Green Sonoextraction of Protein from Oleaginous Press Rapeseed Cake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
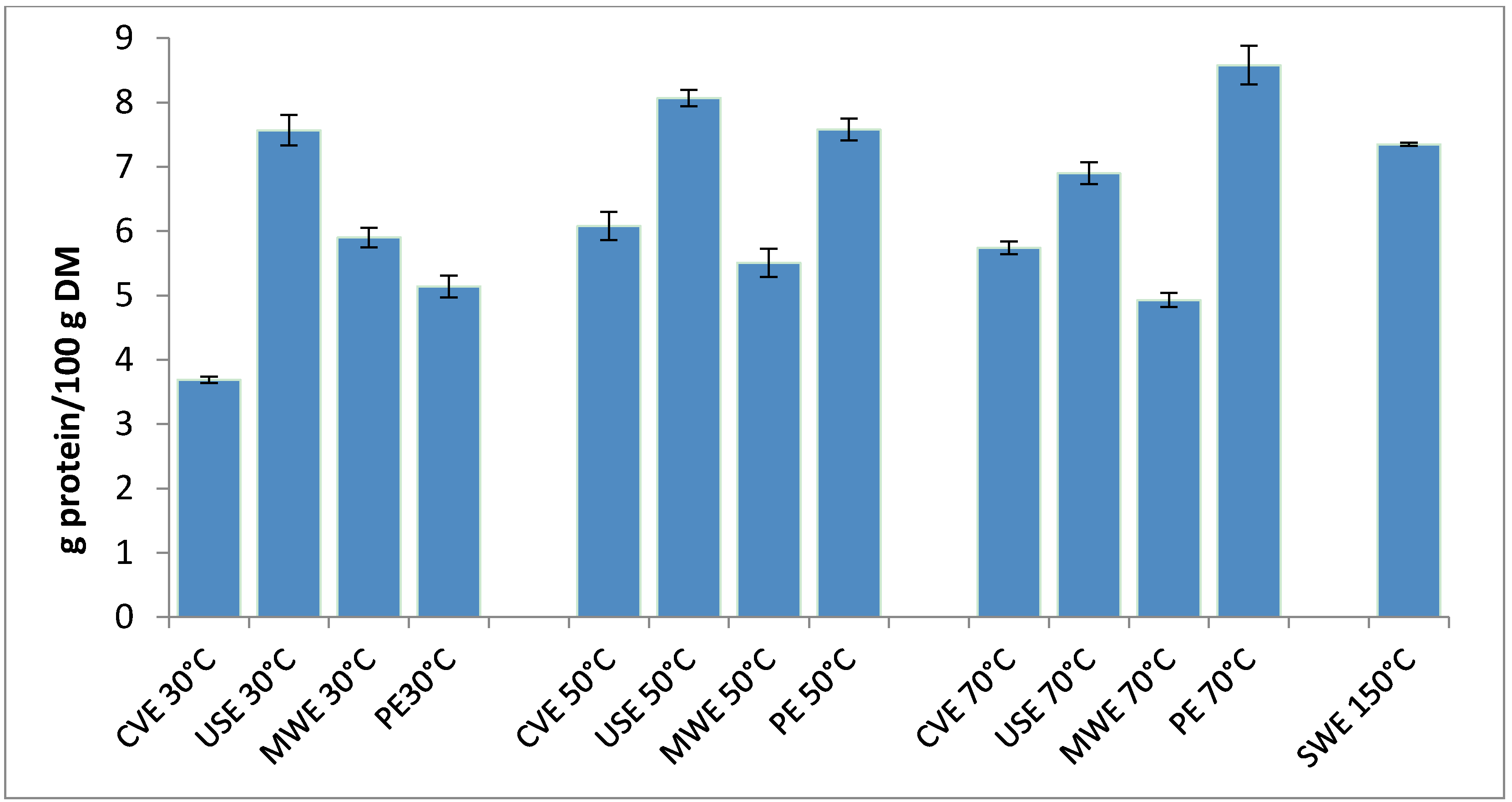
2.1. Preliminary Study of Protein Extraction
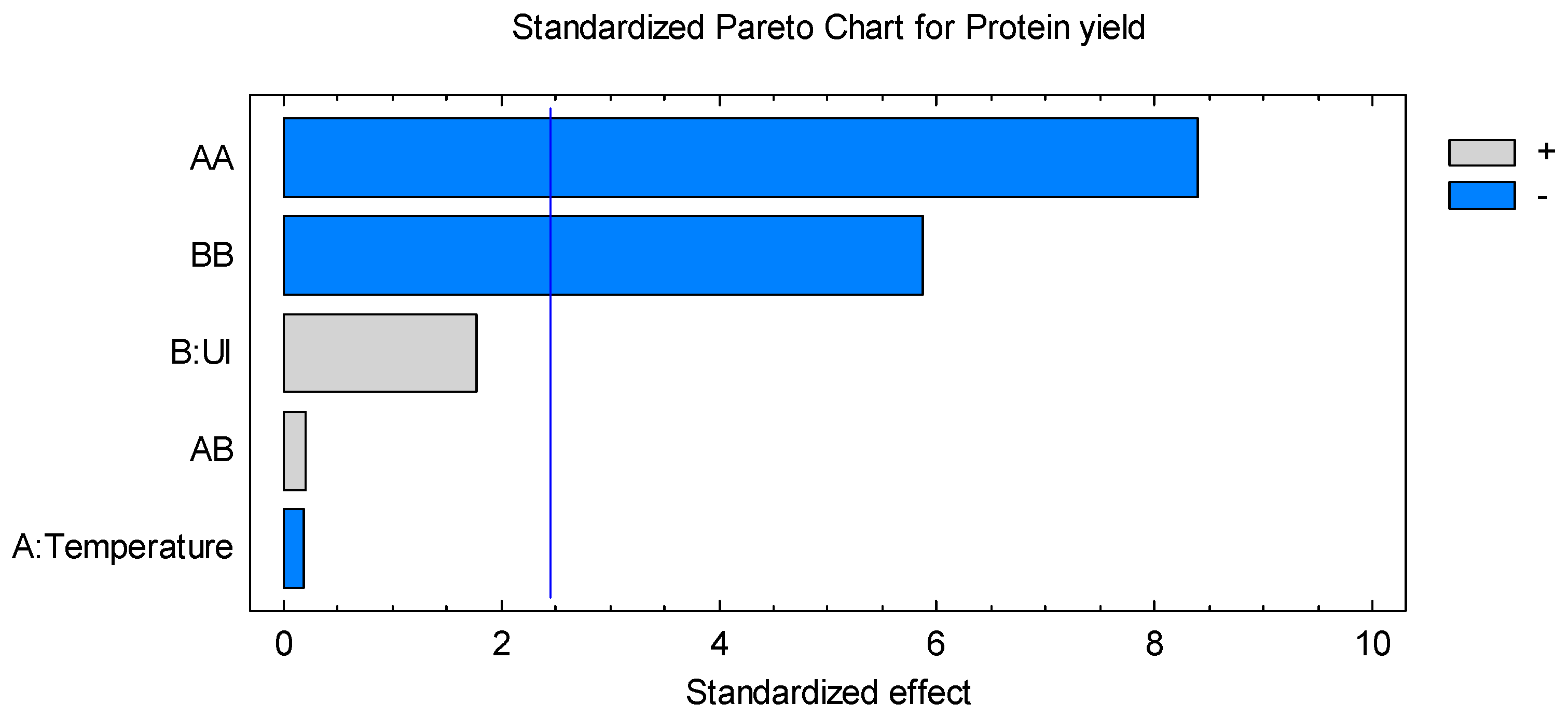
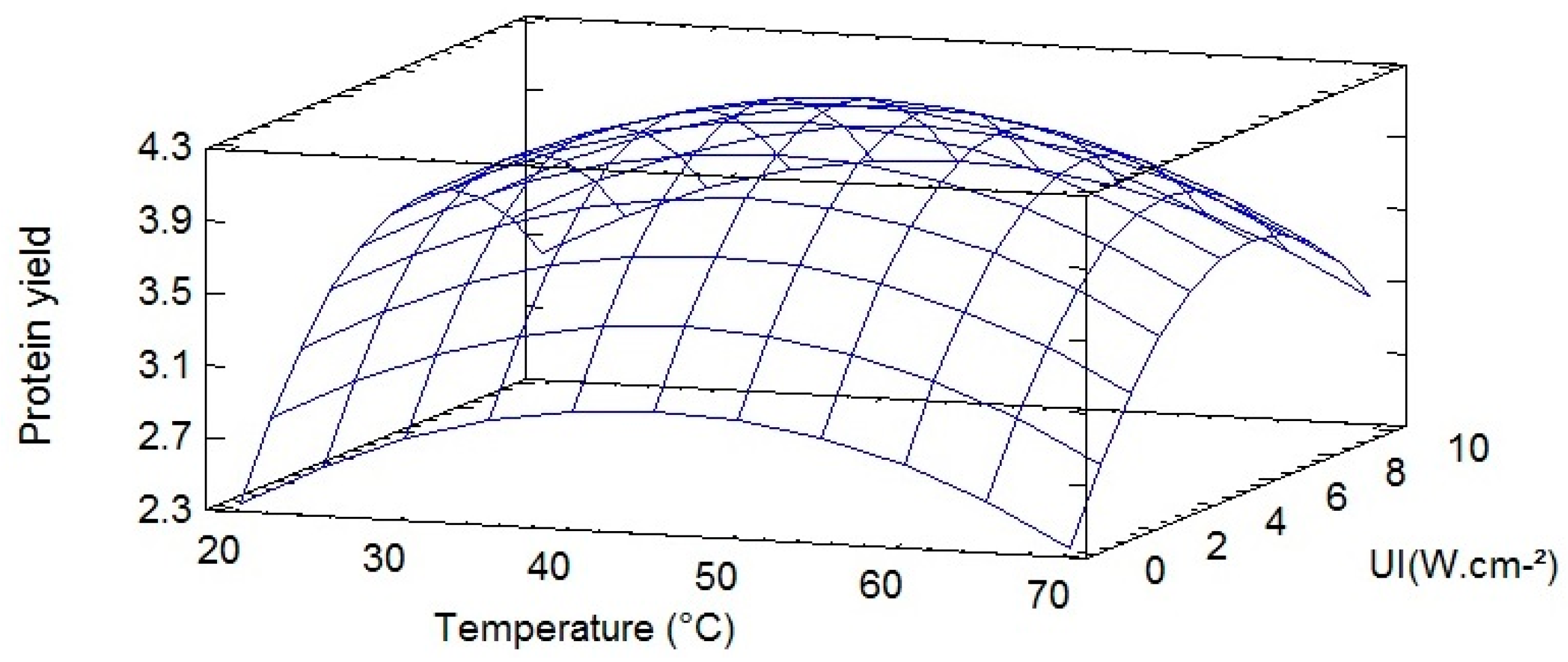
2.2. Statistical Analysis for UAE Extraction of Proteins According to the Experimental Design
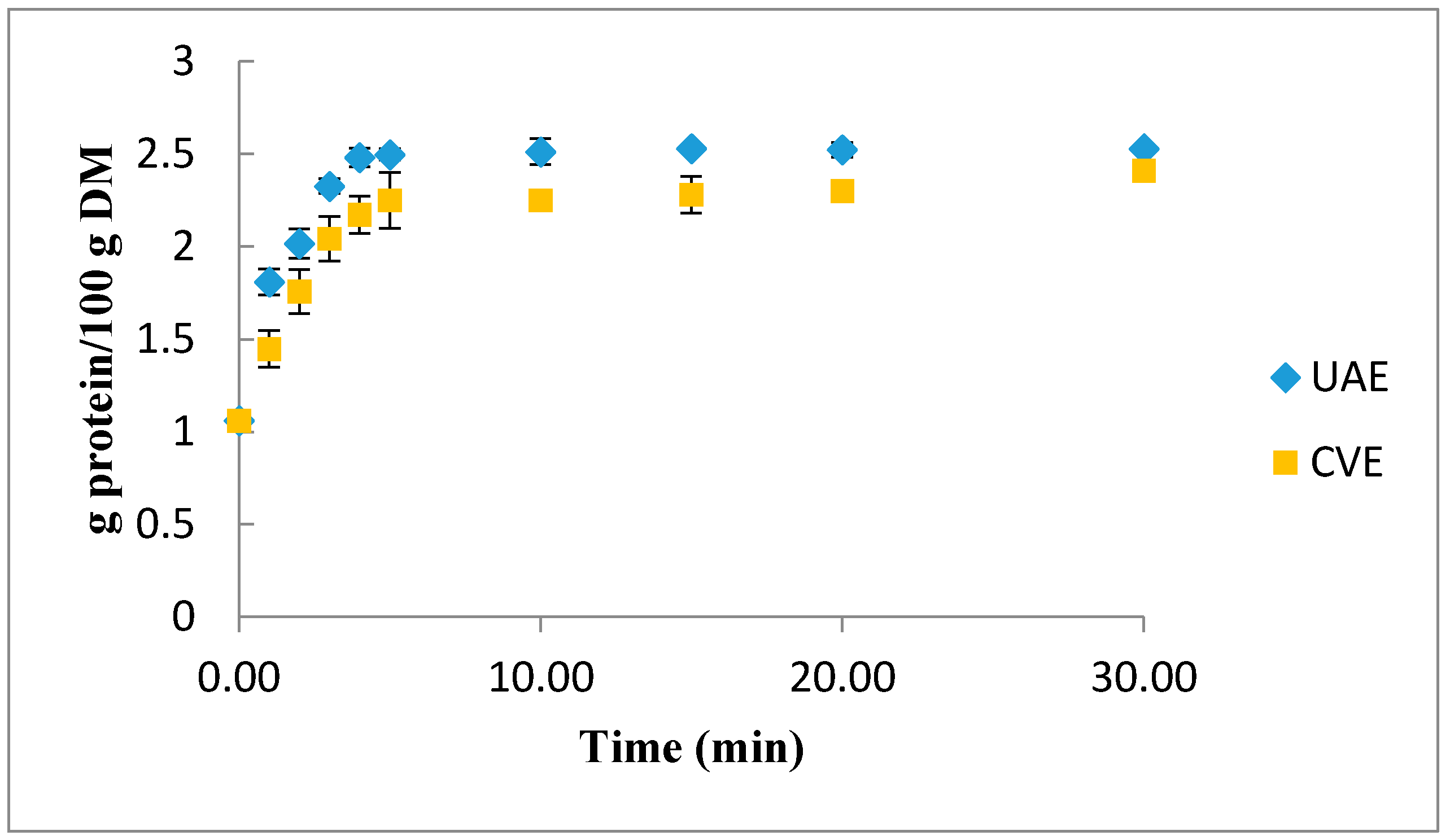
2.3. Comparison between UAE and CE of Protein
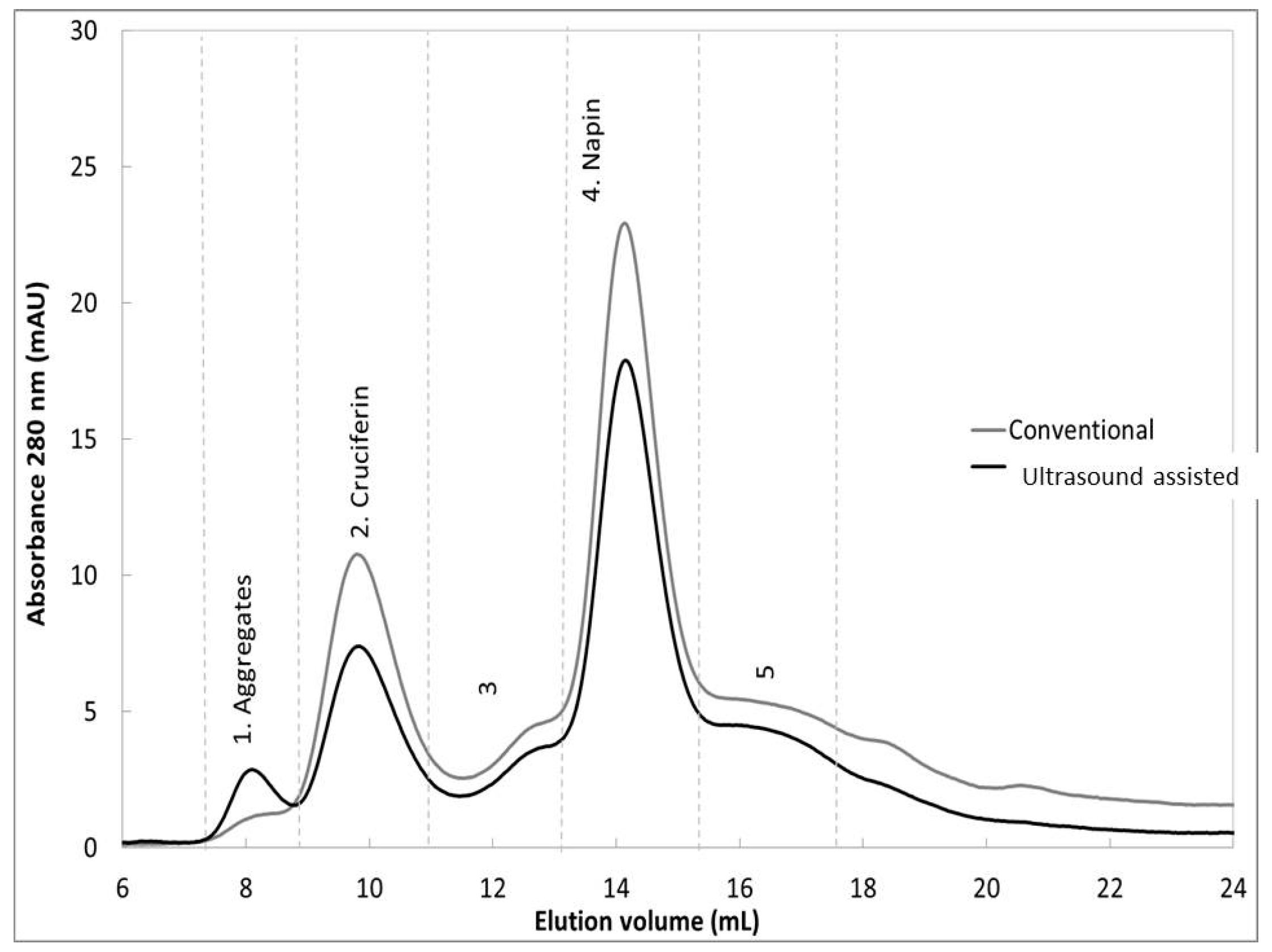
2.3.1. Size Exclusion Chromatography
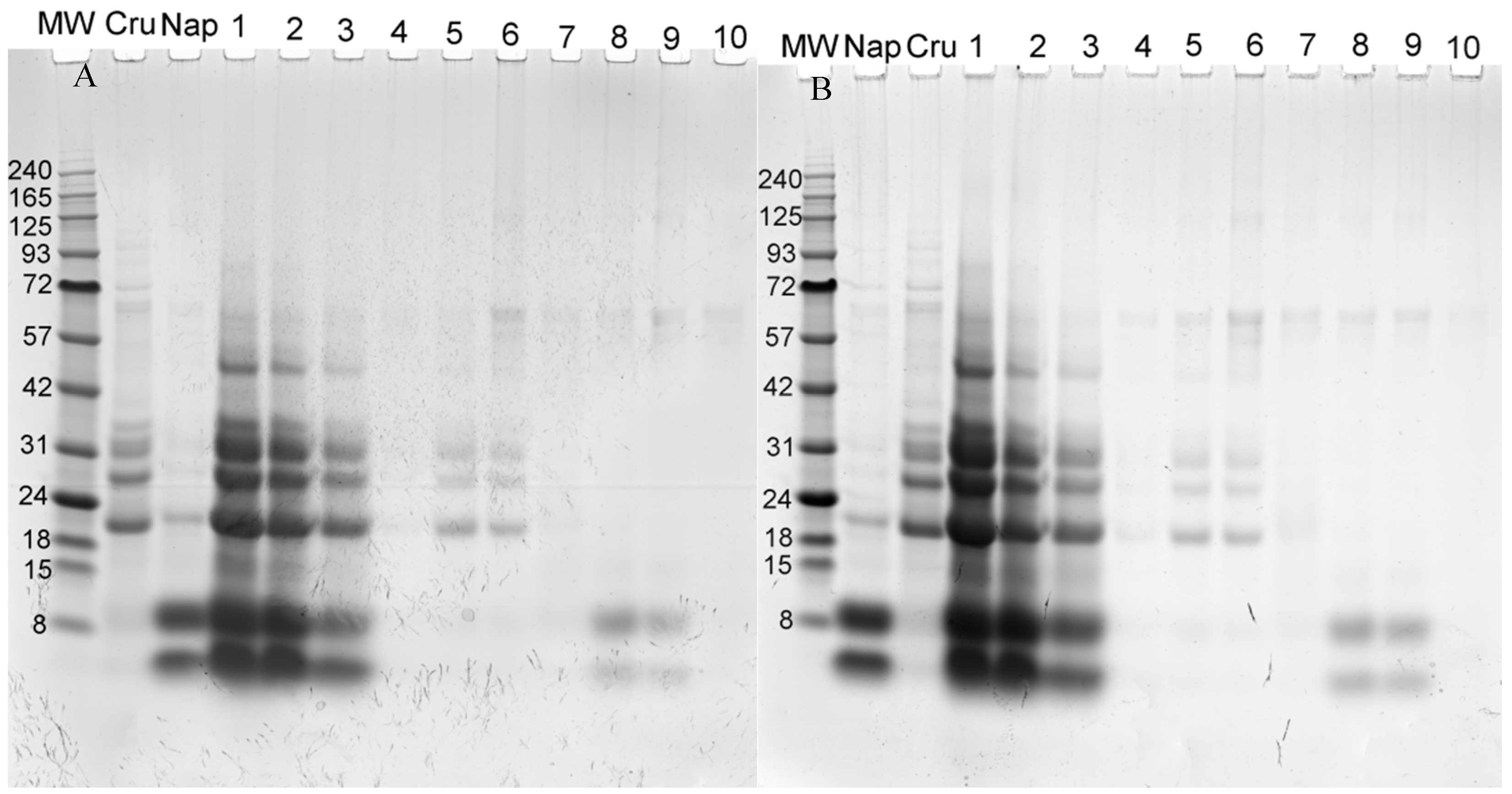
2.3.2. Electrophoresis
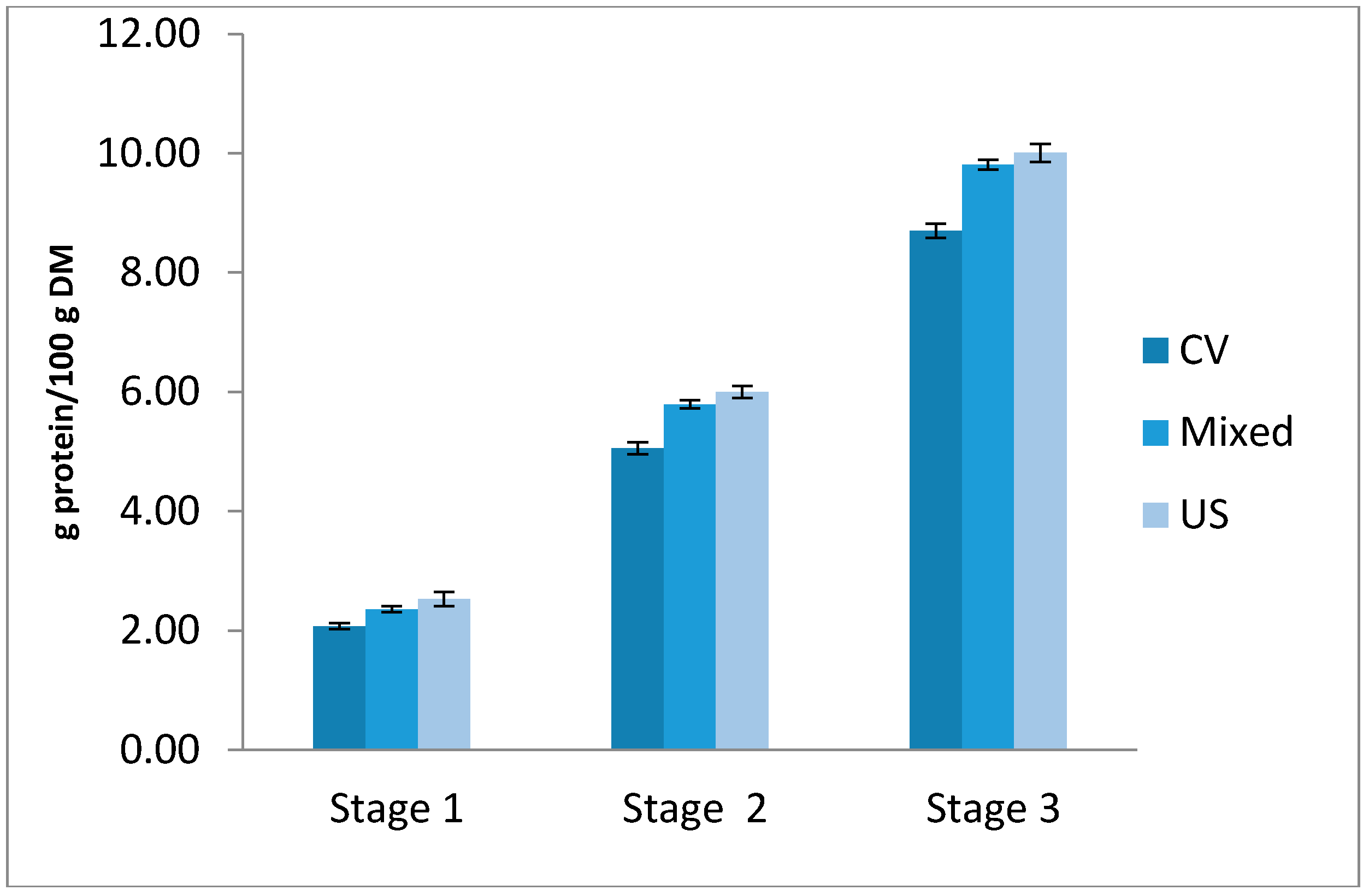
2.4. Multistage Cross-Current Simulation
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Plant Material
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Protocol Treatment
3.3.1. Conventional Extraction Procedure
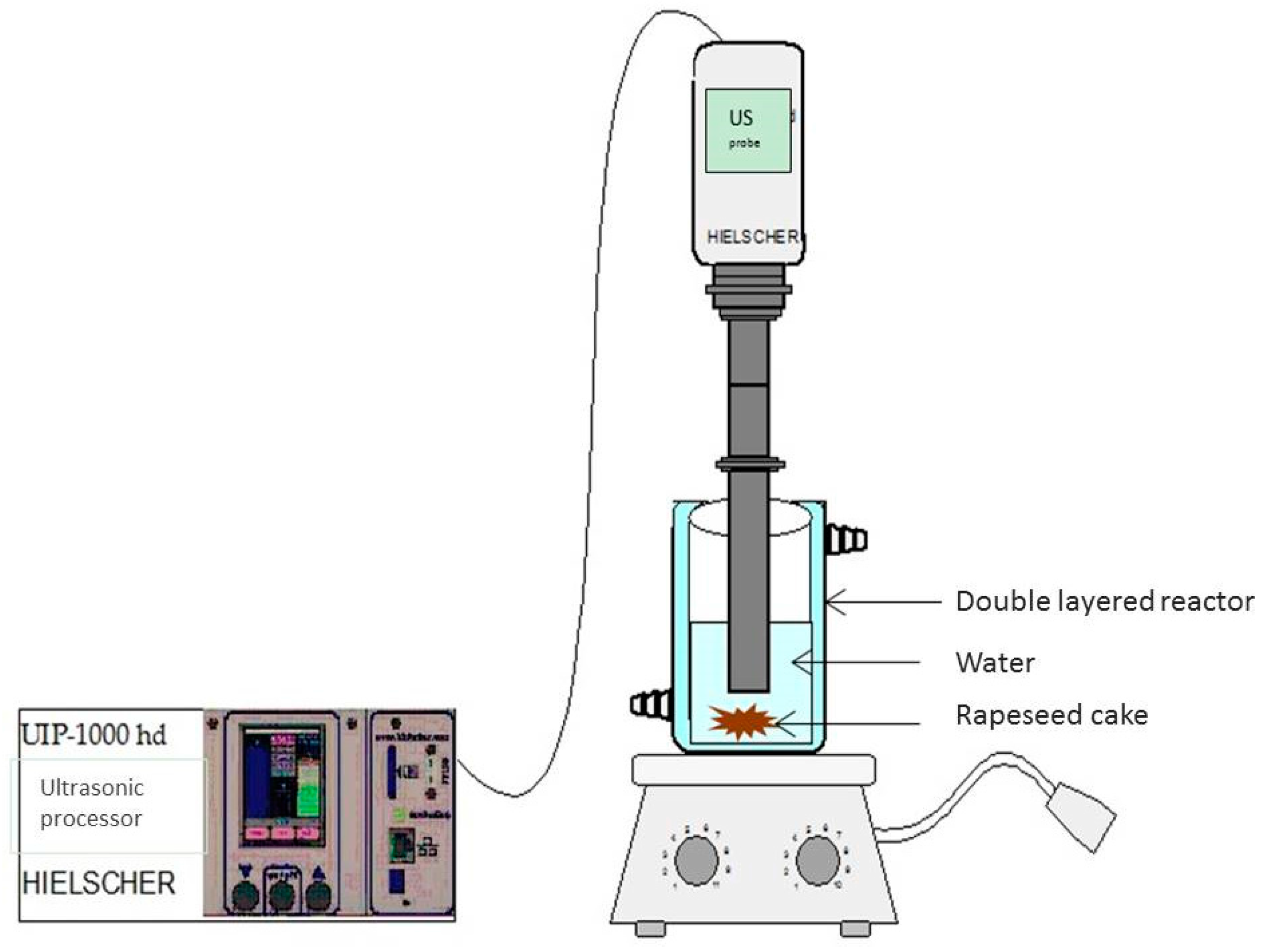
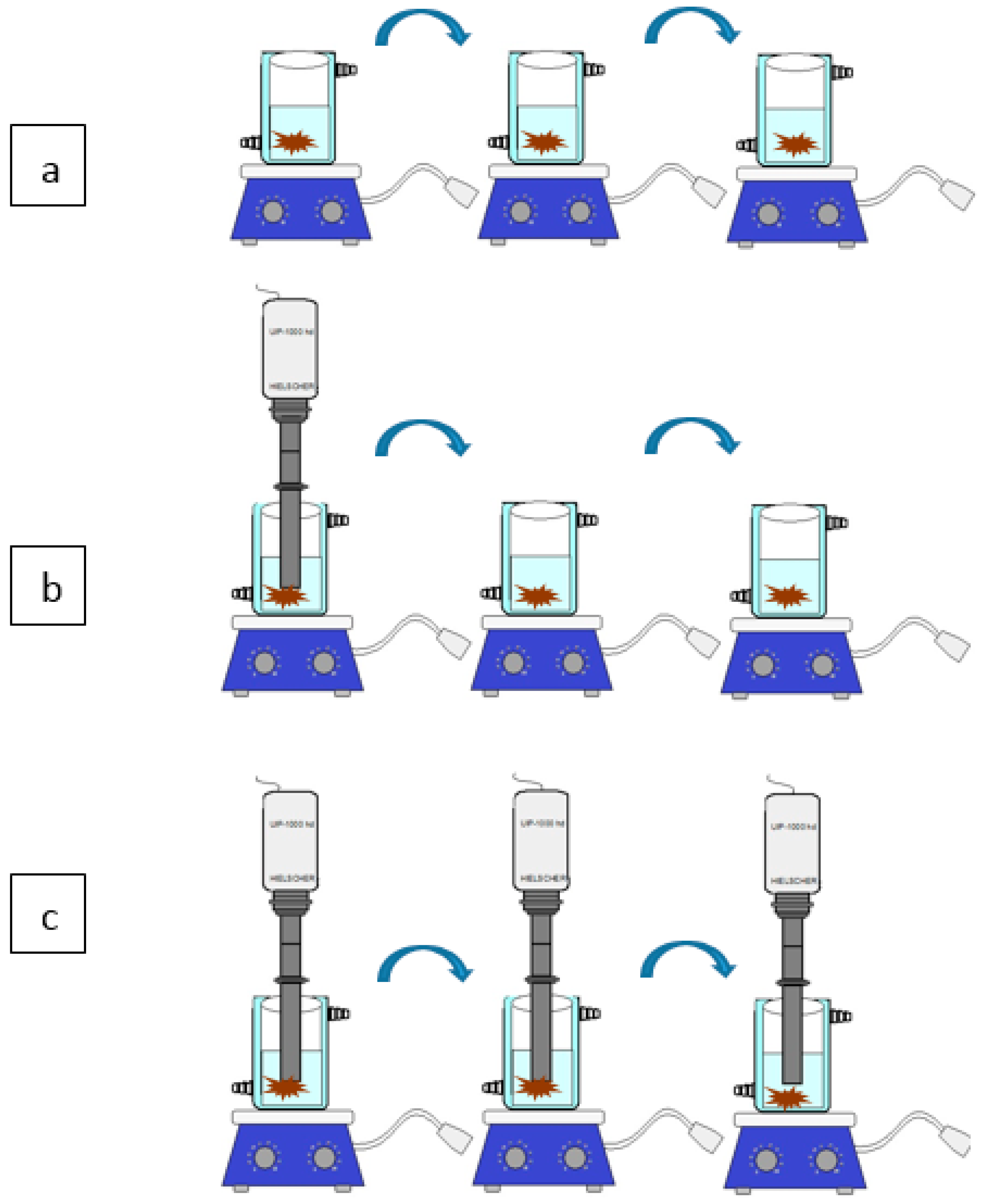
3.3.2. Ultrasound Assisted Extraction (UAE)
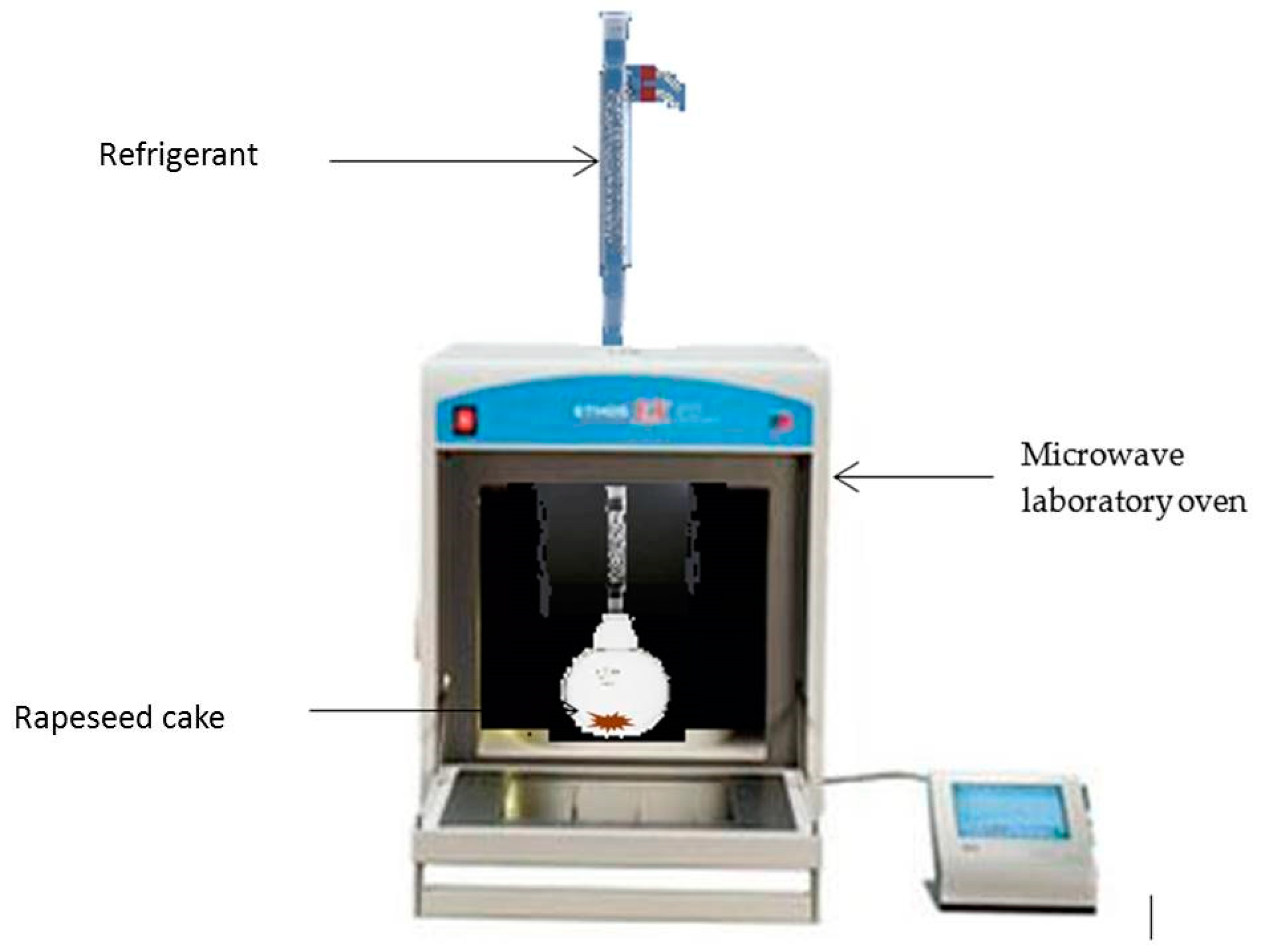
3.3.3. Microwave Assisted Extraction (MAE)
3.3.4. Subcritical Water Extraction (SWE)
3.3.5. Percolation Extraction (PE)
3.4. Experimental Design
3.5. Multistage Cross-Current Simulation
3.6. Total Protein Yield (TPY)
