Large-Scale Analysis of Antimicrobial Activities in Relation to Amphipathicity and Charge Reveals Novel Characterization of Antimicrobial Peptides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. AMPs with Anti-Gram-Negative Bacterial Activities Strongly Favor Amphipathicity and Cationic Charge
2.2. AMPs with Anti-Gram-Positive Bacterial Activities Differ from Other AMPs in Amphipathicity and Net Charge
2.3. Trends of Antimicrobial Activities of AMPs in Terms of Amphipathicity and Net Charge
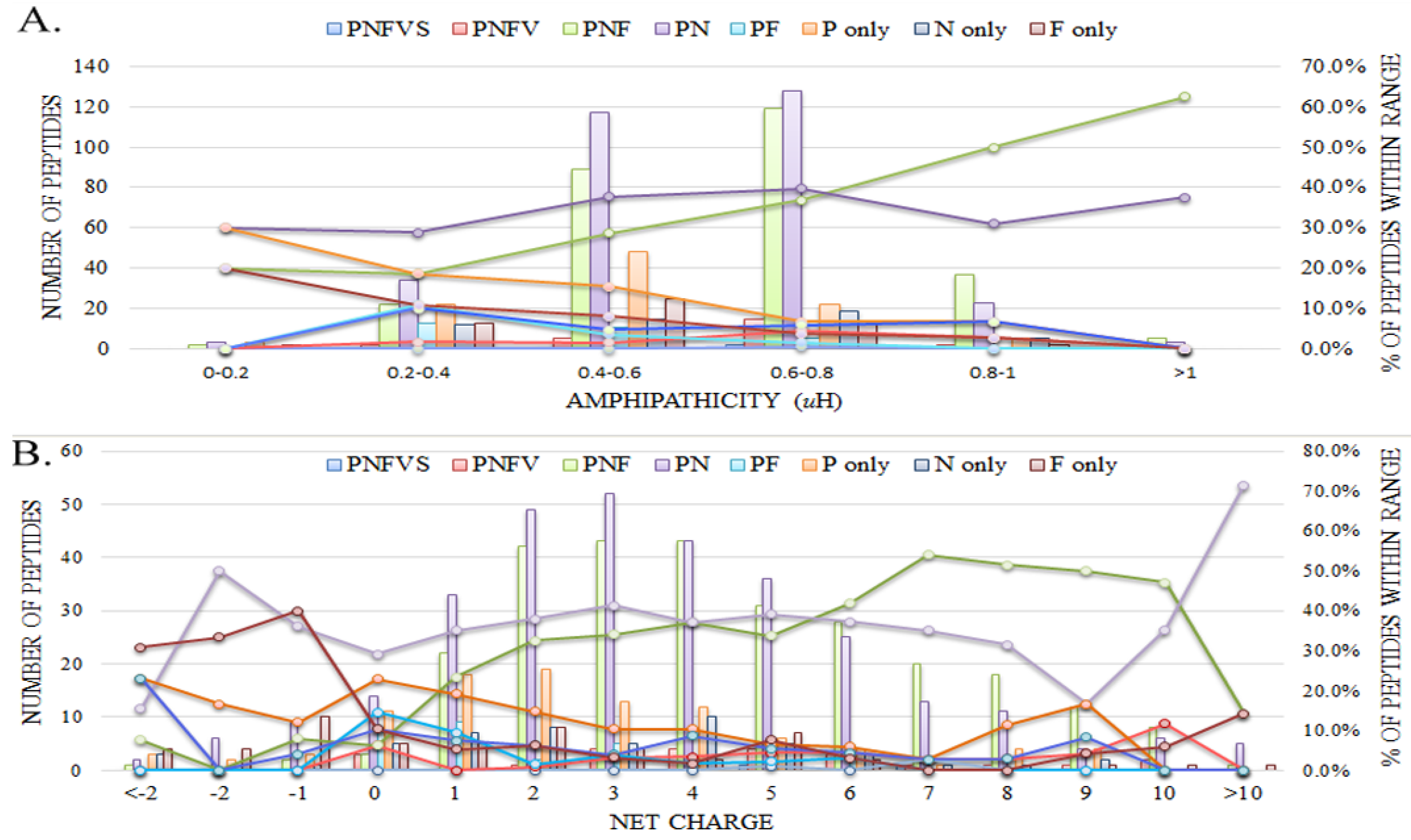
2.4. The Higher Amphipathicity, the Greater the Proportion of AMPs Possessing Antibacterial/Antifungal Activities
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Non-Redundant Experimentally-Validated AMPs
4.2. AMP Amphipathicity
4.3. AMP Net Charge
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMP | Anti-microbial peptide |
References
- Lauth, X.; Shike, H.; Burns, J.C.; Westerman, M.E.; Ostland, V.E.; Carlberg, J.M.; Van Olst, J.C.; Nizet, V.; Taylor, S.W.; Shimizu, C.; et al. Discovery and characterization of two isoforms of moronecidin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from hybrid striped bass. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 5030–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachinger, M.; Kleinschmidt, A.; Winder, D.; von Pechmann, N.; Ludvigsen, A.; Neumann, M.; Holle, R.; Salmons, B.; Erfle, V.; Brack-Werner, R. Antimicrobial peptides melittin and cecropin inhibit replication of human immunodeficiency virus 1 by suppressing viral gene expression. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ng, T.B. Ganodermin, an antifungal protein from fruiting bodies of the medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lucidum. Peptides 2006, 27, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.J.; Parent, R.; Guillaume, C.; Deregnaucourt, C.; Delarbre, C.; Ojcius, D.M.; Montagne, J.J.; Celerier, M.L.; Phelipot, A.; Amiche, M.; et al. Isolation and characterization of Psalmopeotoxin I and II: Two novel antimalarial peptides from the venom of the tarantula Psalmopoeus cambridgei. FEBS Lett. 2004, 572, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabrane, A.; Sabri, A.; Compere, P.; Jacques, P.; Vandenberghe, I.; Van Beeumen, J.; Thonart, P. Characterization of serracin P, a phage-tail-like bacteriocin, and its activity against Erwinia amylovora, the fire blight pathogen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5704–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tossi, A.; Sandri, L. Molecular diversity in gene-encoded, cationic antimicrobial polypeptides. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2002, 8, 743–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.T.; Lee, C.C.; Yang, J.R.; Lai, J.Z.; Chang, K.Y. A large-scale structural classification of antimicrobial peptides. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 475062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. APD3: The antimicrobial peptide database as a tool for research and education. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D1087–D1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waghu, F.H.; Barai, R.S.; Gurung, P.; Idicula-Thomas, S. CAMPR3: A database on sequences, structures and signatures of antimicrobial peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D1154–D1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, D.; Shukla, S.K.; Prakash, O.; Zhang, G. Structural determinants of host defense peptides for antimicrobial activity and target cell selectivity. Biochimie 2010, 92, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Dong, N.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, I.; Ma, Q.; Shan, A. Design of imperfectly amphipathic alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides with enhanced cell selectivity. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G. Antimicrobial Peptides: Discovery, Design and Novel Therapeutic Strategies; Cabi: Wallingford, UK, 2010; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Koren, E.; Torchilin, V.P. Cell-penetrating peptides: Breaking through to the other side. Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogden, K.A. Antimicrobial peptides: Pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.Y.; Lin, T.P.; Shih, L.Y.; Wang, C.K. Analysis and prediction of the critical regions of antimicrobial peptides based on conditional random fields. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Niu, B.; Gao, Y.; Fu, L.; Li, W. CD-HIT Suite: A web server for clustering and comparing biological sequences. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, D.; Weiss, R.M.; Terwilliger, T.C. The helical hydrophobic moment: A measure of the amphiphilicity of a helix. Nature 1982, 299, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janin, J. Surface and inside volumes in globular proteins. Nature 1979, 277, 491–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Not Available. |
| Activities | N | Amphipathicity | Net Charge | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | Range | p-Value | Median | Range | p-Value | ||
