Permutation Entropy and Its Niche in Hydrology: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
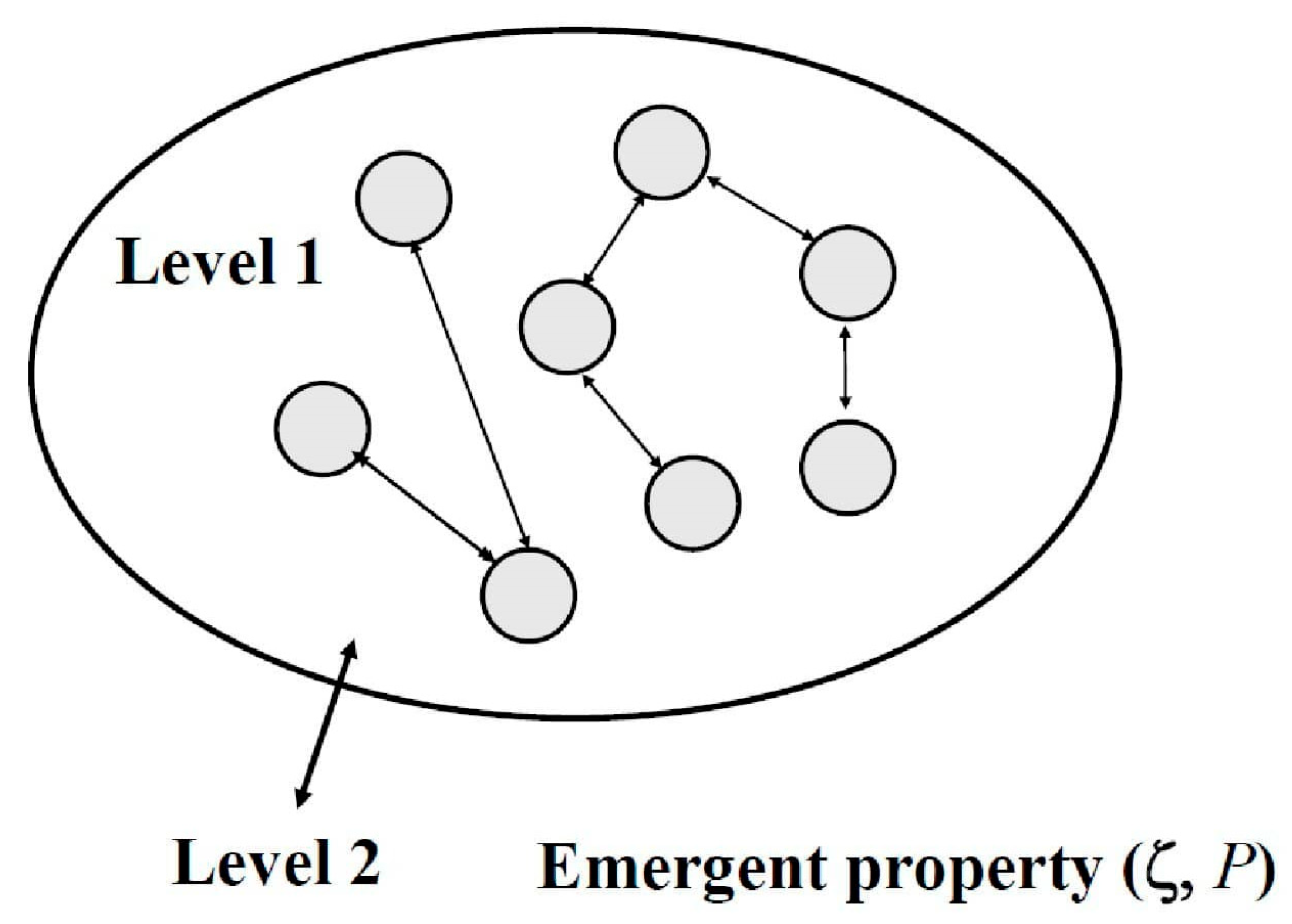
1.1. What Is Complex System?
1.2. Permutation Entropy and Time Series Analysis
2. Permutation Entropy: Its Advantages and Limitations
- 1.
