Optimized Enzymatic Synthesis of Hesperidin Fatty Acid Esters in a Two-Phase System Containing Ionic Liquid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
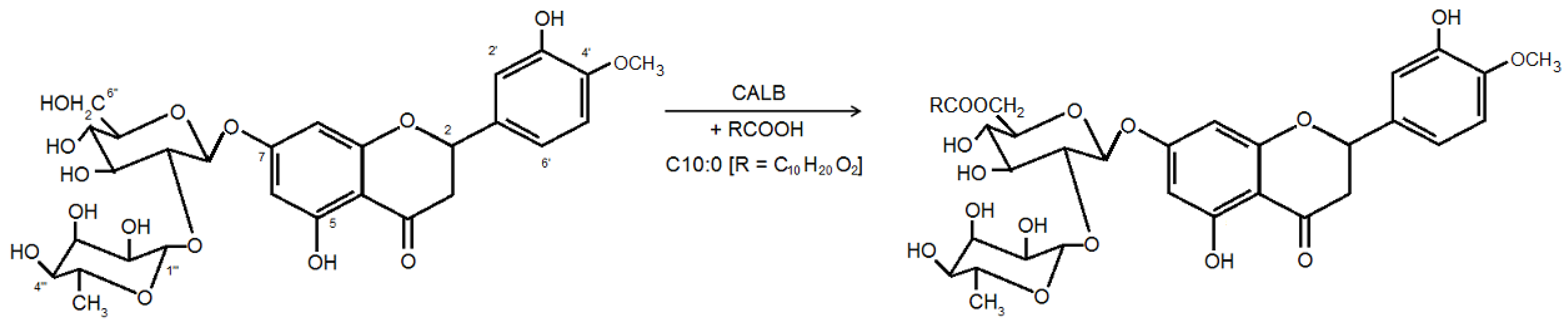
2. Results and Discussion
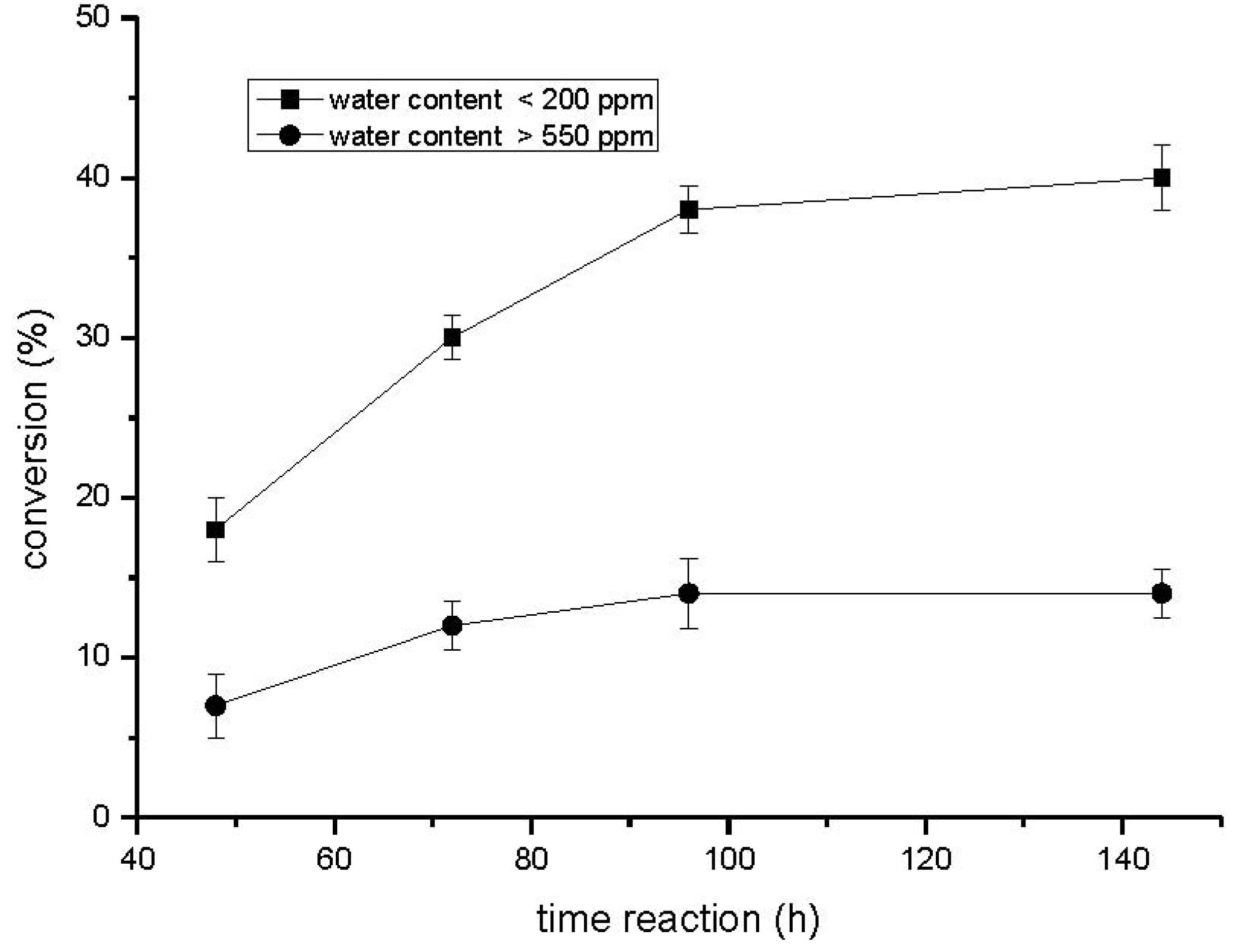
2.1. Influence of the Reaction Time and Hydration State
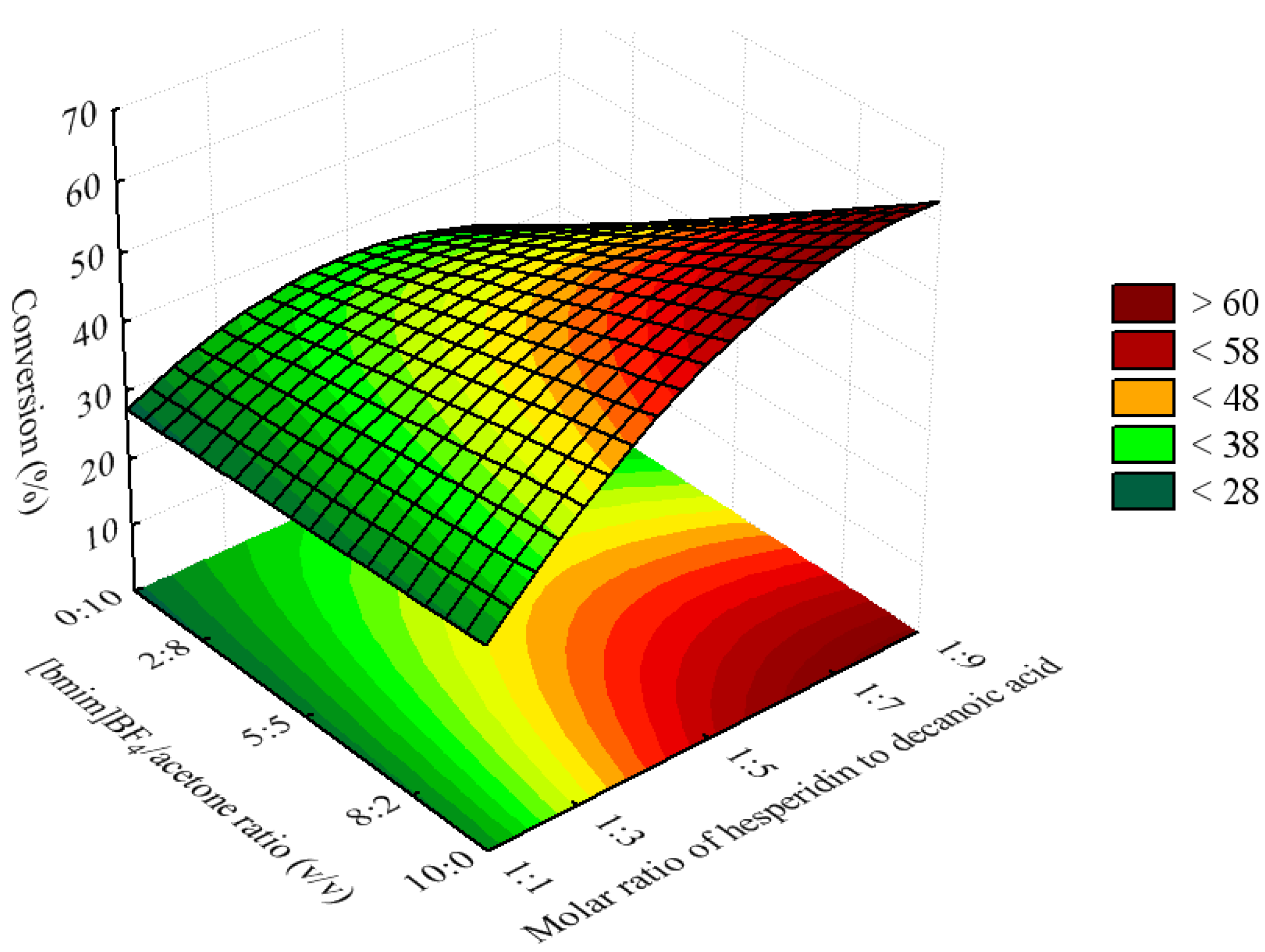
2.2. Optimization of the Esterification Process Using Response Surface Methodology
| Variable | Coded variable levels | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1.68 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 1.68 | ||
| Molar ratio of hesperidin to decanoic acid | X1 | 1:1 | 1:3 | 1:5 | 1:7 | 1:9 |
| [bmim]BF4/acetone ratio (v/v) | X2 | 10:0 | 8:2 | 5:5 | 2:8 | 0:10 |
| Lipase concentration (mg/mL) | X3 | 2.0 | 4.4 | 8.0 | 11.6 | 14.0 |
| Run | Coded variable levels | Observed conversion yield a (%) | Predicted conversion yield a (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | |||
| 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 29.2 | 29.25 |
| 2 | +1 | −1 | −1 | 47.0 | 44.45 |
| 3 | −1 | +1 | −1 | 28.2 | 23.47 |
| 4 | +1 | +1 | −1 | 23.7 | 27.07 |
| 5 | −1 | −1 | +1 | 42.5 | 40.67 |
| 6 | +1 | −1 | +1 | 55.3 | 55.87 |
| 7 | −1 | +1 | +1 | 27.2 | 34.89 |
| 8 | +1 | +1 | +1 | 38.3 | 38.49 |
| 9 | −1.68 | 0 | 0 | 23.1 | 23.01 |
