Hyperjaponol H, A New Bioactive Filicinic Acid-Based Meroterpenoid from Hypericum japonicum Thunb. ex Murray
Abstract
1. Introduction
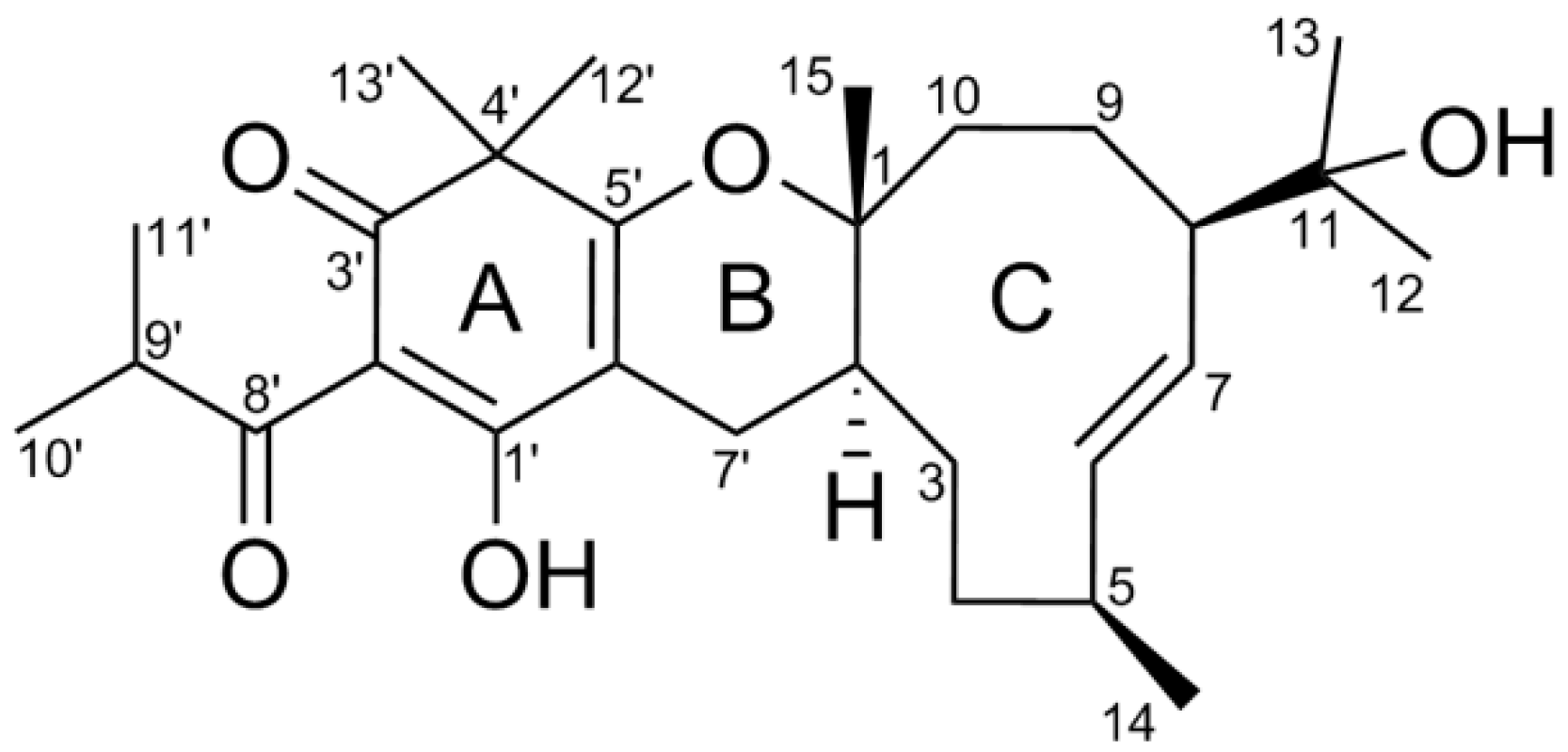
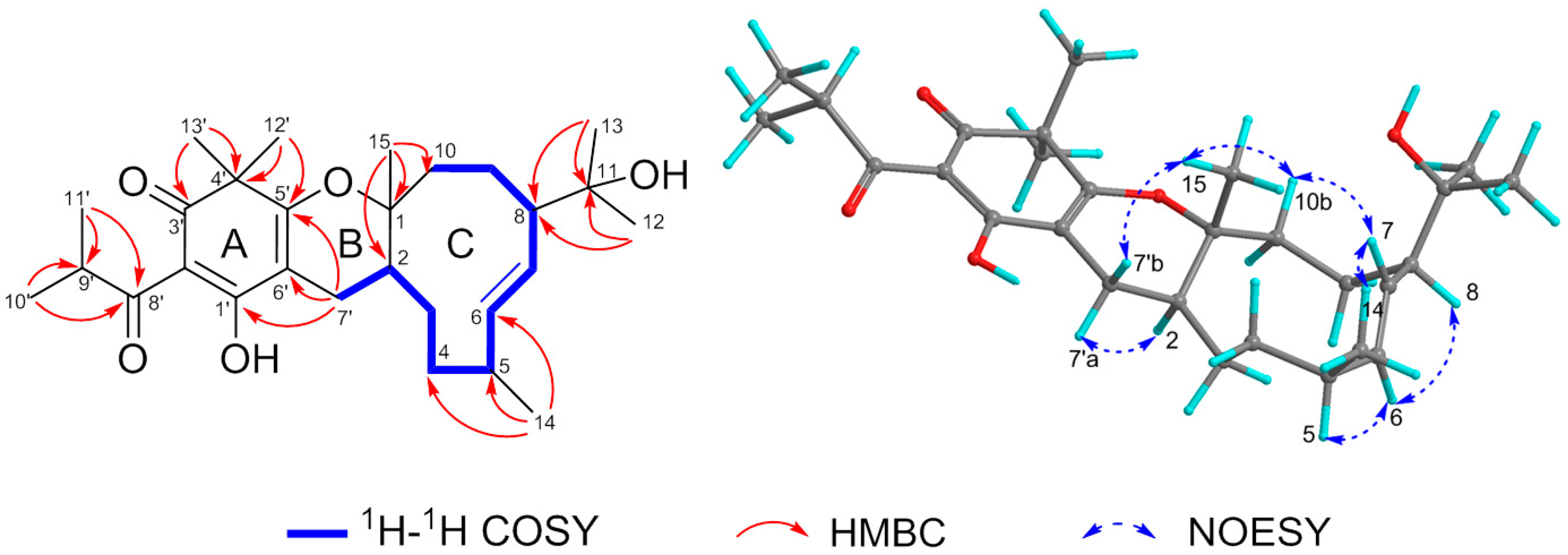
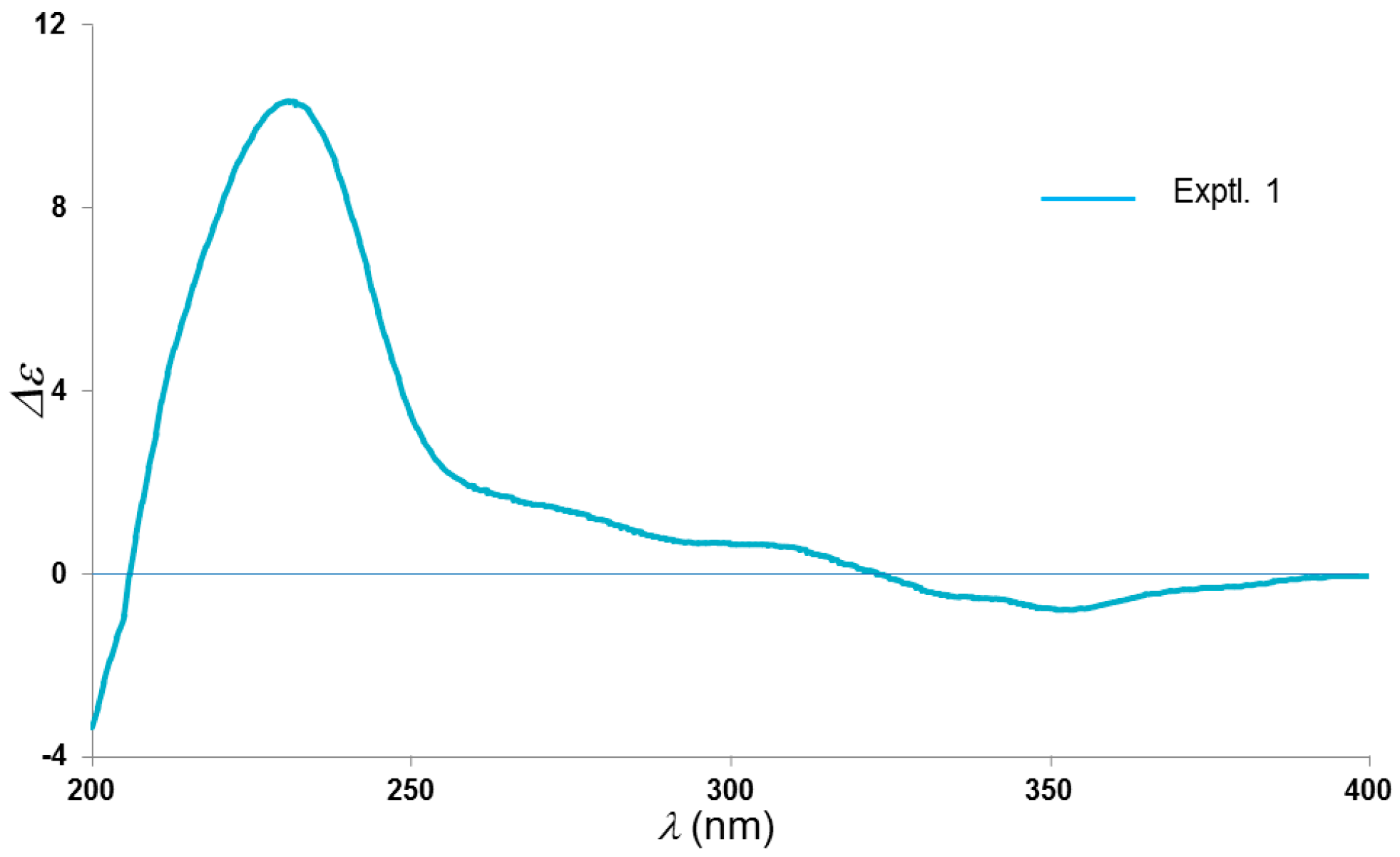
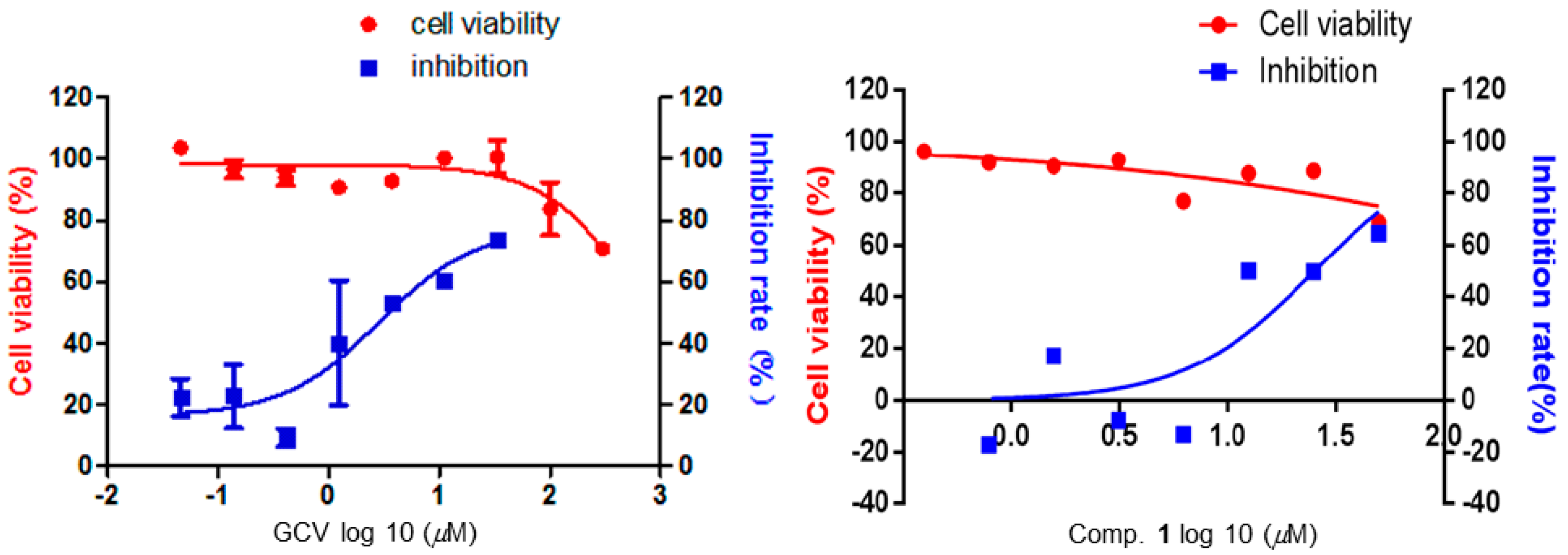
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experiments
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Anti-EBV Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, I.P.; Sidana, J.; Bansal, P.; Foley, W.J. Phloroglucinol compounds of therapeutic interest: Global patent and technology status. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2009, 19, 847–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenning, A.J.; Boyce, J.H.; Porco, J.A., Jr. Rapid synthesis of polyprenylated acylphloroglucinol analogs via dearomative conjunctive allylic annulation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11799–11804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, I.P.; Sidana, J.; Bharate, S.B.; Foley, W.J. Phloroglucinol compounds of natural origin: Synthetic aspects. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 393–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Mi, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y. Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetic study of eight components in rat plasma by UHPLC-MS/MS after oral administration of Hypericum japonicum Thunb extract. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 118, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.S.; Liu, M.H.; He, J.Y. Hypericum japonicum Thunb. ex Murray: phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality control and pharmacokinetics of an important herbal medicine. Molecules 2014, 19, 