3.7. Gel Exclusion Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kussmann, M.; van Bladeren, P. The extended nutrigenomics-understanding the interplay between the genomes of food, gut microbes, and human host. Front. Genet. 2011, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Gaucher, E. Protein. In Encyclopedia of Astrobiology; Gargaud, M., Amils, R., Quintanilla, J.C., Cleaves, H.J., Irvine, W.M., Pinti, D.L., Viso, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1348–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, I.M.; Coelho, J.F.; Carvalho, M.G.V. Isolation and valorisation of vegetable proteins from oilseed plants: Methods, limitations and potential. J. Food Eng. 2012, 109, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larochette, B.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, J. Cinquante ans de Consommation Alimentaire: Une Croissance Modérée, Mais de Profonds Changements; Division Synthèses des Biens et Services: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Karaca, A.C.; Low, N.; Nickerson, M. Emulsifying properties of canola and flaxseed protein isolates produced by isoelectric precipitation and salt extraction. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2991–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, M.; Carter, C. Dietary phytase supplementation and the utilisation of phosphorus by Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fed a canola-meal-based diet. Aquaculture 2004, 240, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.; Capper, B.; Matty, A. Evaluation of some plant proteins in complete diets for the tilapia Sarotherodon mossambicus. Aquaculture 1982, 27, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oomah, B.D. Flaxseed as a functional food source. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, N.; Yu, S.; Badger, T.M. Comprehensive Phytochemical Profile of Soy Protein Isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 4012–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Thompson, L.U.; Jenkins, D. The effect of phytic acid on in vitro rate of starch digestibility and blood glucose response. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1983, 38, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.H.; Mailer, R.J.; Blanchard, C.L.; Agboola, S.O. Canola proteins for human consumption: Extraction, profile, and functional properties. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, R16–R28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.Y.; Guo, L.L.; Wei, F.; Li, J.F.; Jiang, M.L.; Li, G.M.; Zhao, Y.D.; Chen, H. Some characteristics and functional properties of rapeseed protein prepared by ultrasonication, ultrafiltration and isoelectric