Ultra-Small Pd(0) Nanoparticles into a Designed Semisynthetic Lipase: An Efficient and Recyclable Heterogeneous Biohybrid Catalyst for the Heck Reaction under Mild Conditions
Abstract
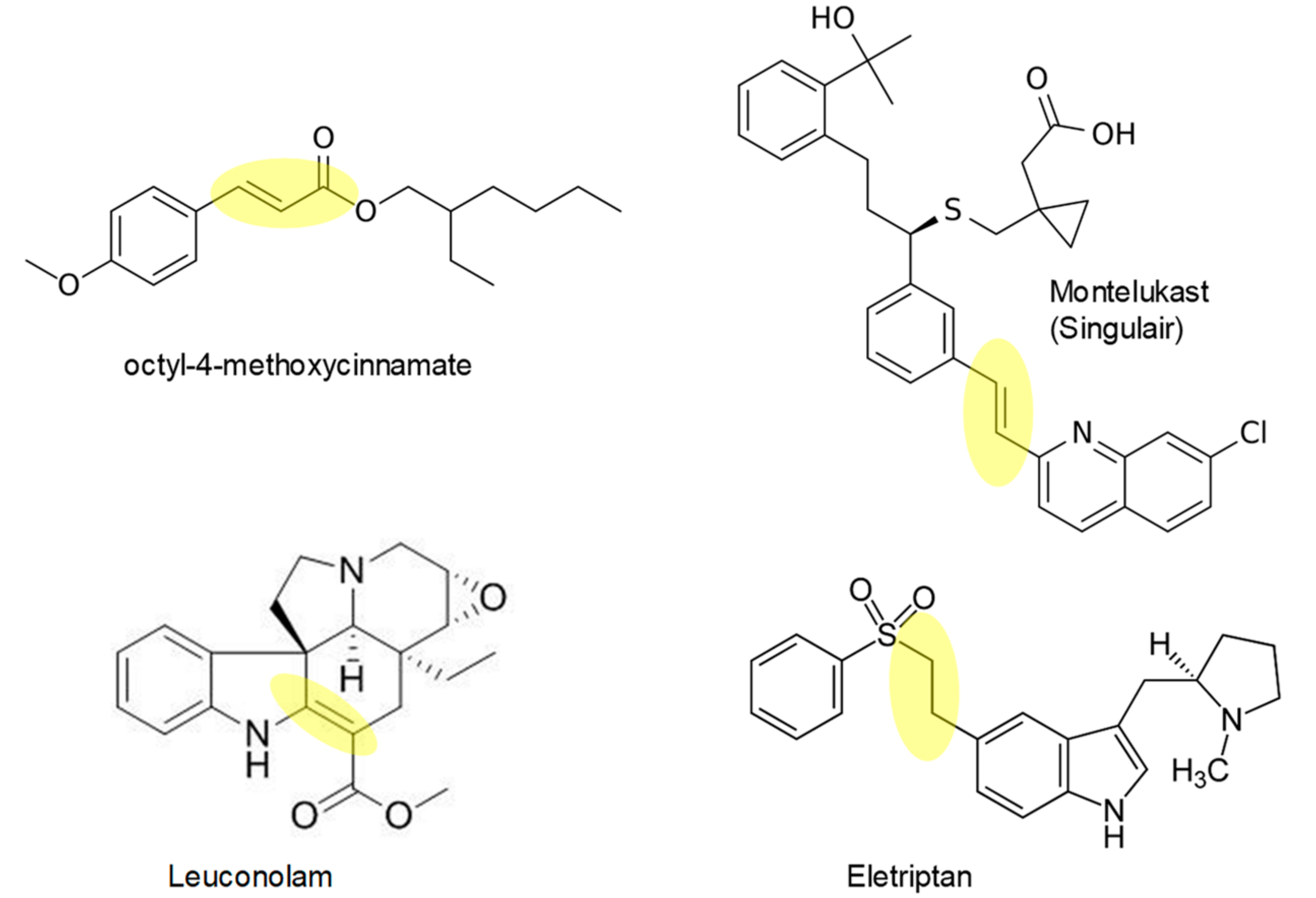
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
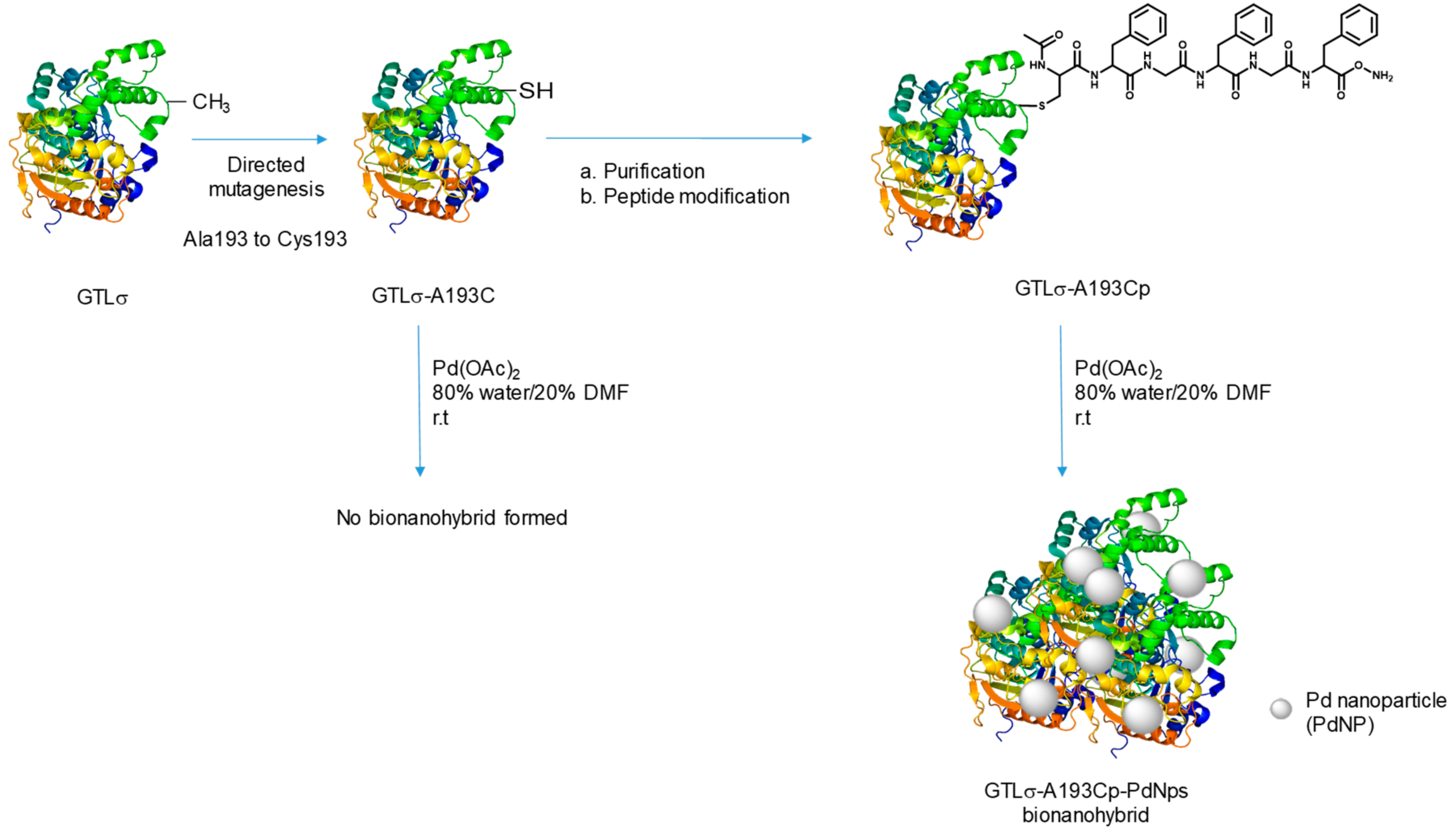
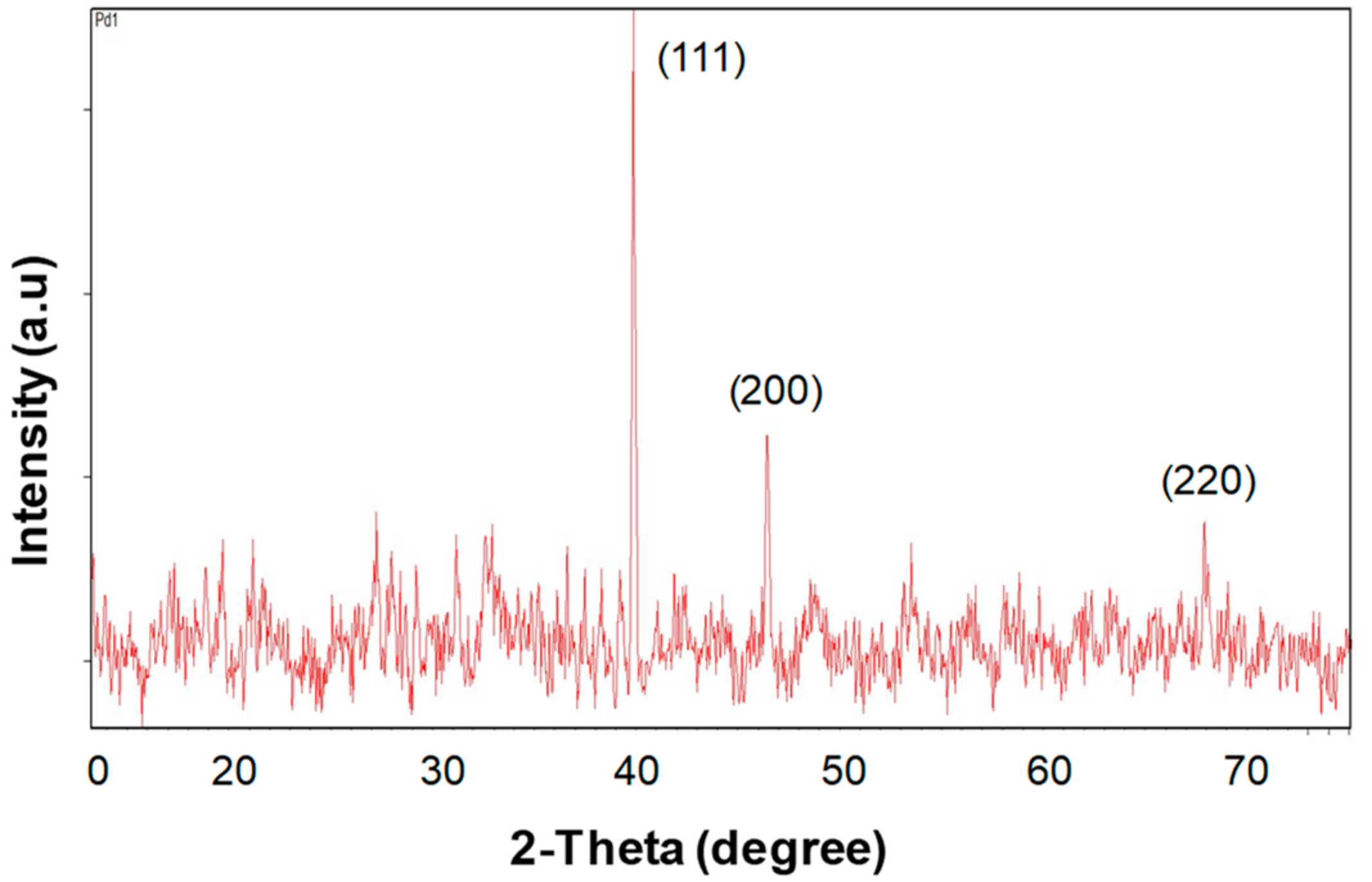
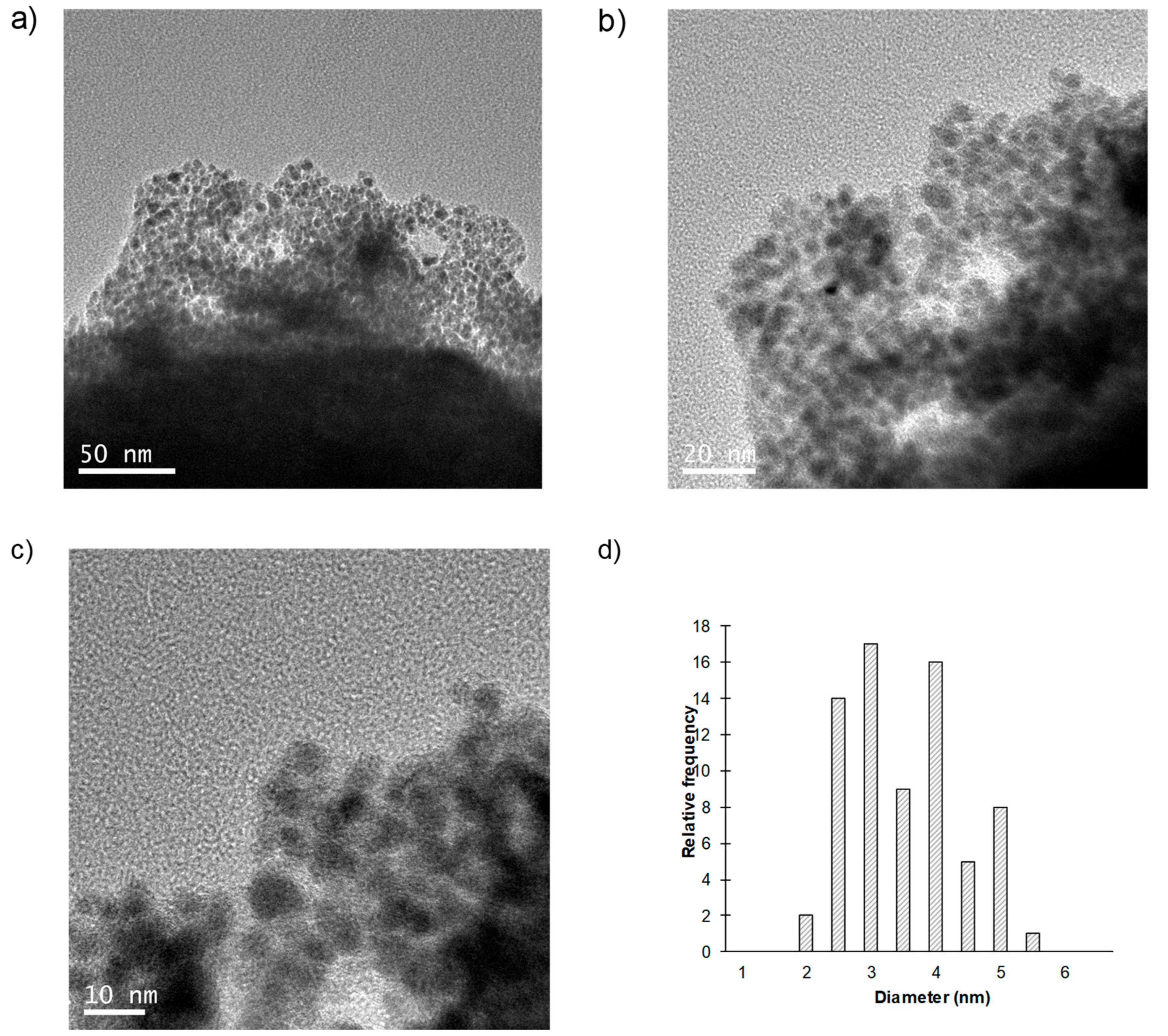
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Bionanohybrid
2.2. Heck Reaction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1 General
3.2. Site-Directed Mutagenesis, Cloning, and Expression of Geobacillus Thermocatenulatus Lipase (GTL)
3.3. Purification of GTLσ-A193C
3.4. Irreversible Site-Specific Chemical Modification of GTLσ-A193C by Thiol-Containing Peptides
3.5. Enzymatic Activity of the Artificial GTL Variants on Hydrolysis of p-Nitrophenyl Propionate (pNPP)
3.6. Synthesis of GTLσ-A193Cp-PdNPs Bionanohybrid
3.7. General Procedure for Heck Reaction
