Simon’s Algorithm in the NISQ Cloud
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Hidden Subgroups and Simon’s Problem
3. The Quantum Cloud
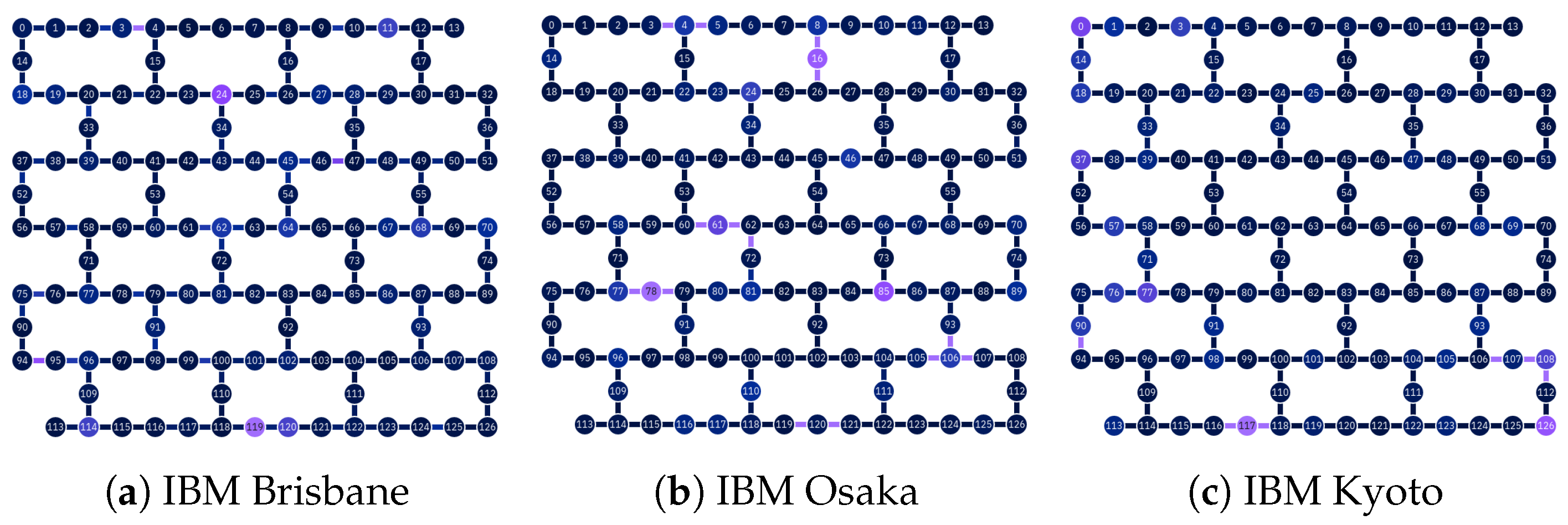
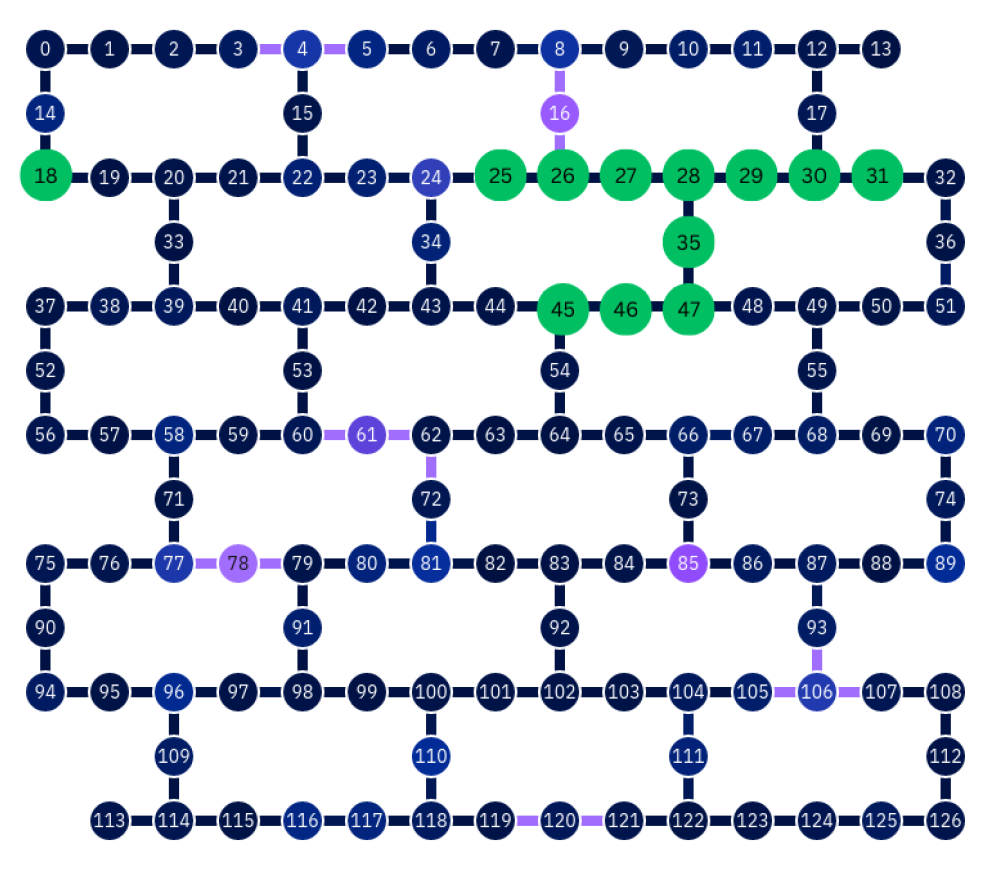
3.1. Superconducting Qubits—IBM
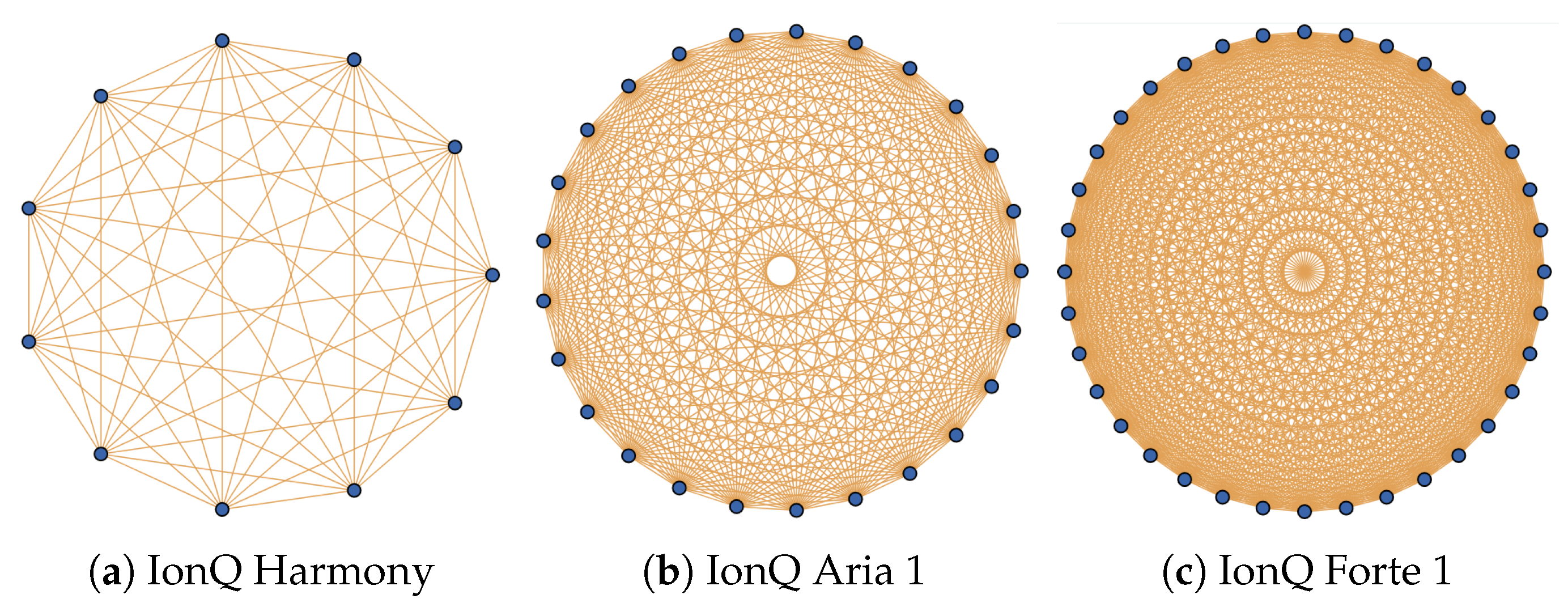
3.2. Ion Traps—IonQ
4. Simon’s Algorithm on NISQ
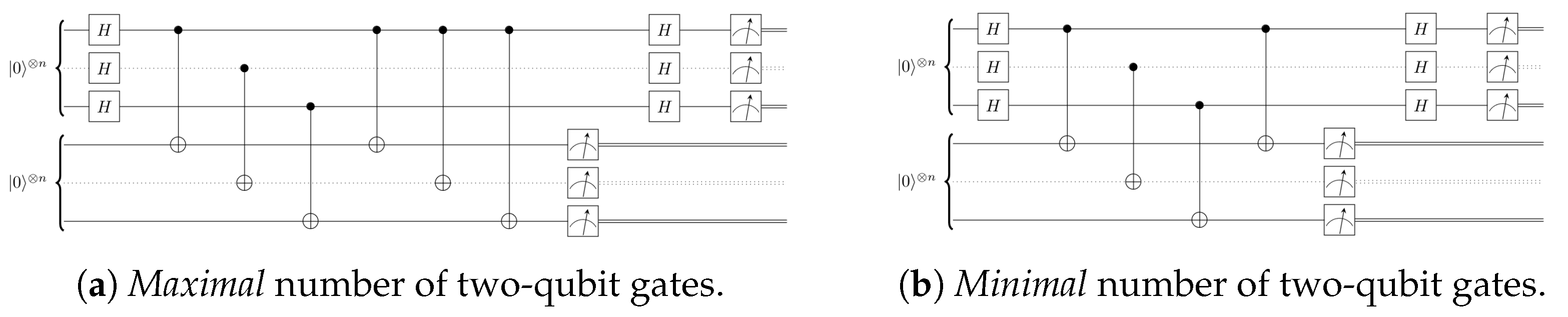
4.1. Implementation of the Algorithm
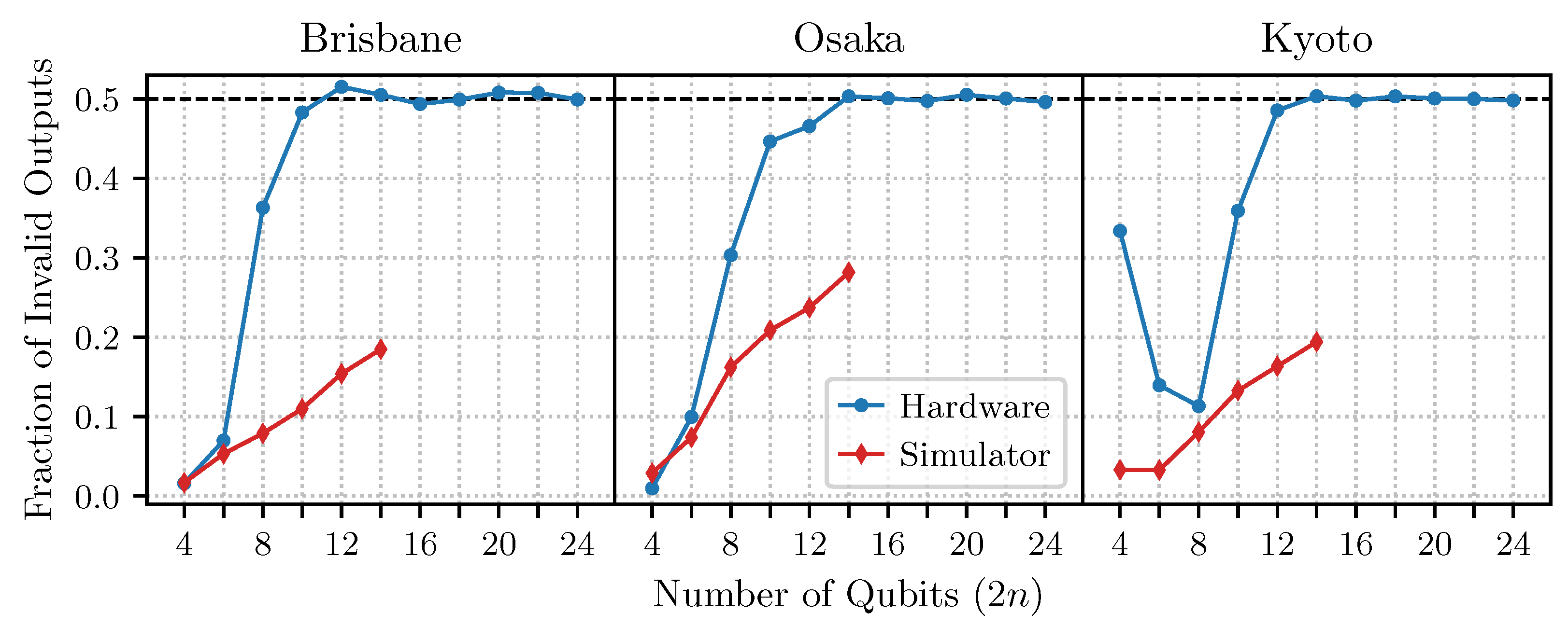
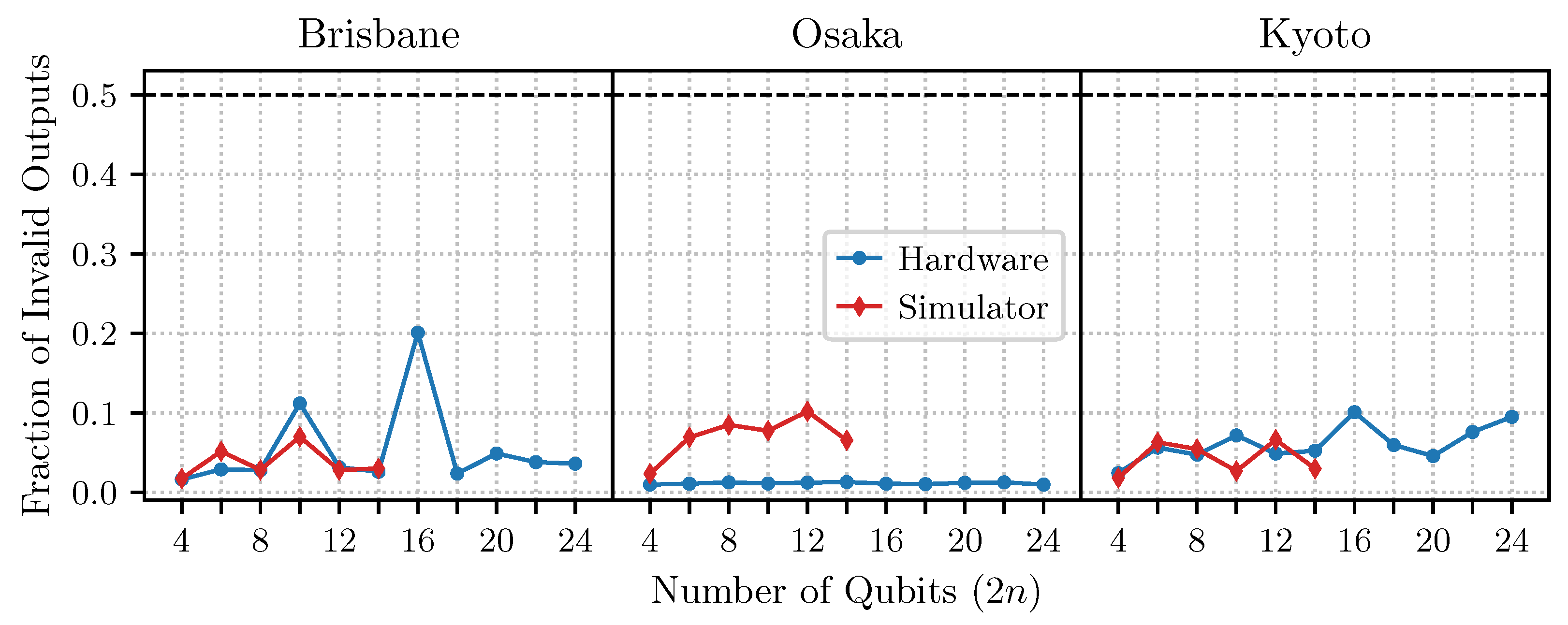
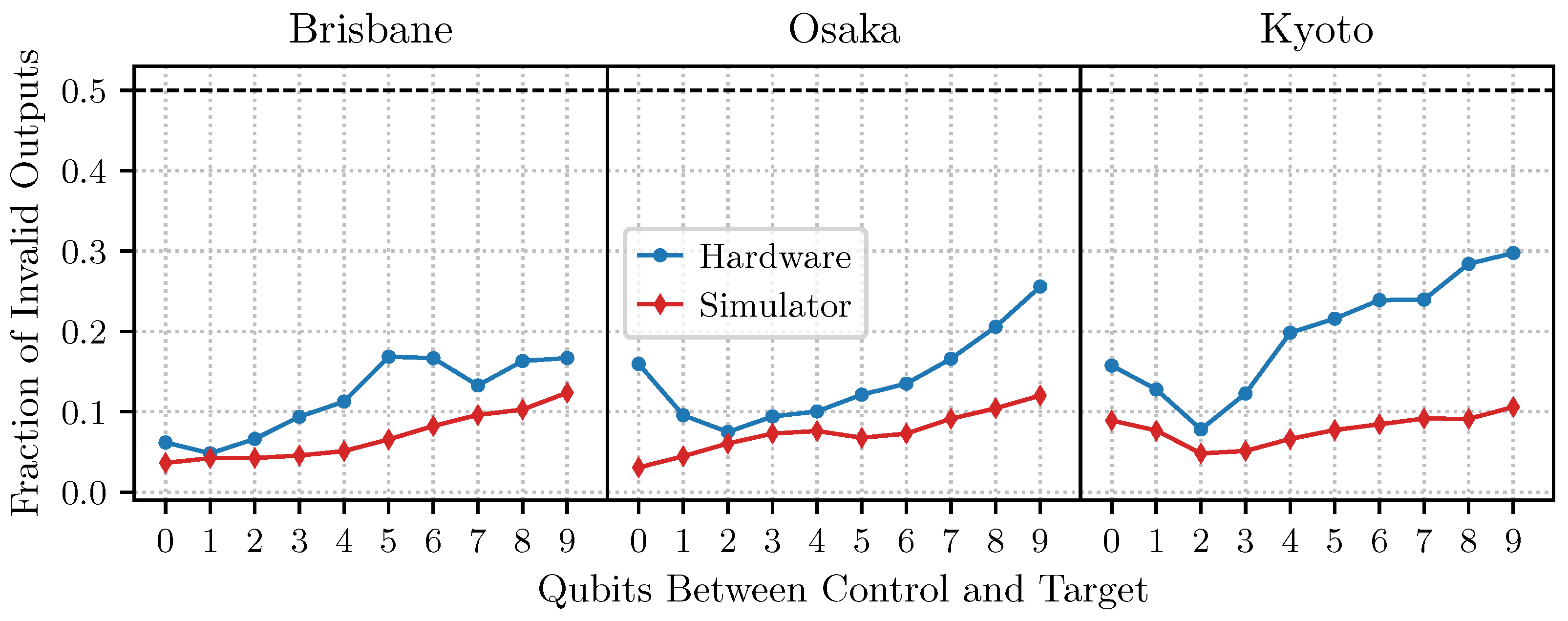
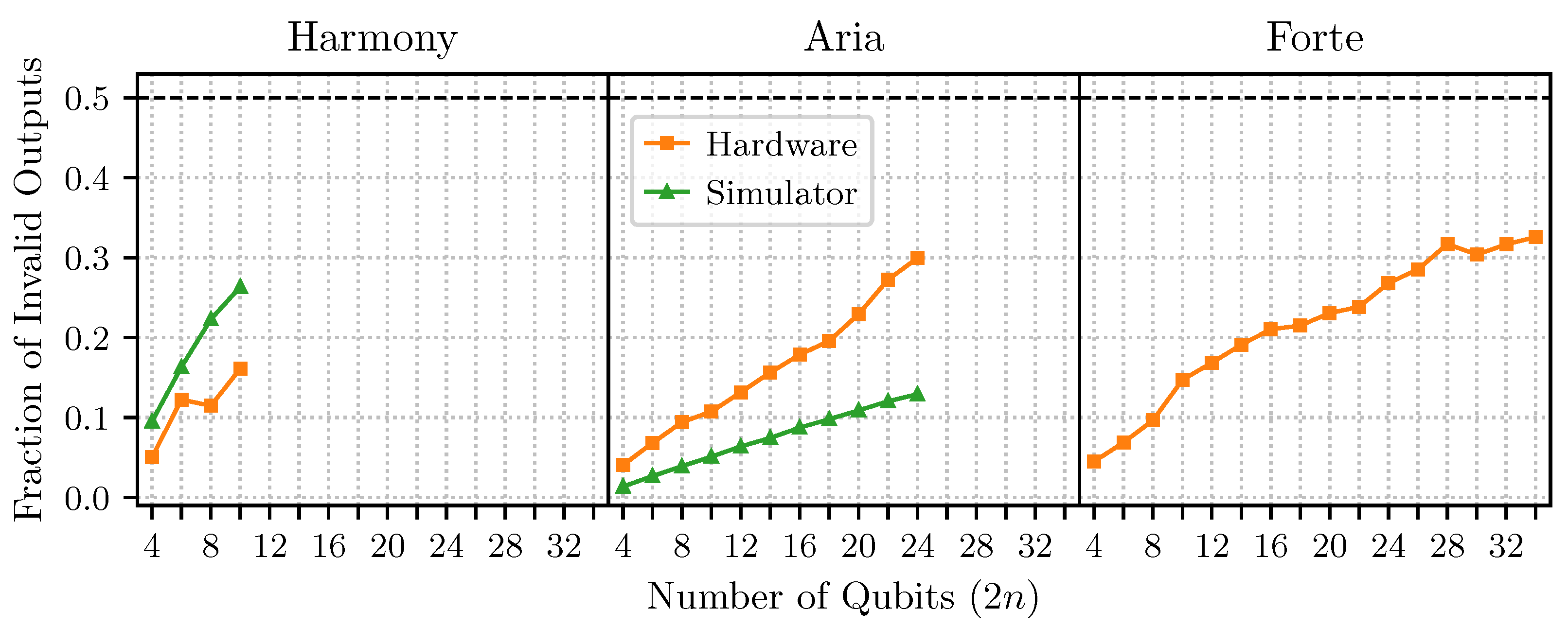
4.2. Results on IBM Devices
4.3. Results on IonQ Devices
5. Concluding Remarks
Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NISQ | Noisy intermediate scale quantum |
| QPU | Quantum processing unit |
| SPAM | State preparation and measurement |
| XOR | Exclusive-or |
Appendix A. Physical Parameters of the NISQ Devices
| Parameter | Brisbane | Osaka | Kyoto | Forte | Aria 1 | Harmony |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | IBM | IBM | IBM | IonQ | IonQ | IonQ |
| T1 Time | 213.12 µs | 297.17 µs | 215.43 µs | 100 s | 100 s | 10,000 s |
| T2 Time | 145.97 µs | 127.23 µs | 109.44 µs | 1 s | 1 s | 0.2 s |
| 2-Q Gate Speed | 660 ns | 660 ns | 660 ns | 970 µs | 600 µs | 200 µs |
| 1-Q Gate Error | 0.03% | 0.03% | 0.03% | 0.09% | 0.06% | 0.67% |
| 2-Q Gate Error | 0.74% | 0.93% | 0.92% | 0.74% | 8.57% | 3.07% |
| Avg SPAM Error | 1.32% | 2.18% | 1.48% | 0.5% | 0.52% | 0.42% |
| Total Qubits | 127 | 127 | 127 | 11 | 25 | 36 |
| Topology | Eagle r3 | Eagle r3 | Eagle r3 | all-to-all | all-to-all | all-to-all |
Appendix B. Comparison of IBM Device Before and After Update

References
- McKinsey. Quantum Technology Sees Record Investments, Progress on Talent Gap. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/quantum-technology-sees-record-investments-progress-on-talent-gap (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Nielsen, M.A.; Chuang, I.L. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information: 10th Anniversary Edition; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Singkanipa, P.; Kasatkin, V.; Zhou, Z.; Quiroz, G.; Lidar, D.A. Demonstration of Algorithmic Quantum Speedup for an Abelian Hidden Subgroup Problem. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2401.07934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, B.C. How to Build a Quantum Computer; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017; pp. 2399–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, N. Quantum computers compete for Supremacy. Sci. Am. 2018, 27, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Arute, F.; Arya, K.; Babbush, R.; Bacon, D.; Bardin, J.C.; Barends, R.; Biswas, R.; Boixo, S.; Brandao, F.G.S.L.; Buell, D.A.; et al. Quantum supremacy using a programmable superconducting processor. Nature 2019, 574, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.S.; Wang, H.; Deng, Y.H.; Chen, M.C.; Peng, L.C.; Luo, Y.H.; Qin, J.; Wu, D.; Ding, X.; Hu, Y.; et al. Quantum computational advantage using photons. Science 2020, 370, 1460–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Bao, W.S.; Cao, S.; Chen, F.; Chen, M.C.; Chen, X.; Chung, T.H.; Deng, H.; Du, Y.; Fan, D.; et al. Strong Quantum Computational Advantage Using a Superconducting Quantum Processor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 180501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.S.; Deng, Y.H.; Qin, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, M.C.; Peng, L.C.; Luo, Y.H.; Wu, D.; Gong, S.Q.; Su, H.; et al. Phase-Programmable Gaussian Boson Sampling Using Stimulated Squeezed Light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 180502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, L.S.; Laudenbach, F.; Askarani, M.F.; Rortais, F.; Vincent, T.; Bulmer, J.F.F.; Miatto, F.M.; Neuhaus, L.; Helt, L.G.; Collins, M.J.; et al. Quantum computational advantage with a programmable photonic processor. Nature 2022, 606, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Cao, S.; Chen, F.; Chen, M.C.; Chen, X.; Chung, T.H.; Deng, H.; Du, Y.; Fan, D.; Gong, M.; et al. Quantum computational advantage via 60-qubit 24-cycle random circuit sampling. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.D.; Nocera, A.; Rams, M.M.; Dziarmaga, J.; Wiersema, R.; Bernoudy, W.; Raymond, J.; Kaushal, N.; Heinsdorf, N.; Harris, R.; et al. Computational supremacy in quantum simulation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.00910. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, M.P.; Ryan-Anderson, C.; Bello-Rivas, J.M.; Chernoguzov, A.; Dreiling, J.M.; Foltz, C.; Frachon, F.; Gaebler, J.P.; Gatterman, T.M.; Grans-Samuelsson, L.; et al. Demonstration of logical qubits and repeated error correction with better-than-physical error rates. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.02280. [Google Scholar]
- Preskill, J. Quantum Computing in the NISQ era and beyond. Quantum 2018, 2, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Kumar, A.; Singh, H.; Singh, M.; Kaur, K.; Usman, M.; Buyya, R. Quantum computing: A taxonomy, systematic review and future directions. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2022, 52, 66–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.W.Z.; Lim, K.H.; Shrotriya, H.; Kwek, L.C. NISQ computing: Where are we and where do we go? AAPPS Bull. 2022, 32, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zolanvari, M.; Jain, R. A Survey of Important Issues in Quantum Computing and Communications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 1059–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.; Potharaju, A.; Li, B.; Roy, R.B.; Tiwari, D. Experimental Evaluation of NISQ Quantum Computers: Error Measurement, Characterization, and Implications. In Proceedings of the SC20: International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, Atlanta, GA, USA, 9–19 November 2020; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordzanganeh, M.; Buchberger, M.; Kyriacou, B.; Povolotskii, M.; Fischer, W.; Kurkin, A.; Somogyi, W.; Sagingalieva, A.; Pflitsch, M.; Melnikov, A. Benchmarking Simulated and Physical Quantum Processing Units Using Quantum and Hybrid Algorithms. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2023, 6, 2300043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Humble, T.S. Stability of noisy quantum computing devices. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.09472. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, S.; Humble, T.S. Characterizing the Stability of NISQ Devices. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Quantum Computing and Engineering (QCE), Denver, CO, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, A.; Bausch, J.; Gilyén, A. Scalable Benchmarks for Gate-Based Quantum Computers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.10698. [Google Scholar]
- Tomesh, T.; Gokhale, P.; Omole, V.; Ravi, G.S.; Smith, K.N.; Viszlai, J.; Wu, X.C.; Hardavellas, N.; Martonosi, M.R.; Chong, F.T. SupermarQ: A Scalable Quantum Benchmark Suite. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), San Jose, CA, USA, 27 November–3 December 2022; pp. 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkers, H.; Mesman, K.; Al-Ars, Z.; Möller, M. QPack Scores: Quantitative performance metrics for application-oriented quantum computer benchmarking. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.12142. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Stein, S.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Ang, J. QASMBench: A Low-Level Quantum Benchmark Suite for NISQ Evaluation and Simulation. ACM Trans. Quantum Comput. 2023, 4, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salm, M.; Barzen, J.; Breitenbücher, U.; Leymann, F.; Weder, B.; Wild, K. The NISQ Analyzer: Automating the Selection of Quantum Computers for Quantum Algorithms. In Service-Oriented Computing; Dustdar, S., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 66–85. [Google Scholar]
