Functional Impact of the N-terminal Arm of Proline Dehydrogenase from Thermus thermophilus
Abstract
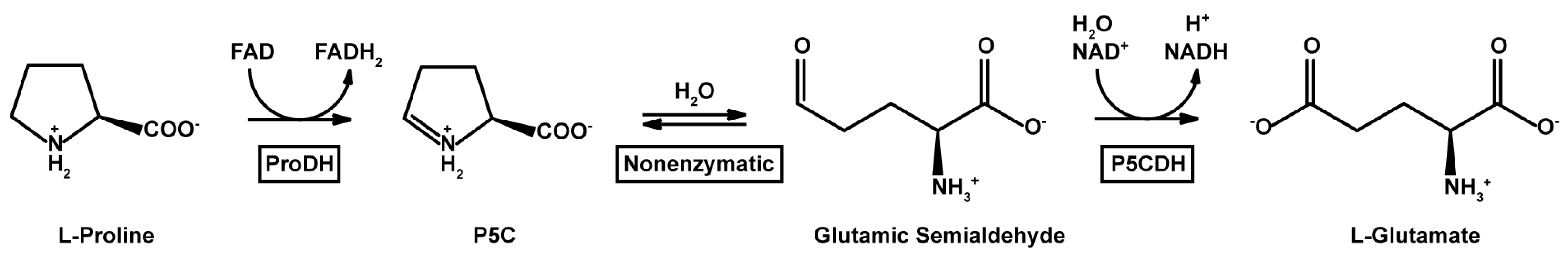
:1. Introduction
2. Results
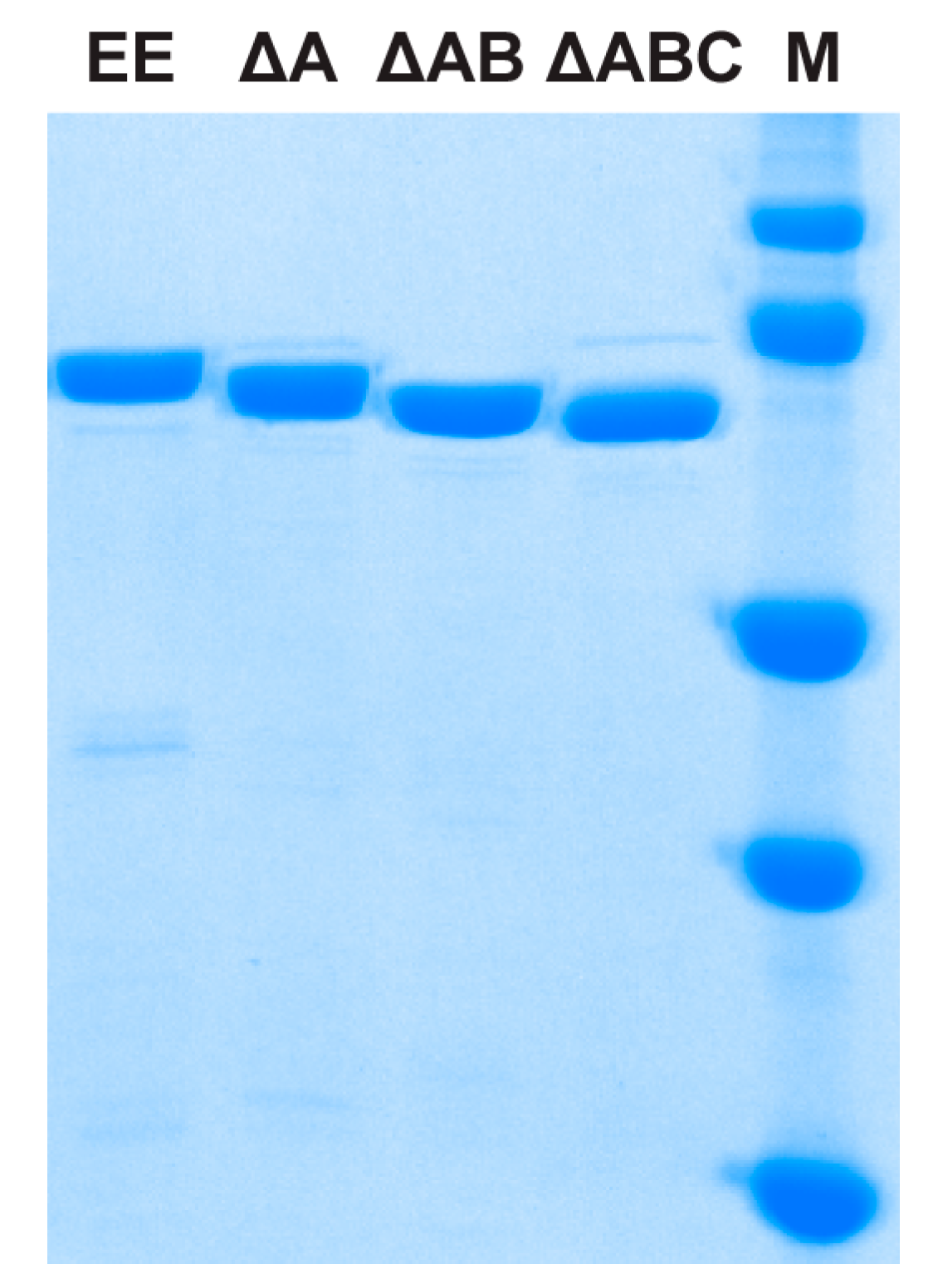
2.1. Protein Expression and Purification
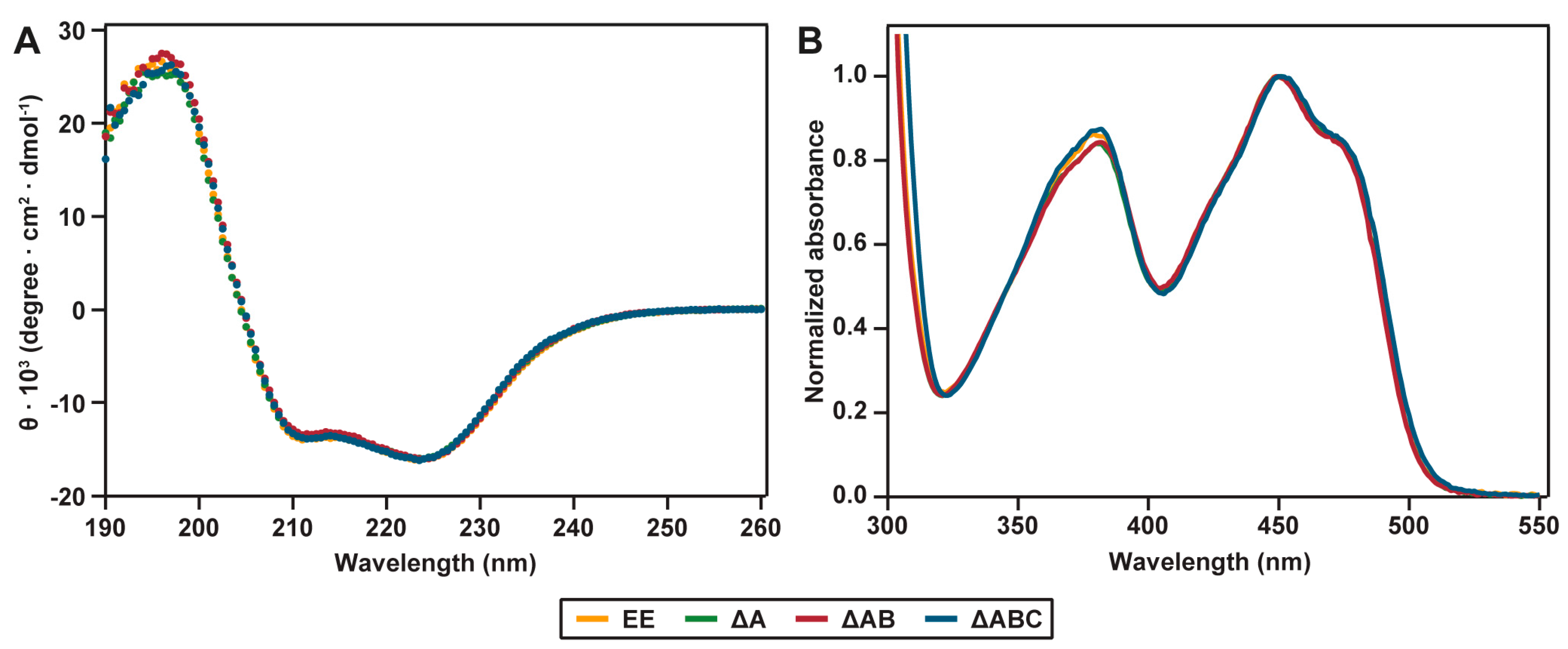
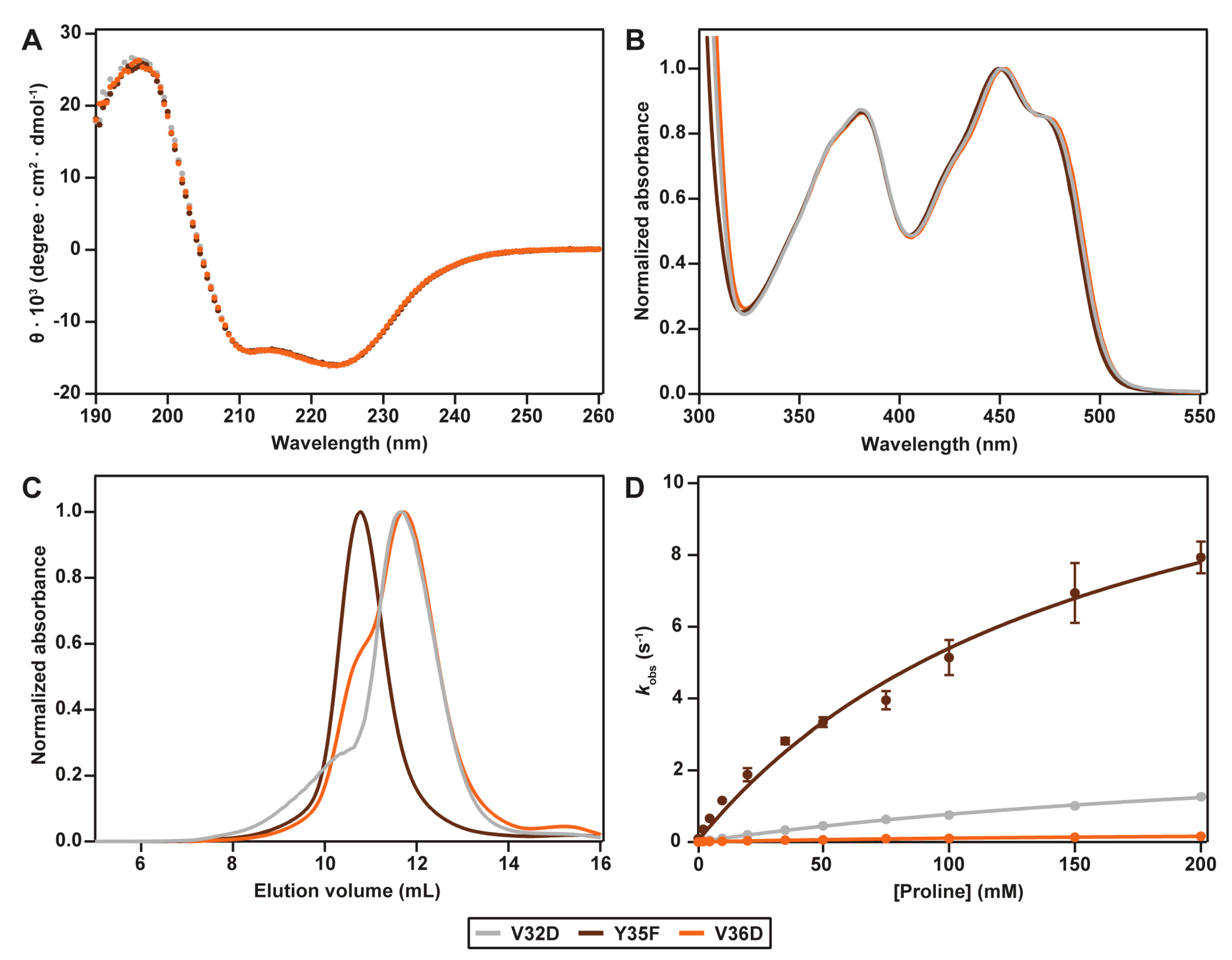
2.2. Spectral Properties
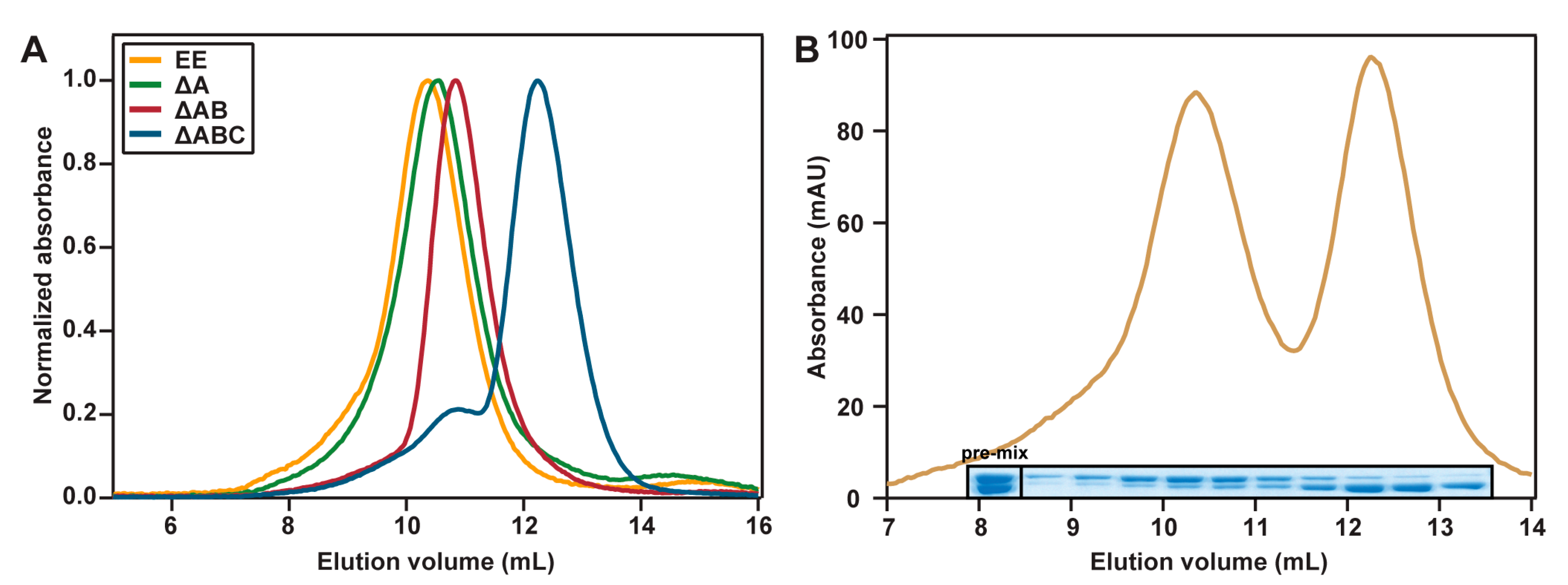
2.3. Hydrodynamic Properties
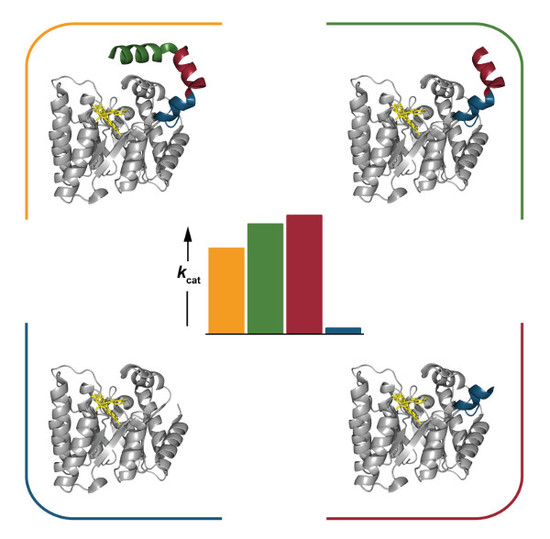
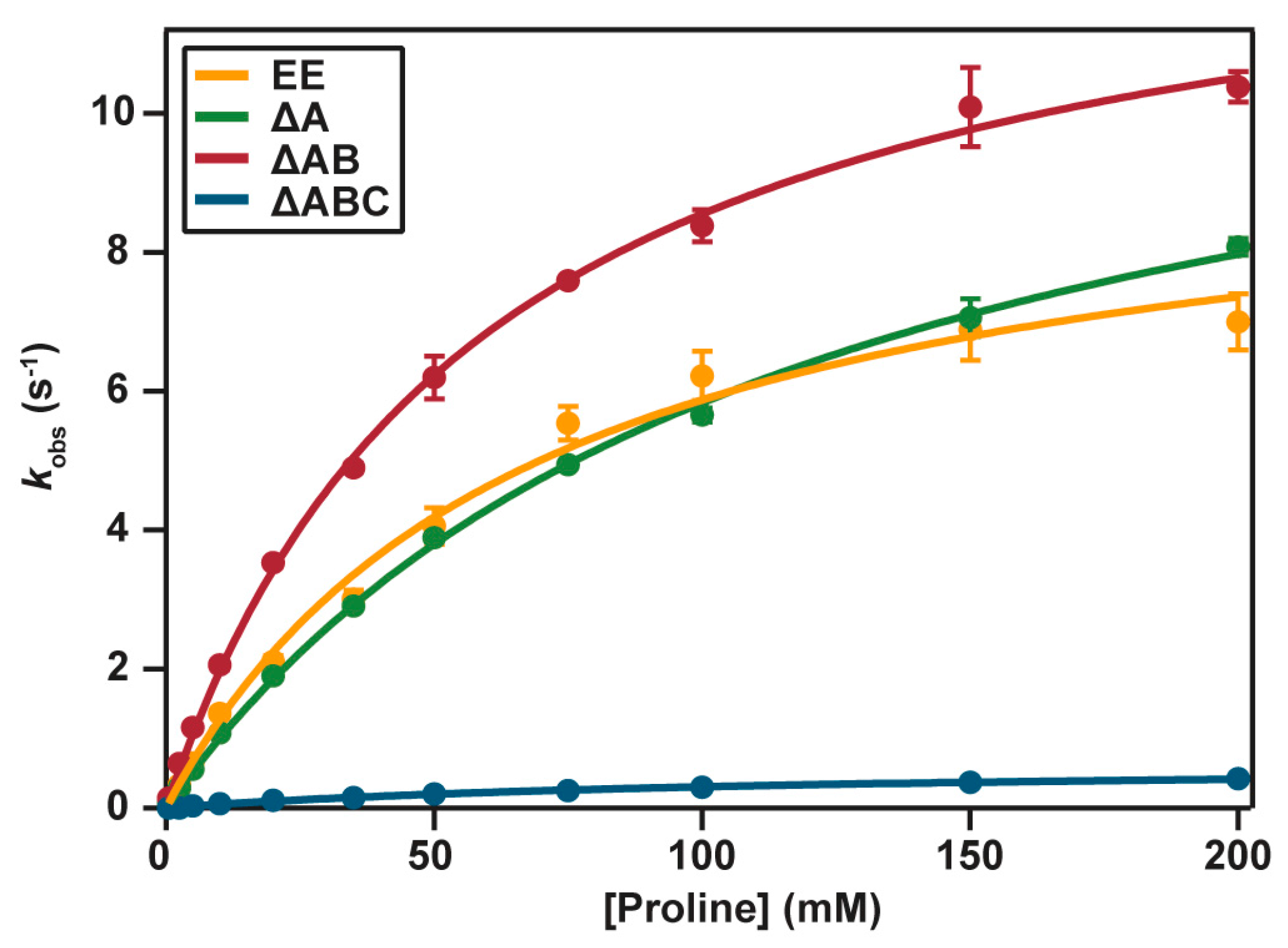
2.4. Catalytic Properties
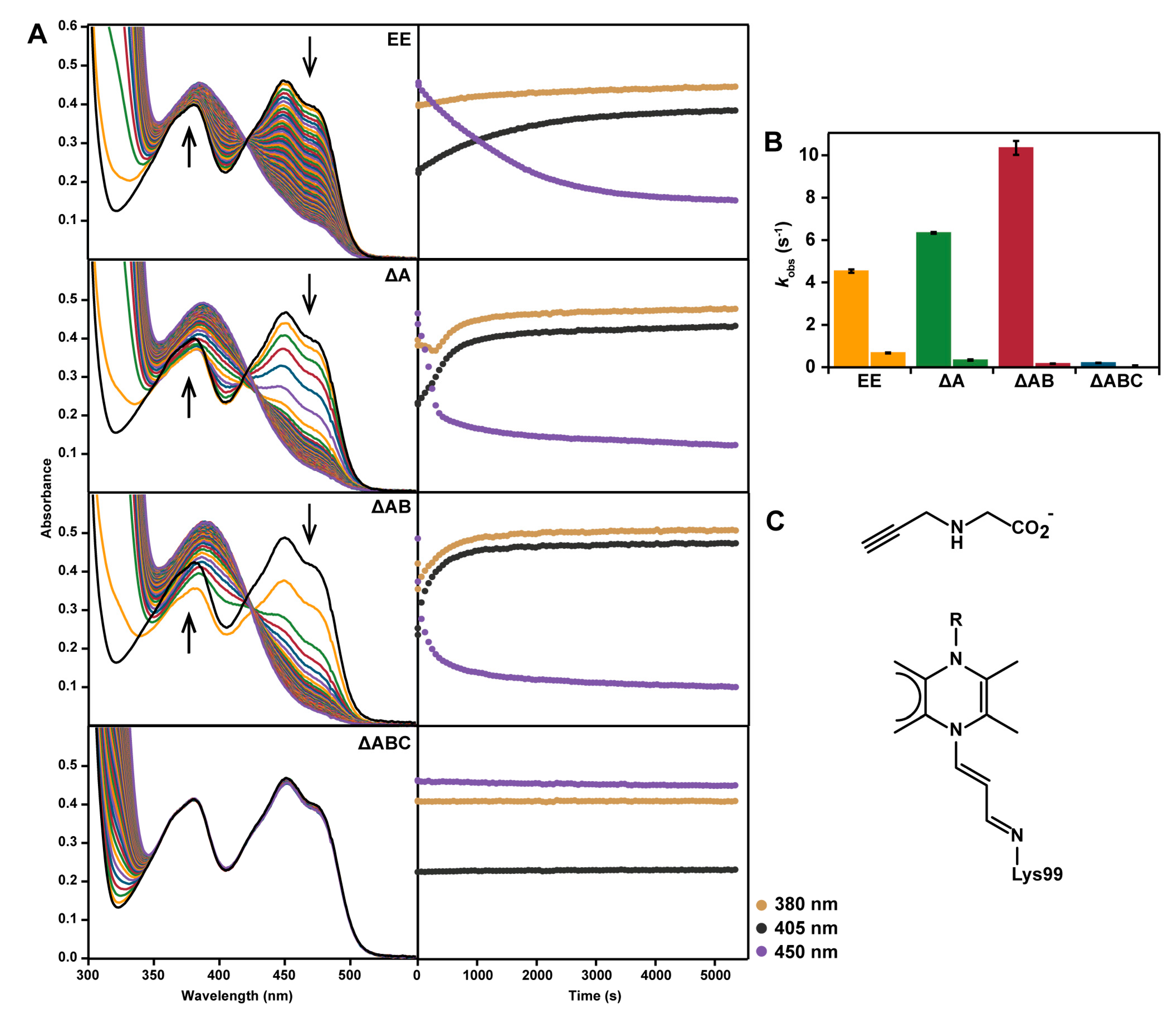
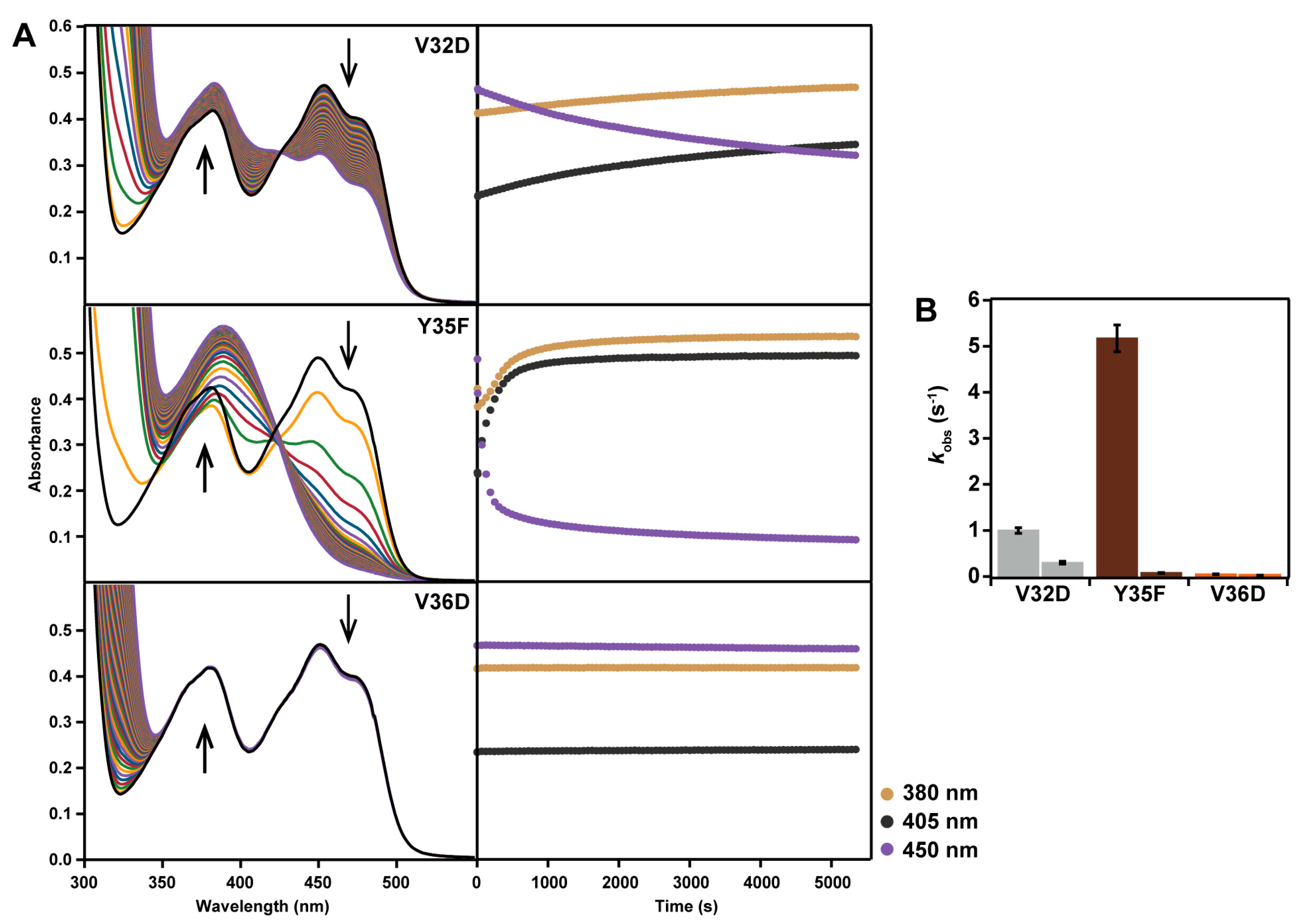
2.5. Reaction with N-propargylglycine
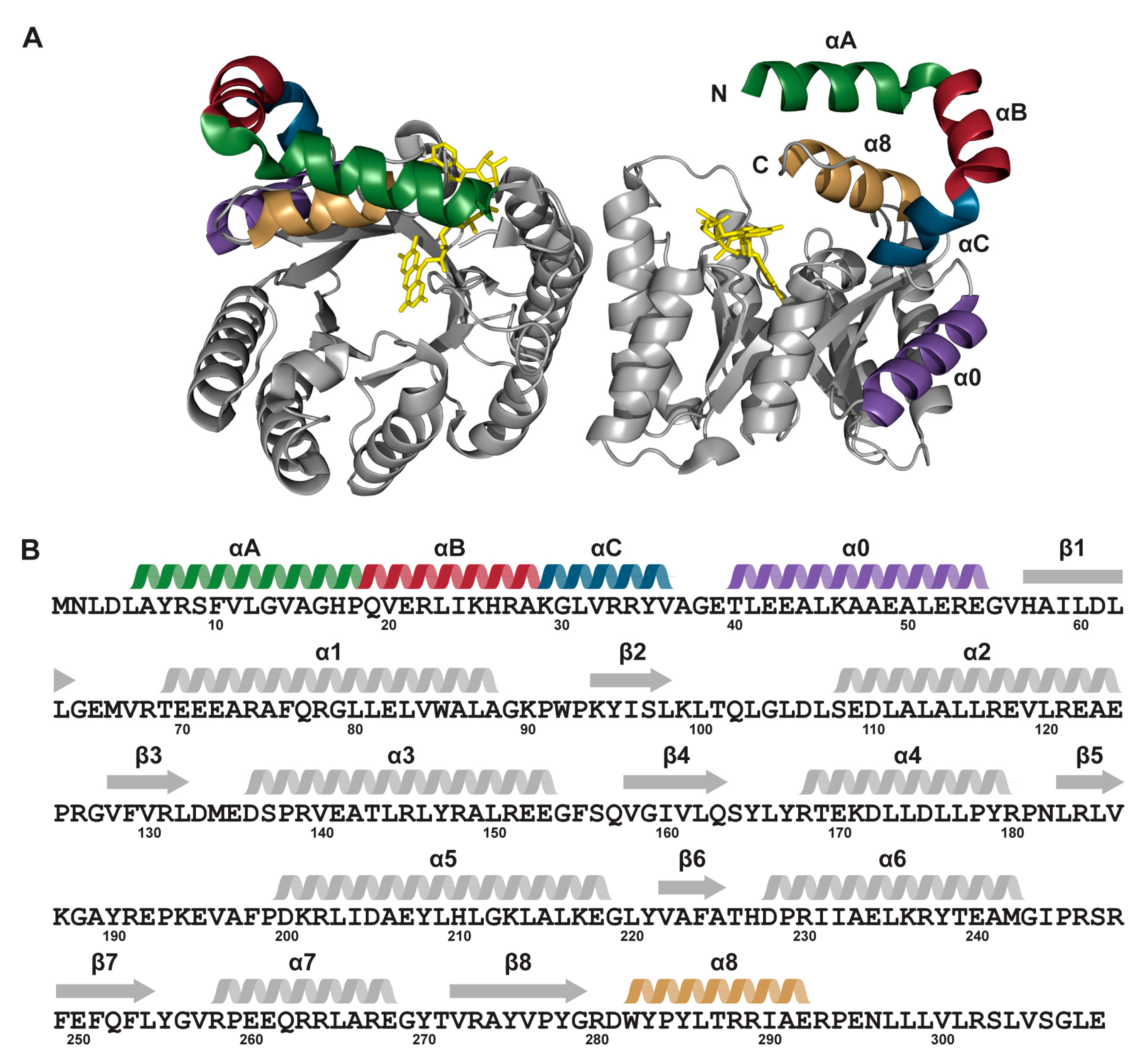
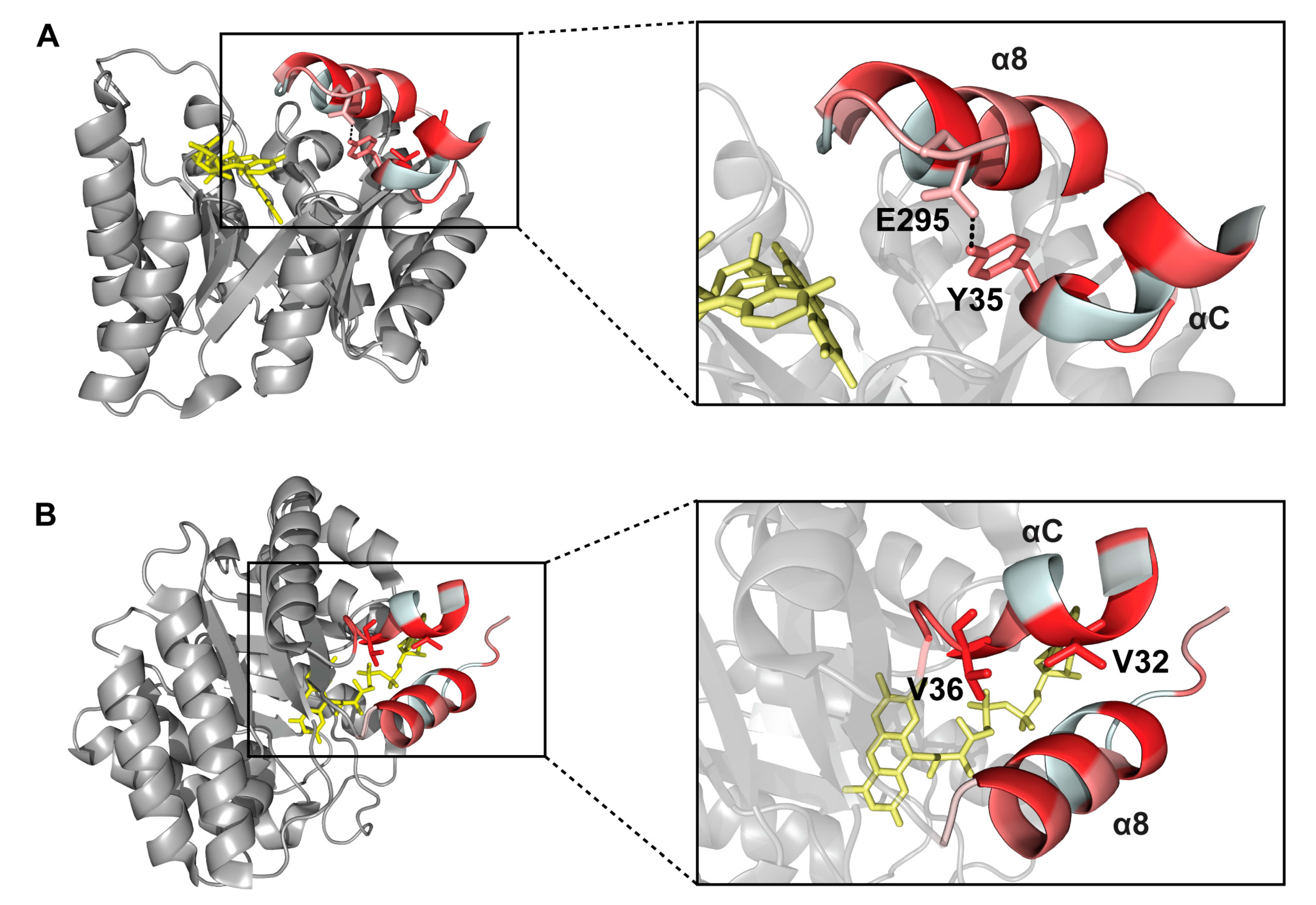
2.6. Interactions between Helix αC and Helix α8
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Construction of MBP-TtProDH Variants
4.2. Expression and Purification of MBP-TtProDH Variants
4.3. Protein Analysis
4.4. Analytical Gel Filtration
4.5. ESI-MS
4.6. Spectral Analysis
4.7. Enzyme Activity
4.8. Inactivation with N-propargylglycine
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CD | circular dichroism |
| DCPIP | dichlorophenolindophenol |
| ESI-MS | electron spray ionization mass spectrometry |
| FAD | flavin adenine dinucleotide |
| FMN | flavin mononucleotide |
| GSA | glutamic semialdehyde |
| MBP | maltose-binding protein |
| ProDH | proline dehydrogenase |
