Hypoglycemic Effects in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats of the Phenolic Extract from Mongolian Oak Cups Enriched in Ellagic Acid, Kaempferol and Their Derivatives
Abstract
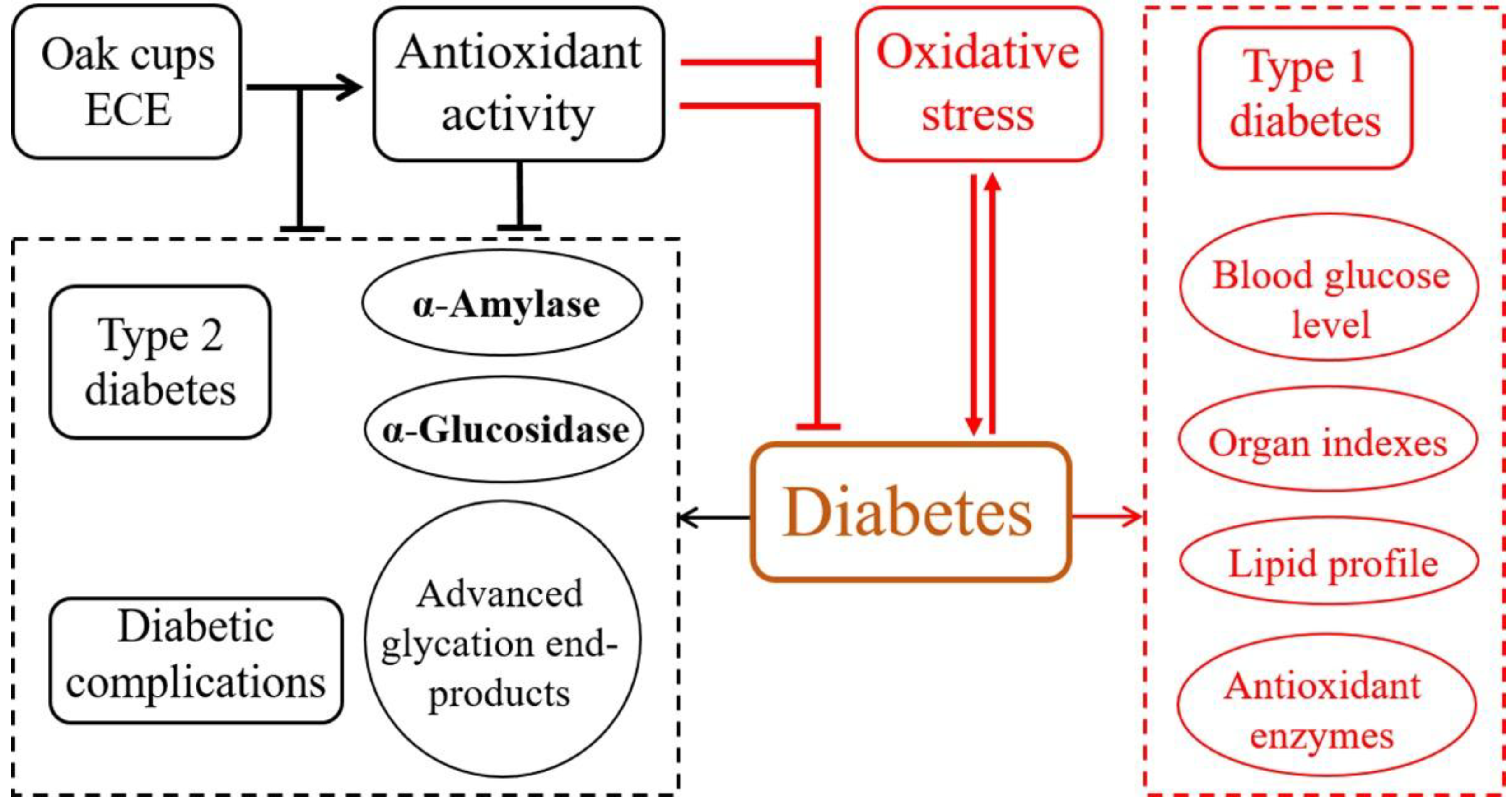
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
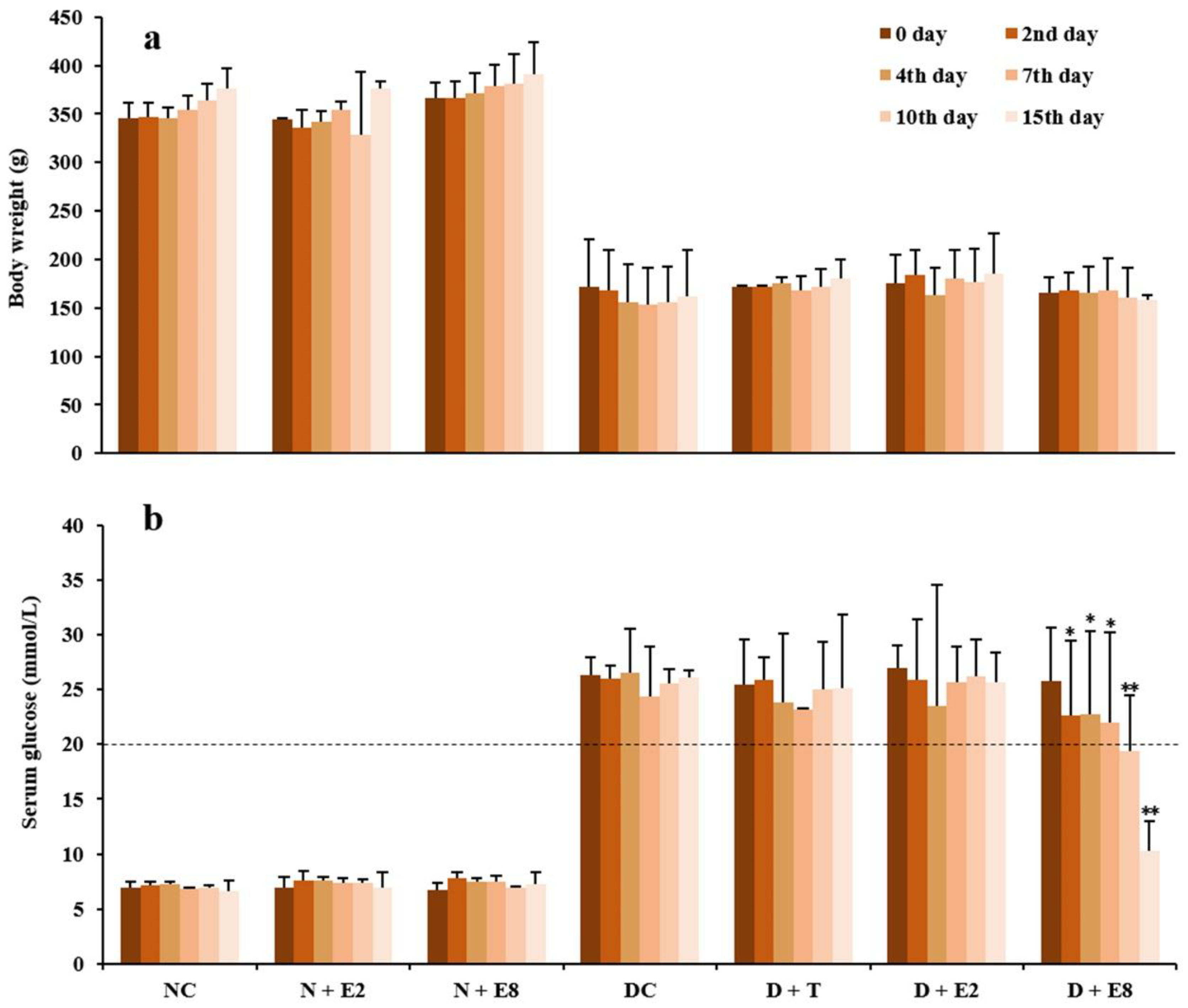
2.1. Effects of ECE on Fasting Blood Glucose of Normal and Diabetic Rats
2.2. Lipid Profiles and AST Levels in Serum of Normal and Diabetic Rats
2.2.1. Effects of ECE on Serum Lipid Profiles
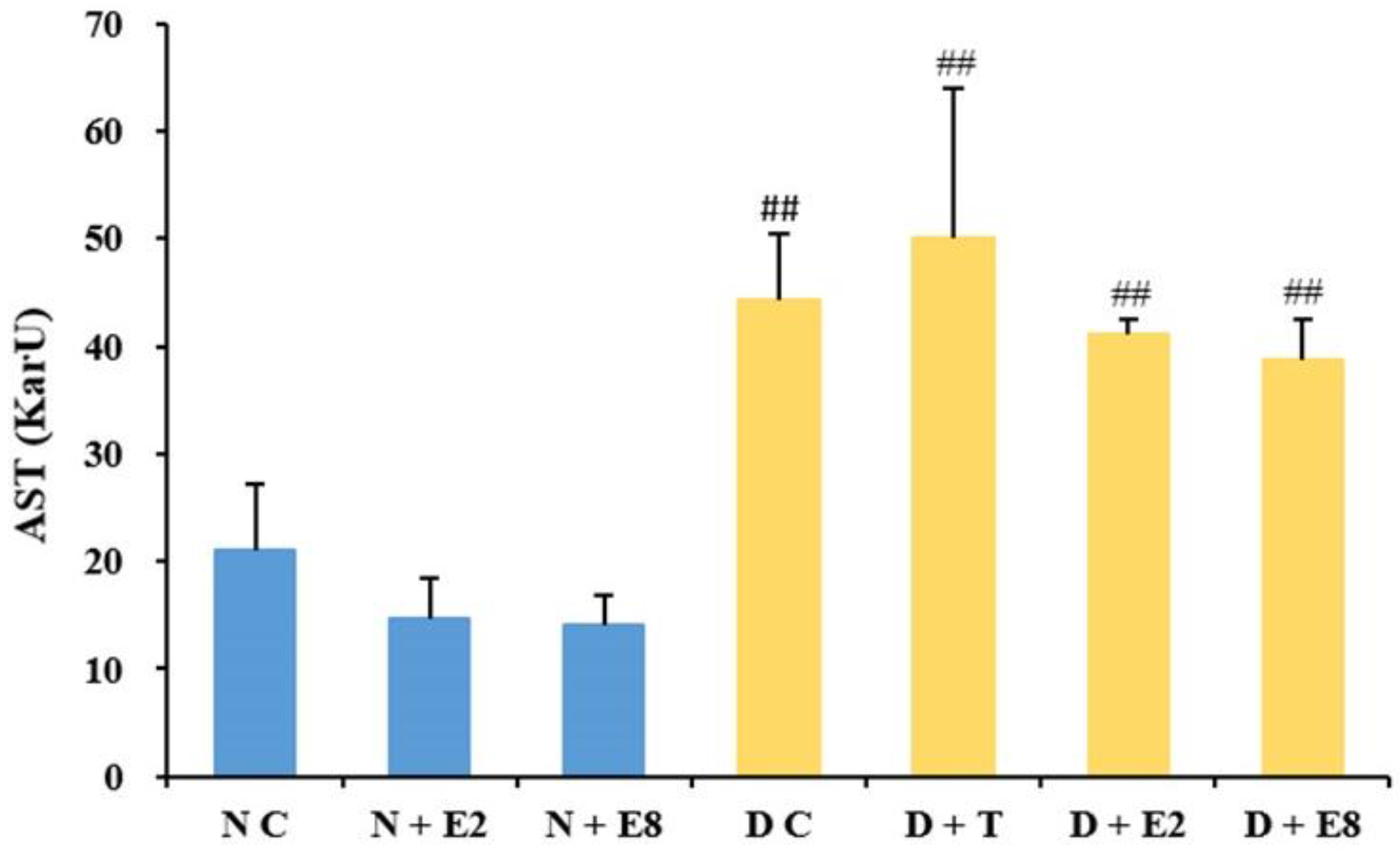
2.2.2. Effects of ECE on Serum AST Levels
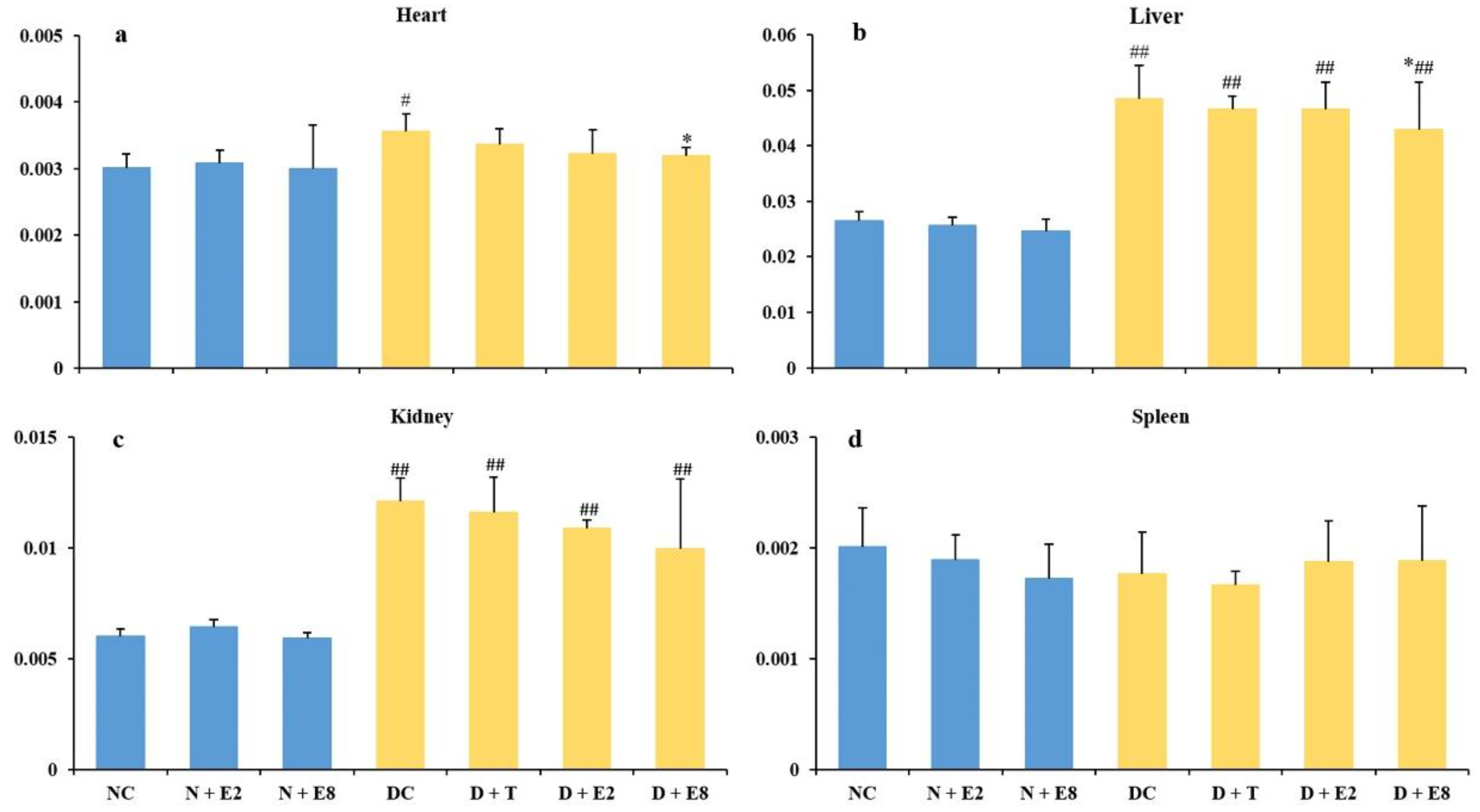
2.3. Effects of ECE on Four Organ Indexes of Normal and Diabetic Rats
2.4. Antioxidant Activities of ECE in Organs of Normal and Diabetic Rats
2.4.1. Effects of ECE on GSH Levels
2.4.2. Effects of ECE on MDA Levels
2.4.3. Effects of ECE on SOD Activities
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Animals
3.2. Preparation of Ethanol Crude Extract from Mongolian Oak Cups
3.3. Induction of Experimental Diabetes
3.4. Experimental Design
3.5. Blood Tests of Lipid Profile and AST Level
3.6. Determination of Three Antioxidant Indicators
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, P.; Yang, L.; Xue, Q.; Yu, M.; Yao, F.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y. Identification and inhibitory activities of ellagic acid- and kaempferol-derivatives from Mongolian oak cups against α-glucosidase, α-amylase and protein glycation linked to type II diabetes and its complications and their influence on HepG2 cells’ viability. Arab. J. Chem. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramar, M.; Manikandan, B.; Raman, T.; Priyadarsini, A.; Palanisamy, S.; Velayudam, M.; Munusamy, A.; Marimuthu Prabhu, N.; Vaseeharan, B. Protective effect of ferulic acid and resveratrol against alloxan-induced diabetes in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 690, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buko, V.; Zavodnik, I.; Kanuka, O.; Belonovskaya, E.; Naruta, E.; Lukivskaya, O.; Kirko, S.; Budryn, G.; Żyżelewicz, D.; Oracz, J. Antidiabetic effects and erythrocyte stabilization by red cabbage extract in streptozotocin-treated rats. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 1850–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juarez-Reyes, K.; Brindis, F.; Medina-Campos, O.N.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Bye, R.; Linares, E.; Mata, R. Hypoglycemic, antihyperglycemic, and antioxidant effects of the edible plant Anoda cristata. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 161, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, B.; Lv, F. Involvement of the PI3K/Akt signal pathway in the hypoglycemic effects of tea polysaccharides on diabetic mice. Int. J. Boil. Macromol. 2015, 81, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.; Zhao, S.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Shi, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Ma, C. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of polyphenols from burs of Castanea mollissima Blume. Molecules 2011, 16, 9764–9774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J.; Jin, H.; Zheng, S.L.; Xia, P.; Cai, Y.; Ni, X.J. Phytoecdysteroids from Ajuga iva act as potential antidiabetic agent against alloxan-induced diabetic male albino rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, K.K.M.; Chung, W.-S.; Leung, A.W.N.; Cheng, C.H.K. Redox changes precede the occurrence of oxidative stress in eyes and aorta, but not in kidneys of diabetic rats. Life. Sci. 2003, 73, 2557–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Hyun, T.K.; Kim, M.-J. The inhibitory effects of ethanol extracts from sorghum, foxtail millet and proso millet on α-glucosidase and α-amylase activities. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custódio, L.; Patarra, J.; Alberício, F.; Neng, N.D.R.; Nogueira, J.M.F.; Romano, A. Phenolic composition, antioxidant potential and in vitro inhibitory activity of leaves and acorns of Quercus suber on key enzymes relevant for hyperglycemia and Alzheimer’s disease. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 64, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Jimenez, M.R.; Trujillo-Esquivel, F.; Gallegos-Corona, M.A.; Reynoso-Camacho, R.; Gonzalez-Laredo, R.F.; Gallegos-Infante, J.A.; Rocha-Guzman, N.E.; Ramos-Gomez, M. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticarcinogenic activities of edible red oak (Quercus spp.) infusions in rat colon carcinogenesis induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 80, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmouzi, S. Optimization of polysaccharides from Zagros oak leaf using RSM: Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 106, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.; Yang, L.; Li, K.; Fan, H.; Xue, Q.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y. Bioactive components and antioxidant activities of oak cup crude extract and its four partially purified fractions by HPD-100 macroporous resin chromatography. Arab. J. Chem. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilova, I.G.; Bulavintceva, T.S.; Gette, I.F.; Medvedeva, S.Y.; Emelyanov, V.V.; Abidov, M.T. Partial recovery from alloxan-induced diabetes by sodium phthalhydrazide in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Chen, M.; Liang, B.; Xu, J.; Ye, T.; Xia, Z. Hypoglycemic effect of abandoned Porphyra haitanensis polysaccharides in alloxan-induced diabetic mice. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2016, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szkudelski, T. The mechanism of alloxan and streptozotocin action in B cells of the rat pancreas. Physiol. Res. 2001, 50, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ratzmann, K.P.; Schulz, B.; Heinke, P.; Besch, W. Tolbutamide does not alter insulin requirement in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes. Diabetologia 1984, 27, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.Z.; Chen, S.X.; Huang, S.; Jiang, D.X.; Zhou, C.J.; Chen, C.Q.; Liang, Y.M.; Lai, X.P. The hypoglycemic activity of Lithocarpus polystachyus Rehd. leaves in the experimental hyperglycemic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, G.; Manjula, P.; Paari, N. A review: Anti diabetic medicinal plants used for diabetes mellitus. J. Acute Dis. 2013, 2, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encarnação, S.; de Mello-Sampayo, C.; Graça, N.A.G.; Catarino, L.; da Silva, I.B.M.; Lima, B.S.; Silva, O.M.D. Total phenolic content, antioxidant activity and pre-clinical safety evaluation of an Anacardium occidentale stem bark Portuguese hypoglycemic traditional herbal preparation. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 82, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollica, A.; Zengin, G.; Locatelli, M.; Stefanucci, A.; Mocan, A.; Macedonio, G.; Carradori, S.; Onaolapo, O.; Onaolapo, A.; Adegoke, J.; et al. Anti-diabetic and anti-hyperlipidemic properties of Capparis spinosa L.: In vivo and in vitro evaluation of its nutraceutical potential. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 35, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollica, A.; Zengin, G.; Locatelli, M.; Stefanucci, A.; Macedonio, G.; Bellagamba, G.; Onaolapo, O.; Onaolapo, A.; Azeez, F.; Ayileka, A.; et al. An assessment of the nutraceutical potential of Juglans regia L. leaf powder in diabetic rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 107 Pt B, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollica, A.; Stefanucci, A.; Macedonio, G.; Locatelli, M.; Luisi, G.; Novellino, E.; Zengin, G. Chemical composition and biological activity of Capparis spinosa L. from Lipari Island. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedge, M.; Lortz, S.; Drinkgern, J.; Lenzen, S. Relation between antioxidant enzyme gene expression and antioxidative defense status of insulin-producing cells. Diabetes 1997, 46, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, W.Y.; Wang, H.; Waisundara, V.Y.; Huang, D. Inhibiting enzymatic starch digestion by hydrolyzable tannins isolated from Eugenia jambolana. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakulnarmrat, K.; Konczak, I. Composition of native Australian herbs polyphenolic-rich fractions and in vitro inhibitory activities against key enzymes relevant to metabolic syndrome. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picot, M.C.N.; Zengin, G.; Mollica, A.; Stefanucci, A.; Carradori, S.; Mahomoodally, M.F. In vitro and in silico Studies of Mangiferin from Aphloia theiformis on Key Enzymes Linked to Diabetes Type 2 and Associated Complications. Med. Chem. 2017, 13, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, R.; Varshney, R.; Mishra, R.; Roy, P. Kaempferol alleviates palmitic acid-induced lipid stores, endoplasmic reticulum stress and pancreatic β-cell dysfunction through AMPK/mTOR-mediated lipophagy. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Igarashi, K.; Yu, C. The anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects of kaempferol glycosides from unripe soybean leaves in high-fat-diet mice. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Dai, Y.; Peng, J. Natural products for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Pharmacology and mechanisms. Pharmacol. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanović, I.; Šavikin, K.; Đedović, N.; Živković, J.; Saksida, T.; Momčilović, M.; Koprivica, I.; Vujičić, M.; Stanisavljević, S.; Miljković, Đ.; et al. Pomegranate peel extract ameliorates autoimmunity in animal models of multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 35, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Yang, H.; Tang, C.; Yao, G.; Kong, L.; He, H.; Zhou, Y. Kaempferol alleviates insulin resistance via hepatic IKK/NF-kappaB signal in type 2 diabetic rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi-Madiseh, M.; Heidarian, E.; Kheiri, S.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Effect of hydroalcoholic Allium ampeloprasum extract on oxidative stress, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 86, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Sharma, S.B.; Bansal, S.K.; Prabhu, K.M. Antihyperglycemic and hypolipidemic activity of aqueous extract of Cassia auriculata L. leaves in experimental diabetes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 123, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgary, S.; Kelishadi, R.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Najafi, S.; Najafi, M.; Sahebkar, A. Investigation of the lipid-modifying and antiinflammatory effects of Cornus mas L. supplementation on dyslipidemic children and adolescents. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2013, 34, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Yin, P.; Fan, H.