- Shor, P. Algorithms for quantum computation: Discrete logarithms and factoring. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 14–16 November 1994; pp. 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, I.L.; Vandersypen, L.M.K.; Zhou, X.; Leung, D.W.; Lloyd, S. Experimental realization of a quantum algorithm. Nature 1998, 393, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouland, A.; Fefferman, B.; Landau, Z.; Liu, Y. Noise and the Frontier of Quantum Supremacy. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 62nd Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 14–17 November 2021; pp. 1308–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cotler, J.; Huang, H.Y.; Li, J. The complexity of NISQ. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelofske, E.; Golden, J.; Bärtschi, A.; O’Malley, D.; Eidenbenz, S. Sampling on NISQ Devices: “Who’s the Fairest One of All?”. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Quantum Computing and Engineering (QCE), Broomfield, CO, USA, 17–22 October 2021; pp. 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.R. On the Power of Quantum Computation. SIAM J. Comput. 1997, 26, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.H.; Bernstein, E.; Brassard, G.; Vazirani, U. Strengths and Weaknesses of Quantum Computing. SIAM J. Comput. 1997, 26, 1510–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasi, O.; Krishnamoorthy, S. The Impact of Logical Errors on Quantum Algorithms. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2111.03733. [Google Scholar]
- Mermin, N.D. Quantum Computer Science: An Introduction; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, A.W.; Bishop, L.S.; Sheldon, S.; Nation, P.D.; Gambetta, J.M. Validating quantum computers using randomized model circuits. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 100, 032328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelofske, E.; Bärtschi, A.; Eidenbenz, S. Quantum Volume in Practice: What Users Can Expect From NISQ Devices. IEEE Trans. Quantum Eng. 2022, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knill, E.; Leibfried, D.; Reichle, R.; Britton, J.; Blakestad, R.B.; Jost, J.D.; Langer, C.; Ozeri, R.; Seidelin, S.; Winel, D.J. Randomized benchmarking of quantum gates. Am. Phys. Soc. 2008, 77, 012307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boixo, S.; Isakov, S.V.; Smelyanskiy, V.N.; Babbush, R.; Ding, N.; Jiang, Z.; Bremner, M.J.; Martinis, J.M.; Neven, H. Characterizing quantum supremacy in near-term devices. Nat. Phys. 2018, 14, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennakhi, A.; Byrd, G.T.; Franzon, P. Solving the B-SAT Problem Using Quantum Computing: Smaller Is Sometimes Better. Entropy 2024, 26, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakin, S.; Reinhardt, S.P. A Survey of Programming Tools for D-Wave Quantum-Annealing Processors. In High Performance Computing; Yokota, R., Weiland, M., Keyes, D., Trinitis, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 103–122. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Neill, C.; Roushan, P.; Leung, N.; Fang, M.; Barends, R.; Kelly, J.; Campbell, B.; Chen, Z.; Chiaro, B.; et al. Qubit Architecture with High Coherence and Fast Tunable Coupling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 220502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, J.M.; Dreiling, J.M.; Figgatt, C.; Gaebler, J.P.; Moses, S.A.; Allman, M.S.; Baldwin, C.H.; Foss-Feig, M.; Hayes, D.; Mayer, K.; et al. Demonstration of the trapped-ion quantum CCD computer architecture. Nature 2021, 592, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, S.A.; Baldwin, C.H.; Allman, M.S.; Ancona, R.; Ascarrunz, L.; Barnes, C.; Bartolotta, J.; Bjork, B.; Blanchard, P.; Bohn, M.; et al. A Race-Track Trapped-Ion Quantum Processor. Phys. Rev. X 2023, 13, 041052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtz, J.; Bylinskii, A.; Braverman, B.; Amato-Grill, J.; Cantu, S.H.; Huber, F.; Lukin, A.; Liu, F.; Weinberg, P.; Long, J.; et al. Aquila: QuEra’s 256-qubit neutral-atom quantum computer. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.11727. [Google Scholar]