3.8. Recyclability Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beletskaya, I.P.; Cheprakov, A.V. Heck reaction as a sharpening stone of palladium catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 3009–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagtap, S. Heck Reaction—State of the Art. Catalysts 2017, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magano, J.; Dunetz, J.R. Large-scale applications of transition metal-catalyzed couplings for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2177–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, J.G. The Heck reaction in the production of fine chemicals. Can. J. Chem. 2001, 79, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelisti, C.; Panziera, N.; Pertici, P.; Vitulli, G.; Salvadori, P.; Battocchio, C.; Polzonetti, G. Palladium nanoparticles supported on polyvinylpyridine: Catalytic activity in Heck-type reactions and XPS structural studies. J. Catal. 2009, 262, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, X.; Chen, D.; Yuan, W. Carbon nanofiber-supported palladium nanoparticles as potential recyclable catalysts for the Heck reaction. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2009, 352, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzabadi, H.; Iranpoor, N.; Gholinejad, M.; Akbari, S.; Jeddi, N. Palladium nanoparticles supported on agarose-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles of Fe3O4 as a recyclable catalyst for C–C bond formation via Suzuki–Miyaura, Heck–Mizoroki and Sonogashira–Hagihara coupling reactions. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 17060–17070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzabadi, H.; Iranpoor, N.; Ghaderi, A. Solvent-free Mizoroki-Heck reaction catalyzed by palladium nano-particles deposited on gelatin as the reductant, ligand and the non-toxic and degradable natural product support. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2011, 347, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamblin, M.; Nassar-Hardy, L.; Hierso, J.C.; Fouquet, E.; Felpin, F.X. Recyclable heterogeneous palladium catalysts in pure water: Sustainable developments in Suzuki, Heck, Sonogashira and Tsuji-Trost reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2010, 352, 33–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalafi-Nezhad, A.; Panahi, F. Immobilized palladium nanoparticles on a silica-starch substrate (PNP–SSS): As an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for Heck and copper-free Sonogashira reactions in water. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, J.M.; Filice, M. Biosynthesis of Metal Nanoparticles: Novel Efficient Heterogeneous Nanocatalysts. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani-Choghamarani, A.; Taherinia, Z. Synthesis of peptide nanofibers decorated with palladium nanoparticles and its application as an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of sulfides via reaction of aryl halides with thiourea or 2-mercaptobenzothiazole. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 59410–59421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani-Choghamarani, A.; Taherinia, Z. Synthesis of biaryls using palladium nanoparticles immobilized on peptide nanofibers as catalyst and hydroxybenzotriazole as novel phenylating reagent. Chin. J. Catal. 2017, 38, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomma, E.Y.; Ding, S.N. One-Pot hydrothermal synthesis of magnetite prussian blue Nano-Composites and their application to fabricate glucose biosensor. Sensors 2016, 16, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prastaro, A.; Ceci, P.; Chiancone, E.; Boffi, A.; Cirilli, R.; Colone, M.; Fabrizi, G.; Stringaro, A.; Cacchi, S. Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling catalyzed by protein-stabilized palladium nanoparticles under aerobic conditions in water: Application to a one-pot chemoenzymatic enantioselective synthesis of chiral biaryl alcohols. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, O.; De las Rivas, B.; Lopez-Tejedor, D.; Palomo, J.M. Effect of Site-Specific Peptide-Tag Labeling on the Biocatalytic Properties of Thermoalkalophilic Lipase from Geobacillus thermocatenulatus. ChemBioChem 2018, 19, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, O.; Filice, M.; De las Rivas, B.; Carrasco-Lopez, C.; Klett, J.; Morreale, A.; Hermoso, J.A.; Guisan, J.M.; Abian, O.; Palomo, J.M. Semisynthetic peptide-lipase conjugates for improved biotransformations. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 9053–9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filice, M.; Marciello, M.; del Puerto Morales, M.; Palomo, J.M. Synthesis of heterogeneous enzyme–metal nanoparticle biohybrids in aqueous media and their applications in C–C bond formation and tandem catalysis. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Dannert, C.; Rúa, M.L.; Atomi, H.; Schmid, R.D. Thermoalkalophilic lipase of Bacillus thermocatenulatus. I. Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, purification and some properties. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Lipids Lipid Met. 1996, 1301, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
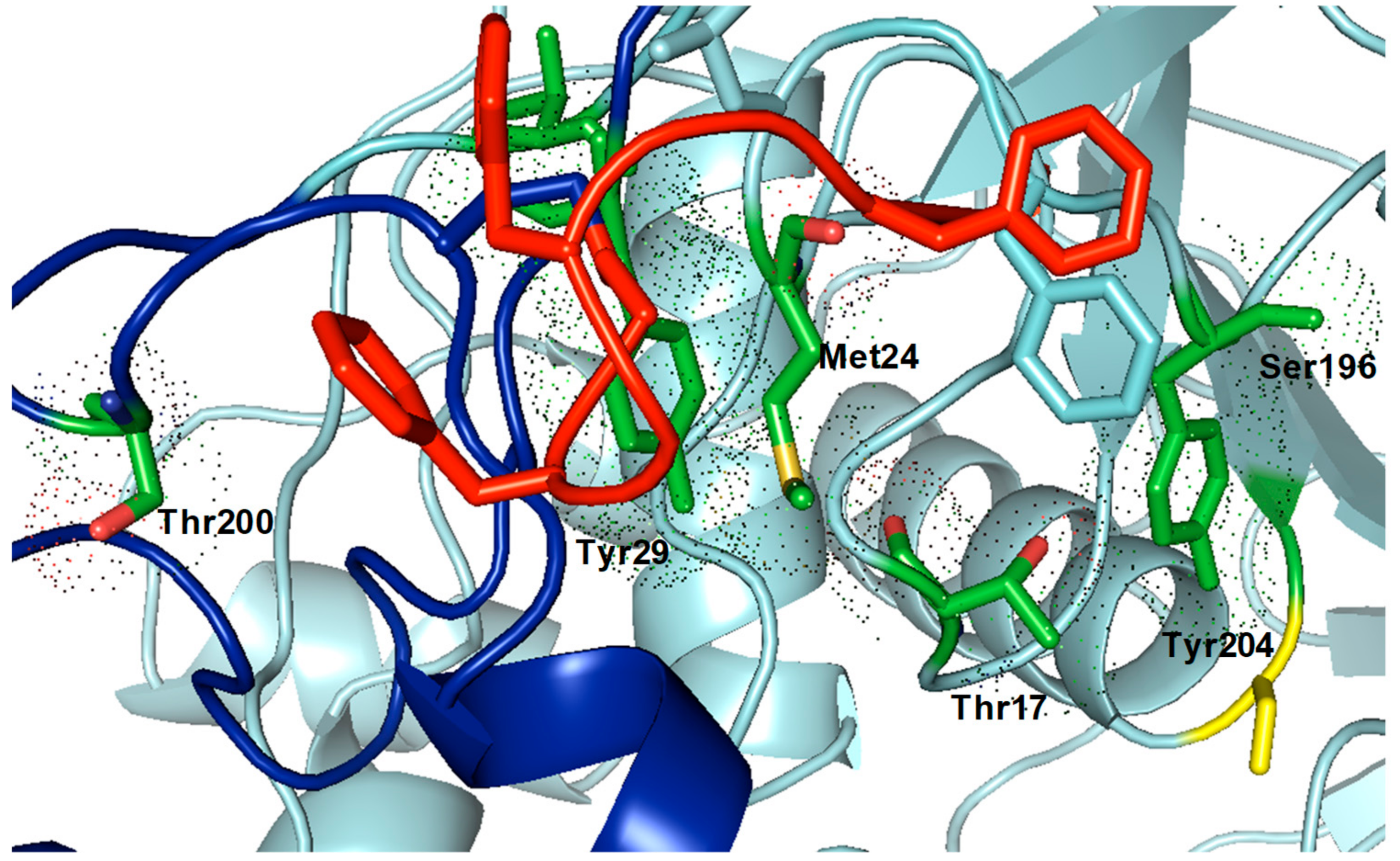
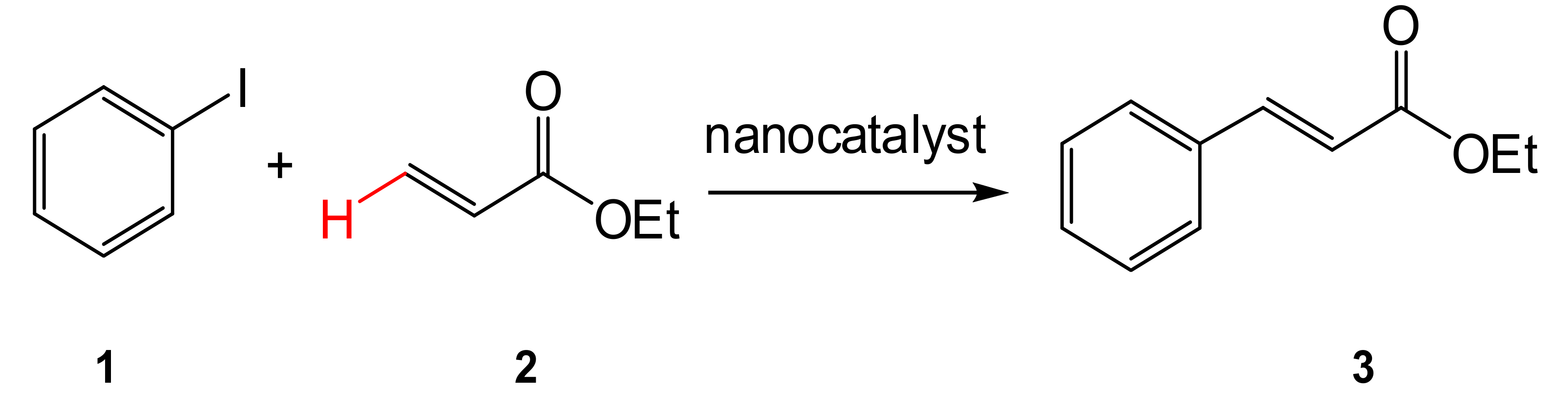
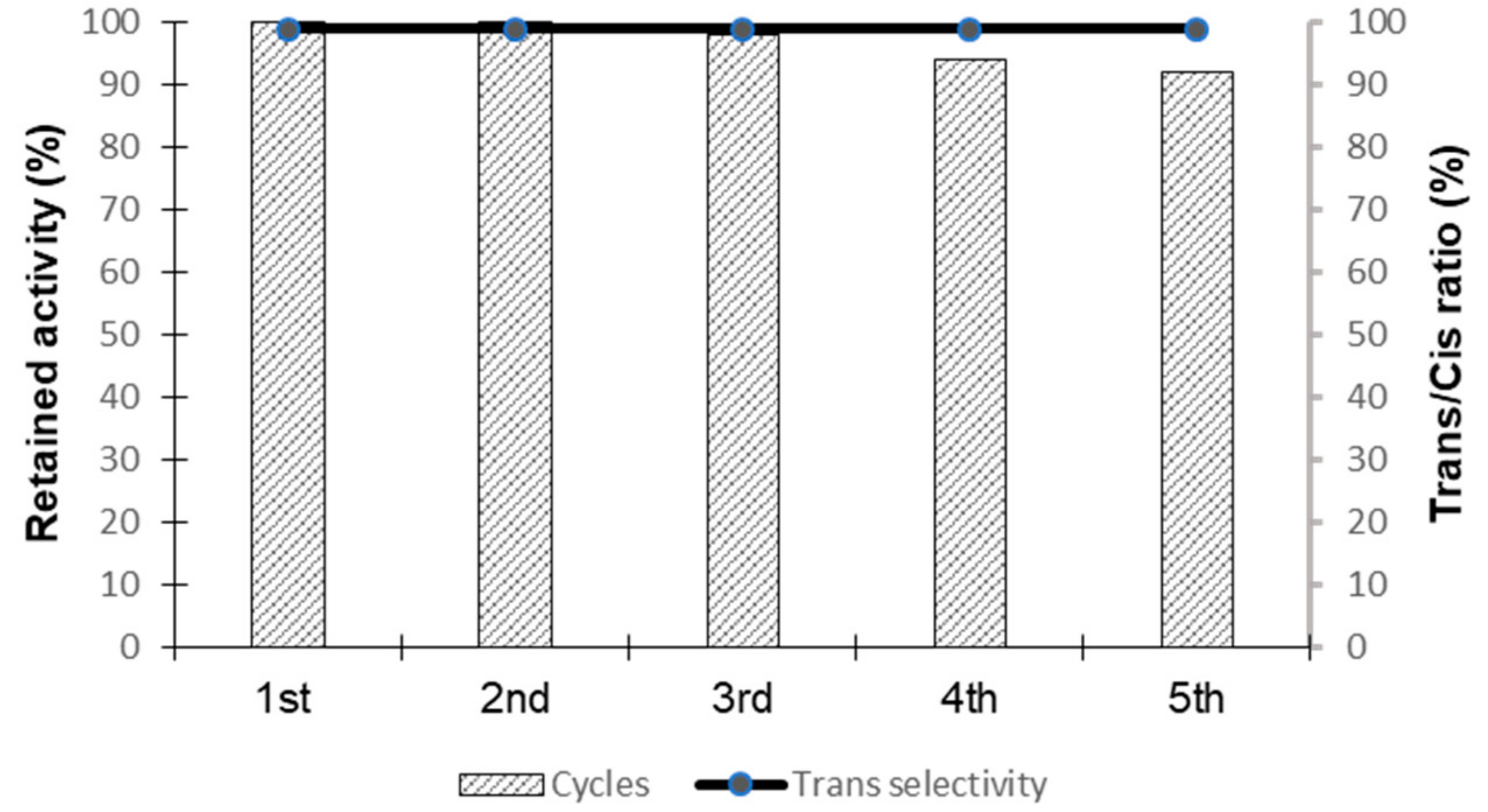
| Entry | Base | Conversion of 3 [%] | TON | TOF (h−1) | Selectivity trans/cis (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DMAP | 0 | - | - | - |