10733–10754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.L.; Wang, S.P.; Zhang, S.M.; Yang, J.S.; Xiao, P.G. Chromone glycosides and flavonoids from Hypericum japonicum. Phytochemistry 1998, 49, 1417–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.D.; Fu, P.; Liu, R.H.; Li, T.Z.; Li, H.L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H.S. A new bisxanthone from Hypericum japonicum. Fitoterapia 2007, 78, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.S.; Padalia, R.C.; Chauhan, A.; Chanotiya, C.S.; Yadav, A. Chemical composition of the aliphatic compounds rich essential oil of Hypericum japonicum Thunb. ex Murray from India. J. Essent. Oil. Res. 2012, 24, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Mao, Y.; Wang, N.L.; Yao, X.S. A new phloroglucinol diglycoside derivative from Hypericum japonicum Thunb. Molecules 2008, 13, 2796–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiguro, K.; Nagata, S.; Fukumoto, H.; Yamaki, M.; Isoi, K. Phloroglucinol derivatives from Hypericum japonicum. Phytochemistry 1994, 35, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.H.; Khoo, C.W.; Vittal, J.J.; Sim, K.Y. Phloroglucinol derivatives from Hypericum japonicum. Phytochemistry 2000, 53, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Chen, C.; Yang, J.; Li, X.N.; Liu, J.; Sun, B.; Huang, S.X.; Li, D.; Yao, G.; Luo, Z.; et al. Bioactive acylphloroglucinols with adamantyl skeleton from Hypericum sampsonii. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 6322–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Chen, C.; Liu, J.; Sun, B.; Wei, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yao, G.; Luo, Z.; Xue, Y.; et al. Hyperascyrones A–H, polyprenylated spirocyclic acylphloroglucinol derivatives from Hypericum