| 10 | +1.68 | 0 | 0 | 39,2 | 38.79 |
| 11 | 0 | −1.68 | 0 | 48.5 | 49.72 |
| 12 | 0 | +1.68 | 0 | 35.1 | 30.26 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | −1.68 | 24.3 | 30.39 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | +1.68 | 50.2 | 49.58 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 42.0 | 39.99 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 38.6 | 39.99 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 39.5 | 39.99 |
| 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 43.3 | 39.99 |
| Regression | Standard Error | t(8) | p | −90,% | +90,% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean/Interc. * | 40.8465 | 2.06081 | 19.8205 | 0.00000 | 36.0943 | 45.5988 |
| X1 a(L)(Linear) * | 4.7039 | 1.11755 | 4.2091 | 0.00296 | 2.1268 | 7.2810 |
| X1(Q)(Quadratic) * | −3.3864 | 1.16242 | −2.9132 | 0.01949 | −6.0670 | −0.7059 |
| X2 b (L) * | −5.7903 | 1.11755 | −5.1812 | 0.00084 | −8.3674 | −3.2132 |
| X2 (Q) | 0.2983 | 1.16242 | 0.2566 | 0.80393 | −2.3822 | 2.9788 |
| X3 c (L) * | 5.7100 | 1.11755 | 5.1093 | 0.00091 | 3.1329 | 8.2871 |
| X3 (Q) | −1.2606 | 1.16242 | −1.0844 | 0.30974 | −3.9411 | 1.4199 |
| X1L by X2L * | −2.9000 | 1.45951 | −1.9869 | 0.08215 | −6.2656 | 0.4656 |
| X1L by X3L | 1.3750 | 1.45951 | 0.9420 | 0.37372 | −1.9906 | 4.7406 |
