Continuous Flow Alcoholysis of Dialkyl H-Phosphonates with Aliphatic Alcohols
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
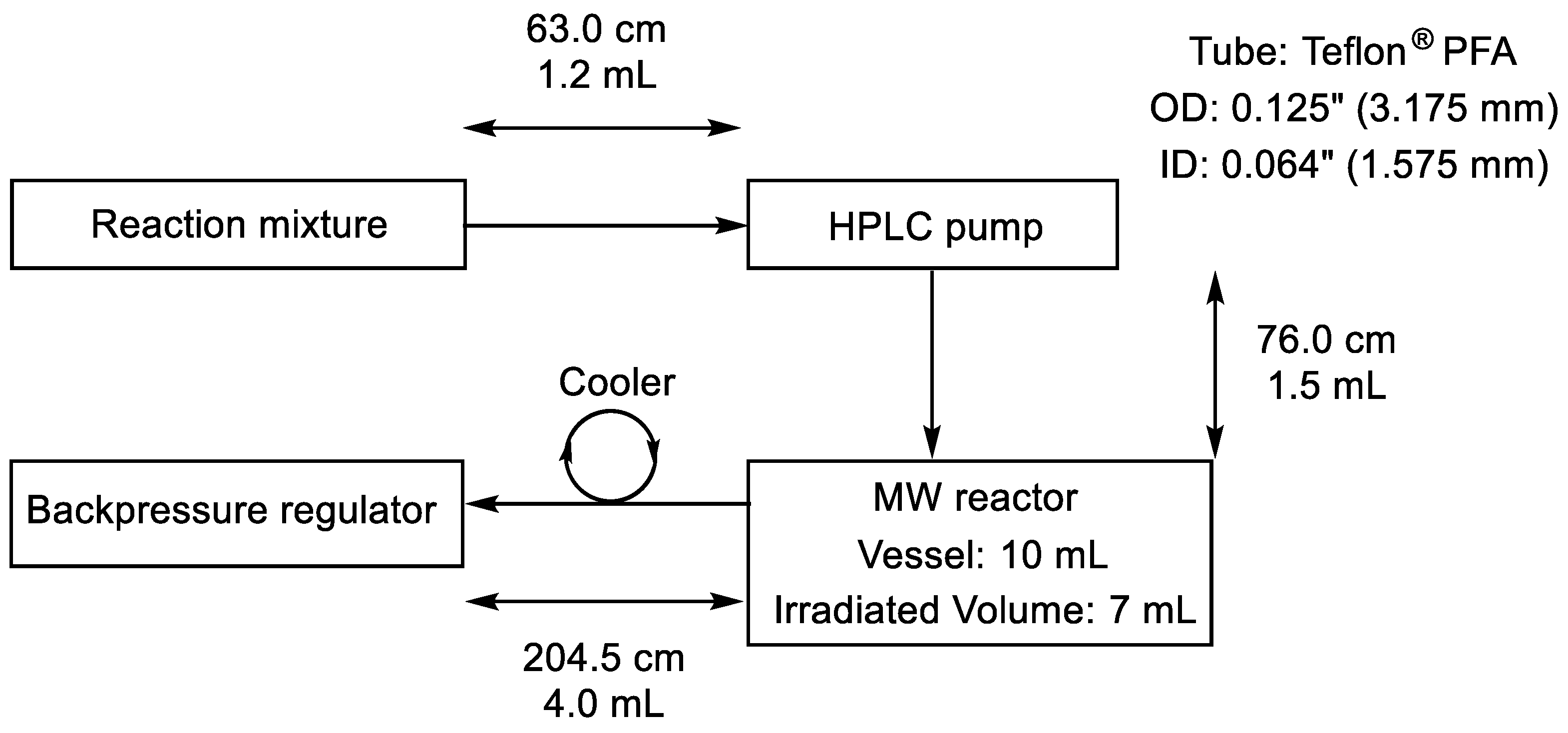
3.2. Equipment
3.3. General Procedure for the Continuous Flow Alcoholysis of Dialkyl H-Phosphonates
3.4. General Procedure for the Comparative Batch Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plutschack, M.B.; Pieber, B.; Gilmore, K.; Seeberger, P.H. The Hitchhiker’s guide to flow chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 11796–11893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasnov, T. Continuous-Flow Chemistry in the Research Laboratory; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-32194-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bálint, E.; Keglevich, G. The Spread of the Application of the Microwave Technique in Organic Synthesis. In Milestones in Microwave Chemistry; Keglevich, G., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–10. ISBN 978-3-319-30632-2. [Google Scholar]
- de la Hoz, A.; Loupy, A. (Eds.) Microwaves in Organic Synthesis, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; ISBN 978-3-527-65131-3. [Google Scholar]
- Moseley, J.D. Microwave heating as a tool for process chemistry. In Microwave Heating as a Tool for Sustainable Chemistry; Leadbeater, N., Ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 105–147. ISBN 9781138111981. [Google Scholar]
- Kappe, C.O.; Stadler, A.; Dallinger, D. Microwaves in Organic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; Volume 52, ISBN 978-3-527-33185-7. [Google Scholar]
- Estela, L.; Pouxb, M.; Benamaraa, N.; Polaerta, I. Continuous flow-microwave reactor: Where are we? Chem. Eng. Process. 2016, 113, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxendale, I.; Hayward, J.; Ley, S. Microwave reactions under continuous flow conditions. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2007, 10, 802–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riemenschneider, W.; Bolt, H.M. Esters, Organic. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 7th ed.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; pp. 245–265. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2. [Google Scholar]
