Ordinal Spectrum: Mapping Ordinal Patterns into Frequency Domain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
| Steps |
| (1) Choose embedding parameters and form for . |
| (2) Map each to its permutation and obtain the symbolic sequence over the ordinal patterns (). |
| (3) Estimate the stationary probabilities and the m-step transition probabilities from . |
| (4) Compute the rank autocovariance using Equations (1)–(2). |
| (5) Obtain the ordinal spectrum from via Equation (3). |
| (6) Assess significance by comparing with IAAFT-surrogate spectra and corrected for multiple comparisons. |
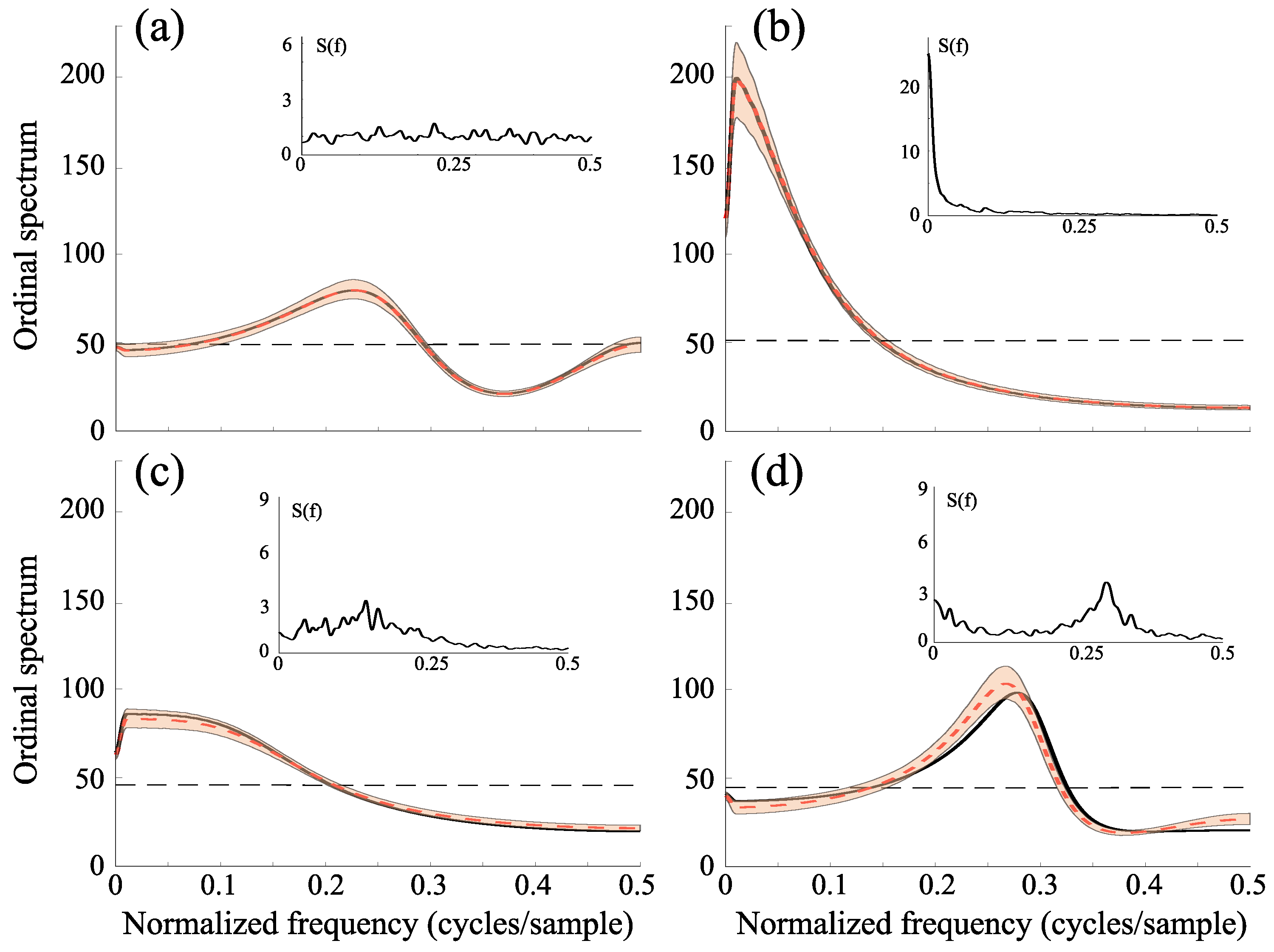
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abarbanel, H.D.; Brown, R.; Sidorowich, J.J.; Tsimring, L.S. The analysis of observed chaotic data in physical systems. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1993, 65, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutchfield, J.; Farmer, D.; Packard, N.H.; Shaw, R.; Jones, G.; Donnelly, R.J. Power spectral analysis of a dynamical system. Phys. Lett. A 1980, 76, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, J.D. Spectral broadening of period-doubling bifurcation sequences. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1981, 47, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, R.S.; Brumer, P. Characteristics of power spectra for regular and chaotic systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1988, 88, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebe, R.; Virgin, L.N. A heuristic method for identifying chaos from frequency content. Chaos 2012, 22, 013136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koussoulas, N.T. Spectral moments and the analysis of chaotic systems. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 2001, 11, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafon, A.; Rossi, A.; Vidal, C. Mesure du niveau de chaos à partir du spectre de Fourier dans des régimes dynamiques expérimentaux. J. Phys. 1983, 44, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigeti, D.; Horsthemke, W. High-frequency power spectra for systems subject to noise. Phys. Rev. A 1987, 35, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigeti, D.E. Exponential decay of power spectra at high frequency and positive Lyapunov exponents. Phys. D 1995, 82, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.; Bowers, R.G.; Begon, M. Red/blue chaotic power spectra. Nature 1996, 381, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.; Begon, M.; Bowers, R.G. Explaining the colour of power spectra in chaotic ecological models. Proc. R. Soc. B 1996, 263, 1731. [Google Scholar]
- Theiler, J.; Eubank, S.; Longtin, A.; Galdrikian, B. Testing for Nonlinearity in Time Series: The Method of Surrogate Data. Phys. D 1992, 58, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, T.; Schmitz, A. Surrogate Time Series. Phys. D 2000, 142, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, M.; Tse, C.K. Detecting determinism in time series: The method of surrogate data. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 2003, 50, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba Rao, T. Analysis of nonlinear time series (and chaos) by bispectral methods. In Nonlinear Modeling and Forecasting, SFI Studies in the Sciences of Complexity, Proc. Vol XII; Casdagli, M., Eubank, S., Eds.; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1991; pp. 199–226. [Google Scholar]
- Chandran, V.; Elgar, S.; Pezeshki, C. Bispectral and trispectral characterization of transition to chaos in the Duffing oscillator. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos Appl. Sci. Eng. 1993, 3, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshki, C.; Elgar, S.; Krishna, R.C. Bispectral analysis of possessing chaotic motion. J. Sound Vib. 1990, 137, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulp, C.W.; Smith, S. Characterization of noisy symbolic time series. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 83, 026201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulp, C.W.; Zunino, L. Discriminating chaotic and stochastic dynamics through the permutation spectrum test. Chaos 2014, 24, 033116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Small, M. From phase space to frequency domain: A time-frequency analysis for chaotic time series. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 76, 016220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprott, J.C. Chaos and Time-Series Analysis; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mischaikow, K.; Mrozek, M.; Reiss, J.; Szymczak, A. Construction of symbolic dynamics from experimental time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Micco, L.; Gonzalez, C.M.; Larrondo, H.A.; Martín, M.T.; Plastino, A.; Rosso, O.A. Randomizing nonlinear maps via symbolic dynamics. Phys. A 2008, 387, 3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandt, C.; Pompe, B. Permutation entropy: A natural complexity measure for time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 174102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanin, M.; Zunino, L.; Rosso, O.A.; Papo, D. Permutation entropy and its main biomedical and econophysics applications: A review. Entropy 2012, 14, 1553–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigó, J.M.; Keller, K.; Unakafova, V.A. Ordinal symbolic analysis and its application to biomedical recordings. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2015, 373, 20140091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.H.; José, J.R.; Zanin, M. On the complementarity of ordinal patterns-based entropy and time asymmetry metrics. Chaos 2023, 33, 033138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.K. Multiscale entropy analysis of complex physiologic time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 068102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humeau-Heurtier, A. The multiscale entropy algorithm and its variants: A review. Entropy 2015, 17, 3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, L.; Soriano, M.C.; Rosso, O.A. Distinguishing chaotic and stochastic dynamics from time series by using a multiscale symbolic approach. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 046210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigó, J.M. Permutation Complexity in Dynamical Systems: Ordinal Patterns, Permutation Entropy and All That; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Daw, C.S.; Finney, C.E.A.; Tracy, E.R. A review of symbolic analysis of experimental data. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2003, 74, 915–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, O.A.; Larrondo, H.A.; Martín, M.T.; Plastino, A.; Fuentes, M.A. Distinguishing noise from chaos. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 154102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, K.; Unakafov, A.M.; Unakafova, V.A. Ordinal patterns, entropy, and EEG. Entropy 2014, 16, 6212–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basawa, I.V. Estimation of the autocorrelation coefficient in simple Markov chains. Biometrika 1972, 59, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuh, C.D. Bootstrapping the autocorrelation coefficient of finite Markov chains. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 1992, 32, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, R.F. Evolution of long-range fractal correlations and 1/f noise in DNA base sequences. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 3805–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Schonfeld, D. Mapping equivalence for symbolic sequences: Theory and applications. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 4895–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.; Kravtsiv, A.; Schneider, G.; Jordan, D. Teaching ordinal patterns to a computer: Efficient encoding algorithms based on the Lehmer code. Entropy 2019, 21, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, K.; Sinn, M.; Emonds, J. Time series from the ordinal viewpoint. Stoch. Dynam. 