- Nersisyan, A.; Poletto, S.; Alidoust, N.; Manenti, R.; Renzas, R.; Bui, C.V.; Vu, K.; Whyland, T.; Mohan, Y.; Sete, E.A.; et al. Manufacturing low dissipation superconducting quantum processors. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–11 December 2019; pp. 31.1.1–31.1.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.; Yu, T.M.; Gambetta, J.; Houck, A.A.; Schuster, D.I.; Majer, J.; Blais, A.; Devoret, M.H.; Girvin, S.M.; Schoelkopf, R.J. Charge-insensitive qubit design derived from the Cooper pair box. Phys. Rev. A 2007, 76, 042319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deffner, S. Demonstration of entanglement assisted invariance on IBM’s quantum experience. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelvecchi, D. IBM releases first-ever 1,000-qubit quantum chip. Nature 2023, 624, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, G.S.; Smith, K.N.; Gokhale, P.; Chong, F.T. Quantum Computing in the Cloud: Analyzing job and machine characteristics. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Workload Characterization (IISWC), Austin, TX, USA, 24–26 October 2021; pp. 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Quantum. Composer. Available online: https://quantum.ibm.com/composer (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Allen, S.; Kim, J.; Moehring, D.L.; Monroe, C.R. Reconfigurable and Programmable Ion Trap Quantum Computer. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Rebooting Computing (ICRC), San Jose, CA, USA, 16–18 October 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amazon Braket Console. Available online: https://aws.amazon.com/braket/ (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Qiskit Transpilier. Available online: https://docs.quantum.ibm.com/api/qiskit/transpiler (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Device Backend Noise Model Simulations—Qiskit Aer 0.13.1. Available online: https://qiskit.github.io/qiskit-aer/tutorials/2_device_noise_simulation.html (accessed on 16 February 2024).