| X2L by X3L | −0.9500 | 1.45951 | −0.6509 | 0.53335 | −4.3156 | 2.4156 |
| Source of variation | Sum of squares | Degrees of freedom | Mean square | F-value | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression | 1412 | 5 | 282.476 | 18.56 | 0.000028 |
| Residual | 183 | 12 | 15.21833 | ||
| Lack of fit | 169 | 9 | 18.77778 | 4.14 | |
| Pure error | 14 | 3 | 4.54 | ||
| Total | 1595 | 17 |


2.3. Verification of the Optimal Conditions
3. Experimental
3.1. General
3.2. Enzymatic Acylation Procedure
3.3. Experimental Design

3.4. Statistical Analysis
3.5. Validation of the Experimental Model
3.6. UPLC-MS Quantification
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgment
Conflict of Interest
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.
References
- Harborne, J.B.; Williams, C.A. Advances in flavonoid research since 1992. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havsteen, B.H. The biochemistry and medical significance of the flavonoids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 96, 67–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiero, H.; Tew, K.D.; Nguyen, B.G.; Mathe, G. Polyphenols: Do they play a role in the prevention of human pathologies? Biomed. Pharmacother. 2002, 56, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.K. Pharmcacological properties of flavonoids including flavolignans - Integration of petrocrops with drug development from plants. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2006, 65, 477–484. [Google Scholar]
- di Carlo, G.; Mascolo, N.; Izzo, A.A.; Capasso, F. Flavonoids: Old and new aspects of a class of natural therapeutic drugs. Life Sci. 1999, 65, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaeli, H.; Sobrattee, S.; Pierce, G.N. The importance of lipid solubility in antioxidants and free radical generating systems for determining lipoprotein peroxidation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, K.E.; Tagliaferro, A.R.; Bibilya, D.J. Flavonoid antioxidants: Chemistry, metabolism and structure-activity relationships. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebil, L.; Humeau, C.; Anthony, J.; Dehez, F.; Engasser, J.M.; Ghoul, M. Solubility of flavonoids in organic solvents. J. Chem. Eng. 2007, 52, 1552–1556. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, A.; Garg, S.; Zaneveld, L.J.; Singla, A.K. Chemistry and pharmacology of the citrus bioflavonoid hesperidin. Phytother. Res. 2001, 15, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, E.; Mariotte, A.M.; Boumendjel, A.; Bresson-Rival, D. Nouveaux esters de flavonoides et leur utilization en cosmétique, dermopharmacie, en pharmacie et en agro-alimentaire. FR2778663-A1, 1998.