| P5C | Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate |
| P5CDH | Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase |
| PutA | proline utilization A |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| Tt | Thermus thermophilus |
| EE | MBP-TtProDH with Phe10 and Leu12 replaced by Glu |
| ΔA | MBP-TtProDH lacking helix αA |
| ΔAB | MBP-TtProDH lacking helices αA and αB |
| ΔABC | MBP-TtProDH lacking helices αA, αB and αC |
References
- White, T.A.; Krishnan, N.; Becker, D.F.; Tanner, J.J. Structure and kinetics of monofunctional proline dehydrogenase from Thermus thermophilus. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14316–14327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korasick, D.A.; Gamage, T.T.; Christgen, S.; Stiers, K.M.; Beamer, L.J.; Henzl, M.T.; Becker, D.F.; Tanner, J.J. Structure and characterization of a class 3B proline utilization A: Ligand-induced dimerization and importance of the C-terminal domain for catalysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 9652–9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christgen, S.L.; Zhu, W.; Sanyal, N.; Bibi, B.; Tanner, J.J.; Becker, D.F. Discovery of the membrane binding domain in trifunctional proline utilization A. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 6292–6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arentson, B.W.; Luo, M.; Pemberton, T.A.; Tanner, J.J.; Becker, D.F. Kinetic and structural characterization of tunnel-perturbing mutants in Bradyrhizobium japonicum proline utilization A. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 5150–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Becker, D.F.; Tanner, J.J. Structure, function, and mechanism of proline utilization A (PutA). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 632, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moxley, M.A.; Sanyal, N.; Krishnan, N.; Tanner, J.J.; Becker, D.F. Evidence for hysteretic substrate channeling in the proline dehydrogenase and Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase coupled reaction of proline utilization A (PutA). J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 3639–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Arentson, B.W.; Becker, D.F.; Tanner, J.J. Structures of the PutA peripheral membrane flavoenzyme reveal a dynamic substrate-channeling tunnel and the quinone-binding site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3389–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, D.; Zhu, W.; Johnson, W.H., Jr.; Whitman, C.P.; Becker, D.F.; Tanner, J.J. The structure of the proline utilization A proline dehydrogenase domain inactivated by N-propargylglycine provides insight into conformational changes induced by substrate binding and flavin reduction. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surber, M.W.; Maloy, S. The PutA protein of Salmonella typhimurium catalyzes the two steps of proline degradation via a leaky channel. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1998, 354, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, T.A.; Johnson, W.H., Jr.; Whitman, C.P.; Tanner, J.J. Structural basis for the inactivation of Thermus thermophilus proline dehydrogenase by N-propargylglycine. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 5573–5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, J.J.; Becker, D.F. PutA and proline metabolism. In Handbook of Flavoproteins. Volume 1—Oxidases, Dehydrogenases and Related Systems; Hille, R., Miller, S.M., Palfey, B., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tanner, J.J. Structural biology of proline catabolism. Amino Acids 2008, 35, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Nadaraia, S.; Gu, D.; Becker, D.F.; Tanner, J.J. Structure of the proline dehydrogenase domain of the multifunctional PutA flavoprotein. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003, 10, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; White, T.A.; Schuermann, J.P.; Baban, B.A.; Becker, D.F.; Tanner, J.J. Structures of the Escherichia coli PutA proline dehydrogenase domain in complex with competitive inhibitors. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 12539–12548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallarita, E.; Pollegioni, L.; Servi, S.; Molla, G. Expression in Escherichia coli of the catalytic domain of human proline oxidase. Protein Expr. Purif. 2012, 82, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, N.; Arentson, B.W.; Luo, M.; Tanner, J.J.; Becker, D.F. First evidence for substrate channeling between proline catabolic enzymes: A validation of domain fusion analysis for predicting protein-protein interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 2225–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huijbers, M.M.E.; van Berkel, W.J.H. High yields of active Thermus thermophilus proline dehydrogenase are obtained using maltose-binding protein as a solubility tag. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huijbers, M.M.E.; Martínez-Júlvez, M.; Westphal, A.H.; Delgado-Arciniega, E.; Medina, M.; van Berkel, W.J.H. Proline dehydrogenase from Thermus thermophilus does not discriminate between FAD and FMN as cofactor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huijbers, M.M.E.; van Berkel, W.J.H. A more polar N-terminal helix releases Thermus thermophilus proline dehydrogenase from self-association. J. Mol. Catal. B 2016, 134, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, D.; Schwarz, E.; Komaromy, M.; Wall, R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J. Mol. Biol. 1984, 179, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Arentson, B.W.; Srivastava, D.; Becker, D.F.; Tanner, J.J. Crystal structures and kinetics of monofunctional proline dehydrogenase provide insight into substrate recognition and conformational changes associated with flavin reduction and product release. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 10099–10108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, D.; Schuermann, J.P.; White, T.A.; Krishnan, N.; Sanyal, N.; Hura, G.L.; Tan, A.; Henzl, M.T.; Becker, D.F.; Tanner, J.J. Crystal structure of the bifunctional proline utilization A flavoenzyme from Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2878–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowley, G.L.; Greenleaf, A.L.; Kenyon, G.L. On the specificity of creatine kinase. New glycocyamines and glycocyamine analogs related to creatine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1971, 93, 5542–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the gene constructs reported here are available from the authors. |
| Native | Denatured | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetramer | Dimer | Monomer | ||||||
| Pred. | Exp. | Pred. | Exp. | Pred. | Exp. | Pred. | Exp. | |
| MBP-TtProDH EE * | 317.8 | 319.6 | 158.9 | 158.9 | 79.5 | - | 78.7 | 78.7 |
| MBP-TtProDH ΔA | 310.1 | 311.3 | 155.0 | 154.9–155.7 | 77.5 | - | 76.7 | 76.8 |
