Morphological, Release and Antibacterial Performances of Amoxicillin-Loaded Cellulose Aerogels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
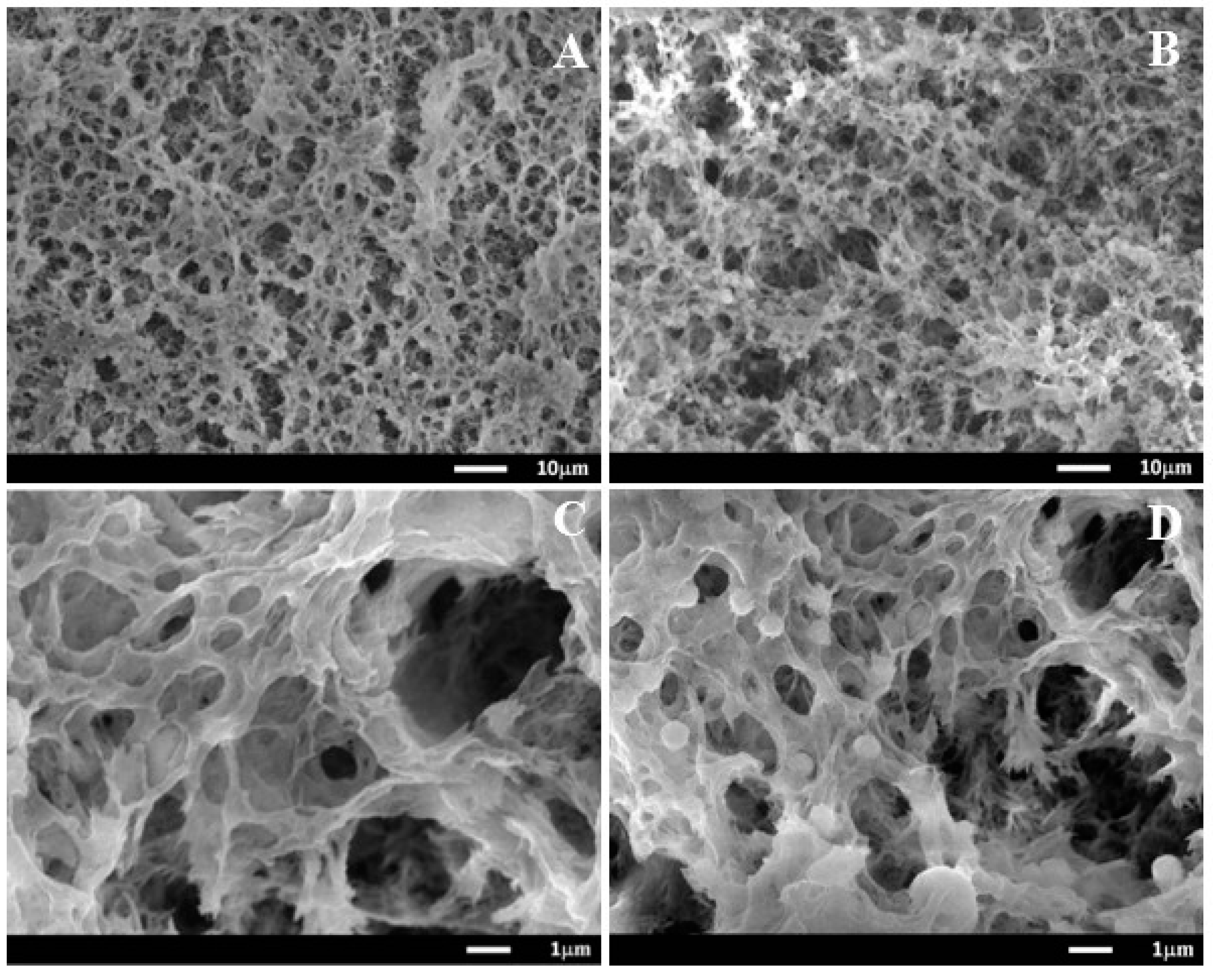
2.1. Morphology
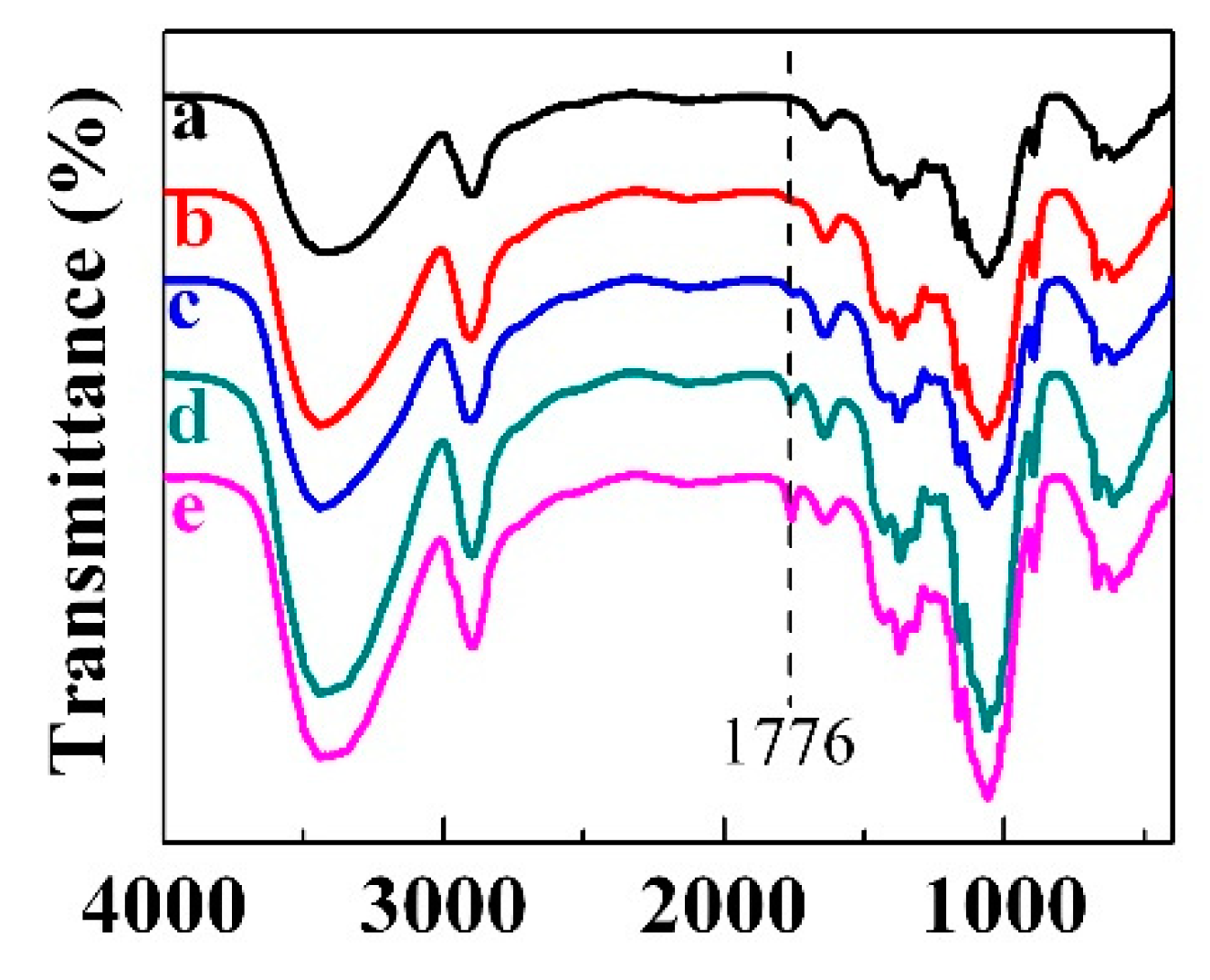
2.2. FTIR Characterization
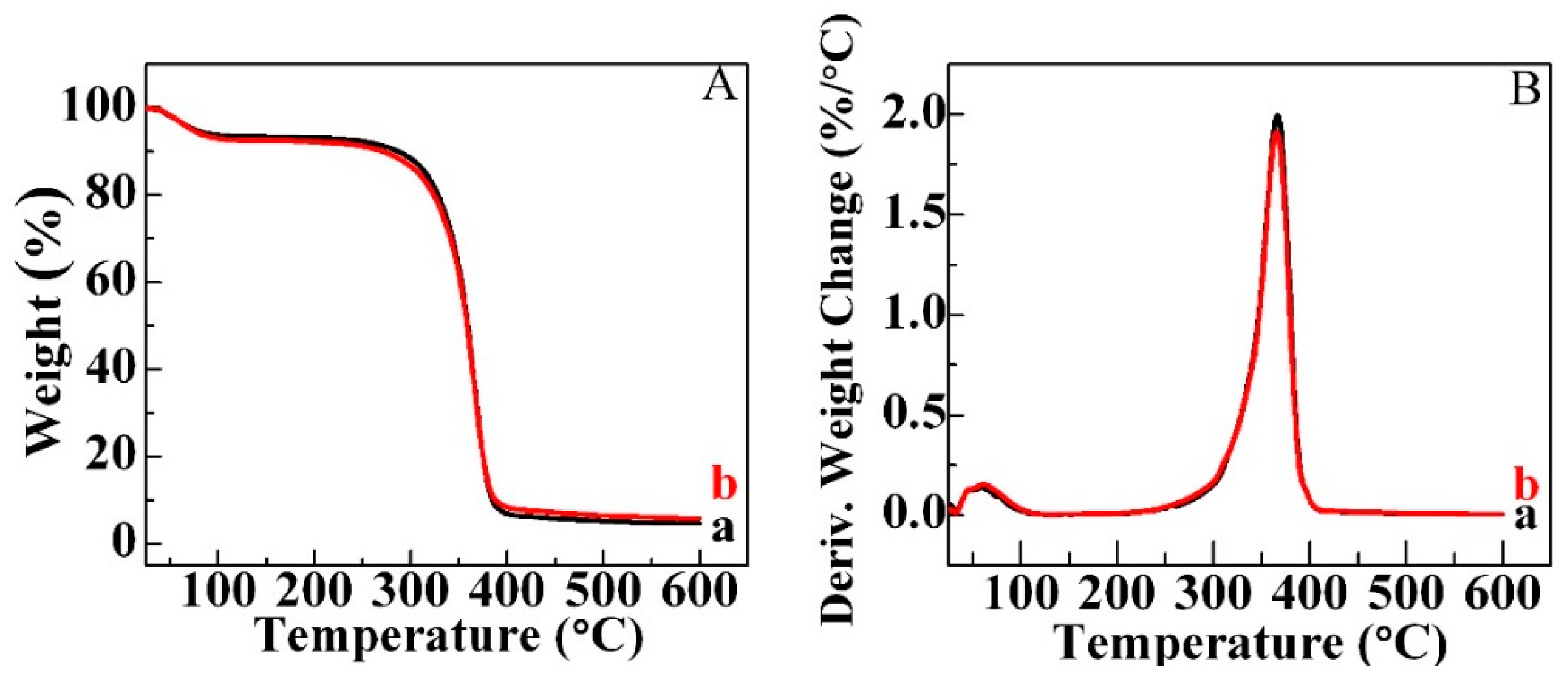
2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TG) Analysis
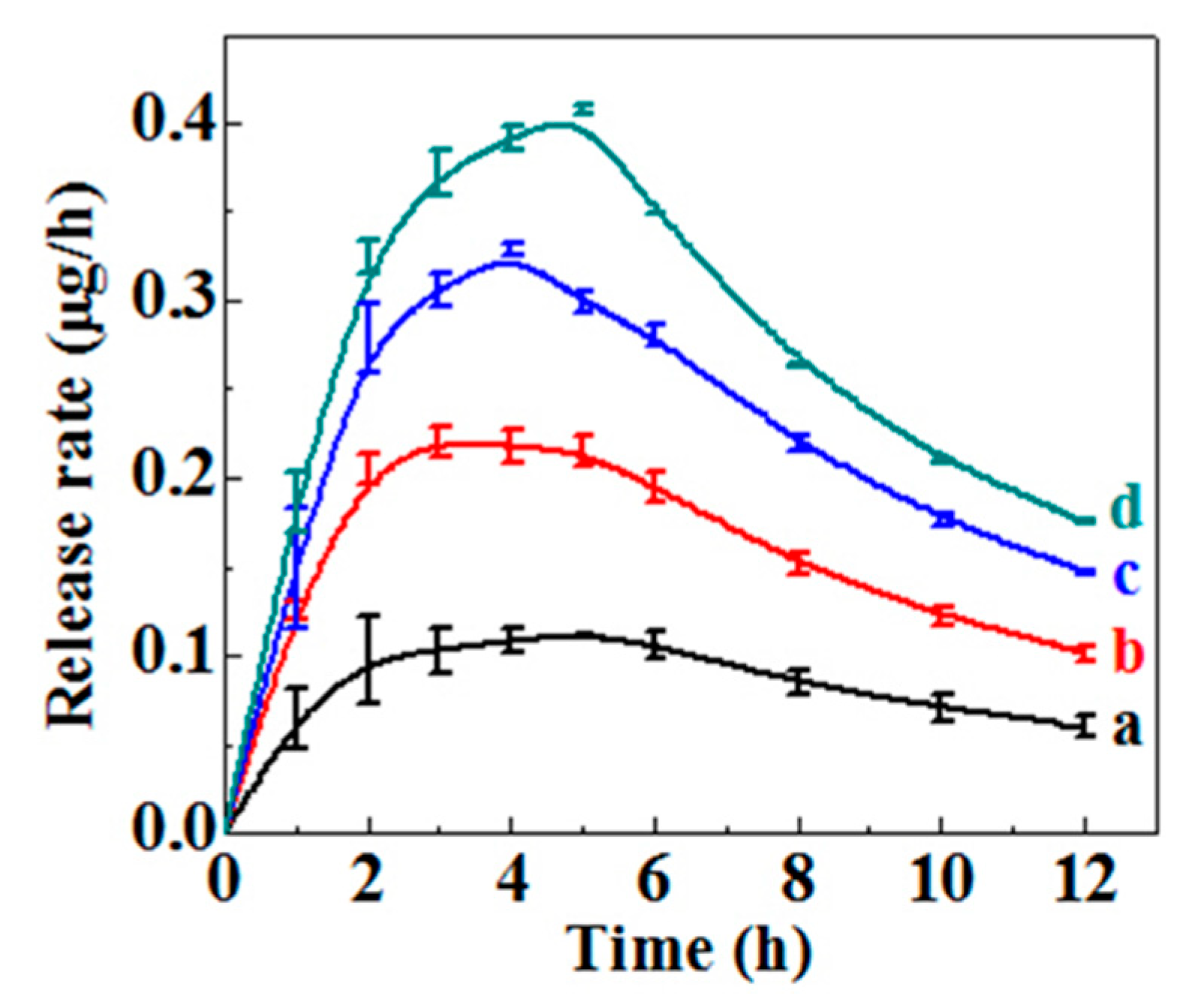
2.4. Drug Loading and Drug Release
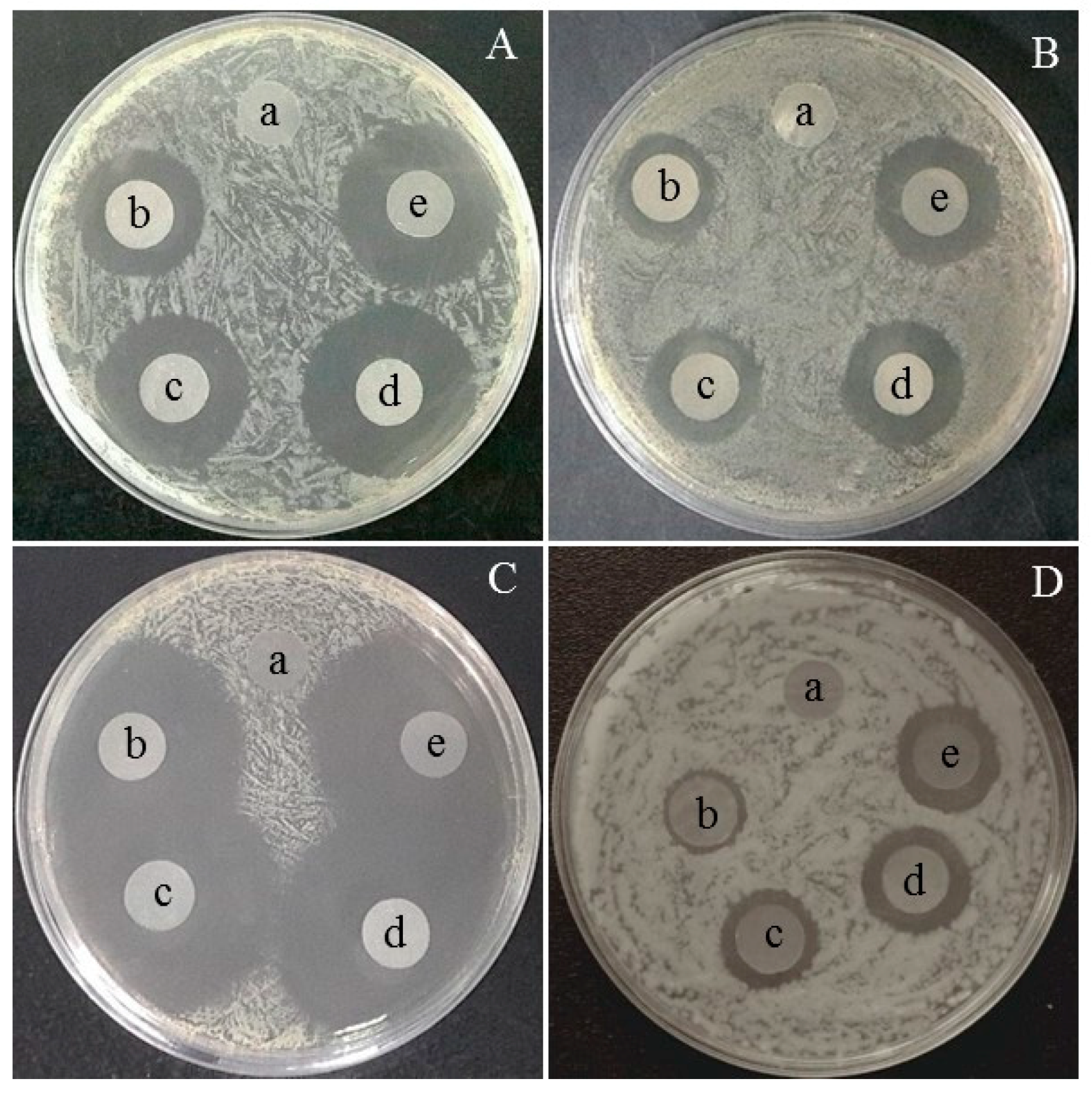
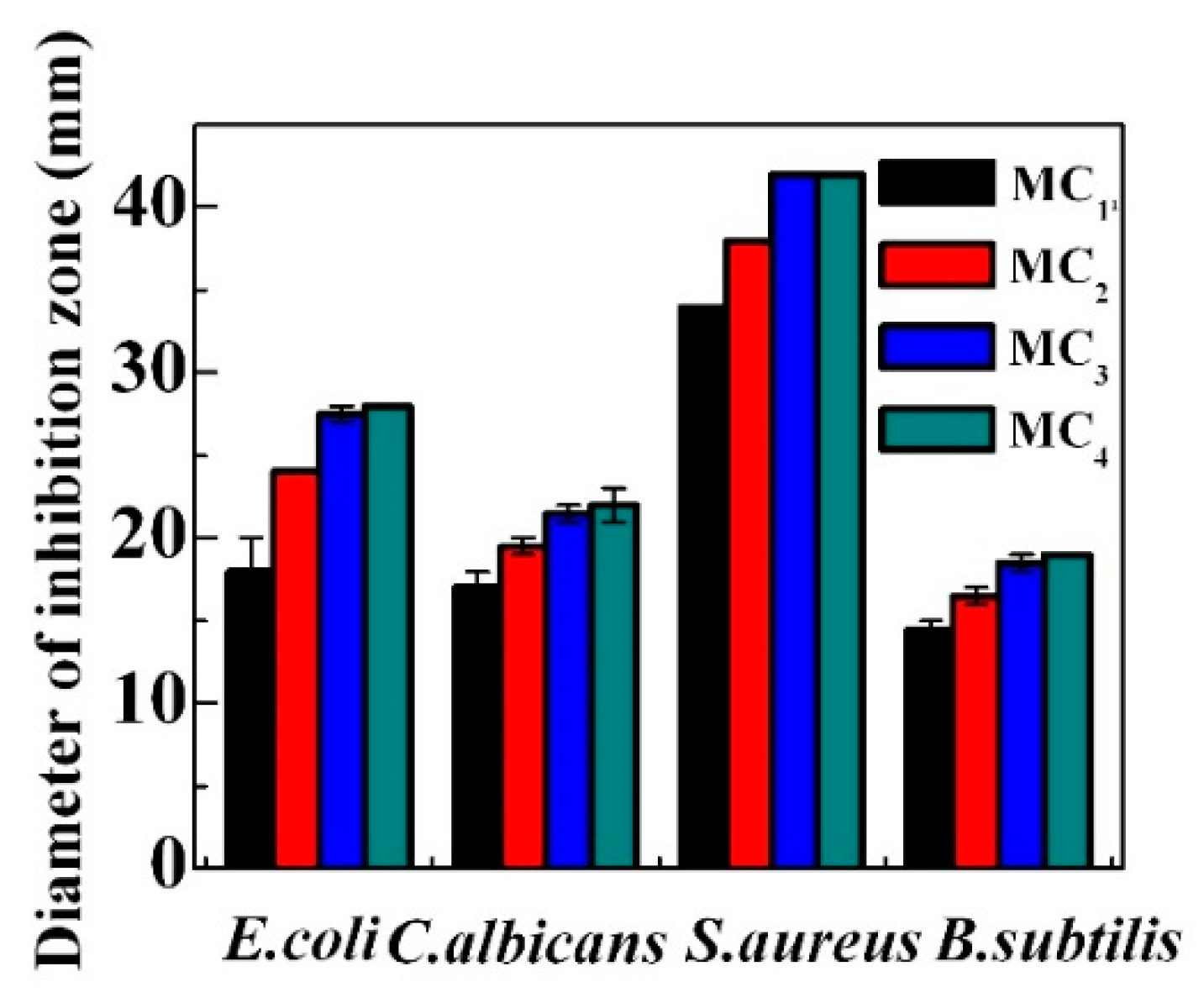
2.5. Antibacterial and Antifungal Performance
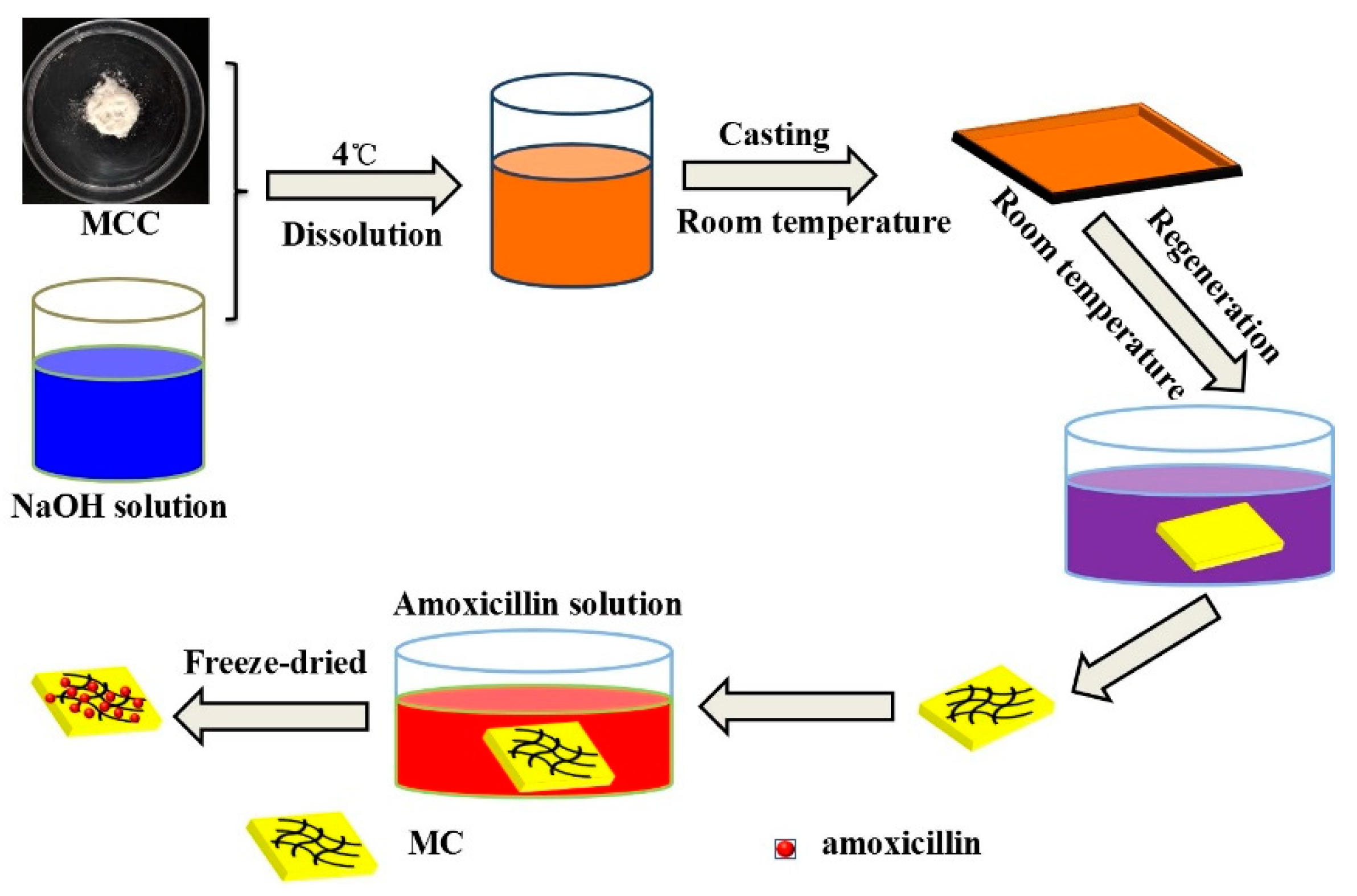
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Cellulose Aerogels
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Amoxicillin Loading Determination
3.4. In Vitro Release Assays
3.5. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Osorio, D.A.; Seifried, B.; Moquin, P.; Grandfield, K.; Cranston, E.D. Morphology of cross-linked cellulose nanocrystal aerogels: Cryo-templating versus pressurized gas expansion processing. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 9842–9860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Gao, J.; Lei, C.; Xie, Y.; Cai, Y.; Ni, Q.; Yao, J. Recyclable metal-organic framework/cellulose aerogels for activating peroxymonosulfate to degrade organic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfaoui, J.; Ghorbel, A.; Petitto, C.; Delahay, G. Novel V2O5-CeO2-TiO2-SO42− nanostructured aerogel catalyst for the low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 in excess O2. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2018, 224, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, M.; Jia, Q. Preparation and composition analysis of catalysts supported by CuO-CoO-MnO/SiO2 nanocomposite aerogels. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 261, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Dixit, V.; Shukla, V.; Shaz, M.A.; Sinha, A.S.K.; Srivastava, O.N.; Sekkar, V. Synthesis, characterization and hydrogen storage characteristics of ambient pressure dried carbon aerogel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 3561–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovskaya, D.D.; Lebedev, A.E.; Menshutina, N.V. Aerogels as drug delivery systems: In vitro and in vivo evaluations. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2015, 106, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Freyburger, A.; Kunz, W.; Zollfrank, C. Cellulose and chitin composite materials from an ionic liquid and a green co-solvent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Aziz, M.E.; Kamal, K.H.; Ali, K.A.; Abdel-Aziz, M.S.; Kamel, S. Biodegradable grafting cellulose/clay composites for metal ions removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Wang, P.L.; Zhao, S.W.; Guo, Y.R.; Li, L.; Yuan, F.L.; Pan, Q.J. Cellulose nanofiber induced self-assembly of zinc oxide nanoparticles: Theoretical and experimental study on interfacial interaction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.; Meng, J.; Wang, X.; Meng, X.; Sun, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Ni, Y. Synthesis of novel cellulose- based antibacterial composites of Ag nanoparticles@ metal-organic frameworks@ carboxymethylated fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 193, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.-R.; Wang, J.-J.; Guo, X. Fabrication of Cellulose Aerogels Using a Green/Clean Procedure. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2017, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volova, T.G.; Shumilova, A.A.; Shidlovskiy, I.P.; Nikolaeva, E.D.; Sukovatiy, A.G.; Vasiliev, A.D.; Shishatskaya, E.I. Antibacterial