precipitation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1488–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Bals, O.; Grimi, N.; Vorobiev, E. A new way for the oil plant biomass valorization: Polyphenols and proteins extraction from rapeseed stems and leaves assisted by pulsed electric fields. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 74, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Gouyo, T.; Grimi, N.; Bals, O.; Vorobiev, E. Pulsed electric field pretreatment of rapeseed green biomass (stems) to enhance pressing and extractives recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba, F.J.; Boussetta, N.; Vorobiev, E. Emerging technologies for the recovery of isothiocyanates, protein and phenolic compounds from rapeseed and rapeseed press-cake: Effect of high voltage electrical discharges. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 31, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, Y.W.; Bruins, M.E.; Sanders, J.P. Enzyme assisted protein extraction from rapeseed, soybean, and microalgae meals. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Huang, Y.; Wen, Q.; Ding, X. Development of green betaine-based deep eutectic solvent aqueous two-phase system for the extraction of protein. Talanta 2016, 152, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, N.; Wen, Q. A green deep eutectic solvent-based aqueous two-phase system for protein extracting. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 864, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenta, S.; de La Guardia, M.; Esteve-Turrillas, F.A. Hard cap espresso machines in Analytical Chemistry. What else? Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6570–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulton, K.; Wang, L. A Pilot-Plant Study of Continuous Ultrasonic Extraction of Soybean Protein. J. Sci. 1982, 47, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozel, M.Z.; Gogus, F.; Lewis, A.C. Subcritical water extraction of essential oils from Thymbra spicata. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibañez, E.; Kubátová, A.; Señoráns, F.J.; Cavero, S.; Reglero, G.; Hawthorne, S.B. Subcritical Water Extraction of Antioxidant Compounds from Rosemary Plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Z.; Howard, L.R. Subcritical water and sulfured water extraction of anthocyanins and other phenolics from dried red grape skin. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, S270–S276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.S.Y.; Dutta, R.; Prasad, D.; Misra, K. Subcritical water extraction of antioxidant compounds from Seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) leaves for the comparative evaluation of antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.M. Superheated water: The ultimate green solvent for separation science. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watchararuji, K.; Goto, M.; Sasaki, M.; Shotipruk, A. Value-added subcritical water hydrolysate from rice bran and soybean meal. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6207–6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiboonsirikul, J.; Mori, M.; Khuwijitjaru, P.; Adachi, S. Properties of extract from okara by its subcritical water treatment. Int. J. Food Prop. 2013, 16, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.; Choi, S.J.; Chun, J.K.; Moon, T.W. Extraction yield of soluble protein and microstructure of soybean affected by microwave heating. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2006, 30, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebovka, N.; Vorobiev, E.; Chemat, F. Enhancing Extraction Processes in the Food Industry, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; p. 570. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.; Sparks, D.; Page, A.; Helmke, P.; Loeppert, R.; Soltanpour, P.; Tabatabai, M.; Johnston, C.; Sumner, M. Nitrogen-total. Methods Soil Anal. 1996, 1085–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Pingret, D.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.-S.; Bourvellec, C.L.; Renard, C.M.; Chemat, F. Lab and pilot-scale ultrasound-assisted water extraction of polyphenols from apple pomace. J. Food Eng. 2012, 111, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérot, S.; Compoint, J.; Larré, C.; Malabat, C.; Guéguen, J. Large scale purification of rapeseed proteins (Brassica napus L.). J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 818, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.



| Run | Coded Variables | Decoded Variables | Response | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | Temperature (°C) | UI (W/cm2) | YProtein (g Protein/100 g DM) | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 45 | 5.5 | 4.3 |
| 2 | +1 | −1 | 70 | 2 | 3.25 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 45 | 5.5 | 4.2 |
| 4 | 0 | +α | 45 | 10.4 | 3.43 |
| 5 | +1 | +1 | 70 | 9 | 3.45 |
| 6 | −1 | −1 | 20 | 2 | 3.22 |
| 7 | −1 | +1 | 20 | 9 | 3.34 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 45 | 5.5 | 4.25 |
| 9 | 0 | −α | 45 | 0.5 | 2.98 |
| 10 | +α | 0 | 80.3 | 5.5 | 2.74 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 45 | 5.5 | 4.2 |
| 12 | −α | 0 | 9.6 | 5.5 | 2.91 |
| Seed Storage Protein Peak Area | Conventional | Ultra-Sound Assisted | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Cruciferin (12S globulins) | 14.0 | 0.2 | 9.7 | 0.2 |
