penicillium raistrichii. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.H.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhong, M.J.; Ma, L.Y.; Liu, D.S.; Liu, W.Z.; Ren, H. Potential antiviral xanthones from a coastal saline soil fungus Aspergillus iizukae. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wijeratne, E.M.; Bashyal, B.P.; Zhan, J.; Seliga, C.J.; Liu, M.X.; Pierson, E.E.; Pierson III, L.S.; VanEtten, H.D.; Gunatilaka, A.A. Cytotoxic and other metabolites of Aspergillus inhabiting the rhizosphere of Sonoran desert plants. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1985–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkinshaw, J.H.; Oxford, A.E.; Raistrick, H. Studies in the biochemistry of micro-organisms. Biochem. J. 1936, 30, 394–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Nakahara, S.; Fujioka, S. Aspyrone, a nematocidal compound isolated from the fungus, Aspergillus melleus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996, 60, 1375–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.-H.; Lu, X.; Pei, Y.-H.; Wu, X.; Pan, B.; Hua, H.-M.; et al. A new compound along with seven known compounds from an endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp HS-05. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2013, 7, 320–324. [Google Scholar]
- Matoba, K.; Yamazaki, T. Reduction of some vinylogous esters with lithium aluminum hydride. IV Yakugaku Zasshi. 1972, 92, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bao, J.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Yao, Q.-F.; Xu, X.-Y.; Nong, X.-H.; Qi, S.H. Secondary metabolites from the co-culture of gorgonian-associated fungi Aspergillus sclertoiorum and Penicillium citrinum. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2014, 26, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, D.L.; Wang, L.S.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yan, C.R. Chemical constituents of Acroscyphus sphaerophoroides. Plant Sci. J. 2011, 29, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.W.; Dai, S.J.; Liu, W.; Li, G.H. Chemical constituents from the vines of Pueraria lobata. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2010, 8, 196–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, T.G.C.; Rodrigues, F.A.R.; Jimenez, P.C.; Angelim, A.L.; Melo, V.M.M.; Filho, E.R.; Oliveira, M.C.F.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V. Cytotoxic activity of fungal strains isolated from the ascidian Eudistoma vannamei. Chem. Biodivers. 2012, 9, 2203–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vansteelandt, M.; Blanchet, E.; Egorov, M.; Petit, F.; Toupet, L.; Bondon, A.; Monteau, F.; Le Bizec, B.; Thomas, O.P.; Pouchus, Y.F.; et al. Ligerin, an antiproliferative chlorinated sesquiterpenoid from a marine-derived Penicillium strain. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.-J.; Xu, L.-L.; Li, Y.-Y.; Han, T.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Ming, Q.-L.; Rahman, K.; Qin, L.P. Cytotoxic metabolites from the cultures of endophytic fungi from Panax ginseng. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 7617–7625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.-M.; Meng, L.-H.; Wang, B.-G. Polyketides from the marine mangrove-derived fungus Aspergillus ochraceus MA-15 and their activity against aquatic pathogenic bacteria. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 12, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Luis, S.; González, M.C.; Ulloa, M.; Mata, R. Phytotoxins from the fungus Malbranchea aurantiaca. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Kimura, T.; Saito, F.; Ando, K. Antitumor and antiviral properties of penicillic acid. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1971, 35, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.W.; Kim, S.W. New antifungal activity of penicillic acid against Phytophthora species. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Liu, W.; Huang, Y.; Xian, G. Two acid sorbicillin analogues from saline lands-derived fungus Trichoderma sp. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.-X.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.-M.; Jin, X.-J.; Yu, B.; Fang, J.-G.; Wu, Q.-X. Isolation, identification, and activity evaluation of chemical constituents from the soil fungus Fusarium avenaceum SF-1502 and endophytic fungus Fusarium proliferatum AF-04. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; She, Z. Anti-inflammatory activity from the mangrove endophytic fungus Ascomycota sp. CYSK-4. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of all the compounds are available from the authors. |