- Time series embedding. Given a time series define embedding dimension (also called order or pattern length) and delay (step between consecutive points). Create vectors:
- 2.
- Ordinal pattern extraction. For each vector , determine the permutation π representing the ranks of its elements in ascending order. Example: For , ranks are , corresponding to permutation π .
- 3.
- Probability distribution calculation. Compute the relative frequency of each permutation pattern
- 4.
- Shannon entropy computation. Calculate the Shannon entropy of the permutation distribution:
- 5.
- Normalization. Normalize by the maximum entropy :
3. Permutation Entropy in Hydrology: Diverse Applications and Insights
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Hydrologists typically analyze complexity by applying information measures to measured time series—a natural source of information—instead of using heuristic hydrological models. PE is perhaps the most widely used complexity measure in hydrology.
- (2)
- We briefly discuss its advantages, which include an intuitive background, computational efficiency, robustness to noise, and minimal parameter requirements, and discrimination of dynamics. However, PE also has several drawbacks: loss of amplitude information, difficulties in handling equal values, reliance on heuristic methods for parameter selection, inability to differentiate between distinct patterns, sensitivity to certain processes, and complexity in interpretation.
- (3)
- We reviewed the diverse applications of PE in hydrology, categorizing its uses across various subfields. Specifically, we examined PE’s role in runoff prediction, streamflow analysis, water level forecasting, assessment of hydrological changes, and evaluating the impact of infrastructure on hydrology.
- (4)
- Finally, we (1) offer practical recommendations for applying PE in hydrology, (2) highlight current research gaps, and (3) outline future directions to advance this field.
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, P.W. More Is Different: Broken Symmetry and the Nature of the Hierarchical Structure of Science. Science 1972, 177, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailović, D.; Kapor, D.; Crvenković, S.; Mihailović, A. Physics of Complex Systems: Discovery in the Age of Gödel; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; 200p. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, R. Life Itself: A Comprehensive Inquiry into the Nature, Origin, and Fabrication of Life; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, M. Complexity and the emergence of physical properties. Entropy 2014, 16, 4489–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshinov, V.; Fuchs, C. Preface. In Causality, Emergence, Self-Organization; Arshinov, V., Fuchs, C., Eds.; NIAPriroda: Moscow, Russia, 2003; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Shalizi, C.R. Methods and Techniques of Complex Systems Science: An Overview. arXiv 2003, arXiv:nlin/0307015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.; Matos, A.; Souto, A.; Antunes, L. Entropy Measures vs. Kolmogorov Complexity. Entropy 2011, 13, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Entropy estimation in Turing’s perspective. Neural Comput. 2012, 24, 1368–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S. Algorithmic entropy and complexity. In Nanoscale Device Physics: Science and Engineering Fundamentals; Oxford Academic: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenil, H.; Hernández-Orozco, S.; Kiani, N.A.; Soler-Toscano, F.; Rueda-Toicen, A.; Tegnér, J. A Decomposition Method for Global Evaluation of Shannon Entropy and Local Estimations of Algorithmic Complexity. Entropy 2018, 20, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Downey, R. Turing and randomness. In The Turing Guide; Oxford Academic: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, K. Measuring Complexity Using Information. Qeios 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailović, D.T.; Singh, V.P. Information in Complex Physical Systems: Kolmogorov Complexity Plane of Interacting Amplitudes. Phys. Complex Syst. 2024, 5, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempel, A.; Ziv, J. On the Complexity of Finite Sequences. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1976, 22, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandt, C.; Pompe, B. Permutation Entropy: A Natural Complexity Measure for Time Series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 174102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, M.; Zunino, L.; Rosso, O.A.; Papo, D. Permutation Entropy and Its Main Biomedical and Econophysics Applications: A Review. Entropy 2012, 14, 1553–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.S.; Bahmer, A. Increase in Mutual Information During Interaction with the Environment Contributes to Perception. Entropy 2019, 21, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Y. Fault Diagnosis for Rail Vehicle Axle-Box Bearings Based on Energy Feature Reconstruction and Composite Multiscale Permutation Entropy. Entropy 2019, 21, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echegoyen, I.; López-Sanz, D.; Martínez, J.H.; Maestú, F.; Buldú, J.M. Permutation Entropy and Statistical Complexity in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: An Analysis Based on Frequency Bands. Entropy 2020, 22, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Liu, F.; Gao, J.; Cheng, C.; Song, C. Characterizing Complexity Changes in Chinese Stock Markets by Permutation Entropy. Entropy 2017, 19, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, L.; Zanin, M.; Tabak, B.M.; Perez, D.G.; Rosso, O.A. Forbidden patterns, permutation entropy and stock market inefficiency. Physica A 2009, 388, 2854–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raath, J.L.; Olivier, C.P.; Engelbrecht, N.E. A permutation entropy analysis of Voyager interplanetary magnetic field observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2022, 127, e2021JA030200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renin, S. Unveiling hidden structures: Applications of permutation entropy in data analysis. Adv.Robot. Autom. 2023, 12, 268. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, B.; Myers, A.; Boydston, T.; Ellwein, E.; Mackenzie, C.; Alvarez, I.; Lentz, E. Permutation entropy for signal analysis. Discrete Math. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2024, 26, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.Y.; Wu, S.H.; Li, S.C. Measurement of Climate Complexity Using Permutation Entropy. Geogr. Res. 2007, 26, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Tirabassi, G.; Duque-Gijon, M.; Tiana-Alsina, J.; Masoller, C. Permutation entropy-based characterization of speckle patterns generated by semiconductor laser light. APL Photon. 2023, 8, 126112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machiwal, D.; Jha, M.K. Time Series Analysis of Hydrologic Data for Water Resources Planning and Management: A Review. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2006, 54, 237–257. [Google Scholar]
- Neppel, F.; Renard, B.; Lang, M.; Aryal, P.-A.; Coeur, D.; Gaume, E.; Jacob, N.; Payrastre, O.; Pobanz, K.; Vinet, F. Flood Frequency Analysis Using Historical Data: Accounting for Random and Systematic Errors. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2010, 55, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, G.R.; Jadidoleslam, N.; Krajewski, W.F.; Tsonis, A.A. Insights on Streamflow Predictability Across Scales Using Horizontal Visibility Graph Based Networks. Front. Water 2020, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, L.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J. A global streamflow indices time series dataset for large-sample hydrological analyses on streamflow regime (until 2022). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 4463–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastour, H.; Hassan, Q.K. A Machine-Learning Framework for Modeling and Predicting Monthly Streamflow Time Series. Hydrology 2023, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.; Judge, G. Permutation Entropy and Information Recovery in Nonlinear Dynamic Economic Time Series. Econometrics 2019, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutjahr, T.; Keller, K. Conditional permutation entropy as a measure for the complexity of dynamical systems. In Proceedings of the Entropy 2021: The Scientific Tool of the 21st Century, Online, 5–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.T.; Plastino, A.; Rosso, O.A. Generalized Statistical Complexity Measures: Geometrical and Analytical Properties. Physica A 2006, 369, 439–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, O.A.; Larrondo, H.A.; Martin, M.T.; Plastino, A.; Fuentes, M.A. Distinguishing Noise from Chaos. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 154102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serinaldi, F.; Zunino, L.; Rosso, O.A. Complexity–Entropy Analysis of Daily Stream Flow Time Series in the Continental United States. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 1685–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, H.; Rosso, O.; Hauhs, M. Ordinal Pattern and Statistical Complexity Analysis of Daily Stream Flow Time Series. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2013, 222, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, R. Permutation Entropies and Chaos; Department of Physics, UC Davis: Davis, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.; He, S.; Sun, K. Design of a Network Permutation Entropy and Its Applications for Chaotic Time Series and EEG Signals. Entropy 2019, 21, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Tao, M.; Poskuviene, K.; Alkayem, N.F.; Cao, M.; Ragulskis, M. Permutation Entropy Based on Non-Uniform Embedding. Entropy 2018, 20, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Henry, M. Permutation Entropy. Aptech, Published online: 25 May 2023. Available online: https://www.aptech.com/blog/permutation-entropy/ (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- Riedl, M.; Müller, A.; Wessel, N. Practical considerations of permutation entropy: A tutorial review. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2013, 222, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, L.; Politi, A. Permutation Entropy of Weakly Noise-Affected Signals. Entropy 2021, 24, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, M.; Rodríguez-González, A.; Menasalvas Ruiz, E.; Papo, D. Assessing Time Series Reversibility through Permutation Patterns. Entropy 2018, 20, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaretto, B.R.R.; Budzinski, R.C.; Rossi, K.L. Discriminating Chaotic and Stochastic Time Series Using Permutation Entropy and Artificial Neural Networks. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, A.; Khasawneh, F.A. On the automatic parameter selection for permutation entropy. Chaos 2020, 30, 033130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, A.D.; Chumley, M.M.; Khasawneh, F.A. Delay Parameter Selection in Permutation Entropy Using Topological Data Analysis. La Mat. 2024, 3, 1103–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ma, X.; Fu, J.; Li, Y. Ensemble Improved Permutation Entropy: A New Approach for Time Series Analysis. Entropy 2023, 25, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigó, J.M.; Dale, R.; Tempesta, P. A Generalized Permutation Entropy for Random Processes. arXiv 2003, arXiv:2003.13728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, K.; Mangold, T.; Stolz, I.; Werner, J. Permutation Entropy: New Ideas and Challenges. Entropy 2017, 19, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutjahr, T.; Keller, K. Equality of Kolmogorov-Sinai and permutation entropy for one-dimensional maps consisting of countably many monotone parts. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. 2019, 39, 4207–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, L.; Kulp, C.W. Detecting nonlinearity in short and noisy time series using the permutation entropy. Phys. Lett. A 2017, 381, 3627–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Liang, H.; Yu, J. Improved Permutation Entropy for Measuring Complexity of Time Series under Noisy Condition. Complexity 2019, 2019, 1403829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta-Frau, D.; Molina-Picó, A.; Vargas, B.; González, P. Permutation Entropy: Enhancing Discriminating Power by Using Relative Frequencies Vector of Ordinal Patterns Instead of Their Shannon Entropy. Entropy 2019, 21, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta-Frau, D. Permutation entropy: Influence of amplitude information on time series classification performance. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2019, 16, 6842–6857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, L.; Olivares, F.; Scholkmann, F.; Rosso, O.A. Permutation entropy-based time series analysis: Equalities in the input signal can lead to false conclusions. Phys. Lett. A 2017, 381, 1883–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Shang, H.L.; Pitt, D. Permutation entropy and its variants for measuring temporal dependence. Aust. N. Z. J. Stat. 2022, 64, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, L.; Soriano, M.C.; Rosso, O.A. Distinguishing chaotic and stochastic dynamics from time series by using a multiscale symbolic approach. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 041910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, P.L.; Malik, A.S.; Bornot, J. Weighted-permutation entropy as a complexity measure for electroencephalographic time series of different physiological states. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 8–10 December 2014; pp. 979–984. [Google Scholar]