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y. Flaxseed oil ameliorates alcoholic liver disease via anti-inflammation and modulating gut microbiota in mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihailović, M.; Živković, M.; Jovanović, J.A.; Tolinački, M.; Sinadinović, M.; Rajić, J.; Uskoković, A.; Dinić, S.; Grdović, N.; Golić, N.; et al. Oral administration of probiotic Lactobacillus paraplantarum BGCG11 attenuates diabetes-induced liver and kidney damage in rats. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhor, V.M.; Raghuram, N.; Sivakami, S. Oxidative damage and altered antioxidant enzyme activities in the small intestine of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoyamanaka, N.; Yamanaka, H.; Nagasawa, S. Glutathione-related detoxication functions in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1993, 55, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, M.; Orhan, N.; Orhan, D.D.; Ergun, F. Hypoglycemic activity and antioxidant potential of some medicinal plants traditionally used in Turkey for diabetes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 128, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orhan, D.D.; Aslan, M.; Sendogdu, N.; Ergun, F.; Yesilada, E. Evaluation of the hypoglycemic effect and antioxidant activity of three Viscum album subspecies (European mistletoe) in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 98, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, Y.; Zaltzberg, H.; Ben-Amotz, A.; Kanter, Y.; Aviram, M. β-Carotene affects antioxidant status in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Pathophysiology 1999, 6, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Zhang, J.; Yan, L.; Yang, L.; Sun, L.; Shi, L.; Ma, C.; Liu, Y. Urolithin C, a gut metabolite of ellagic acid, induces apoptosis in PC12 cells through a mitochondria-mediated pathway. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 17254–17263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oršolić, N.; Bašić, I.; Govil, J.N.; Singh, V.K. Honey bee products and their polyphenolic compounds in treatment of diabetes. Phytopharmacol. Ther. Values IV 2008, 22, 455–553. [Google Scholar]