- Otera, J.; Nishikido, J. (Eds.) Esterification: Methods, Reactions, and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; ISBN 978-3-527-32289-3. [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock, L.L.; Wiles, C.; Greenway, G.M.; Watts, P.; Wells, A.; Eyley, S. Enzymatic synthesis of a series of alkyl esters using novozyme 435 in a packed-bed, miniaturized, continuous flow reactor. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2008, 26, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, I.I.; Flores, M.C.; Sutili, F.K.; Leite, S.G.F.; Miranda, L.S.D.M.; Leal, I.C.R.; de Souza, R.O.M.A. Fatty acids residue from palm oil refining process as feedstock for lipase catalyzed monoacylglicerol production under batch and continuous flow conditions. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2012, 77, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutili, F.K.; Ruela, H.S.; Leite, S.G.F.; Miranda, L.S.D.M.; Leal, I.C.R.; de Souza, R.O.M.A. Lipase-catalyzed esterification of steric hindered fructose derivative by continuous flow and batch conditions. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2013, 85–86, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.G.; Benaskar, F.; Rebrov, E.V.; Meuldijk, J.; Hulshof, L.A.; Hessel, V.; Schouten, J.C. Scale-up of Microwave Assisted Flow Synthesis by Transient Processing through Monomode Cavities in Series. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2014, 18, 1400–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutili, F.K.; Ruela, H.S.; Nogueira, D.D.O.; Leal, I.C.R.; Miranda, L.S.D.M.; de Souza, R.O.M.A. Enhanced production of fructose ester by biocatalyzed continuous flow process. Sustain. Chem. Process. 2015, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, Y.; Isomura, S.; Sugamata, A.; Tamahori, K.; Fukuhara, A.; Kashiwagi, M.; Kitagawa, Y.; Kasai, E.; Takeda, K. Convenient and Simple Esterification in Continuous-Flow Systems using g-DMAP. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 3587–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koreniuk, A.; Maresz, K.; Odrozek, K.; Jarzebski, A.B.; Mrowiec-Bialon, J. Highly effective continuous-flow monolithic silica microreactors for acid catalyzed processes. Appl. Catal. A 2015, 489, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, H.; Minakawa, M.; Yamada, Y.M.A.; Han, J.W.; Uozumi, Y. In-Water and Neat Batch and Continuous-Flow Direct Esterifcation and Transesterifcation by a Porous Polymeric Acid Catalyst. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, A.; Fukuyama, T.; Ryu, I. Efficient Flow Fischer Esterification of Carboxylic Acids with Alcohols Using Sulfonic Acid-Functionalized Silica as Supported Catalyst. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2017, 90, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iemhoff, A.; Sherwood, J.; McElroy, C.R.; Hunt, A.J. Towards sustainable kinetic resolution, a combination of bio-catalysis, flow chemistry and bio-based solvents. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, T.; Glasnov, T.N.; Kappe, C.O. Continuous-Flow Microreactor Chemistry under High-Temperature/Pressure Conditions. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archambault, C.M.; Leadbeater, N.E. A benchtop NMR spectrometer as a tool for monitoring mesoscale continuous-flow organic synthesis: Equipment interface and assessment in four organic transformations. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 101171–101177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumel, A.M.; Annuar, M.S.M. Thermomyces lanuginosus lipase-catalyzed synthesis of natural flavor esters in a continuous flow microreactor. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajti, Á.; Tóth, N.; Bálint, E.; Keglevich, G. Esterification of benzoic acid in a continuous flow microwave reactor. J. Flow Chem. 2017, 8, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krull, M.; Moschhaeuser, R. Continuous Method for Producing Esters of Aromatic Carboxylic Acids. U.S. Patent 0088918, 12 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cablewski, T.; Faux, A.F.; Strauss, C.R. Development and Application of a Continuous Microwave Reactor for Organic Synthesis. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 3408–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-T.; Chiou, S.-H.; Wang, K.-T. Preparative scale organic synthesis using a kitchen microwave oven. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1990, 807–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipus, G.; Plazl, I.; Koloini, T. Esterification of benzoic acid in microwave tubular flow reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2000, 76, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, M.; Hooper, J.F.; Lupton, D.W. Biodiesel synthesis using integrated acid and base catalysis in continuous flow. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 3729–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, A.; Bergman, J.; Branalt, J.; Savmarker, J.; Larhed, M. Continuous Flow Synthesis under High-Temperature/High-Pressure Conditions Using a Resistively Heated Flow Reactor. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.-T.; Chang, J.-S.; Lee, D.-J. Recent insights into continuous-flow biodiesel production via catalytic and non-catalytic transesterification processes. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 376–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbridge, D.E.C. Phosphorus: Chemistry, Biochemistry and Technology, 6th ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-439-84088-7. [Google Scholar]
