Technological Aspects of Chemoenzymatic Epoxidation of Fatty Acids, Fatty Acid Esters and Vegetable Oils: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Methods for Epoxidation of Vegetable Oils
- Epoxidation in the presence of aluminium trioxide, obtained by a sol-gel method [50],
3. Reactions of Chemoenzymatic Epoxidation
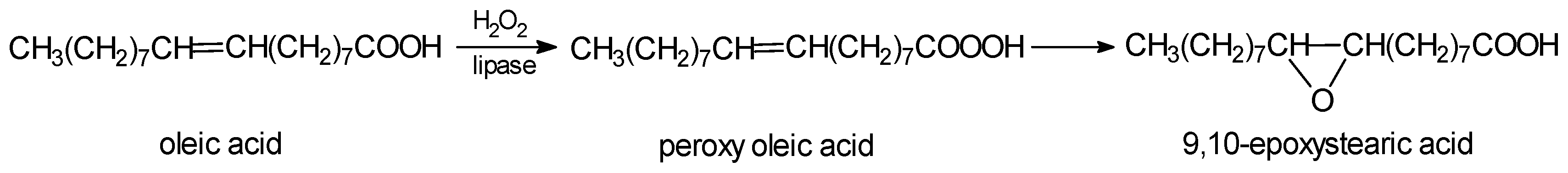
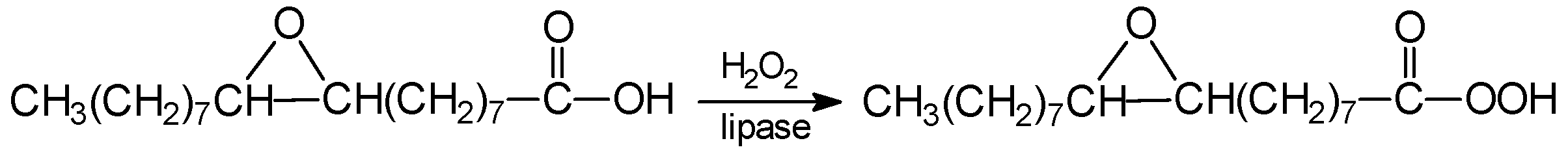
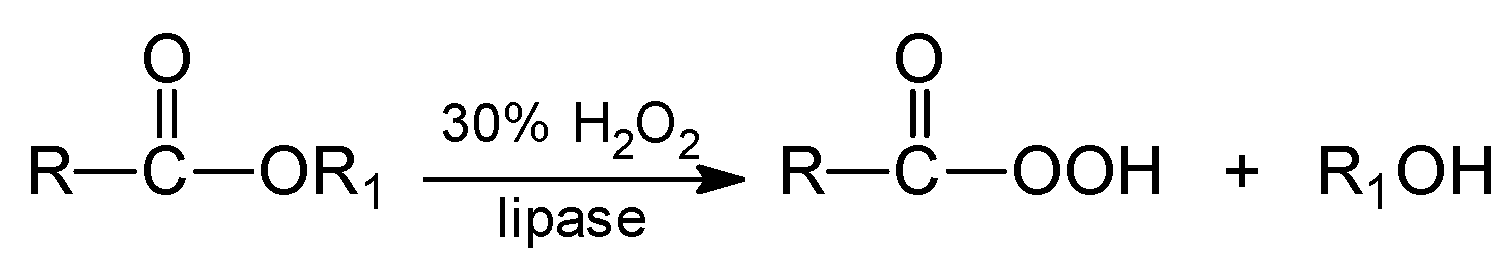
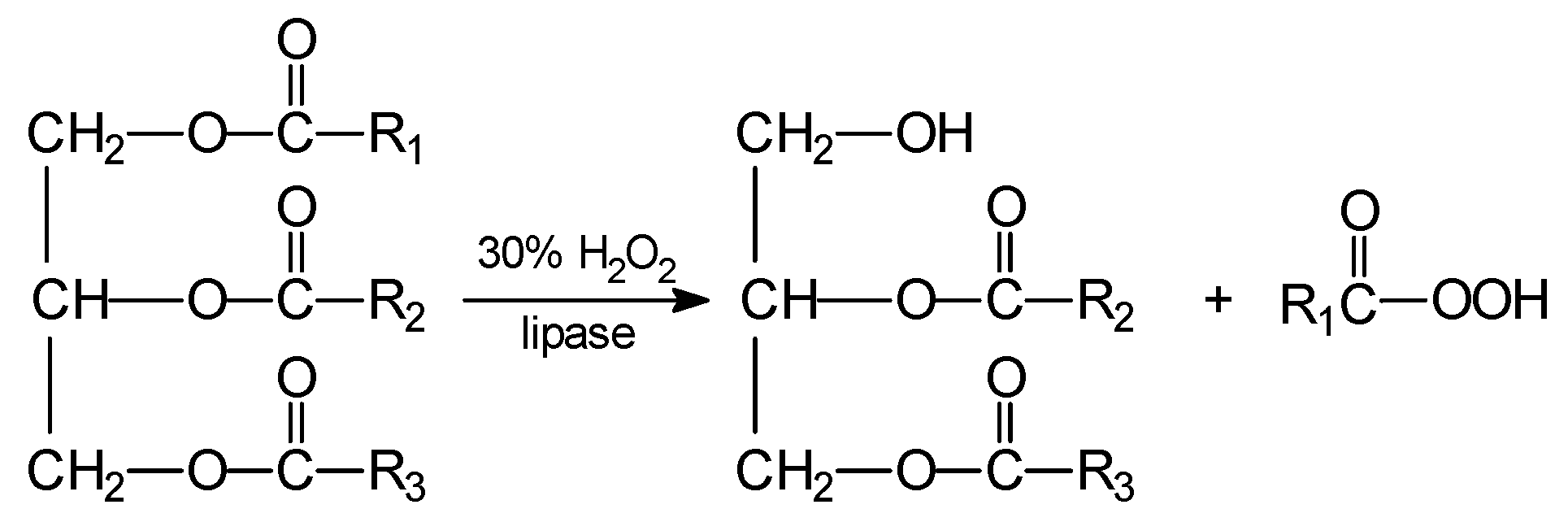
- -
- hydrolysis of ester to alcohol and free acid,
- -
- perhydrolysis of ester with hydrogen peroxide to alcohol and peroxy acid,
- -
- oxidation of free fatty acid with hydrogen peroxide to peroxy acid.
4. Technological Parameters of Chemoenzymatic Epoxidation
4.1. Amount of Hydrogen Peroxide and Time of Reaction
4.2. The Effect of Process Temperature and Type of Solvent
4.3. The Presence of Free Fatty Acids in Oils or Fatty Acids Esters
4.4. Effect of Simultaneous Changes in a Few Parameters
5. Stability and Inactivation of Lipase B
6. Conclusions
- -
- mild reaction conditions, 25–55 °C,
- -
- neutral pH of the reaction mixture,
- -
- possibility of carrying out the process without solvent, which facilitates product separation,
- -
- formation of stable carboxylic peroxyacids under the effect of hydrogen peroxide and in the presence of the enzyme applied; when vegetable oils are used – the above formation also takes place as a result of perhydrolysis,
- -
- possibility of useing immobilized lipase as a biocatalyst (native enzymes can occur in the form of liquids or solid powders),
- -
- high chemo-, region- and stereoselectivity,
- -
- often high conversion of unsaturated bonds in vegetable oils, unsaturated fatty acids and fatty acids esters,
- -
- small contribution or the absence of side reactions (high selectivity),
- -
- the method is safe and environmentally friendly.