- Ugochukwu, N.H.; Babady, N.E. Antihyperglycemic effect of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Gongronema latifolium leaves on glucose and glycogen metabolism in livers of normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Life Sci. 2003, 73, 1925–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, M.; Matuo, T.; Tsuno, T.; Hosoda, A.; Nomura, E.; Taniguchi, H.; Sasaki, H.; Morishita, H. Antioxidant activity and hypoglycemic effect of ferulic acid in STZ-induced diabetic mice and KK-Ay mice. BioFactors 2004, 21, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
| Group | Cholesterol | Triglyceride | HDL | LDL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 1.562 ± 0.319 | 0.286 ± 0.057 | 1.730 ± 0.466 | 0.407 ± 0.033 |
| N + E2 | 1.517 ± 0.258 | 0.548 ± 0.058 | 0.742 ± 0.142 # | 0.735 ± 0.045 ## |
| N + E8 | 1.385 ± 0.116 | 0.354 ± 0.110 | 0.745 ± 0.104 # | 0.677 ± 0.230 ## |
| DC | 2.760 ± 0.198 ## | 2.001 ± 0.380 ## | 1.107 ± 0.018 # | 0.793 ± 0.186 # |
| D + T | 3.056 ± 0.177 ## | 2.057 ± 0.163 ## | 1.553 ± 0.094 *# | 0.742 ± 0.179 # |
| D + E2 | 2.459 ± 0.383 # | 1.134 ± 0.244 ##* | 1.243 ± 0.157 # | 0.728 ± 0.164 # |
| D + E8 | 1.947 ± 0.453 * | 0.860 ± 0.563 * | 1.670 ± 0.303 * | 0.648 ± 0.158 # |
| Group | GSH ± SEM (μmol/g prot) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart | Liver | Kidney | Spleen | |
| NC | 0.50 ± 0.10 | 2.53 ± 0.30 | 1.10 ± 0.12 | 5.68 ± 0.14 |
| N + E2 | 0.47 ± 0.09 | 2.50 ± 1.35 | 1.02 ± 0.44 | 5.70 ± 1.06 |
| N + E8 | 0.48 ± 0.19 | 2.72 ± 0.37 | 1.08 ± 0.13 | 5.78 ± 0.11 |
| DC | 0.59 ± 0.04 # | 2.74 ± 0.23 | 1.38 ± 0.33 | 9.98 ± 4.54 # |
| D + T | 0.48 ± 0.20 | 1.82 ± 0.29 *# | 1.51 ± 0.32 | 7.12 ± 0.40 # |
| D + E2 | 0.37 ± 0.12 ** | 2.52 ± 0.36 | 1.43 ± 0. 36 | 6.62 ± 1.56 |
| D + E8 | 0.32 ± 0.04 **# | 1.78 ± 0.29 *# | 1.17 ± 0.27 | 7.33 ± 1.69 |
| Group | MDA ± SEM (μmol /mg prot) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart | Liver | Kidney | Spleen | |
| NC | 0.94 ± 0.17 | 1.20 ± 0.40 | 0.12 ± 0.06 | 1.24 ± 0.80 |
| N + E2 | 0.93 ± 0.40 | 1.41 ± 0.95 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 1.26 ± 0.11 |
| N + E8 | 0.78 ± 0.08 | 1.19 ± 0.12 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 1.07 ± 0.22 |
| DC | 1.22 ± 0.48 # | 3.54 ± 1.32 ## | 0.17 ± 0.04 # | 1.31 ± 0.13 |
| D + T | 0.60 ± 0.51 * | 3.10 ± 0.48 ## | 0.08 ± 0.04 * | 1.04 ± 0.65 |