- Troev, K.D. Chemistry and Application of H-Phosphonates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; ISBN 978-0-080-47649-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bálint, E.; Tajti, Á.; Tripolszky, A. Synthesis of α-aminophosphonates by the Kabachnik–Fields reaction and by the Pudovik reaction. In Organophosphorus Chemistry; Keglevich, G., Ed.; Walter de Gruyter GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 108–147. ISBN 978-3-11-053453-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rádai, Z.; Kiss, N.Z.; Keglevich, G. Synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates, an important class of bioactive compounds. In Organophosphorus Chemistry; Keglevich, G., Ed.; Walter de Gruyter GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 91–107. ISBN 978-3-11-053453-5. [Google Scholar]
- Henyecz, R.; Keglevich, G. P-C couplings by the Hiaro reaction. In Organophosphorus Chemistry; Keglevich, G., Ed.; Walter de Gruyter GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 158–178. ISBN 978-3-11-053453-5. [Google Scholar]
- Enders, D.; Saint-Dizier, A.; Lannou, M.-I.; Lenzen, A. The phospha-Michael addition in organic synthesis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajti, Á.; Bálint, E.; Keglevich, G. Synthesis of ethyl octyl α-aminophosphonate derivatives. Curr. Org. Synth. 2016, 13, 638–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, E.; Tajti, Á.; Kalocsai, D.; Mátravölgyi, B.; Konstantin, K.; Czugler, M.; Keglevich, G. Synthesis and utilization of optically active α-aminophosphonate derivatives by Kabachnik-Fields reaction. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 5659–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrard, W. The interaction of n-butyl alcohol and the chlorides and oxychloride of phosphorus in the absence and in the presence of pyridine. J. Chem. Soc. 1940, 1466–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, E.E.; Anniston, A.; Kosolapoff, G.M. Halogenated Compounds and Process for Making Same. U.S. Patent 2409039, 8 October 1946. [Google Scholar]
- Foss, O. Di-O-alkylmonothiophosphates and the corresponding pseudohalogens. Acta Chem. Scand. 1947, 1, 8–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, C.H.; Chadwick, D.H.; Kaufman, S. Continuous process for preparing dialkyl phosphites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1957, 49, 1871–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitschke, K.