ascyron Linn. Phytochemistry 2015, 115, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Xue, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, B.; Liu, J.; Yao, G.; Zhang, J.; Du, G.; Zhang, Y. Hyperattenins A–I, bioactive polyprenylated acylphloroglucinols from Hypericum attenuatum Choisy. RSC. Adv. 2015, 5, 5277–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, N.; Chen, C.; Huang, J.; Li, X.N.; Liu, J.; Zhu, H.; Tong, Q.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Z.; et al. Tricyclic polyprenylated acylphloroglucinols from St John′s Wort, Hypericum perforatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Li, X.N.; Sun, W.; Zeng, J.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y. Filicinic acid-based meroterpenoids with anti-Epstein-Barr virus activities from Hypericum japonicum. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 2272–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiguro, K.; Yamaki, M.; Takagi, S.; Yamaga, Y.; Tomita, K. X-ray crystal structure of sarothralin, a novel antibiotic compound from Hypericum japonicum. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1985, 26–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, K.; Yamaki, M.; Kashihara, M.; Takagi, S. Sarothralen A and B from H. japomicum. Planta Med. 1986, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.P.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Feng, G.K.; Du, Y.; Xiong, D.; Zhong, Q.; Liu, W.L.; Du, H.; Li, M.Z.; Huang, W.L.; Tsao, S.W.; Hutt Fletcher, L.; Zeng, Y.X.; Kieff, E.; Zeng, M.S. Neuropilin 1 is an entry factor that promotes EBV infection of nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6240–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, F.M.; Gomez, V.E.; Albuquerque, E.M.; Klumb, E.M.; Shoenfeld, Y. Lupus