| MBP-TtProDH ΔAB | 305.1 | 307.6–307.8 | 152.6 | 152.6–153.7 | 76.3 | - | 75.5 | 75.5 |
| MBP-TtProDH ΔABC | 300.7 | 290.0–290.7 | 150.4 | 145.0–146.0 | 75.2 | 71.9–72.7 | 74.4 | 71.9 |
| MBP-TtProDH ΔAB V32D | 305.2 | 296.2–304.4 | 152.6 | 146.5–149.0 | 76.3 | 73.0–76.0 | 75.5 | 73.0 75.5 |
| MBP-TtProDH ΔAB Y35F | 305.1 | 307.4 | 152.5 | 152.3–152.9 | 76.3 | - | 75.5 | 75.5 |
| MBP-TtProDH ΔAB V36D | 305.2 | 296.2 | 152.6 | 151.1–151.9 | 76.3 | - | 75.5 | 73.0 75.5 |
| Proline:DCPIP Assay | Proline:O2 Assay | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Km (mM) | kcat (s−1) | kcat/Km (s−1 M−1) | Specific Activity (mU/mg) | |
| MBP-TtProDH EE * | 68 ± 8 | 9.8 ± 0.5 | 146 | 266 ± 12 |
| MBP-TtProDH ΔA | 116 ± 5 | 12.6 ± 0.3 | 109 | 405 ± 15 |
| MBP-TtProDH ΔAB | 60 ± 3 | 13.6 ± 0.3 | 229 | 228 ± 8 |
| MBP-TtProDH ΔABC | 114 ± 8 | 0.7 ± 0.02 | 6 | 20 ± 1 |
| MBP-TtProDH ΔAB V32D | 309 ± 25 | 3.2 ± 0.2 | 10 | 265 ± 4 |
| MBP-TtProDH ΔAB Y35F | 161 ± 29 | 14.1 ± 1.5 | 88 | 388 ± 5 |
| MBP-TtProDH ΔAB V36D | 189 ± 27 | 0.3 ± 0.03 | 1.6 | 21 ± 1 |
| Variant | Oligonucleotide Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| ΔA, forward | AATTAGAATTCCAGGTTGAACGTCTGATTAAACATCGTGCAAAAGG |
| ΔAB, forward | AAT TAGAATTCAAAGGTCTGGTTCGTCGTTATGTTGCCGGTG |
| ΔABC, forward | AATTAGAATTCCAGGTTGAACGTCTGATTAAACATCGTGCAAAAGG |
| ΔA, ΔAB, ΔABC, reverse | GCCCAAGCTTTTATTCTAGACCGCTAACCAGGC |
| ΔAB, V32D, forward * | CGAGGGAAGGATTTCAGAATTCAAAGGTCTGGATCGTCGTTATGTTGCCGGTGAAACCCTGG |