| 2 | DMAP/NEt3 | 20 | 18.27 | 0.76 | >99 |
| 3 | NEt3 | 78(>99) [b] | 71.2(91.33) | 2.96 (1.90) | >99 |
| 4 | DIPEA | 61 | 55.7 | 2.32 | >99 |
| 5 | NEt3 | 44 [c] | 40.2 | 1.67 | >99 |
| 6 | NEt3 | 7 [d] | 6.4 | 0.27 | >99 |
| 7 | NEt3 | 17 [e] | 15.52 | 0.64 | >99 |
| Entry | Co-Solvent [% v/v, H2O] | T [°C] | Conversion of 3 [%] | TON | TOF (h−1) | Selectivity trans/cis (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 65 | 56 | 51.15 | 2.13 | >99 | This work |
| 2 | 10 | 65 | 86 | 78.54 | 3.27 | >99 | This work |
| 3 | 25 | 65 | 78 | 71.23 | 2.96 | >99 | This work |
| 4 | 40 | 65 | 50 | 45.65 | 1.90 | >99 | This work |
| 5 | 0 | 70 | 0 | - | - | - | [18] |
| 7 | 50 | 70 | 20 | 18.27 | 0.76 | >99 | [18] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopez-Tejedor, D.; De las Rivas, B.; Palomo, J.M. Ultra-Small Pd(0) Nanoparticles into a Designed Semisynthetic Lipase: An Efficient and Recyclable Heterogeneous Biohybrid Catalyst for the Heck Reaction under Mild Conditions. Molecules 2018, 23, 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092358
Lopez-Tejedor D, De las Rivas B, Palomo JM. Ultra-Small Pd(0) Nanoparticles into a Designed Semisynthetic Lipase: An Efficient and Recyclable Heterogeneous Biohybrid Catalyst for the Heck Reaction under Mild Conditions. Molecules. 2018; 23(9):2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092358
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopez-Tejedor, David, Blanca De las Rivas, and Jose M. Palomo. 2018. "Ultra-Small Pd(0) Nanoparticles into a Designed Semisynthetic Lipase: An Efficient and Recyclable Heterogeneous Biohybrid Catalyst for the Heck Reaction under Mild Conditions" Molecules 23, no. 9: 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092358
APA StyleLopez-Tejedor, D., De las Rivas, B., & Palomo, J. M. (2018). Ultra-Small Pd(0) Nanoparticles into a Designed Semisynthetic Lipase: An Efficient and Recyclable Heterogeneous Biohybrid Catalyst for the Heck Reaction under Mild Conditions. Molecules, 23(9), 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092358