- Fadlallah, B.; Chen, B.; Keil, A.; Príncipe, J. Weighted-Permutation Entropy: A Complexity Measure for Time Series Incorporating Amplitude Information. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 87, 022911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goekoop, R.; de Kleijn, R. Permutation Entropy as a Universal Disorder Criterion: How Disorders at Different Scale Levels Are Manifestations of the Same Underlying Principle. Entropy 2021, 23, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpua, E.; Good, S.; Ala-Lahti, M.; Osmane, A.; Koikkalainen, V. Permutation Entropy and Complexity Analysis of Large-Scale Solar Wind Structures and Streams. EGU Gen. Assem. 2023, 2023, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.; Schneider, G.; Kochs, E.F.; Jordan, D. Permutation Entropy: Too Complex a Measure for EEG Time Series? Entropy 2017, 19, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Chen, F.; Long, A.; Qian, Y.; Tang, H. Improving the Precision of Monthly Runoff Prediction Using the Combined Non-stationary Methods in an Oasis Irrigation area. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 279, 108161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Q. A Novel Hybrid Model by Integrating TCN with TVFEMD and Permutation Entropy for Monthly Non-Stationary Runoff Prediction. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, Q.; An, J. Runoff prediction using a multi-scale two-phase processing hybrid model. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2025, 39, 1059–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Song, C.; Cheng, C.; Ye, S. The coupling impact of climate change on streamflow complexity in the headwater area of the northeastern Tibetan Plateau across multiple timescales. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 124996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.C.; Fullerton, A.H.; Kopp, D.; Tromboni, F.; Shogren, A.J.; Webb, J.A.; Ruffing, C.; Heaton, M.; Kuglerová, L.; Allen, D.C.; et al. The Music of Rivers: The Mathematics of Waves Reveals Global Structure and Drivers of Streamflow Regime. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 597, e2023WR034484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailović, D.T.; Nikolić-Đorić, E.; Drešković, N.; Mimić, G. Complexity Analysis of the Turbulent Environmental Fluid Flow Time Series. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2014, 395, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stosic, T.; Telesca, L.; Ferreira, D.V.D.; Stosic, B. investigating anthropically induced effects in streamflow dynamics by using permutation entropy and statistical complexity analysis: A case study. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriano, M.; Caram, L.F.; Rosso, O.A. Daily Streamflow of Argentine Rivers Analysis Using Information Theory Quantifiers. Entropy 2024, 26, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stosic, T.; Stosic, B.; Singh, V.P. Optimizing Streamflow Monitoring Networks Using Joint Permutation Entropy. J. Hydrol. 2017, 554, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, B.; Qin, T.; Nie, H.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Shen, Z. Assessment of Hydrological Changes and Their Influence on the Aquatic Ecology over the last 58 Years in Ganjiang Basin, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, J.; Jones, T.R.; Neuder, M.; Morris, V.; White, J.W.C.; Bradley, E. Anomaly Detection in Paleoclimate Records Using Permutation Entropy. Entropy 2018, 20, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cheng, C.; Gao, P. Permutation Entropy-Based Analysis of Temperature Complexity Spatial-Temporal Variation and Its Driving Factors in China. Entropy 2019, 21, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, L.E.; Torregrosa, A. Evaluating Hydrological Responses to Climate Change. Water 2020, 12, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; He, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Forecasting Gate-Front Water Levels Using a Coupled GRU–TCN–Transformer Model and Permutation Entropy Algorithm. Water 2024, 16, 3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Hao, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. Reservoir Dynamic Interpretability for Time Series Prediction: A Permutation Entropy View. Entropy 2022, 24, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, D.; Singh, V.P.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Zou, X.; Liu, J.; Zou, Y.; He, R. Optimization of rainfall networks using information entropy and temporal variability analysis. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 136–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezsonnyi, V. Use of the Entropy Approach in Water Resource Monitoring Systems. Visnyk V. N. Karazin Kharkiv Natl. Univ. Ser. Geol. Geogr. Ecol. 2023, 58, 302–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mihailović, D.T. Permutation Entropy and Its Niche in Hydrology: A Review. Entropy 2025, 27, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060598
Mihailović DT. Permutation Entropy and Its Niche in Hydrology: A Review. Entropy. 2025; 27(6):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060598
Chicago/Turabian StyleMihailović, Dragutin T. 2025. "Permutation Entropy and Its Niche in Hydrology: A Review" Entropy 27, no. 6: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060598
APA StyleMihailović, D. T. (2025). Permutation Entropy and Its Niche in Hydrology: A Review. Entropy, 27(6), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27060598