and leprosy: Beyond the coincidence. Immunol. Res. 2015, 61, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafini, B.; Rosicarelli, B.; Franciotta, D.; Magliozzi, R.; Reynolds, R.; Cinque, P.; Andreoni, L.; Trivedi, P.; Salvetti, M.; Faggioni, A.; et al. Dysregulated Epstein-Barr virus infection in the multiple sclerosis brain. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2899–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balandraud, N.; Roudier, J.; Roudier, C. Epstein-Barr virus and rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2004, 3, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billaud, G.; Thouvenot, D.; Morfin, F. Drug targets in herpes simplex and Epstein Barr virus infections. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2009, 9, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coen, D.M.; Schaffer, P.A. Antiherpesvirus drugs: a promising spectrum of new drugs and drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.J.; Sun, H.X.; Mo, X.M.; Li, S.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, H.A. Development of a broad-spectrum antiviral agent with activity against herpesvirus replication and gene expression. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballout, M.; Germi, R.; Fafi-Kremer, S.; Guimet, J.; Bargues, G.; Seigneurin, J.M.; Morand, P. Real-time quantitative PCR for assessment of antiviral drug effects against Epstein-Barr virus replication and EBV late mRNA expression. J. Virol. Methods 2007, 143, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedmer, A.; Wang, P.; Zhou, J.; Rennekamp, A.J.; Tiranti, V.; Zeviani, M.; Lieberman, P.M. Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early protein Zta co-opts mitochondrial single-stranded DNA binding protein to promote viral and inhibit mitochondrial DNA replication. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 4647–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, S.J.; Vervoort, M.B.; van den Brule, A.J.; Meenhorst, P.L.; Meijer, C.J.; Middeldorp, J.M. Monitoring of Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in peripheral blood by quantitative competitive PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2852–2857. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Asahi Ozaki, Y.; Sato, Y.; Kanno, T.; Sata, T.; Katano, H. Quantitative analysis of Kaposi Sarcoma–Associated Herpesvirus (KSHV) in KSHV-associated diseases. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 193, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compound 1 are available from the authors. |
| Position | δH (J) | δC | Position | δH (J) | δC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 84.9 | 14 | 1.00 d (7.0) | 16.4 | |
| 2 | 1.47 m | 36.1 | 15 | 1.02 s | 21.3 |
| 3 | 0.91 m | 25.2 | 1′ | 188.7 | |
| 1.32 m | 2′ | 104.6 | |||
| 4 | 1.58 m | 31.4 | 3′ | 197.1 | |
| 1.51 m | 4′ | 48.5 | |||
| 5 | 2.65 m | 33.9 | 5′ | 173.1 | |
| 6 | 5.59 dd (16.2, 4.7) | 136.8 | 6′ | 101.9 | |
| 7 | 5.47 d (16.2, 8.0) | 127.5 | 7′ | 2.74 dd (16.6, 5.2) | 21.8 |
| 8 | 2.31 t (7.0) | 50.0 | 1.69 dd (16.6, 11.3) | ||
| 9 | 1.90 m | 24.7 | 8′ | 207.9 | |
| 1.43 m | 9′ | 3.93 sept (13.5, 6.7) | 35.5 | ||
| 10 | 1.79 ddd (14.7, 10.0, 4.5) | 32.1 | 10′ | 1.10 d (6.7) | 19.15 |
| 2.03 dt (14.8, 3.9) | 11′ | 1.11 d (6.7) | 19.24 | ||
| 11 | 73.0 | 12′ | 1.24 s | 24.1 | |
| 12 | 1.19 s | 27.9 | 13′ | 1.29 s | 25.4 |
| 13 | 1.20 s | 28.7 |
| Compounds | CC50 a | EC50 b | Selectivity Index (CC50/EC50) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GCV | >300 | 2.86 | >104.50 |