- Rice-Evans, C.A.; Miller, N.J.; Paganga, G. Structure-antioxidant activity relationships of flavonoids and phenolic acids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 933–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Nakajima, N. Structural aspects of acylated plant pigments: Stabilization of flavonoid glucosides and interpretation of their functions. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2003, 23, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H.; Yamagami, A. Antioxidative activity of monoacylated anthocyanins isolated from Muscat Bailey A grape. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 1994, 42, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rantwick, F.; Lau, R.M.; Sheldon, R.A. Biocatalytic transformations in ionic liquids. Trends Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rantwijk, F.; Sheldon, R.A. Biocatalysis in ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2757–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.S. Properties of ionic liquids solvents for catalysis. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2004, 214, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.J. Methods for stabilizing and activating enzymes in ionic liquids - A review. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 891–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoura, M.H.; Polydera, A.C.; Katapodis, P.; Kolisis, F.N.; Stamatis, H. Effect of different reaction parameters on the lipase-catalyzed selective acylation of polyhydroxylated natural compounds in ionic liquids. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirozzi, D.; Greco, F.G., Jr. Activity and stability of lipases in the synthesis of butyl lactate. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2004, 34, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. Effect of ions and other compatible solutes on enzyme activity, and its implication for biocatalysis using ionic liquids. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2005, 37, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulon, D.; Ismail, A.; Girardin, M.; Rovel, B.; Ghoul, M. Effect of different biochemical parameters on the enzymatic synthesis of fructose oleate. J. Biotechnol. 1996, 51, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Kontogianni, A.; Skouridou, V.; Sereti, V.; Stamatis, H.; Kolisis, F.N. Lipase-catalyzed esterification of rutin and naringin with fatty acids of medium carbon chain. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2003, 21, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellou, F.; Lazari, D.; Skaltsa, H.; Tselepis, A.D.; Kolisis, F.N.; Stamatis, H. Biocatalytic preparation of acylated derivatives of flavonoid glycosides enhances their antioxidant and antimicrobial activity. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 116, 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Kontogianni, A.; Skouridou, V.; Sereti, V.; Stamatis, H.; Kolisis, F.N. Regioselective acylation of flavonoids catalyzed by lipase in low toxicity media. Eur. J. Lipid. Sci. Technol. 2001, 103, 655–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellou, F.; Loutrari, H.; Stamatis, H.; Roussos, C.; Kolisis, F.N. Enzymatic esterification of flavonoids with unsaturated fatty acids: Effect of the novel esters on vascular endothelial growth factor release from K562 cells. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 2029–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Araújo, M.E.M.B.d.; Contesini, F.J.; Franco, Y.E.M.; Sawaya, A.C.H.F.; Alberto, T.G.; Dalfré, N.; Carvalho, P.d.O. Optimized Enzymatic Synthesis of Hesperidin Fatty Acid Esters in a Two-Phase System Containing Ionic Liquid. Molecules 2011, 16, 7171-7182. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16087171
Araújo MEMBd, Contesini FJ, Franco YEM, Sawaya ACHF, Alberto TG, Dalfré N, Carvalho PdO. Optimized Enzymatic Synthesis of Hesperidin Fatty Acid Esters in a Two-Phase System Containing Ionic Liquid. Molecules. 2011; 16(8):7171-7182. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16087171
Chicago/Turabian StyleAraújo, Maria Elisa Melo Branco de, Fabiano Jares Contesini, Yollanda Edwirges Moreira Franco, Alexandra C.H. Frankland Sawaya, Thiago Grando Alberto, Natália Dalfré, and Patrícia de Oliveira Carvalho. 2011. "Optimized Enzymatic Synthesis of Hesperidin Fatty Acid Esters in a Two-Phase System Containing Ionic Liquid" Molecules 16, no. 8: 7171-7182. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16087171
APA StyleAraújo, M. E. M. B. d., Contesini, F. J., Franco, Y. E. M., Sawaya, A. C. H. F., Alberto, T. G., Dalfré, N., & Carvalho, P. d. O. (2011). Optimized Enzymatic Synthesis of Hesperidin Fatty Acid Esters in a Two-Phase System Containing Ionic Liquid. Molecules, 16(8), 7171-7182. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16087171




