Correlations of Molecular Weights of β-Glucans from Qingke (Tibetan Hulless Barley) to Their Multiple Bioactivities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Characterization of Qingke β-Glucans with Different Molecular Weights
2.2. Correlation of Molecular Weights of Qingke β-Glucans to Their Binding Properties
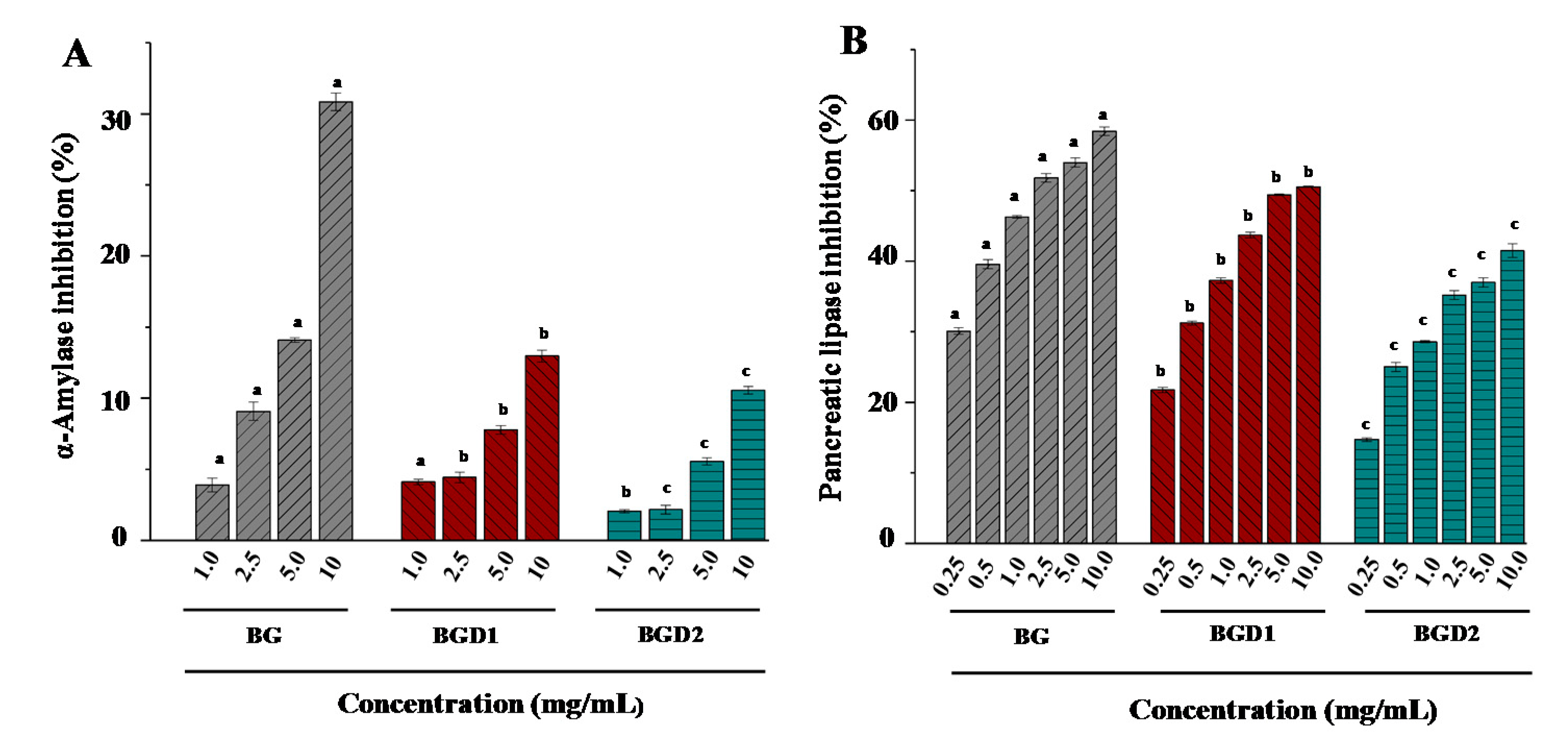
2.3. Correlation of Molecular Weights of Qingke β-Glucans to Their Inhibitory Activities on α-Amylase and Pancreatic Lipase
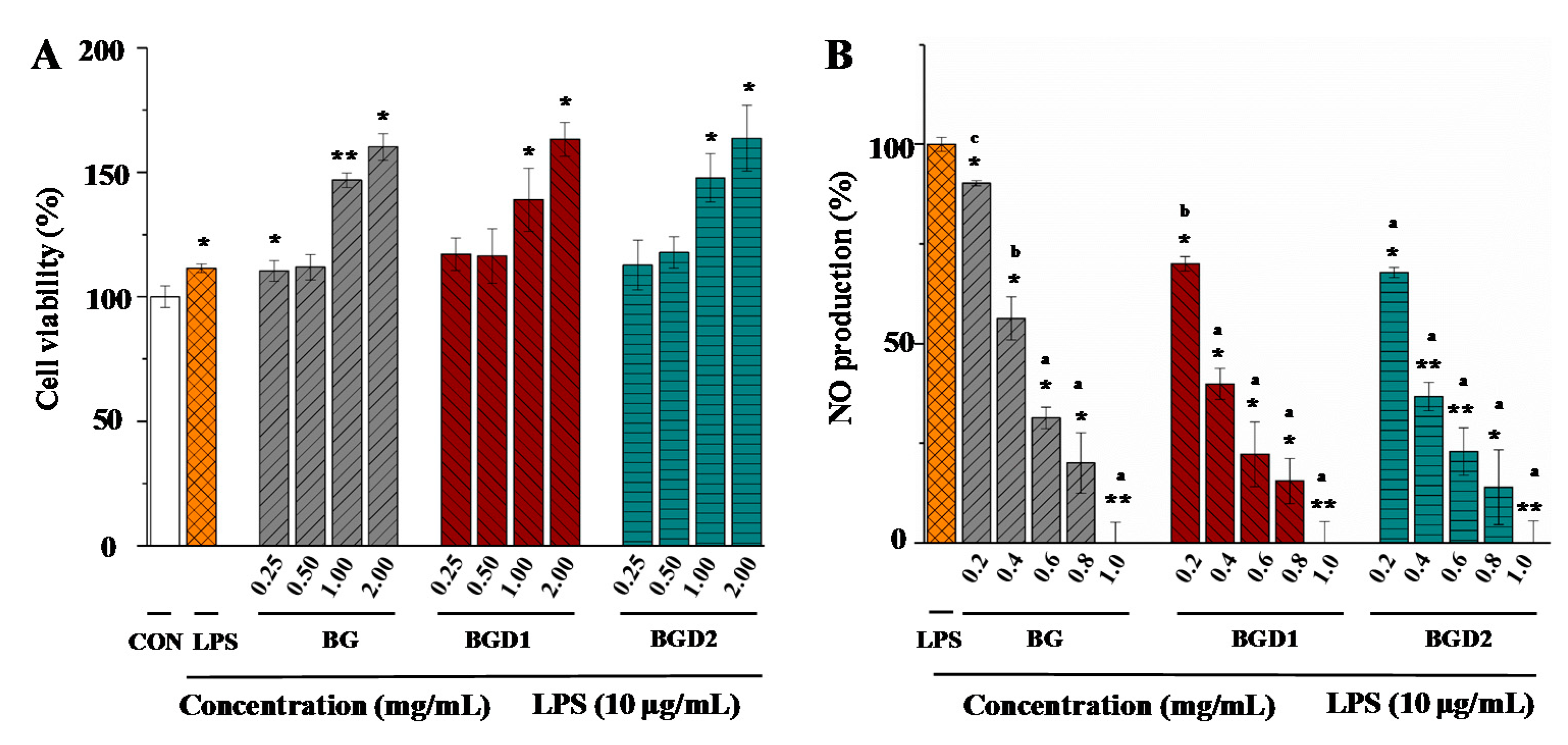
2.4. Correlation of Molecular Weights of Qingke β-Glucans to Their In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activities
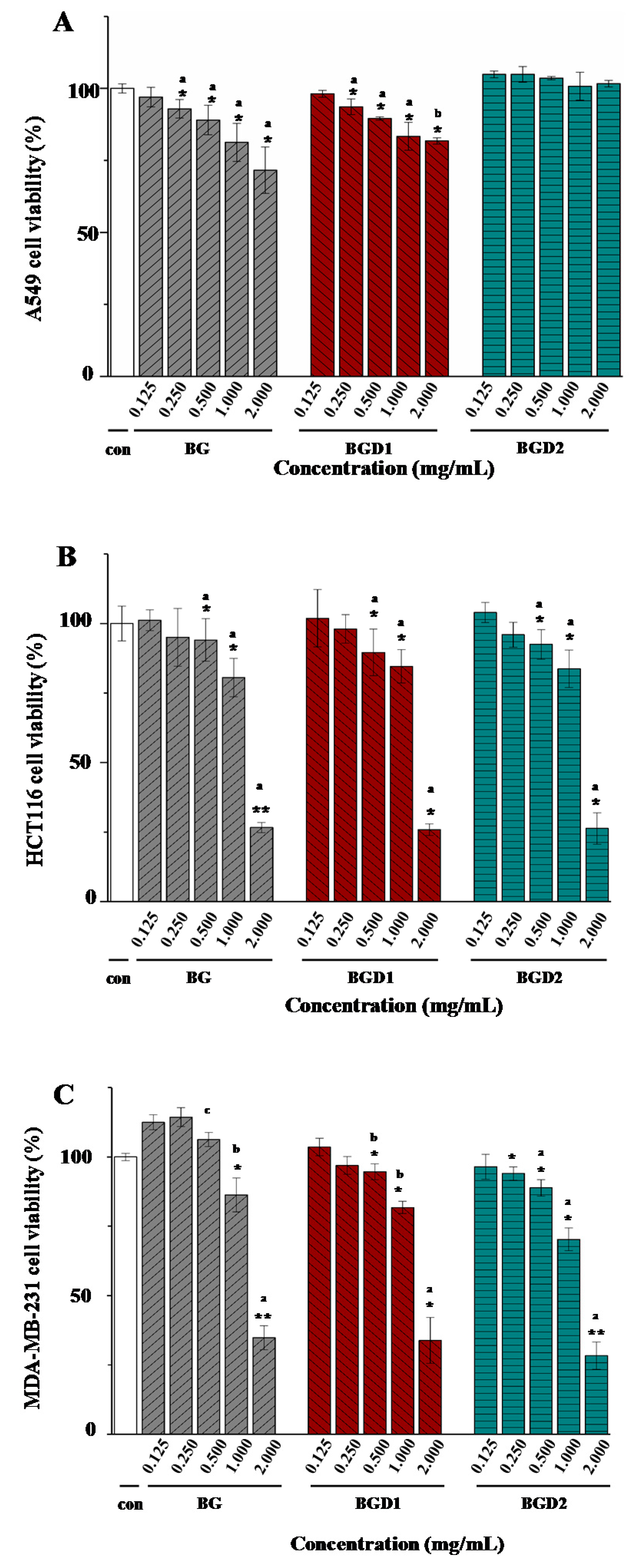
2.5. Correlation of Molecular Weights of Qingke β-Glucans to Their In Vitro Anti-Cancer Activities
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Material and Chemicals
3.2. Extraction and Purification of β-Glucan from Qingke
3.3. Preparation of Qingke β-Glucans with Different Molecular Weights
3.4. Determination of Molecular Weights
3.5. Determination of Intrinsic Viscosities
3.6. In Vitro Binding Properties of Qingke β-Glucans with Different Molecular Weights
3.6.1. Determination of Fat-Binding Capacity
3.6.2. Determination of Cholesterol-Binding Capacity
3.6.3. Determination of Bile Acid-Binding Capacity
3.7. In Vitro Inhibitory Effects of β-Glucans with Different Molecular Weights on the α-Amylase and Pancreatic Lipase
3.8. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Qingke β-Glucans with Different Molecular Weights
3.8.1. Cell Culture
3.8.2. Cell Viability
3.8.3. NO Production
3.9. In Vitro Anti-Cancer Activity of Qingke β-Glucans with Different Molecular Weights
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramakrishna, R.; Sarkar, D.; Schwarz, P.; Shetty, K. Phenolic linked anti-hyperglycemic bioactives of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cultivars as nutraceuticals targeting type 2 diabetes. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 107, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Long, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Tang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Mao, L.; Deng, G. The draft genome of Tibetan hulless barley reveals adaptive patterns to the high stressful Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idehen, E.; Tang, Y.; Sang, S. Bioactive phytochemicals in barley. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comino, P.; Shelat, K.; Collins, H.; Lahnstein, J.; Gidley, M.J. Separation and purification of soluble polymers and cell wall fractions from wheat, rye and hull less barley endosperm flours for structure-nutrition studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 12111–12122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izydorczyk, M.S.; Dexter, J.E. Barley β-glucans and arabinoxylans: Molecular structure, physicochemical properties, and uses in food products—A review. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 850–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, G.; Sowrirajan, S.; Joseph, B. Extraction and isolation of β-Glucan from grain sources—A review. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.Y.; Bai, Y.Y.; Tang, J.; Chen, W. Antioxidation and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of barley polysaccharides modified with sulfation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błaszczyk, K.; Wilczak, J.; Harasym, J.; Gudej, S.; Suchecka, D.; Królikowski, T.; Lange, E.; Gromadzka-Ostrowska, J. Impact of low and high molecular weight oat beta-glucan on oxidative stress and antioxidant defense in spleen of rats with LPS induced enteritis. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridou, A.; Papoutsi, Z.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Moutsatsou, P. Effect of oat and barley β-glucans on inhibition of cytokine-induced adhesion molecule expression in human aortic endothelial cells: Molecular structure–function relations. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choromanska, A.; Kulbacka, J.; Rembialkowska, N.; Pilat, J.; Oledzki, R.; Harasym, J.; Saczko, J. Anticancer properties of low molecular weight oat beta-glucan—An in vitro study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Ahmad, M.; Ashwar, B.A.; Gani, A.; Masoodi, F.A.; Wani, I.A.; Wani, S.M.; Gani, A. Effect of γ-irradiation on structure and nutraceutical potential of β-d-glucan from barley (Hordeum vulgare). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rösch, C.; Meijerink, M.; Delahaije, R.J.B.M.; Taverne, N.; Gruppen, H.; Wells, J.M.; Schols, H.A. Immunomodulatory properties of oat and barley β-glucan populations on bone marrow derived dendritic cells. J. Funct. Food. 2016, 26, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casieri, V.; Matteucci, M.; Cavallini, C.; Torti, M.; Torelli, M.; Lionetti, V. Long-term intake of pasta containing barley (1–3) beta-d-glucan increases neovascularization-mediated cardioprotection through endothelial upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and parkin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hu, B.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Qi, X. The anti-diabetic activity of oat β-d-glucan in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoe, S.; Ichinose, Y.; Kohyama, N.; Komae, K.; Takahashi, A.; Abe, D.; Yoshioka, T.; Yanagisawa, T. Effects of high β-glucan barley on visceral fat obesity in Japanese individuals: A randomized, double-blind study. Nutrition 2017, 42, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Gani, A.; Shah, A.; Gani, A.; Masoodi, F.A. Germination and microwave processing of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) changes the structural and physicochemical properties of β-d-glucan & enhances its antioxidant potential. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Masoodi, F.A.; Gani, A.; Ashwar, B.A. Effect of γ-irradiation on antioxidant and antiproliferative properties of oat β-glucan. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2015, 117, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, N.Y.; Byun, E.H.; Kwon, S.K.; Song, B.S.; Choi, J.I.; Kim, J.H.; Byun, M.W.; Yoo, Y.C.; Kim, M.R.; Lee, J.W. Immune-enhancing activities of low molecular weight β-glucan depolymerized by gamma irradiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2009, 78, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczak, J.; Błaszczyk, K.; Kamola, D.; Gajewska, M.; Harasym, J.P.; Jałosińska, M.; Gudej, S.; Suchecka, D.; Oczkowski, M.; Gromadzkaostrowska, J. The effect of low or high molecular weight oat beta-glucans on the inflammatory and oxidative stress status in the colon of rats with LPS-induced enteritis. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; White, P.J. In vitro bile-acid binding and fermentation of high, medium, and low molecular weight β-Glucan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, C.; Navarro, A.; Manzanares, P.; Horta, A.; Carbonell, J.V. Physical and structural properties of barley (1 → 3),(1 → 4)-β-d-glucan. Part I. Determination of molecular weight and macromolecular radius by light scattering. Carbohydr. Polym. 1997, 32, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, H.L.; Jang, G.Y.; Min, Y.K.; Hwang, I.G.; Kim, H.Y.; Woo, K.S.; Mi, J.L.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, J.; Jeong, H.S. Physicochemical and in vitro binding properties of barley β-glucan treated with hydrogen peroxide. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 729–735. [Google Scholar]
- Vaikousi, H.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Izydorczyk, M.S. Solution flow behavior and gelling properties of water-soluble barley (1 → 3,1 → 4)-β-glucans varying in molecular size. J. Cereal Sci. 2004, 39, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsędek, A.; Majewska, I.; Redzynia, M.; Sosnowska, D.; Koziołkiewicz, M. In Vitro Inhibitory Effect on Digestive Enzymes and Antioxidant Potential of Commonly Consumed Fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 4610–4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Li, G.; Ding, Y.; Ren, T.; Zheng, J.; Kan, J. Effect of whole grain Qingke (Tibetan Hordeum vulgare L. Zangqing 320) on the serum lipid levels and intestinal microbiota of rats under high-fat diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2686–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, I.L.; Arc, C.; Lcgf, P.; Santana-Filho, A.P.; Chavante, S.F.; Sassaki, G.L. Structural characterization of polysaccharides from Cabernet Franc, Cabernet Sauvignon and Sauvignon Blanc wines: Anti-inflammatory activity in LPS stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 186, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, R.; Xia, L.; Shao, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, D. Polysaccharide isolated from Chinese jujube fruit (Zizyphus jujuba cv. Junzao) exerts anti-inflammatory effects through MAPK signaling. J. Funct. Food. 2018, 40, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.H.; Linshiau, S.Y.; Lin, J.K. Comparative studies on the suppression of nitric oxide synthase by curcumin and its hydrogenated metabolites through down-regulation of IkappaB kinase and NFkappaB activation in macrophages. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 60, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, P.R.; Rather, S.A.; Suradkar, P.P. Structural characterization and evaluation of antioxidant, anticancer and hypoglycemic activity of radiation degraded oat (Avena sativa) β-glucan. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2018, 144, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.T.; Lam, S.C.; Cheong, K.L.; Feng, W.; Lin, P.C.; Long, Z.R.; Lv, X.J.; Jing, Z.; Ma, S.C.; Li, S.P. Simultaneous determination of molecular weights and contents of water-soluble polysaccharides and their fractions from Lycium barbarum collected in China. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 129, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, B.E.; Ulset, A.S.; Beer, M.U.; Knuckles, B.E.; Williams, D.L.; Fishman, M.L.; Chau, H.K.; Wood, P.J. Macromolecular characterisation of three barley β-glucan standards by size-exclusion chromatography combined with light scattering and viscometry: An inter-laboratory study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 45, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L. Branching structure and chain conformation of water-soluble glucan extracted from Auricularia auricula-judae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3498–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Q.; Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Li, K.; Li, P. Effect of the molecular weight of water-soluble chitosan on its fat-/cholesterol-binding capacities and inhibitory activities to pancreatic lipase. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziedzic, K.; Górecka, D.; Kucharska, M.; Przybylska, B. Influence of technological process during buckwheat groats production on dietary fibre content and sorption of bile acids. Food Res. Int. 2012, 47, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Chang, S.K.C.; Zhang, Y. Comparison of α-amylase, α-glucosidase and lipase inhibitory activity of the phenolic substances in two black legumes of different genera. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, J.; Wang, L.; Bao, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wan, J.; Su, H. Purification, structural characterization and anticancer activity of the novel polysaccharides from Rhynchosia minima root. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of raw material of Qingke and Qingke β-glucans are available from the authors. |