-H. Method for the Combined Production of Diethyl Phosphite and Ethyl Chloride. Application Number WO200424742 A1, 25 March 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, A.J.; Salazar, C.A.; Martino, P.F.; Tyler, D.R. Direct conversion of phosphonates to phosphine oxides: An improved synthetic route to phosphines including the first synthesis of methyl JohnPhos. Organometallics 2014, 33, 6171–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosolapoff, G.M. Preparation of some mixed dialkyl phosphites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, E. The synthesis of esters of substituted amino phosphonic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 1528–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, A.A. Synthesis of cyclic phosphorus acid esters by transesterification. Can. J. Chem. 1959, 37, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuskov, V.K.; Gradis, G.K. Reaction of diethyl phosphite with sodium alcoholates. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1953, 92, 323–324. [Google Scholar]
- Froneman, M.; Modro, T.A. The titanium-mediated transesterification of phosphorus esters. Tetrahedron Lett. 1988, 27, 3327–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, R.A.; Collett, C.J.; Mesher, S.T.E. Convenient preparation of long-chain dialkyl phosphates: Synthesis of dialkyl phosphates. Synthesis 2012, 44, 2515–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, E.; Tajti, Á.; Drahos, L.; Ilia, G.; Keglevich, G. Alcoholysis of dialkyl phosphites under microwave conditions. Curr. Org. Chem. 2013, 17, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrougui, R.; Raouafi, N.; Lemordant, D. New series of green cyclic ammonium-based room temperature ionic liquids with alkylphosphite-containing anion: Synthesis and physicochemical characterization. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2014, 59, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salin, A.V.; Il’in, A.V.; Shamsutdinova, F.G.; Fatkhutdinov, A.R.; Galkin, V.I.; Islamov, D.R.; Kataeva, O.N. Phosphine-catalyzed addition of P(O)-H compounds to ethyl phenylpropiolate. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 6282–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernsberger, M.L.; Hill, J.W. Preparation of Organic Phosphorus Compounds, and in Particular, of Dialkyl Phosphites. U.S. Patent 2661364, 1 December 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Budnikova, Y.G.; Kargin, Y.M. Electrosynthesis of aliphatic esters of phosphorus acids from white phosphorus in alcohol solutions, involving radical cations of phenothiazine and triarylamine. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 1995, 65, 504–507. [Google Scholar]