- Get Started with Hardware Noise Model Simulation. Available online: https://ionq.com/docs/get-started-with-hardware-noise-model-simulation (accessed on 31 January 2024).
- Moon, T.K.; Jensen, J.O.; Gunther, J.H. Soft Solution of Noisy Linear GF(2) Equations. In Proceedings of the 2022 Intermountain Engineering, Technology and Computing (IETC), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 13–14 October 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekhnovich, M. More on average case vs approximation complexity. In Proceedings of the 44th Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Cambridge, MA, USA, 12–14 October 2003; pp. 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Quantum Platform Dashboard. Available online: https://quantum.ibm.com/ (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- IonQ Cloud Console. Available online: https://cloud.ionq.com/jobs (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- IonQ. Getting Started with Native Gates. Available online: https://docs.ionq.com/guides/getting-started-with-native-gates (accessed on 24 June 2024).
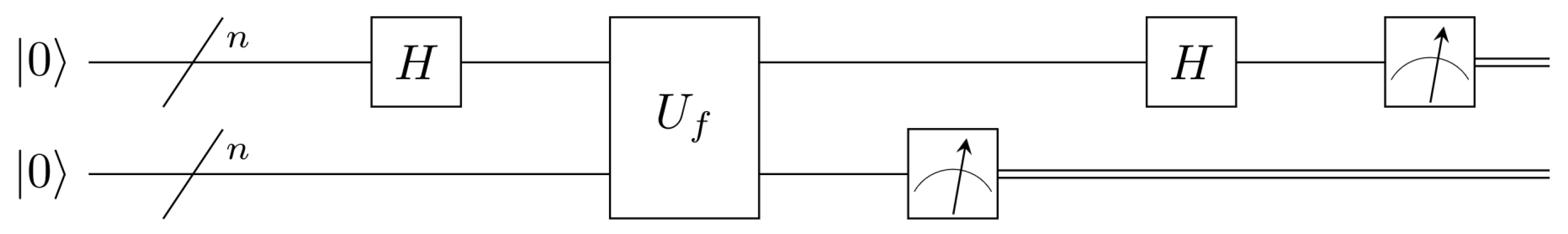
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robertson, R.; Doucet, E.; Spicer, E.; Deffner, S. Simon’s Algorithm in the NISQ Cloud. Entropy 2025, 27, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070658
Robertson R, Doucet E, Spicer E, Deffner S. Simon’s Algorithm in the NISQ Cloud. Entropy. 2025; 27(7):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070658
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobertson, Reece, Emery Doucet, Ernest Spicer, and Sebastian Deffner. 2025. "Simon’s Algorithm in the NISQ Cloud" Entropy 27, no. 7: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070658
APA StyleRobertson, R., Doucet, E., Spicer, E., & Deffner, S. (2025). Simon’s Algorithm in the NISQ Cloud. Entropy, 27(7), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070658