| 1 | >50 | 25.00 | >2 |
| (+)-hyperjaponol A | >41.35 | 10.33 | >4.00 |
| (−)-hyperjaponol A | >300 | 119.4 | >2.50 |
| (+)-hyperjaponol B | >30 | 0.57 | >52.63 |
| (−)-hyperjaponol B | >120 | 6.60 | >18.18 |
| (+)-hyperjaponol C | 31.75 | − | − |
| (−)-hyperjaponol C | 17.78 | − | − |
| hyperjaponol D | 48.05 | 0.49 | 106.78 |
| hyperjaponol E | 60.49 | 17.53 | 3.45 |
| hyperjaponol F | 41.62 | 14.47 | 2.87 |
| hyperjaponol G | >300 | >300 | − |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, R.; Le, Z.; Wang, Z.; Tian, S.; Xue, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Y. Hyperjaponol H, A New Bioactive Filicinic Acid-Based Meroterpenoid from Hypericum japonicum Thunb. ex Murray. Molecules 2018, 23, 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030683
Wu R, Le Z, Wang Z, Tian S, Xue Y, Chen Y, Hu L, Zhang Y. Hyperjaponol H, A New Bioactive Filicinic Acid-Based Meroterpenoid from Hypericum japonicum Thunb. ex Murray. Molecules. 2018; 23(3):683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030683
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Rongrong, Zijun Le, Zhenzhen Wang, Shuying Tian, Yongbo Xue, Yong Chen, Linzhen Hu, and Yonghui Zhang. 2018. "Hyperjaponol H, A New Bioactive Filicinic Acid-Based Meroterpenoid from Hypericum japonicum Thunb. ex Murray" Molecules 23, no. 3: 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030683
APA StyleWu, R., Le, Z., Wang, Z., Tian, S., Xue, Y., Chen, Y., Hu, L., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Hyperjaponol H, A New Bioactive Filicinic Acid-Based Meroterpenoid from Hypericum japonicum Thunb. ex Murray. Molecules, 23(3), 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030683