| Substrate | Amount of Free Fatty Acid | H2O2/C=C Molar Ratio mol/mol | Temperature (°C) | Catalyst (wt %) | Solvent | Mixing (rpm) | Reaction Time (h) | Conversion (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean oil | Oleic acid 8 wt %/SO | 2:1 | 50 | Lipase B/acrylic resin | Toluene | 350 | 24 | 95–99 | [73] |
| Soybean oil methyl esters IN = 133.0 g/100 g oil | FFA/SME = 0.001:1 mol/g | 1.4 g H2O2/1 g SME | 55 | 3% Lipase B/acrylic resin | 5:1 g/g toluene/esters | 800 | 10–12 | 98 | [72] |
| Sunflower oil methyl esters | Octanoic acid/esters = 10 mmol/g | not specified | 30 | Lipase B 10 times was reused | CH2Cl2, CH2Cl2-H2O | not specified | 16 | 99 | [76] |
| Oleic acid or ethyl oleate | not specified | H2O2 concentration in solution 0.2 wt % | 55 | 10% Amano lipase from Burkholderia cepacia * | Ethyl acetate | 150 | 3 | 88 | [27] |
| Safindus muko rossi seed oil IN = 84.8 g/100 g oil | Stearic acid | 4:1 | 50 | 2 wt % Lipase B/oil | Toluene | 800 | 7 | 90.2 | [75] |
| Rapeseed methyl esters | FFA are formed by ester hydrolysis | H2O2 concentration in water phase-15 M | 40 | 3 wt % Lipase B/RME | Solvent-free | 450 | 14 | 83 | [85] |
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muturi, P.; Wang, D.; Dirlikov, S. Epoxidized vegetable oils as reactive diluents. Comparison of vernonia, epoxidized soybean and epoxidized linseed oils. Prog. Org. Coat. 1994, 25, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhvaryu, A.; Erhan, S.Z. Epoxidized soybean oil as a potential source of high-temperature lubricants. Ind. Crops Prod. 2002, 15, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, A.; Rustoy, E.; Baldessaria, A.; Baltanas, M.A. Lubricants from chemically modified vegetable oils. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crivello, J.V.; Narayan, R.; Sternstein, S.S. Photoinitiated cationic polymerization of naturally occurring epoxidized triglycerides. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 64, 2073–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantoni, L.; Simoneau, C. European survey of contamination of homogenized baby food by epoxidized soybean oil migration from plasticized PVC gaskets. Food Addit. Contam. 2003, 20, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soucek, M.D.; Johnson, A.H.; Wegner, J.M. Ternary evaluation of UV-curable seed oil inorganic/organic hybrid coatings using experimental design. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 51, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, W.D.; Kumar, R.N.; Mek Zah, S.; Hilmi, M.M. UV radiation curing of epoxidized palm oil-cycloaliphatic diepoxide system induced by cationic photoinitiator for surface coating. Eur. Polym. J. 2003, 39, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, N.O.; Kandeel, E.M.; Badr, E.E.; El-Sawy, M.M. Syntheses and properties of renewable environment-friendly epoxy resins for surface coatings. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2008, 29, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thames, S.F.; Yu, H.B. Cationic UV-cured coatings of epoxide-containing vegetable oils. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 115, 2008–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wool, R.; Küsefoglu, S.; Palmese, G.; Khot, S.; Zhao, R. High Modulus Polymers and Composites from Plant Oils. USA Patent 6 121 398, 19 September 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, H.; Adhvaryu, A.; Erhan, S.Z. Preparation and properties of lubricant base stocks from epoxidized soybean oil and 2-ethylhexanol. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2003, 80, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.; Erhan, S.Z. Modification of epoxidized soybean oil for lubricant formulations with improved oxidative stability and low pour point. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2001, 78, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, D. The study of epoxidized rapeseed oil used as a potential biodegradable lubricant. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirpsza, Z. Polyurethanes: Chemistry, Technology, Application; WNT: Warsaw, Poland, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski, B. Zagadnienia z Chemii i Technologii Poliuretanów; Kazimierz Wielki University in Bydgoszcz: Bydgoszcz, Poland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Metzger, J.O.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Lipids as renewable resources: Current state of chemical and biotechnological conversion and divesification. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2006, 71, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteavaro, L.L.; da Silva, E.O.; Costa, A.P.O.; Samios, D.; Gerbase, A.E.; Petzhold, C.L. Polyurethane networks from formiated soy polyols: Synthesis and mechanical characterization. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2005, 82, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagawa, H.; Mohanty, A.K.; Drzal, L.T.; Misra, M. Nanocomposites from biobased epoxy and single-wall carbon nanotubes: Synthesis, and mechanical and thermophysical properties evaluation. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khot, S.N.; Lascala, J.J.; Can, E.; Moyre, S.S.; Wiliams, G.I.; Palmese, G.R.; Kusefoglu, S.H.; Wool, P. Development and Application of Triglyceride-Based Polymers and Composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 82, 703–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermandez-Lopez, S.; Vigueras-Santiago, E.; Marcado-Posadas, J.; Sanchez-Mendieta, V. Electricial properties of acrylated-epoxidized soybean oil polymers-based composites. Adv. Technol. Mater. Mat. Process. J. 2006, 8, 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- Gerbase, A.E.; Petzhold, C.L.; Costa, A.P.O. Dynamic mechanical and thermal behavior of epoxy resins based on soybean oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2002, 79, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Adhvaryu, A.; Gordon, S.H.; Erhan, S.Z.; Willet, J.L. Synthesis of diethylamine-functionalized soybean oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 9485–9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Scala, J.; Wool, R.P. Property analysis of triglyceride-based thermosets. Polymer 2005, 46, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroaki, M.; Robert, J.J.; Amar, K.M.; Manjusri, M.; Lawrence, T.D. Biobased epoxy/clay nanocomposites as a new matrix for CFRP. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.Y.; Liu, Z.S.; Erhan, S.Z.; Carriere, C.J. A potential biodegradable rubber—Viscoelastic properties of a soybean oil-based composite. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2002, 79, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, I.; Bothe, D.; Prüss, J.; Warnecke, H.J. Chemoenzymatic epoxidation of unsaturated plant oils. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Abrêu, F.; Sutili, F.K.; Miranda, L.S.M.; Leite, S.G.F.; de Souza, R.M.A.; Leal, I.C.R. Epoxidation of oleic acid catalyzed by PSCI-Amano lipase optimized by experimental design. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2012, 81, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Goud, V.V.; Patwardhan, A.V.; Pradhan, N.C. Studies on the epoxidation of mahua oil (Madhumica Indica) by hydrogen peroxide. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimon, J.; Salih, N. Improved low temperature properties of 2-ethylhexyl-9(10)-hydroxy-10(9)—Acyloxystearate derivatives. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2009, 31, 583–591. [Google Scholar]
- Campanella, A.; Fontanini, C.; Baltanas, M.A. High yield epoxidation of fatty acid methyl esters with performic acid generated in situ. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 144, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, J.L.; Wool, R.P. Effect of FA Composition on epoxidation kinetics of TAG. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2002, 79, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, V.V.; Pradhan, N.C.; Patwardhan, A.V. Epoxidation of karanja (Pongamia glabra) oil by H2O2. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2006, 83, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinadovic-Fiser, S.; Jankovic, M.; Petrovic, Z.S. Kinetics of in situ epoxidation of soybean oil in bulk catalyzed by ion exchange resin. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2001, 78, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, V.V.; Patwardhan, A.V.; Dinda, S.; Pradhan, N.C. Epoxidation of karanja (Pongamia glabra) oil catalyzed by acidic ion exchange resin. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2007, 109, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, P.D.; Puri, R.G.; Patil, H.V. Epoxidation of wild safflower (Carthamus oxyacantha) oil with peroxy acid in presence of strongly acidic cation exchange resin IR-122 as catalyst. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2011, 3, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Gurbanov, M.S.; Chalabiev, Ch.A.; Mamedov, B.A.; Efendiev, A.A. Epoxidation of soybean oil in the course of cooxidation with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of propanoic acid and chlorinated KU-2 8 cation exchanger. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2005, 78, 1678–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungroo, R.; Pradhan, N.C.; Goud, V.V.; Dalai, A.K. Epoxidation of canola oil with hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by acidic ion exchange resin. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2008, 85, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, V.V.; Patwardhan, A.V.; Dinda, S.; Pradhan, N.C. Kinetics of epoxidation of jatropha oil with peroxyacetic and peroxyformic acid catalysed by acidic ion exchange resin. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 4065–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, M.; Ravasio, N.; Psaro, R.; Gianotti, E.; Coluccia, S.; Marchese, L. Epoxidation of unsaturated FAMEs obtained from vegetable source over Ti(IV)-grafted silica catalysts: A comparison between ordered and non-ordered mesoporous materials. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2006, 250, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blayo, A.; Gandini, A.; le Nest, J.F. Chemical and rheological characterizations of some vegetable oils derivatives commonly used in printing inks. Ind. Crops Prod. 2001, 14, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbanov, M.S.; Mamedov, B.A. Epoxidation of flax oil with hydrogen peroxide in a conjugate system in the presence of acetic acid and chlorinated cation exchanger KU-2 × 8 as catalyst. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2009, 82, 1483–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, E.; Clacens, J.M.; Barrault, J.; Pouilloux, Y. Solvent-free selective epoxidation of fatty esters over a tungsten-based catalyst. Catal. Today 2009, 140, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benanibaa, M.T.; Belhaneche-Bensemrab, N.; Gelbard, G. Kinetics of tungsten-catalyzed sunflower oil epoxidation studied by 1H-NMR. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2007, 109, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, A.; Baltanas, M.A.; Capel-Sanchez, M.C.; Campos-Martin, J.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Soybean oil epoxidation with hydrogen peroxide using an amorphous Ti/SiO2 catalyst. Green Chem. 2004, 6, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, A.; Baltanas, M.A. Degradation of the oxirane ring of epoxidized vegetable oils in a liquid-liquid-solid heterogeneous reaction system. Chem. Eng. Process. 2007, 46, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, L.A.; Weckes, P.; Schuster, H.; Hoelderich, W.F. Mesoporous and amorphous Ti-silicas on the epoxidation of vegetable oils. J. Catal. 2005, 232, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, P.; Dong, Y.; Jia, Ch.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H. Novel Ti and mesoporous molecular sieves: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity in the epoxidation of vegetable oil. Catal. Lett. 2010, 137, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Tekin, A.; Hammond, E.G.; Woo, L.K. Catalytic epoxidation of methyl linoleate. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2004, 4, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbase, A.E.; Gregorio, J.R.; Martinelli, M.; Brasil, M.C.; Mendes, N.F. Epoxidation of soybean oil by the methyltrioxorenium CH2Cl2/H2O2 catalytic biphasic system. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2002, 79, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, J.S.; Teixera, M.; Schuchardt, U. Alumina catalyzed epoxidation of unsaturated fatty esters with hydrogen peroxide. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 318, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüsch gen. Klaas, M.; Warwel, S. Chemoenzymatic epoxidation of unsaturated fatty acid esters and plant oils. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1996, 73, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüsch gen. Klaas, M.; Warwel, S. Complete and partial epoxidation of plant oils by lipase-catalyzed perhydrolysis. Ind. Crop Prod. 1999, 9, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüsch gen. Klaas, M.; Warwel, S. Lipase-catalysed preparation of peroxy acids and their use for epoxidation. J. Mol. Catal A: Chem. 1997, 117, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwel, S.; Rüsch gen. Klaas, M. Chemoenzymatic epoxidation of unsaturated carboxylic acids. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 1995, 1, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, S.; Patwardhan, A.V.; Goud, V.V.; Pradhan, N.C. Epoxidation of cottonseed oil by aqueous hydrogen peroxide catalysed by liquid inorganic acids. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3737–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, R.; Alex, R.; Vinod, V.S.; Premalatha, C.K.; Kuriakose, B. Studies on epoxidized rubber seed oil as plasticizer for acrylonitrile butadiene rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okieimen, F.E.; Bakare, O.I.; Okieimen, C.O. Studies on the epoxidation of rubber seed oil. Ind. Crop Prod. 2002, 15, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjőrkling, F.; Frykman, H.; Goldtfredsen, S.E.; Kirk, O. Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of peroxycarboxylic acids and lipase-mediated oxidations. Tetrahedron 1992, 48, 4587–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.D.; Devi, K.M. Enzymatic synthesis of perlauric acid using Novozym® 435. BioChem. Eng. J. 2002, 10, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelle, M. Lipases from Candida antarctica and Humicola Lanuginosa—Structure-Activity Relationships and Applied Catalysis; Tekniska högsk: Stockholm, Sweden, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Biermann, U.; Friedt, W.; Lang, S.; Lühs, W.; Machmüller, G.; Metzger, J.O.; Rüsch gen. Klaas, M.; Schäfer, H.J.; Schneider, M.P. New synthesis with oils and fats as renewable raw materials for the chemical industry. Angew. Chem. Int Ed. 2000, 39, 2206–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppenberg, J.; Hansen, N.T.; Patkar, S.; Jones, T.A. The sequence, crystal structure determination and refinement of two crystal forms of lipase B from Candida antarctica. Structure 1994, 2, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiran, C.; Lecomte, J.; Dubreucq, E.; Villeneuve, P. Chemoenzymatic epoxidation of fatty compounds—Focus on processes involving a lipase-catalyzed perhydrolysis step. OCL 2008, 15, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana-Coca, C.; Camocho, S.; Adlercreutz, D.; Mattiasson, B.; Hatti-Kaul, R. Chemoenzymatic epoxidation of linoleic acid: Parameters influencing the reaction. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2005, 107, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, B.M.; Salimon, J. Epoxidation of vegetable oils and fatty acids: Catalyst methods and advantages. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar]