| Sample | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Mw/Mn | Purity (%) | Protein (%) | [η] (dL/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn × 105 (Error) | Mw × 105 (Error) | |||||
| BG | 1.236 (±0.69%) | 1.962 (±0.54%) | 1.59 | 93.8 | 2.15 | 1.86 |
| BGD1 | 0.456 (±2.27%) | 0.638 (±2.35%) | 1.40 | 93.1 | 0.72 | 0.98 |
| BGD2 | 0.245 (±3.14%) | 0.358 (±2.65%) | 1.46 | 93.3 | 0.49 | 0.58 |
| Sample | Fat Binding (g/g) | Cholesterol Binding (mg/g) | Bile Acid Binding (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BG | 2.23 ± 0.03 a | 40.37 ± 0.43 a | 26.49 ± 0.18 b |
| BGD1 | 1.77 ± 0.02 b | 22.68 ± 0.31 b | 23.39 ± 0.22 c |
| BGD2 | 1.39 ± 0.02 c | 10.56 ± 0.28 d | 11.54 ± 0.25 d |
| PC | 0.89 ± 0.01 d | 18.59 ± 0.18 c | 41.53 ± 0.15 a |
| NC | N/A | N/A | 3.81 ± 0.21 e |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.; Guo, H.; Lu, M.; Lu, M.-Y.; Gong, J.D.B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, W.; Wu, D.-T. Correlations of Molecular Weights of β-Glucans from Qingke (Tibetan Hulless Barley) to Their Multiple Bioactivities. Molecules 2018, 23, 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071710
Lin S, Guo H, Lu M, Lu M-Y, Gong JDB, Wang L, Zhang Q, Qin W, Wu D-T. Correlations of Molecular Weights of β-Glucans from Qingke (Tibetan Hulless Barley) to Their Multiple Bioactivities. Molecules. 2018; 23(7):1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071710
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Shang, Huan Guo, Min Lu, Ming-Yuan Lu, Jia Duo Bu Gong, Lu Wang, Qing Zhang, Wen Qin, and Ding-Tao Wu. 2018. "Correlations of Molecular Weights of β-Glucans from Qingke (Tibetan Hulless Barley) to Their Multiple Bioactivities" Molecules 23, no. 7: 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071710
APA StyleLin, S., Guo, H., Lu, M., Lu, M.-Y., Gong, J. D. B., Wang, L., Zhang, Q., Qin, W., & Wu, D.-T. (2018). Correlations of Molecular Weights of β-Glucans from Qingke (Tibetan Hulless Barley) to Their Multiple Bioactivities. Molecules, 23(7), 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071710