| D + E2 | 0.91 ± 0.06 * | 3.40 ± 1.64 ## | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 1.27 ± 0.19 |
| D + E8 | 0.94 ± 0.05 * | 2.95 ± 0.43 ## | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 1.25 ± 0.26 |
| Group | SOD ± SEM (kNU/g prot) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart | Liver | Kidney | Spleen | |
| NC | 117.46 ± 7.37 | 115.61 ± 17.05 | 118.66 ± 5.63 | 130.00 ± 17.96 |
| N + E2 | 126.77 ± 14.16 | 119.21 ± 30.49 | 115.98 ± 9.76 | 121.22 ± 26.09 |
| N + E8 | 141.75 ± 6.56 # | 114.57 ± 28.75 | 116.83 ± 15.93 | 131.48 ± 6.22 |
| DC | 99.27 ± 3.28 # | 106.76 ± 6.27 ## | 89.46 ± 12.02 ## | 96.02 ± 4.49 # |
| D + T | 105.48 ± 11.15 | 102.69 ± 13.15 | 103.94 ± 34.42 * | 118.43 ± 16.59 * |
| D + E2 | 111.08 ± 19.69 * | 121.07 ± 8.95 *## | 102.98 ± 22.98 * | 122.87 ± 31.40 * |
| D + E8 | 108.19 ± 14.81 * | 118.82 ± 21.77 *## | 113.18 ± 19.02 * | 125.14 ± 13.39 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Sui, J.; Liu, Y. Hypoglycemic Effects in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats of the Phenolic Extract from Mongolian Oak Cups Enriched in Ellagic Acid, Kaempferol and Their Derivatives. Molecules 2018, 23, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051046
Yin P, Wang Y, Yang L, Sui J, Liu Y. Hypoglycemic Effects in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats of the Phenolic Extract from Mongolian Oak Cups Enriched in Ellagic Acid, Kaempferol and Their Derivatives. Molecules. 2018; 23(5):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051046
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Peipei, Yu Wang, Lingguang Yang, Jinling Sui, and Yujun Liu. 2018. "Hypoglycemic Effects in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats of the Phenolic Extract from Mongolian Oak Cups Enriched in Ellagic Acid, Kaempferol and Their Derivatives" Molecules 23, no. 5: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051046
APA StyleYin, P., Wang, Y., Yang, L., Sui, J., & Liu, Y. (2018). Hypoglycemic Effects in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats of the Phenolic Extract from Mongolian Oak Cups Enriched in Ellagic Acid, Kaempferol and Their Derivatives. Molecules, 23(5), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051046