| Napin (2S albumins) | 28.3 | 0.4 | 22.7 | 1.0 |
| 12S/2S ratio | 0.495 | 0.014 | 0.428 | 0.012 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boukroufa, M.; Sicaire, A.-G.; Fine, F.; Larré, C.; Goff, A.L.; Jamault, V.S.; Rakotomanomana, N.; Chemat, F. Green Sonoextraction of Protein from Oleaginous Press Rapeseed Cake. Molecules 2017, 22, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010080
Boukroufa M, Sicaire A-G, Fine F, Larré C, Goff AL, Jamault VS, Rakotomanomana N, Chemat F. Green Sonoextraction of Protein from Oleaginous Press Rapeseed Cake. Molecules. 2017; 22(1):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010080
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoukroufa, Meryem, Anne-Gaëlle Sicaire, Frederic Fine, Colette Larré, Aude Le Goff, Véronique Solé Jamault, Njara Rakotomanomana, and Farid Chemat. 2017. "Green Sonoextraction of Protein from Oleaginous Press Rapeseed Cake" Molecules 22, no. 1: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010080
APA StyleBoukroufa, M., Sicaire, A.-G., Fine, F., Larré, C., Goff, A. L., Jamault, V. S., Rakotomanomana, N., & Chemat, F. (2017). Green Sonoextraction of Protein from Oleaginous Press Rapeseed Cake. Molecules, 22(1), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010080