| P+ | |||||||
| Yes | 778 | 0.599 | 0.118∼1.219 | 4.05 × 10−5 | 3 | −6∼14 | 3.35 × 10−7 |
| No | 142 | 0.540 | 0.072∼0.981 | 2 | −7∼13 | ||
| N+ | |||||||
| Yes | 704 | 0.615 | 0.118∼1.219 | 4.07 × 10−18 | 4 | −6∼14 | 9.31 × 10−17 |
| No | 216 | 0.485 | 0.072∼0.963 | 2 | −7∼13 | ||
| F+ | |||||||
| Yes | 414 | 0.603 | 0.072∼1.189 | 9.11 × 10−3 | 4 | −7∼14 | 1.29 × 10−4 |
| No | 506 | 0.572 | 0.118∼1.219 | 3 | −6∼13 | ||
| P+N+ | |||||||
| Yes | 642 | 0.616 | 0.118∼1.219 | 7.84 × 10−17 | 4 | −6∼14 | 3.59 × 10−16 |
| No | 278 | 0.504 | 0.072∼0.981 | 2 | −7∼13 | ||
| P+F+ | |||||||
| Yes | 346 | 0.618 | 0.180∼1.189 | 6.22 × 10−6 | 4 | −3∼14 | 5.12 × 10−10 |
| No | 574 | 0.566 | 0.072∼1.219 | 3 | −7∼13 | ||
| N+F+ | |||||||
| Yes | 321 | 0.625 | 0.180∼1.189 | 1.39 × 10−10 | 4 | −3∼14 | 4.71 × 10−15 |
| No | 599 | 0.558 | 0.072∼1.219 | 3 | −7∼13 | ||
| P+N+F+ | |||||||
| Yes | 313 | 0.626 | 0.180∼1.189 | 8.96 × 10−11 | 4 | −3∼14 | 1.58 × 10−14 |
| No | 607 | 0.558 | 0.072∼1.219 | 3 | −7∼13 | ||
| P+ vs. N+F+ | |||||||
| P+ (Yes) | 778 | 0.599 | 0.118∼1.219 | 2.63 × 10−4 | 3 | −6∼14 | 9.76 × 10−6 |
| N+F+ (Yes) | 321 | 0.625 | 0.180∼1.189 | 4 | −3∼14 | ||
| P+ vs. P+N+F+ | |||||||
| P+ (Yes) | 778 | 0.599 | 0.118∼1.219 | 1.82 × 10−4 | 3 | −6∼14 | 1.17 × 10−5 |
| P+N+F+ (Yes) | 313 | 0.626 | 0.180∼1.189 | 4 | −3∼14 | ||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.-K.; Shih, L.-Y.; Chang, K.Y. Large-Scale Analysis of Antimicrobial Activities in Relation to Amphipathicity and Charge Reveals Novel Characterization of Antimicrobial Peptides. Molecules 2017, 22, 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112037
Wang C-K, Shih L-Y, Chang KY. Large-Scale Analysis of Antimicrobial Activities in Relation to Amphipathicity and Charge Reveals Novel Characterization of Antimicrobial Peptides. Molecules. 2017; 22(11):2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112037
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chien-Kuo, Ling-Yi Shih, and Kuan Y. Chang. 2017. "Large-Scale Analysis of Antimicrobial Activities in Relation to Amphipathicity and Charge Reveals Novel Characterization of Antimicrobial Peptides" Molecules 22, no. 11: 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112037
APA StyleWang, C.-K., Shih, L.-Y., & Chang, K. Y. (2017). Large-Scale Analysis of Antimicrobial Activities in Relation to Amphipathicity and Charge Reveals Novel Characterization of Antimicrobial Peptides. Molecules, 22(11), 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112037