properties of films of cellulose composites with silver nanoparticles and antibiotics. Polym. Test. 2018, 65, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, M.; Sowti Khiabani, M.; Rezaei Mokarram, R.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Samadi Kafil, H. Development and evaluation of chitosan based active nanocomposite films containing bacterial cellulose nanocrystals and silver nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, T.I.; Fouda, A. Green approach for one-pot synthesis of silver nanorod using cellulose nanocrystal and their cytotoxicity and antibacterial assessment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, L.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, D.; Kim, J. Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial property of eco-friendly Ag/cellulose nanocomposite film. Int. J. Polymer. Mater. Polymer. Biomater. 2018, 67, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.D.; Prosenc, F.; Franko, M. Facile synthesis, structure, biocompatibility and antimicrobial property of gold nanoparticle composites from cellulose and keratin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 510, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Teng, C.; Liu, B.; Tian, H.; Wang, J. Characterization and long term antimicrobial activity of the nisin anchored cellulose films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutiya, P.L.; Mahajan, M.S.; Abdul Rasheed, M.; Pandey, M.; Zaheer Hasan, S.; Misra, N. Zinc oxide nanorod clusters deposited seaweed cellulose sheet for antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, M.; Shi, X. Electrospun PEGylated PLGA nanofibers for drug encapsulation and release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Hamzah, E.; Abbasizadeh, N.; Najafinezhad, A.; Kashefian, M. Synthesis of novel nanostructured bredigite–amoxicillin scaffolds for bone defect treatment: Cytocompatibility and antibacterial activity. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2018, 86, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aycan, D.; Alemdar, N. Development of pH-responsive chitosan-based hydrogel modified with bone ash for controlled release of amoxicillin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, M.; Dong, Q.-J.; Raja, M.A.; Zeenat, S.; Chi, Z.; Liu, C.-G. Development of novel pH-sensitive thiolated chitosan/PMLA nanoparticles for amoxicillin delivery to treat Helicobacter pylori. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 83, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, F.-X.; Yu, J.-Y.; Hsieh, Y.-L. Dissolution behaviour and solubility of cellulose in NaOH complex solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Xu, M. Novel regenerated cellulose films prepared by coagulating with water: Structure and properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kian, L.K.; Jawaid, M.; Ariffin, H.; Karim, Z. Isolation and characterization of nanocrystalline cellulose from roselle-derived microcrystalline cellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, R.D.S.; Leal, R.C.; da Silva, M.S.; Morais, A.I.S.; Marques, T.H.C.; Osajima, J.A.; Meneguin, A.B.; da Hernane, S.B.; da Edson, C.S.F. Direct Modification of Microcrystalline Cellulose with Ethylenediamine for use as Adsorbent for Removal Amitriptyline Drug from Environment. Molecules 2017, 22, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, A.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Yang, H.; Huang, W. Isolation and characterization of microcrystalline cellulose from pomelo peel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thombre, N.A.; Gide, P.S. Floating-bioadhesive gastroretentive Caesalpinia pulcherrima-based beads of amoxicillin trihydrate for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Chen, Z.; Lin, X.; Ren, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and characterization of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) from tea waste. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wen, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C. Acetylation of Microcrystalline Cellulose by Transesterification in AmimCl/DMSO Cosolvent System. Molecules 2017, 22, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guncum, E.; Bakirel, T.; Anlas, C.; Ekici, H.; Isiklan, N. Novel amoxicillin nanoparticles formulated as sustained release delivery system for poultry use. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 41, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.; Wang, S.X.; Liu, X.F.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.M.; Zhang, R.; Min, H.H.; Huang, M. Tetracycline hydrochloride loaded regenerated cellulose composite membranes with controlled release and efficient antibacterial performance. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 3068–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
| Initial Amoxicillin Concentration (mg/mL) | Amoxicillin Loading (μg/cm2) | |
|---|---|---|