- Abdreimova, R.R.; Akbayeva, D.N.; Polimbetova, G.S.; Caminade, A.-M.; Majoral, J.-P. Chlorine free synthesis of organophosphorus compounds based on the functionalization of white phosphorus (P4). Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2000, 156, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, B.; Timokhin, B.; Gusarova, N.; Kazantseva, M. Golubin, Cu-catalyzed oxidative phosphorylation of alkanols with white phosphorus and H2O2. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2002, 177, 2385–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budnikova, Y.H.; Kafiyatullina, A.G.; Sinyashin, O.G.; Abdreimova, R.R. Electrochemical synthesis of phosphorus esters from white phosphorus in the presence of copper complexes and ethanol. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2003, 52, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budnikova, Y.H.; Yakhvarov, D.G.; Sinyashin, O.G. Electrocatalytic eco-efficient functionalization of white phosphorus. J. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 690, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, H.C.; Prost, L.; Montchamp, J.L. Organophosphorus chemistry without PCl3: A bridge from hypophosphorous acid to H-phosphonate diesters. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 7973–7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluba, M.; Zwierzak, A. Alkylation of tetra-n-butylaminium alkyl hydrogen phosphites. A new route to mixed dialkyl phosphites. Synthesis 1978, 2, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilia, G.; Kurunczi, L. Synthesis of mixed alkylphosphites and alkylphosphates. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2003, 178, 1513–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchel, M.; Haddad, J.; Le Corre, S.S.; Haelters, J.-P.; Jaffrès, P.-A. Synthesis of lipid-based unsymmetrical O,O-dialkylphosphites. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 2345–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guin, J.; Wang, Q.; van Gemmeren, M.; List, B. The catalytic asymmetric Abramov reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Schreeve, J.M. Rapid and high yield oxidation of phosphine, phosphite and phosphinite compounds to phosphine oxides, phosphates and phosphinates using hypofluorous acid–acetonitrile complex. J. Fluorine Chem. 2005, 126, 1054–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santschi, N.; Togni, A. Electrophilic Trifluoromethylation of S-Hydrogen Phosphorothioates. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 4189–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kers, A.; Kers, I.; Stawinski, J.; Sobkowski, M.; Kraszewski, A. Studies on Aryl H-Phosphonates; Part 2: A General Method for the Preparation of Alkyl H-Phosphonate Monoesters. Synthesis 1995, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 2a–d, 3a–d, 5a–d are available from the authors. |