| Position | 1 a | 2 b | 5 b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH | δC | δH | δC | δH | |
| 1 | 170.2, C | 172.9, C | 203.8, C | |||
| 2 | 118.9, C | 6.18, s | 119.5, CH | 5.86, br s | 127.6, CH | 6.37, d (2.6) |
| 3 | 165.7, C | 168.7, C | 158.2, C | |||
| 4 | 105.7, C | 110.1, C | 74.2, CH | 4.37, dd (2.6, 1.6) | ||
| 5 | 201.5, C | 84.2, CH | 3.56, dd (7.0, 3.2) | 51.1, CH | 2.20, dq (7.5, 1.6) | |
| 6 | 24.7, CH | 2.25, s | 62.4, CH2 | 3.90, m; 3.66, dd (11.7, 7.0) | 13.3, CH3 | 1.20, d (7.5) |
| 7 | 12.7, CH | 1.96, s | 13.4, CH3 | 2.09, br s | 57.7, CH3 | 3.75, s |
| 8 | 60.6, CH3 | 3.50, s | ||||
| OH | 8.50, s | |||||
| Position | 3 | 4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH, mult (J in Hz) | δC | δH, mult (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 170.7, C | 169.9, C | ||
| 2 | 90.2, CH | 5.20, s | 91.2, CH | 5.44, s |
| 3 | 180.9, C | 178.4, C | ||
| 4 | 106.3, C | 104.2, C | ||
| 5 | 39.7, CH | 2.35, m | 31.4, CH | 2.35 c |
| 6 | 26.4, CH2 | 2.58, dd (13.6, 11.2); 2.08 a | 27.1, CH2 | 2.77, m; 2.35 c |
| 7 | 117.1, C | 112.2, C | ||
| 8 | 157.3, C | 153.2, C | ||
| 9 | 101.2, CH | 6.38, d (1.6) | 101.8, CH | 6.18, d (2.2) |
| 10 | 156.8, C | 157.3, C | ||
| 11 | 109.7, CH | 6.20, d (1.6) | 111.9, CH | 6.38, d (2.2) |
| 12 | 139.4, C | 138.6, C | ||
| 13 | 20.1, CH3 | 2.19, s | 19.1, CH3 | 2.16, s |
| 14 | 60.0, CH3 | 3.94, s | 60.7, CH3 | 4.07, s |
| 15 | 13.3, CH3 | 0.86, br s b | 15.1, CH3 | 0.99, d (5.6) |
| Position | 6a | 6b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH, mult (J in Hz) | δC | δH, mult (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 169.9, C | 170.0, C | ||
| 2 | 89.3, CH | 5.28, s | 89.4, CH | 5.23, s |
| 3 | 179.9, C | 179.5, C | ||
| 4 | 103.7, C | 104.3, C | ||
| 5 | 41.6, CH | 2.02, m | 40.5, CH | 1.99, m |
| 6 | 61.4, CH2 | 3.39, dt (10.5, 4.6); 3.09, m | 61.1, CH2 | 3.76, dt (10.5, 5.0); 3.19, m |
| 7 | 59.6, CH3 | 3.83, s | 59.7, CH3 | 3.86, s |
| 8 | 11.0, CH3 | 0.93, d (6.9) | 11.3, CH3 | 0.78, d (6.9) |
| 4-OH | 7.44, s | 7.52, s | ||
| 6-OH | 4.51, t (5.3) | 4.68, t (5.3) | ||
| Position | (±)-6c | (±)-6d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH, mult (J in Hz) | δC | δH, mult (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 168.6, C | 168.5, C | ||
| 2 | 91.2, CH | 5.66, s | 91.1, CH | 5.64, s |
| 3 | 177.1, C | 177.3, C | ||
| 4 | 102.4, C | 102.2, C | ||
| 5 | 37.8, CH | 2.4, m | 38.2, CH | 2.45, m |
| 6 | 62.9, CH2 | 4.25, dd (11.2, 4.8); | 63.0, CH2 | 3.93, dd (11.6, 6.2); |
| 3.96, dd (11.2, 7.0) | 3.86, dd (11.6, 6.0) | |||
| 7 | 60.5, CH3 | 3.92, s | 60.5, CH3 | 3.92, s |
| 8 | 10.6, CH3 | 0.89, d (7.0) | 10.8, CH3 | 1.03, d (6.9) |
| 9 | 170.2, C | 170.1, C | ||
| 10 | 20.6, CH3 | 2.02, s | 20.6, CH3 | 2.06, s |
| 11 | 167.9, C | 168.0, C | ||
| 12 | 21.1, CH3 | 2.08, s | 21.1, CH3 | 2.08, s |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | Control | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | > 400 | 200 | 200 | > 400 | - | > 400 | > 400 | 6.25 | > 400 | 3.12 a |
| E. coli | > 400 | 200 | 200 | > 400 | - | - | - | 12.5 | - | 6.25 a |
| C. albicans | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 50 | - | 6.25 b |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, L.-Y.; Zhang, H.-B.; Kang, H.-H.; Zhong, M.-J.; Liu, D.-S.; Ren, H.; Liu, W.-Z. New Butenolides and Cyclopentenones from Saline Soil-Derived Fungus Aspergillus Sclerotiorum. Molecules 2019, 24, 2642. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142642
Ma L-Y, Zhang H-B, Kang H-H, Zhong M-J, Liu D-S, Ren H, Liu W-Z. New Butenolides and Cyclopentenones from Saline Soil-Derived Fungus Aspergillus Sclerotiorum. Molecules. 2019; 24(14):2642. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142642
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Li-Ying, Huai-Bin Zhang, Hui-Hui Kang, Mei-Jia Zhong, De-Sheng Liu, Hong Ren, and Wei-Zhong Liu. 2019. "New Butenolides and Cyclopentenones from Saline Soil-Derived Fungus Aspergillus Sclerotiorum" Molecules 24, no. 14: 2642. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142642
APA StyleMa, L.-Y., Zhang, H.-B., Kang, H.-H., Zhong, M.-J., Liu, D.-S., Ren, H., & Liu, W.-Z. (2019). New Butenolides and Cyclopentenones from Saline Soil-Derived Fungus Aspergillus Sclerotiorum. Molecules, 24(14), 2642. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142642