- Törnvall, U.; Orellana-Coca, C.; Hatti-Kaul, R.; Adlercreutz, D. Stability of immobilized Candida antarctica lipase B during chemoenzymatic epoxidation of fatty acids. Enzyme Microbial. Technol. 2007, 40, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana-Coca, C.; Billakanti, J.M.; Mattiasson, B.; Htti-Kaul, R. Lipase mediated simultaneous esterification and epoxidation of oleic acid for the production of alkylepoxystearates. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2007, 44, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana-Coca, C.; Törnvall, U.; Adler-Creutz, D.; Mattiasson, B.; Hatti-Kaul, R. Chemoenzymatic epoxidation of oleic acid and methyl oleate in solvent-free medium. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2005, 23, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjőrkling, F.; Gadtfredsen, S.E.; Kirk, O. Lipase mediated formation of peroxycarboxylic acids used in catalytic epoxidation of alkenes. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1990, 1301–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, W.S.D.; Lapis, A.A.M.; Suarez, P.A.Z.; Neto, B.A.D. Enzyme mediated epoxidation of methyl oleate supported by imidazolium based ionic liquid. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2011, 68, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Torres, M.; Jiménez-Osés, G.; Mayoral, J.A.; Pires, E. Evaluation of several catalytic systems for epoxidation of methyl oleate using H2O2 as oxidant. Catal. Today 2012, 195, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Sun, S.; Bi, Y.; Yang, G.; Ma, R.; Yang, H. Enzymatic epoxidation of soybean oil methyl esters in the presence of free fatty acids. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlcek, T.; Petrovic, Z. Optimization of the chemoenzymatic epoxidation of soybean oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2006, 83, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yang, G.; Bi, Y.; Liang, H. Enzymatic epoxidation of corn oil by perstearic acid. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 1567–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Ke, X.; Cui, L.; Yang, G.; Bi, Y.; Song, F.; Xu, X. Enzymatic epoxidation of Sapindus mukorossi seed oil by perstearic acid optimized using response surface methodology. Ind. Crop Prod. 2011, 33, 676–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.C.S.; Lara, L.R.S.; Bitecourt, T.B.; Nascimento, M.G.; Nunes Marta, M.R. Chemoenzymatic epoxidation of sunflower oil methyl esters. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2009, 20, 1473–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Téllez, G.L.; Vigueras-Santiago, E.; Hermandez-Lopez, S. Characterization of linseed oil epoxidized at different percentages. Superf. Vacio 2009, 22, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kazariya, A.; Matsumura, S. Enzymatic synthesis and crosslinking of novel high molecular weight polyepoxyricinoleate. Polymers 2012, 4, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouf, Ch.; Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; Figuerola-Espinoza, M.C.; Dubreucq, E.; Fulcrand, H.; Villeneuve, P. The use of lipases as biocatalysts for the epoxidation of fatty acids and phenolic compounds. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1740–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valivety, R.H.; Halling, P.J.; Peilov, A.D.; Macrae, A.R. Lipases from different sources vary widely in dependence of catalytic activity on water activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1992, 1122, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, P. Lipases in lipophilization reactions. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 515–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, M.A.; Hang, Y.D. Enzymatic synthesis of esters in organic medium with lipase from Byssochlamys fulva. Biotechnol. Lett. 1995, 17, 1081–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Schmid, R. Lipase catalyzed synthesis of vitamin C fatty acid esters. Biotechnol. Lett. 1999, 21, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutur, O.; Dubreucq, E.; Galzy, P. Factors influencing ester synthesis catalyzed in aqueous media by the lipase from Candida deformans (Zach) Langeron and Guerra. J. Biotechnol. 1995, 42, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severiano, A.; Hagström, A.; Hatti-Kaul, R.; Da Fonseca, M.M.R. Chemoenzymatic Epoxidation of Rapeseed Methyl Esters: Parameters Influencing the Reaction and Enzyme Stability. Available online: https://fenix.tecnico.ulisboa.pt/downloadFile/395137861152/Epoxidation%20of%20RME.pdf (access on 24 November 2015).
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milchert, E.; Malarczyk, K.; Kłos, M. Technological Aspects of Chemoenzymatic Epoxidation of Fatty Acids, Fatty Acid Esters and Vegetable Oils: A Review. Molecules 2015, 20, 21481-21493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201219778
Milchert E, Malarczyk K, Kłos M. Technological Aspects of Chemoenzymatic Epoxidation of Fatty Acids, Fatty Acid Esters and Vegetable Oils: A Review. Molecules. 2015; 20(12):21481-21493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201219778
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilchert, Eugeniusz, Kornelia Malarczyk, and Marlena Kłos. 2015. "Technological Aspects of Chemoenzymatic Epoxidation of Fatty Acids, Fatty Acid Esters and Vegetable Oils: A Review" Molecules 20, no. 12: 21481-21493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201219778
APA StyleMilchert, E., Malarczyk, K., & Kłos, M. (2015). Technological Aspects of Chemoenzymatic Epoxidation of Fatty Acids, Fatty Acid Esters and Vegetable Oils: A Review. Molecules, 20(12), 21481-21493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201219778