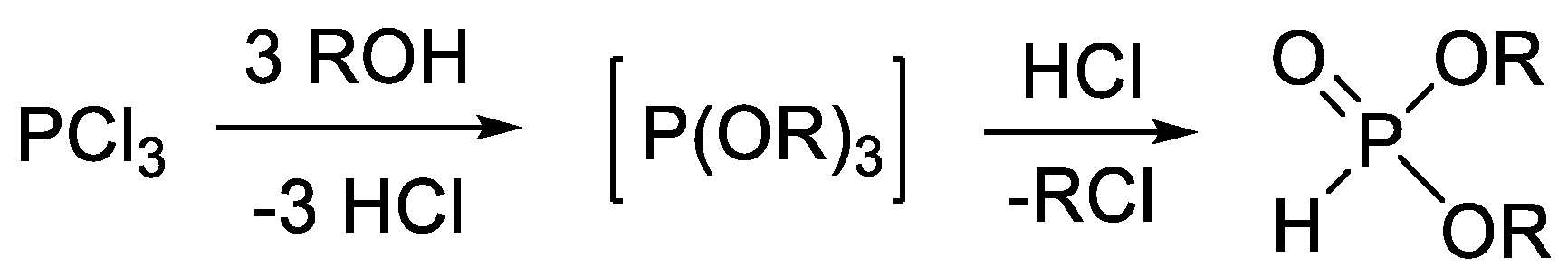

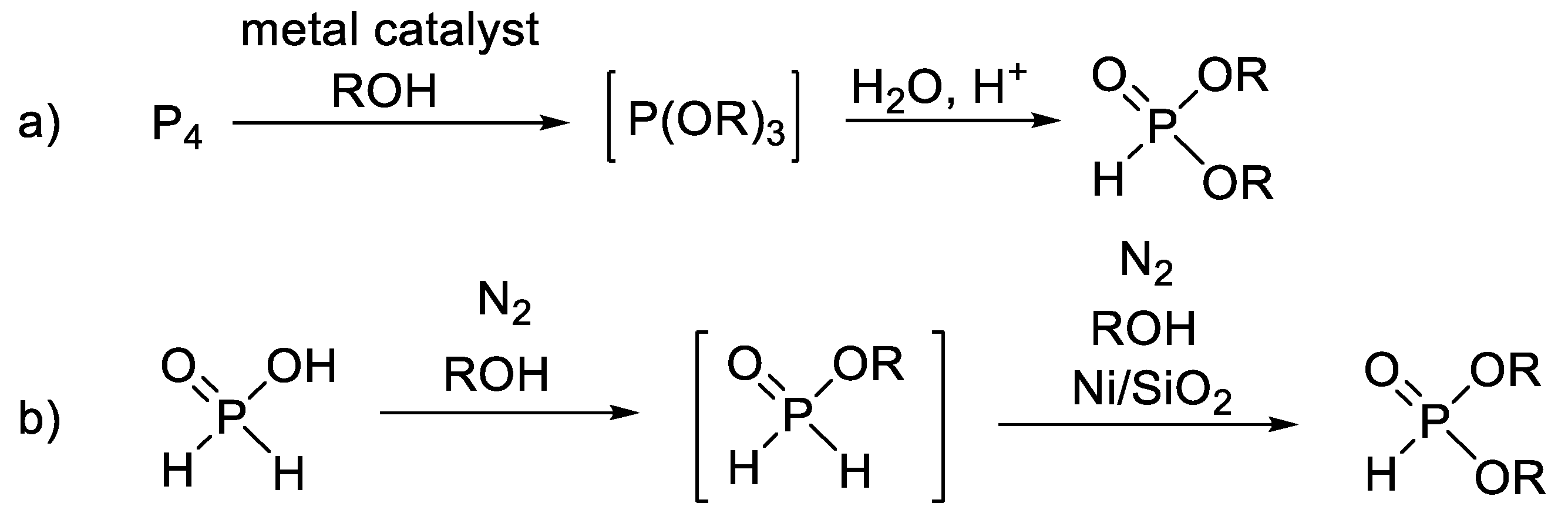




| Entry | Reaction | Average Yield (%) | Flow Compatible | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 30–50 | + | [46,50,52] |
| 2 |  | 50–70 | − | [62,63] |
| 3 |  | 50–85 | − | [64] |
| 4 |  | 30–60 | − | [65] |

| Entry | R1 | R2 | R2OH (equiv) | T (°C) | t (min) | Composition (%) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | ||||||
| 1 | Me | Et | 25 | 100 | 120 | 22 | 56 | 22 |
| 2 | Me | Et | 50 | 175 | 40 | 0 | 4 | 96 |
| 3 | Me | nBu | 25 | 125 | 60 | 0 | 40 | 60 |
| 4 | Me | nBu | 50 | 150 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 96 |
| 5 | Et | Me | 25 | 125 | 120 | 49 | 38 | 13 |
| 6 | Et | Me | 50 | 175 | 40 | 0 | 21 | 79 |
| 7 | Et | iPr | 25 | 125 | 60 | 26 | 57 | 17 |
| 8 | Et | iPr | 50 | 175 | 40 | 0 | 6 | 94 |
| 9 | Et | nBu | 25 | 125 | 60 | 25 | 54 | 21 |
| 10 | Et | nBu | 50 | 175 | 40 | 0 | 2 | 98 |
| 11 | Et | nPent | 25 | 125 | 60 | 3 | 52 | 45 |
| 12 | Et | nPent | 50 | 175 | 40 | 0 | 8 | 92 |

| Entry | Mode of Heating | Power (W) | T (°C) a | Flow Rate | τ (min) | Conversion (%) | Composition (%) c | Yield (%) d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mL/min) b | 1 | 2a | 3a | |||||||
| 1 | MW | 22 | 100 | 1.4 | 5 | 26 | 74 | 25 | 1 | - |
| 2 | MW | 14 | 100 | 0.45 | 15 | 52 | 48 | 44 | 8 | - |
| 3 | MW | 10 | 100 | 0.25 | 30 | 65 | 35 | 53 | 12 | 48 (2a) |
| 4 | MW | 8 | 100 | 0.15 | 45 | 76 | 24 | 50 | 26 | - |
| 5 | MW | 5 | 100 | 0.10 | 60 | 83 | 18 | 47 | 35 | - |
| 6 | Δ | - | 100 | 0.25 | 30 | 15 | 85 | 15 | 0 | - |
| 7 | MW | 18 | 125 | 0.25 | 30 | 93 | 7 | 43 | 50 | - |
| 8 | MW | 38 | 150 | 0.25 | 30 | 100 | 0 | 22 | 78 | - |
| 9 | MW | 59 | 175 | 0.25 | 30 | 100 | 0 | 9 | 91e,f | 88 (3a) |
| 10 | Δ | - | 175 | 0.25 | 30 | 98 | 2 | 15 | 83 | - |

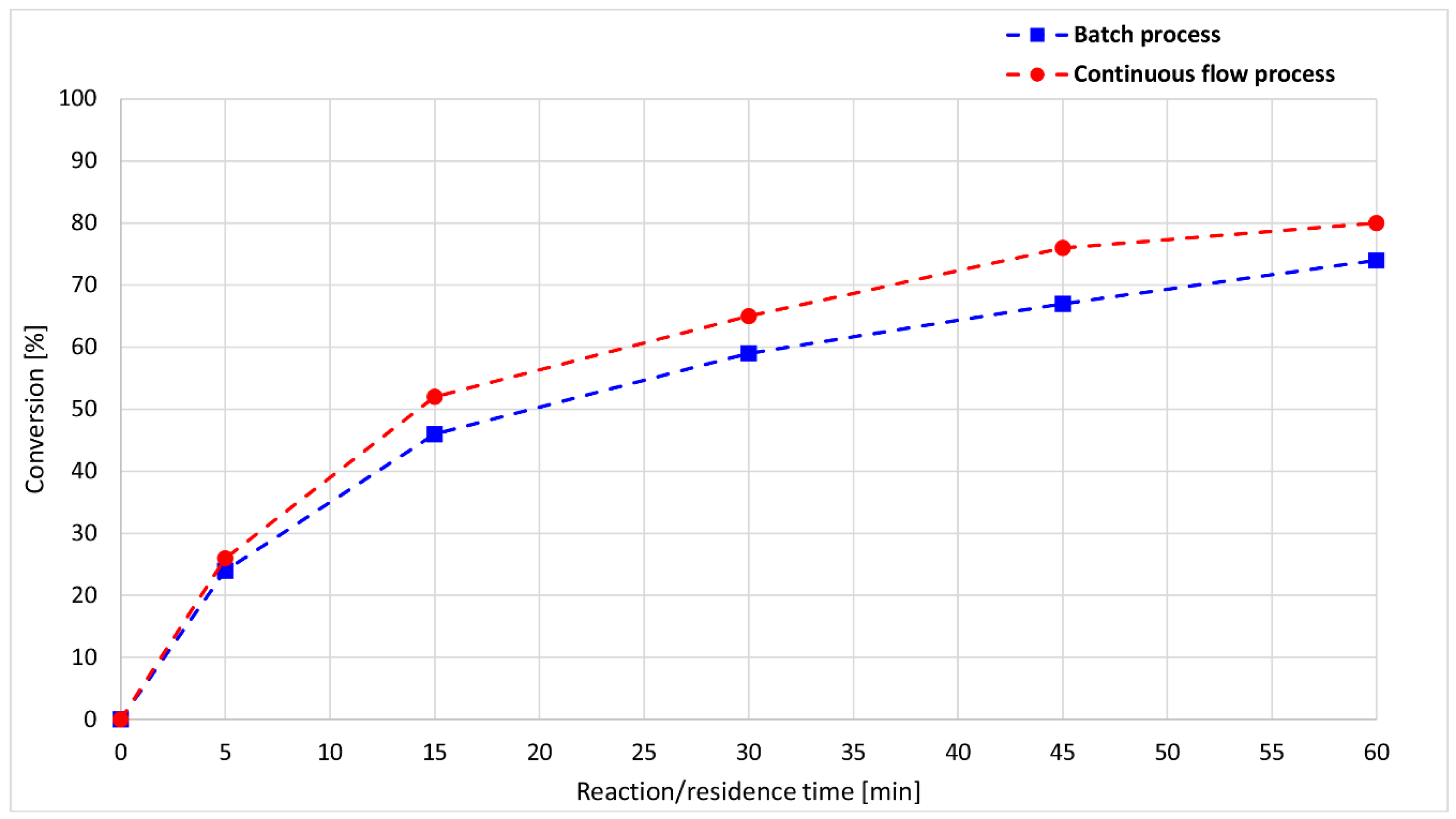
| Entry | t (min) | Conversion (%) | Composition (%) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2a | 3a | |||
| 1 | 5 | 24 | 76 | 20 | 4 |
| 2 | 15 | 46 | 54 | 37 | 9 |
| 3 | 30 | 59 | 41 | 47 | 12 |
| 4 | 45 | 67 | 33 | 49 | 18 |
| 5 | 60 | 73 | 26 | 45 | 29 |

| Entry | R | Power (W) | T (°C) a | Composition (%) b | Yield (%) c | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |||||