| MC1 | 0.3 | 4.03 ± 0.07 |
| MC2 | 0.6 | 8.62 ± 0.55 |
| MC3 | 0.9 | 11.85 ± 0.61 |
| MC4 | 1.2 | 13.45 ± 0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, S.; He, S.; Su, C.; Jiang, L.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Shao, W. Morphological, Release and Antibacterial Performances of Amoxicillin-Loaded Cellulose Aerogels. Molecules 2018, 23, 2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23082082
Ye S, He S, Su C, Jiang L, Wen Y, Zhu Z, Shao W. Morphological, Release and Antibacterial Performances of Amoxicillin-Loaded Cellulose Aerogels. Molecules. 2018; 23(8):2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23082082
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Shan, Shu He, Chen Su, Lei Jiang, Yanyi Wen, Zhongjie Zhu, and Wei Shao. 2018. "Morphological, Release and Antibacterial Performances of Amoxicillin-Loaded Cellulose Aerogels" Molecules 23, no. 8: 2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23082082
APA StyleYe, S., He, S., Su, C., Jiang, L., Wen, Y., Zhu, Z., & Shao, W. (2018). Morphological, Release and Antibacterial Performances of Amoxicillin-Loaded Cellulose Aerogels. Molecules, 23(8), 2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23082082