2007, 7, 247–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therrien, C.W. Discrete Random Signals and Statistical Signal Processing; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Carpi, L.C.; Saco, P.M.; Rosso, O.A. Missing ordinal patterns in correlated noises. Phys. A 2010, 389, 2020–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, R.M. Simple mathematical models with very complicated dynamics. Nature 1976, 261, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diks, C.; van Houwelingen, J.C.; Takens, F.; DeGoede, J. Reversibility as a criterion for discriminating time series. Phys. Lett. A 1995, 201, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Measles Incidence Dataset (Prof. Ben Bolker, McMaster University). Available online: https://ms.mcmaster.ca/~bolker/measdata.html (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Bolker, B.M.; Grenfell, B.T. Chaos and biological complexity in measles dynamics. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 1993, 251, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, L.F.; Truty, G.L.; Schaffer, W.M. Oscillations and chaos in epidemics: A nonlinear dynamic study of six childhood diseases in Copenhagen, Denmark. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1988, 33, 344–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelle, K.; Rodó, X.; Pascual, M.; Yunus, M.; Mostafa, G. Refractory periods and climate forcing in cholera dynamics. Nature 2005, 436, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, I.B. Small amplitude, long period outbreaks in seasonally driven epidemics. J. Math. Biol. 1992, 30, 473–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.A.; Ionides, E.L.; Pascual, M.; Bouma, M.J. Inapparent infections and cholera dynamics. Nature 2008, 454, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørnstad, O.N. epimdr: Functions and Data for “Epidemics: Models and Data in R”; R Package Version 0.6-5. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=epimdr (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Letellier, C.; Aguirre, L.A.; Maquet, J.; Gilmore, R. Evidence for low dimensional chaos in sunspot cycles. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 449, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Solar Influences Data Analysis Center (SIDC), Belgium. Sunspot Time Series. Available online: https://sidc.be/SILSO/home (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Stam, C.J.; Pijn, J.P.M.; Pritchard, W.S. Reliable detection of nonlinearity in experimental time series with strong periodic components. Phys. D 1998, 112, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrzejak, R.G.; Lehnertz, K.; Mormann, F.; Rieke, C.; David, P.; Elger, C.E. Indications of nonlinear deterministic and finite-dimensional structures in time series of brain electrical activity: Dependence on recording region and brain state. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 061907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quian Quiroga, R.; Blanco, S.; Rosso, O.A.; Garcia, H.; Rabinowicz, A. Searching for hidden information with Gabor transform in generalized tonic–clonic seizures. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1997, 103, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Simmons, A.; Rivera-Villicana, J.; Barnett, S.; Sivathamboo, S.; Perucca, P.; Ge, Z.; Kwan, P.; Kuhlmann, L.; Vasa, R.; et al. EEG datasets for seizure detection and prediction—A review. Epilepsia Open 2023, 8, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chavez, M.; Martínez, J.H. Ordinal Spectrum: Mapping Ordinal Patterns into Frequency Domain. Entropy 2025, 27, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101027
Chavez M, Martínez JH. Ordinal Spectrum: Mapping Ordinal Patterns into Frequency Domain. Entropy. 2025; 27(10):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101027
Chicago/Turabian StyleChavez, Mario, and Johann H. Martínez. 2025. "Ordinal Spectrum: Mapping Ordinal Patterns into Frequency Domain" Entropy 27, no. 10: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101027
APA StyleChavez, M., & Martínez, J. H. (2025). Ordinal Spectrum: Mapping Ordinal Patterns into Frequency Domain. Entropy, 27(10), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101027