| 1 | nPr | 10 | 100 | 45 | 46 | 9 | 42 (2b) |
| 2 | 57 | 175 | 0 | 10 | 90 | 85 (3b) | |
| 3 | iBu | 10 | 100 | 38 | 51 | 11 | 46 (2c) |
| 4 | 71 | 175 | 0 | 10 | 90 | 86 (3c) | |
| 5 | nPent | 10 | 100 | 32 | 55 | 13 | 51 (2d) |
| 6 | 55 | 175 | 0 | 8 | 92 | 88 (3d) | |

| Entry | R | Power (W) | T (°C) a | Composition (%) b | Yield (%) c | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 5 | 3 | |||||
| 1 | nBu | 10 | 100 | 58 | 34 | 8 | - |
| 2 | 17 | 125 | 44 | 42 | 14 | 38 (5a) | |
| 3 | 38 | 150 | 7 | 32 | 61 | - | |
| 4 | 57 | 175 | 0 | 11 | 89 d,e | 85 (3a) | |
| 5 | nPr | 18 | 125 | 51 | 41 | 8 | 36 (5b) |
| 6 | 54 | 175 | 4 | 22 | 74 | – | |
| 7 | 83 | 200 | 2 | 14 | 84 d,e | 78 (3b) | |
| 8 | iBu | 21 | 125 | 21 | 40 | 39 | 36 (5c) |
| 9 | 63 | 175 | 3 | 26 | 71 | – | |
| 10 | 105 | 200 | 0 | 16 | 84 d,e | 77 (3c) | |
| 11 | nPent | 10 | 125 | 31 | 44 | 25 | 40 (5d) |
| 12 | 39 | 175 | 2 | 13 | 85 d,e | 80 (3d) | |
| Compound | δP (CDCl3) | δP [Ref] | [M + H]+found | [M + H]+requires |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2a | 9.3 (695.0) | 9.3 [52] | 153.0684 | 153.0681 |
| 2b | 9.3 (695.4) | ‒ | 139.0522 | 139.0523 |
| 2c | 6.7 (695.7) | ‒ | 153.0676 | 153.0681 |
| 2d | 6.8 (695.2) | ‒ | 167.0833 | 167.0837 |
| 3a | 7.8 | 7.9 [66] | 195.1153 | 195.1150 |
| 3b | 7.9 | 7.8 [67] | 167.0833 | 167.0837 |
| 3c | 8.1 | 8.0 [67] | 195.1145 | 195.1150 |
| 3d | 7.8 | 8.1 [68] | 223.1462 | 223.1463 |
| 5a | 7.6 (693.0) | 7.6 [52] | 167.0840 | 167.0837 |
| 5b | 8.6 (692.4) | ‒ | 153.0673 | 153.0681 |
| 5c | 7.8 (692.8) | ‒ | 167.0832 | 167.0837 |
| 5d | 7.7 (692.1) | 7.7 [52] | 181.0992 | 181.0994 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bálint, E.; Tajti, Á.; Tóth, N.; Keglevich, G. Continuous Flow Alcoholysis of Dialkyl H-Phosphonates with Aliphatic Alcohols. Molecules 2018, 23, 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071618
Bálint E, Tajti Á, Tóth N, Keglevich G. Continuous Flow Alcoholysis of Dialkyl H-Phosphonates with Aliphatic Alcohols. Molecules. 2018; 23(7):1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071618
Chicago/Turabian StyleBálint, Erika, Ádám Tajti, Nóra Tóth, and György Keglevich. 2018. "Continuous Flow Alcoholysis of Dialkyl H-Phosphonates with Aliphatic Alcohols" Molecules 23, no. 7: 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071618
APA StyleBálint, E., Tajti, Á., Tóth, N., & Keglevich, G. (2018). Continuous Flow Alcoholysis of Dialkyl H-Phosphonates with Aliphatic Alcohols. Molecules, 23(7), 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071618