| ΔAB, Y35F, forward * | CGAGGGAAGGATTTCAGAATTCAAAGGTCTGGTTCGTCGTTTTGTTGCCGGTGAAACCCTGG |
| ΔAB, V36D, forward * | CGAGGGAAGGATTTCAGAATTCAAAGGTCTGGTTCGTCGTTATGATGCCGGTGAAACCCTGG |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huijbers, M.M.E.; Van Alen, I.; Wu, J.W.; Barendregt, A.; Heck, A.J.R.; Van Berkel, W.J.H. Functional Impact of the N-terminal Arm of Proline Dehydrogenase from Thermus thermophilus. Molecules 2018, 23, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010184
Huijbers MME, Van Alen I, Wu JW, Barendregt A, Heck AJR, Van Berkel WJH. Functional Impact of the N-terminal Arm of Proline Dehydrogenase from Thermus thermophilus. Molecules. 2018; 23(1):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010184
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuijbers, Mieke M. E., Ilona Van Alen, Jenny W. Wu, Arjan Barendregt, Albert J. R. Heck, and Willem J. H. Van Berkel. 2018. "Functional Impact of the N-terminal Arm of Proline Dehydrogenase from Thermus thermophilus" Molecules 23, no. 1: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010184
APA StyleHuijbers, M. M. E., Van Alen, I., Wu, J. W., Barendregt, A., Heck, A. J. R., & Van Berkel, W. J. H. (2018). Functional Impact of the N-terminal Arm of Proline Dehydrogenase from Thermus thermophilus. Molecules, 23(1), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010184